The Orbital Destruction Intensity Classification—An Easy-to-Use, Numerical Scale for Assessing the Severity of Orbital Fractures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection Process
2.2. Included Classification
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Information
3.2. Main Causes of Fractures
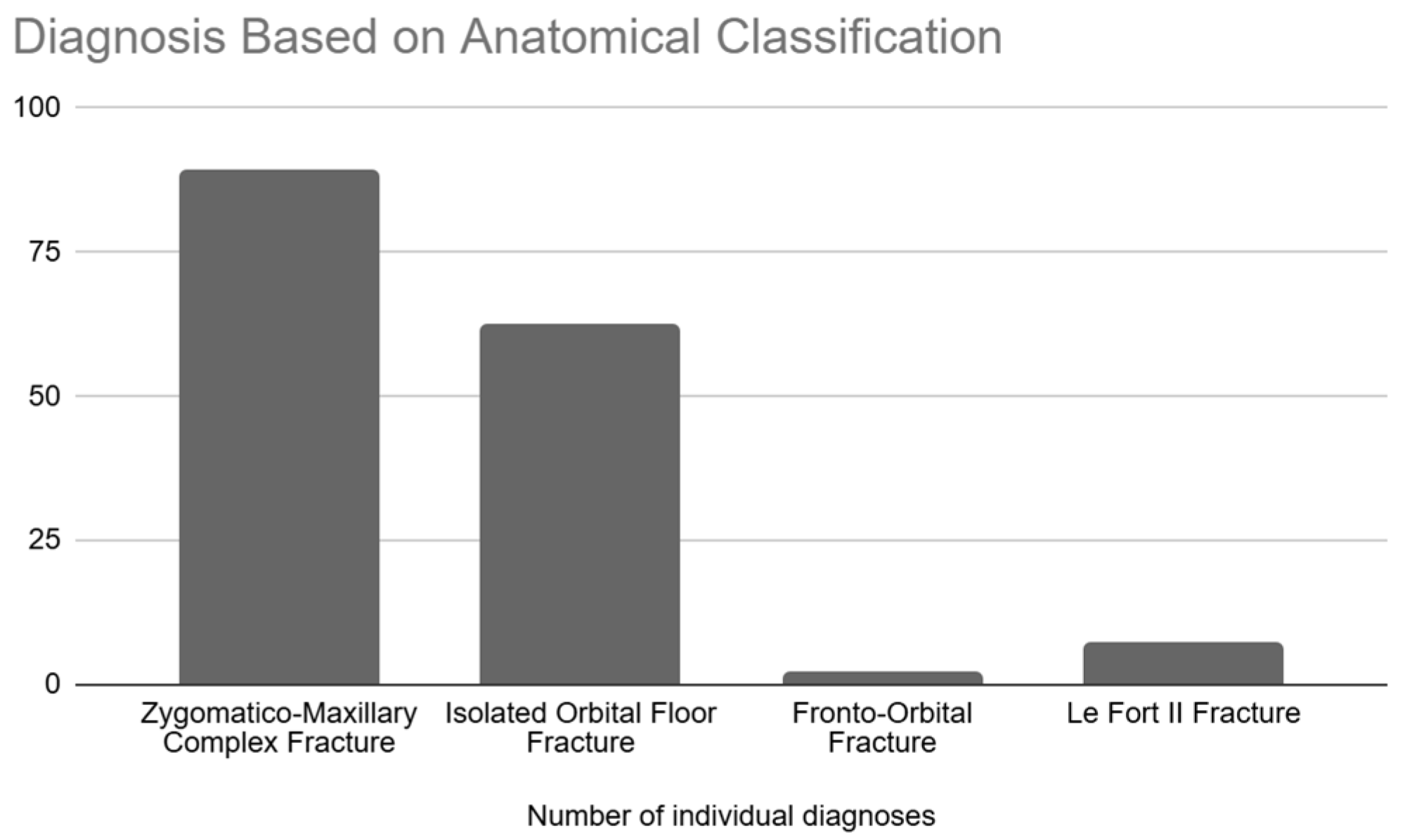
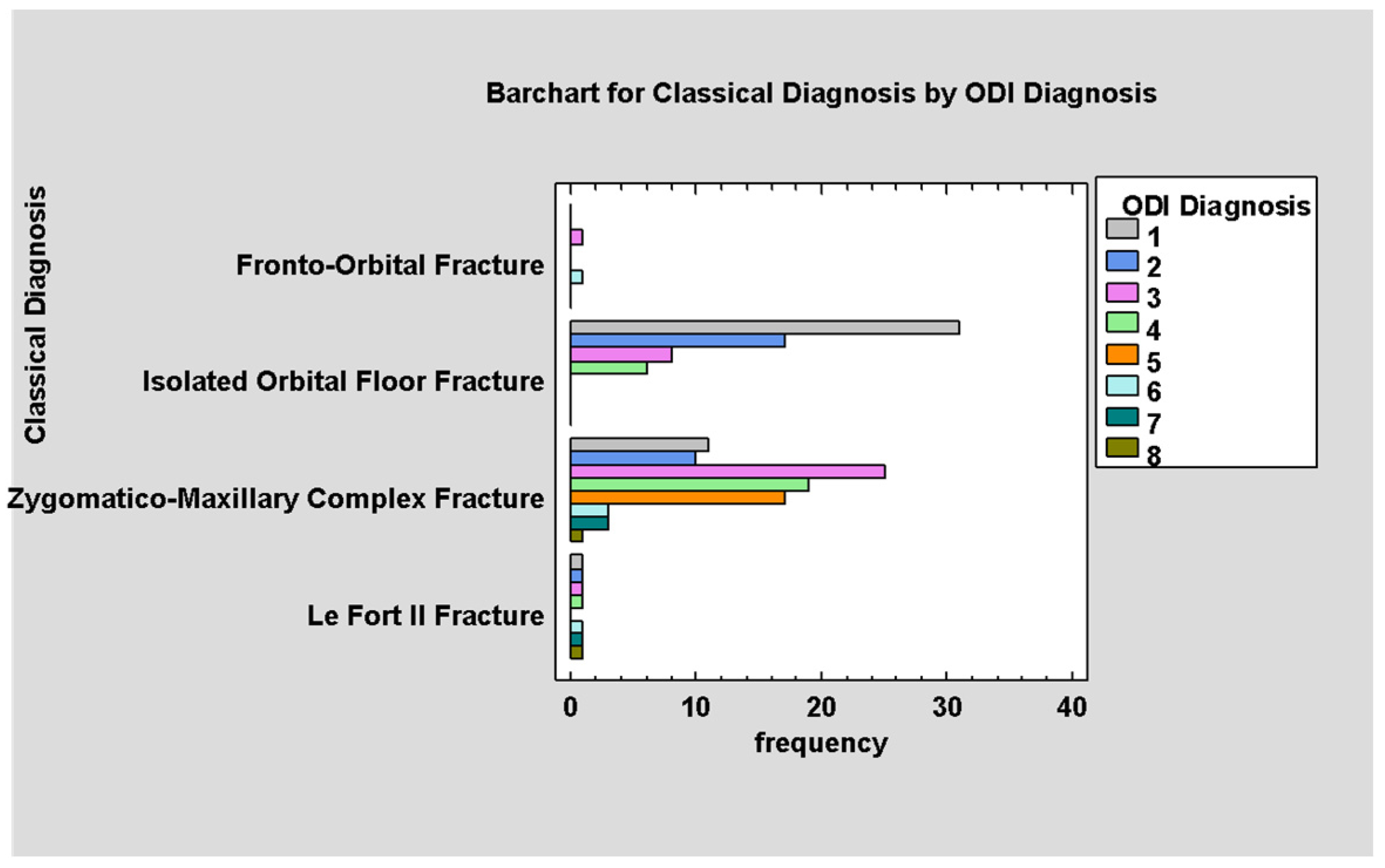
3.3. Types of Fractures/Diagnosis
3.4. Intoxicants
3.5. Post-Traumatic Complications
3.5.1. Periorbital Hematoma
3.5.2. Maxillary Sinus Lesions
3.5.3. Eye Globe Position
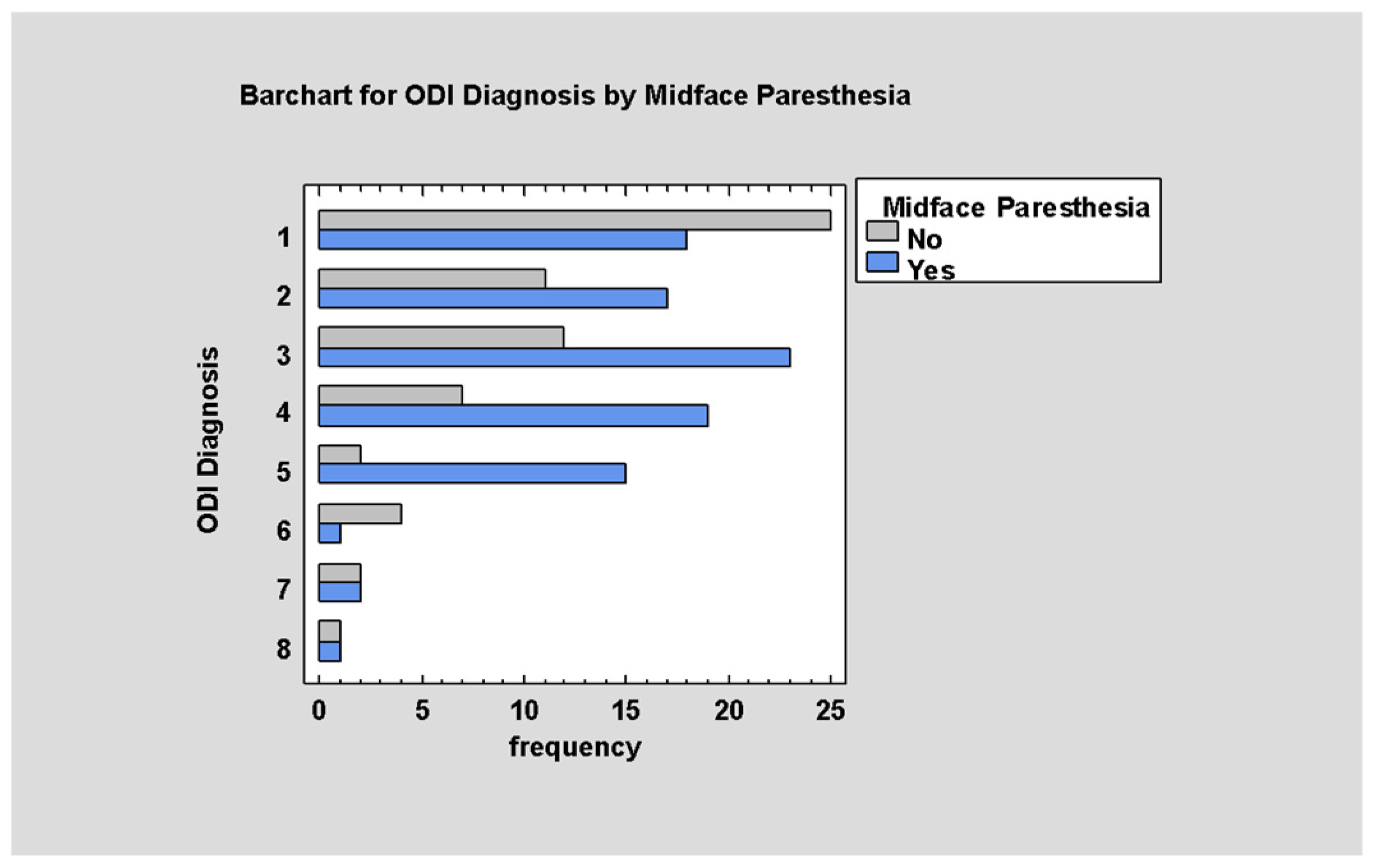
3.5.4. Trigeminal Nerve Disturbances
3.5.5. Teeth Injury
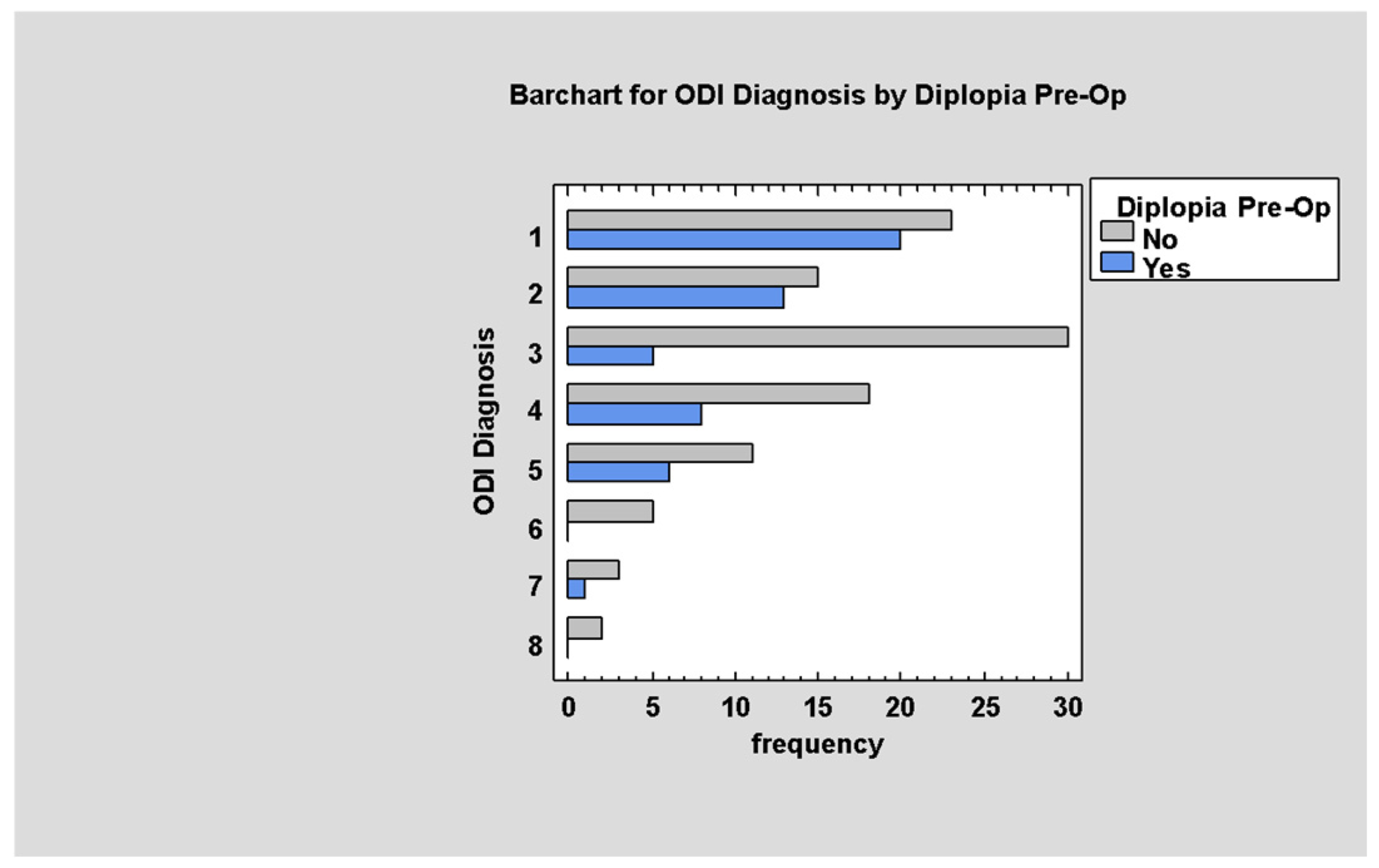
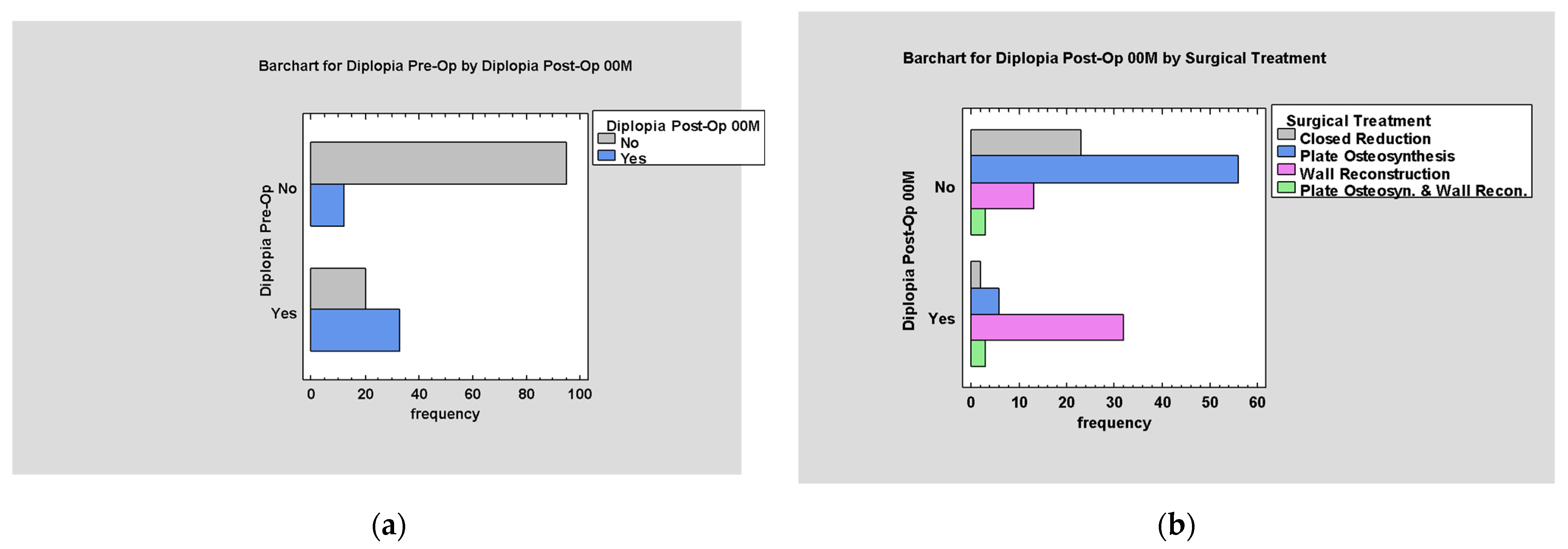
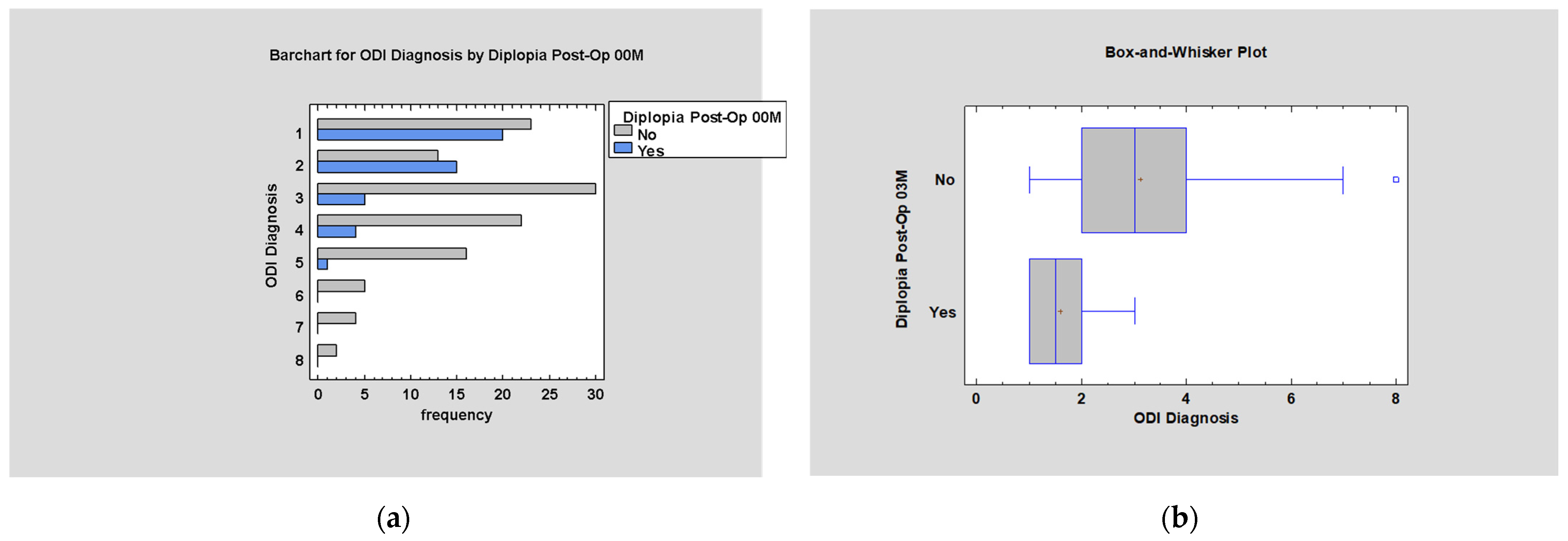
3.5.6. Post-Traumatic Diplopia
Post-Traumatic Diplopia According to the ODI Scale
Post-Traumatic Diplopia According to Anatomical Classification
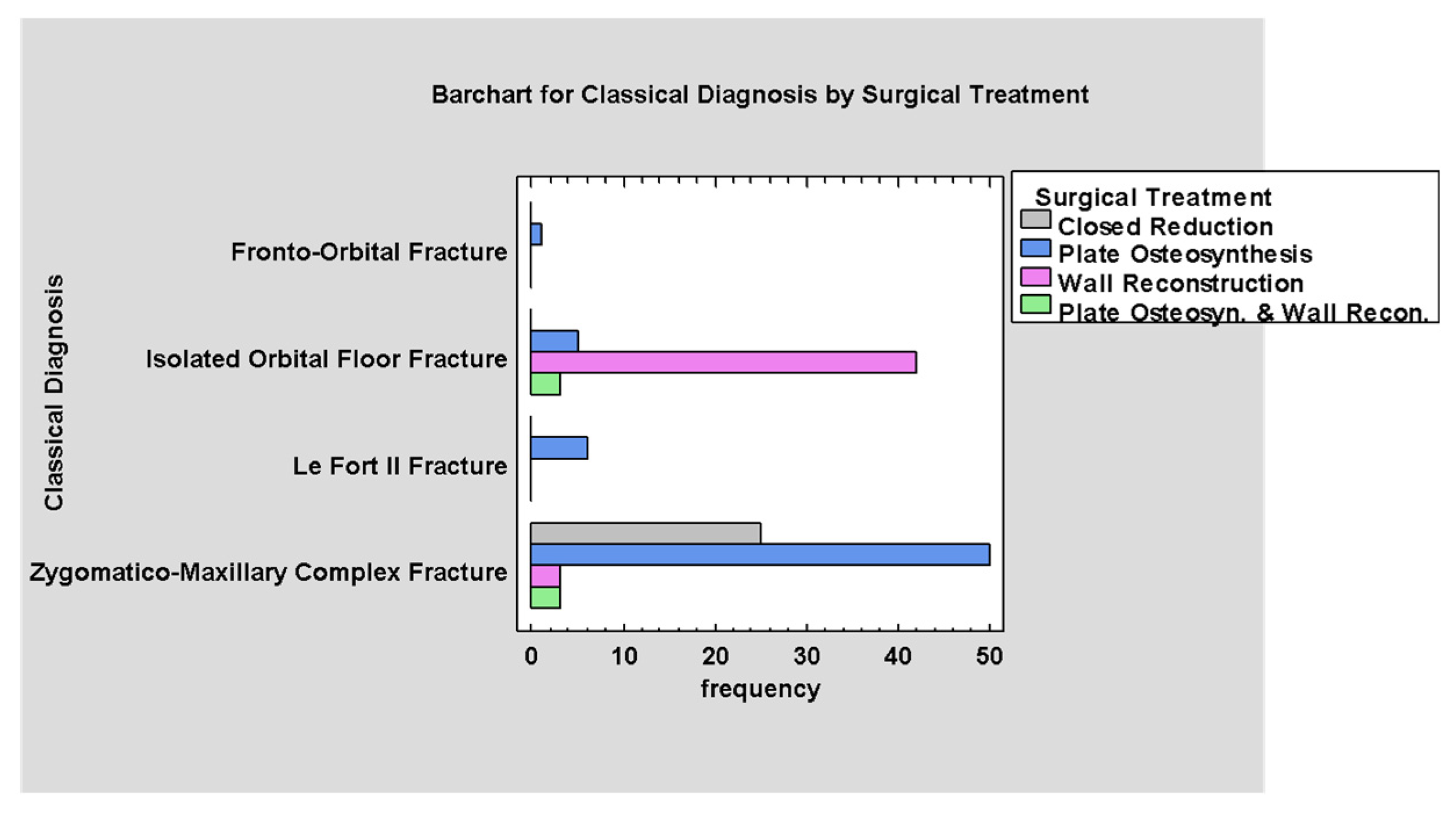
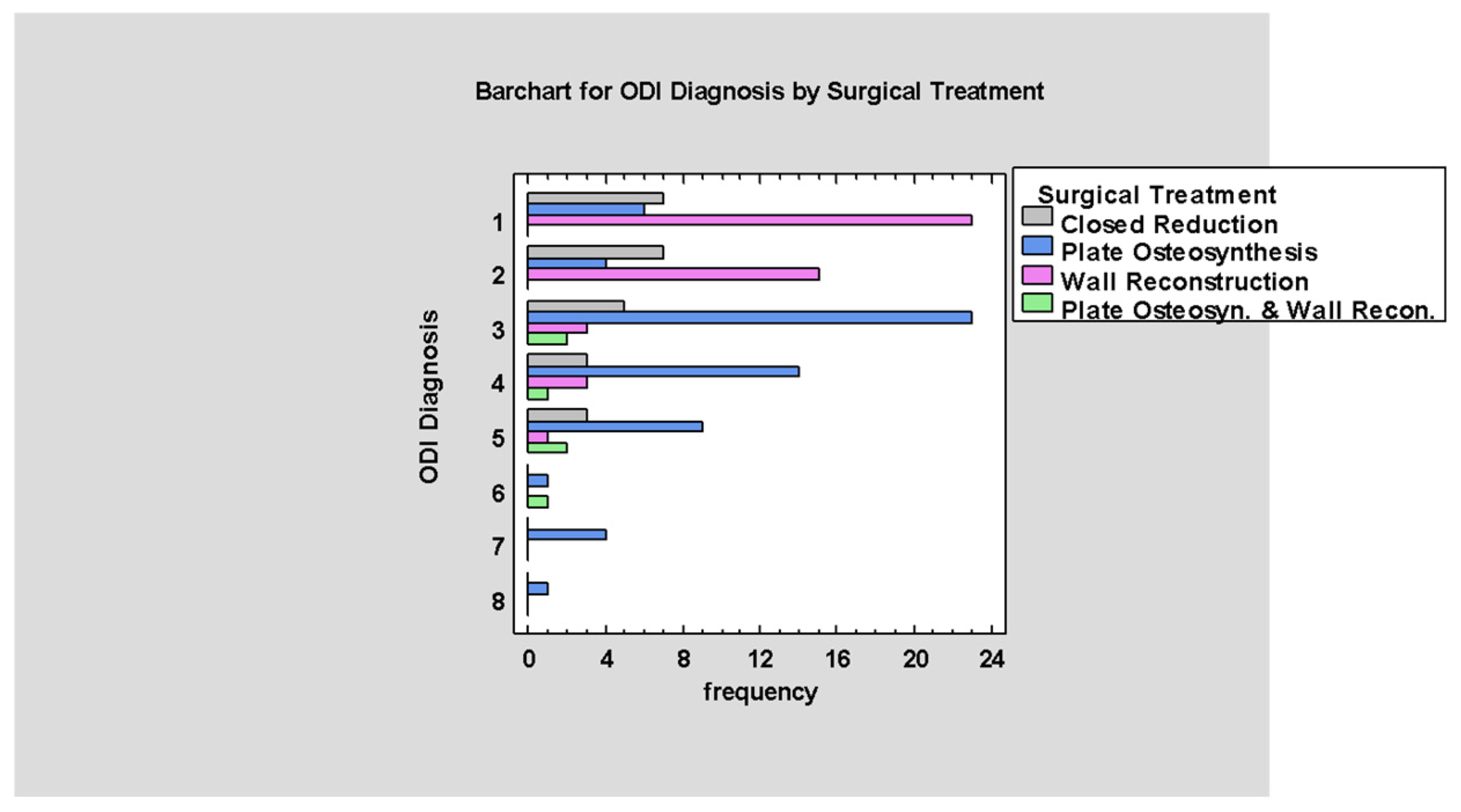
3.6. Treatment
4. Discussion
4.1. The Extent of Orbital Trauma and Its Association with the ODI Classification
4.2. Post-Traumatic Complications and Their Occurrence According to ODI Classification
4.2.1. Post-Traumatic Diplopia
4.2.2. Connection with the Maxillary Sinus
4.2.3. Trigeminal Nerve Disturbances
4.2.4. Dental Trauma
4.2.5. Periorbital Hematoma
4.2.6. ODI Scale Values Concerning Post-Traumatic Complications
4.3. Surgical Treatment According to ODI Classification
4.4. Post-Operative Diplopia
4.5. ODI Classification in Comparison to Other Widely Used Scales for Evaluating Midface Fractures
4.5.1. Description of Commonly Used Scales
4.5.2. Current Limitations of Commonly Used Classification Systems
4.5.3. ODI Classification and Its Application to Other Systems
4.6. Limitations
4.6.1. Study Limitations
4.6.2. The ODI Scale Limitations
4.7. The Clinical Application of the ODI Classification System
4.7.1. Selection of Treatment Method Based on ODI Classification Results
