Cutaneous Nodules and Inflammatory Arthritis: Two Illustrative Cases of Rare Mimics of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case 1
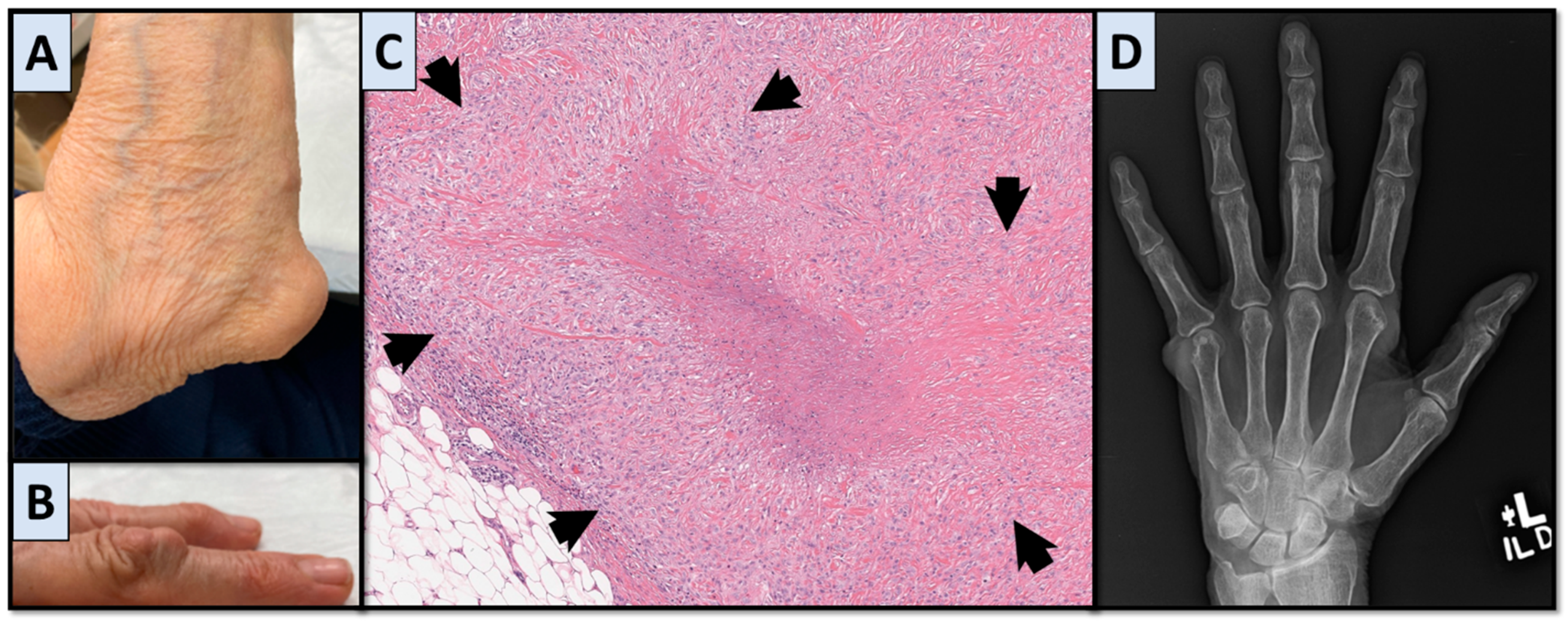
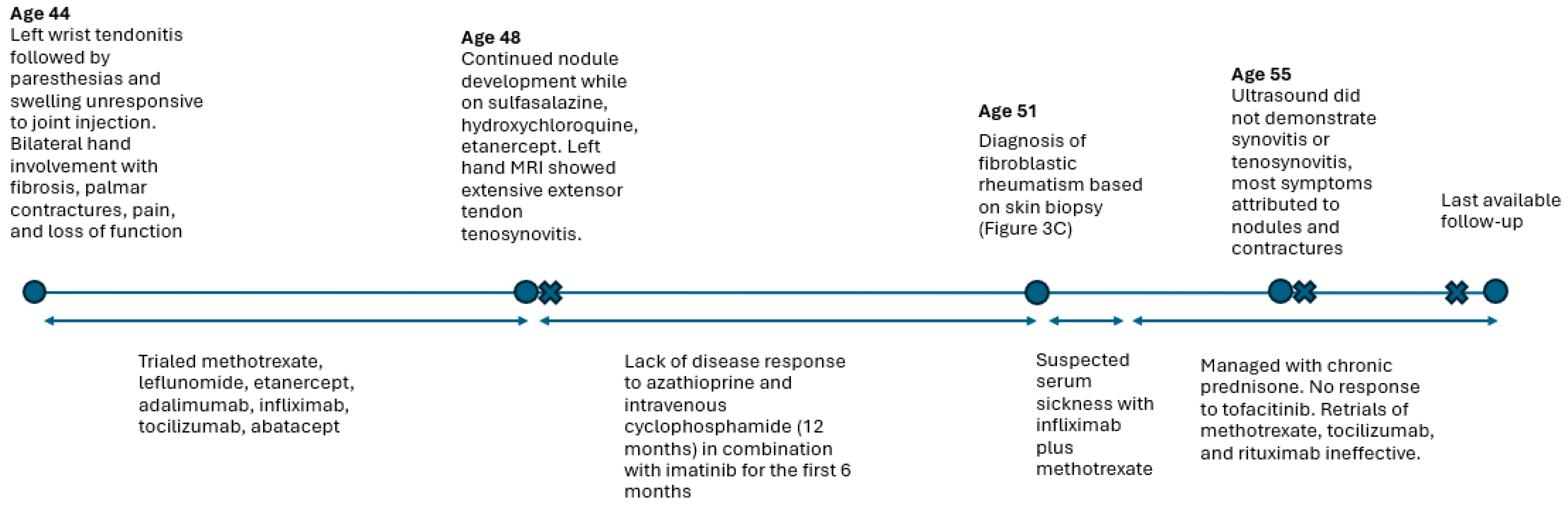
3. Case 2
4. Disease Characteristics
5. Other Considerations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| FR | Fibroblastic rheumatism |
| MRH | Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis |
| MCP | Metacarpophalangeal |
| PIP | Proximal interphalangeal |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Gabriel, S.E. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 27, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilstra, J.S.; Lienesch, D.W. Rheumatoid Nodules. Dermatol. Clin. 2015, 33, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaouat, Y.; Aron-Brunetiere, R.; Faures, B.; Binet, O.; Ginet, C.; Aubart, D. Une nouvelle entite: Le rhumatisme fibroblastique. Rev. Rhum. Mal. Osteoartic. 1980, 47, 345–351. [Google Scholar]
- Pieta, A.; Zioga, A.; Skalkou, A.; Venetsanopoulou, A.I.; Drosos, A.A.; Voulgari, P.V. Fibroblastic rheumatism: An uncommon arthritis. A case-based review. Rheumatol. Int. 2022, 42, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courties, A.; Guégan, S.; Miquel, A.; Duriez, P.; Berenbaum, F.; Sellam, J. Fibroblastic rheumatism: Immunosuppressive therapy is not always required. Jt. Bone Spine 2014, 81, 178–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, F.; Colina, M. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis and fibroblastic rheumatism. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 26, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toz, B.; Büyükbabani, N.; İnanç, M. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: Rheumatology perspective. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 30, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, C.; Wu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; You, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, L.; Zuo, X. Tumor necrosis factor antagonists in the treatment of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: Current clinical evidence. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelisto, A.; Werth, V.; Schumacher, H.R. What is that nodule?: A diagnostic approach to evaluating subcutaneous and cutaneous nodules. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 12, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Condition | Joint Features | Nodule Features | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Erosions | Juxta-Articular Osteopenia | Joint Space | Distribution | Characteristics | Size | Histopathology | References | |
