Safety and Long-Term Efficacy of Intravitreal rtPA, Bevacizumab and SF6 Injection in Patients with Submacular Hemorrhage Secondary to Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval and Patient Consent
2.2. Selection of Patients and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Treatment Procedure and Subsequent Anti-VEGF Therapy
2.4. Outcome Measures and Follow-Up Period
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hochman, M.A.; Seery, C.M.; Zarbin, M.A. Pathophysiology and management of subretinal hemorrhage. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1997, 42, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matt, G.; Sacu, S.; Stifter, E.; Prünte, C.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Combination of Intravitreal rTPA, gas and ranibizumab for extensive subfoveal haemorrhages secondary to neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 2010, 227, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhli-Hattenbach, C.; Fischer, I.B.; Schalnus, R.; Hattenbach, L.O. Subretinal hemorrhages associated with age-related macular degeneration in patients receiving anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 149, 316–321.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, M.; Mainguy, A.; Chatziralli, I.; Pakzad-Vaezi, K.; Ruiz-Medrano, J.; Bodaghi, B.; Loewenstein, A.; Ambati, J.; de Smet, M.D.; Tadayoni, R.; et al. Macular Hemorrhage Due to Age-Related Macular Degeneration or Retinal Arterial Macroaneurysm: Predictive Factors of Surgical Outcome. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanescu-Segall, D.; Balta, F.; Jackson, T.L. Submacular hemorrhage in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: A synthesis of the literature. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2016, 61, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, G.; Loiudice, P.; Menchini, M.; Sartini, F.; De Cillà, S.; Figus, M.; Nardi, M. Traumatic submacular hemorrhage: Available treatment options and synthesis of the literature. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2019, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scupola, A.; Coscas, G.; Soubrane, G.; Balestrazzi, E. Natural history of macular subretinal hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmologica 1999, 213, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko, M.; Posekany, A.; Szabo, S.; Scharer, S.; Kiechl, S.; Knoflach, M.; Serles, W.; Ferrari, J.; Lang, W.; Sommer, P.; et al. Trends of r-tPA (Recombinant Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator) Treatment and Treatment-Influencing Factors in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattenbach, L.O.; Klais, C.; Koch, F.H.; Gümbel, H.O. Intravitreous injection of tissue plasminogen activator and gas in the treatment of submacular hemorrhage under various conditions. Ophthalmology 2001, 108, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Cao, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Xu, K.; Yu, L.; Xing, Y.; Yang, N. Efficacy Evaluation of Tissue Plasminogen Activator with Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Drugs for Submacular Hemorrhage Treatment: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthoff, R.; Guthoff, T.; Meigen, T.; Goebel, W. Intravitreous injection of bevacizumab, tissue plasminogen activator, and gas in the treatment of submacular hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2011, 31, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waizel, M.; Todorova, M.G.; Rickmann, A.; Blanke, B.R.; Szurman, P. Efficacy of Vitrectomy Combined with Subretinal rtPA Injection with Gas or Air Tamponade. Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 2017, 234, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herranz Cabarcos, A.; Quiroz Quiroga, M.J.; Alarcón Valero, I.; Castilla Martí, M.; Pospoki, V.; Vilaplana Blanch, D. Vitrectomy with subretinal tissue plasminogen activator (r-TPA) and intravitreal injection of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) for submacular hemorrhages treatment: Retrospective analysis of 22 cases. Arch. Soc. Esp. Oftalmol. 