Longitudinal Changes in Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome Stages and Their Impact on Outcomes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
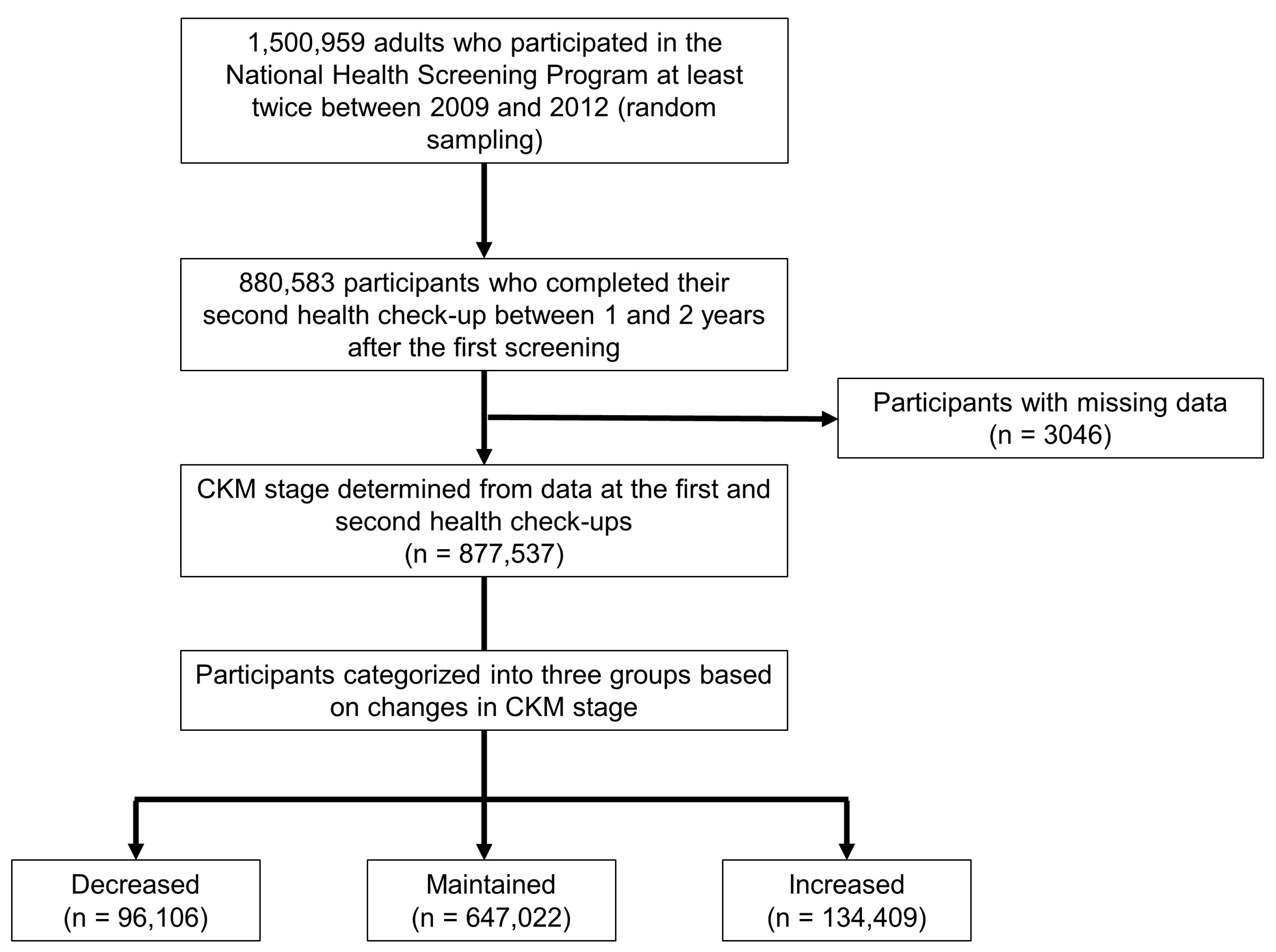
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Definition and Staging of CKM Syndrome
2.4. Study Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
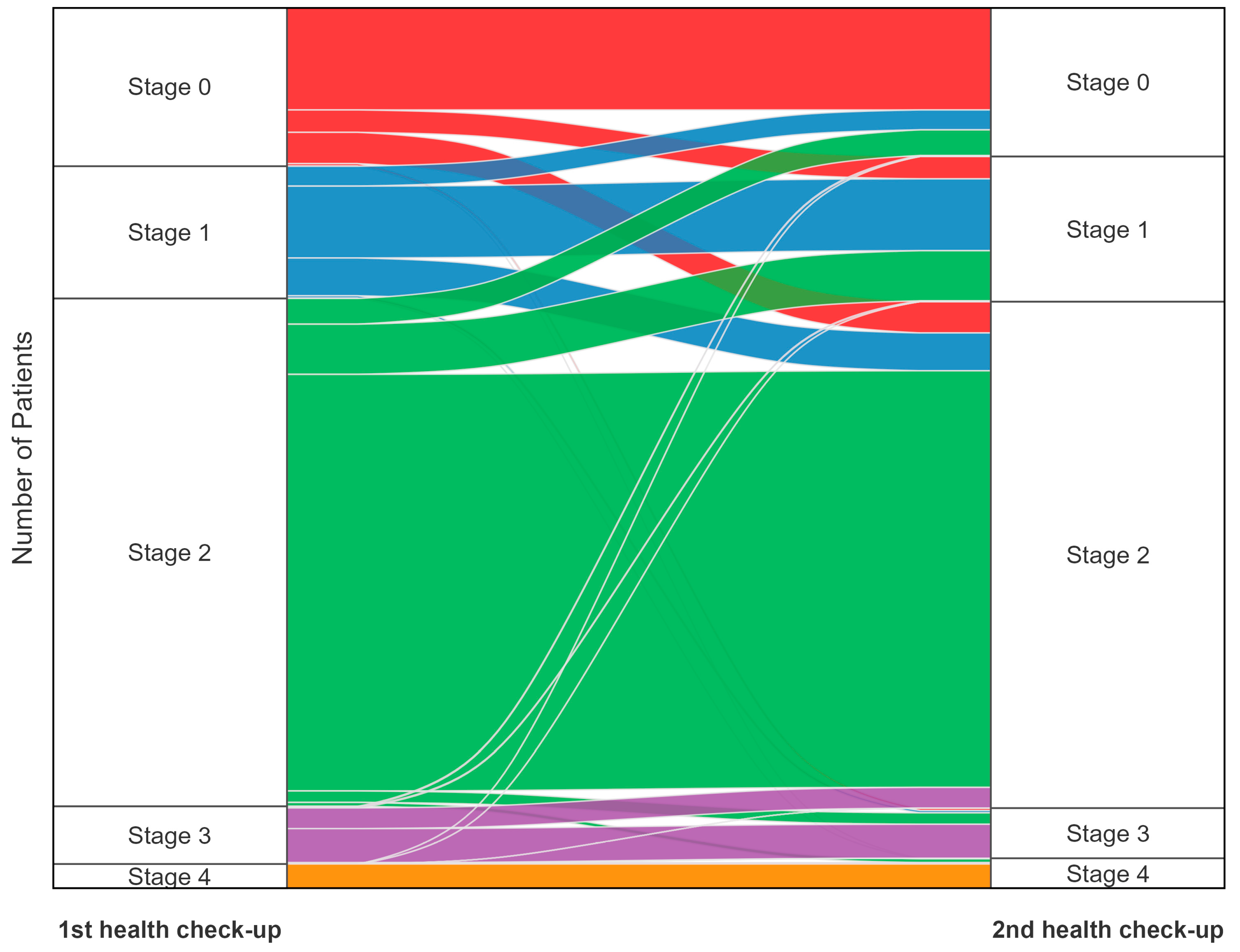
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Changes in CKM Stages Between Health Check-Ups
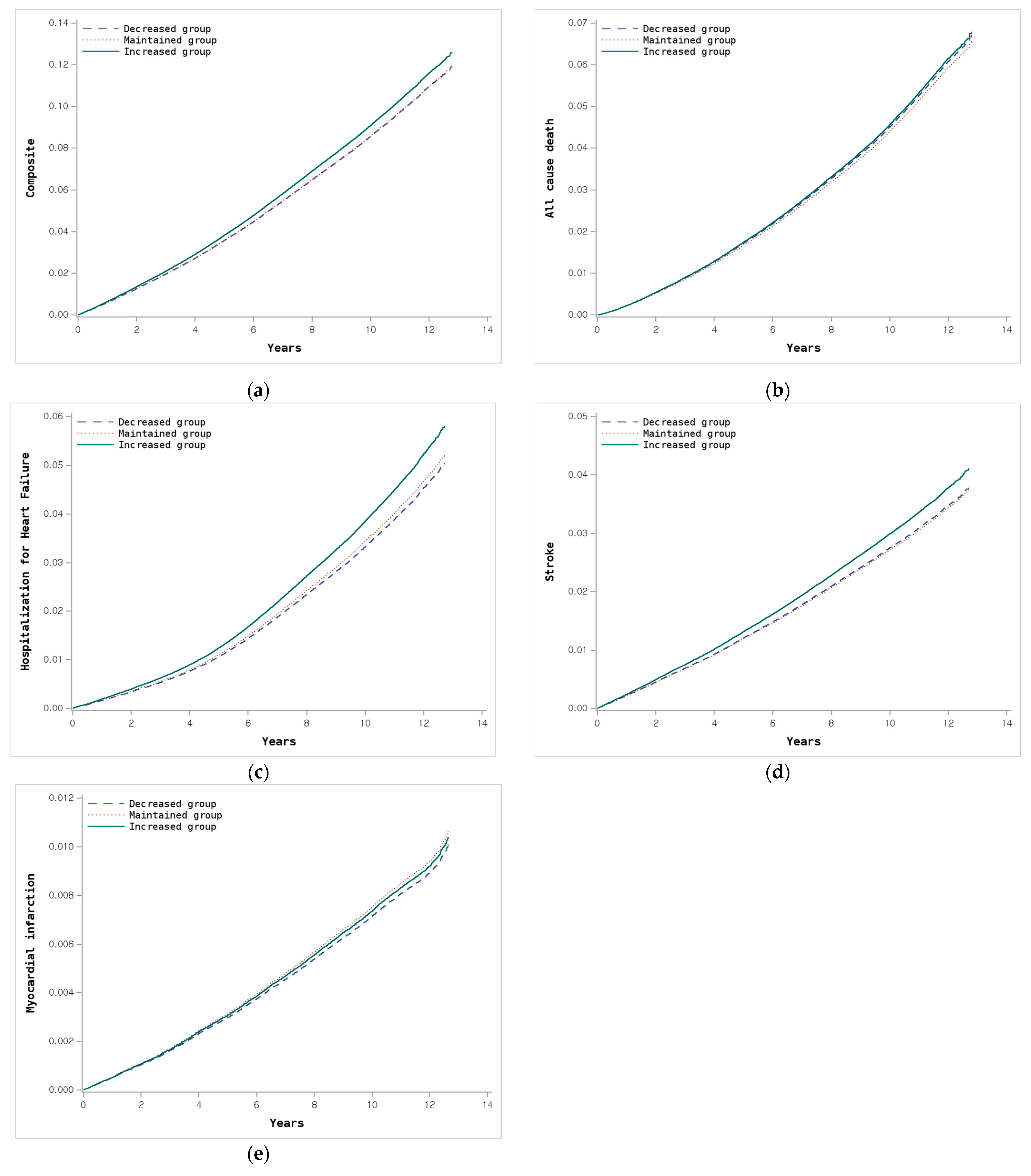
3.3. Clinical Outcomes According to Changes in CKM Stage
3.4. Age and Sex Differences in Clinical Outcomes According to Changes in CKM Stage
3.5. Clinical Outcomes According to Baseline CKM Stage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CKM | Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision |
| MI | Myocardial infarction |
| NHID | National Health Insurance Database |
| PREVENT | Predicting risk of cardiovascular disease events |
| SAS | Statistical analysis system |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
References
- Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Chow, S.L.; Mathew, R.O.; Khan, S.S.; Coresh, J.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; Després, J.P.; et al. A Synopsis of the Evidence for the Science and Clinical Management of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 1636–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndumele, C.E.; Rangaswami, J.; Chow, S.L.; Neeland, I.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Khan, S.S.; Coresh, J.; Mathew, R.O.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; et al. Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 1606–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Shu, R.; Song, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Shi, H.; Gao, H.; et al. Association between different stages of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome and the risk of all-cause mortality. Atherosclerosis 2024, 397, 118585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindbohm, J.V.; Sipilä, P.N.; Mars, N.; Knüppel, A.; Pentti, J.; Nyberg, S.T.; Frank, P.; Ahmadi-Abhari, S.; Brunner, E.J.; Shipley, M.J.; et al. Association between change in cardiovascular risk scores and future cardiovascular disease: Analyses of data from the Whitehall II longitudinal, prospective cohort study. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e434–e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattler, E.L.P.; Lassale, C.; Diaw, M.; Joseph, J.J.; Singh, G.; Samb, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Gaye, B. Changes in Cardiovascular Health at Midlife and Subsequent Cardiovascular Outcomes in Individuals with Diabetes. JACC Adv. 2025, 4, 101450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Ren, X. Association between 5-year change in cardiovascular risk and the incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases: A multi-cohort study. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, S.C.; Kim, Y.Y.; Park, S.K.; Khang, Y.H.; Kim, H.C.; Park, J.H.; Kang, H.J.; Do, C.H.; Song, J.S.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Cohort profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haam, J.H.; Kim, B.T.; Kim, E.M.; Kwon, H.; Kang, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, K.K.; Rhee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, K.Y. Diagnosis of Obesity: 2022 Update of Clinical Practice Guidelines for Obesity by the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 32, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Jung, M.H.; Kwon, C.H.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.L.; Kim, W.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.M.; et al. Disparities in Mortality and Cardiovascular Events by Income and Blood Pressure Levels Among Patients with Hypertension in South Korea. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e018446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.S.; Matsushita, K.; Sang, Y.; Ballew, S.H.; Grams, M.E.; Surapaneni, A.; Blaha, M.J.; Carson, A.P.; Chang, A.R.; Ciemins, E.; et al. Development and Validation of the American Heart Association’s PREVENT Equations. Circulation 2024, 149, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Kang, D.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, W.; Jeong, Y.W.; Chun, K.-H.; Han, S.H.; Koh, K.K. Metabolic Syndrome Fact Sheet 2024: Executive Report. CardioMetabolic Syndr. J. 2024, 4, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.S.; Coresh, J.; Pencina, M.J.; Ndumele, C.E.; Rangaswami, J.; Chow, S.L.; Palaniappan, L.P.; Sperling, L.S.; Virani, S.S.; Ho, J.E.; et al. Novel Prediction Equations for Absolute Risk Assessment of Total Cardiovascular Disease Incorporating Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 1982–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, B.S.; Rhee, T.M.; Lee, H.J.; Han, K.D.; Park, J.B.; Na, J.O.