4.7.2. Broad Implementation of the ODI Classification Across Medical Disciplines
4.7.3. Improvement in Patient Care
4.7.4. Combination of ODI and Artificial Intelligence (AI)—The Future of Diagnosis of Orbital Fractures?
4.8. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ODI | Orbital Destruction Intensity |
| ZMCO | Zygomaticomaxillary complex |
| NOE | Naso-orbito-ethmoid |
| ZCON | Złamanie czaszkowooczodołowonosowe (cranio-orbito-nasal fracture) |
| ZIDO | Złamanie izolowane dna oczodołu (isolated orbital floor fracture) |
| ZJSO | Złamanie jarzmowoszczękowooczodołowe (zygomaticomaxillo-orbital fracture) |
| ZJO | Złamanie jarzmowooczodołowe (zygomatico-orbital fracture) |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| WL | Window level |
| WW | Window width |
| W | Walls |
| M | Margins |
References
- Malla, A.; Hassan, B.; Er, S.; Liang, F.; Ptak, T.; Manson, P.N.; Grant, M.P. Traumatic Brain Injury and Its Association with Orbital Fracture Characteristics and Repair. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettschen, D.; Tsichlaki, D.; Chatzimichail, E.; Klukowska-Rötzler, J.; Müller, M.; Sauter, T.C.; Exadaktylos, A.K.; Ziaka, M.; Doulberis, M.; Burkhard, J.-P. Epidemiology of Maxillofacial Trauma in Elderly Patients Receiving Oral Anticoagulant or Antithrombotic Medication; a Swiss Retrospective Study. BMC Emerg. Med. 2024, 24, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colangeli, W.; Ferragina, F.; Kallaverja, E.; Celano, C.; Cristofaro, M.G. Orbital Fractures Treated in a University Hospital of Southern Italy: Epidemiology, Outcomes and Prognostic Factors Resulting from 538 Retrospectively Analyzed Cases. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 28, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seen, S.; Young, S.; Lang, S.S.; Lim, T.-C.; Amrith, S.; Sundar, G. Orbital Implants in Orbital Fracture Reconstruction: A Ten-Year Series. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma Reconstr. 