2022, 97, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berufsverband der Augenärzte Deutschlands e.V. RG Stellungnahme der Deutschen Ophthalmologischen Gesellschaft, der Retinologischen Gesellschaft und des Berufsverbandes der Augenärzte Deutschlands; Berufsverband der Augenärzte Deutschlands e.V.: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, R.W.; Moke, P.S.; Turpin, A.H.; Ferris, F.L.; SanGiovanni, J.P.; Johnson, A.C.; Birch, E.E.; Chandler, D.L.; Cox, A.T.; Blair, R.C.; et al. A computerized method of visual acuity testing: Adaptation of the early treatment of diabetic retinopathy study testing protocol. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 135, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabano, D.; Borkar, D.S.; Garmo, V.; Shaia, J.K.; Kuo, B.; Myers, R.; LaPrise, A.; Leng, T.; Singh, R.P. FARETINA-DME-Early Treatment Patterns and Outcomes in Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema Treated with Faricimab: An IRIS RegistryTM Analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 2699. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, N.; Kato, A.; Araki, T.; Kimura, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Okamoto, F.; Murakami, T.; Mitamura, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Miki, A.; et al. Visual prognosis of submacular hemorrhage secondary to age-related macular degeneration: A retrospective multicenter survey. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, S.R.; Bindra, M.S. Early treatment of acute submacular haemorrhage secondary to wet AMD using intravitreal tissue plasminogen activator, C3F8, and an anti-VEGF agent. Eye 2016, 30, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohmann, C.; Dimopoulos, S.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.U.; Schindler, P.; Katz, T.; Spitzer, M.S.; Skevas, C. Surgical management of submacular hemorrhage due to n-AMD: A comparison of three surgical methods. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2020, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veritti, D.; Sarao, V.; Martinuzzi, D.; Menzio, S.; Lanzetta, P. Submacular hemorrhage during neovascular age-related macular degeneration: A meta-analysis and meta-regression on the use of tPA and anti-VEGFs. Ophthalmologica 2024, 247, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolewska, B.; Utebey, E.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.U.; Tatar, O. Long-term visual outcome and its predictive factors following treatment of acute submacular hemorrhage with intravitreous injection of tissue plasminogen factor and gas. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 30, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Abraham, P.; Meyer, C.H.; Kokame, G.T.; Kaiser, P.K.; Rauser, M.E.; Gross, J.G.; Nuthi, A.S.; Lin, S.G.; Daher, N.S. Optical coherence tomography-measured pigment epithelial detachment height as a predictor for retinal pigment epithelial tears associated with intravitreal bevacizumab injections. Retina 2010, 30, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doguizi, S.; Ozdek, S. Pigment epithelial tears associated with anti-VEGF therapy: Incidence, long-term visual outcome, and relationship with pigment epithelial detachment in age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2014, 34, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre-Ibáñez, M.; Martínez-Rubio, C.; Molina-Pallete, R.; Martínez-López-Corell, P.; Wu, L.; Arévalo, J.F.; Gallego-Pinazo, R. Retinal pigment epithelial tears. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2019, 42, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Guo, N.; Zhao, Z.; Duan, J. Association between retinal pigment epithelium tear and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Retina 2024, 44, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattenbach, L.O.; Brieden, M.; Koch, F.; Gümbel, H. Intravitreal injection of rt-PA and gas in the management of minor submacular haemorrhages secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 2002, 219, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.; Barak, A.; Loewenstein, A.; Zur, D. Predictive Factors for Visual Outcome after Submacular Hemorrhage—A comparative Treatment Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 1800. [Google Scholar]

| Characteristics | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Number of eyes/Number of patients | 37/35 |
| Sex | |
| male | 21 (56.8) |
| female | 16 (43.2) |
| Age in years (mean ± SD) | 78.2 ± 6.8 |
| Laterality | |
| right | 23 (62.1) |
| left | 14 (37.9) |
| Lens status, phakia/pseudophakia | 21/16 |
| Prior treatment history | |
| Patients having received prior anti-VEGF injections (mean ± SD) | 5 (13.5%) |
