Th Cell Phenotypes and Their Correlations with Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Data Cohort
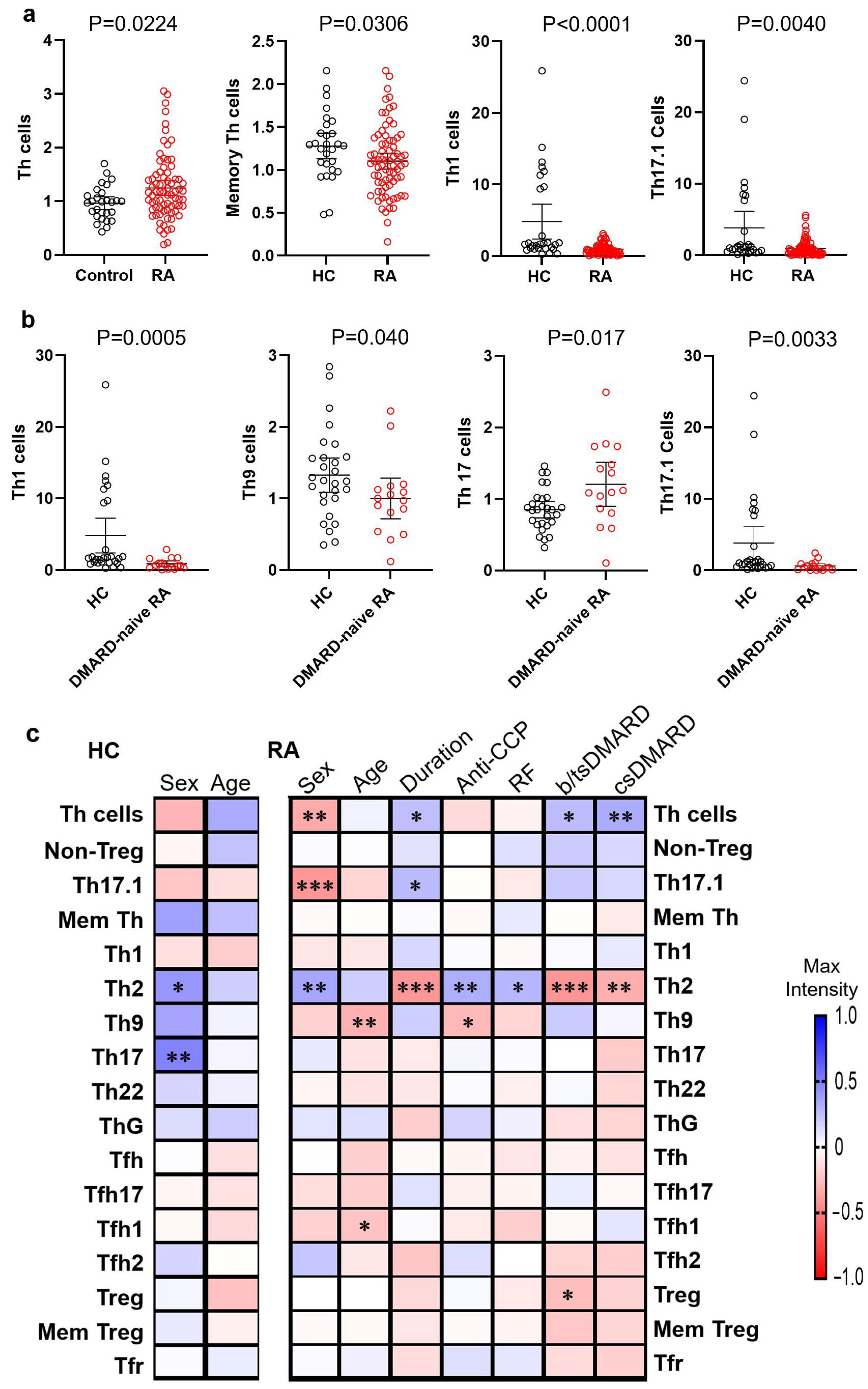
3.2. Differential Frequencies of Circulating Th Cells and Subsets in RA Patients and HCs
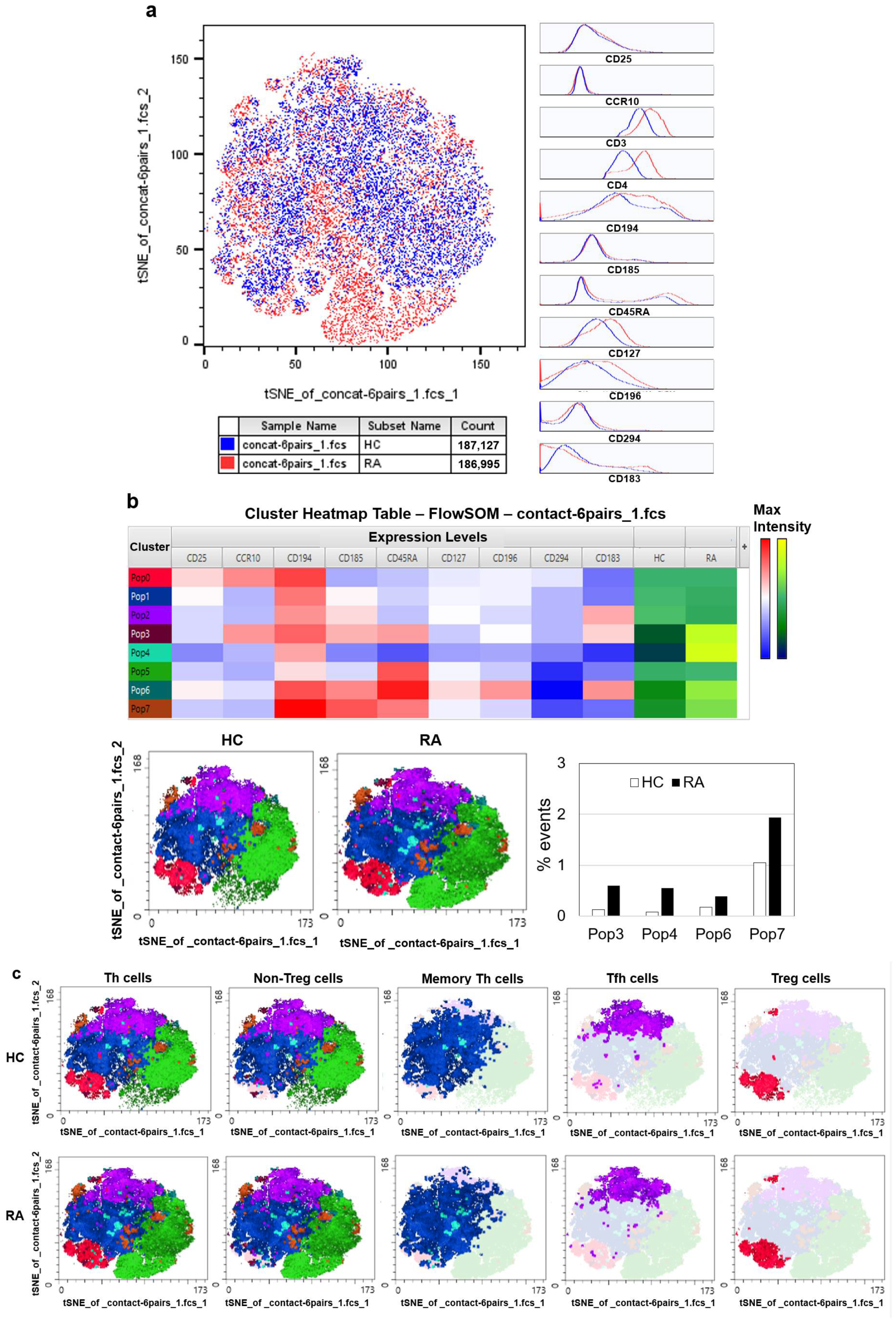
3.3. Automated Clustering Reveals Distinct Cell Subset Profiles in Early RA
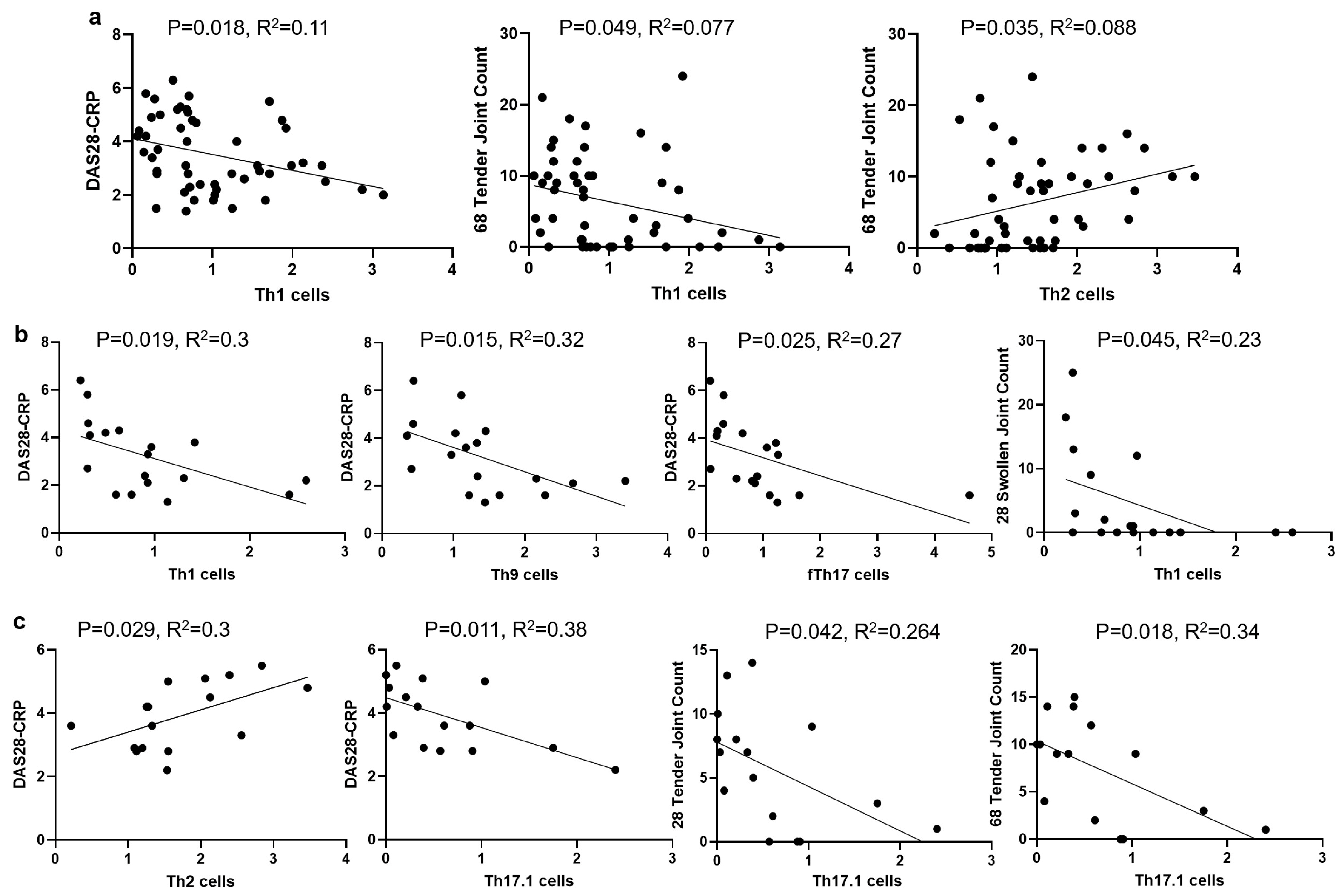
3.4. The Correlations of Circulating Th Cells and Their Subsets with RA Disease Activity
3.5. The Correlations of Th Cell Subsets with CRP and ESR in RA Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Anti-CCP | anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide |
| b/ts | biologic or targeted synthetic |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| cs | conventional synthetic |
| DMARD | disease-modifying antirheumatic drug |
| ESR | erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| HCs | healthy controls |
| MEM | marker enrichment modeling |
| PBMCs | peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| RF | rheumatoid factor |
| SJC | swollen joint count |
| Tfh cells | T follicular helper cells |
| Th cells | CD4+ T helper cells |
| TJC | tender joint count |
| Tfr | T follicular regulatory |
| tSNE | t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding |
References
- Raphael, I.; Joern, R.R.; Forsthuber, T.G. Memory CD4(+) T Cells in Immunity and Autoimmune Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, S.P.; Hansda, A.K.; Goswami, R. Rheumatoid arthritis: ‘melting pot’ of T helper subsets. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 38, 212–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Ferrante, A.; Raimondo, S.; Bignone, R.; Rodolico, V.; Peralta, S.; Van Tok, M.; Cannizzaro, A.; Schinocca, C.; et al. Interleukin-9 Overexpression and Th9 Polarization Characterize the Inflamed Gut, the Synovial Tissue, and the Peripheral Blood of Patients With Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Roon, J.A.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Lafeber, F.P. Suppression of inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis may require a concerted action of Th2 cytokines. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2002, 3, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Yang, G.