2020, 14, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, D.; Al-Mulki, K.; Henriquez, O.A.; Cheng, A.; Roser, S.; Abramowicz, S. Review of Orbital Fractures in an Urban Level I Trauma Center. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma Reconstr. 2020, 13, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E. Orbital Trauma. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 24, 629–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwulebe, S.; Hogrefe, C. The Diagnosis and Management of Facial Bone Fractures. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 37, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starck, E.; Lusila, N.; Suojanen, J.; Kormi, E. Are Age and Trauma Mechanism Associated with Volume Change in the Fractures of the Bony Orbit? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, P.S.; Kumar, R.; Saini, M.; Gupta, T.; Gaba, S.; Sharma, R.K. Three-Dimensional Computer Navigation in the Reconstruction of Complex Unilateral Orbital Fractures: Evaluation and Review of Applications. Arch. Craniofacial Surg. 2024, 25, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.K.; Vivek, N.; Yang, S.F.; Stephan, S.J.; Patel, P.N. Time-to-Operation Delays and in-Hospital Complications in Operative Facial Trauma: A National Analysis. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2023, 45, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakiewicz, M.; Elgalal, M.; Piotr, L.; Broniarczyk-Loba, A.; Stefanczyk, L. Treatment with Individual Orbital Wall Implants in Humans—1-Year Ophthalmologic Evaluation. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samolczyk-Wanyura, D. Upper Facial Fractures. An Attempt of Classification. Ph.D. Thesis, Warsaw Medical University, Warszawa, Poland, 1989. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Varma, D.; Brown, P.; Clements, W. Importance of the Mechanism of Injury in Trauma Radiology Decision-Making. Korean J. Radiol. 2023, 24, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Flores, I.; Santos-Armentia, E.; Fernández-Sanromán, J.; Costas-López, A.; Fernández-Ferro, M. Diplopía secundaria a fractura orbitaria en adultos. Arch. Soc. Espanola Oftalmol. 