| Number of prior anti-VEGF injections (mean ± SD) | 21.8 ± 14.3 |
| Days since bleeding event at triple injection (mean ± SD) | 5.6 ± 5.7 |
| Size of submacular hemorrhage in disc areas (mean ± SD) | 11.4 ± 9.4 |
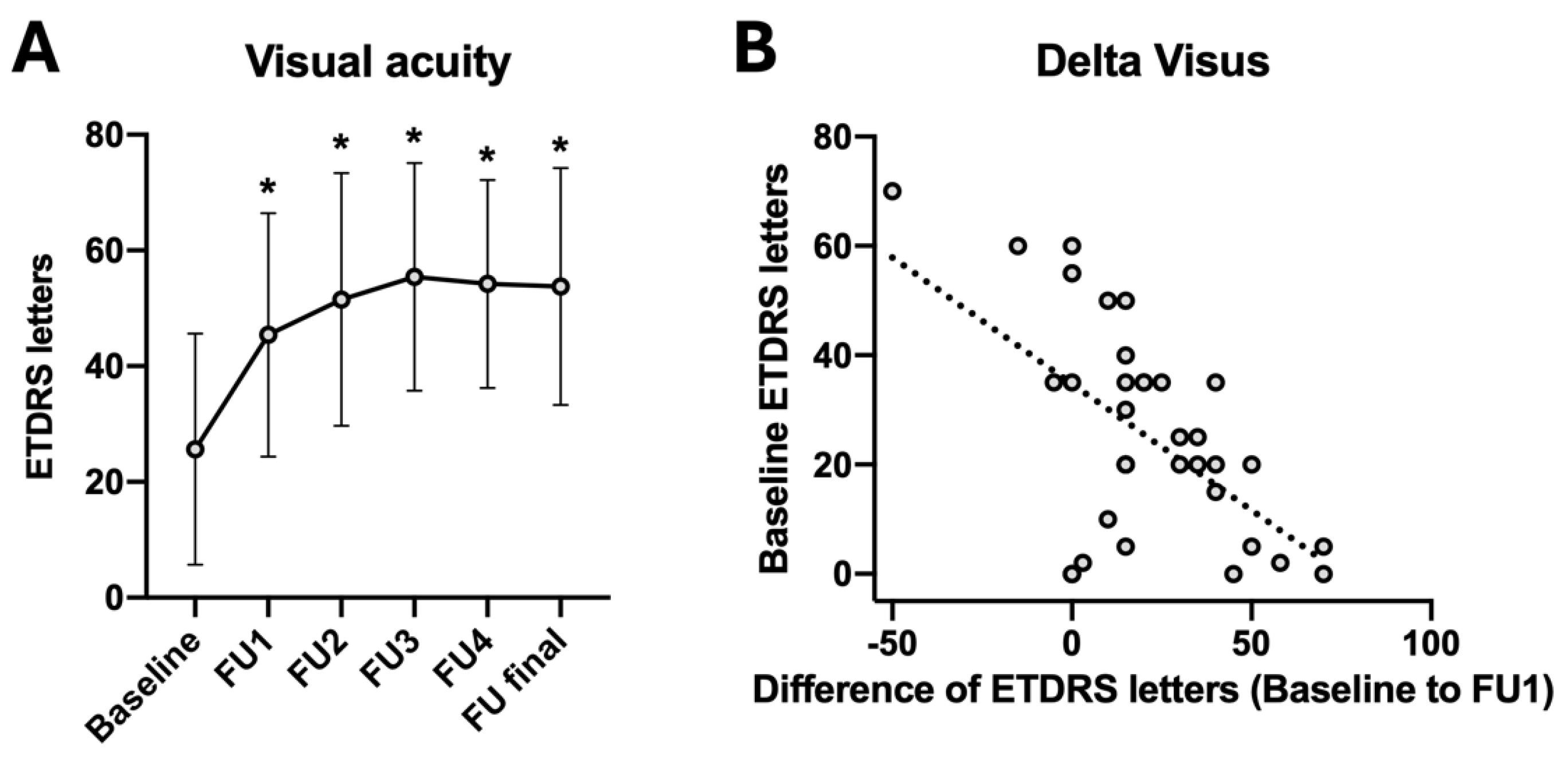
| Mean ± SD | Difference to Baseline | p-Value (Compared to Baseline) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ETDRS baseline | 25.6 ± 20.0 | ||
| ETDRS FU1 | 45.4 ± 21.0 | +19.8 | <0.001 * |
| ETDRS FU2 | 51.5 ± 21.8 | +25.9 | <0.001 * |
| ETDRS FU3 | 55.4 ± 19.7 | +29.8 | <0.001 * |
| ETDRS FU4 | 54.2 ± 18.0 | +28.6 | <0.001 * |
| ETDRS final | 53.8 ± 20.5 | +28.2 | <0.001 * |
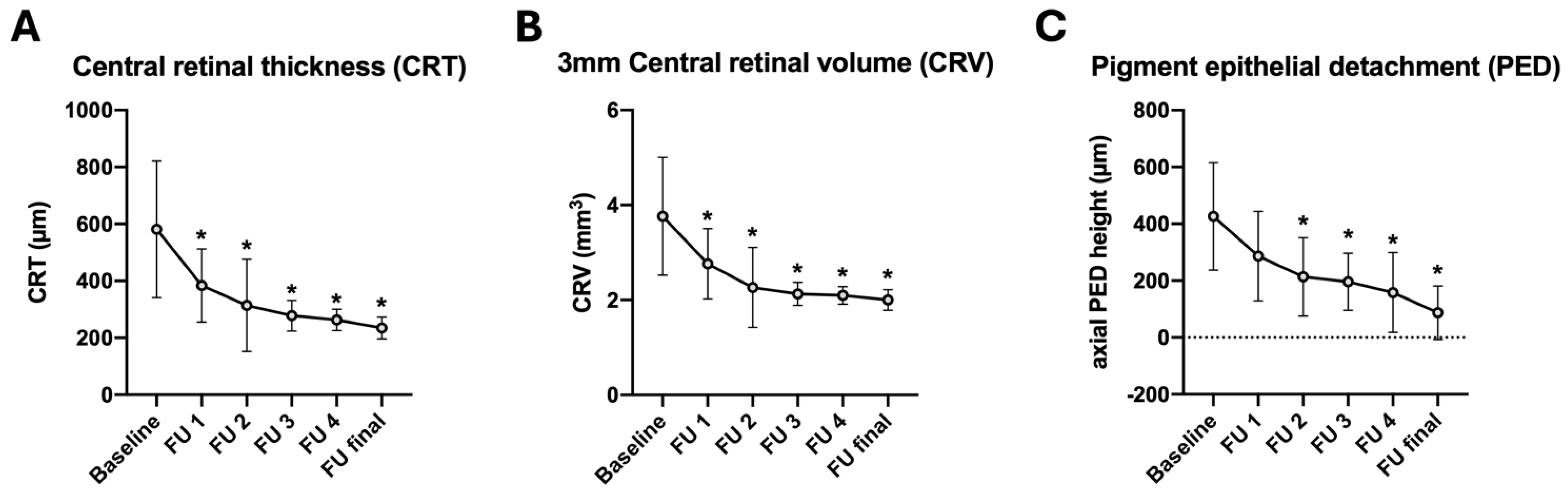
| CRT (µm) baseline | 581.1 ± 239.8 | ||
| CRT (µm) FU1 | 384.1 ± 128.4 | −197.0 | 0.005 * |
| CRT (µm) FU2 | 314.0 ± 162.2 | −267.1 | <0.001 * |
| CRT (µm) FU3 | 277.5 ± 53.7 | −303.6 | <0.001 * |
| CRT (µm) FU4 | 263.1 ± 37.6 | −318.0 | <0.001 * |
| CRT (µm) final | 234.5 ± 38.2 | −346.6 | <0.001 * |
| CRV (μm3) baseline | 3.8 ± 1.2 | ||
| CRV (μm3) FU1 | 2.8 ± 0.7 | −1.0 | 0.007 * |
| CRV (μm3) FU2 | 2.3 ± 0.8 | −1.5 | <0.001 * |
| CRV (μm3) FU3 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | −1.7 | <0.001 * |
| CRV (μm3) FU4 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | −1.7 | <0.001 * |
| CRV (μm3) final | 2.0 ± 0.2 | −1.8 | <0.001 * |
| Axial PED (µm) baseline | 426.3 ± 189.6 | ||
| Axial PED (µm) FU1 | 286.0 ± 157.4 | −140.3 | 0.087 |
| Axial PED (µm) FU2 | 213.4 ± 138.0 | −212.9 | <0.001 * |
| Axial PED (µm) FU3 | 195.9 ± 100.2 | −230.4 | <0.001 * |
| Axial PED (µm) FU4 | 158.2 ± 87.0 | −268.1 | <0.001 * |
| Axial PED (µm) final | 140.4 ± 94.4 | −285.9 | <0.001 * |
| eAMD Without SMH (n = 32) | eAMD with SMH (n = 32) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) at first treatment (mean ± SD) | 75.8 ± 6.8 | 77.9 ± 7.0 | 0.09 |
| Baseline ETDRS score (mean ± SD) | 65.5 ± 11.9 | 27.8 ± 19.9 | <0.001 * |
| 12. months ETDRS score (mean ± SD) | 69.8 ± 12.1 | 46.4 ± 20.0 | <0.001 * |
| 24 months ETDRS score (mean ± SD) | 69.1 ± 9.5 | 53.2 ± 20.9 | <0.001 * |
| Baseline CRT (mean ± SD) | 342.0 ± 69.7 | 571.3 ± 236.0 | <0.001 * |
| 12 months CRT (mean ± SD) | 286 ± 57.2 | 388.1 ± 137.9 | 0.015 * |
