Comparative Effects of Dulaglutide and Semaglutide on Renal Function Decline and Proteinuria Reduction in Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Definitions of Parameters and Outcomes
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Baseline Characteristics of Patients
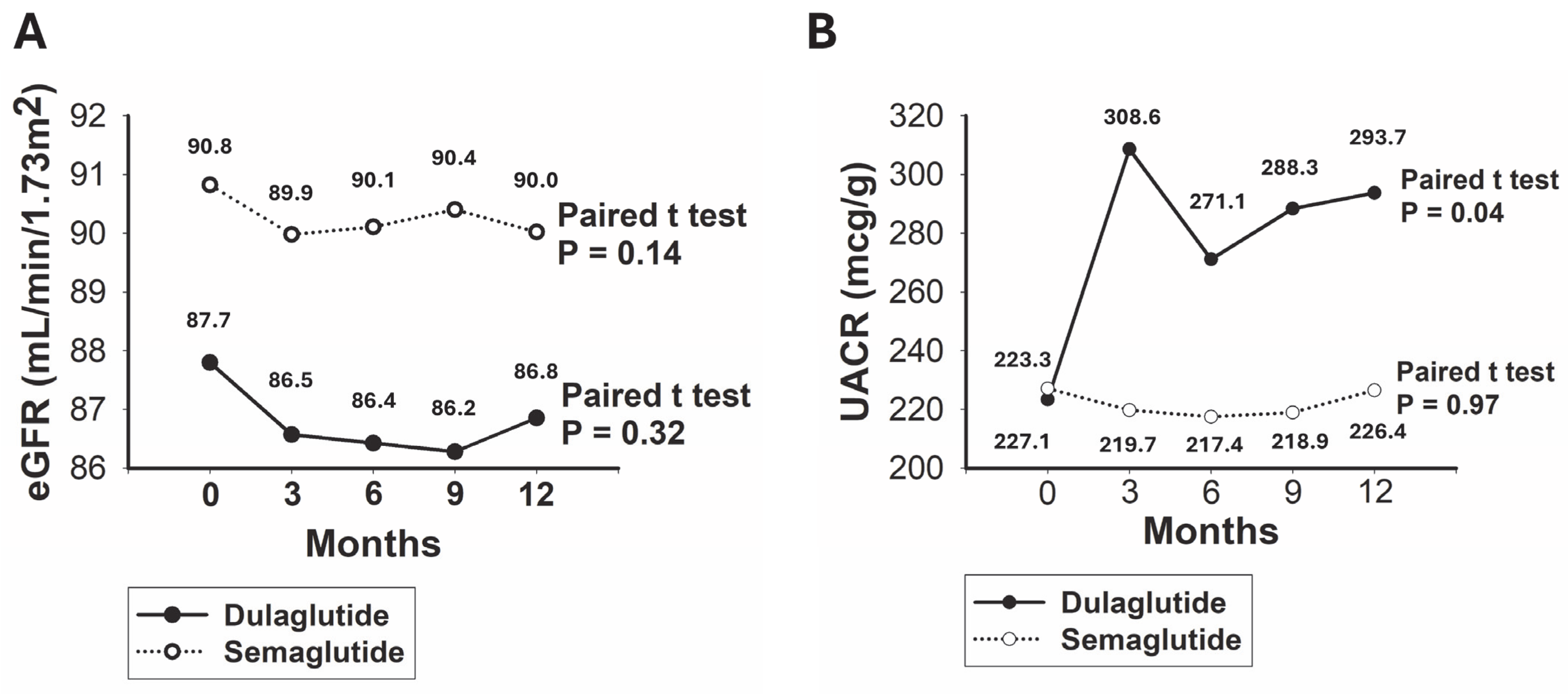
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Renal Outcomes in Patients Treated with Dulaglutide Versus Semaglutide
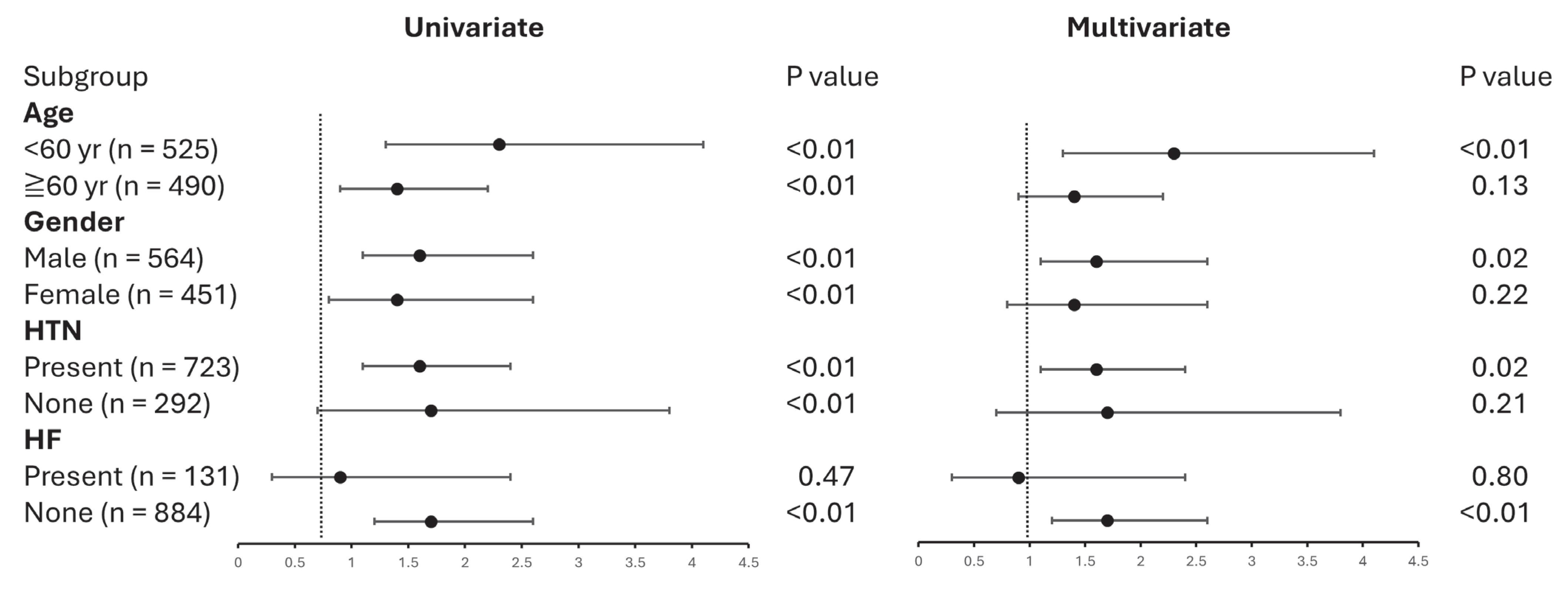
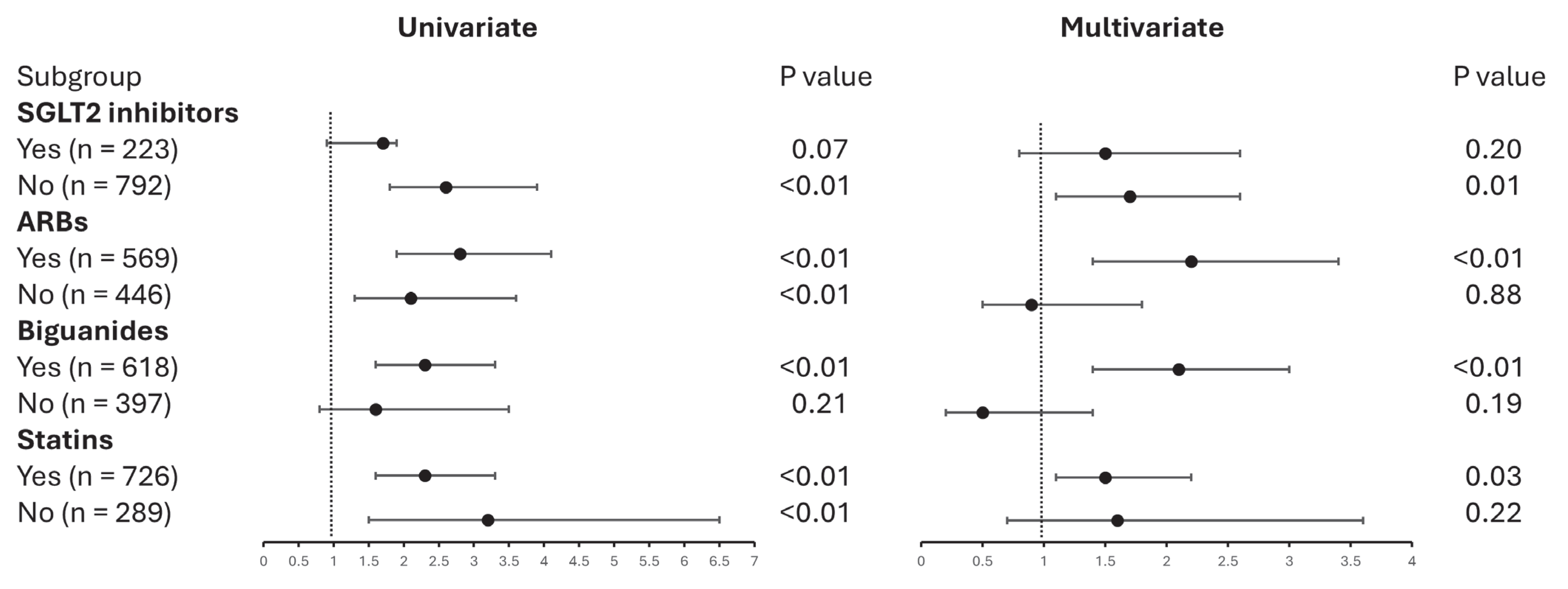
3.3. UACR Subgroup Outcomes in Patients Using Dulaglutide Versus Semaglutide
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cade, W.T. Diabetes-related microvascular and macrovascular diseases in the physical therapy setting. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1322–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.X.; Kiberd, B.A.; Clark, W.F.; Haynes, R.B.; Clase, C.M. Albuminuria and renal insufficiency prevalence guides population screening: Results from the NHANES III. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-T.; Xu, X.; Lim, P.S.; Hung, K.-Y. Worldwide Epidemiology of Diabetes-Related End-Stage Renal Disease, 2000–2015. Diabetes Care 2020, 44, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yen, F.; Lin, K.; Shin, S.; Hsu, Y.; Hsu, C. Diabetes Kidney Disease Research Committee of the Diabetes Association of the Republic of China (Taiwan) Epidemiological characteristics of diabetic kidney disease in Taiwan. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 2112–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duru, O.K.; Middleton, T.; Tewari, M.K.; Norris, K. The Landscape of Diabetic Kidney Disease in the United States. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Sharma, K.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Glycemic control in diabetic CKD patients: Where do we stand? Am J Kidney Dis. 2008, 52, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Atsumi, Y.; Matsuoka, K.; Onuma, T.; Tohjima, T.; Kawamori, R. Role of glycemic control and blood pressure in the development and progression of nephropathy in elderly Japanese NIDDM patients. Diabetes. Care. 1998, 21, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Bain, R.P.; Rohde, R.D.; The Collaborative Study Group. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Clarke, W.R.; Berl, T.; Pohl, M.A.; Lewis, J.B.; Ritz, E.; Atkins, R.C.; Rohde, R.; Raz, I.; et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Keane, W.F.; Mitch, W.E.; Parving, H.H.; Remuzzi, G.; Snapinn, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Shahinfar, S.; et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, D.K.; Shih, W.J.; Cosentino, F.; Charbonnel, B.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Pratley, R.; Greenberg, M.; Wang, S.; Huyck, S.; et al. Association of SGLT2 Inhibitors with Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis. JAMA. Cardiol. 2021, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, W.G.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.B.; Hauske, S.J.; Emberson, J.R.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K.J.; Ng, S.Y.A.; et al. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kintscher, U.; Bakris, G.L.; Kolkhof, P. Novel non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in cardiorenal disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3220–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissele, R.; Göke, R.; Willemer, S.; Harthus, H.P.; Vermeer, H.; Arnold, R.; GÖKE, B. Glucagon-like peptide-1 cells in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas of rat, pig and man. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 22, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orskov, C.; Wettergren, A.; Holst, J.J. Secretion of the incretin hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 and gastric inhibitory polypeptide correlates with insulin secretion in normal man throughout the day. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1996, 31, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhre, R.E.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Hartmann, B.; Deacon, C.F.; Holst, J.J. Measurement of the incretin hormones: Glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2020, 44, S125–S150. [Google Scholar]
- Cosentino, F.; Grant, P.; Aboyans, V.; Bailey, C.J.; Ceriello, A.; Delgado, V.; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2019 ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 255–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Diabetes Working Group. KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, S1–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaman, A.M.; Bain, S.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Buse, J.B.; Idorn, T.