Predicting Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Patients with HFpEF: Development of a Simple Clinical Risk Score
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Data Collection
2.3. Functional and Cognitive Assessment
2.4. Ethics Statement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Risk Model Development and Performance Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Predictors of Cognitive Impairment
3.3. Cognitive Risk Score Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahim, B.; Kapelios, C.J.; Savarese, G.; Lund, L.H. Global Public Health Burden of Heart Failure: An Updated Review. Card. Fail. Rev. 2023, 9, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapelios, C.J.; Shahim, B.; Lund, L.H.; Savarese, G. Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics and Cause-Specific Outcomes in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Card. Fail. Rev. 2023, 9, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chioncel, O.; Lainscak, M.; Seferovic, P.M.; Anker, S.D.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Harjola, V.; Parissis, J.; Laroche, C.; Piepoli, M.F.; Fonseca, C.; et al. Epidemiology and One-Year Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Preserved, Mid-Range and Reduced Ejection Fraction: An Analysis of the ESC Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 1574–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Sharma, K.; Shah, S.J.; Ho, J.E. Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: JACC Scientific Statement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 1810–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, G.V.; Aruna, V.; Krishna, B.H. Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Acad. Med. Pharm. 2024, 6, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.A.; Moffitt, P.; Perez-Moreno, A.C.; Walters, M.R.; Broomfield, N.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Quinn, T.J. Cognitive Impairment and Heart Failure: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Card. Fail. 2017, 23, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, F.Q.; Kong, W.K.F.; Wong, R.C.C.; Chong, Y.F.; Chew, N.W.S.; Yeo, T.-C.; Sharma, V.K.; Poh, K.K.; Sia, C.-H. Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure: A Review. Biology 2022, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Didomenico, R.J.; Pressler, S.J.; Ibeh, C.; White-Williams, C.; Allen, L.A.; Gorodeski, E.Z.; Albert, N.; Fudim, M.; Lekavich, C.; et al. Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure: A Heart Failure Society of America Scientific Statement. J. Card. Fail. 2024, 30, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nieuwkerk, A.C.; Delewi, R.; Wolters, F.J.; Muller, M.; Daemen, M.; Biessels, G.J. Heart-Brain Connection Consortium. Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cardiac Disease: Implications for Clinical Practice. Stroke 2023, 54, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, E.; Sapra, A.; Bhandari, P.; Albers, C.E.; Ajmeri, M.S. Cognitive Assessment of Geriatric Patients in Primary Care Settings. Cureus 2020, 12, e10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehner, W.; Ural, D.; Haeusler, K.G.; Čelutkienė, J.; Bestetti, R.; Cavusoglu, Y.; Peña-Duque, M.A.; Glavas, D.; Iacoviello, M.; Laufs, U.; et al. Heart and Brain Interaction in Patients with Heart Failure: Overview and Proposal for a Taxonomy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, A.L.; Beiser, A.S.; Himali, J.J.; Seshadri, S.; O’donnell, C.J.; Manning, W.J.; Wolf, P.A.; Au, R.; Benjamin, E.J. Low cardiac index is associated with incident dementia and Alzheimer disease: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2015, 131, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göpfert, D.; Traub, J.; Sell, R.; Homola, G.A.; Vogt, M.; Pham, M.; Frantz, S.; Störk, S.; Stoll, G.; Frey, A. Profiles of Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Heart Failure—A Cluster Analytic Approach. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1126553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.H.; Pitt, B.; Metra, M. Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction as the Primary Heart Failure Phenotyping Parameter. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 1158–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, F.; Nakagawa, S.; Matsumoto, J.; Dohgu, S. Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction Amplifies the Development of Neuroinflammation: Understanding of Cellular Events in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells for Prevention and Treatment of BBB Dysfunction. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 661838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, J.; Sridhar, V.S.; Bouabdallaoui, N.; Tardif, J.C.; White, M. Inflammation in heart failure: Pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. Inflamm Res. 2024, 73, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, E.L.; McKnight, B.; Psaty, B.M.; Longstreth, W.; Sitlani, C.M.; Dublin, S.; Arnold, A.M.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Gottesman, R.F.; Heckbert, S.R. Atrial fibrillation and cognitive decline: A longitudinal cohort study. Neurology 2013, 81, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarvand, D.; Panthakey, J.; Heidari, A.; Hassan, A.; Ahmed, M.H. The Intersection between Frailty, Diabetes, and Hypertension: The Critical Role of Community Geriatricians and Pharmacists in Deprescribing. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, C.W.; Jessup, M.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Drazner, M.H.; Filipatos, G.S.; Fonarow, G.C.; Givertz, M.M.; Hollenberg, J.L.; et al. Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: JACC Scientific Expert Panel. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 776–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, A.M.; Sharrett, A.R.; Schneider, A.L.; Coresh, J.; Albert, M.; Couper, D.; Griswold, M.; Gottesman, R.F.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Windham, B.G.; et al. Diabetes in Midlife and Cognitive Change over 20 Years: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 161, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duinkerken, E.; Ryan, C.M. Diabetes Mellitus in the Young and the Old: Effects on Cognitive Functioning across the Life Span. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, K.M.P.; Dickson, V.V.P.; Fletcher, J.; Katz, S.D.; Chang, P.P.M.; Gottesman, R.F.; Witt, L.S.; Shah, A.M.; Melkus, G.E.D. Factors Associated with Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2022, 37, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandhi, A.; Khalid, U.; Garg, A. Cognition and Outcomes in Heart Failure. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Dewan, P.; Ferreira, J.P.; Cunningham, J.W.; Jhund, P.S.; Anand, I.S.; Chandra, A.; Chiang, L.M.; Clagget, B.; Desai, A.S.; et al. Clinical Correlates and Prognostic Impact of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction: Insights From PARAGON. Circulation 2024, 150, 1913–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, M.; Spinhoven, P.; Korrelboom, K.; Deen, M.; van der Meer, I.; Danner, U.N.; van der