TMEM14A Gene Affects Hippocampal Sclerosis in Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Study Approval
2.3. Genotyping and Quality Control of SNPs
2.4. Genome-Wide Association Study
2.5. Allele Frequency in Normal Population
2.6. Genetic Correlation Analysis
2.7. Phenome-Wide Association Study
2.8. Quantitative Trait Locus Analyses
2.9. TMEM14A Expression Across Bulk Tissues
2.10. Transcriptomic Analysis in MTLE with HS
2.11. Transcriptomic Analysis in an Epilepsy Mouse Model
2.12. Prediction of Human and Mouse Phenotypes
2.13. Data Availability
3. Results
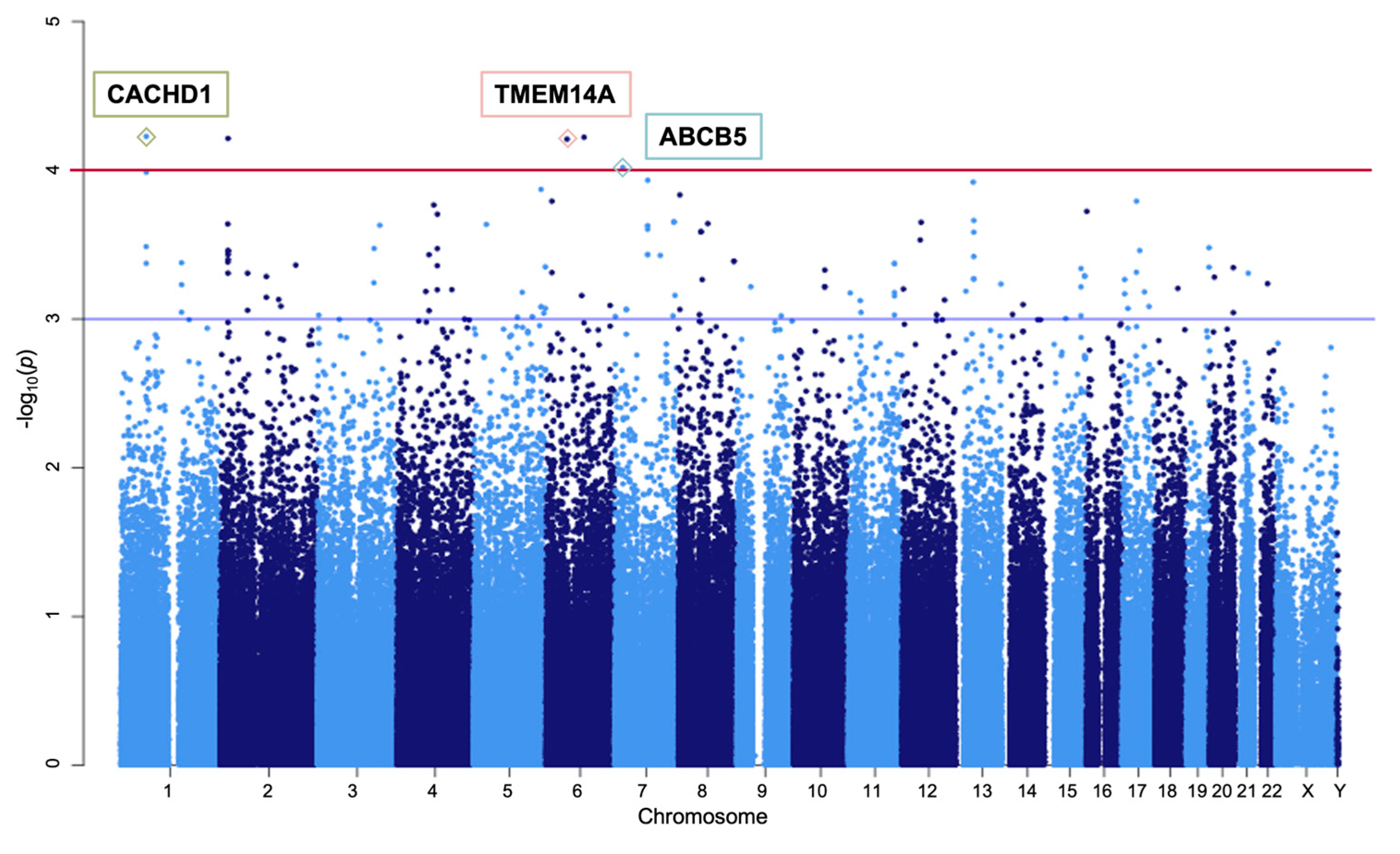
3.1. Genome-Wide Association Study
3.2. Phenome-Wide Association Study
3.3. Comparative Genetic Architecture Across Ancestries and Subtypes
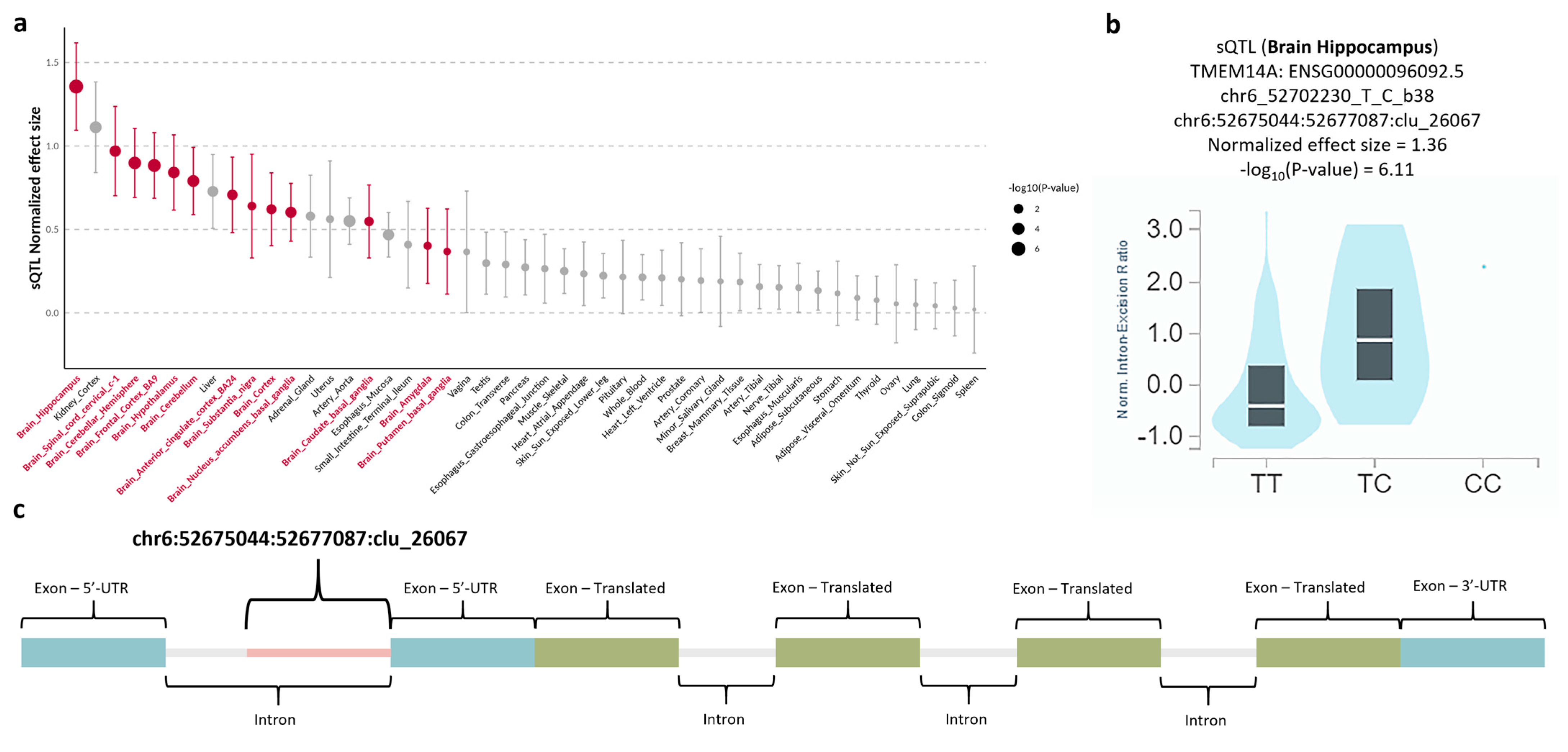
3.4. Quantitative Trait Locus Analysis for rs6924849
3.5. Transcriptomic Investigation for TMEM14A
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HS | hippocampal sclerosis |
| SNPs | single-nucleotide polymorphisms |
| MTLE | mesial temporal lobe epilepsy |
| sQTL | splicing quantitative trait loci |
| eQTL | expression quantitative trait loci |
| GTEx | Genotype-Tissue Expression |
| NES | normalized effect size |
| LD | linkage disequilibrium |
| EAS | East Asian |
| EUR | European |
References
- Helbig, I.; Scheffer, I.E.; Mulley, J.C.; Berkovic, S.F. Navigating the channels and beyond: Unravelling the genetics of the epilepsies. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International League Against Epilepsy Consortium on Complex Epilepsies. Genetic determinants of common epilepsies: A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Khalil, B.; Auce, P.; Avbersek, A.; Bahlo, M.; Balding, D.J.; Bast, T.; Baum, L.; Becker, A.J.; Becker, F.; Berghuis, B.; et al. Genome-wide mega-analysis identifies 16 loci and highlights diverse biological mechanisms in the common epilepsies. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevelink, R.; Campbell, C.; Chen, S.; Abou-Khalil, B.; Adesoji, O.M.; Afawi, Z.; Amadori, E.; Anderson, A.; Anderson, J.; Andrade, D.M.; et al. GWAS meta-analysis of over 29,000 people with epilepsy identifies 26 risk loci and subtype-specific genetic architecture. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümcke, I.; Thom, M.; Aronica, E.; Armstrong, D.D.; Bartolomei, F.; Bernasconi, A.; Bernasconi, N.; Bien, C.G.; Cendes, F.; Coras, R.; et al. International consensus classification of hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy: A Task Force report from the ILAE Commission on Diagnostic Methods. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittau, F.; Bisulli, F.; Mai, R.; Fares, J.E.; Vignatelli, L.; Labate, A.; Naldi, I.; Avoni, P.; Parmeggiani, A.; Santucci, M.; et al. Prognostic factors in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009, 50 (Suppl. 1), 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperaviciute, D.; Catarino, C.B.; Matarin, M.; Leu, C.; Novy, J.; Tostevin, A.; Leal, B.; Hessel, E.V.; Hallmann, K.; Hildebrand, M.S.; et al. Epilepsy, hippocampal sclerosis and febrile seizures linked by common genetic variation around SCN1A. Brain 2013, 136, 3140–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.R.; Kanai, M.; Kamatani, Y.; Okada, Y.; Neale, B.M.; Daly, M.J. Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. ILAE classification of the epilepsies: Position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.A.; Pettersson, F.H.; Clarke, G.M.; Cardon, L.R.; Morris, A.P.; Zondervan, K.T. Data quality control in genetic case-control association studies. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weale, M.E. Quality control for genome-wide association studies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 628, 341–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.J.; Park, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.-J. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifying a Novel Gene Related to a History of Febrile Convulsions in Patients with Focal Epilepsy. J. Clin. Neurol. 2025, 21, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, N.; Price, A.L.; Reich, D. Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Finucane, H.K.; Anttila, V.; Gusev, A.; Day, F.R.; Loh, P.-R.; Duncan, L.; Perry, J.R.B.; Patterson, N.; Robinson, E.B.; et al. An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongen, H.; Buil, A.; Brown, A.A.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Delaneau, O. Fast and efficient QTL mapper for thousands of molecular phenotypes. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.I.; Knowles, D.A.; Humphrey, J.; Barbeira, A.N.; Dickinson, S.P.; Im, H.K.; Pritchard, J.K. Annotation-free quantification of RNA splicing using LeafCutter. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.Q.; Zhan, S.K.; Song, J.J.; Deng, Y.L.; Wei, L.; Peng, H.; Jing, Z.; Sun, Z.F.; Che, Z.Q.; Liu, J. Altered immune pathways in patients of temporal lobe epilepsy with and without hippocampal sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, A.B.; Banerjee, J.; Srivastava, A.; Tripathi, M.; Sarkar, C.; Kakkar, A.; Jain, M.; Chandra, P.S. RNA-seq analysis of hippocampal tissues reveals novel candidate genes for drug refractory epilepsy in patients with MTLE-HS. Genomics 2016, 107, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, L.; Romagnolo, A.; Luinenburg, M.J.; Anink, J.J.; Godard, P.; Rajman, M.; van Eyll, J.; Mühlebner, A.; Skelton, A.; Mills, J.D.; et al. Identification of gene regulatory networks affected across drug-resistant epilepsies. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, N.G.; Wang, Y.; Hulette, C.M.; Halvorsen, M.; Cronin, K.D.; Walley, N.M.; Haglund, M.M.; Radtke, R.A.; Skene, J.H.; Sinha, S.R.; et al. Differential gene expression in dentate granule cells in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with and without hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, M.F.; Sprissler, R.; Bina, R.W.; Lau, B.; Johnstone, L.; Walter, C.M.; Labiner, D.M.; Weinand, M.E. Altered expression of signaling pathways regulating neuronal excitability in hippocampal tissue of temporal lobe epilepsy patients with low and high seizure frequency. Epilepsy Res. 2019, 155, 106145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjær, C.; Barzaghi, G.; Bak, L.K.; Goetze, J.P.; Yde, C.W.; Woldbye, D.; Pinborg, L.H.; Jensen, L.J. Transcriptome analysis in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 2019, 142, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Brureau, M.; Milior, G.; Royer, J.; Chali, F.; Le Duigou, C.; Savary, E.; Blugeon, C.; Jourdren, L.; Akbar, D.; Dupont, S.; et al. Microglial phenotypes in the human epileptic temporal lobe. Brain 2018, 141, 3343–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, G.H.; Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Pimanda, J.E.; Zanini, F. Analysing high-throughput sequencing data in Python with HTSeq 2.0. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2943–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Parmigiani, G.; Johnson, W.E. ComBat-seq: Batch effect adjustment for RNA-seq count data. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2020, 2, lqaa078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E. GeoTcgaData: Processing Various Types of Data on GEO and TCGA. R Package Version 2.8.0. 2025. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages/GeoTcgaData (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Popova, E.Y.; Kawasawa, Y.I.; Leung, M.; Barnstable, C.J. Temporal changes in mouse hippocampus transcriptome after pilocarpine-induced seizures. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1384805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, A.; Torre, D.; Keenan, A.B.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lee, H.J.; Wang, L.; Silverstein, M.C.; Ma’ayan, A. Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaue, S.; Kanai, M.; Tanigawa, Y.; Karjalainen, J.; Kurki, M.; Koshiba, S.; Narita, A.; Konuma, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Akiyama, M.; et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Baum, L.W.; Sham, P.C.; Wong, V.; Ng, P.W.; Lui, C.H.; Sin, N.C.; Tsoi, T.H.; Tang, C.S.; Kwan, J.S.; et al. Two-stage genome-wide association study identifies variants in CAMSAP1L1 as susceptibility loci for epilepsy in Chinese. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Koike, Y.; Ashikawa, K.; Otomo, N.; Takahashi, A.; Aoi, T.; Kamatani, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Kubo, M.; Kamatani, Y.; et al. Genome-wide association study of epilepsy in a Japanese population identified an associated region at chromosome 12q24. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, I.S.; Jin, H.; Kang, E.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, K.C.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, W.S.; Seo, H.G. TMEM14A inhibits N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced apoptosis through the stabilization of mitochondrial membrane potential. Cancer Lett. 2011, 309, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| HS Group (N = 52) | Non-HS Group (N = 105) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 36.5 ± 9.9 | 35.4 ± 10.7 | 0.496 |
| Sex, female percentage | 51.9 | 45.7 | 0.573 |
| Etiology, n (%) | - | - | <0.001 |
| Symptomatic | 52 (100.0) | 45 (42.9) | - |
