Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Cardiac Function and Quality of Life in Patients with Heart Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
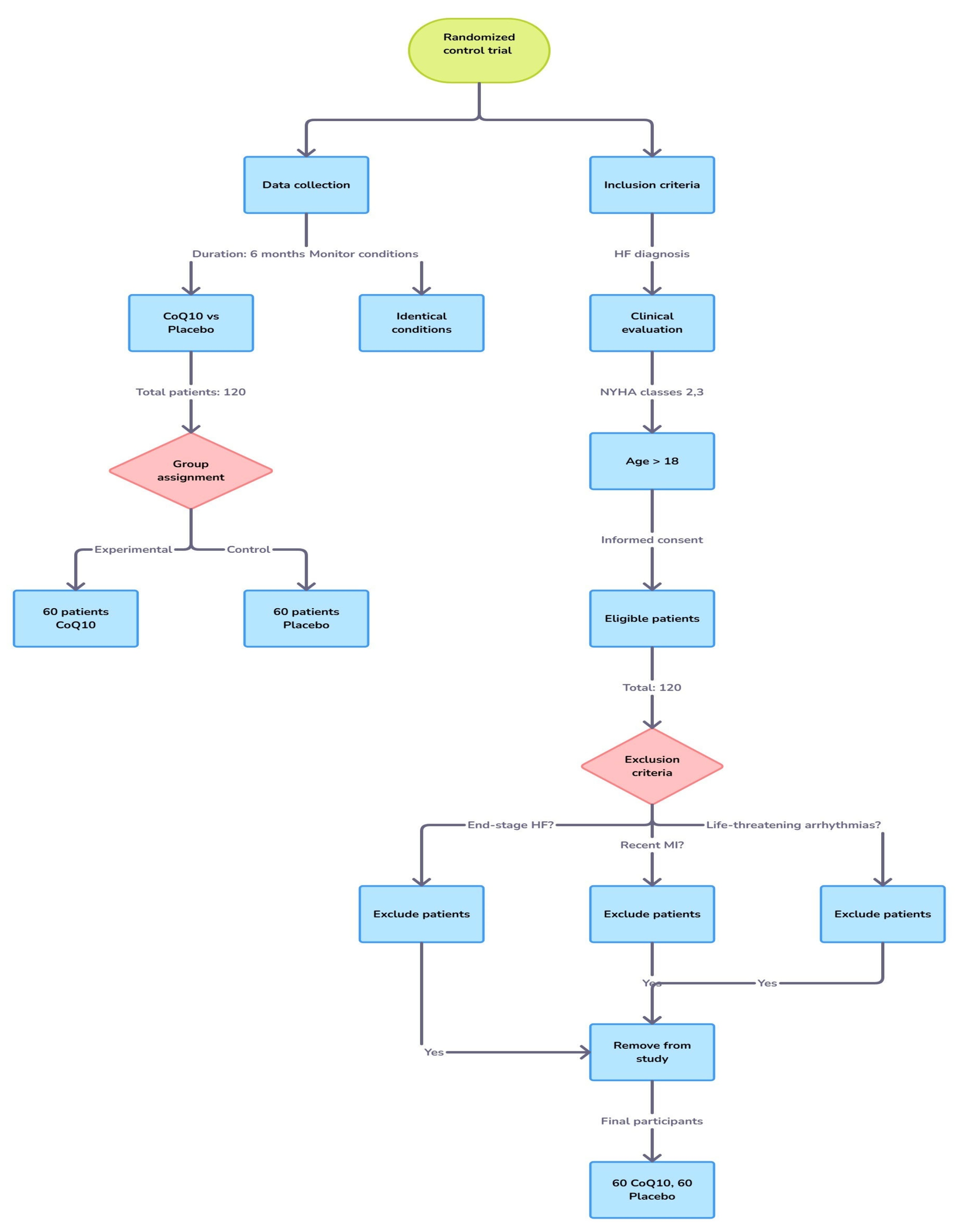
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Randomization and Blinding
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
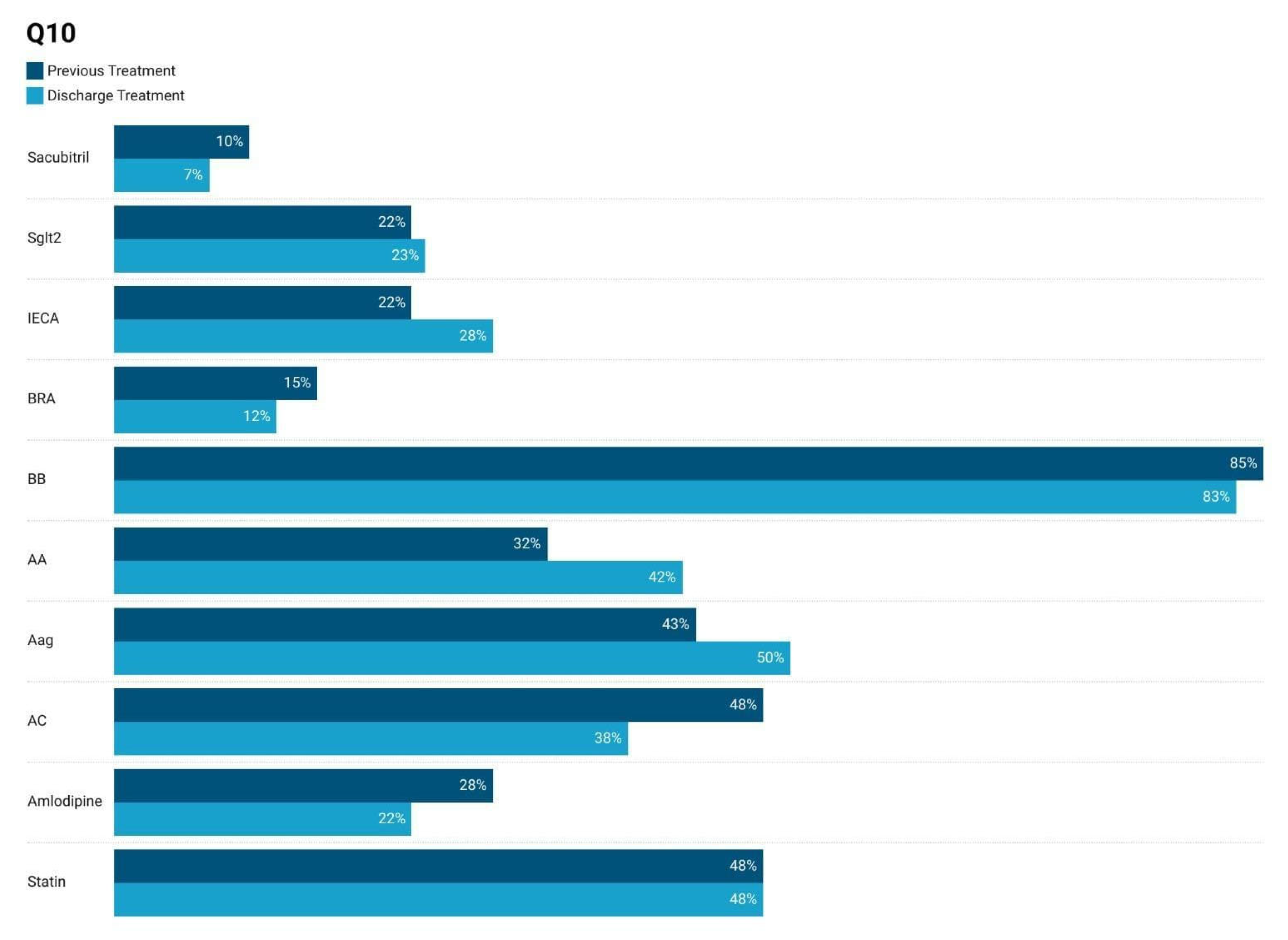
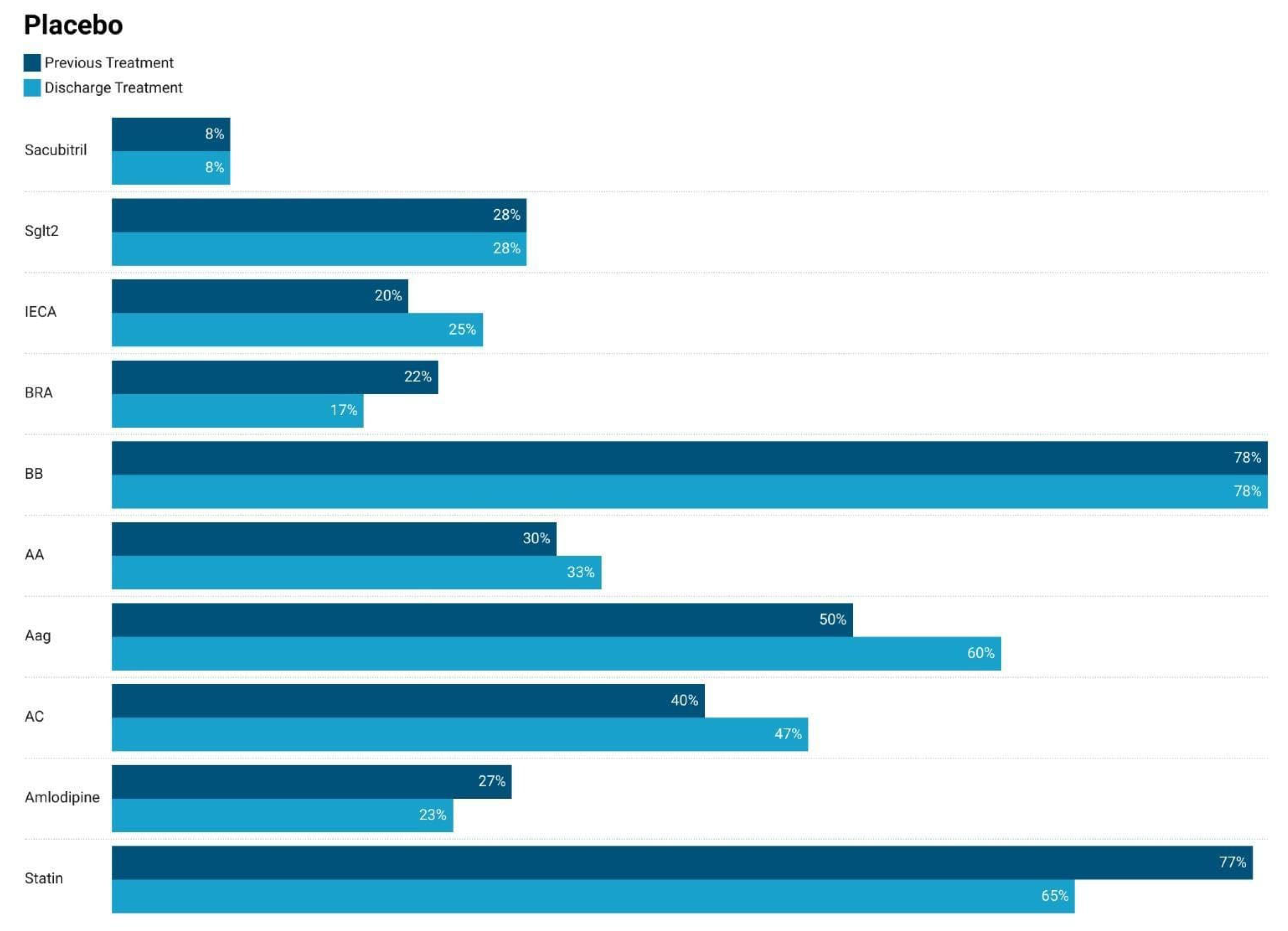
3.1. Comparison of Medication Usage at Admission–Discarge
3.2. Endpoint Results (6-Month Evaluation)
4. Discussion
5. Future Directions
6. Limitations and Areas for Further Research
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunlay, S.M.; Pereira, N.L.; Kushwaha, S.S. Contemporary Strategies in the Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 662–676. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0025619614000536 (accessed on 2 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Giallauria, F.; Vigorito, C.; Piepoli, M.F.; Coats, A.J.S. Effects of Cardiac Contractility Modulation by Non-Excitatory Electrical Stimulation on Exercise Capacity and Quality of Life: An Individual Patient’s Data Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 175, 352–357. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167527314010729 (accessed on 2 October 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, S.S.; Wang, T.J. The Epidemiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Contributions from the Framingham Heart Study. Glob. Heart 2013, 8, 77–82. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211816012002669 (accessed on 2 October 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaper, J.; Meiser, E.; Stämmler, G. Ultrastructural Morphometric Analysis of Myocardium from Dogs, Rats, Hamsters, Mice, and from Human Hearts. Circ. Res. 1985, 56, 377–391. Available online: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/01.RES.56.3.377 (accessed on 16 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Tian, R. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Pathophysiology of Heart Failure. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3716–3726. Available online: https://www.jci.org/articles/view/120849 (accessed on 16 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Saini, R. Coenzyme Q10: The Essential Nutrient. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littaru, G.P.; Ho, L.; Folkers, K. Deficiency of Coenzyme Q 10 in Human Heart Disease. I. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1972, 42, 291–305. [Google Scholar]
- Langsjoen, P.H.; Folkers, K. Isolated Diastolic Dysfunction of the Myocardium and Its Response to CoQ10 Treatment. Clin. Investig. 1993, 71, S140–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarter, B. Coenzyme Q10 and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2002, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, S.A.; Rosenfeldt, F.; Kumar, A.; Dolliner, P.; Filipiak, K.J.; Pella, D.; Alehagen, U.; Steurer, G.; Littarru, G.P.; Q-SYMBIO Study Investigators. The Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on Morbidity and Mortality in Chronic Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2014, 2, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaby, A.R. The Role of Coenzyme Q10 in Clinical Medicine: Part 1. Alt. Med. Rev. 1996, 1, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Pallotti, F.; Bergamini, C.; Lamperti, C.; Fato, R. The Roles of Coenzyme Q in Disease: Direct and Indirect Involvement in Cellular Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, T. Coenzyme Q10 Therapy on the Cardiac Dysfunction in Patients with Mitral Valve Prolapse. Dose vs Effect and Dose vs Serum Level of Coenzyme Q10. Biomed. Clin. Asp. Coenzym. Q 1986, 5, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Rabanal-Ruiz, Y.; Llanos-González, E.; Alcain, F.J. The Use of Coenzyme Q10 in Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, S.A.; Vadhanavikit, S.; Baandrup, U.; Folkers, K. Long-Term Coenzyme Q10 Therapy: A Major Advance in the Management of Resistant Myocardial Failure. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1985, 11, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.S.; Scalia, G.M.; Galbraith, A.; Burstow, D.J.; Bett, N.; Aroney, C.N. Lack of Effect of Coenzyme Q on Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure1. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999, 33, 1549–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, T.; Morita, Y.; Toyama, S.; Yamagami, T.; Tsukamoto, N.; Wada, N.; Ohkubo, M.; Yamamura, Y. A Clinical Study of the Effect of Coenzyme Q on Congestive Heart Failure. Jpn. Heart J. 1976, 17, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judy, W.V.; Hall, J.H.; Toth, P.; Folkers, K. Influence of Coenzyme-q10 on Cardiac-Function in Congestive Heart-Failure Patients. In Federation Proceedings; Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1984; Volume 43, p. 358. [Google Scholar]
- Baggio, E.; Gandini, R.; Plancher, A.C.; Passeri, M.; Carmosino, G. Italian Multicenter Study on the Safety and Efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 as Adjunctive Therapy in Heart Failure. Mol. Asp. Med. 1994, 15, s287–s294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biering-Sørensen, T.; Solomon, S.D. Assessing Contractile Function When Ejection Fraction Is Normal: A Case for Strain Imaging. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8, e004181. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26546484/ (accessed on 11 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Flachskampf, F.A.; Blankstein, R.; Grayburn, P.A.; Kramer, C.M.; Kwong, R.Y.; Marwick, T.H.; Nagel, E.; Sengupta, P.P.; Zoghbi, W.A.; Chandrashekhar, Y. Global Longitudinal Shortening: A Positive Step Towards Reducing Confusion Surrounding Global Longitudinal Strain. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1566–1567. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31395245/ (accessed on 11 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Russo, C.; Jin, Z.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Rundek, T.; Homma, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Di Tullio, M.R. Prevalence and Prognostic Value of Subclinical Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction by Global Longitudinal Strain in a Community-Based Cohort. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; McCabe, E.L.; Larson, M.G.; Merz, A.A.; Osypiuk, E.; Lehman, B.T.; Stantchev, P.; Aragam, J.; Solomon, S.D.; Benjamin, E.J.; et al. Distinct Aspects of Left Ventricular Mechanical Function Are Differentially Associated with Cardiovascular Outcomes and All-Cause Mortality in the Community. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwick, T.H. Global Longitudinal Strain Monitoring to Guide Cardioprotective Medications During Anthracycline Treatment. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, D.E.; Motofelea, A.C.; Buda, V.; Velimirovici, D.E.; Bodea, O.; Duda-Seiman, D.M.; Luca, C.T.; Dragan, S.-R. Left Atrial Strain in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Narrative Review. Life 2025, 15, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springhetti, P.; Tomaselli, M.; Benfari, G.; Milazzo, S.; Ciceri, L.; Penso, M.; Pilan, M.; Clement, A.; Rota, A.; Del Sole, P.A.; et al. Peak Atrial Longitudinal Strain and Risk Stratification in Moderate and Severe Aortic Stenosis. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 25, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeldt, F.; Hilton, D.; Pepe, S.; Krum, H. Systematic Review of Effect of Coenzyme Q10 in Physical Exercise, Hypertension and Heart Failure. BioFactors 2003, 18, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langsjoen, P.; Langsjoen, P.; Willis, R.; Folkers, K. Treatment of Essential Hypertension with Coenzyme Q10. Mol. Asp. Med. 1994, 15, s265–s272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | CoQ10 Group | Placebo Group | Total (N = 120) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 60) | (N = 60) | |||
| Age | 0.624 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 66.5 (12.8) | 67.7 (14.3) | 67.1 (13.5) | |
| Environment | 0.581 | |||
| Rural (%) | 28 (46.7%) | 25 (41.7%) | 53 (44.2%) | |
| Urban (%) | 32 (53.3%) | 35 (58.3%) | 67 (55.8%) | |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 0.56 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 32.4 (7.0) | 33.2 (8.1) | 32.8 (7.5) | |