Schuur, S.; Schoorl, M.; Hoek, H.W. Effectiveness of Enhanced Cognitive Behavior Therapy for Eating Disorders: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2023 Focused Update of the 2021 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3627–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.; Rana, B.; Oxborough, D.; Steeds, R.; Monaghan, M.; Stout, M.; Pearce, K.; Harkness, A.; Ring, L.; Paton, M.; et al. A Practical Guideline for Performing a Comprehensive Transthoracic Echocardiogram in Adults: The British Society of Echocardiography Minimum Dataset. Echo Res. Pract. 2020, 7, G59–G93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, A.; Nyman, E.; Grönlund, C.; Wester, P.; Näslund, U.; Fhärm, E.; Norberg, M. Multi-View Carotid Ultrasound Is Stronger Associated with Cardiovascular Risk Factors than Presence of Plaque or Single Carotid Intima Media Thickness Measurements in Subclinical Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 39, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Wan, Y.; Barinas-Mitchell, E.; Fujiyoshi, A.; Cui, H.; Maimaiti, A.; Xu, R.; Li, J.; Suo, C.; Zaid, M. Varying Definitions of Carotid Intima–Media Thickness and Future Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e031217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spertus, J.A.; Jones, P.G. Development and Validation of a Short Version of the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2015, 8, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesavage, J.A.; Brink, T.L.; Rose, T.L.; Lum, O.; Huang, V.; Adey, M.; Leirer, V.O. Development and Validation of a Geriatric Depression Screening Scale: A Preliminary Report. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1982, 17, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crum, R.M.; Anthony, J.C.; Bassett, S.S.; Folstein, M.F. Population-Based Norms for the Mini-Mental State Examination by Age and Educational Level. JAMA 1993, 269, 2386–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rist, P.M.; Chalmers, J.; Arima, H.; Anderson, C.; Macmahon, S.; Woodward, M.; Kurth, T.; Tzourio, C. Baseline cognitive function, recurrent stroke, and risk of dementia in patients with stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 1790–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; Teo, K.; Gao, P.; Arima, H.; Dans, A.; Unger, T.; Commerford, P.; Dyal, L.; Schumacher, H.; ONTARGET and TRANSCEND Investigators; et al. Renin-angiotensin system blockade and cognitive function in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease: Analysis of data from the ONTARGET and TRANSCEND studies. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Beckett, N.; Forette, F.; Tuomilehto, J.; Clarke, R.; Ritchie, C.; Waldman, A.; Walton, I.; Poulter, R.; Ma, S.; et al. Incident dementia and blood pressure lowering in the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial cognitive function assessment (HYVET-COG): A double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnode, C.D.; Perdue, L.A.; Rossom, R.C.; Rushkin, M.C.; Redmond, N.; Thomas, R.G.; Lin, J.S. Screening for Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: Updated Evidence Report. JAMA 2020, 323, 764–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MedCalc® Statistical Software Version 23.1.6. MedCalc Software Ltd.: Ostend, Belgium; Available online: https://www.medcalc.org (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Shen, L.; Dewan, P.; Ferreira, J.P.; Cunningham, J.W.; Jhund, P.S.; Anand, I.S.; Chandra, A.; Chiang, L.-M.; Claggett, B.; Desai, A.S.; et al. Cardiac Hemodynamics and Cognitive Function in HFpEF: Insights from ARIC. Circulation 2024, 149, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, M.R.; Ringel, J.B.; Safford, M.M.; Goyal, P.; Khodneva, Y.; McClure, L.A.; Durant, R.W.; Jacob, A.E.; Levitan, E.B. Trajectory of Cognitive Decline After Incident Heart Failure Hospitalization: Findings From the REGARDS Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e032986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Zainul, O.; Sharma, Y.; Reich, A.; Osma, P.; Lau, J.D.; Massou, E.; Turchioe, M.; Russell, D.; Creber, R.M.; et al. Geriatric Vulnerabilities Among Adults With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Cross-Continent Evaluation. JACC Adv. 2025, 4, 101602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, A.P.; Georgiopoulou, V.V.; Butler, J. Neurocognitive Dysfunction in HF: A Contemporary Review. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Angiogr. Interv. 2024, 3, 278–287. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, Q.L.; Negishi, K.; De Pasquale, C.G.; Hare, J.L.; Leung, D.; Stanton, T.; Marwick, T.H. Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure: Implications for Patient Outcomes. J. Card. Fail. 2020, 26, 588–597. [Google Scholar]
