Anti-Factor Xa Activity of Apixaban in Extremely Low Body Weight
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. The Studied Population
2.3. Trial Procedures
2.4. Trial Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Study Population
3.2. The Study Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phrommintikul, A.; Detnuntarat, P.; Prasertwitayakij, N.; Wongcharoen, W. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation in Thai elderly. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 270–273. [Google Scholar]
- Suwanwela, N.C.; Chutinet, A.; Autjimanon, H.; Ounahachok, T.; Decha-Umphai, C.; Chockchai, S.; Indrabhakti, S.; Kijpaisalratana, N.; Akarathanawat, W.; Travanichakul, S.; et al. Atrial fibrillation prevalence and risk profile from novel community-based screening in Thailand: A prospective multi-centre study. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2021, 32, 100709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risk factors for stroke and efficacy of antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation. Analysis of pooled data from five randomized controlled trials. Arch. Intern. Med. 1994, 154, 1449–1457. [CrossRef]
- Frost, L.; Engholm, G.; Johnsen, S.; Moller, H.; Henneberg, E.W.; Husted, S. Incident thromboembolism in the aorta and the renal, mesenteric, pelvic, and extremity arteries after discharge from the hospital with a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Wolf, P.A.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Silbershatz, H.; Kannel, W.B.; Levy, D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1998, 98, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; E Dilaveris, P.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar]
