Evaluating In-Hospital Arrhythmias in Critically Ill Acute Kidney Injury Patients: Predictive Models, Mortality Risks, and the Efficacy of Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources
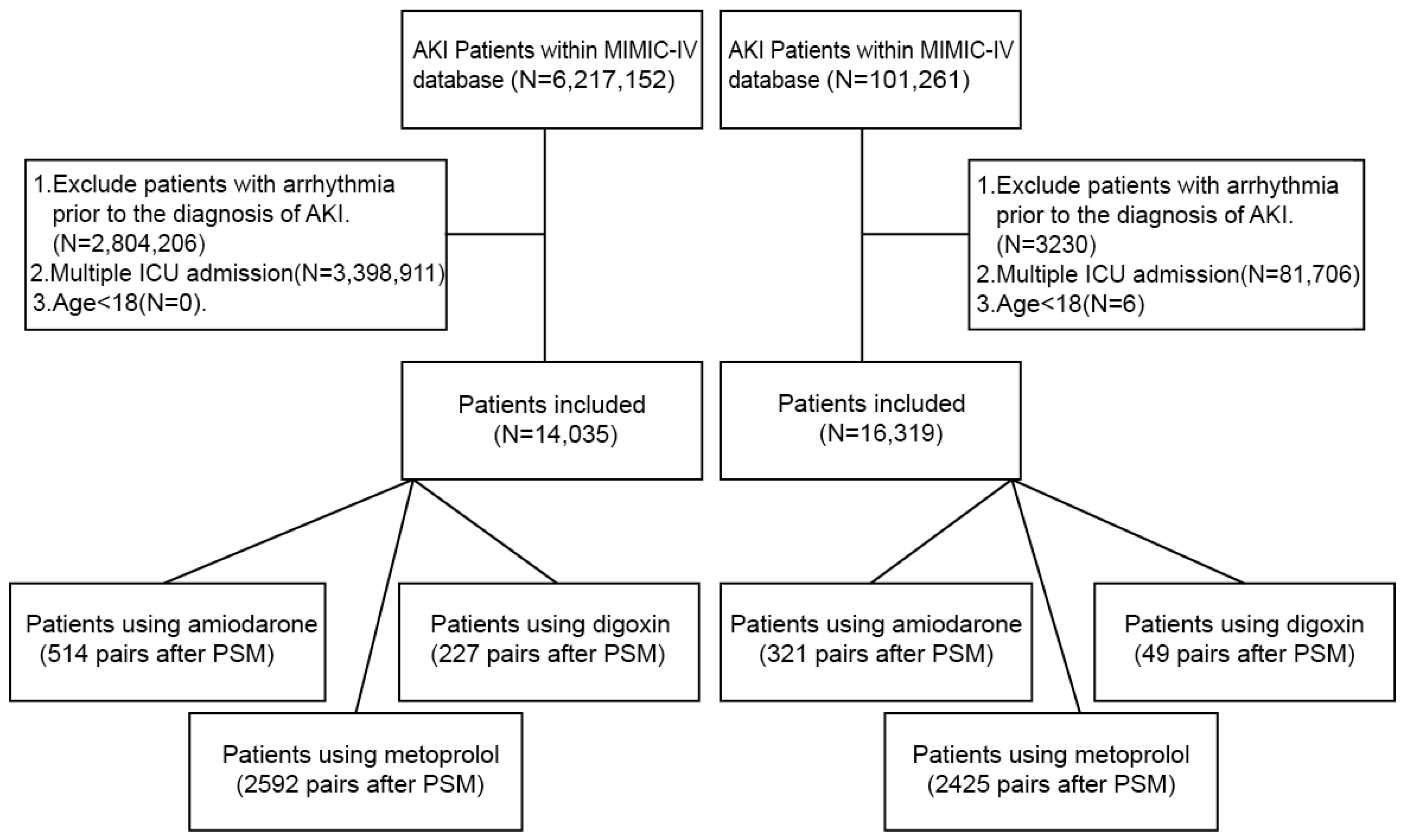
2.2. Participant Selection and Inclusion Criteria
- 1.