- Pulignano, G.; Del Sindaco, D.; Di Lenarda, A.; Tarantini, L.; Cioffi, G.; Gregori, D. Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Patients with Heart Failure: A Multicenter Study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 527–536. [Google Scholar]
- Pinter, D.; Stelzer, J.; Schumacher, J.; Wollenweber, F.A. Vascular Cognitive Impairment. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 3922–3934. [Google Scholar]
- Ovsenik, A.; Podbregar, M.; Fabjan, A. Cerebral Blood Flow Impairment and Cognitive Decline in Heart Failure. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e02176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, P.; Gupta, D.; Lip, G.Y.H. The Neurocognitive Effects of Atrial Fibrillation: Benefits of the ABC Pathway. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2023, 9, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, J.; Li, C.; Gao, D.; Ma, Q.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, W.; Zheng, F. Age at Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation and Incident Dementia. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2342744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
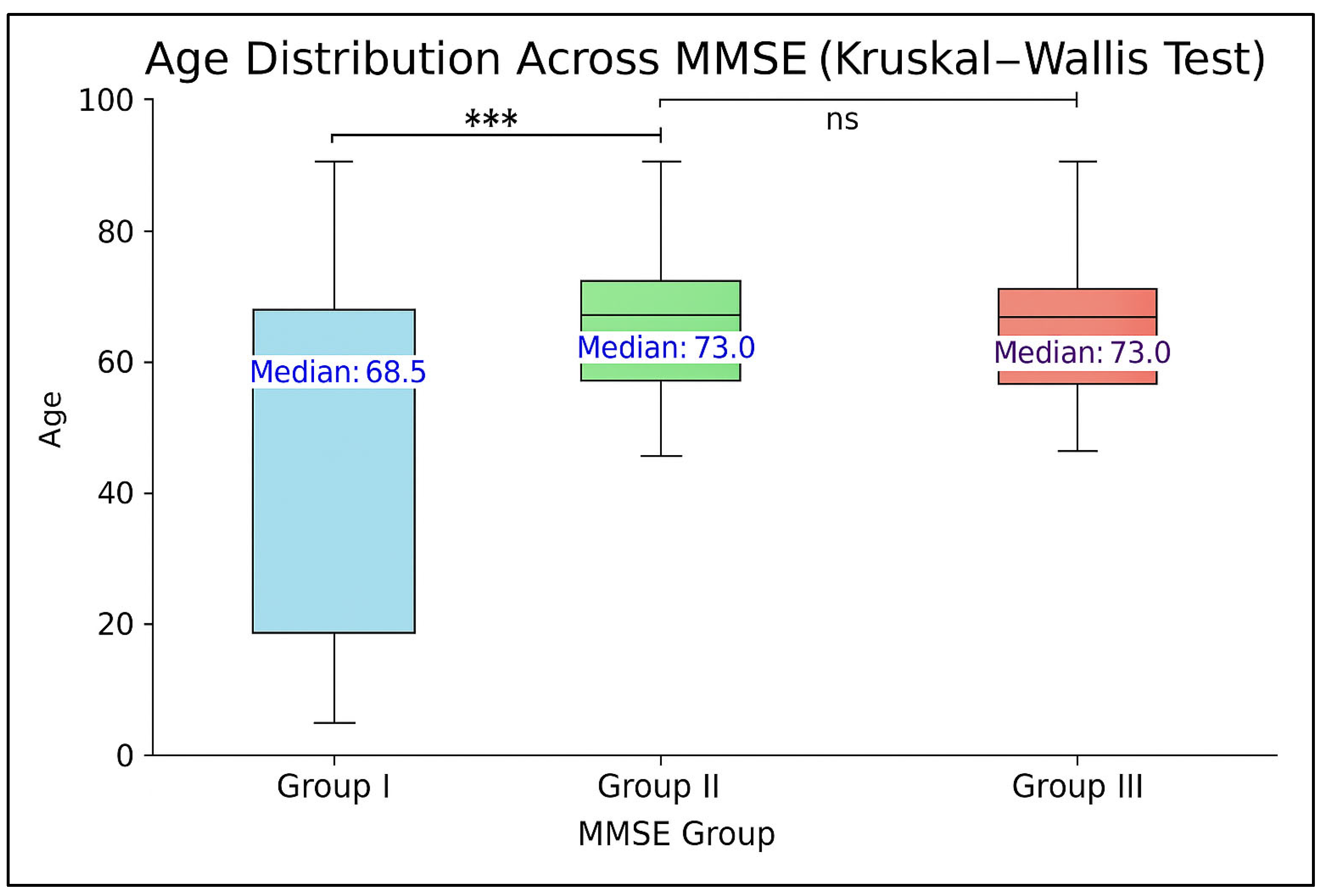
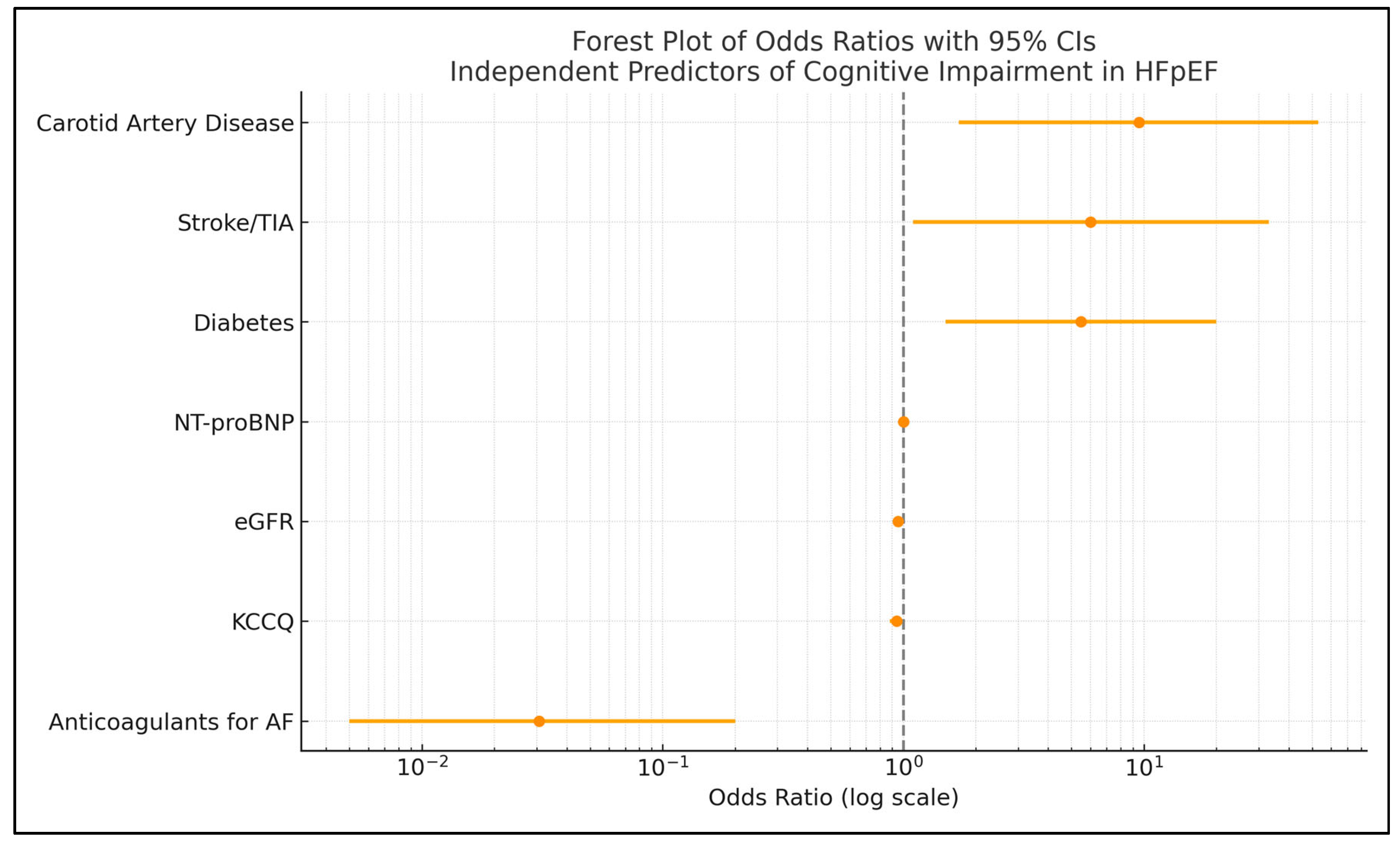



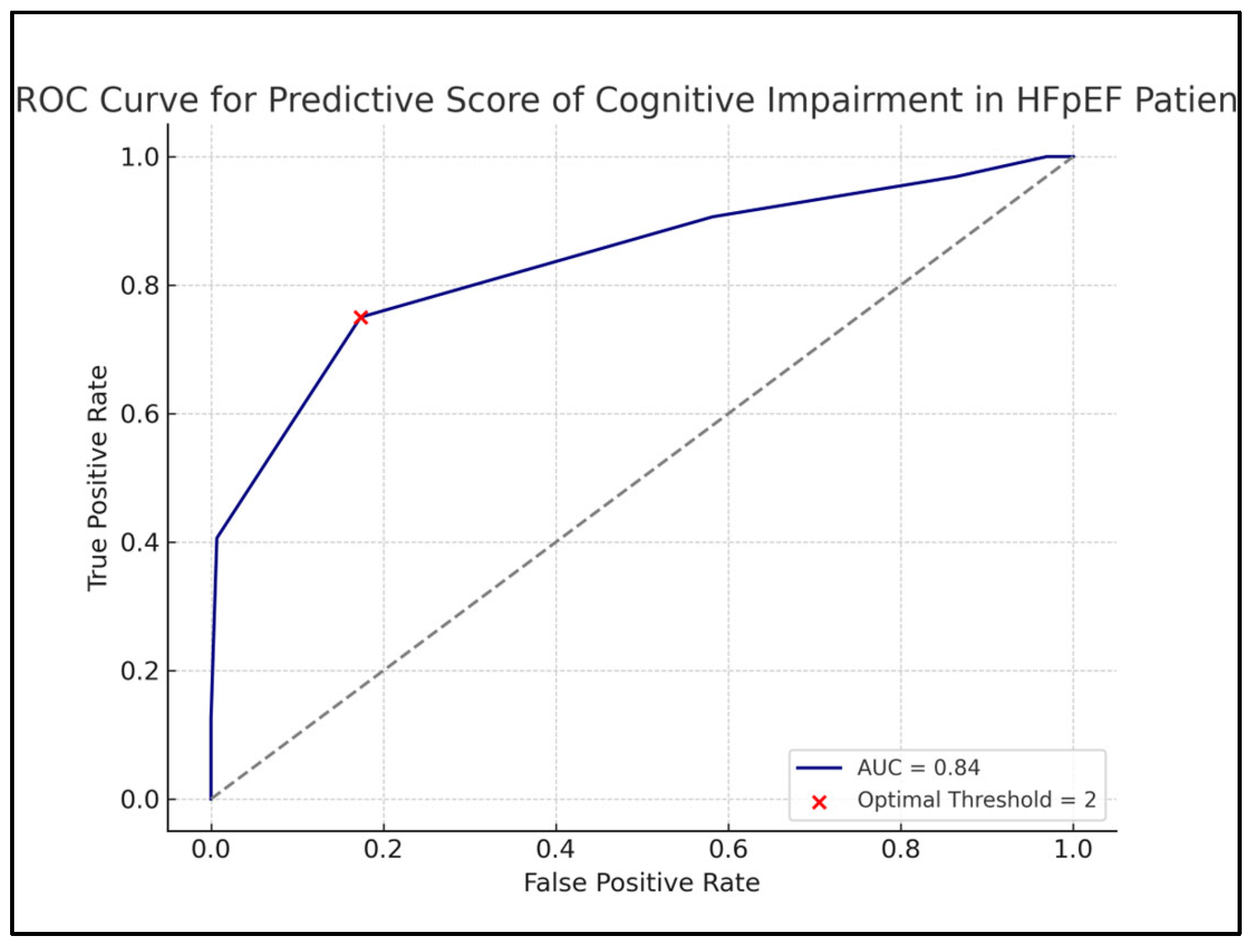
| Variable | MMSE Score Category | p for Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (28–30) n = 220 | II (24–27) n = 74 | III (<24) n = 32 | ||
| MMSE score | 29.3 ± 0.7 | 25.1 ± 1.1 | 20.5 ± 2.9 | <0.0001 |
| Age, y | 72.2 ± 5.4 | 73.4 ± 5.2 | 74.6 ± 6.3 | <0.0001 |
| Women | 108 (49) | 39 (52) | 19 (59) | 0.31 |
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 128.4 ± 14.5 | 129.5 ± 15.7 | 130.2 ± 15.9 | 0.10 |
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 75.4 ± 5.9 | 72.8 ± 6.3 | 71.5 ± 5.9 | <0.001 |
| Pulse pressure, mm Hg | 70.3 ± 6.3 | 70.2 ± 6.1 | 70.1 ± 4.9 | 0.44 |
| Pulse rate, beats/min | 80.5 ± 10.5 | 80.3 ± 10.7 | 80.8 ± 12.5 | 0.38 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 29.8 ± 3.8 | 29.9 ± 5.4 | 29.8 ± 4.9 | 0.40 |
| NYHA class III/IV | 33 (15) | 10 (14) | 5 (16) | 0.84 |
| 12-KCCQ | 77.3 (67.8–87.5) | 75.7 (58.5–93.4) | 74.8 (60.4–88.6) | 0.043 |
| LVEF, % | 57.4 ± 7.3 | 56.9 ± 6.8 | 55.6 ± 4.9 | 0.37 |
| Alcohol use | 18 (8) | 7 (9) | 4 (12) | 0.32 |
| Current smoker | 11 (5.0) | 5 (6.7) | 3 (9.3) | 0.27 |