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.; et al. Comparative cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes patients taking dapagliflozin versus empagliflozin: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Loberiza, F.R.; Klein, J.P.; Zhang, M.J. A SAS macro for estimation of direct adjusted survival curves based on a stratified Cox regression model. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2007, 88, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittelson, K.S.; Junior, A.G.; Fillmore, N.; da Silva Gomes, R. Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome—An integrative review. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2024, 87, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Sabanayagam, C.; Matsushita, K.; Cheng, C.Y.; Rim, T.H.; Sheng, B.; Li, H.; Tham, Y.C.; Cheng, S.; Wong, T.Y. Sex Differences in Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome: 30-Year US Trends and Mortality Risks-Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2025, 45, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Wong, N.D.; Wang, J. Impact of Aging on Cardiovascular Diseases: From Chronological Observation to Biological Insights: JACC Family Series. JACC Asia 2024, 4, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.I. Risk Stratification of Cardiovascular Disease According to Age Groups in New Prevention Guidelines: A Review. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2023, 12, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marassi, M.; Fadini, G.P. The cardio-renal-metabolic connection: A review of the evidence. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-L.; Lee, E.M.; Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, K.-i.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.-M.; Cho, E.J.; et al. The 2022 focused update of the 2018 Korean Hypertension Society Guidelines for the management of hypertension. Clin. Hypertens. 2023, 29, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Cao, S. Prognostic value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain in chronic kidney disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Cerini, F.; Fagiani, V.; Nicolosi, G.L.; Rumi, M.G.; Lombardo, M.; Muti, P. Effect of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) on Left Ventricular Mechanics in Patients Without Overt Cardiac Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Definition |
|---|
| Stage 0: no CKM risk factors |
| Individuals without overweight/obesity, metabolic risk factors (hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes mellitus), CKD, or subclinical/clinical CVD. |
