On the Use of 4D-PET/CT for the Safe SBRT Re-Irradiation of Central Lung Recurrence Within Radiation-Induced Fibrosis: A Clinical Case
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Detailed Case Description
2.1. Patient Description and Case History
2.2. Planning Image Acquisitions
2.3. Target Volume Segmentation
2.4. Treatment Planning and Delivery
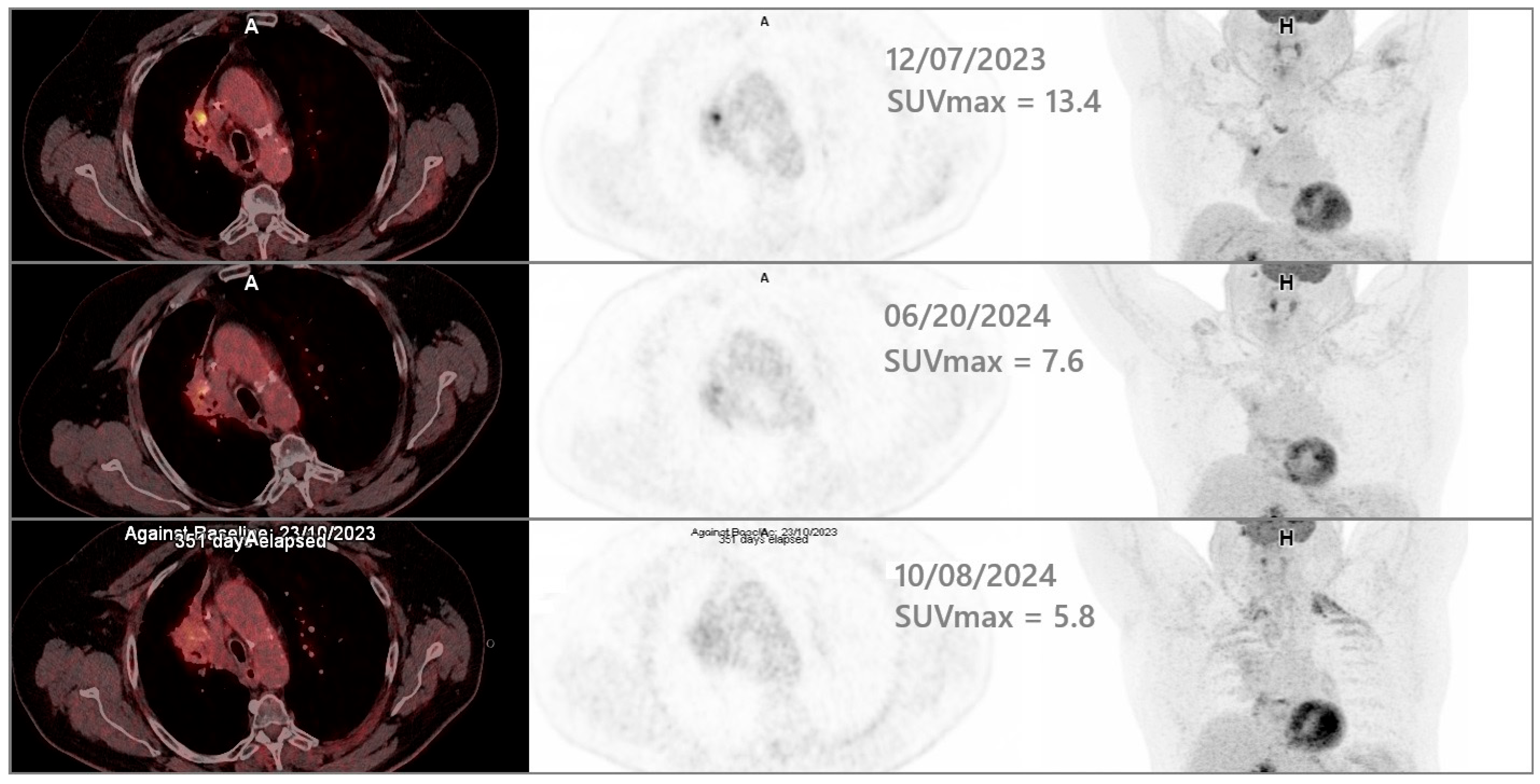
2.5. Clinical Outcomes
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4D-CT | Four-Dimensional Computed Tomography |
| 4D-PET/CT | Four-Dimensional Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography |
| AIP | Average Intensity Projection |
| CBCT | Cone Beam Computed Tomography |
| GTV | Gross Tumor Volume |
| ITV | Internal Garget Volume |
| MIP | Maximum Intensity Projection |
| OAR | Organ At Risk |
| PTV | Planning Target Volume |
| RGSC | Respiratory Gating for SCanners |
| ROI | Region Of Interest |
| SBRT | Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SUV | Standardized Uptake Value |
| TPS | Treatment Planning System |
References
- Badra, E.V.; Baumgartl, M.; Fabiano, S.; Jongen, A.; Guckenberger, M. Stereotactic radiotherapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: Current standards and ongoing research. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1930–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Louie, A.V.; Kotecha, R.; Ahmed, A.; Zhang, Z.; Guckenberger, M.; Kim, M.-S.; Lo, S.S.; Scorsetti, M.; Tree, A.C.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for Ultra-Central lung Tumors: A systematic review and Meta-Analysis and International Stereotactic Radiosurgery Society practice guidelines. Lung Cancer 2023, 182, 107281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchberger, D.S.; Videtic, G.M. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for the Management of Early-Stage Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Clinical Overview. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2023, 19, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladbury, C.; Sidiqi, B.; Cantrell, N.; Jones, G.; Skalina, K.A.; Fekrmandi, F.; Andraos, T.Y.; Gogineni, E.; Dolan, J.; Siva, S.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Primary Lung Cancer and Metastases: A Case-Based Discussion on Challenging Cases. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 15, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, H.; Araki, T.; Shirato, H.; Nagata, Y.; Hiraoka, M.; Gomi, K.; Yamashita, T.; Niibe, Y.; Karasawa, K.; Hayakawa, K.; et al. Stereotactic hypofractionated high-dose irradiation for stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 2004, 101, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.C.; Fellman, B.; Hobbs, B.P.; Liao, Z.; Gomez, D.R.; Chen, A.; Hahn, S.M.; Chang, J.Y.; Lin, S.H. Biologically Effective Dose in Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy and Survival for Patients With Early-Stage NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Rosenzweig, K.E. The evolving toxicity profile of SBRT for lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebahr, S.; Collette, S.; Shash, E.; Lambrecht, M.; Le Pechoux, C.; Faivre-Finn, C.; De Ruysscher, D.; Peulen, H.; Belderbos, J.; Dziadziuszko, R.; et al. LungTech, an EORTC Phase II trial of stereotactic body radiotherapy for centrally located lung tumours: A clinical perspective. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20150036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.; Grozman, V.; Karlsson, K.; Onjukka, E.; Lindbäck, E.; Al Jirf, K.; Lax, I.; Wersäll, P.; Persson, G.F.; Josipovic, M.; et al. Expanded HILUS Trial: A Pooled Analysis of Risk Factors for Toxicity From Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy of Central and Ultracentral Lung Tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 117, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhidasan, S.; Woody, N.M.; Stephans, K.L.; Videtic, G.M. Does Motion Management Technique for Lung SBRT Influence Local Control? A Single Institutional Experience Comparing Abdominal Compression to Breath-Hold Technique. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 11, e180–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoganathan, S.; Das, K.M.; Agarwal, A.; Kumar, S. Magnitude, impact, and management of respiration-induced target motion in radiotherapy treatment: A comprehensive review. J. Med. Phys. 2017, 42, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underberg, R.W.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Cuijpers, J.P.; Slotman, B.J.; Koste, J.R.v.S.d.; Senan, S. Four-dimensional CT scans for treatment planning in stereotactic radiotherapy for stage I lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 60, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aristophanous, M.; Berbeco, R.I.; Killoran, J.H.; Yap, J.T.; Sher, D.J.; Allen, A.M.; Larson, E.; Chen, A.B. Clinical Utility of 4D FDG-PET/CT Scans in Radiation Treatment Planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 82, e99–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, A.; Nguyen, N.P. 4D PET/CT as a Strategy to Reduce Respiratory Motion Artifacts in FDG-PET/CT. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindoni, A.; Minutoli, F.; Pontoriero, A.; Iatì, G.; Baldari, S.; Pergolizzi, S. Usefulness of four dimensional (4D) PET/CT imaging in the evaluation of thoracic lesions and in radiotherapy planning: Review of the literature. Lung Cancer 2016, 96, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, J.; Brandon, D.; Halkar, R. 4D PET/CT integration: Optimizing radiation and therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 1706. [Google Scholar]