- Granger, C.B.; Alexander, J.H.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lopes, R.D.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Ansell, J.; Atar, D.; Ave-zum, A.; et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Lin, T.-Y.; Chang, S.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Hung, K.-C.; Wen, M.-S. Body mass index is an independent predictor of major bleeding in non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients taking dabigatran. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 228, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Choi, E.K.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, S.R.; Cha, M.J.; Oh, S. Increased risk of major bleeding in underweight patients with atrial fibrillation who were prescribed non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, B.; Fox, K.A.; Ajjan, R.A.; Andreotti, F.; Baigent, C.; Collet, J.P.; Grove, E.L.; Halvorsen, S.; Huber, K.; Morais, J.; et al. Antithrombotic therapy and body mass: An expert position paper of the ESC Working Group on Thrombosis. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1672–1686f. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upreti, V.V.; Wang, J.; Barrett, Y.C.; Byon, W.; Boyd, R.A.; Pursley, J.; LaCreta, F.P.; Frost, C.E. Effect of extremes of body weight on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability of apixaban in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffel, J.; Collins, R.; Antz, M.; Cornu, P.; Desteghe, L.; Haeusler, K.G.; Oldgren, J.; Reinecke, H.; Roldan-Schilling, V.; Rowell, N.; et al. 2021 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the Use of Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Europace 2021, 23, 1612–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byon, W.; Garonzik, S.; Boyd, R.A.; Frost, C.E. Apixaban: A