The Diagnostic Accuracy of the Nasopharyngeal Reflux Endoscopic Score (NRES) for Identifying Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
- CRS with LPRD (n = 116);
- CRS without LPRD (n = 69);
- Healthy controls (n = 31).
- Reference standard for LPRD.
- −
- The Reflux Symptom Score (RSS) with a cut-off of >13 [15].
- −
- The Reflux Symptom Index (RSI) [16].
- −
- Physician judgment incorporating symptom patterns and response to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy. In cases where diagnosis was uncertain, 24 h dual-probe pH monitoring and gastrointestinal endoscopy were performed to confirm gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and characterize the reflux phenotype. The assessors were blinded to the Nasopharyngeal Reflux Endoscopic Score (NRES) results.
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Blinding
2.5. Statistical Methods
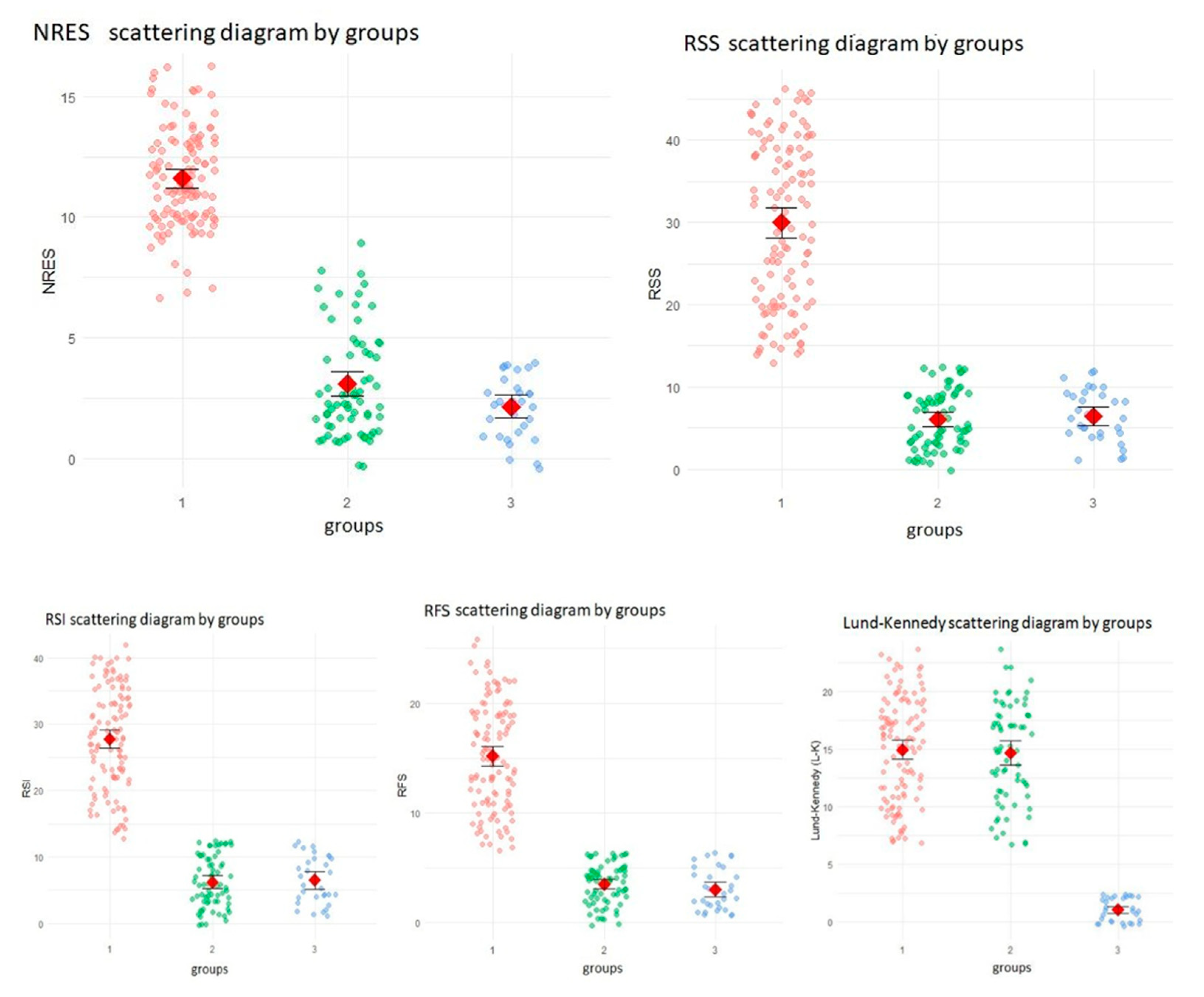
3. Results
3.1. Participant Flow and Baseline Characteristics
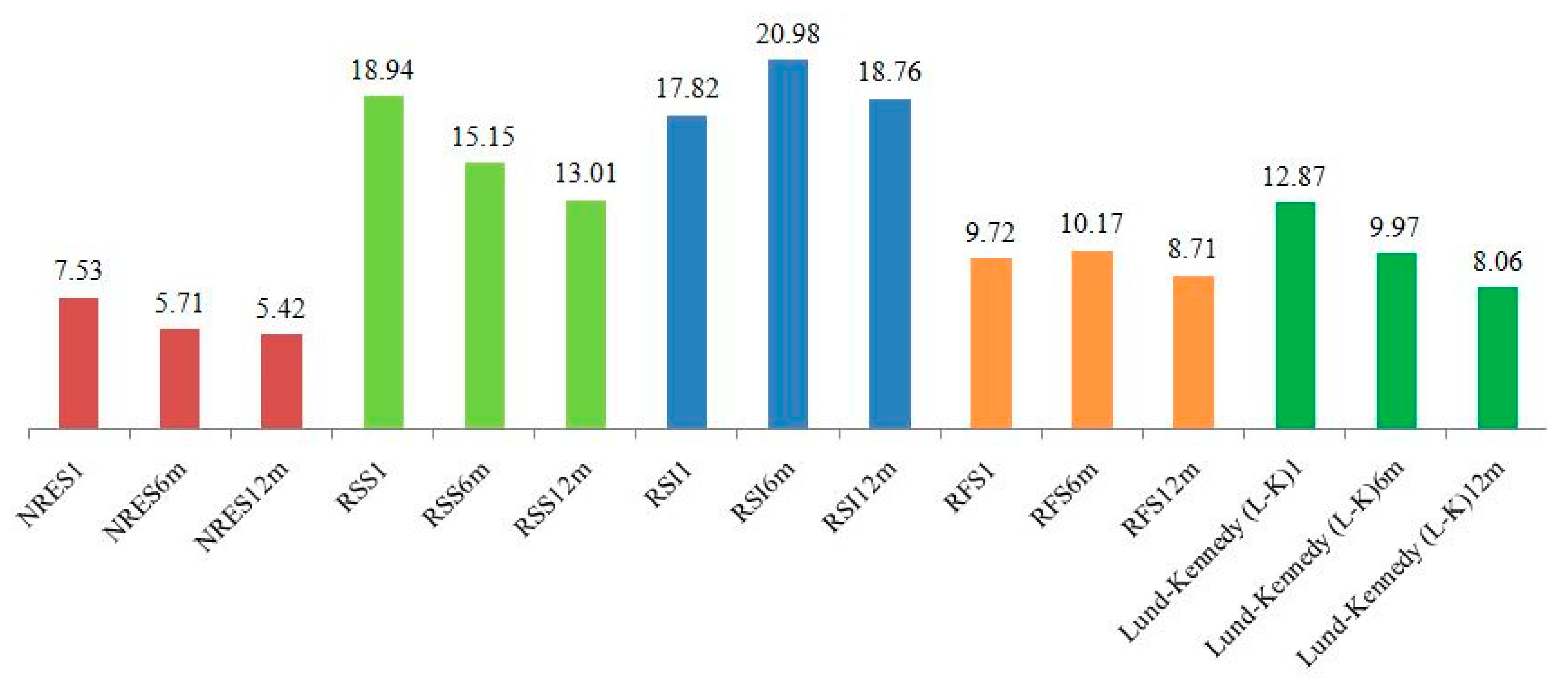
3.2. Longitudinal Changes in Scores
3.3. Correlation Across Scales
3.4. Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Applicability of the NRES
4.2. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRSwNP/CRSsNP | chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps |
| LPRD | laryngopharyngeal reflux disease |
| RSI | Reflux Symptom Index |
| RSS | Reflux Symptom Score |
| NRES | Nasopharyngeal Reflux Endoscopic Score |
| L-K | Lund–Kennedy |
| EPOS | European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020 |
| RFS | Reflux Finding Score |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| PPIs | proton pump inhibitors |
| GERD | gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| MII-pH | multichannel intraluminal impedance–pH |
| EER | extraesophageal reflux |
References
- Lechien, J.R.; Ragrag, K.; Kasongo, J.; Favier, V.; Mayo-Yanez, M.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Iannella, G.; Cammaroto, G.; Saibene, A.M.; Vaira, L.A.; et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori, reflux and chronic rhinosinusitis: A systematic review. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldajani, A.; Alhussain, F.; Mesallam, T.; AbaAlkhail, M.; Alojayri, R.; Bassam, H.; Alotaibi, O.; Alqahtani, M.; Alsaleh, S. Association Between Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Reflux Diseases in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2024, 38, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyawali, C.P.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Savarino, E.; Zerbib, F.; Mion, F.; Smout, A.J.P.M.; Vaezi, M.; Sifrim, D.; Fox, M.R.; Vela, M.F.; et al. Modern diagnosis of GERD: The Lyon Consensus. Gut 2018, 67, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brown, H.J.; Kuhar, H.N.; Plitt, M.A.; Husain, I.; Batra, P.S.; Tajudeen, B.A. The Impact of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux on Patient-reported Measures of Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2020, 129, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sella, G.C.P.; Tamashiro, E.; Anselmo-Lima, W.T.; Valera, F.C.P. Relation between chronic rhinosinusitis and gastroesophageal reflux in adults: Systematic review. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 83, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bohnhorst, I.; Jawad, S.; Lange, B.; Kjeldsen, J.; Hansen, J.M.; Kjeldsen, A.D. Prevalence of chronic rhinosinusitis in a population of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2015, 29, e70–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniaci, A.; Vaira, L.A.; Cammaroto, G.; Favier, V.; Lechien, J.R. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, laryngopharyngeal reflux, and nasopharyngeal reflux in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 3295–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Xie, H. Gastroesophageal Reflux and Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 3086–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, H. Pathogenesis of pepsin-induced gastroesophageal reflux disease with advanced diagnostic tools and therapeutic implications. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1516335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Maev, I.V.; Livzan, M.A.; Mozgovoi, S.I.; Gaus, O.V.; Bordin, D.S. Esophageal Mucosal Resistance in Reflux Esophagitis: What We Have Learned So Far and What Remains to Be Learned. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, I.; Kasmin, F. Esophageal pH Monitoring. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cumpston, E.C.; Blumin, J.H.; Bock, J.M. Dual pH with Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance Testing in the Evaluation of Subjective Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Symptoms. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 155, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belafsky, P.C.; Postma, G.N.; Koufman, J.A. The validity and reliability of the reflux finding score (RFS). Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokkens, W.J.; De Corso, E.; Backer, V.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Bjermer, L.; von Buchwald, C.; Chaker, A.; Diamant, Z.; Gevaert, P.; Han, J.; et al. EPOS2020/EUFOREA expert opinion on defining disease states and therapeutic goals in CRSwNP. Rhinology 2024, 62, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Bobin, F.; Muls, V.; Thill, M.P.; Horoi, M.; Ostermann, K.; Huet, K.; Harmegnies, B.; Dequanter, D.; Dapri, G.; et al. Validity and reliability of the reflux symptom score. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, E98–E107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belafsky, P.C.; Postma, G.N.; Koufman, J.A. Validity and reliability of the reflux symptom index (RSI). J. Voice. 2002, 16, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadlapati, R.; Chan, W.W. Modern Day Approach to Extraesophageal Reflux: Clearing the Murky Lens. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sidhwa, F.; Moore, A.; Alligood, E.; Fisichella, P.M. Diagnosis and Treatment of the Extraesophageal Manifestations of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, M.; Dong, L.; Jin, M.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xue, F.; Jiang, L.; et al. Causal association of gastroesophageal reflux disease with chronic sinusitis and chronic disease of the tonsils and adenoids. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagandykova, K.; Papulova, N.; Azhenov, T.; Darbekova, A.; Aigozhina, B.; Lechien, J.R. Endoscopic Features of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Medicina 2024, 60, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, G.; Guo, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Causal analysis between gastroesophageal reflux disease and chronic rhinosinusitis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.W.; Vela, M.F.; Peterson, K.A.; Carlson, D.A. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Diagnosis and Management of Extraesophageal Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Expert Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 1414–1421.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianella, P.; Roncone, S.; Ala, U.; Bottero, E.; Cagnasso, F.; Cagnotti, G.; Bellino, C. Upper digestive tract abnormalities in dogs with chronic idiopathic lymphoplasmacytic rhinitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gong, X.; Han, Z.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, H. The interplay of inflammation and remodeling in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis: Current understanding and future directions. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1238673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Choi, H.G.; Kong, I.G. The association between chronic rhinosinusitis and proton pump inhibitor use: A nested case-control study using a health screening cohort. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, B.; Lim, H.; Kim, M.; Kong, I.G.; Choi, H.G. Gastroesophageal reflux disease increases the risk of chronic rhinosinusitis: A nested case-control study using a national sample cohort. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.K.; Vaezi, M.F. Gastroesophageal reflux monitoring: pH (catheter and capsule) and impedance. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 19, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Han, J.K.; Desrosiers, M.; Hellings, P.W.; Amin, N.; Lee, S.E.; Mullol, J.; Greos, L.S.; Bosso, J.V.; Laidlaw, T.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): Results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials. Lancet 2019, 394, 1638–1650, Erratum in Lancet 2019, 394, 1618. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32218-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzić, S.A.; Turkalj, M.; Župan, A.; Labor, M.; Plavec, D.; Baudoin, T. Eight weeks of omeprazole 20 mg significantly reduces both laryngopharyngeal reflux and comorbid chronic rhinosinusitis signs and symptoms: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018, 43, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Qian, T.; Sun, S.; Jiang, J.J. Laryngopharyngeal Reflux and Inflammatory Responses in Mucosal Barrier Dysfunction of the Upper Aerodigestive Tract. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 13, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gokani, S.A.; Espehana, A.; Pratas, A.C.; Luke, L.; Sharma, E.; Mattock, J.; Gavrilovic, J.; Clark, A.; Wileman, T.; Philpott, C.M. Systematic Review of Protein Biomarkers in Adult Patients With Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2023, 37, 705–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Prithviraj, S.M.; Anbarasan, S.; Sankar, S.; Haritha, S. Role of Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: A Prospective Study. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 76, 5505–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Derycke, L.; Holtappels, G.; Wang, X.D.; Zhang, L.; Bachert, C.; Zhang, N. Th2 cytokines orchestrate the secretion of MUC5AC and MUC5B in IL-5-positive chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Allergy 2019, 74, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Signs of Nasopharyngeal Reflux Exposure | 0 (Absent) | 1 (Moderately Expressed) | 2 (Severely Expressed) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nose | |||