2018, 93, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Tsay, P.-K.; Leow, A.-M.; Pan, C.-H.; Chen, C.-T. Surgical Timing and Fracture Type on the Outcome of Diplopia After Orbital Fracture Repair. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76 (Suppl. 1), S91–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mujaini, A.; Wali, U.; Alkhabori, M. Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: Indications and Complications in the Ophthalmic Field. Oman Med. J. 2009, 24, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, S.S.; Hemal, K.; Runyan, C.M. Outcomes in Orbital Floor Trauma: A Comparison of Isolated and Zygomaticomaxillary-Associated Fractures. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2021, 32, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, R.M.; Taparello, C.; Tres, R.; Sawazaki, R. Orbital Blowout Fracture with Globe Displacement into the Maxillary Sinus: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, e1–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, A.; Rizen, V.; Nikolic, V.; Banovic, B. The role of orbital wall morphological properties and their supporting structures in the etiology of “blow-out” fractures. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 1989, 11, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, E.; Saadat, L.V.; Spitz, J.A.; Bryar, P.J.; Chambers, C.B. Etiology of orbital fractures at a level I trauma center in a large metropolitan city. Taiwan J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 6, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.; Bahk, S.; Eo, S. Anatomical Study of the Infraorbital Nerve and Surrounding Structures for the Surgery of Orbital Floor Fractures. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2017, 28, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstine, M.A. Clinical recommendations for repair of isolated orbital floor fractures. Ophthalmology 2002, 109, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, S.M.; Park, C.H. The Effectiveness of 1-Point Fixation for Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fractures. Arch. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2012, 138, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Chu, Y.; Xu, X. Minimally Invasive Treatment with Zygomatic Complex Fracture Reduction by Percutaneous Bone Hook Traction. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 1514–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poxleitner, P.; Steybe, D.; Bublitz, B.; Schlager, S.; Fuessinger, M.A.; Voss, P.J.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Cornelius, C.-P.; Metzger, M. Analysis of the accuracy of a novel preformed osteosynthesis plate for the reduction and fixation of zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures. J. Cranio-Maxillofacial Surg. 2019, 47, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magarakis, M.; Mundinger, G.S.; Kelamis, J.A.; Dorafshar, A.H.; Bojovic, B.; Rodriguez, E.D. Ocular Injury, Visual Impairment, and Blindness Associated with Facial Fractures. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkin, A.F.; Woodson, G.E.; Miller, R.H. Visual Loss due to Orbital Fracture: The Role of Early Reduction. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1987, 113, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loba, P.; Kozakiewicz, M.; Nowakowska, O.; Omulecki, W.; Broniarczyk-Loba, A. Management of persistent diplopia after surgical repair of orbital fractures. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2012, 16, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodankar, N.; Dhupar, V.; Vijay, V. Classifications and Theories of Orbital Fractures: A Review of Literature. Med. Res. Chron. 2023, 10, 248–260. [Google Scholar]