| Smoking status | 0.453 | |||
| Non-smokers (%) | 35 (58.3%) | 39 (65.0%) | 74 (61.7%) | |
| Smokers (%) | 25 (41.7%) | 21 (35.0%) | 46 (38.3%) | |
| Length of stay (days) | 0.625 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 10.7 (5.4) | 10.2 (5.8) | 10.4 (5.6) | |
| SBP at Admission (mmHg) | 0.560 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 124.2 (13.3) | 126.8 (18.2) | 130.0 (16.9) | |
| DBP at Admission (mmHg) | 0.489 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 78.2 (9.2) | 80.3 (10.4) | 77.3 (10.2) | |
| HR at Admission (bpm) | 0.542 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 74.3 (13.1) | 72.8 (13.8) | 73.6 (13.4) | |
| Laboratory Data | ||||
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | 0.987 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 1401.9 (1501.0) | 1397.4 (1503.1) | 1399.7 (1495.7) | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0.157 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 12.7 (0.7) | 12.5 (1.2) | 12.6 (1.0) | |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 0.101 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 113.0 (35.7) | 126.5 (51.9) | 119.7 (44.9) | |
| eGFR (mL/min) | 0.114 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 73.1 (16.7) | 69.4 (25.0) | 71.25 (21.7) | |
| Functional capacity | ||||
| GLS (%) | 0.497 | |||
| Mean (SD) | −11.2 (3.8) | −11.6 (3.8) | −11.4 (3.8) | |
| 6MWT Distance (m) | 0.47 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 299.4 (102.3) | 292.1 (96.8) | 295.8 (100.4) | |
| MLHFQ | 0.227 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 57.6 (16.6) | 54.0 (16.1) | 55.8 (16.4) | |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Diabetes Type 2 | 25 (41.7%) | 27 (45.0%) | 52 (43.3%) | 0.713 |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 33 (55.0%) | 24 (40.0%) | 57 (47.5%) | 0.1 |
| COPD | 22 (36.7%) | 14 (23.3%) | 36 (30.0%) | 0.111 |
| Heart Failure | 55 (91.7%) | 50 (83.3%) | 105 (87.5%) | 0.168 |
| Respiratory Failure | 2 (3.3%) | 6 (10.0%) | 8 (6.7%) | 0.143 |