Clinical Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limcharoen, S.; Pongchaidecha, M.; Pimsi, P.; Limprasert, S.; Suphanklang, J.; Saelim, W.; Santimaleeworagun, W.; Boonmuang, P. Do Apixaban Plasma Levels Relate to Bleeding? The Clinical Outcomes and Predictive Factors for Bleeding in Patients with Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwa, M.; Nohara, Y.; Morii, I.; Kino, M. Safety and Efficacy Re-Evaluation of Edoxaban and Rivaroxaban Dosing with Plasma Concentration Monitoring in Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation: With Observations of On-Label and Off-Label Dosing. Circ. Rep. 2023, 5, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, P.A.; Lehr, T.; Haertter, S.; Connolly, S.J.; Yusuf, S.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Nehmiz, G.; Wang, S.; Wallentin, L.; et al. The effect of dabigatran plasma concentrations and patient characteristics on the frequency of ischemic stroke and major bleeding in atrial fibrillation patients: The RE-LY Trial (Randomized Evaluation of Long-Term Anticoagulation Therapy). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stretton, B.; Kovoor, J.; Bacchi, S.; Gupta, A.; Edwards, S.; Boey, J.P.; Gluck, S.; Reddi, B.; Maddern, G.; Boyd, M. Quantifying time from last dose: Do direct oral anticoagulant assays correlate with patient’s reported last dose. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2023, 34, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolowiec, L.; Kusiak, M.; Budzynski, J.; Wolowiec, A.; Jaśniak, A.; Wiciński, M.; Pedrycz-Wieczorska, A.; Rogowicz, D.; Grześk, G. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Extremely Low and High Body Weight-Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.A.; Lee, C.R.; Farrell, T.M.; Moll, S. Oral Anticoagulant Use After Bariatric Surgery: A Literature Review and Clinical Guidance. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remko, M. Molecular structure and stability of perindopril erbumine and perindopril L-arginine complexes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, J.I.; Connolly, S.J.; Patel, I.; Salazar, D.; Rohatagi, S.; Mendell, J.; Kastrissios, H.; Jin, J.; Kunitada, S. Randomised, parallel-group, multicentre, multinational phase 2 study comparing edoxaban, an oral factor Xa inhibitor, with warfarin for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 104, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadosaka, T.; Nagai, T.; Suzuki, S.; Sakuma, I.; Akao, M.; Yamashita, T.; Anzai, T.; Okumura, K.; J-ELDAFinvestigators. Association of Low Body Weight with Clinical Outcomes in Elderly Atrial Fibrillation Patients Receiving Apixaban-J-ELD AF Registry Subanalysis. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2022, 36, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, S.; Konstantinides, S.; Hu, Y.; Tang, L.V. Venous Thromboembolic Diseases: Diagnosis, Management and Thrombophilia Testing: Observations on NICE Guideline [NG158]. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 1143–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
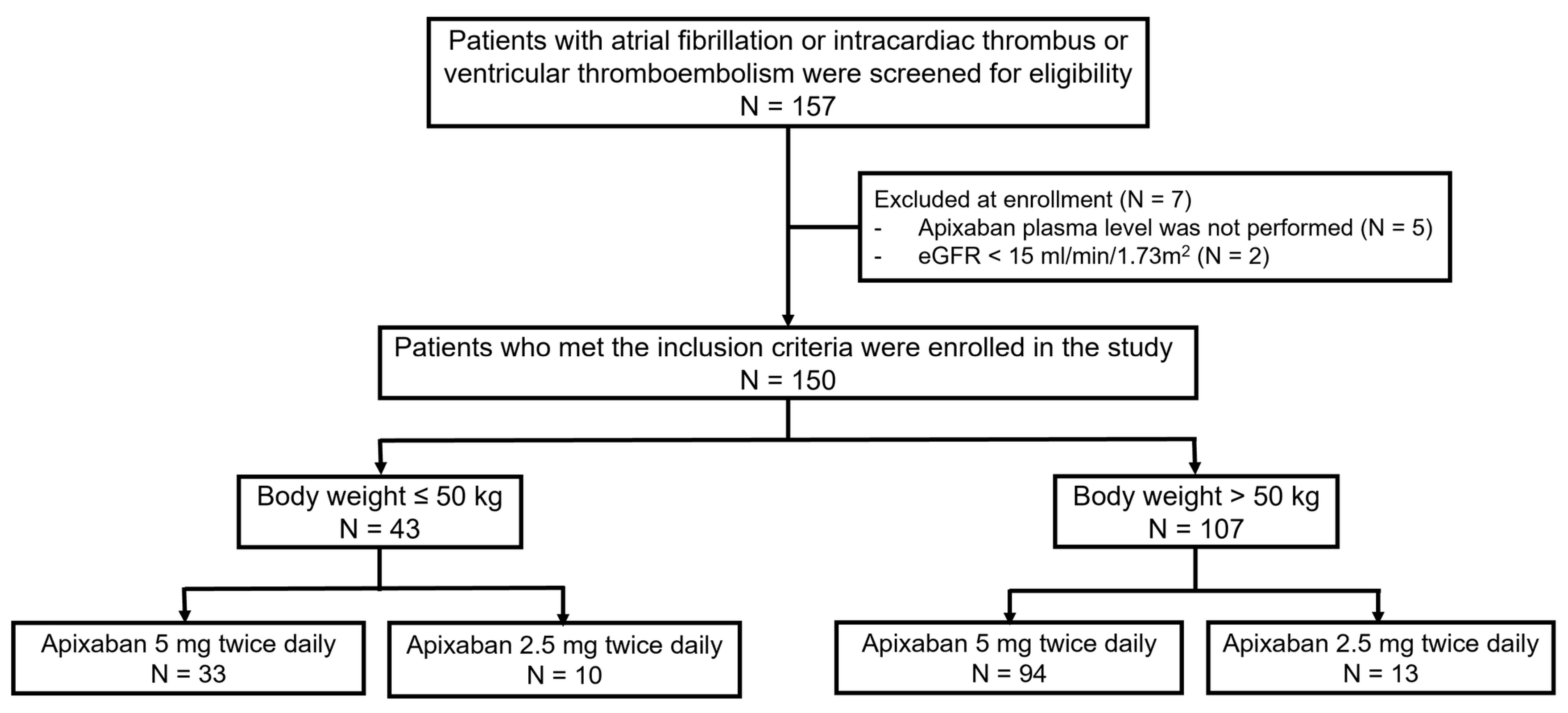
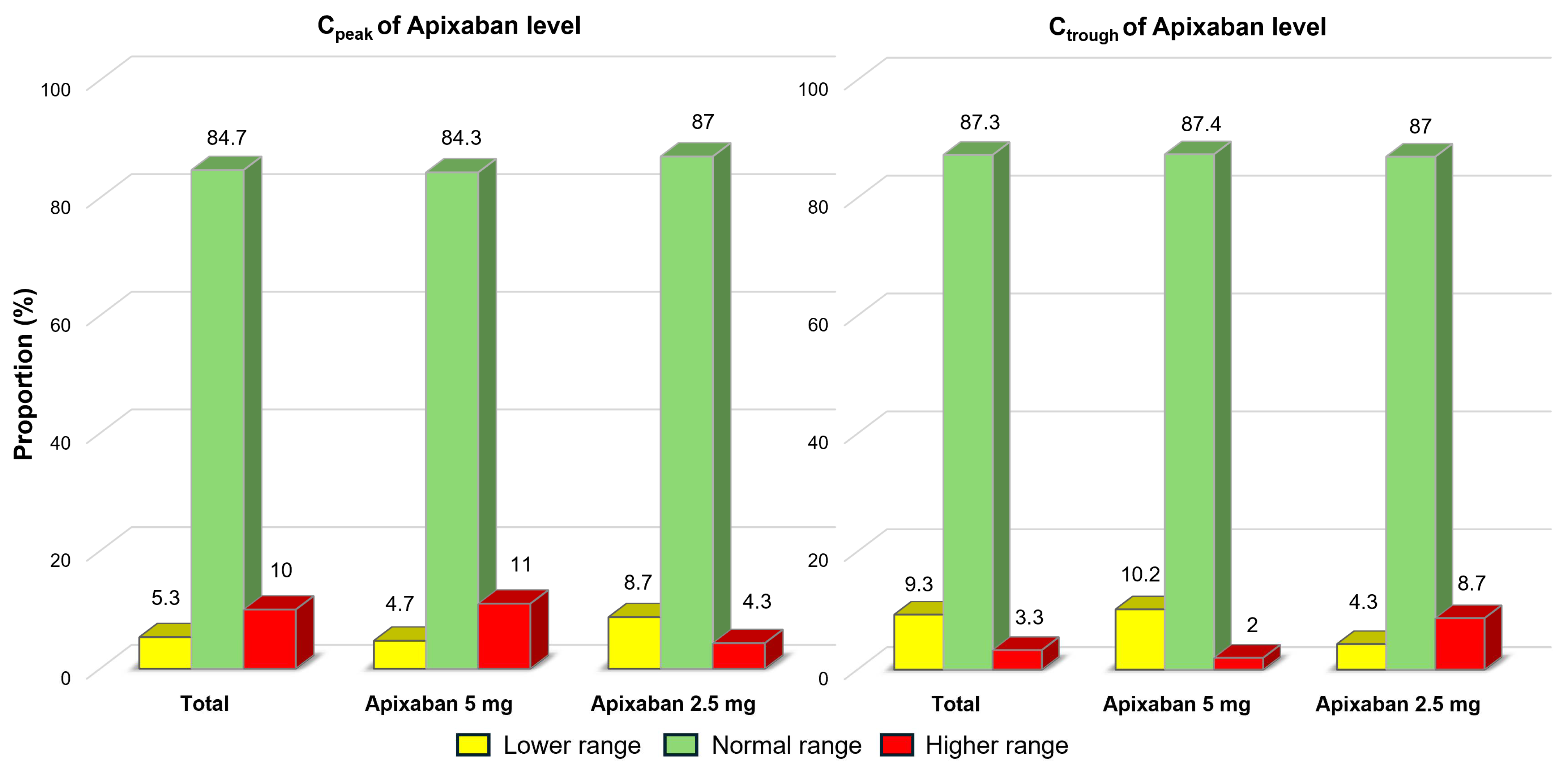
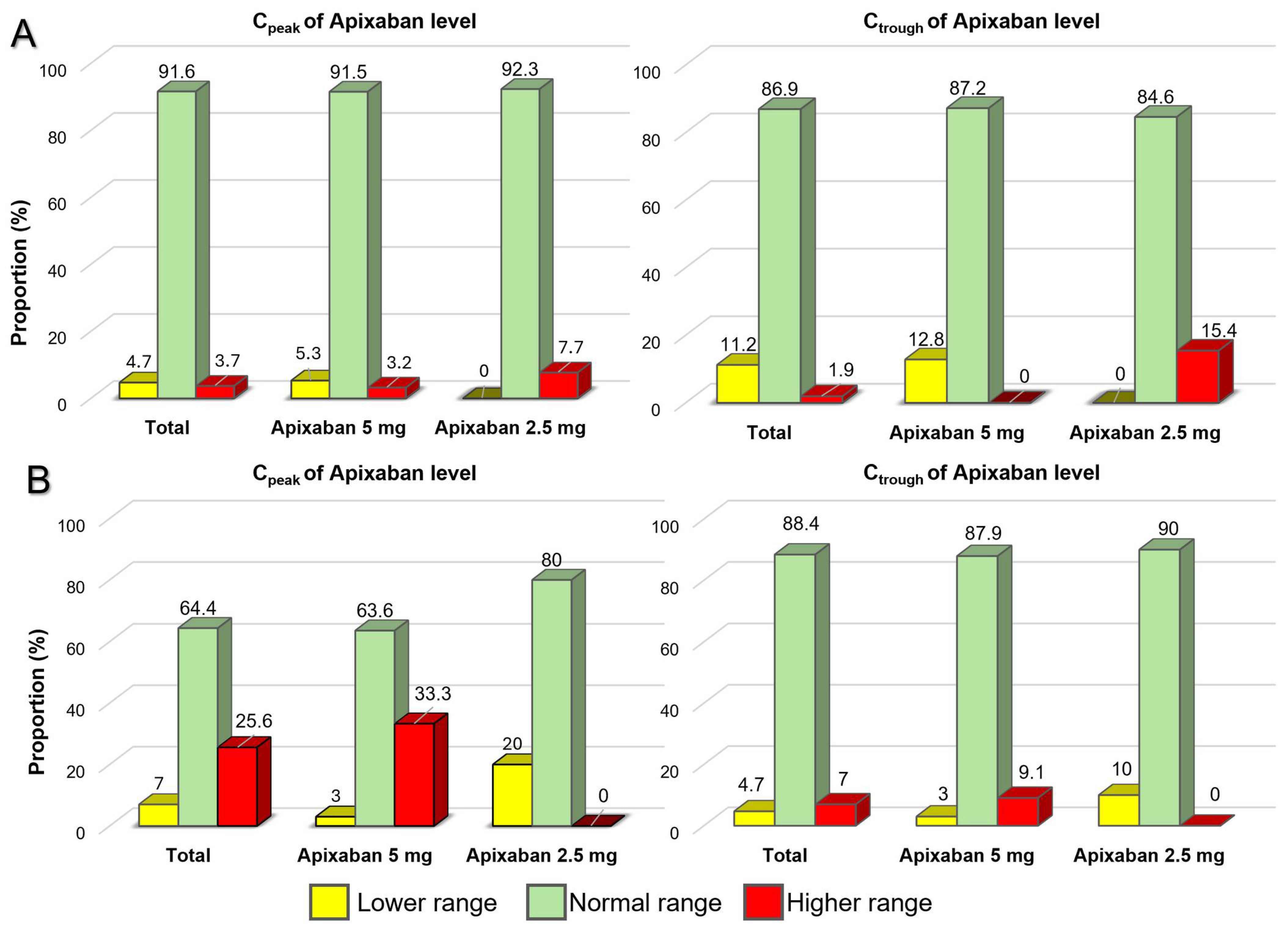
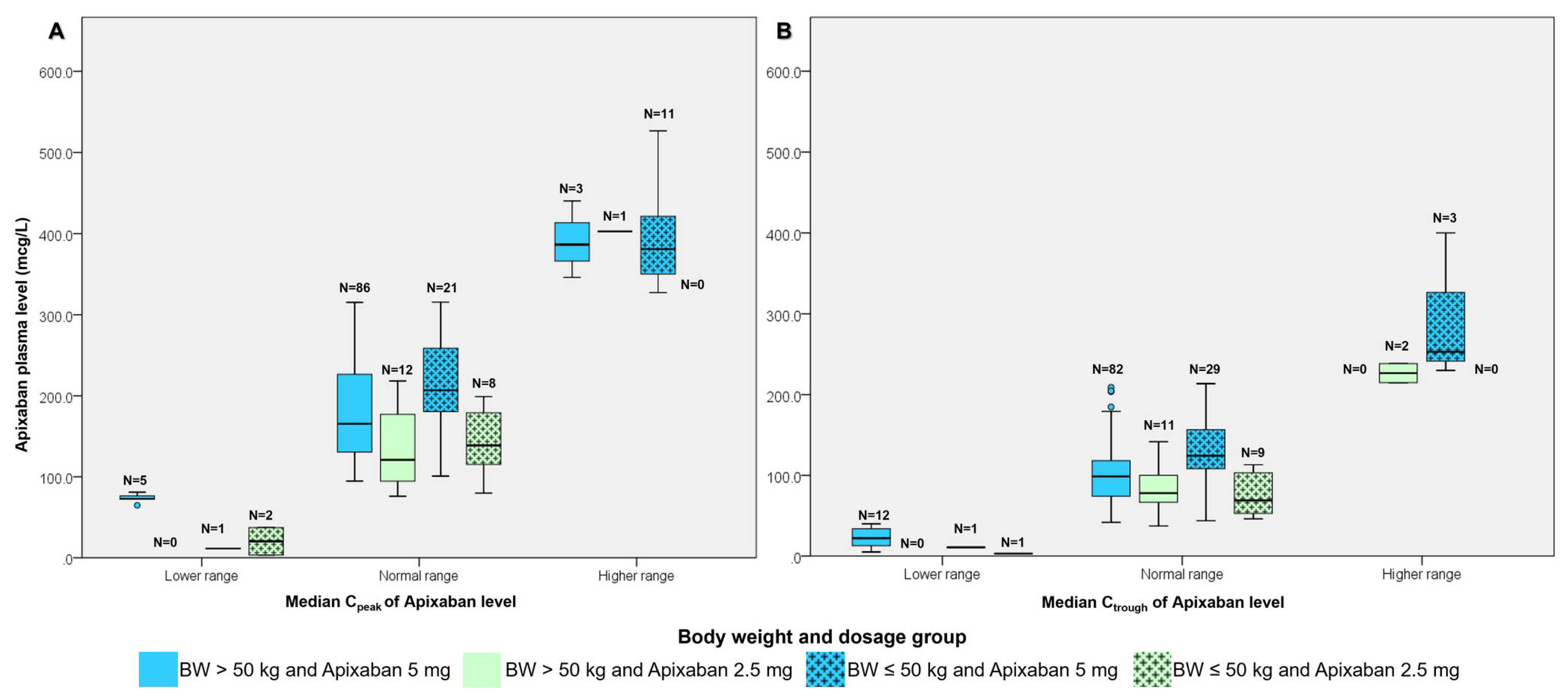
| Total (n = 150) | Body Weight ≤ 50 kg (n = 43) | Body Weight > 50 kg (n = 107) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.03 ± 12.69 | 69.71 ± 10.44 | 61.74 ± 12.84 | <0.001 |
| Male (%) | 80 (53.30%) | 12 (27.90%) | 68 (63.6%) | <0.001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.86 ± 4.74 | 19.24 ± 1.78 | 25.73 ± 4.26 | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.63 ± 2.06 | 11.57 ± 2.14 | 13.06 ± 1.89 | <0.001 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.13 ± 0.46 | 1.12 ± 0.44 | 1.14 ± 0.48 | 0.786 |
