An Overlooked Etiology of Acute Kidney Injury: A Clinicopathological Analysis of Phosphate Nephropathy and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Main Points
3. Methods
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Portales-Castillo, I.; Rieg, T.; Khalid, S.B.; Nigwekar, S.U.; Neyra, J.A. Physiopathology of Phosphate Disorders. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2023, 30, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavatta, G.; Altieri, P.; Vandi, G.; Vicennati, V.; Pagotto, U.; Vescini, F. Phosphate Metabolism and Pathophysiology in Parathyroid Disorders and Endocrine Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Aliaga, I. Phosphate and Kidney Healthy Aging. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2020, 45, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salcedo-Betancourt, J.D.; Moe, O.W. The Effects of Acid on Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, C.; Viswanathan, P. Vitamin D and Acute Kidney Injury: A Reciprocal Relationship. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, G.S.; Perazella, M.A. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Harada, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Sugiyama, M.; Kanno, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Ehara, T.; Shimojo, H.; Shigematsu, H.; Kamijo, Y. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy with Diffuse Tubular Injury Despite Limited Calcium Phosphate Deposition. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanner, S.J.; MacDonald, P.H.; Paterson, W.G.; Prentice, R.S.; Da Costa, L.R.; Beck, I.T. A Randomized Prospective Trial Comparing Oral Sodium Phosphate with Standard Polyethylene Glycol-Based Lavage Solution (Golytely) in the Preparation of Patients for Colonoscopy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1990, 85, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approval Letter for Visicol and OsmoPrep (Sodium Phosphate Products)—Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS); U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 7 May 2009. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2009/021097s014,021892s004ltr.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Lieberman, D.A.; Ghormley, J.; Flora, K. Effect of Oral Sodium Phosphate Colon Preparation on Serum Electrolytes in Patients with Normal Serum Creatinine. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1996, 43, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, A.; Sugimoto, M.; Luiz, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, G.; Han, Y.; Zhu, L.; Deng, H.; Deng, J.; et al. Comparison of Oral Sodium Phosphate Tablets and Polyethylene Glycol Lavage Solution for Colonoscopy Preparation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1088630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonlusen, G.; Akgun, H.; Ertan, A.; Olivero, J.; Truong, L.D. Renal Failure and Nephrocalcinosis Associated with Oral Sodium Phosphate Bowel Cleansing: Clinical Patterns and Renal Biopsy Findings. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2006, 130, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, N.; Moledina, D.G.; Perazella, M.A. Toxic Nephropathies of the Tubulointerstitium: Core Curriculum 2024. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2024, 83, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, G.S.; Perazella, M.A. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy. UpToDate. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/acute-phosphate-nephropathy (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.R. Von Kossa and His Staining Technique. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 156, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, G.S.; Stokes, M.B.; Radhakrishnan, J.; D’Agati, V.D. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy Following Oral Sodium Phosphate Bowel Purgative: An Underrecognized Cause of Chronic Renal Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3389–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ori, Y.; Herman, M.; Tobar, A.; Chernin, G.; Gafter, U.; Chagnac, A.; Ben Izhak, O.; Korzets, A. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy—An Emerging Threat. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 336, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Juárez, G.; Parejo, L.; Villacorta, J.; Tato, A.; Cazar, R.; Guerrero, C.; Marin, I.M.; Ocaña, J.; Mendez-Abreu, A.; López, K.; et al. Kidney injury after sodium phosphate solution beyond the acute renal failure. Nefrologia 2016, 36, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmeules, S.; Bergeron, M.J.; Isenring, P. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy and Renal Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1006–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, P.; Somerfield, J.; Simpson, I.; Barber, A.; Zwi, J. Bilateral Uraemic Optic Neuritis Complicating Acute Nephrocalcinosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 2957–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasebø, W.; Scott, H.; Ganss, R. Kidney Biopsies Taken Before and After Oral Sodium Phosphate Bowel Cleansing. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 920–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyea, A.; Block, C.; Schned, A. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy Following Oral Sodium Phosphate Solution to Cleanse the Bowel for Colonoscopy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 50, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, T.I.; Samir, A.E.; Cornell, L.D. Case 27-2008: A 64-Year-Old Man with Abdominal Pain, Nausea, and an Elevated Level of Serum Creatinine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, A.; Sykes, L.; Roberts, I.S.; Weston, C.E. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy after Sodium Phosphate Preparations. BMJ 2008, 337, a182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, B.H.; Kwon, S.H.; Jeon, J.S.; Noh, H.J.; Han, D.C.; Jin, S.Y. A Case of Acute Phosphate Nephropathy after Sodium Phosphate Preparation. Korean J. Nephrol. 2008, 27, 374–377. [Google Scholar]
- Rocuts, A.K.; Waikar, S.S.; Alexander, M.P.; Rennke, H.G.; Singh, A.K. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoulin, N.; Jadoul, M.; Cosyns, J.P.; Labriola, L. An Easily Overlooked Iatrogenic Cause of Renal Failure. Clin. Nephrol. 2008, 70, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slee, T.M.; Vleming, L.J.; Valentijn, R.M. Renal Failure Due to Acute Phosphate Nephropathy. Neth. J. Med. 2008, 66, 438–441. [Google Scholar]
- Loganathan, A.; Tan, K.S.; Moore, J.; Oliver, K. A Case of Acute Phosphate Nephropathy. Med. J. Aust. 2016, 204, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, E.; Purto, D.; Kutscher, S.; Cornejo, C.; Severino, N.; Méndez, G.P.; Tagle, R. Acute phosphate nephropathy secondary to the use of oral sodium phosphate laxatives. Rev. Med. Chile 2021, 149, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.; Chang, F.C. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy—An Old Issue in the New Era. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2018, 117, 348–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J.; Thorp, M.L. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy: A Cause of Chronic Kidney Disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 2011, bcr0420102876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.R.P.; Williams, D.; Niewiadomski, O.D. Phosphate nephropathy: An avoidable complication of bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Intern. Med. J. 2018, 48, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markantonis, S.-L.; Markou, N.; Karagkounis, A.; Koutrafouri, D.; Stefanatou, H.; Kousovista, R.; Karalis, V. The Pharmacokinetics of Levetiracetam in Critically Ill Adult Patients: An Intensive Care Unit Clinical Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M.; Littrell, E.; Khan, A.; Patterson, M.E. Estimated GFR Decline Following Sodium Phosphate Enemas Versus Polyethylene Glycol for Screening Colonoscopy: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, F.P.; Abbott, K.C. Acute Phosphate Nephropathy. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2009, 18, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zago, A.; Occhipinti, A.A.; Bramuzzo, M.; Ceconi, V.; Colacino, V.; Barbi, E.; Poropat, F. The Risks of Phosphate Enemas in Toddlers: A Life-Threatening Unawareness. Children 2024, 11, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
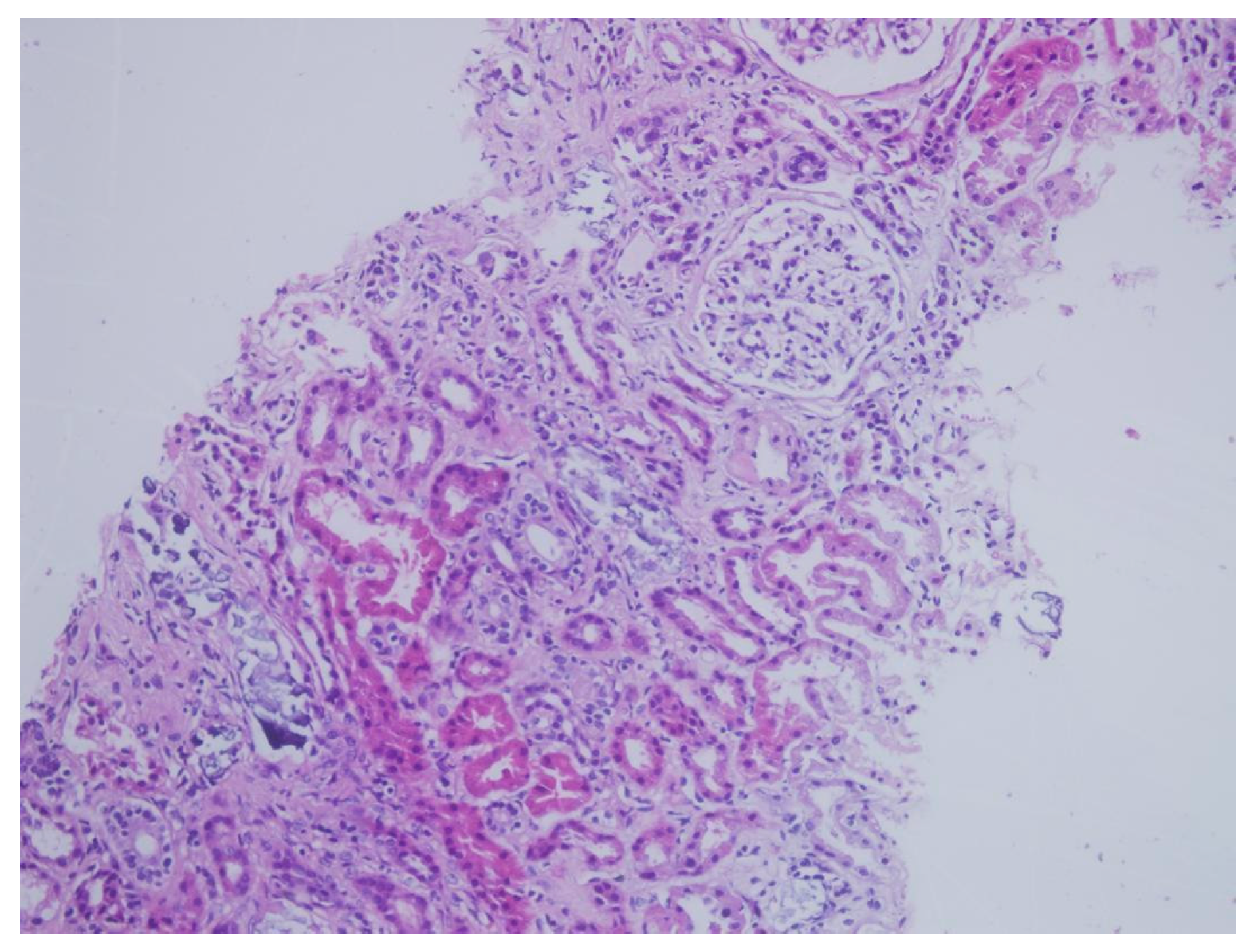
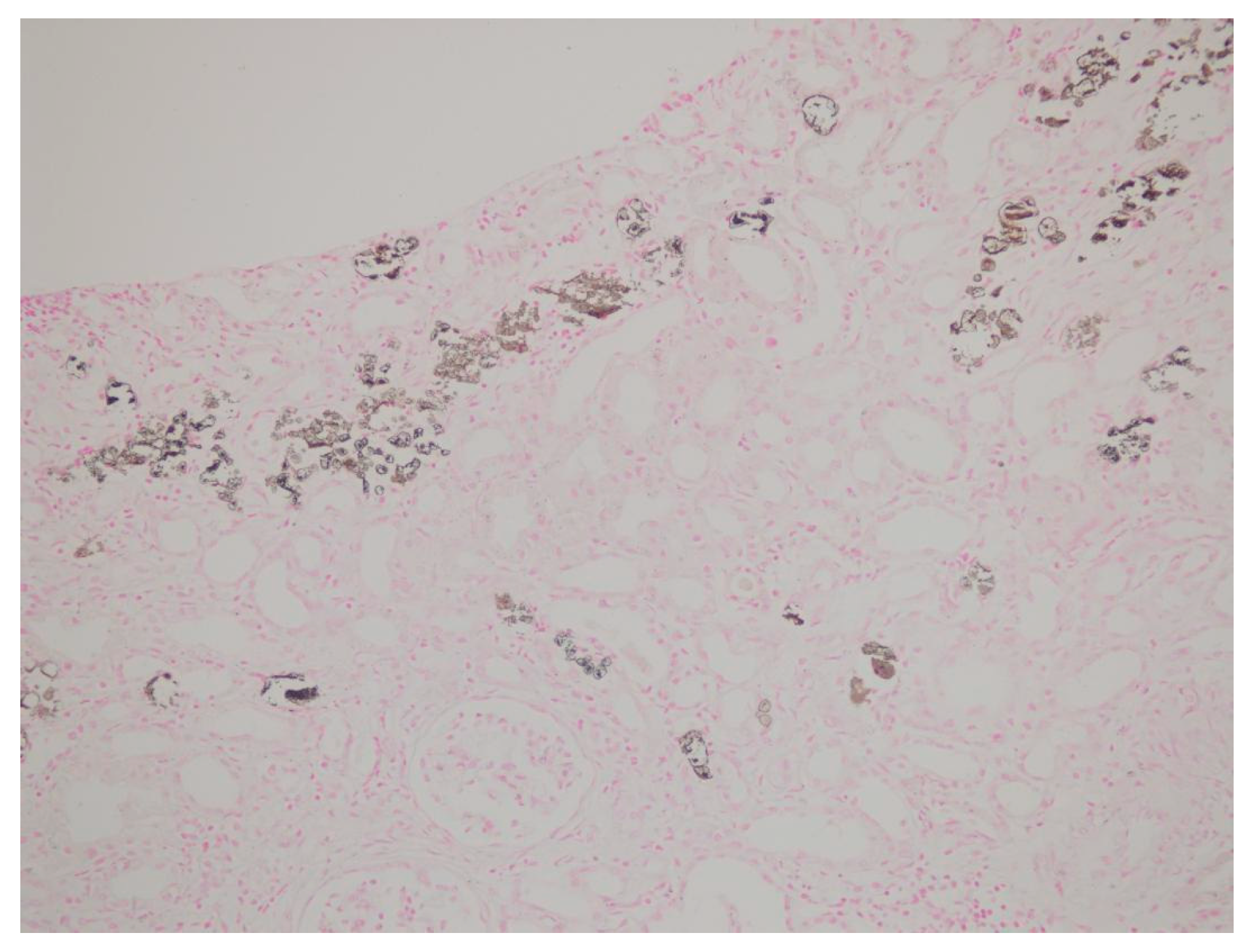
| Patient | Age | Sex | Medical History | * Time | Concomitant Medications | Creatinine (mg/dL) ** Day 0 | Creatinine (mg/dL) ** Day 14 | Creatinine (mg/dL) ** Day 30 | Creatinine (mg/dL) ** Day 90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 57 | M | None | 50 | None | 1.14 | 2.54 | 1.9 | ESRD |
| 2 | 66 | F | DM, HT, HL | 116 | ACE-Is, statins, OADs | 0.8 | 2.96 | 2.27 | 2.4 |
| 3 | 53 | F | HT, Asthma, Epilepsy | 20 | ARBs, CCBs, levetiracetam, ASAs | 0.9 | 1.72 | 1.63 | 1.47 |
| 4 | 68 | F | DM, Epilepsy | 125 | Quetiapine, valproic acid | 0.8 | 2.5 | 1.72 | 1.68 |
| 5 | 48 | M | DM, HT, HL | 52 | ACE-Is, statins, OADs, ASAs | 0.8 | 1.84 | 1.7 | 1.64 |
| 6 | 51 | M | HT | 43 | ARBs | 0.7 | 1.93 | 1.88 | 1.71 |
| 7 | 73 | M | HT | 82 | CCBs | 0.94 | 2.19 | 1.87 | 1.56 |
| 8 | 59 | M | HT, HL | 97 | ARBs, statins | 0.82 | 1.94 | 1.86 | 1.75 |
| 9 | 54 | M | HT, HL | 28 | ACE-Is, CCBs, statins | 0.84 | 2.33 | 2.04 | 1.98 |
| Parameter | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | Case 6 | Case 7 | Case 8 | Case 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of glomeruli | 8 | 5 | 23 | 15 | 14 | 17 | 13 | 13 | 16 |
| Global glomerulosclerosis | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| Basement membrane thickening | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | + |
| Mesangial hypercellularity * | Mild | Mild | − | − | Mild | − | − | Mild | Mild |
| Mesangial expansion * | Mild | − | Mild | Mild | Mild | Mild | − | − | + |
| Interstitial inflammation * | Mild; Eo, Mn | Mild; Lym | Mild; Mn | Mild; Lym | Mild; Lym | Mild; Lym | Mild; Lym | Mild; Mn | Mild; Lym |
| Tubular atrophy * | − | Moderate | Mild | − | − | − | Mild | Moderate | − |
| Tubulointerstitial deposition | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Interstitial fibrosis * | − | − | Mild | − | − | − | − | Mild | − |
| Tubular necrosis | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Direct immuno-fluorescence | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Immuno-histochemistry | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| von Kossa staining | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Study (Reference) | N | Age/Gender (Min–Max) | Baseline sCr (Min–Max) | * Final sCr (Min–Max) | Medications/Drugs | Co-Morbidities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markowitz et al. [18] | 21 | 39–82/F = 17, M = 4 | 0.59–1.60 | 1.49–3.38 (ESRD = 4) | ACE-Is or ARBs = 14, diuretics = 4, NSAIDs = 3 | CKD = 4, DM = 4 HT = 15, |