| Asymmetry between the anterior and posterior regions of the nasal cavity | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Predominantly unilateral hypertrophy of the posterior end of the inferior turbinate | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Absence of mucus in the middle nasal passage | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Nasopharynx | |||
| Hypertrophy of the posterior wall of the nasopharynx | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Hypertrophy of the Eustachian tube opening | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Increased vascular pattern | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Presence of mucus | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Erythema or inflammation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Atrophic changes in the mucosa | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Presence of granulations or fibrotic changes | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ |
| Characteristic | Group 1: CRS with LPRD (n = 116) | Group 2: CRS Without LPRD (n = 69) | Group 3: Healthy Controls (n = 31) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD), years | 45.2 (12.3) | 44.8 (11.9) | 43.5 (10.7) |
| Female, n (%) | 68 (58.6%) | 39 (56.5%) | 18 (58.1%) |
| CRS with nasal polyps, n (%) | 52 (44.8%) | 30 (43.5%) | N/A |
| Metric | Estimate (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| AUC | 0.998 (0.994–1.000) |
| Sensitivity | 98% (94–100%) |
| Specificity, True Negative Rate, TNR | 96% (91–99%) |
| Positive Predictive Value | 97% (93–99%) |
| Negative Predictive Value | 97% (92–99%) |
| NRES | RSS | RSI | RFS | Lund–Kennedy (L-K) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRES | 1.000 | 0.768 * | 0.766 * | 0.769 * | 0.221 * |
| RSS | 0.768 * | 1.000 | 0.787 * | 0.729 * | 0.242 * |
| RSI | 0.766 * | 0.787 * | 1.000 | 0.758 * | 0.278 * |
| RFS | 0.769 * | 0.729 * | 0.758 * | 1.000 | 0.284 * |
| Lund–Kennedy (L-K) | 0.221 * | 0.242 * | 0.278 * | 0.284 * | 1.000 |
| Term | Estimate | Std. Error | Statistic | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 12.94621936 | 0.766071047 | 16.89950222 | 0.000 |
| age | −0.02046886 | 0.014314153 | −1.429973523 | 0.156 |
| race | −0.452673187 | 0.40994756 | −1.104222178 | 0.272 |
| LA Classification B | −0.153630492 | 0.432067518 | −0.355570567 | 0.723 |
| LA Classification C | −1.023346692 | 0.537950794 | −1.902305385 | 0.060 |
| LA Classification D | −0.860190641 | 1.46213281 | −0.588312248 | 0.558 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sagandykova, K.; Papulova, N.; Muhamadieva, G.; Azhenov, T.; Lechien, J.R. The Diagnostic Accuracy of the Nasopharyngeal Reflux Endoscopic Score (NRES) for Identifying Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124293
Sagandykova K, Papulova N, Muhamadieva G, Azhenov T, Lechien JR. The Diagnostic Accuracy of the Nasopharyngeal Reflux Endoscopic Score (NRES) for Identifying Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124293
Chicago/Turabian StyleSagandykova, Kalamkas, Nataliya Papulova, Gul’mira Muhamadieva, Talapbek Azhenov, and Jerome R. Lechien. 2025. "The Diagnostic Accuracy of the Nasopharyngeal Reflux Endoscopic Score (NRES) for Identifying Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease in Chronic Rhinosinusitis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124293
APA StyleSagandykova, K., Papulova, N., Muhamadieva, G., Azhenov, T., & Lechien, J. R. (2025). The Diagnostic Accuracy of the Nasopharyngeal Reflux Endoscopic Score (NRES) for Identifying Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124293