| Stage 1: excess and/or dysfunctional adiposity infarction |
| Individuals with overweight/obesity, abdominal obesity, or dysfunctional adipose tissue, without the presence of other metabolic risk factors or CKD. (1) BMI ≥ 23 kg/m2; (2) Waist circumference ≥ 85/90 cm in women/men; (3) Fasting blood glucose: 100–125 mg/dL. |
| Stage 2: metabolic risk factors and CKD |
| Individuals with metabolic risk factors (hypertriglyceridemia, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes), or CKD. (1) Triglyceride ≥ 135 mg/dL; (2) Hypertension defined as blood pressure ≥ 140/90 mmHg or history of hypertension or use of antihypertensive drugs; (3) Metabolic syndrome defined as at least 3 of the following: -Abdominal obesity (waist circumference ≥ 85/90 cm in women/ men); -Fasting glucose ≥ 100 mg/dL or history of diabetes or use of glucose-lowering drugs; -Blood pressure ≥ 130/85 mmHg or history of hypertension or use of antihypertensive drugs; -Triglycerides ≥ 150 mg/dL; -HDL cholesterol < 40 mg/dL (men) or <50 mg/dL (women); (4) Diabetes mellitus defined as fasting glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL or history of diabetes mellitus or use of glucose-lowering drugs; (5) CKD defined as eGFR 30–59 mL/min/1.73 m2. |
| Stage 3: subclinical CVD |
| (1) Very-high-risk CKD defined as eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2; (2) High predicted 10-year CVD risk (PREVENT score ≥ 20%). |
| Stage 4: clinical CVD |
| Clinical CVD (coronary heart disease, heart failure, stroke, peripheral artery disease, and atrial fibrillation) among individuals with excess/dysfunctional adiposity, other metabolic risk factors, or CKD. |
| Total Patients (N = 877,537) | CKM Stage Changes | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decreased (n = 96,106) | Maintained (n = 947,022) | Increased (n = 134,409) | |||
| Age, years | 45.20 ± 13.12 | 49.43 ± 13.91 | 46.04 ± 14.00 | <0.001 | |
| Sex, n (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Men | 56,303 (58.58) | 353,242 (54.60) | 81,051 (60.30) | ||
| Women | 39,803 (41.42) | 293,780 (45.40) | 53,358 (39.70) | ||
| Blood pressure, mmHg | |||||
| SBP | 118.30 ± 12.17 | 122.61 ± 14.79 | 122.66 ± 15.04 | <0.001 | |
| DBP | 73.90 ± 8.35 | 76.41 ± 9.95 | 76.50 ± 9.97 | <0.001 | |
| Smoking, n (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Never | 54,909 (57.13) | 391,275 (60.47) | 74,849 (55.69) | ||
| Past | 14,607 (15.20) | 107,301 (16.58) | 21,768 (16.20) | ||
| Current | 26,590 (27.67) | 148,446 (22.94) | 37,792 (28.12) | ||