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Cui, D. Function and Role of Regulatory T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 626193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, R.; Schmitt, N.; Bentebibel, S.E.; Ranganathan, R.; Bourdery, L.; Zurawski, G.; Foucat, E.; Dullaers, M.; Oh, S.; Sabzghabaei, N.; et al. Human blood CXCR5(+)CD4(+) T cells are counterparts of T follicular cells and contain specific subsets that differentially support antibody secretion. Immunity 2011, 34, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunde, A.C.; Hale, J.S.; Lamb, T.J. Cytokine-skewed Tfh cells: Functional consequences for B cell help. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Niu, H.; Zhao, X.; Gao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, C. T-Follicular Regulatory Cells: Potential Therapeutic Targets in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhearn, B.; Marshall, L.; Sutcliffe, M.; Hannes, S.K.; Fonseka, C.; Hussell, T.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Barton, A.; Viatte, S. Automated clustering reveals CD4(+) T cell subset imbalances in rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1094872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, E.A.; Rieck, M.; Pieper, J.; Gebe, J.A.; Yue, B.B.; Tatum, M.; Peda, M.; Sandin, C.; Klareskog, L.; Malmstrom, V.; et al. Citrulline-specific Th1 cells are increased in rheumatoid arthritis and their frequency is influenced by disease duration and therapy. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1712–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.G.; Li, Y.H.; Qi, L.; Liu, X.G.; Yuan, C.Z.; Hu, N.W.; Ma, D.X.; Li, Z.F.; Yang, Q.; et al. Increased frequencies of Th22 cells as well as Th17 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.M.; Liu, X.G.; Ma, D.X.; Hu, N.W.; Li, Y.G.; Li, W.; Hu, Y.; Yu, S.; Qu, X.; et al. Elevated Th22 cells correlated with Th17 cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Zhang, K.; Lv, M.; Li, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Han, Q.; Guo, N.; Fan, C.; Zhu, P. Circulating Th17 and Th1 cells expressing CD161 are associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 43, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Roon, J.A.; van Roy, J.L.; Duits, A.; Lafeber, F.P.; Bijlsma, J.W. Proinflammatory cytokine production and cartilage damage due to rheumatoid synovial T helper-1 activation is inhibited by interleukin-4. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1995, 54, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Bozec, A.; Ramming, A.; Schett, G. Anti-inflammatory and immune-regulatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, K.; Falciani, F.; Curnow, S.J.; Ross, E.J.; Lee, C.Y.; Akbar, A.N.; Lord, J.M.; Gordon, C.; Buckley, C.D.; Salmon, M. Early rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by a distinct and transient synovial fluid cytokine profile of T cell and stromal cell origin. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R784–R795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Shima, Y.; Wing, J.B.; Sakaguchi, S.; Ogata, A.; Kumanogoh, A. The Proportion of Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashiri, S.Y.; Kawakami, A.; Okada, A.; Koga, T.; Tamai, M.; Yamasaki, S.; Nakamura, H.; Origuchi, T.; Ida, H.; Eguchi, K. CD4+CD25(high)CD127(low/-) Treg cell frequency from peripheral blood correlates with disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Qian, F.Y.; Zhang, M.F.; Xu, A.L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, B.P.; Zhou, L.L. Th17 cell pathogenicity and plasticity in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizinski, A.M.; Fox, D.A. T cell subsets and their role in the pathogenesis of rheumatic disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2014, 26, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingender, G.; Kronenberg, M. OMIP-030: Characterization of human T cell subsets via surface markers. Cytom. A 2015, 87, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penatti, A.; Facciotti, F.; De Matteis, R.; Larghi, P.; Paroni, M.; Murgo, A.; De Lucia, O.; Pagani, M.; Pierannunzii, L.; Truzzi, M.; et al. Differences in serum and synovial CD4+ T cells and cytokine profiles to stratify patients with inflammatory osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Rui, J.; Shan, W.; Xue, F.; Feng, D.; Dong, L.; Mao, J.; Shu, Y.; Mao, C.; Wang, X. Imbalance of Th17, Treg, and helper innate lymphoid cell in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 3837–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H. The Search for the Pathogenic T Cells in the Joint of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Which T-Cell Subset Drives Autoimmune Inflammation? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, J.; Haag, S.; Holmdahl, R. MHC class II alleles associated with Th1 rather than Th17 type immunity drive the onset of early arthritis in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Li, B.; Wu, R.; Xie, Y.; Gao, A.; Gao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Stratified distribution of Th17 and Treg cells in patients with multi-stage rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, J.M.; Lundell, A.C.; Hallström, M.; Andersson, K.; Nordström, I.; Rudin, A. Circulating T helper and T regulatory subsets in untreated early rheumatoid arthritis and healthy control subjects. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.; Wei, X.; Song, S. IL-10-Expressing Th2 Cells Contribute to the Elevated Antibody Production in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammation 2016, 39, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, J.; Ekwall, A.H.; Mark, L.; Bergström, B.; Andersson, K.; Gjertsson, I.; Lundell, A.C.; Rudin, A. T helper cells in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis primarily have a Th1 and a CXCR3(+)Th2 phenotype. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyaman, W.; Bradshaw, E.M.; Uyttenhove, C.; Dardalhon, V.; Awasthi, A.; Imitola, J.; Bettelli, E.; Oukka, M.; van Snick, J.; Renauld, J.C.; et al. IL-9 induces differentiation of TH17 cells and enhances function of FoxP3+ natural regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12885–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Rizzo, A.; Manzo, A.; Vitolo, B.; La Manna, M.P.; Giardina, G.; Sireci, G.; Dieli, F.; Montecucco, C.M.; et al. Potential involvement of IL-9 and Th9 cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 2264–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu-Raychaudhuri, S.; Abria, C.; Raychaudhuri, S.P. IL-9, a local growth factor for synovial T cells in inflammatory arthritis. Cytokine 2016, 79, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauber, S.; Luber, M.; Weber, S.; Maul, L.; Soare, A.; Wohlfahrt, T.; Lin, N.Y.; Dietel, K.; Bozec, A.; Herrmann, M.; et al. Resolution of inflammation by interleukin-9-producing type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutakoli, P.; Papadaki, G.; Repa, A.; Avgoustidis, N.; Kalogiannaki, E.; Flouri, I.; Bertsias, A.; Zoidakis, J.; Samiotaki, M.; Bertsias, G.; et al. A Peripheral Blood Signature of Increased Th1 and Myeloid Cells Combined with Serum Inflammatory Mediators Is Associated with Response to Abatacept in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Cells 2023, 12, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimeno, R.; Leceta, J.; Garín, M.; Ortiz, A.M.; Mellado, M.