- As our objective was to identify arrhythmias occurring in patients with acute kidney injury (AKI), we first identified AKI cases using the KDIGO criteria [12]. To enhance clinical validity, we further verified these cases by confirming a corresponding ICD-10 diagnostic code for AKI. In total, we included 6,217,152 creatinine-based abnormal records from the MIMIC-IV database and 101,261 records from the eICU database (note that a single patient may have multiple laboratory entries over time).
- 2.
- Arrhythmias were defined based on diagnostic reports generated after the patient underwent an electrocardiogram (ECG) examination. The arrhythmia types analyzed included atrial fibrillation (AF), sinus tachycardia (ST), ventricular tachycardia (VT), sinus bradycardia, first-degree atrioventricular block (1st AV block), right bundle branch block (RBBB), left bundle branch block (LBBB), second-degree AV block (2nd AV block), third-degree AV block (3rd AV block), atrial flutter, and supraventricular tachycardia (SVT).
- 3.
- We excluded patients who were ≤18 years old.
- 4.
- Only the first ICU admission for each patient was retained; subsequent admissions were excluded.
- 5.
- Patients with a documented arrhythmia prior to the diagnosis of AKI were excluded to ensure temporal causality.
2.3. Variable Selection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. XGBoost
3.3. BIC Best Subset Selection
3.4. Subgroup Analysis and Models Performance
3.5. Prognostic Factor Analysis
3.6. Intervention Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uchino, S.; Kellum, J.A.; Bellomo, R.; Doig, G.S.; Morimatsu, H.; Morgera, S.; Schetz, M.; Tan, I.; Bouman, C.; Macedo, E.; et al. Acute Renal Failure in Critically Ill Patients: A Multinational, Multicenter Study. JAMA 2005, 294, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patschan, D.; Marahrens, B.; Jansch, M.; Patschan, S.; Ritter, O. Experimental Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 3: What Is Known so Far? J. Clin. Med. Res. 2022, 14, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovesi, S.; Regolisti, G.; Burlacu, A.; Covic, A.; Combe, C.; Mitra, S.; Basile, C.; EuDial Working Group of ERA. The Conundrum of the Complex Relationship between Acute Kidney Injury and Cardiac Arrhythmias. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 1097–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faubel, S.; Shah, P.B. Immediate Consequences of Acute Kidney Injury: The Impact of Traditional and Nontraditional Complications on Mortality in Acute Kidney Injury. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2016, 23, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, G. Arrhythmias in the ICU. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawwa, K.; Kompotiatis, P.; Bobart, S.A.; Mara, K.C.; Wiley, B.M.; Jentzer, J.C.; Kashani, K.B. New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Acute Kidney Injury on Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy. J. Crit. Care 2021, 62, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, T.; Uusalo, P.; Järvisalo, M.J. New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Critically Ill Acute Kidney Injury Patients on Renal Replacement Therapy. Europace 2022, 24, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singbartl, K.; Kellum, J.A. AKI in the ICU: Definition, Epidemiology, Risk Stratification, and Outcomes. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Fu, P. Risk Factors for the Prognosis of Acute Kidney Injury under the Acute Kidney Injury Network Definition: A Retrospective, Multicenter Study in Critically Ill Patients. Nephrology 2012, 17, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Cozzi, M.; Bush, E.L.; Rabb, H. Distant Organ Dysfunction in Acute Kidney Injury: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, R.K.; Wheeler, D.S. Kidney-Lung Cross-Talk and Acute Kidney Injury. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2013, 28, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Nadim, M.K.; Parikh, C.R. News in Pathophysiology, Definition and Classification of Hepatorenal Syndrome: A Step beyond the International Club of Ascites (ICA) Consensus Document. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.E.W.; Bulgarelli, L.; Shen, L.; Gayles, A.; Shammout, A.; Horng, S.; Pollard, T.J.; Hao, S.; Moody, B.; Gow, B.; et al. MIMIC-IV, a Freely Accessible Electronic Health Record Dataset. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, T.J.; Johnson, A.E.W.; Raffa, J.D.; Celi, L.A.; Mark, R.G.; Badawi, O. The eICU Collaborative Research Database, a Freely Available Multi-Center Database for Critical Care Research. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Carlin, J.B. Multiple Imputation for Missing Data: Fully Conditional Specification versus Multivariate Normal Imputation. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Missing Data Imputation: Focusing on Single Imputation. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Univariate Description and Bivariate Statistical Inference: The First Step Delving into Data. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Variable Selection with Stepwise and Best Subset Approaches. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.; Chen, H.; DeGrave, A.; Prutkin, J.M.; Nair, B.; Katz, R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bansal, N.; Lee, S.-I. From Local Explanations to Global Understanding with Explainable AI for Trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Kattan, M.W. Methodologic Issues Specific to Prediction Model Development and Evaluation. Chest 2023, 164, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annane, D.; Sébille, V.; Duboc, D.; Le Heuzey, J.-Y.; Sadoul, N.; Bouvier, E.; Bellissant, E. Incidence and Prognosis of Sustained Arrhythmias in Critically Ill Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinelt, P.; Karth, G.D.; Geppert, A.; Heinz, G. Incidence and Type of Cardiac Arrhythmias in Critically Ill Patients: A Single Center Experience in a Medical-Cardiological ICU. Intensive Care Med. 2001, 27, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.; Shirov, T.; Weissman, C. Supraventricular Arrhythmias in Intensive Care Unit Patients: Short and Long-Term Consequences. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 104, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trappe, H.-J.; Brandts, B.; Weismueller, P. Arrhythmias in the Intensive Care Patient. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2003, 9, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.C.; Tadros, R.; Davies, B.; Krahn, A.D. Genetic Testing in Inherited Arrhythmias: Approach, Limitations, and Challenges. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.D.; Vittinghoff, E.; Lu, A.T.; Alonso, A.; Wang, B.; Sitlani, C.M.; Mohammadi-Shemirani, P.; Fornage, M.; Kornej, J.; Brody, J.A.; et al. Epigenetic Age and the Risk of Incident Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2021, 144, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwlaat, R.; Connolly, B.J.; Hubers, L.M.; Cuddy, S.M.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Yusuf, S.; Connolly, S.J. Quality of Individual INR Control and the Risk of Stroke and Bleeding Events in Atrial Fibrillation Patients: A Nested Case Control Analysis of the ACTIVE W Study. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.; Heel, R.C.; Fitton, A. Amiodarone. An Overview of Its Pharmacological Properties, and Review of Its Therapeutic Use in Cardiac Arrhythmias. Drugs 1992, 43, 69–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.V.; Lavalle, C.; Palombi, M.; Pierucci, N.; Trivigno, S.; D’Amato, A.; Filomena, D.; Cipollone, P.; Laviola, D.; Piro, A.; et al. SGLT2i Reduce Arrhythmic Events in Heart Failure Patients with Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices. ESC Heart Fail. 2025, 12, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cardiac Dysrhythmias (5614) | Non-Cardiac Dysrhythmias (8421) | p | SMD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| demographic information | ||||
| in-hospital death (%) | 636 (11.3) | 587 (7.0) | <0.01 | 0.105 |
| age (years) | 72 [60–82] | 66 [55–77] | <0.01 | 0.279 |
| LOS (days (median [IQR])) | 2.64 [1.43–5.01] | 2.23 [1.26–4.23] | <0.01 | 0.166 |
| gender, male (%) | 3355 (59.8) | 4871 (57.8) | 0.025 | 0.04 |
| comorbidities | ||||
| cerebral infarction (%) | 500 (8.9) | 699 (8.3) | 0.22 | 0.021 |
| CKD (%) | 1980 (35.3) | 2526 (30.0) | <0.01 | 0.119 |
| diabetes (%) | 1132 (20.2) | 1833 (21.8) | 0.02 | 0.039 |
| heart failure (%) | 2772 (49.4) | 2541 (30.2) | <0.01 | 0.4 |
| hypertension (%) | 2361 (42.1) | 3885 (46.1) | <0.01 | 0.081 |
| Infarct circulation (%) | 898 (16.0) | 1239 (14.7) | 0.041 | 0.036 |
| pancreatitis (%) | 176 (3.1) | 265 (3.15) | 1 | 0.003 |
| medication usage | ||||
| antibiotic usage (%) | 4062 (72.4) | 5878 (69.8) | <0.01 | 0.06 |
| blood products (%) | 1958 (34.9) | 2771 (32.9) | 0.016 | 0.04 |
| colloids (%) | 1131 (20.1) | 1638 (19.5) | 0.321 | 0.014 |
| crystalloids (%) | 2998 (53.4) | 4541 (53.9) | 0.554 | 0.01 |
| furosemide (%) | 3455 (61.5) | 4398 (52.2) | <0.01 | 0.188 |
| insulin (%) | 2283 (40.7) | 3283 (39) | 0.048 | 0.034 |
| nitroglycerin (%) | 1283 (22.9) | 1671 (19.8) | <0.01 | 0.08 |
| pressor (%) | 1846 (32.9) | 2205 (26.2) | <0.01 | 0.147 |
| anticoagulant (%) | 4279 (76.2) | 6200 (73.6) | <0.01 | 0.06 |
| sodiumbicarbonate (%) | 712 (12.7) | 1120 (13.3) | 0.299 | 0.02 |
| laboratory examinations | ||||
| WBC_valuenum (K/mcL (median [IQR])) | 10.8 [7.6–15.3] | 10.8 [7.6–15.1] | 0.659 | 0.02 |
| WBC_max (K/mcL (median [IQR])) | 11.8 [8.2–16.7] | 11.9 [8.3–16.6] | 0.895 | 0.015 |
| WBC_min (K/mcL (median [IQR])) | 9.8 [7–13.6] | 9.8 [6.9–13.4] | 0.235 | 0.025 |
| AG_valuenum (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 15 [12–17] | 14 [12–17] | <0.01 | 0.053 |
| AG_max (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 16 [13,19] | 16 [13,19] | 0.012 | 0.03 |
| AG_min (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 14 [12–16] | 13 [11–16] | <0.01 | 0.07 |
| BUN_valuenum (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 30 [20–47] | 27 [18–43] | <0.01 | 0.119 |
| BUN_max (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 32 [21–49] | 28 [19–45] | <0.01 | 0.111 |
| BUN_min (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 28 [19–44] | 25 [17–40] | <0.01 | 0.134 |
| chloride_valuenum (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 104 [100–108] | 105 [101–108] | <0.01 | 0.09 |
| chloride_max (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 105 [101–109] | 106 [102–110] | <0.01 | 0.103 |
| chloride_min (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 103 [98–106] | 103 [99–107] | <0.01 | 0.09 |
| creatinine_valuenum (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 1.4 [1–2] | 1.3 [1–2] | <0.01 | 0.04 |