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Rasmussen, S.; Rossing, P.; et al. Effect of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists semaglutide and liraglutide on kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: Pooled analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and LEADER. Circulation 2022, 145, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Khurmi, N.S. Efpeglenatide and Heart and Kidney Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2107. [Google Scholar]
- Branch, K.R.; Dagenais, G.R.; Avezum, A.; Basile, J.; Conget, I.; Cushman, W.C.; Jansky, P.; Lakshmanan, M.; Lanas, F.; Leiter, L.A.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular and heart failure outcomes in patients with and without heart failure: A post-hoc analysis from the REWIND randomized trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Botros, F.T.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: An exploratory analysis of the REWIND randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botros, F.T.; Gerstein, H.C.; Malik, R.; Nicolay, C.; Hoover, A.; Turfanda, I.; Colhoun, H.M.; Shaw, J.E. Dulaglutide and Kidney Function-Related Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: A REWIND Post Hoc Analysis. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.J. Long-acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: A review of their efficacy and tolerability. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, S279–S284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallwitz, B. GLP-1 agonists and dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 203, 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- Okerson, T.; Chilton, R.J. The cardiovascular effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2012, 30, e146–e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, I.; Tsioufis, K.; Katsi, V. Spotlight on the Mechanism of Action of Semaglutide. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 14514–14541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badve, S.V.; Bilal, A.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Sattar, N.; Gerstein, H.C.; Ruff, C.T.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on kidney and cardiovascular disease outcomes: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieske, B.; Tschöpe, C.; A de Boer, R.; Fraser, A.G.; Anker, S.D.; Donal, E.; Edelmann, F.; Fu, M.; Guazzi, M.; Lam, C.S.P.; et al. How to diagnose heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: The HFA-PEFF diagnostic algorithm: A consensus recommendation from the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3297–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CKD-EPI Creatinine Equation. 