- Käsmann, L.; Dietrich, A.; Staab-Weijnitz, C.A.; Manapov, F.; Behr, J.; Rimner, A.; Jeremic, B.; Senan, S.; De Ruysscher, D.; Lauber, K.; et al. Radiation-induced lung toxicity—Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis, management, and literature review. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, C.; Bello, R.D.; Andratschke, N.; Guckenberger, M.; Boda-Heggemann, J.; Gkika, E.; Mantel, F.; Specht, H.M.; Stromberger, C.; Zehentmayr, F.; et al. In-field stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) reirradiation for pulmonary malignancies as a multicentre analysis of the German Society of Radiation Oncology (DEGRO). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Kim, D.-Y.; Wu, H.-G.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J. Treatment outcomes of re-irradiation using stereotactic ablative radiotherapy to lung: A propensity score matching analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulach, R.; Ball, D.; Chua, K.L.; Dahele, M.; De Ruysscher, D.; Franks, K.; Gomez, D.; Guckenberger, M.; Hanna, G.G.; Louie, A.V.; et al. An International Expert Survey on the Indications and Practice of Radical Thoracic Reirradiation for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 6, 100653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strange, T.A.; Erasmus, L.T.; Ahuja, J.; Agrawal, R.; Shroff, G.S.; Truong, M.T.; Strange, C.D. Spectrum of Imaging Patterns of Lung Cancer following Radiation Therapy. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.; Chan, D.; Kuo, E.; Harkenrider, M. Thoracic Reirradiation with Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for Recurrent Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 14, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, A.; Romano, E.; Casutt, A.; Moeckli, R.; Vallet, V.; El Chammah, S.; Ozsahin, M.; Kinj, R. Stereotactic Lung Re-Irradiation After a First Course of Stereotactic Radiotherapy with In-Field Relapse: A Valuable Option to Be Considered. Cancers 2025, 17, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanlan, Z.; Xianfeng, L.; Lingjun, H. Consideration of the target area of radiotherapy for lung cancer with 4DPET. Precis. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 5, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; Chesson, B.; Callahan, J.W.; Hardcastle, N.; Crawford, L.; Antippa, P.; Wright, G.; MacManus, M.P.; Hicks, R.J.; Kron, T.; et al. Dosimetric Consequences of 3D Versus 4D PET/CT for Target Delineation of Lung Stereotactic Radiotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trémolières, P.; Gonzalez-Moya, A.; Paumier, A.; Mege, M.; Blanchecotte, J.; Theotime, C.; Autret, D.; Dufreneix, S. Lung stereotactic body radiation therapy: Personalized PTV margins according to tumor location and number of four-dimensional CT scans. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retif, P.; Sidikou, A.D.; Letellier, R.; Verrecchia-Ramos, E.; Quetin, P. Technical Note: A 3D-printed phantom for radiochromic film evaluation of moving lung tumor SBRT without dose convolution. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 3453–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, J.; Kron, T.; Schneider-Kolsky, M.; Dunn, L.; Thompson, M.; Siva, S.; Aarons, Y.; Binns, D.; Hicks, R.J. Validation of a 4D-PET Maximum Intensity Projection for Delineation of an Internal Target Volume. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 86, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirindel, A.; Adebahr, S.; Schimek-Jasch, T.; Schanne, D.H.; Mix, M.; Meyer, P.; Grosu, A.-L.; Brunner, T.; Nestle, U. Impact of 4D-18FDG-PET/CT imaging on target volume delineation in SBRT patients with central versus peripheral lung tumors. Multi-reader comparative study. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 115, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guneyli, S.; Tor, M.; Hassoy, H.; Aygun, M.S.; Altinmakas, E.; Altintas, S.D.; Savas, R. Spin-echo and diffusion-weighted MRI in differentiation between progressive massive fibrosis and lung cancer. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 27, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
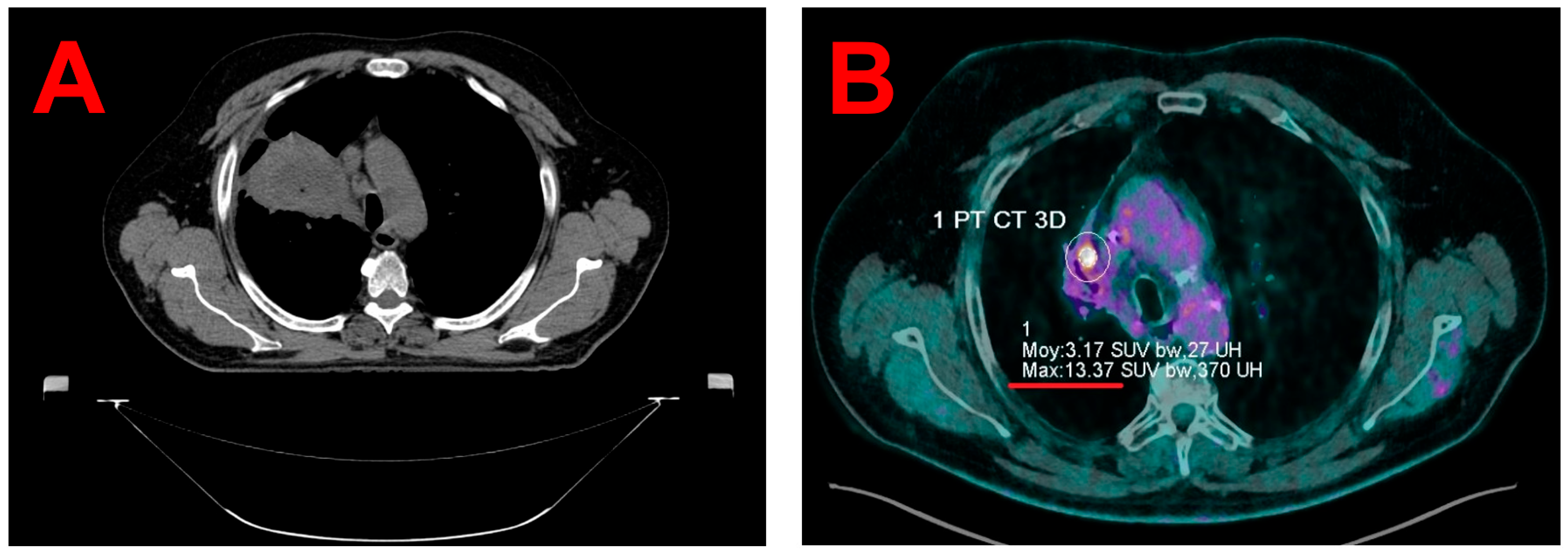

| Imaging Modality Used for Target Volumes Contouring | 4D PET/CT MIP | Static PET/CT |
|---|---|---|
| Primary target volume | ITV Volume = 0.9 cc Maximal dimension in infero superior axis = 13.1 mm | GTV Volume = 0.5 cc Maximal dimension in infero superior axis = 8.0 mm |
| Planning Target Volume (primary target volume + 3 mm isotropic margins) | Clinical PTV Volume = 3.3 cc Maximal dimension in infero superior axis = 19.1 mm | Theoretical PTV Volume = 2.0 cc Maximal dimension in infero superior axis = 14.0 mm |
| Clinical PTV coverage at the prescription dose of 60 Gy | 95.0% | 61.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Retif, P.; Verrecchia-Ramos, E.; Saleh, M.; Djibo Sidikou, A.; Letellier, R.; Al Salah, A.; Pfletschinger, E.; Taesch, F.; Ben-Mahmoud, S.; Michel, X. On the Use of 4D-PET/CT for the Safe SBRT Re-Irradiation of Central Lung Recurrence Within Radiation-Induced Fibrosis: A Clinical Case. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124015
Retif P, Verrecchia-Ramos E, Saleh M, Djibo Sidikou A, Letellier R, Al Salah A, Pfletschinger E, Taesch F, Ben-Mahmoud S, Michel X. On the Use of 4D-PET/CT for the Safe SBRT Re-Irradiation of Central Lung Recurrence Within Radiation-Induced Fibrosis: A Clinical Case. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124015
Chicago/Turabian StyleRetif, Paul, Emilie Verrecchia-Ramos, Motchy Saleh, Abdourahamane Djibo Sidikou, Romain Letellier, Anwar Al Salah, Estelle Pfletschinger, Fabian Taesch, Sinan Ben-Mahmoud, and Xavier Michel. 2025. "On the Use of 4D-PET/CT for the Safe SBRT Re-Irradiation of Central Lung Recurrence Within Radiation-Induced Fibrosis: A Clinical Case" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124015
APA StyleRetif, P., Verrecchia-Ramos, E., Saleh, M., Djibo Sidikou, A., Letellier, R., Al Salah, A., Pfletschinger, E., Taesch, F., Ben-Mahmoud, S., & Michel, X. (2025). On the Use of 4D-PET/CT for the Safe SBRT Re-Irradiation of Central Lung Recurrence Within Radiation-Induced Fibrosis: A Clinical Case. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124015