| Physical activity, times/week | <0.001 | ||||
| 0 | 53,059 (55.21) | 370,487 (57.26) | 75,213 (55.96) | ||
| 1–2 | 26,356 (27.42) | 165,944 (25.65) | 37,917 (28.21) | ||
| 3–4 | 10,674 (11.11) | 70,348 (10.87) | 13,863 (10.31) | ||
| 5–6 | 4350 (4.53) | 27,730 (4.29) | 5172 (3.85) | ||
| 7 | 1667 (1.73) | 12,513 (1.93) | 2244 (1.67) | ||
| Alcohol consumption, times/week | <0.001 | ||||
| 0 | 45,779 (47.63) | 336,909 (52.07) | 63,249 (47.06) | ||
| 1–2 | 37,648 (39.17) | 225,149 (34.80) | 52,041 (38.72) | ||
| 3–4 | 9577 (9.97) | 61,983 (9.58) | 14,225 (10.58) | ||
| ≥5 | 3102 (3.23) | 22,981 (3.55) | 4894 (3.64) | ||
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 22.91 ± 2.93 | 23.92 ± 3.26 | 23.65 ± 2.98 | <0.001 | |
| <18.5 | 4458 (4.64) | 21406 (3.31) | 3737 (2.78) | <0.001 | |
| 18.5–22.9 | 51,125 (53.20) | 234,807 (36.29) | 50,805 (37.80) | ||
| 23.0–24.9 | 19,323 (20.11) | 159,768 (24.69) | 40,785 (30.34) | ||
| ≥25 | 21,200 (22.06) | 231,041 (35.71) | 39,082 (29.08) | ||
| Waist circumference, cm | 78.13 ± 8.50 | 80.80 ± 9.21 | 80.26 ± 8.61 | <0.001 | |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 93.07 ± 16.59 | 97.69 ± 22.49 | 97.99 ± 21.28 | <0.001 | |
| <100 | 77,513 (80.65) | 447,052 (69.09) | 85,838 (63.86) | <0.001 | |
| 100–125.9 | 16,371 (17.03) | 158,264 (24.46) | 39,482 (29.37) | ||
| ≥126 | 2222 (2.31) | 41,706 (6.45) | 9089 (6.76) | ||
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 187.82 ± 29.50 | 195.40 ± 36.99 | 194.66 ± 35.34 | <0.001 | |
| <200 | 62,391 (64.92) | 374,244 (57.84) | 78,704 (58.56) | <0.001 | |
| 200–239.9 | 32,001 (33.30) | 196,324 (30.34) | 39,855 (29.65) | ||
| ≥240 | 1714 (1.78) | 76,454 (11.82) | 15,850 (11.79) | ||
| LDL, mg/dL | 111.79 ± 27.58 | 114.31 ± 33.62 | 111.77 ± 32.73 | <0.001 | |
| HDL, mg/dL | 56.49 ± 13.07 | 54.81 ± 13.50 | 54.79 ± 13.80 | <0.001 | |
| <40 for men or <50 for women, n (%) | 13,365 (13.91) | 130,261 (20.13) | 26,079 (19.40) | <0.001 | |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 97.30 ± 51.69 | 132.31 ± 85.12 | 144.19 ± 109.42 | <0.001 | |
| ≥150, n (%) | 5803 (6.04) | 198,749 (30.72) | 47,674 (35.47) | <0.001 | |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 86.78 ± 17.37 | 84.49 ± 18.59 | 79.90 ± 26.25 | <0.001 | |
| Household income, quartile | <0.001 | ||||
| first | 21,320 (22.18) | 142,689 (22.05) | 28,042 (20.86) | ||
| second | 21,201 (22.06) | 130,296 (20.14) | 28,830 (21.45) | ||
| third | 26,257 (27.32) | 169,047 (26.13) | 36,926 (27.47) | ||