2021. Available online: https://www.kidney.org/ckd-epi-creatinine-equation-2021 (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Apperloo, E.M.; I Cherney, D.Z.; Kuhlman, A.B.; E Mann, J.F.; Rasmussen, S.; Rossing, P.; Tuttle, K.R.; Vrhnjak, B.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Effect of semaglutide on kidney function across different levels of baseline HbA1c, blood pressure, body weight and albuminuria in SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2025, 40, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; An, J.N.; Song, Y.R.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, H.S.; Cho, A.; Kim, J.-K.; Bulum, T. Effect of once-weekly dulaglutide on renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Li, H.; Huang, S.; Shen, L. Semaglutide vs. dulaglutide for glycemic and weight control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed. Rep. 2024, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingvay, I.; Bauer, R.; Baker-Knight, J.; Lawson, J.; Pratley, R. An Indirect Treatment Comparison of Semaglutide 2.0 mg vs Dulaglutide 3.0 mg and 4.5 mg Using Multilevel Network Meta-regression. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar]
- E Pratley, R.; Aroda, V.R.; Catarig, A.-M.; Lingvay, I.; Lüdemann, J.; Yildirim, E.; Viljoen, A. Impact of patient characteristics on efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus dulaglutide: SUSTAIN 7 post hoc analyses. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e037883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, A.; Shojaei, S.; Soleimani, H.; Semirani-Nezhad, D.; Ebrahimi, P.; Zafari, A.; Ebrahimi, R.; Roozbehi, K.; Harrison, A.; Syed, M.A.; et al. Safety, efficacy, and cardiovascular benefits of combination therapy with SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2025, 17, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simms-Williams, N.; Treves, N.; Yin, H.; Lu, S.; Yu, O.; Pradhan, R.; Renoux, C.; Suissa, S.; Azoulay, L. Effect of combination treatment with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on incidence of cardiovascular and serious renal events: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2024, 385, e078242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdy, P.; Darmon, P.; Dievart, F.; Halimi, J.-M.; Guerci, B. Combining glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Character | Total | Dulaglutide | Semaglutide | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number, n | 1015 | 268 | 747 | n/a |