| creatinine_max (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 1.5 [1.1–2.2] | 1.4 [1.1–2.2] | 0.06 | 0.051 |
| creatinine_min (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 1.2 [0.9–1.8] | 1.3 [1.0–1.9] | <0.01 | 0.027 |
| glucose_valuenum (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 126.5 [104–163] | 129 [104–165] | 0.02 | 0.055 |
| glucose_max (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 150 [117–196] | 151 [118–204] | <0.01 | 0.073 |
| glucose_min (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 150 [117–196] | 151 [118–204] | 0.172 | 0.15 |
| hemoglobin_valuenum (g/dL (median [IQR])) | 10 [8.6–11.6] | 10 [8.6–11.5] | 0.497 | 0.015 |
| hemoglobin_max (g/dL (median [IQR])) | 10.5 [9.2–12] | 10.5 [9.2–12] | 0.732 | 0.01 |
| hemoglobin_min (g/dL (median [IQR])) | 9.6 [8.2–11.2] | 9.6 [8.1–11.2] | 0.503 | 0.02 |
| INR_valuenum (median [IQR]) | 1.4 [1.2–1.8] | 1.3 [1.1–1.6] | <0.01 | 0.219 |
| INR_max (median [IQR]) | 1.4 [1.2–1.9] | 1.3 [1.2–1.7] | <0.01 | 0.21 |
| INR_min (median [IQR]) | 1.3 [1.2–1.6] | 1.2 [1.1–1.5] | <0.01 | 0.206 |
| pH_valuenum (units (median [IQR])) | 7.37 [7.32–7.42] | 7.37 [7.32–7.42] | <0.01 | 0.026 |
| pH_max (units (median [IQR])) | 7.4 [7.36–7.44] | 7.4 [7.35–7.44] | <0.01 | 0.045 |
| pH_min (units (median [IQR])) | 7.35 [7.29–7.4] | 7.35 [7.28–7.4] | 0.09 | 0.022 |
| PLT_valuenum (K/uL (median [IQR])) | 182 [129–247] | 186 [128–255] | <0.01 | 0.034 |
| PLT_max (K/uL (median [IQR])) | 190 [138–255] | 192 [137–261] | <0.01 | 0.029 |
| PLT_min (K/uL (median [IQR])) | 168 [116–232] | 173 [116–237] | 0.104 | 0.029 |
| potassium_valuenum (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 4.2 [3.8–4.8] | 4.2 [3.8–4.7] | 0.024 | 0.035 |
| potassium_max (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 4.5 [4–5] | 4.4 [4–5] | 0.021 | 0.035 |
| potassium_min (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 3.9 [3.5–4.3] | 3.9 [3.5–4.3] | 0.074 | 0.029 |
| PT_valuenum (sec (median [IQR])) | 15.3 [13.2–19.4] | 14.3 [12.6–16.9] | <0.01 | 0.254 |
| PT_max (sec (median [IQR])) | 15.7 [13.4–20.1] | 14.5 [12.7–17.6] | <0.01 | 0.23 |
| PT_min (sec (median [IQR])) | 14.5 [12.8–18] | 13.7 [12.3–16.1] | <0.01 | |
| sodium_valuenum (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 138 [135–141] | 138 [135–141] | 0.384 | 0.018 |
| sodium_max (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 139 [137–142] | 140 [137–142] | 0.139 | 0.019 |
| sodium_min (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 137 [134–140] | 137 [134–140] | 0.41 | 0.019 |
| bicarbonate_valuenum (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 22 [19–25] | 22 [19–25] | <0.01 | 0.08 |
| bicarbonate_max (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 23 [21–26] | 23 [21–26] | <0.01 | 0.09 |
| bicarbonate_min (mEq/L (median [IQR])) | 23 [21–26] | 23 [21–26] | <0.01 | 0.085 |
| totalcalcium_valuenum (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 8.3 [7.8–8.8] | 8.3 [7.8–8.8] | <0.01 | 0.046 |
| totalcalcium_max (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 8.5 [8–8.9] | 8.4 [8–8.9] | 0.07 | 0.022 |
| totalcalcium_min (mg/dL (median [IQR])) | 8.2 [7.6–8.7] | 8.1 [7.6–8.6] | <0.01 | 0.059 |
| RBC_valuenum (m/uL (median [IQR])) | 3.39 [2.9–3.96] | 3.39 [2.89–3.93] | 0.30 | 0.025 |
| RBC_max (m/uL (median [IQR])) | 3.53 [3.09–4.04] | 3.51 [3.07–4.01] | 0.163 | 0.032 |
| RBC_min (m/uL (median [IQR])) | 3.26 [2.77–3.8] | 3.23 [2.76–3.77] | 0.06 | 0.041 |
| vital signs | ||||
| APSIII (median [IQR]) | 51 [40–67] | 47 [37–62] | <0.01 | 0.154 |
| HR_valuenum (bpm/min (median [IQR])) | 90 [76–108] | 86 [76–99] | <0.01 | 0.188 |