| Previous HF hospitalization | 90 (41) | 33 (45) | 15 (48) | 0.44 |
| Old MI | 42 (19) | 16 (22) | 7 (24) | 0.4 |
| Angina pectoris | 68 (31) | 22 (30) | 10 (32) | 0.95 |
| CABG or PCI | 53 (24) | 19 (26) | 9 (27) | 0.6 |
| Hypertension | 196 (89) | 65 (88) | 29 (90) | 0.95 |
| Diabetes | 68 (31) | 33 (44) | 15 (48) | 0.014 |
| AFF history | 119 (54) | 41 (55) | 14 (45) | 0.2 |
| AFF on ECG | 64 (29) | 23 (31) | 10 (32) | 0.72 |
| Stroke or TIA | 22 (10) | 11 (15) | 7 (21) | 0.031 |
| Carotid AD | 11 (5) | 6 (8) | 5 (15) | 0.015 |
| PAD | 13 (6) | 6 (8) | 3 (9) | 0.37 |
| Depression | 13 (6) | 10 (13) | 5 (17) | 0.015 |
| COPD | 31 (14) | 9 (12) | 4 (13) | 0.69 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 68.5 ± 14.5 | 65.3 ± 18.4 | 60,1 ± 9.2 | <0.01 |
| Hematocrit, % | 42.7 ± 4.6 | 42.5 ± 4.8 | 41.8 ± 4.3 | 0.35 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.6 ± 4.2 | 13.4 ± 4.5 | 13.1 ± 4.1 | 0.373 |
| Hemoglobin A1c, % | 5.6 ± 1.4 | 6.2 ± 1.5 | 6.9 ± 2,2 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 210 ± 34 | 227 ± 36 | 224 ± 32 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides, mgl/dL | 178 ± 26 | 213 ± 25 | 244 ± 16 | <0.001 |
| Uric acid, mgl/dL | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| NT-proBNP, pg/mL | 823 (250–1420) | 1054 (481–1635) | 1114 (593–2516) | <0.0001 |
| Diuretics | 204 (93) | 70 (94) | 29 (92) | 0.82 |
| Digoxin | 18 (8.4) | 7 (8.9) | 3 (9.3) | 0.73 |
| ACEI or ARB | 183 (83) | 63 (85) | 27 (84) | 0.75 |
| Beta-blockers | 167 (76) | 55 (74) | 23 (73) | 0.6 |
| MRAs | 123 (56) | 40 (54) | 15 (48) | 0.37 |
| CCB | 103 (47) | 38 (52) | 16 (49) | 0.55 |
| Antiplatelets | 163 (74) | 56 (76) | 23 (72) | 0.93 |
| Anticoagulants | 75 (34) | 21 (29) | 6 (18) | 0.036 |
| Statins | 185 (84) | 58 (79) | 26 (82) | 0.4 |
| Pacemaker | 13 (6) | 4 (5) | 1 (4) | 0.56 |
| Univariate Regression Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age | 1.07 | 1.02–1.12 | 0.005 |
| KCCQ | 0.18 | 0.08–0.39 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 2.44 | 1.17–5.11 | 0.01 |
| Stroke/TIA | 4.78 | 2.09–10.91 | <0.001 |
| Carotid artery disease | 5.43 | 2.12–13.87 | 0.001 |
| Depression | 3.16 | 1.81–11.45 | <0.01 |
| eGFR mL/min/1.73 m2 | 0.95 | 0.93–0.98 | <0.01 |
| Total Cholesterol | 1.01 | 0.65–1.59 | <0.01 |
| Triglycerides | 1.02 | 1.01–1.09 | 0.03 |
| Uric acid | 2.44 | 2.13–8.90 | 0.04 |
| NT-proBNP | 1.02 | 1.0–1.03 | <0.0001 |
