The Clinical and Economic Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease in Poland: Inside Patient-Level Microsimulation Modelling of CKD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of Model and Clinical Burden
2.2. Economic Burden
2.3. Statement of Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
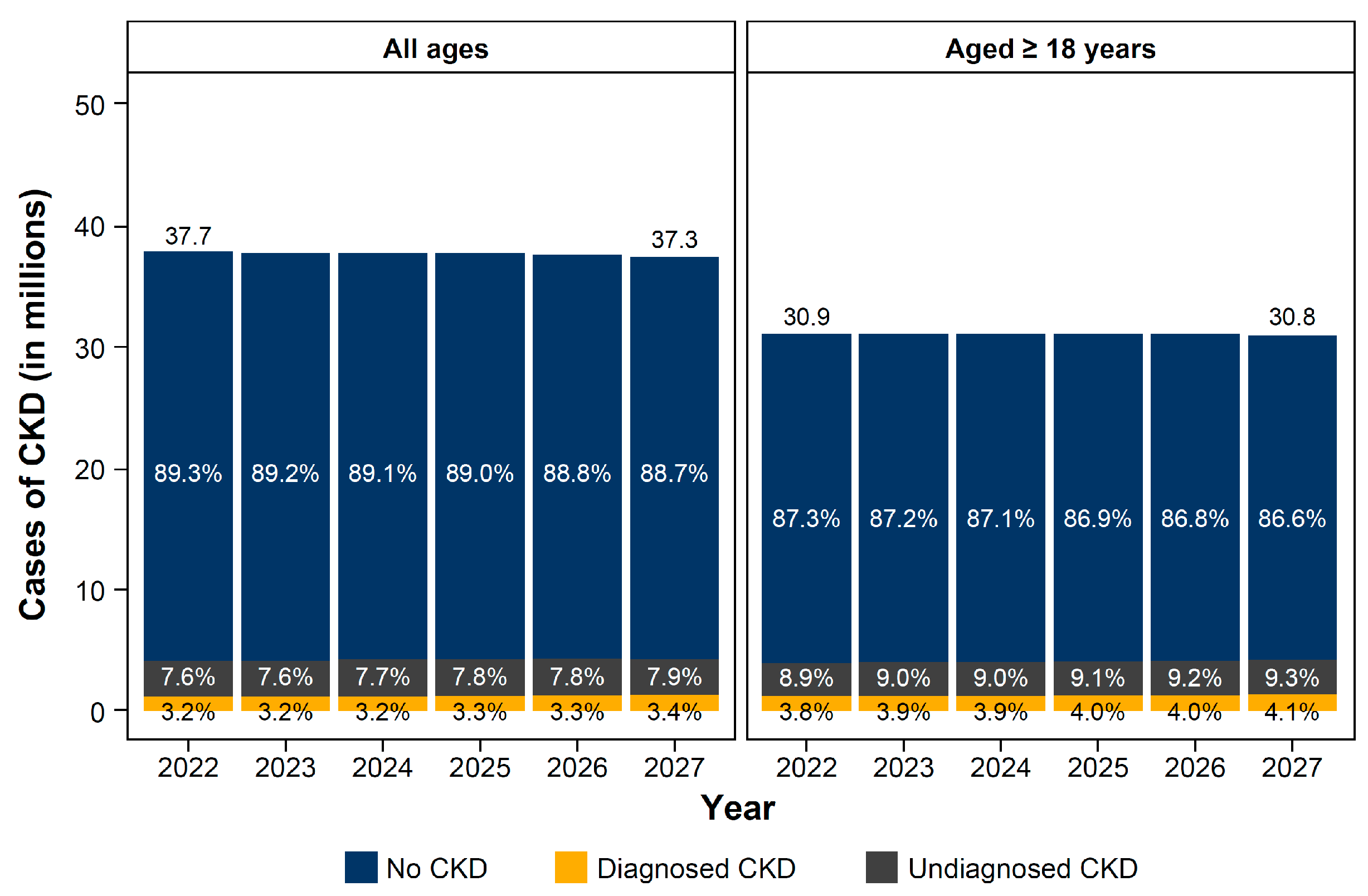
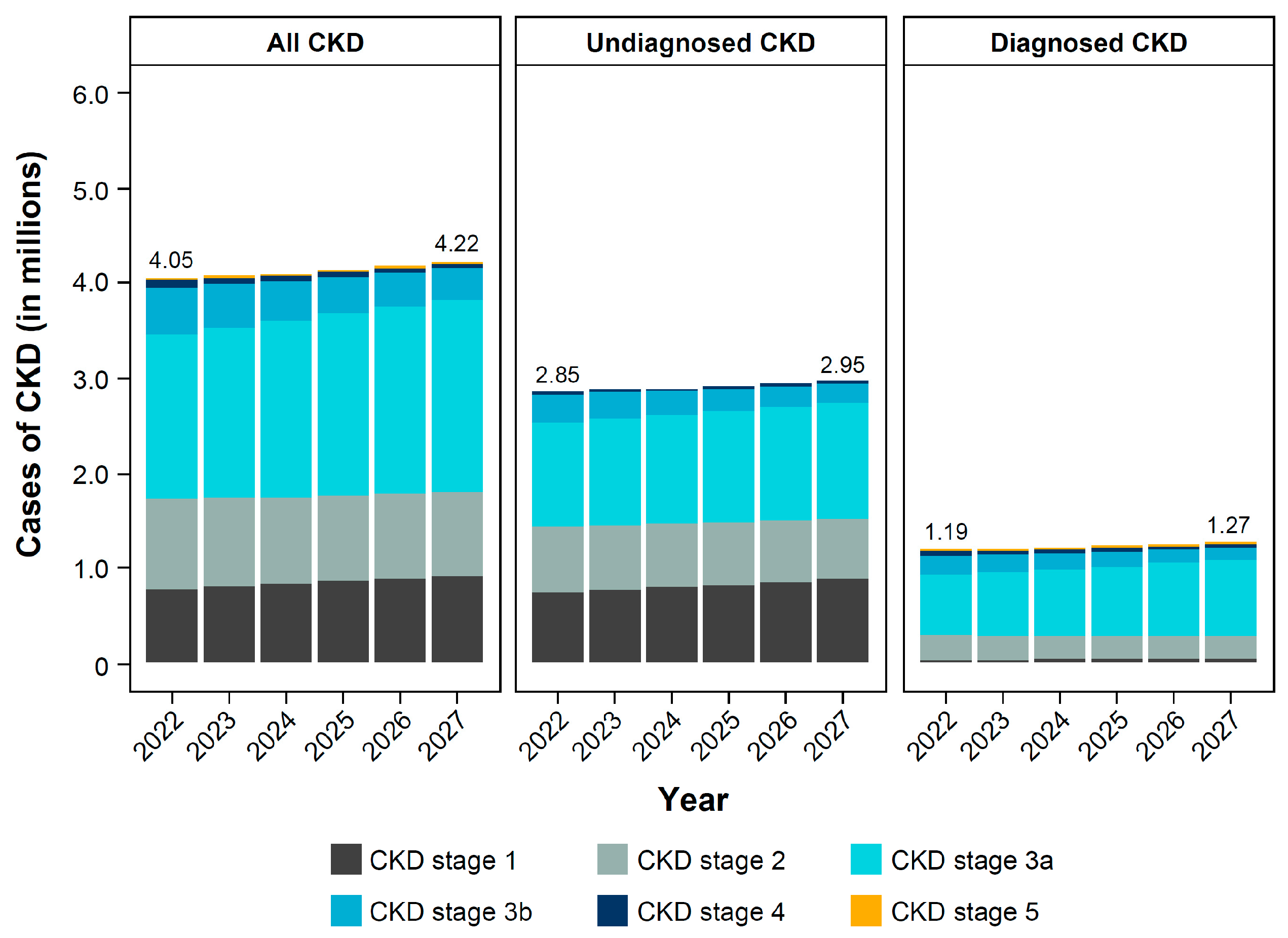
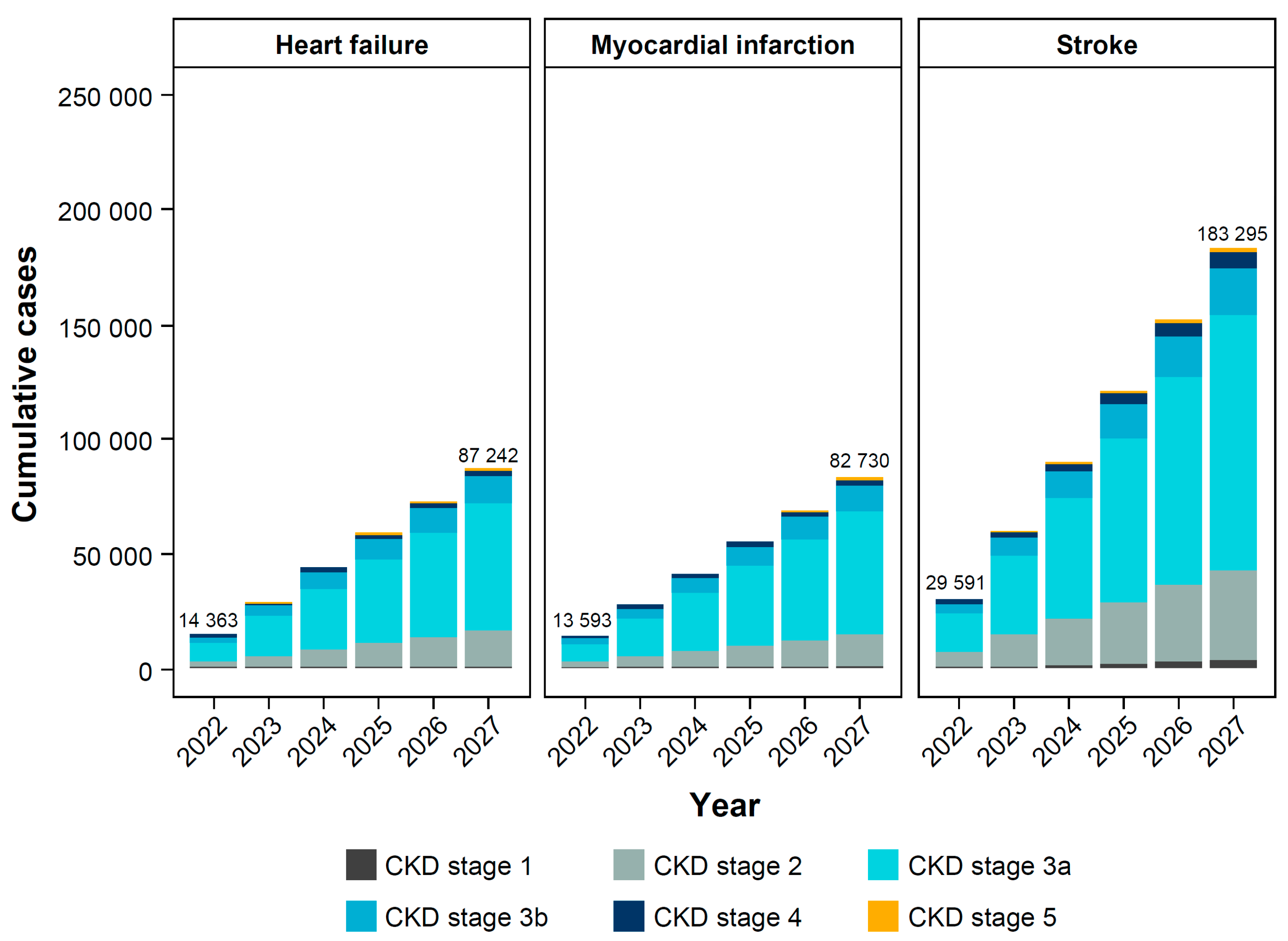
3.2. Clinical Burden of CKD
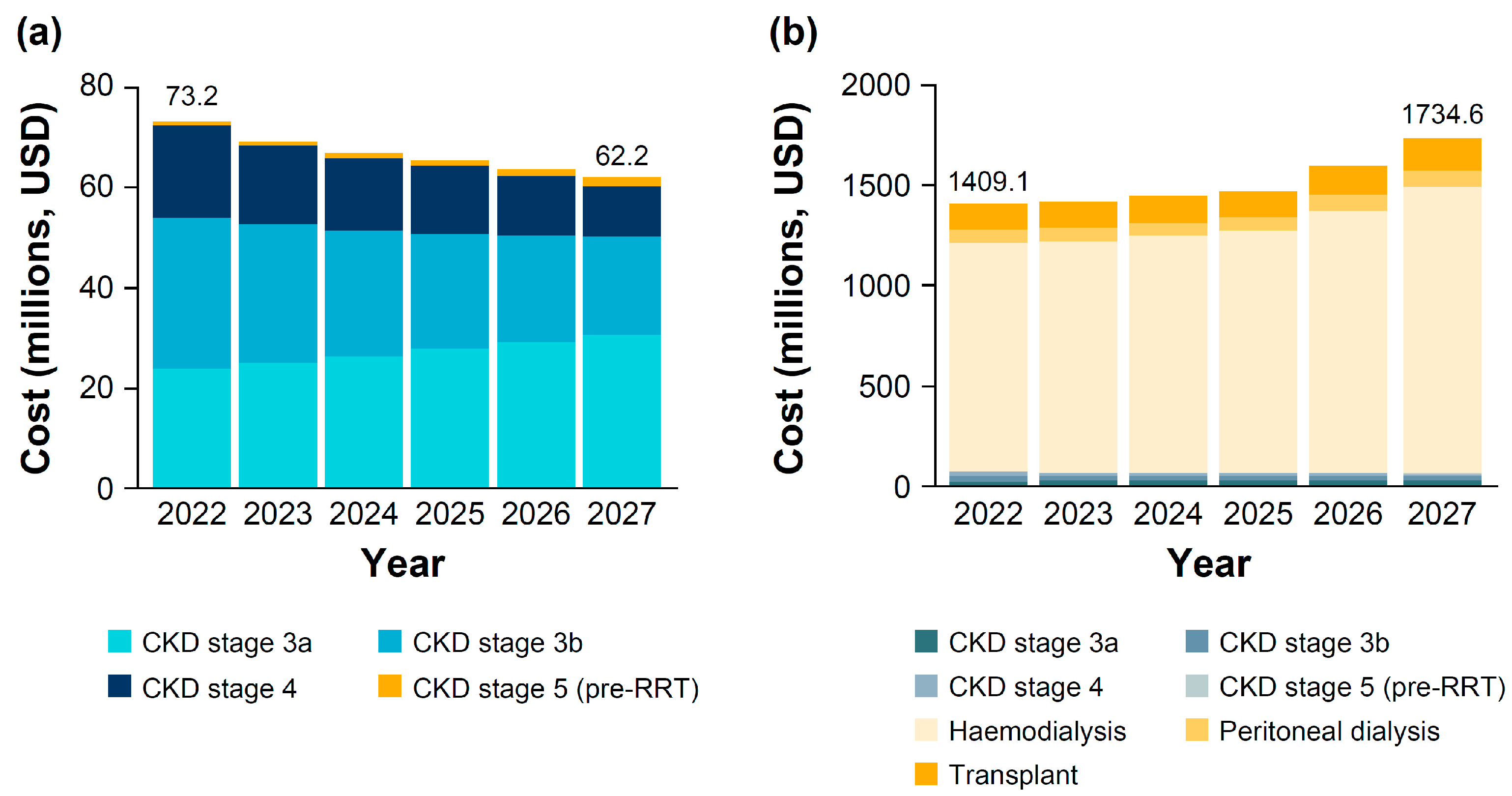