- Kunz, C.; Audigé, L.; Cornelius, C.-P.; Buitrago-Téllez, C.H.; Rudderman, R.; Prein, J. The Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System: Orbital Fractures—Level 3 Tutorial. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma Reconstr. 2014, 7 (Suppl. 1), 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, C.; Audigé, L.; Cornelius, C.-P.; Buitrago-Téllez, C.H.; Frodel, J.; Rudderman, R.; Prein, J. The Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System: Midface Fractures—Level 2 Tutorial. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma Reconstr. 2014, 7 (Suppl. 1), 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, M.; Leadrach, K.; Chen, J.; Chowdhury, K.; Vuillemin, T.; Sutter, F.; Raveh, J.; Eppley, B.L. Classification and Treatment of Zygomatic Fractures: A Review of 1025 Cases. J. Craniofacial Surg. 1993, 4, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusiak, K.; Arkuszewski, P. Characteristics and Epidemiology of Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fractures. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2010, 21, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.S.; Rudolph, M.A.; Hemal, K.; Steele, T.; Runyan, C.M. A Novel Classification Method of Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fractures by Suture Comminution to Better Predict Clinical Outcomes. FACE 2020, 1, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaquiéry, C.; Aeppli, C.; Cornelius, P.; Palmowsky, A.; Kunz, C.; Hammer, B. Reconstruction of orbital wall defects: Critical review of 72 patients. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 36, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohman, M.H.; Patel, B.C.; Waseem, M. Le Fort Fractures. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.-T.; Mittal, R.; Kang, G.; Chen, C.-T. Le Fort Fractures with Maxillary Immobility: Classification and the Moment Concept to Rationalize Optimal Surgical Treatment. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2021, 86, S58–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardò, F.P.; Frati, P.; Santurro, A.; Zaami, S.; Fineschi, V. Errors and Malpractice Lawsuits in Radiology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Radiol. Med. 2015, 120, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Holmes, S.B.; Coulthard, P. A Review on Artificial Intelligence for the Diagnosis of Fractures in Facial Trauma Imaging. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1278529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, B.; Vinayachandran, D.; Ganesh, C.; Shanthi, M.; Krithika, C.L. Bibliometric Analysis of the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Detecting Maxillofacial Fractures. Cureus 2024, 16, e75630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
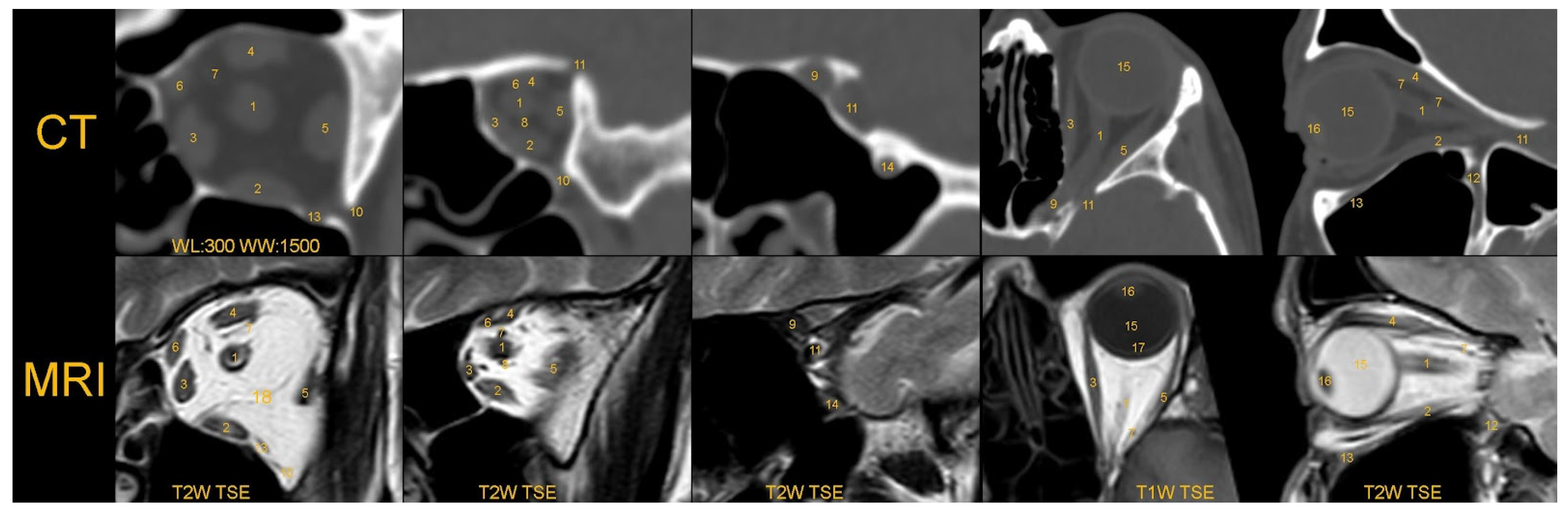
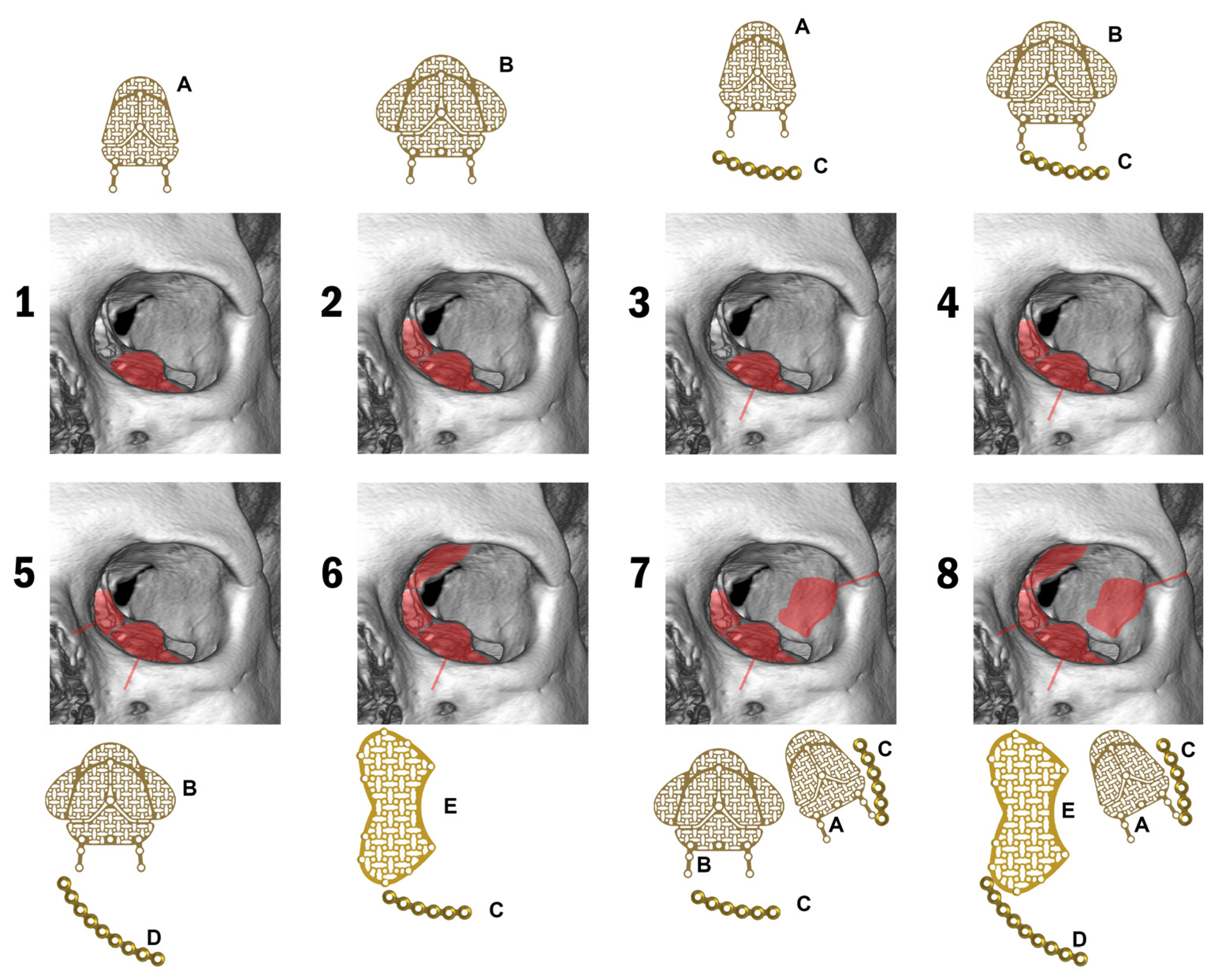





| Initial Classification | Converted Classification |
|---|---|
| ZJSO | Zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture (ZMCO) |
| ZIDO | Isolated orbital floor fracture |
| ZCO/ZCON | Fronto-orbital fracture |
| Le Fort | Le Fort (no change) |
| ODI Scale | Description | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Destruction of the floor, involving one wall | 1W |
| 2 | Destruction of the floor plus one wall (medial or lateral) | 2W |
| 3 | Destruction of the floor plus one wall and one orbital margin | 1W + 1M |
| 4 | Destruction of the floor plus two walls and one orbital margin | 2W + 1M |
| 5 | Destruction of the floor plus one wall and two orbital margins | 2W + 2M |
| 6 | Destruction of the floor plus two walls and one orbital margin | 3W + 1M |
| 7 | Destruction of the floor plus one or two walls and two orbital margins | 3W + 2M |
| 8 | Destruction of the floor plus two or three walls and more than one orbital margin | 3–4W + 2–4M |
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Complete patient history available at the Maxillofacial Surgery Department | Incomplete medical records |
| ICD-10 codes—S02.3 and S02.4 | No orbital fracture |
| Available radiological examination or its full description | |
| Patients treated primarily at the Maxillofacial Surgery Department |
| Variable | Age | ODI Diagnosis | Timing to Register | Hospitalization Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 40.0 ± 17.5 | 2.9 ± 1.7 | 0.9 ± 2.5 | 3.3 ± 1.2 |