| HR_max (bpm/min (median [IQR])) | 107 [89–123] | 99 [88–111] | <0.01 | 0.273 |
| HR_min (bpm/min (median [IQR])) | 72 [60–86] | 70 [61–79] | <0.01 | 0.203 |
| MAP_valuenum (mmHg (median [IQR])) | 80 [69–93] | 81 [70–94] | <0.01 | 0.064 |
| MAP_max (mmHg (median [IQR])) | 100 [89–114] | 101 [90–115] | <0.01 | 0.036 |
| MAP_min (mmHg (median [IQR])) | 57 [50–65] | 58 [51–66] | <0.01 | 0.100 |
| RR_valuenum (insp/min (median [IQR])) | 19 [16–24] | 19 [15–23] | <0.01 | 0.08 |
| RR_max (insp/min (median [IQR])) | 28 [24–32] | 27 [24–31] | <0.01 | 0.142 |
| RR_min (insp/min (median [IQR])) | 13 [10–15] | 12 [10–15] | <0.01 | 0.063 |
| temperature_valuenum (°F (median [IQR])) | 98 [97.4–98.6] | 98.1 [97.5–98.7] | <0.01 | 0.046 |
| temperature_max (°F (median [IQR])) | 98.8 [98.3–99.6] | 98.9 [98.4–99.7] | <0.01 | 0.047 |
| temperature_min (°F (median [IQR])) | 97.5 [96.7–97.9] | 97.6 [96.9–98] | <0.01 | 0.055 |
| output_valuenum (ml/min (median [IQR])) | 145 [60–275] | 150 [65–300] | <0.01 | 0.087 |
| output_max (ml/min (median [IQR])) | 275 [150–400] | 300 [160–450] | <0.01 | 0.08 |
| output_min (ml/min (median [IQR])) | 30 [15–60] | 30 [15–75] | <0.01 | 0.085 |
| treatment measures | ||||
| CRRT (%) | 411 (7.3) | 598 (7.1) | 0.645 | 0.008 |
| ventilation (%) | 3712 (66.1) | 5042 (59.9) | <0.01 | 0.13 |
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 | Brier | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | |||||
| Train | 0.900 | 0.871 | 0.880 | 0.876 | 0.103 |
| Internal validation | 0.671 | 0.640 | 0.616 | 0.597 | 0.203 |
| External validation | 0.616 | 0.632 | 0.577 | 0.586 | 0.217 |
| Atrial Fibrillation | |||||
| Train | 0.85 | 0.695 | 0.685 | 0.555 | 0.083 |
| Internal validation | 0.81 | 0.525 | 0.552 | 0.434 | 0.095 |
| External validation | 0.79 | 0.443 | 0.454 | 0.378 | 0.109 |
| Sinus bradycardia | |||||
| Train | 0.92 | 0.480 | 0.606 | 0.343 | 0.0416 |
| Internal validation | 0.91 | 0.420 | 0.551 | 0.305 | 0.0422 |
| External validation | 0.90 | 0.300 | 0.504 | 0.230 | 0.0358 |
| Sinus Tachycardia | |||||
| Train | 0.89 | 0.613 | 0.377 | 0.467 | 0.079 |
| Internal validation | 0.89 | 0.561 | 0.359 | 0.438 | 0.082 |
| External validation | 0.88 | 0.383 | 0.360 | 0.370 | 0.056 |
| Atrial Fibrillation | Sinus Tachycardia | Sinus Bradycardia | AV Block | Atrial Flutter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before PSM | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.165 | 0.176 |
| After PSM | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.755 | 0.309 | 0.497 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, W.; Franz, H.; Yakulov, T.A. Evaluating In-Hospital Arrhythmias in Critically Ill Acute Kidney Injury Patients: Predictive Models, Mortality Risks, and the Efficacy of Antiarrhythmic Drugs. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134552
Xie W, Franz H, Yakulov TA. Evaluating In-Hospital Arrhythmias in Critically Ill Acute Kidney Injury Patients: Predictive Models, Mortality Risks, and the Efficacy of Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134552
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Wanqiu, Henriette Franz, and Toma Antonov Yakulov. 2025. "Evaluating In-Hospital Arrhythmias in Critically Ill Acute Kidney Injury Patients: Predictive Models, Mortality Risks, and the Efficacy of Antiarrhythmic Drugs" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134552
APA StyleXie, W., Franz, H., & Yakulov, T. A. (2025). Evaluating In-Hospital Arrhythmias in Critically Ill Acute Kidney Injury Patients: Predictive Models, Mortality Risks, and the Efficacy of Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134552