| fourth | 27,328 (28.44) | 204,990 (31.68) | 40,611 (30.21) | ||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 9342 (9.72) | 335,204 (51.81) | 44,999 (33.48) | <0.001 | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 4069 (4.23) | 72,045 (11.13) | 13,189 (9.81) | <0.001 | |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 6883 (7.16) | 191,461 (29.59) | 27,153 (20.20) | <0.001 | |
| Use of antihypertensive drugs, n (%) | 8443 (8.8) | 284,293 (30.0) | 30,164 (22.4) | ||
| Use of glucose-lowering drugs, n (%) | 3589 (3.73) | 55,722 (8.61) | 7551 (5.62) | <0.001 | |
| Use of lipid-lowering drugs, n (%) | 6106 (6.35) | 143,817 (22.23) | 13,441 (10.00) | <0.001 | |
| Use of antiplatelet drugs, n (%) | 10,017 (10.42) | 152,463 (23.56) | 20,675 (15.38) | <0.001 | |
| PREVENT score | 3.33 ± 4.87 | 6.05 ± 8.07 | 6.92 ± 10.57 | <0.001 | |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects | Events | Person-year | IR | HR | 95% CI | p value | HR | 95% CI | p value | HR | 95% CI | p value | |
| Composite primary outcome (all-cause death, heart failure, stroke, or myocardial infarction) | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 96,106 | 6631 | 1,057,145 | 6.27 | 0.877 | 0.856–0.900 | <0.001 | 0.875 | 0.853–0.897 | <0.001 | 0.997 | 0.972–1.024 | 0.849 |
| Maintained | 647,022 | 69,728 | 6,949,014 | 10.03 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 134,409 | 12,307 | 1,461,135 | 8.42 | 1.031 | 1.012–1.051 | 0.002 | 1.014 | 0.995–1.034 | 0.153 | 1.071 | 1.050–1.092 | <0.001 |
| All-cause death | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 96,106 | 3568 | 1,072,485 | 3.33 | 0.977 | 0.943–1.011 | 0.179 | 0.927 | 0.895–0.959 | <0.001 | 1.028 | 0.992–1.065 | 0.124 |
| Maintained | 647,022 | 37,056 | 7,127,035 | 5.20 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 134,409 | 6470 | 1,493,786 | 4.33 | 1.032 | 1.005–1.060 | 0.018 | 1.009 | 0.983–1.036 | 0.512 | 1.043 | 1.015–1.071 | 0.002 |
| Heart failure | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 96,106 | 2170 | 1,065,497 | 2.04 | 0.762 | 0.729–0.796 | <0.001 | 0.789 | 0.755–0.824 | <0.001 | 0.966 | 0.924–1.010 | 0.127 |
| Maintained | 647,022 | 26,777 | 7,036,946 | 3.81 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 134,409 | 4724 | 1,477,392 | 3.20 | 1.046 | 1.014–1.079 | 0.005 | 1.038 | 1.007–1.071 | 0.017 | 1.131 | 1.096–1.166 | <0.001 |
| Stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 96,106 | 1899 | 1,064,757 | 1.78 | 0.869 | 0.829–0.911 | <0.001 | 0.886 | 0.845–0.929 | <0.001 | 1.012 | 0.965–1.062 | 0.617 |