| CrCl (ml/min) | 63.13 ± 36.32 | 45.21 ± 21.60 | 70.34 ± 38.56 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities (%) | ||||
| 67 (44.70%) | 16 (37.20%) | 51 (47.7%) | 0.279 |
| 40 (26.70%) | 9 (20.90%) | 31 (29.00%) | 0.415 |
| 59 (39.30%) | 11 (25.60%) | 48 (44.90%) | 0.041 |
| 38 (25.30%) | 17 (39.50%) | 21 (19.60%) | 0.021 |
| 19 (12.70%) | 5 (11.60%) | 14 (13.10%) | 1.000 |
| 22 (14.70%) | 4 (9.30%) | 18 (16.80%) | 0.312 |
| OAC indication (%) | 0.167 | |||
| 132 (88.00%) | 35 (81.40%) | 97 (90.70%) | |
| 9 (6.00%) | 5 (11.60%) | 4 (3.70%) | |
| 9 (6.00%) | 3 (7.00%) | 6 (5.60%) | |
| Medications (%) | ||||
| 119 (79.30%) | 32 (74.40%) | 87 (81.30%) | 0.376 |
| 29 (19.30%) | 7 (16.30%) | 22 (20.60%) | 0.651 |
| 3 (2.00%) | 1 (2.30%) | 2 (1.90%) | 1.000 |
| 9 (6.00%) | 2 (4.70%) | 7 (6.50%) | 1.000 |
| 3 (2.00%) | 1 (2.30%) | 2 (1.90%) | 1.000 |
| 98 (65.30%) | 25 (58.10%) | 73 (68.20%) | 0.259 |
| Apixaban dose | 0.130 | |||
| Apixaban 5 mg twice daily | 127 (84.70%) | 33 (76.70%) | 94 (87.90%) | |
| Apixaban 2.5 mg twice daily | 23 (15.30%) | 10 (23.30%) | 13 (12.10%) | |
| CHA2DS2-VASc score Median (Q1, Q3) | 3 (2, 4) | 3 (2, 5) | 3 (2, 4) | 0.106 |
| HAS-BLED score Median (Q1, Q3) | 1 (1, 2) | 2 (1, 3) | 1 (1, 2) | 0.536 |
| Apixaban Dosage | Anti-Factor Xa Activity | Total | Body Weight ≤ 50 kg | Body Weight > 50 kg | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apixaban 5 mg n = 127 | Trough apixaban plasma level (mcg/L) * | 101.60 (70.7–134.50) | 128.30 (104.9–165.00) (n = 33) | 94.85 (65.38–113.75) (n = 94) | 0.001 |
| Peak apixaban plasma level (mcg/L) * | 185.60 (130.80–258.80) | 258.80 (187.05–350.20) (n = 33) | 163.45 (126.35–228.88) (n = 94) | <0.001 | |