| Variable | Baseline (N = 60) | Endpoint (N = 60) | Total (N = 120) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP (mmHg) | 135.8 (18.2) | 124.2 (13.3) | 130.0 (16.9) | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 80.3 (10.4) | 74.2 (9.2) | 77.3 (10.2) | <0.001 |
| HR (bpm) | 75.3 (13.1) | 71.8 (13.8) | 73.5 (13.4) | 0.32 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.7 (0.7) | 12.5 (0.6) | 12.6 (0.7) | 0.026 |
| Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | 126.5 (51.9) | 120.5 (45.3) | 123.5 (48.6) | 0.504 |
| eGFR (mL/min) | 63.4 (25.0) | 73.1 (16.7) | 68.2 (21.7) | 0.014 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 139.9 (3.9) | 140.6 (4.1) | 140.2 (4.0) | 0.295 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.1 (0.6) | 4.0 (0.6) | 4.0 (0.6) | 0.722 |
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | 1401.9 (1501.0) | 815.6 (957.4) | 1108.8 (1287.7) | 0.012 |
| LVEF (%) | 38.9 (6.9) | 40.6 (6.6) | 39.7 (6.8) | 0.17 |
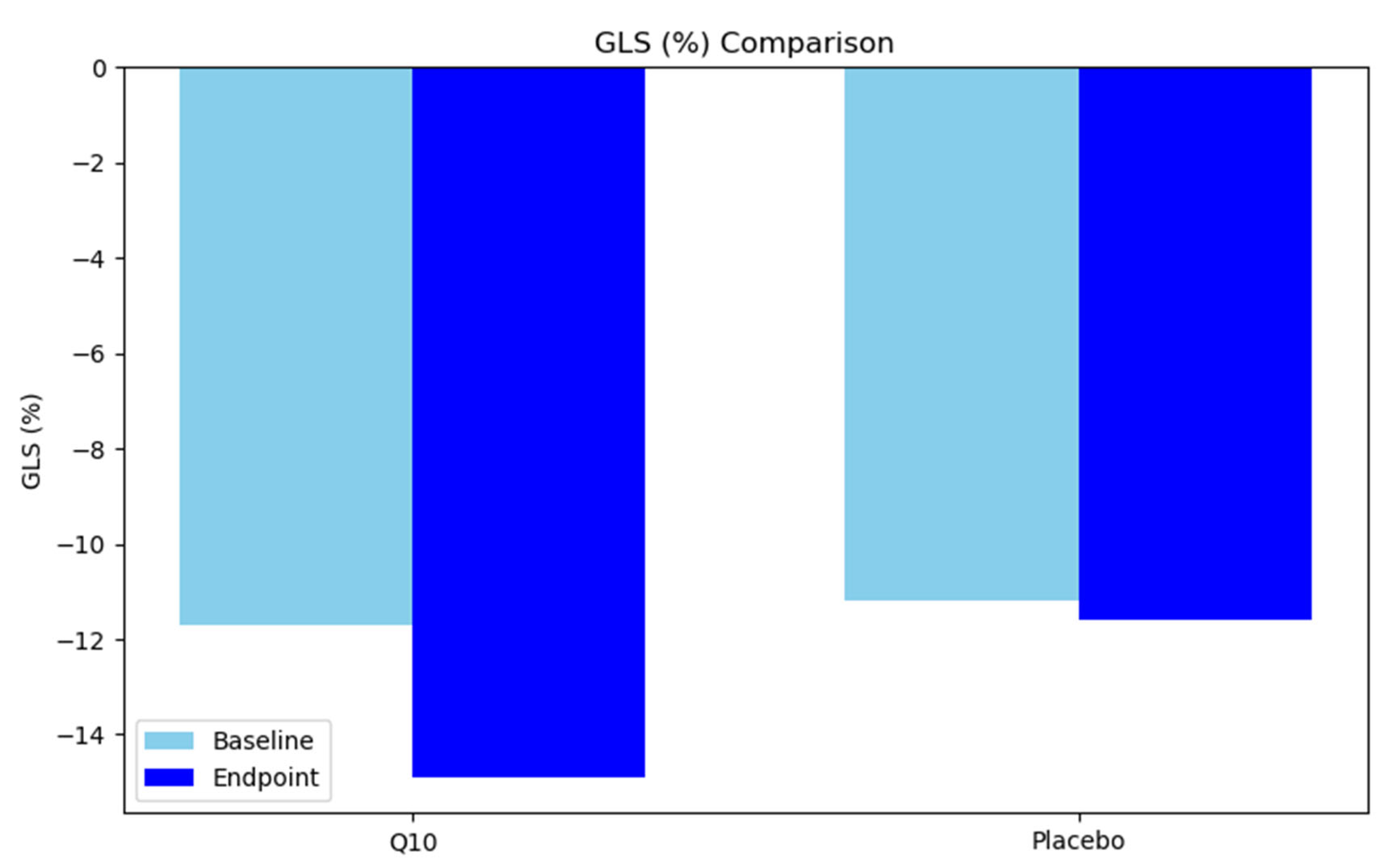
| GLS (%) | −11.7 (−4.4) | −14.9 (−3.7) | −13.3 (−4.4) | <0.001 |
| 6MWT Distance (m) | 267 (95.5) | 349.3 (100.6) | 277.0 (100.6) | 0.008 |
| MLHFQ | 59.0 (14.5) | 52.9 (17.1) | 55.8 (16.4) | 0.043 |
| SaO2 Initial (%) | 97.9 (1.2) | 98.6 (0.6) | 98.2 (1.0) | <0.001 |
| SaO2 Final (%) | 97.5 (1.4) | 98.4 (0.7) | 97.9 (1.2) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Baseline (N = 60) | 6 Months (N = 60) | Total (N = 120) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m²) | 33.2 (8.1) | 31.7 (5.7) | 32.4 (7.0) | 0.218 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 135.8 (18.2) | 134.9 (17.8) | 135.4 (18.0) | 0.912 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 80.3 (10.4) | 79.9 (10.2) | 80.1 (10.3) | 0.894 |
| HR (bpm) | 72.8 (13.8) | 72.3 (13.5) | 72.6 (13.7) | 0.872 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.5 (1.2) | 12.3 (1.1) | 12.4 (1.1) | 0.288 |
| Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | 126.5 (51.9) | 120.5 (45.3) | 123.5 (48.6) | 0.504 |