| Age, yr | 59.5 ± 14.2 | 63.6 ± 15.1 | 58.0 ± 13.6 | <0.01 |
| Male, n (%) | 564 (55.5) | 163 (60.8) | 401 (53.6) | 0.04 |
| HTN, n (%) | 723 (71.2) | 208 (77.6) | 515 (68.9) | <0.01 |
| CKD, n (%) | 636 (62.6) | 169 (63.0) | 467 (62.5) | 0.87 |
| HF, n (%) | 131 (12.9) | 43 (16.0) | 88 (11.7) | 0.07 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 736 (72.5) | 195 (72.7) | 541 (72.4) | 0.91 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.9 ± 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.7 | 0.9 ± 0.5 | 0.08 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 90.0 ± 31.7 | 87.7 ± 34.2 | 90.8 ± 30.8 | 0.20 |
| HbA1c, % | 7.7 ± 1.8 | 8.7 ± 1.7 | 7.3 ± 1.7 | <0.01 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 3.6 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.3 | <0.01 |
| ALT, U/L | 20.0 (17.0) | 21.0 (20.0) | 20.0 (17.0) | 0.09 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 90.4 ± 31.3 | 91.6 ± 31.8 | 90.0 ± 31.1 | 0.47 |
| TRIG, mg/dL | 136.0 (93.0) | 150.5 (114.5) | 132.0 (90.0) | <0.01 |
| UACR, mg/g | 50.0 (88.0) | 50.0 (133.0) | 65.0 (88.0) | 0.98 |
| Character | Total | Dulaglutide | Semaglutide | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number, n | 1015 | 268 | 747 | n/a |
| SGLT2 inhibitor, n (%) | 223 (21.9) | 92 (34.3) | 131 (17.5) | <0.01 |
| ARB, n (%) | 569 (56.0) | 156 (58.2) | 413 (55.2) | 0.40 |
| Spironolactone, n (%) | 39 (3.8) | 14 (5.2) | 25 (3.3) | 0.17 |
| Biguanides, n (%) | 618 (60.8) | 205 (76.4) | 413 (55.2) | <0.01 |
| Loop diuretics, n (%) | 43 (4.2) | 15 (5.6) | 28 (3.7) | 0.19 |
| Thiazide, n (%) | 94 (9.2) | 24 (8.9) | 70 (9.3) | 0.84 |
| Statins, n (%) | 726 (71.5) | 205 (76.4) | 521 (69.7) | 0.03 |
| Outcomes | Total | Dulaglutide | Semaglutide | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR change, mL/min | −0.8 ± 0.4 | −0.9 ± 0.9 | −0.8 ± 0.5 | 0.69 |
| eGFR decline, n (%) | 243 (23.9) | 69 (25.7) | 174 (23.2) | 0.41 |
| UACR change, mcg/g | 18.1 ± 15.9 | 70.3 ± 34.7 | −0.6 ± 17.7 | <0.01 |
| UACR increase, n (%) | 220 (21.6) | 92 (34.3) | 128 (17.1) | <0.01 |
| Death, n (%) | 8 (0.8) | 6 (2.2) | 2 (0.2) | <0.01 |
| Character | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Dulaglutide use | 2.4 | 1.8–3.3 | <0.01 | 1.6 | 1.1–2.3 | <0.01 |