| RA | Symmetric Spares DIP joints | Marginal | Present | Narrowed | Any region, classically extensor surfaces | Firm, nontender, sometimes mobile | 20–50 mm | Palisading granulomatous dermatitis with central fibrin | [6,7,9] |
| FR | Symmetric, DIP joints involved | Marginal or central | Present | Widened | Extensor surfaces and para-articular | Flesh-colored to purplish; can be tender | 2–20 mm (15 is median size) | Increased fibroblasts within a sclerotic dermis, few inflammatory cells | [6,7,9] |
| MRH | Symmetrical, DIP joints involved (marginal), joint widening | Marginal | Absent | Widened | Face, neck, hands; vermicular | Flesh-colored, red, or brown; can be pruritic | Millimeters (up to 20 mm) | Sheets of histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm | [6,7,9] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaman, R.; DiCaudo, D.J.; Sokumbi, O.; Pham, M.M.; Aslam, F.; Griffing, W.L.; Sullivan, M.M. Cutaneous Nodules and Inflammatory Arthritis: Two Illustrative Cases of Rare Mimics of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4940. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144940
Yaman R, DiCaudo DJ, Sokumbi O, Pham MM, Aslam F, Griffing WL, Sullivan MM. Cutaneous Nodules and Inflammatory Arthritis: Two Illustrative Cases of Rare Mimics of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(14):4940. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144940
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaman, Reena, David J. DiCaudo, Olayemi Sokumbi, Michael M. Pham, Fawad Aslam, W. Leroy Griffing, and Megan M. Sullivan. 2025. "Cutaneous Nodules and Inflammatory Arthritis: Two Illustrative Cases of Rare Mimics of Rheumatoid Arthritis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 14: 4940. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144940
APA StyleYaman, R., DiCaudo, D. J., Sokumbi, O., Pham, M. M., Aslam, F., Griffing, W. L., & Sullivan, M. M. (2025). Cutaneous Nodules and Inflammatory Arthritis: Two Illustrative Cases of Rare Mimics of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(14), 4940. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144940