| 24 months CRT (mean ± SD) | 268.9 ± 55.6 | 309.7 ± 164.1 | 0.11 |
| Baseline axial PED (mean ± SD) | 147.0 ± 119.4 | 448.2 ± 178.3 | <0.001 * |
| 12 months axial PED (mean ± SD) | 117.7 ± 78.6 | 320.9 ± 153.1 | 0.002 * |
| 24 months axial PED (mean ± SD) | 101.6 ± 63.2 | 217.9 ± 139.3 | 0.001 * |
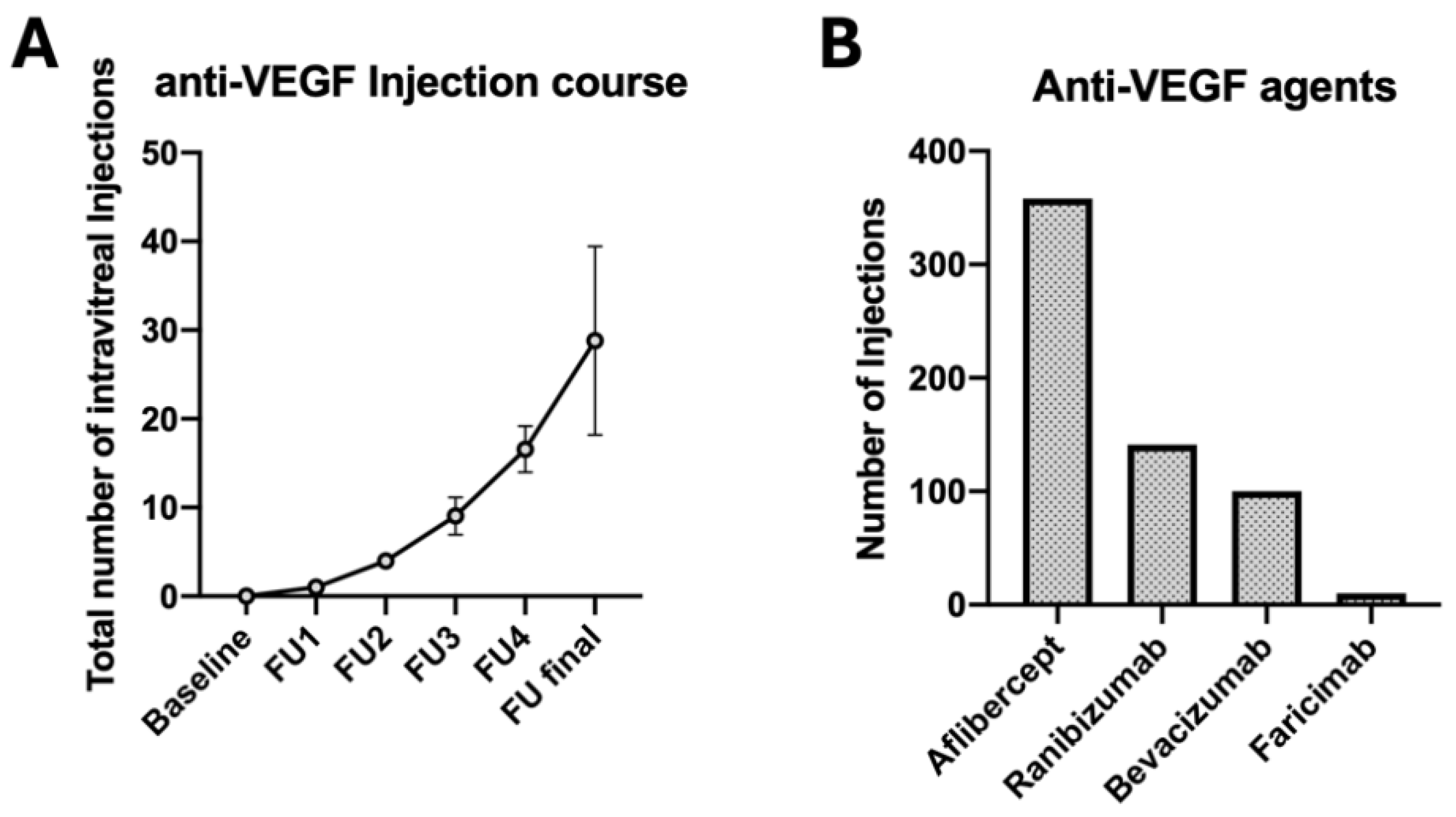
| Nr. of IVI after 12 months (mean ± SD) | 7.6 ± 1.6 | 9.4 ± 1.8 | <0.001 * |
| Nr. of IVI after 24 months (mean ± SD) | 14.4 ± 2.9 | 16.7 ± 2.1 | 0.019 * |
| Correlation Coefficient | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.322 | 0.224 |
| Days since hemorrhage | −0.048 | 0.876 |
| Size of subretinal hemorrhage (disc areas) | −0.365 | 0.269 |
| Visual acuity baseline (ETDRS) | 0.320 | 0.227 |
| Visual acuity 4 weeks after triple injection (ETDRS) | 0.575 | 0.020 * |
| Central retinal thickness baseline (µm) | 0.190 | 0.554 |
| Number of anti-VEGF injections after event | −0.141 | 0.603 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wolfrum, P.; Böhm, E.W.; König, S.; Lorenz, K.; Stoffelns, B.; Korb, C.A. Safety and Long-Term Efficacy of Intravitreal rtPA, Bevacizumab and SF6 Injection in Patients with Submacular Hemorrhage Secondary to Age-Related Macular Degeneration. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103449
Wolfrum P, Böhm EW, König S, Lorenz K, Stoffelns B, Korb CA. Safety and Long-Term Efficacy of Intravitreal rtPA, Bevacizumab and SF6 Injection in Patients with Submacular Hemorrhage Secondary to Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103449
Chicago/Turabian StyleWolfrum, Peter, Elsa Wilma Böhm, Simon König, Katrin Lorenz, Bernhard Stoffelns, and Christina A. Korb. 2025. "Safety and Long-Term Efficacy of Intravitreal rtPA, Bevacizumab and SF6 Injection in Patients with Submacular Hemorrhage Secondary to Age-Related Macular Degeneration" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103449
APA StyleWolfrum, P., Böhm, E. W., König, S., Lorenz, K., Stoffelns, B., & Korb, C. A. (2025). Safety and Long-Term Efficacy of Intravitreal rtPA, Bevacizumab and SF6 Injection in Patients with Submacular Hemorrhage Secondary to Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103449