| Cryptogenic | 0 (0.0) | 60 (57.1) | - |
| Seizure type, n (%) | - | - | - |
| Focal seizure with awareness | 1 (1.9) | 44 (41.9) | <0.001 |
| Focal seizure with impaired awareness | 52 (100.0) | 76 (72.4) | <0.001 |
| Focal to bilateral tonic–clonic | 6 (11.5) | 44 (41.9) | <0.001 |
| Epileptogenic zone, n (%) | |||
| Frontal | 0 (0.0) | 30 (28.6) | - |
| Temporal | 52 (100.0) | 37 (35.2) | - |
| Parietal | 0 (0.0) | 8 (7.6) | - |
| Occipital | 0 (0.0) | 6 (5.7) | - |
| Unknown | 0 (0.0) | 24 (22.9) | - |
| SNP | Chr | Position GRCh37 | Position GRCh38 | Nearest Gene | Region | MAF | Alleles (Major/ Minor) | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Control | Korea | Japan | Europe | |||||||||
| rs1436751 | 1 | 65064340 | 64598657 | CACHD1 | intron | 0.44 | 0.2048 | 0.2611 | 0.1996 | 0.2684 | A/G | 3.194 (1.812, 5.63) | 0.000059 |
| rs452930 | 6 | 94922837 | 94213119 | 0.5577 | 0.3317 | 0.4273 | 0.4113 | 0.3191 | C/T | 3.735 (1.962, 7.109) | 0.000059 | ||
| rs11696024 | 2 | 19812104 | 19612343 | 0.3942 | 0.1810 | 0.2867 | 0.2784 | 0.8340 | G/A | 3.473 (1.889, 6.384) | 0.000061 | ||
| rs6924849 | 6 | 52567028 | 52702230 | TMEM14A | downstream | 0.4423 | 0.1857 | 0.1938 | 0.1923 | 0.0467 | T/C | 2.685 (1.656, 4.353) | 0.000061 |
| rs17219864 | 7 | 20773567 | 20733944 | ABCB5 | intron | 0.3558 | 0.1619 | 0.1983 | 0.1768 | 0.3529 | G/T | 3.549 (1.878, 6.708) | 0.000096 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Jeong, K.H.; Ha, W.-S.; Kim, K.M.; Chu, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, W.-J. TMEM14A Gene Affects Hippocampal Sclerosis in Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113810
Kim J, Cho S, Jeong KH, Ha W-S, Kim KM, Chu MK, Lee JH, Kim S, Kim W-J. TMEM14A Gene Affects Hippocampal Sclerosis in Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113810
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Joonho, Soomi Cho, Kyoung Hoon Jeong, Woo-Seok Ha, Kyung Min Kim, Min Kyung Chu, Ji Hyun Lee, Sangwoo Kim, and Won-Joo Kim. 2025. "TMEM14A Gene Affects Hippocampal Sclerosis in Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113810
APA StyleKim, J., Cho, S., Jeong, K. H., Ha, W.-S., Kim, K. M., Chu, M. K., Lee, J. H., Kim, S., & Kim, W.-J. (2025). TMEM14A Gene Affects Hippocampal Sclerosis in Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113810