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M.; Martínez, C.; Pérez-García, S.; Gomariz, R.P.; Juarranz, Y. Th17 polarization of memory Th cells in early arthritis: The vasoactive intestinal peptide effect. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongratz, G.; Frieser, R.; Brinks, R.; Schneider, M.; Hartung, W.; Fleck, M.; Ehrenstein, B. Association between autoantibody level and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis is dependent on baseline inflammation. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 691–698. [Google Scholar]
- Paulissen, S.M.; van Hamburg, J.P.; Davelaar, N.; Vroman, H.; Hazes, J.M.; de Jong, P.H.; Lubberts, E. CCR6(+) Th cell populations distinguish ACPA positive from ACPA negative rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, C.K.; Najm, A.; Young, F.; McGarry, T.; Biniecka, M.; Fearon, U.; Veale, D.J. The Utility and Limitations of CRP, ESR and DAS28-CRP in Appraising Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, M.; Lin, H.; Lynch, T.; Chand, V.; Sinnathurai, P.; Thomas, R.; Keen, H.; Hill, C.; Lester, S.; Wechalekar, M.; et al. Th Cell Phenotypes and Their Correlations with Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124220
Xue M, Lin H, Lynch T, Chand V, Sinnathurai P, Thomas R, Keen H, Hill C, Lester S, Wechalekar M, et al. Th Cell Phenotypes and Their Correlations with Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124220
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Meilang, Haiyan Lin, Tom Lynch, Vibhasha Chand, Premarani Sinnathurai, Ranjeny Thomas, Helen Keen, Catherine Hill, Susan Lester, Mihir Wechalekar, and et al. 2025. "Th Cell Phenotypes and Their Correlations with Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124220
APA StyleXue, M., Lin, H., Lynch, T., Chand, V., Sinnathurai, P., Thomas, R., Keen, H., Hill, C., Lester, S., Wechalekar, M., Lassere, M., & March, L. (2025). Th Cell Phenotypes and Their Correlations with Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124220