| Anticoagulants for AFF | 0.47 | 0.18–1.19 | <0.04 |
| Predictor | β Coefficient | Odds Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulants for AFF | −3.487 | 0.0306 | 0.0017 |
| Carotid artery disease | +2.255 | 9.5349 | 0.0106 |
| 12-KCCQ | −0.063 | 0.9392 | 0.0470 |
| Diabetes | +1.698 | 5.4651 | 0.0095 |
| Stroke/TIA | +1.790 | 5.9866 | 0.0349 |
| eGFR | −0.050 | 0.9513 | 0.0044 |
| NT-proBNP | +0.0023 | 1.0023 | 0.0028 |
| Risk Factors and Assigned Point Values | ||
|---|---|---|
| Predictor | Criteria | Points |
| 12-KCCQ Score | ≤70 | +1 |
| eGFR | <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | +1 |
| NT-proBNP | ≥900 pg/mL | +1 |
| Diabetes | Present | +1 |
| Stroke/TIA History | Present | +1 |
| Carotid Artery Disease | Present | +1 |
| Anticoagulants for AFF | Present | −2 |
| Max Score = 6, Min Score = −2 | ||
| Score Interpretation | ||
| Total Score | Risk Interpretation | |
| ≤0 | Low risk of cognitive impairment | |
| 1–2 | Moderate risk | |
| ≥3 | High risk of cognitive impairment (MMSE < 24) | |
| Recommended Cutoff and Model Performance | ||
| ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arnautu, S.-F.; Bernad, B.-C.; Korpos, I.G.; Tomescu, M.-C.; Andor, M.; Jianu, C.-D.; Arnautu, D.-A. Predicting Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Patients with HFpEF: Development of a Simple Clinical Risk Score. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113768
Arnautu S-F, Bernad B-C, Korpos IG, Tomescu M-C, Andor M, Jianu C-D, Arnautu D-A. Predicting Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Patients with HFpEF: Development of a Simple Clinical Risk Score. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113768
Chicago/Turabian StyleArnautu, Sergiu-Florin, Brenda-Cristiana Bernad, Istvan Gyalai Korpos, Mirela-Cleopatra Tomescu, Minodora Andor, Catalin-Dragos Jianu, and Diana-Aurora Arnautu. 2025. "Predicting Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Patients with HFpEF: Development of a Simple Clinical Risk Score" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113768
APA StyleArnautu, S.-F., Bernad, B.-C., Korpos, I. G., Tomescu, M.-C., Andor, M., Jianu, C.-D., & Arnautu, D.-A. (2025). Predicting Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Patients with HFpEF: Development of a Simple Clinical Risk Score. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113768