3.3. Economic Burden of CKD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: An update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. (2011) 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockwell, P.; Fisher, L.A. The global burden of chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2020, 395, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdrojewski, Ł.; Zdrojewski, T.; Rutkowski, M.; Bandosz, P.; Król, E.; Wyrzykowski, B.; Rutkowski, B. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in a representative sample of the Polish population: Results of the NATPOL 2011 survey. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinowska, A.; Kowalczyk, M.; Pruszko, C.; Prystacki, T. Dostep do Świadczeń Nefrologicznych w Polsce; Mahta: Warszawa, Poland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shlipak, M.G.; Tummalapalli, S.L.; Boulware, L.E.; Grams, M.E.; Ix, J.H.; Jha, V.; Kengne, A.P.; Madero, M.; Mihaylova, B.; Tangri, N.; et al. The case for early identification and intervention of chronic kidney disease: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazienicka-Kiełb, A.; Babicki, M.; Krajewska, M.; Oko, A.; Kłoda, K.; Mastalerz-Migas, A. Assessment of primary care physicians’ knowledge of chronic kidney disease in Poland. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1032240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.K.; Okpechi, I.G.; Levin, A.; Ye, F.; Damster, S.; Arruebo, S.; Donner, J.A.; Caskey, F.J.; Cho, Y.; Davids, M.R.; et al. An update on the global disparities in kidney disease burden and care across world countries and regions. Lancet Glob. Health 2024, 12, e382–e395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Sultan, A.; Wittbrodt, E.; Malvolti, E.; Guzek, J.; Webber, L.; