Recovery and Protective Effect of Direct Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation in the Treatment of Acute and Subacute Fibular Tunnel Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.1.1. Selection Criteria
- European patients;
- Adult men and women from 21 to 60 years old;
- Duration of FT syndrome is less than 15 days;
- Unilateral lesion;
- Conduction block of common peroneal nerve at the FT level > 30% and/or decreased in motor common peroneal nerve conduction velocity < 40 m/s;
- Ankle dorsiflexion weakness is maximum 4/5 points, patients with paralysis are not included in this study;
- Voluntary consent to participate in this study.
- Epilepsy;
- Cognitive and mental disorders;
- Distal polyneuropathy or L5 radiculopathy;
- Brain and spinal cord disorders;
- Cardiac arrhythmias and cardiac pacemaker;
- Botulinum toxin injections to any muscle of leg in the previous 3 months;
- Vascular atherosclerosis and venous thrombosis of the lower extremities;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Undergoing another physiotherapy treatment or acupuncture;
- Pregnancy.
2.1.2. Ethical Statement and Registration Documents
2.1.3. Patient Randomization into Groups
2.1.4. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Assessment and Outcome Measures
2.3.1. Primary Outcome Measure
Hypoesthesia
Motor Deficit
- 5 points: no visible muscle activation.
- 4 points: muscle activation with no or trace movement.
- 3 points: muscle activation but not against gravity.
- 2 points: muscle activation against gravity but not resistance.
- 1 points: muscle activation against some resistance results in full ankle dorsiflexion.
- 0 points: muscle activation against full resistance results in full ankle dorsiflexion.
Gait Disorder
- Point 0 corresponds to the absence of gait disturbances. When walking, the angle of contact between the heel and the ground is very noticeable.
- Point 1 corresponds to the moderate gait disturbance in which the heel contacts the ground for a very short period of time before the forefoot contacts the ground.
- Point 2 corresponds to the severe gait disturbance in which the entire foot landing on the ground with a characteristic slap.
- Point 3 corresponds to the maximum gait disturbance, in which the forefoot touches the ground before the heel. To avoid falling due to the inability to lift the toe off the ground and the possible impact of the edge of the forefoot on the floor when stepping with the affected leg, the patient has to lift the foot more than its length, performing a characteristic maneuver resembling a rooster’s gait.
2.3.2. Secondary Outcome Measure
Pain Syndrome
Paraesthesia
Global Quality of Life Scale
2.4. Electromyograohy Examination
2.5. Ultrasonography of Peroneal Nerve
2.6. Pharmacotherapy
2.7. Direct Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
2.7.1. Protocol of Sham TENS
2.7.2. Protocol of HF TENS
2.7.3. Protocol of LF TENS
2.7.4. Protocol of HF-LF TENS
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Primary Clinical Outcomes
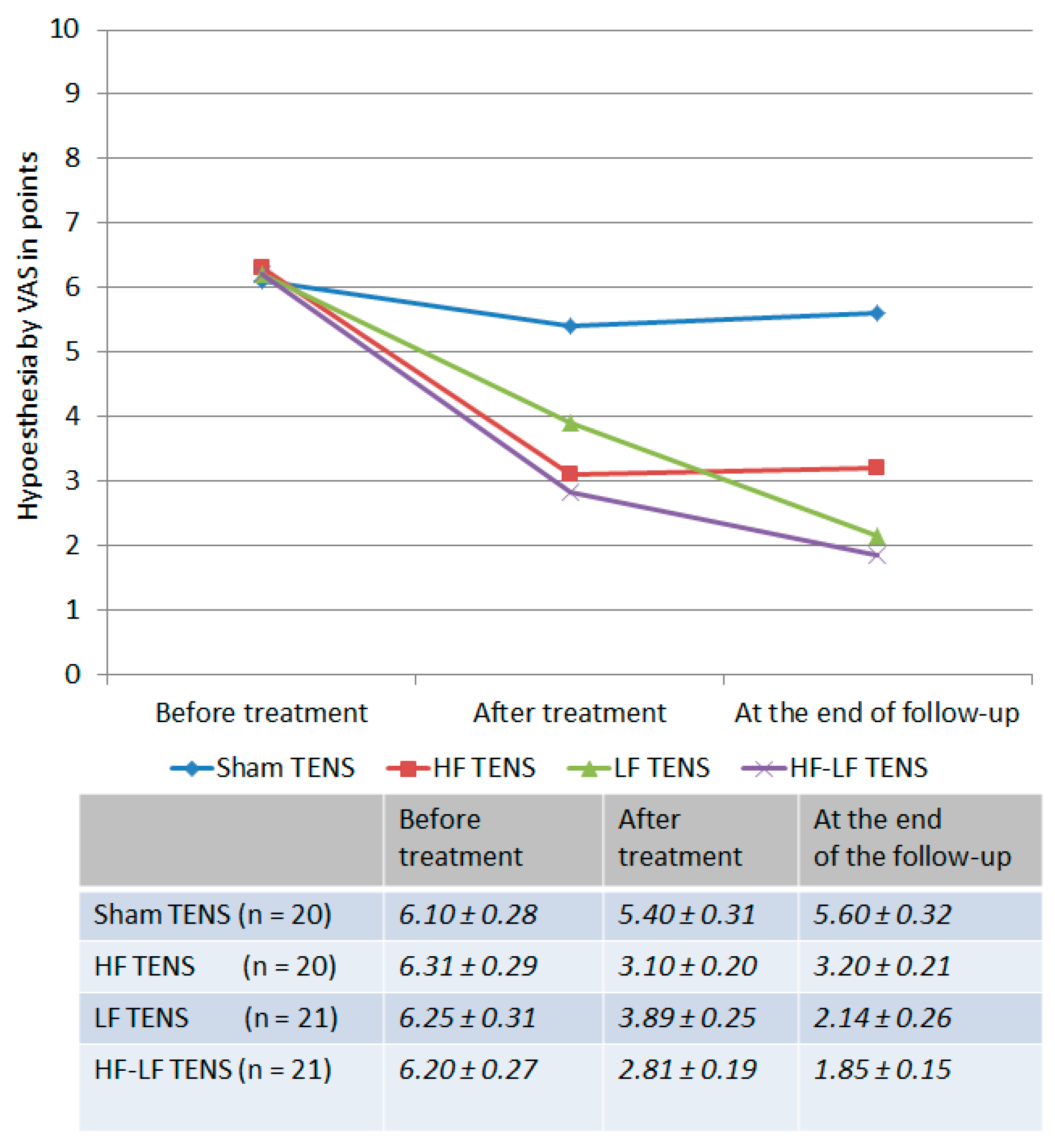
3.1.1. Dynamics of Hypoesthesia
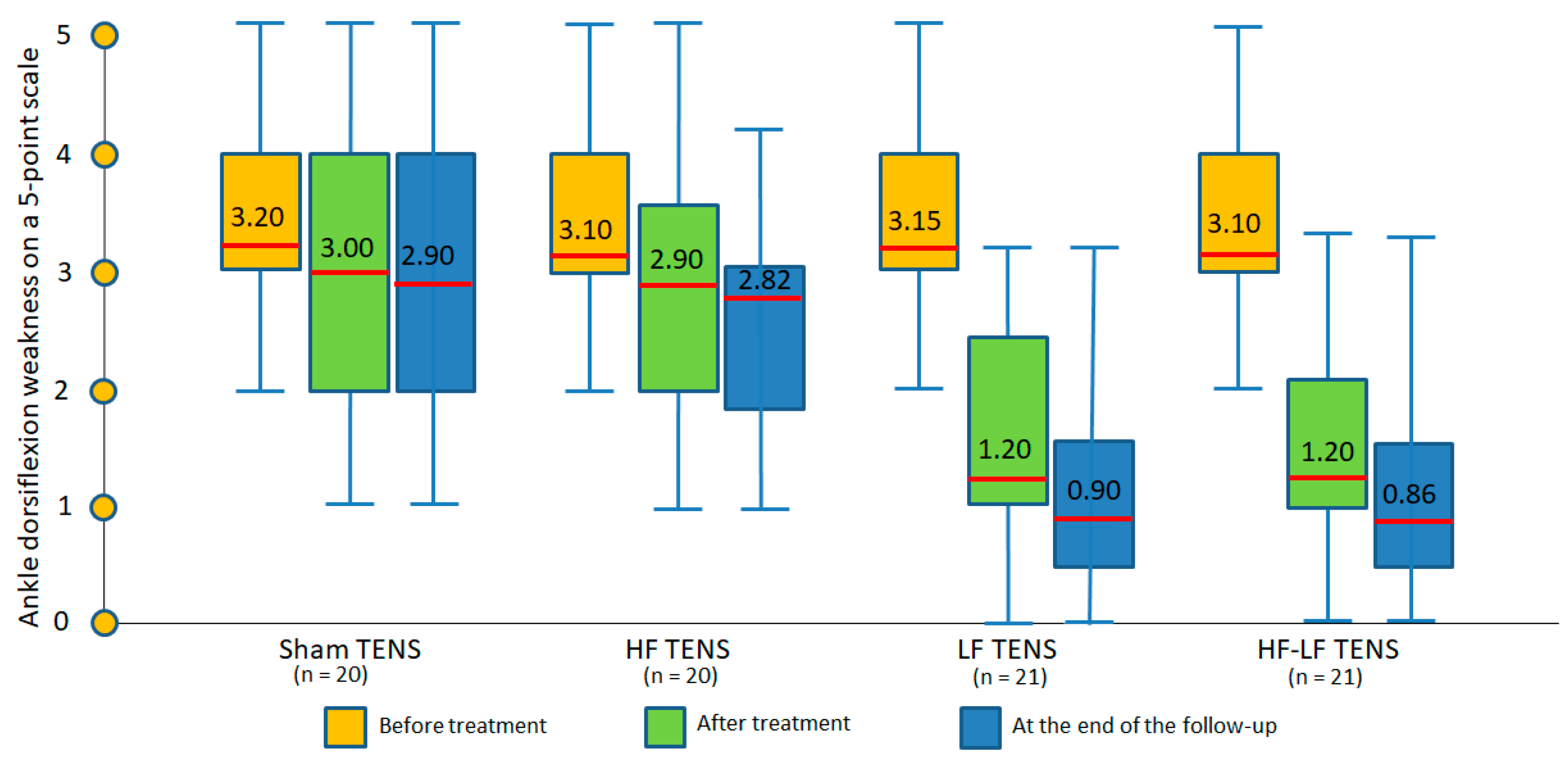
3.1.2. Changes in Ankle Dorsiflexion Strength
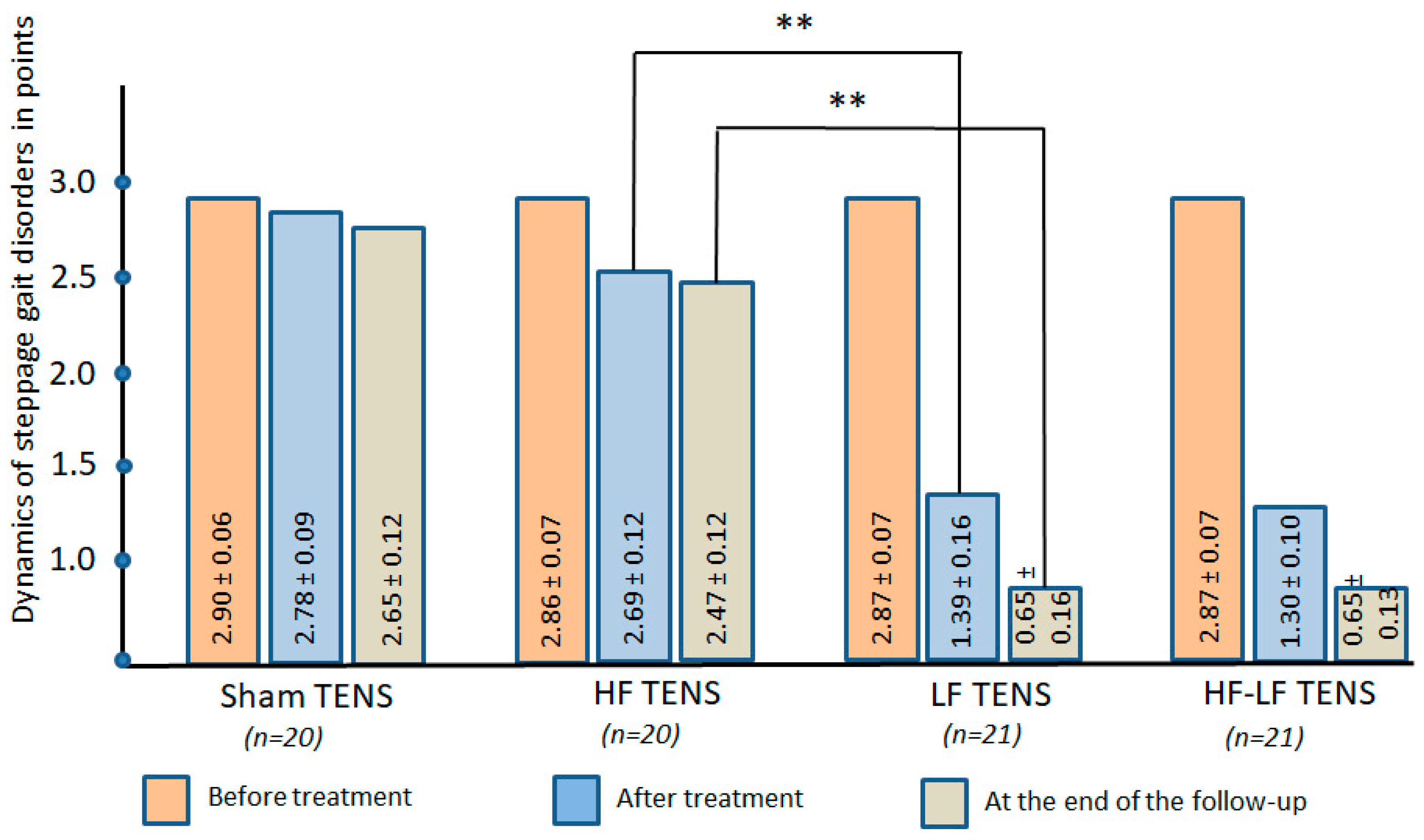
3.1.3. Gait Disorders Assessment
3.2. Secondary Clinical Outcomes
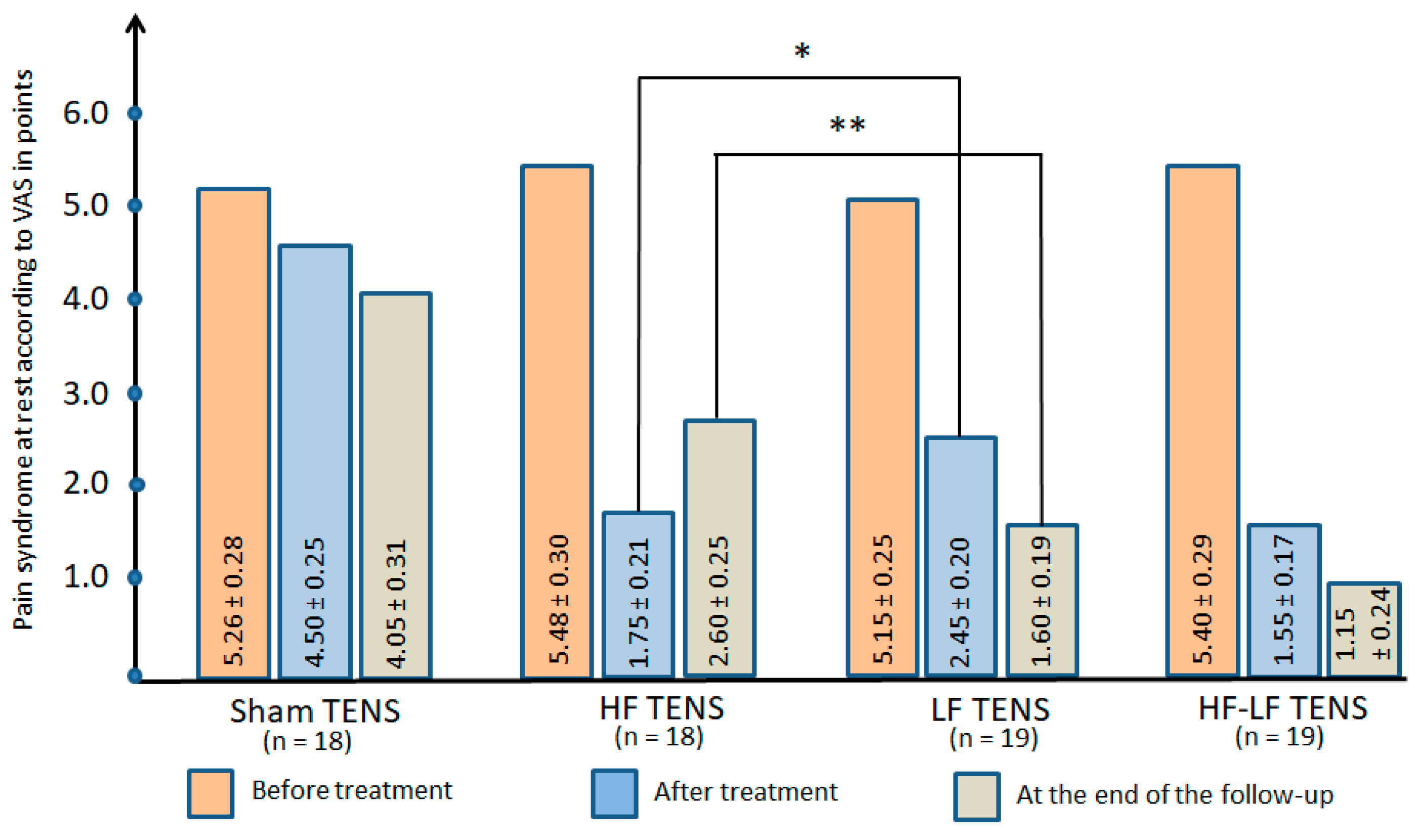
3.2.1. Pain Syndrome at Rest
Comparative Analysis Between Groups
3.2.2. Dynamics of Tinel’s Sig
Comparative Analysis Between Groups
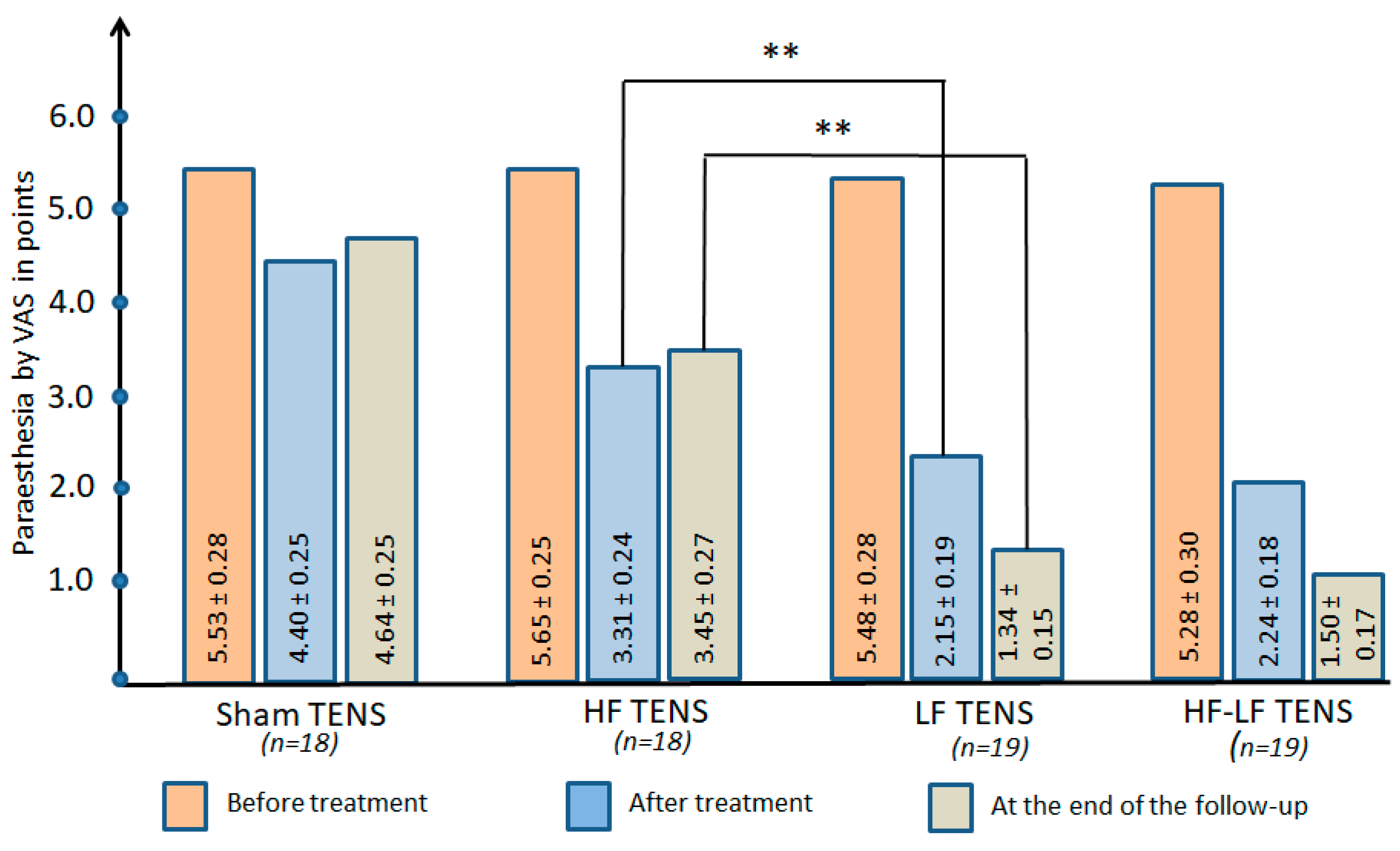
3.2.3. Paraesthesia at Rest
Comparative Analysis Between Groups
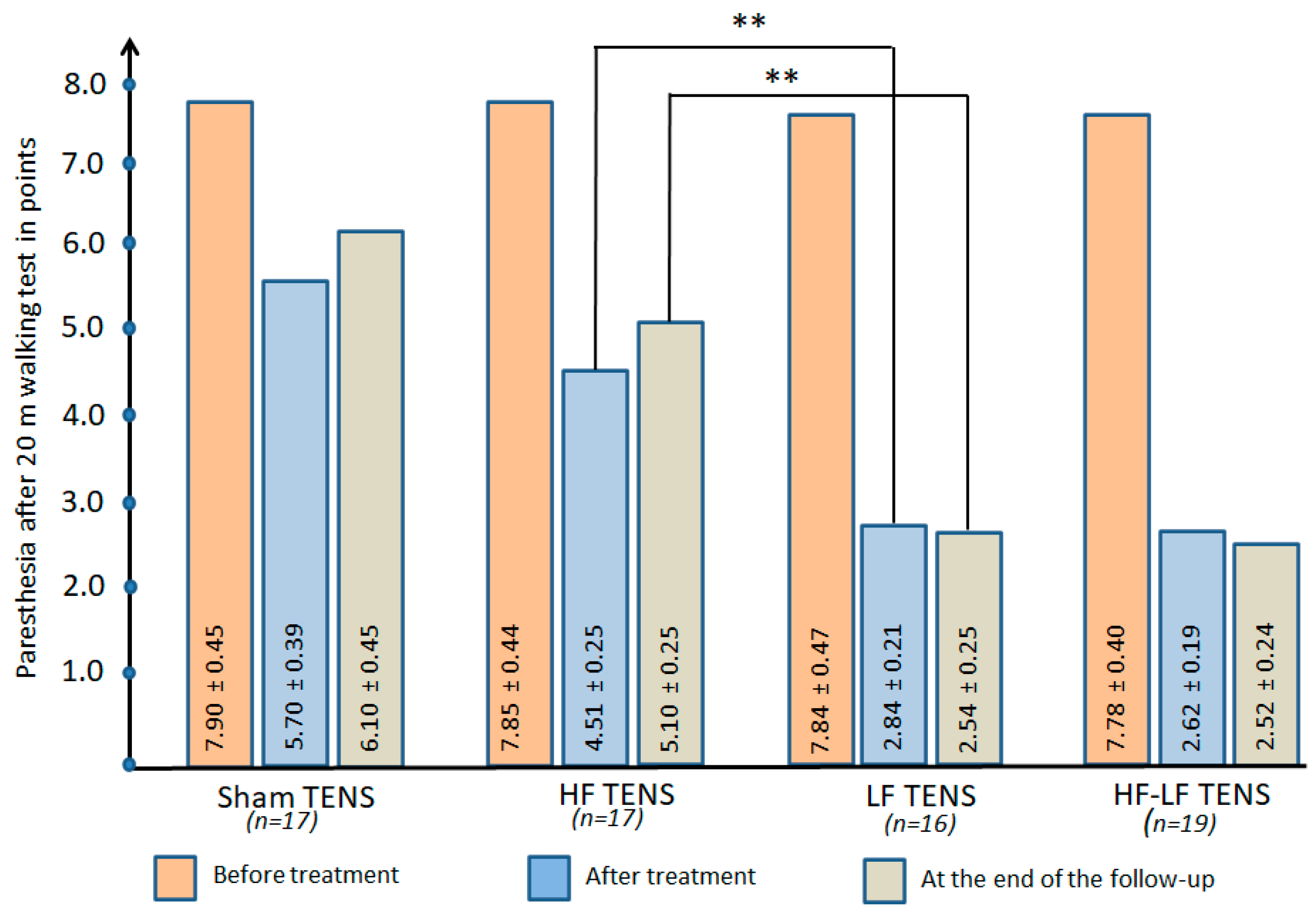
3.2.4. Dynamics of Paraesthesia After 20 m of Walking
Comparative Analysis Between Groups
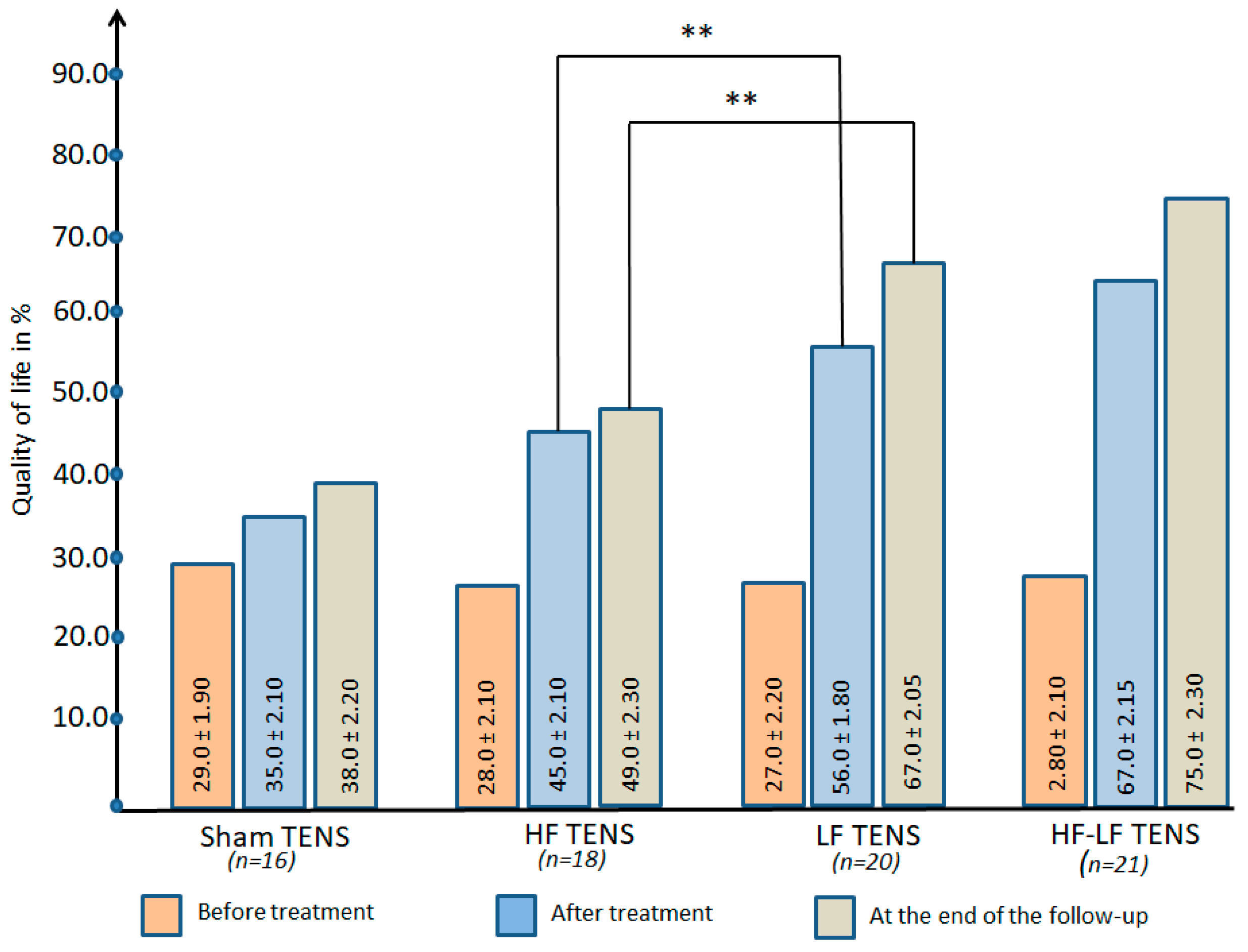
3.2.5. Quality of Life
Comparative Analysis Between Groups
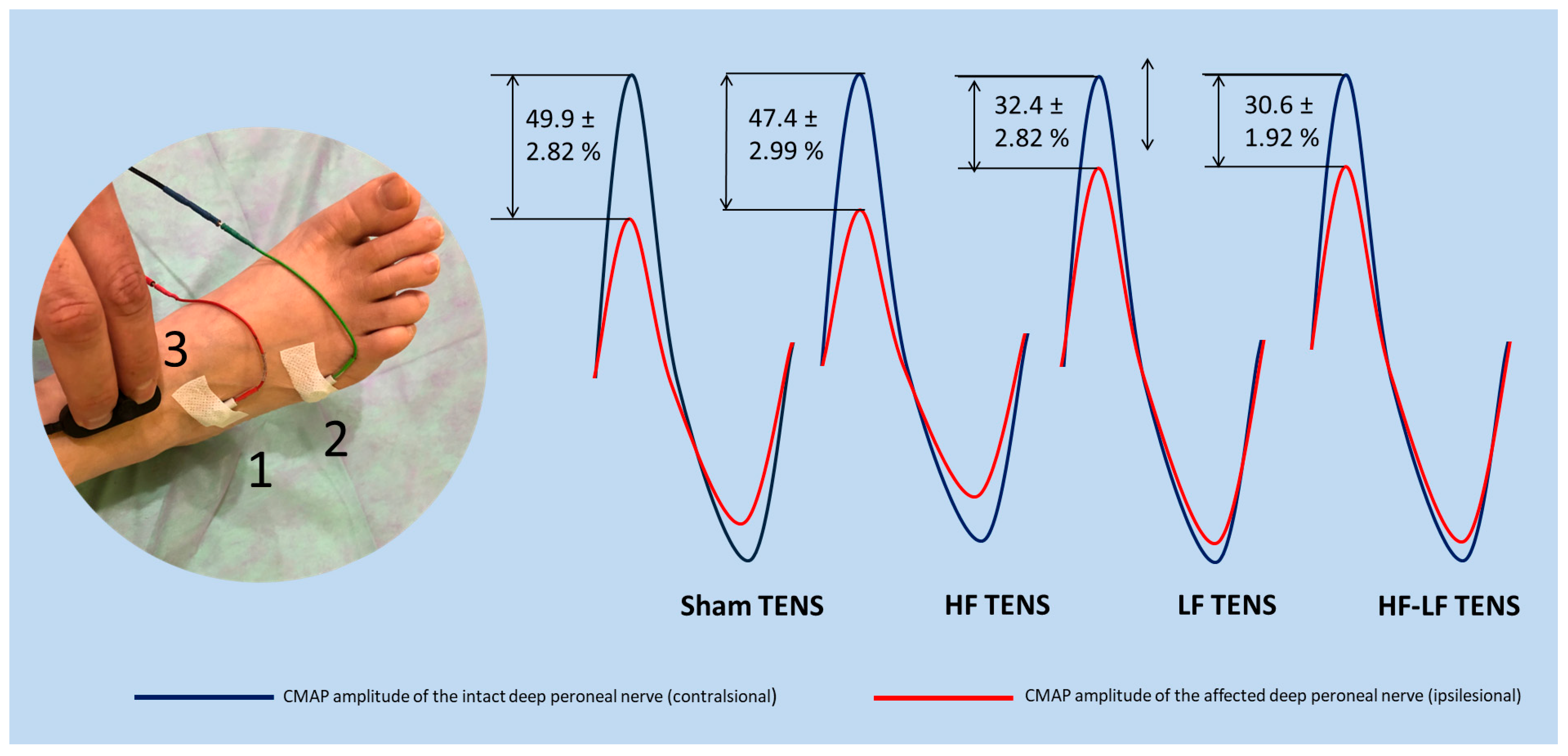
3.3. Ultrasound Examination of CPN
3.4. Electromyography Findings
4. Discussion
4.1. Analgesic Effect of TENS
4.2. The Recovery Effect of TENS
4.3. Comparative Analysis Between HF TENS and LF TENS
4.4. The Benefit of HF TENS and LF TENS Combination
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowley, M.P.; Doughty, C.T. Entrapment Neuropathies of the Lower Extremity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drăghici, N.C.; Văcăraș, V.; Bolchis, R.; Bashimov, A.; Domnița, D.M.; Iluț, S.; Popa, L.L.; Lupescu, T.D.; Mureșanu, D.F. Diagnostic Approach to Lower Limb Entrapment Neuropathies: A Narrative Literature Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppler, L.H.; Groves, A.P.; Sacks, G.; Bansal, A.; Davidge, K.M.; Sledge, J.A.; Tymkew, H.; Yan, Y.; Hasak, J.M.; Potter, P.; et al. Subclinical Peroneal Neuropathy: A Common, Unrecognized, and Preventable Finding Associated with a Recent History of Falling in Hospitalized Patients. Ann. Fam. Med. 2016, 14, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alemán, A.; Nigro, E.; Gonorazky, H.D. High Prevalence of Peroneal Neuropathy Among Children During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 50, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, W.; Mahony, N.; Delaney, M.; O’Brien, M.; Murray, P. Relationship of the common peroneal nerve and its branches to the head and neck of the fibula. Clin. Anat. 2003, 16, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, T.H.; Li, H.M. Endoscopic Resection of Peroneus Quartus. Arthrosc. Tech. 2019, 12, e35–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Athavale, S.A.; Swathi Vangara, S.V. Anatomy of the superior peroneal tunnel. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2011, 93, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Mangi, M.D.; Zadow, S.; Lim, W. Nerve entrapment syndromes of the lower limb: A pictorial review. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fortier, L.M.; Markel, M.; Thomas, B.G.; Sherman, W.F.; Thomas, B.H.; Kaye, A.D. An Update on Peroneal Nerve Entrapment and Neuropathy. Orthop. Rev. 2021, 13, 24937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sarıyıldız, A. Posture-induced compressive peroneal neuropathy during harvesting season: A case series. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 70, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lezak, B.; Massel, D.H.; Varacallo, M.A. Peroneal Nerve Injury. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bahtiyarca, Z.T.; Karaahmet, Ö.Z.; Panpallı Ateş, M.; Kıraç Ünal, Z.K.; Çakcı, F.A. Acute bilateral foot drop in a chronic alcoholic patient. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 65, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wakefield, C.J.; Hamid, K.S.; Lee, S.; Lin, J.; Holmes, G.B., Jr.; Bohl, D.D. Transfer of the Posterior Tibial Tendon for Chronic Peroneal Nerve Palsy. JBJS Rev. 2021, 9, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.R.; Anand, B.; Issac, T.G. Median and common peroneal neuropathy in coir workers of Alappuzha district, Kerala. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2017, 20, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Klifto, K.M.; Azoury, S.C.; Gurno, C.F.; Card, E.B.; Levin, L.S.; Kovach, S.J. Treatment approach to isolated common peroneal nerve palsy by mechanism of injury: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participants’ data. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2022, 75, 683–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nori, S.L.; Das, J.M. Steppage Gait. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capodici, A.; Hagert, E.; Darrach, H.; Curtin, C. An overview of common peroneal nerve dysfunction and systematic assessment of its relation to falls. Int. Orthop. 2022, 46, 2757–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Masakado, Y.; Kawakami, M.; Suzuki, K.; Abe, L.; Ota, T.; Kimura, A. Clinical neurophysiology in the diagnosis of peroneal nerve palsy. Keio J. Med. 2008, 57, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, J. Electrodiagnosis in Diseases of Nerve and Muscle; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Vastamäki, M. Decompression for peroneal nerve entrapment. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1986, 57, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.D.; Gwam, C.U.; Cignetti, N.E.; Dhaliwal, K.K.; Gordon, J.B.; Ma, X.; Li, Z. Outcomes of Common Peroneal Nerve Decompression. Cureus 2024, 16, e68526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Muniz, X.C.; de Assis, A.C.C.; de Oliveira, B.S.A.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Soriano, R.N. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy in nerve injury repair-a new era in therapeutic agents and regenerative treatments. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 4029–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sağir, D.; Bereket, C.; Onger, M.E.; Bakhit, N.; Keskin, M.; Ozkan, E. Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shockwaves Therapy on Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 30, 2635–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, L.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Z. Electrical stimulation therapy for peripheral nerve injury. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1081458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bannaga, A.; Guo, T.; Ouyang, X.; Hu, D.; Lin, C.; Cao, F.; Deng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Luo, Y. Magnetic stimulation accelerating rehabilitation of peripheral nerve injury. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2002, 22, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zamil, M.; Minenko, I.A.; Kulikova, N.G.; Mansur, N.; Nuvakhova, M.B.; Khripunova, O.V.; Shurygina, I.P.; Topolyanskaya, S.V.; Trefilova, V.V.; Petrova, M.M.; et al. Efficiency of Direct Transcutaneous Electroneurostimulation of the Median Nerve in the Regression of Residual Neurological Symptoms After Carpal Tunnel Decompression Surgery. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zamil, M.; Minenko, I.A.; Kulikova, N.G.; Alade, M.; Petrova, M.M.; Pronina, E.A.; Romanova, I.V.; Narodova, E.A.; Nasyrova, R.F.; Shnayder, N.A. Clinical Experience of High Frequency and Low Frequency TENS in Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathic Pain in Russia. Healthcare 2022, 10, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zamil, M.; Kulikova, N.G.; Minenko, I.A.; Mansur, N.; Zalozhnev, D.M.; Uzdenov, M.B.; Dzhanibekova, A.A.; Gochiyayev, A.A.; Shnayder, N.A. Functional Recovery and Regenerative Effects of Direct Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation in Treatment of Post-COVID-19 Guillain–Barré and Acute Transverse Myelitis Overlap Syndrome: A Clinical Case. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.J.; Moore, H.M.; Davies, A.H. Haemodynamic changes with the use of neuromuscular electrical stimulation compared to intermittent pneumatic compression. Phlebology 2015, 30, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodríguez, A.; Senin-Camargo, F.; Raposo-Vidal, I.; Chouza-Insua, M.; Rodríguez-Romero, B.; Jácome, M.A. Effects of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation via peroneal nerve or soleus muscle on venous flow: A randomized cross-over study in healthy subjects. Medicine 2018, 97, e12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Broderick, B.J.; O’cOnnell, S.; Moloney, S.; O’hAlloran, K.; Sheehan, J.; Quondamatteo, F.; Quinlan, L.R.; Ólaighin, G. Comparative lower limb hemodynamics using neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) versus intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC). Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo Almeida, T.C.; Dos Santos Figueiredo, F.W.; Barbosa Filho, V.C.; de Abreu, L.C.; Fonseca, F.L.A.; Adami, F. Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Proinflammatory Cytokines: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1094352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koca Kutlu, A.; Ceçen, D.; Gürgen, S.G.; Sayın, O.; Cetin, F. A Comparison Study of Growth Factor Expression Following Treatment with Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation, Saline Solution, Povidone-Iodine, and Lavender Oil in Wounds Healing. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 361832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alarcón, J.B.; Chuhuaicura, P.B.; Sluka, K.A.; Vance, C.G.T.; Fazan, V.P.S.; Godoy, K.A.; Fuentes, R.E.; Dias, F.J. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation in Nerve Regeneration: A Systematic Review of In Vivo Animal Model Studies. Neuromodulation 2022, 25, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinCalc. Sample Size Calculator. Available online: https://clincalc.com/stats/samplesize.aspx (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Hyland, M.E.; Sodergren, S.C. Development of a new type of global quality of life scale, and comparison of performance and preference for 12 global scales. Qual. Life Res. 1996, 5, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostopoulos, D.; Rizopoulos, K.; McGilvrey, J.; Hauskey, J.; Courcier, J.; Connor-Israel, K.; Koster, H.; von Leden, R. An Open-Label Comparative Study of the Impact of Two Types of Electrical Stimulation (Direct Current Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation and Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation) on Physical Therapy Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2025, 2025, 9970124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kulikova, N.; Khalilovich, A.M.; Konchugova, T.; Rachin, A.; Chkheidze, T.; Kulchitskaya, D.; Anatoliy, F.; Sanina, N.P.; Ivanova, E. Analgesic effects of high-frequency and low-frequency TENS currents in patients with distal neuropathy. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2022, 32, 10687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Megía García, Á.; Serrano-Muñoz, D.; Bravo-Esteban, E.; Ando Lafuente, S.; Avendaño-Coy, J.; Gómez-Soriano, J. Efectos analgésicos de la estimulación eléctrica nerviosa transcutánea en pacientes con fibromialgia: Una revisión sistemática [Analgesic effects of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) in patients with fibromyalgia: A systematic review]. Aten. Primaria 2019, 51, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Motwani, M.; Fadnavis, A.; Dhole, A. Efficacy of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) in the management of trigeminal neuralgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2023, 15, e505–e510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Viderman, D.; Nabidollayeva, F.; Aubakirova, M.; Sadir, N.; Tapinova, K.; Tankacheyev, R.; Abdildin, Y.G. The Impact of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) on Acute Pain and Other Postoperative Outcomes: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Püsküllüoğlu, M.; Tomaszewski, K.A.; Grela-Wojewoda, A.; Pacholczak-Madej, R.; Ebner, F. Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Pain and Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review. Medicina 2022, 58, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Johnson, M.I.; Mulvey, M.R.; Bagnall, A.M. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for phantom pain and stump pain following amputation in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 8, CD007264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Loh, J.; Gulati, A. The use of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) in a major cancer center for the treatment of severe cancer-related pain and associated disability. Pain. Med. 2015, 16, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liebano, R.E.; Sluka, K.A.; Roy, J.; Savinelli, M.; Dailey, D.L.; Riley, S.P. Effects of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on pain, function, and descending inhibition in people with non-specific chronic low-back pain: A study protocol for a randomized crossover trial. Trials 2024, 25, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al-Zamil, M.; Kulikova, N.G.; Shnayder, N.A.; Korchazhkina, N.B.; Petrova, M.M.; Mansur, N.; Smekalkina, L.V.; Babochkina, Z.M.; Vasilyeva, E.S.; Zhhelambekov, I.V. Spatial Distribution Dynamics of Sensory Disturbances in the Treatment of Obesity-Related Meralgia Paresthetica Using Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.G.; Horrar, A.N.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Burns, B.L.; Kalmar, C.L.; Assi, P.E.; Brooks-Horrar, K.N.; Kesayan, T.; Al Kassis, S. Outcomes of transcutaneous nerve stimulation for migraine headaches: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 4021–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, R.; Khanna, J.; Bansal, S.; Bansal, N. Current Insights into Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Clinical Strategies for Prevention and Treatment. Curr. Drug Targets. 2024, 25, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zamil, M.K.; Vasilieva, E.S.; Mikhailova, A.A.; Epifanov, V.A.; Illarionov, V.E.; Ivanova, I.I.; Korchazhkina, N.B. The use of transdermal electroneurostimulation in the rehabilitation of patients after surgical decompression of the carpal tunnel. Vopr. Kurortol. Fizioter. Lech. Fiz. Kult. 2021, 98, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, P.D.; Sweet, W.H. Temporary abolition of pain in man. Science 1967, 155, 108–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzack, R. Prolonged relief of pain by brief, intense transcutaneous somatic stimulation. Pain 1975, 1, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzack, R.; Wall, P.D. Pain mechanisms: A new theory. Science 1965, 150, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, C.G.; Dailey, D.L.; Rakel, B.A.; Sluka, K.A. Using TENS for pain control: The state of the evidence. Pain. Manag. 2014, 4, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ma, Y.T.; Sluka, K.A. Reduction in inflammation-induced sensitization of dorsal horn neurons by transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in anesthetized rats. Exp. Brain Res. 2001, 137, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lütolf, R.; Rosner, J.; Curt, A.; Hubli, M. Indicators of central sensitization in chronic neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Eur. J. Pain 2022, 26, 2162–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ma, Y.C.; Kang, Z.B.; Shi, Y.Q.; Ji, W.Y.; Zhou, W.M.; Nan, W. The Complexity of Neuropathic Pain and Central Sensitization: Exploring Mechanisms and Therapeutic Prospects. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2024, 23, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, H.; Noguchi, K. [Pathophysiology of neuropathic pain: Molecular mechanisms underlying central sensitization in the dorsal horn in neuropathic pain]. Brain Nerve 2012, 64, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pacifico, P.; Menichella, D.M. Molecular mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2024, 179, 279–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeJesus, B.M.; Rodrigues, I.K.L.; Azevedo-Santos, I.F.; DeSantana, J.M. Effect of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Pain-Related Quantitative Sensory Tests in Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain and Acute Experimental Pain: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Pain 2023, 24, 1337–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoli, D.; Dua, A.; An, J. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeda, Y.; Lisi, T.L.; Vance, C.G.; Sluka, K.A. Release of GABA and activation of GABA(A) in the spinal cord mediates the effects of TENS in rats. Brain Res. 2007, 1136, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Perez Navarro, M.; Esquenazi, B. Use of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) for Pain Management During Intrauterine Device Insertion: A Case Series. Cureus 2024, 16, e69324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koca, I.; Boyaci, A.; Tutoglu, A.; Ucar, M.; Kocaturk, O. Assessment of the effectiveness of interferential current therapy and TENS in the management of carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled study. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casale, R.; Damiani, C.; Maestri, R.; Wells, C.D. Pain and electrophysiological parameters are improved by combined 830-1064 high-intensity LASER in symptomatic carpal tunnel syndrome versus Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation. A randomized controlled study. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 49, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gordon, T.; Amirjani, N.; Edwards, D.C.; Chan, K.M. Brief post-surgical electrical stimulation accelerates axon regeneration and muscle reinnervation without affecting the functional measures in carpal tunnel syndrome patients. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 223, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zamil, M.; Kulikova, N.; Shnayder, N.; Mansour, N.; Trefilova, V.; Stepanovich, M.; Minenko, I.; Vasilyeva, E. Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous electroneurostimulation in treatment of Meralgia paresthetica. Eur. J. Neurol. 2023, 30, 278. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zamil, M.; Kulikova, N. TENS leads to greater regression of motor deficits in the treatment of facial paralysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 532–533. [Google Scholar]
- Power, H.A.; Morhart, M.J.; Olson, J.L.; Chan, K.M. Postsurgical electrical stimulation enhances recovery following surgery for severe cubital tunnel syndrome: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivó, M.; Puigdemasa, A.; Casals, L.; Asensio, E.; Udina, E.; Navarro, X. Immediate electrical stimulation enhances regeneration and reinnervation and modulates spinal plastic changes after sciatic nerve injury and repair. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 211, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, G.S., Jr.; Lichstein, P.R.; Whitlock, D.; Harker, C. Response of plasma beta-endorphins to transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in healthy subjects. Phys. Ther. 1984, 64, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, E.L. Pain processing in the human nervous system: A selective review of noci-ceptive and biobehavioral pathways. Prim. Care 2012, 39, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navratilova, E.; Morimura, K.; Xie, J.Y.; Atcherley, C.W.; Ossipov, M.H.; Porreca, F. Positive emotions and brain reward circuits in chronic pain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 1646–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chang, M.C. Chronic Pain: Structural and Functional Changes in Brain Structures and Associated Negative Affective States. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al-Zamil, M.; Kulikova, N.G.; Minenko, I.A.; Shurygina, I.P.; Petrova, M.M.; Mansur, N.; Kuliev, R.R.; Blinova, V.V.; Khripunova, O.V.; Shnayder, N.A. Comparative Analysis of High-Frequency and Low-Frequency Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation of the Right Median Nerve in the Regression of Clinical and Neurophysiological Manifestations of Generalized Anxiety Disorder. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Masoumi Shahrbabak, S.; Bahrami, R.; Rahman, F.N.; Sanchez-Perez, J.A.; Gazi, A.H.; Inan, O.T.; Hahn, J.-O. Non-Pharmacological Mitigation of Acute Mental Stress-Induced Sympathetic Arousal: Comparison Between Median Nerve Stimulation and Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation. Sensors 2025, 25, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zamil, M.; Kulikova, N.G.; Shnayder, N.A.; Korchazhkina, N.B.; Petrova, M.M.; Mansur, T.I.; Blinova, V.V.; Babochkina, Z.M.; Vasilyeva, E.S.; Zhhelambekov, I.V. Efficiency of Lidocaine Intramuscular and Intraosseous Trigger Point Injections in the Treatment of Residual Chronic Pain After Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Decompression Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egloff, N.; Sabbioni, M.E.; Salathé, C.; Wiest, R.; Juengling, F.D. Nondermatomal somatosensory deficits in patients with chronic pain disorder: Clinical findings and hypometabolic pattern in FDG-PET. Pain 2009, 145, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailis-Gagnon, A.; Nicholson, K. Nondermatomal somatosensory deficits: Overview of unexplainable negative sensory phenomena in chronic pain patients. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2010, 23, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmann, G.; Dumat, W.; Egloff, N.; Gantenbein, A.R.; Matter, S.; Pirotta, R.; Sándor, P.S.; Schleinzer, W.; Seifert, B.; Sprott, H.; et al. Bilateral Sensory Changes and High Burden of Disease in Patients with Chronic Pain and Unilateral Nondermatomal Somatosensory Deficits: A Quantitative Sensory Testing and Clinical Study. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matesanz, L.; Hausheer, A.C.; Baskozos, G.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Schmid, A.B. Somatosensory and psychological phenotypes associated with neuropathic pain in entrapment neuropathy. Pain 2021, 162, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, S.; Sachau, J.; Hellriegel, J.; Forstenpointner, J.; Børsting Jacobsen, H.; Harten, P.; Gierthmühlen, J.; Baron, R. Pain matters for central sensitization: Sensory and psychological parameters in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. PAIN Rep. 2021, 6, e901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fox, P.M. The Role of Electrical Stimulation in Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: Current Evidence and Future Directions. J. Hand Surg. Glob. Online 2024, 6, 718–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kubiak, C.A.; Kung, T.A.; Brown, D.L. State-of-the-art techniques in treating peripheral nerve injury. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haastert-Talini, K.; Schmitte, R.; Korte, N.; Klode, D.; Ratzka, A.; Grothe, C. Electrical stimulation accelerates axonal and functional peripheral nerve regeneration across long gaps. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ho, C.; Hsu, S.; Lee, H.; Lin, J.; Yao, C.; Chen, Y. Effects of electrical stimulation at different frequencies on regeneration of transected peripheral nerve. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2008, 22, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobianchi, S.; Casals-Diaz, L.; Jaramillo, J.; Navarro, X. Differential effects of activity dependent treatments on axonal neuropathic pain after nerve. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 240, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desantana, J.M.; Santana-Filho, V.J.; Sluka, K.A. Modulation between high- and low-frequency transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation delays the development of analgesic tolerance in arthritic rats. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]



| Sham TENS | HF TENS | LF TENS | HF-LF TENS | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients in each group | 20 | 20 | 21 | 21 | |
| Age (years) | 39.7 ± 2.88 | 41.2 ± 2.95 | 42.0 ± 3.14 | 39.1 ± 2.90 | p = 0.897 |
| Gender (female: male) | (10:10) | (11:9) | (11:10) | (11:10) | p = 0.992 |
| Disease duration (days) | 8.05 ± 0.7 | 8.24 ± 0.6 | 8.15 ± 0.7 | 8.10 ± 0.7 | p = 0.998 |
| Ankle dorsiflexion weakness (scores) | 3.20 ± 0.17 | 3.10 ± 0.18 | 3.15 ± 0.18 | 3.10 ± 0.19 | p = 0.975 |
| Steppage gait disorder (points) | 2.90 ± 0.06 | 2.86 ± 0.07 | 2.87 ± 0.07 | 2.87 ± 0.07 | p = 0.978 |
| Hypoesthesia (points) | 6.10 ± 0.28 | 6.31 ± 0.29 | 6.25 ± 0.31 | 6.20 ± 0.27 | p = 0.963 |
| F | D | A | Stable Stimulation | Labile Stimulation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham TENS | I Hz | 50 μs | Sensory response | Cathode fixed above the medial level of tibial anterior muscle. Anode fixed above the ankle. | Cathode fixed above the medial level of tibial anterior muscle. Anode was unfixed and moved around the cathode in 2 cm increments, with stimulation at each point lasting 20 s. |
| HF TENS | 50 Hz | 50 μs | Sensory response | Anode fixed over the CPN at the proximal entrance of fibular tunnel Cathode fixed above CPN at the distal entrance of fibular tunnel. | Anode fixed over the CPN at the proximal entrance of fibular tunnel Cathode was unfixed and moved along the peroneal nerve from anode distally in 2 cm increments, with stimulation at each point lasting 20 s. |
| LF TENS | 1 Hz | 200 μs | Motor response | Cathode fixed over the CPN at the proximal entrance of fibular tunnel Anode fixed above CPN at the distal entrance of fibular tunnel | Cathode fixed over the CPN at the proximal entrance of fibular tunnel Anode was unfixed and moved along the peroneal nerve from anode distally in 2 cm increments, with stimulation at each point lasting 20 s. |
| HF-LF TENS | A combined application of HF TENS and LF TENS was used | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Zamil, M.; Minenko, I.A.; Shnayder, N.A.; Petrova, M.M.; Babochkina, Z.M.; Kaskaeva, D.S.; Lim, V.G.; Khripunova, O.V.; Shurygina, I.P.; Garganeeva, N.P. Recovery and Protective Effect of Direct Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation in the Treatment of Acute and Subacute Fibular Tunnel Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124247
Al-Zamil M, Minenko IA, Shnayder NA, Petrova MM, Babochkina ZM, Kaskaeva DS, Lim VG, Khripunova OV, Shurygina IP, Garganeeva NP. Recovery and Protective Effect of Direct Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation in the Treatment of Acute and Subacute Fibular Tunnel Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124247
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Zamil, Mustafa, Inessa A. Minenko, Natalia A. Shnayder, Marina M. Petrova, Zarina M. Babochkina, Darya S. Kaskaeva, Vladimir G. Lim, Olga V. Khripunova, Irina P. Shurygina, and Natalia P. Garganeeva. 2025. "Recovery and Protective Effect of Direct Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation in the Treatment of Acute and Subacute Fibular Tunnel Syndrome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124247
APA StyleAl-Zamil, M., Minenko, I. A., Shnayder, N. A., Petrova, M. M., Babochkina, Z. M., Kaskaeva, D. S., Lim, V. G., Khripunova, O. V., Shurygina, I. P., & Garganeeva, N. P. (2025). Recovery and Protective Effect of Direct Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation in the Treatment of Acute and Subacute Fibular Tunnel Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124247