| Age, per 10 yr increment | 1.3 | 1.2–1.4 | <0.01 | 1.2 | 1.1–1.4 | <0.01 |
| Male | 1.6 | 1.2–2.2 | <0.01 | 1.2 | 0.9–1.7 | 0.22 |
| HTN | 2.0 | 1.4–2.9 | <0.01 | 1.4 | 0.9–2.1 | 0.11 |
| CKD | 1.5 | 1.1–2.2 | 0.02 | 0.8 | 0.5–1.1 | 0.10 |
| HF | 0.6 | 0.4–0.9 | 0.04 | 0.6 | 0.3–0.9 | 0.03 |
| Dyslipidemia | 1.5 | 1.1–2.1 | 0.02 | 1.0 | 0.7–1.5 | 0.84 |
| HbA1c, per 1% increment | 1.3 | 1.2–1.4 | <0.01 | 1.2 | 1.1–1.3 | <0.01 |
| Albumin, per 1 g/dL increment | 1.1 | 0.8–1.5 | 0.58 | |||
| ALT, per 30 U/L increment | 0.8 | 0.7–1.1 | 0.20 | |||
| LDL, per 100 mg/dL increment | 0.5 | 0.3–0.8 | <0.01 | 0.6 | 0.3–1.0 | 0.07 |
| TRIG, per 100 mg/dL increment | 1.0 | 0.9–1.0 | 0.26 | |||
| SGLT2 inhibitors use | 2.1 | 1.5–2.9 | <0.01 | 1.7 | 1.2–2.4 | <0.01 |
| ARB use | 1.8 | 1.3–2.4 | <0.01 | 1.1 | 0.7–1.6 | 0.56 |
| Spironolactone use | 1.1 | 0.5–2.2 | 0.79 | |||
| Biguanides use | 3.4 | 2.4–4.9 | <0.01 | 1.5 | 0.9–2.3 | 0.08 |
| Loop diuretics use | 1.2 | 0.6–2.4 | 0.53 | |||
| Thiazide use | 1.2 | 0.7–1.9 | 0.37 | |||
| Statin use | 2.3 | 1.6–3.3 | <0.01 | 1.3 | 0.8–2.0 | 0.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sue, Y.-M.; Lu, D.-E.; Chang, T.-I.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Hsu, S.-C.; Chu, Y.-L.; Huang, N.-J.; Chen, T.-H.; Lin, F.-Y.; et al. Comparative Effects of Dulaglutide and Semaglutide on Renal Function Decline and Proteinuria Reduction in Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124287
Sue Y-M, Lu D-E, Chang T-I, Chen C-Y, Chen C-H, Hsu S-C, Chu Y-L, Huang N-J, Chen T-H, Lin F-Y, et al. Comparative Effects of Dulaglutide and Semaglutide on Renal Function Decline and Proteinuria Reduction in Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124287
Chicago/Turabian StyleSue, Yuh-Mou, De-En Lu, Te-I Chang, Chun-You Chen, Cheng-Hsien Chen, Shih-Chang Hsu, Yen-Ling Chu, Nai-Jen Huang, Tso-Hsiao Chen, Feng-Yen Lin, and et al. 2025. "Comparative Effects of Dulaglutide and Semaglutide on Renal Function Decline and Proteinuria Reduction in Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124287
APA StyleSue, Y.-M., Lu, D.-E., Chang, T.-I., Chen, C.-Y., Chen, C.-H., Hsu, S.-C., Chu, Y.-L., Huang, N.-J., Chen, T.-H., Lin, F.-Y., Shih, C.-M., Huang, P.-H., Hsieh, H.-L., & Liu, C.-T. (2025). Comparative Effects of Dulaglutide and Semaglutide on Renal Function Decline and Proteinuria Reduction in Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124287