| eGFR (ml/min) | 63.4 (25.0) | 62.1 (24.2) | 62.8 (24.6) | 0.802 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.1 (0.4) | 1.2 (0.4) | 1.1 (0.4) | 0.845 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 140.3 (3.1) | 141.0 (2.9) | 140.6 (3.0) | 0.224 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.3 (0.5) | 4.4 (0.6) | 4.4 (0.6) | 0.42 |
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | 1401.9 (1501.0) | 1378.5 (1492.4) | 1390.2 (1496.7) | 0.79 |
| LVEF (%) | 38.4 (7.3) | 38.4 (7.2) | 38.4 (7.2) | 0.96 |
| 6MWT (meters) | 254.7 (94.4) | 267.0 (96.5) | 260.8 (95.3) | 0.481 |
| GLS (%) | −11.2 (3.8) | −11.6 (3.8) | −11.4 (3.8) | 0.497 |
| MLHFQ | 58.57 (14.39) | 58.30 (14.68) | 57.78 (14.53) | 0.27 |
| SaO2 Initial (%) | 96.5 (4.0) | 96.5 (4.1) | 96.5 (4.0) | 0.964 |
| SaO2 Final (%) | 95.2 (4.5) | 95.2 (4.6) | 95.2 (4.5) | 0.936 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bodea, O.; Boia, E.R.; Craciun, L.M.; Valcovici, M.D.; Motofelea, A.C.; Munteanu, A.M.; Streian, C.G.; Pop, G.N.; Dragan, S.R. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Cardiac Function and Quality of Life in Patients with Heart Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113675
Bodea O, Boia ER, Craciun LM, Valcovici MD, Motofelea AC, Munteanu AM, Streian CG, Pop GN, Dragan SR. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Cardiac Function and Quality of Life in Patients with Heart Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113675
Chicago/Turabian StyleBodea, Olivia, Eugen Radu Boia, Laura Maria Craciun, Mihaela Daniela Valcovici, Alexandru Catalin Motofelea, Andreea Mara Munteanu, Caius Glad Streian, Gheorghe Nicusor Pop, and Simona Ruxanda Dragan. 2025. "Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Cardiac Function and Quality of Life in Patients with Heart Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113675
APA StyleBodea, O., Boia, E. R., Craciun, L. M., Valcovici, M. D., Motofelea, A. C., Munteanu, A. M., Streian, C. G., Pop, G. N., & Dragan, S. R. (2025). Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Cardiac Function and Quality of Life in Patients with Heart Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113675