| Apixaban 2.5 mg n = 23 | Trough apixaban plasma level (mcg/L) * | 72.30 (52.80–106.30) | 63.75 (47.35–103.20) (n = 10) | 79.10 (66.75–128.50) (n = 13) | 0.074 |
| Peak apixaban plasma level (mcg/L) * | 122.30 (94.10–191.90) | 123.25 (69.18–172.23) (n = 10) | 122.30 (94.55–195.50) (n = 13) | 0.280 |
| Predictors | Univariate Analysis Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariate Analysis Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 5.31 (1.43–19.68) | 0.013 | 3.18 (0.78–12.82) | 0.104 |
| Body weight ≤ 50 kg | 8.85 (2.63–29.71) | <0.001 | 4.87 (1.31–18.15) | 0.018 |
| Creatinine clearance | 0.97 (0.94–0.99) | 0.033 | 0.98 (0.94–1.03) | 0.563 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wongcharoen, W.; Pamarapa, A.; Gunaparn, S.; Phrommintikul, A. Anti-Factor Xa Activity of Apixaban in Extremely Low Body Weight. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5238. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155238
Wongcharoen W, Pamarapa A, Gunaparn S, Phrommintikul A. Anti-Factor Xa Activity of Apixaban in Extremely Low Body Weight. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5238. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155238
Chicago/Turabian StyleWongcharoen, Wanwarang, Amarase Pamarapa, Siriluck Gunaparn, and Arintaya Phrommintikul. 2025. "Anti-Factor Xa Activity of Apixaban in Extremely Low Body Weight" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5238. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155238
APA StyleWongcharoen, W., Pamarapa, A., Gunaparn, S., & Phrommintikul, A. (2025). Anti-Factor Xa Activity of Apixaban in Extremely Low Body Weight. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5238. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155238