| Median | 37.5 | 3.0 | 0 | 3.0 |
| Minimum | 13.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 1.0 |
| Maximum | 90.0 | 8.0 | 19.0 | 8.0 |
| Range | 77.0 | 7.0 | 19.0 | 7.0 |
| Type of Treatment | Number of Patients | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical | 138 | 86.3 |
| Conservative | 22 | 13.8 |
| Type of Treatment | Number of Patients | Percent (%) of Surgically Treated Patients |
|---|---|---|
| Plate Osteosynthesis | 62 | 44.9 |
| Wall Reconstruction | 45 | 32.6 |
| Closed Reduction | 25 | 18.1 |
| Plate Osteosyn. and Wall Recon. | 6 | 4.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galant, K.; Kozakiewicz, M.; Ciosek, A.; Bogusiak, K.; Gabryelczak, I. The Orbital Destruction Intensity Classification—An Easy-to-Use, Numerical Scale for Assessing the Severity of Orbital Fractures. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3826. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113826
Galant K, Kozakiewicz M, Ciosek A, Bogusiak K, Gabryelczak I. The Orbital Destruction Intensity Classification—An Easy-to-Use, Numerical Scale for Assessing the Severity of Orbital Fractures. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3826. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113826
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalant, Kacper, Marcin Kozakiewicz, Agata Ciosek, Katarzyna Bogusiak, and Izabela Gabryelczak. 2025. "The Orbital Destruction Intensity Classification—An Easy-to-Use, Numerical Scale for Assessing the Severity of Orbital Fractures" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3826. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113826
APA StyleGalant, K., Kozakiewicz, M., Ciosek, A., Bogusiak, K., & Gabryelczak, I. (2025). The Orbital Destruction Intensity Classification—An Easy-to-Use, Numerical Scale for Assessing the Severity of Orbital Fractures. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3826. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113826