| Maintained | 647,022 | 20,202 | 7,044,115 | 2.87 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 134,409 | 3675 | 1,478,291 | 2.49 | 1.06 | 1.023–1.098 | 0.001 | 1.047 | 1.011–1.085 | 0.011 | 1.106 | 1.068–1.146 | <0.001 |
| Myocardial infarction | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 96,106 | 531 | 1,070,110 | 0.50 | 0.792 | 0.724–0.866 | <0.001 | 0.838 | 0.766–0.916 | <0.001 | 0.948 | 0.866–1.039 | 0.252 |
| Maintained | 647,022 | 5531 | 7,102,163 | 0.78 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 134,409 | 960 | 1,489,420 | 0.64 | 0.928 | 0.867–0.994 | 0.033 | 0.921 | 0.859–0.986 | 0.018 | 0.979 | 0.913–1.049 | 0.541 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects | Events | Person-year | IR | HR | 95% CI | p value | HR | 95% CI | p value | HR | 95% CI | p value | |
| Composite primary outcome according to sex, interaction p-value: <0.001 | |||||||||||||
| Men | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 56,303 | 4392 | 619,251 | 7.09 | 0.900 | 0.872–0.928 | <0.001 | 0.883 | 0.856–0.911 | <0.001 | 0.990 | 0.959–1.022 | 0.521 |
| Maintained | 353,242 | 42,173 | 3,792,676 | 11.12 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 81,051 | 8028 | 882,481 | 9.10 | 1.017 | 0.993–1.042 | 0.155 | 0.992 | 0.968–1.016 | 0.497 | 1.040 | 1.016–1.066 | 0.001 |
| Women | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 39,803 | 2239 | 437,894 | 5.11 | 0.832 | 0.797–0.869 | <0.001 | 0.848 | 0.812–0.885 | <0.001 | 0.994 | 0.951–1.039 | 0.799 |
| Maintained | 293,780 | 27,555 | 3,156,337 | 8.73 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 53,358 | 4279 | 578,654 | 7.39 | 1.056 | 1.023–1.091 | <0.001 | 1.054 | 1.02–1.088 | 0.002 | 1.124 | 1.088–1.161 | <0.001 |
| Composite Primary Outcome According to Age Groups, Interaction p-Value: <0.001 | |||||||||||||
| 20–29 Years | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 15,572 | 154 | 175,172 | 0.88 | 0.857 | 0.721–1.019 | 0.081 | 0.896 | 0.754–1.065 | 0.214 | 0.987 | 0.829–1.176 | 0.886 |
| Maintained | 71,974 | 792 | 809,500 | 0.98 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 22,381 | 231 | 253,233 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.742–0.996 | 0.044 | 0.854 | 0.737–0.989 | 0.035 | 0.906 | 0.781–1.050 | 0.189 |
| 30–39 Years | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 23,728 | 409 | 268,668 | 1.52 | 0.765 | 0.689–0.849 | <0.001 | 0.81 | 0.730–0.900 | <0.001 | 0.904 | 0.813–1.006 | 0.064 |
| Maintained | 117,384 | 2667 | 1,322,499 | 2.02 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 30,890 | 598 | 350,511 | 1.71 | 0.855 | 0.783–0.935 | <0.001 | 0.884 | 0.809–0.967 | 0.007 | 0.958 | 0.875–1.048 | 0.345 |