| Our study | 9 | 48–73/F = 3, M = 6 | 0.70–1.14 | 1.47–2.40 (ESRD = 1) | ACE-Is or ARBs = 5, diuretics = 1, antiepileptic = 2, OADs = 2 | Asthma = 1, DM = 3, Epilepsy = 2, HT = 7, HL = 4, |
| Ori et al. [19] | 5 | 56–73/F = 4, M = 1 | 0.70–1.19 | 1.30–3.09 | ACE-Is/ARBs = 1 | CKD = 3, HT = 5 |
| G. Fernández Juárez et al. [20] | 4 | 61–73/F = 2, M = 2 | 0.5–1.2 | 1.7–2.9 (ESRD = 1) | ACE-Is or ARBs = 3, diuretics = 2 | DM = 2, HT = 3 |
| Cumulative data from 17 single reports [7,12,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35] | 17 | 50–86/F = 14, M = 3 | 0.7–1.39 | 0.85–3.06 | ARBs = 7, diuretics = 6, ACE-Is = 3, none = 4, others = 8 | DM = 1, Epilepsy = 1, HT = 15, Others = 10 |
| Total | 56 | 39–86/F = 40, M = 16 | 0.5–1.6 | 0.85–3.38 (ESRD = 6) | ACE-Is or ARBs = 33, antiepileptic = 3, diuretics = 13, others = 14 | DM = 10, Epilepsy =3, HT = 45, Others = 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özdemir, E.; Özdemir, P.; Yadigar, S.; Yalın, S.F.; Parmaksız, E.; Sarıkaya, Ş.; Özdemir, E.; Altıparmak, M.R. An Overlooked Etiology of Acute Kidney Injury: A Clinicopathological Analysis of Phosphate Nephropathy and Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4081. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124081
Özdemir E, Özdemir P, Yadigar S, Yalın SF, Parmaksız E, Sarıkaya Ş, Özdemir E, Altıparmak MR. An Overlooked Etiology of Acute Kidney Injury: A Clinicopathological Analysis of Phosphate Nephropathy and Review of the Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4081. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124081
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzdemir, Erman, Pınar Özdemir, Serap Yadigar, Serkan Feyyaz Yalın, Ergün Parmaksız, Şükran Sarıkaya, Erdoğan Özdemir, and Mehmet Rıza Altıparmak. 2025. "An Overlooked Etiology of Acute Kidney Injury: A Clinicopathological Analysis of Phosphate Nephropathy and Review of the Literature" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4081. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124081
APA StyleÖzdemir, E., Özdemir, P., Yadigar, S., Yalın, S. F., Parmaksız, E., Sarıkaya, Ş., Özdemir, E., & Altıparmak, M. R. (2025). An Overlooked Etiology of Acute Kidney Injury: A Clinicopathological Analysis of Phosphate Nephropathy and Review of the Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4081. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124081