| 40–49 Years | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 26,458 | 956 | 294,455 | 3.25 | 0.79 | 0.738–0.845 | <0.001 | 0.821 | 0.767–0.878 | <0.001 | 0.981 | 0.916–1.052 | 0.595 |
| Maintained | 162,841 | 7668 | 1,802,825 | 4.25 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 35,866 | 1469 | 399,512 | 3.68 | 0.89 | 0.842–0.941 | <0.001 | 0.907 | 0.858–0.959 | <0.001 | 1.03 | 0.973–1.090 | 0.313 |
| 50–59 years | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 16,949 | 1405 | 184,740 | 7.61 | 0.859 | 0.813–0.908 | <0.001 | 0.859 | 0.813–0.908 | <0.001 | 1.044 | 0.987–1.105 | 0.134 |
| Maintained | 153,472 | 14,629 | 1,655,223 | 8.84 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 22,886 | 2,232 | 247,439 | 9.02 | 1.017 | 0.972–1.063 | 0.466 | 1.01 | 0.966–1.056 | 0.655 | 1.136 | 1.085–1.188 | <0.001 |
| ≥60 years | |||||||||||||
| Decreased | 13,399 | 3707 | 134,111 | 27.64 | 0.923 | 0.892–0.954 | <0.001 | 0.910 | 0.880–0.942 | <0.001 | 1.025 | 0.991–1.061 | 0.156 |
| Maintained | 141,351 | 43,972 | 1,358,967 | 32.36 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | ||||||
| Increased | 22,386 | 7777 | 210,441 | 36.96 | 1.082 | 1.056–1.109 | <0.001 | 1.062 | 1.037–1.088 | <0.001 | 1.096 | 1.070–1.123 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, B.S.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Shin, J.-H.; Sung, K.-C. Longitudinal Changes in Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome Stages and Their Impact on Outcomes: A Nationwide Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113888
Kim BS, Kim H-J, Kim H, Lee J, Shin J-H, Sung K-C. Longitudinal Changes in Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome Stages and Their Impact on Outcomes: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113888
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Byung Sik, Hyun-Jin Kim, Hasung Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Jeong-Hun Shin, and Ki-Chul Sung. 2025. "Longitudinal Changes in Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome Stages and Their Impact on Outcomes: A Nationwide Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113888
APA StyleKim, B. S., Kim, H.-J., Kim, H., Lee, J., Shin, J.-H., & Sung, K.-C. (2025). Longitudinal Changes in Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome Stages and Their Impact on Outcomes: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113888







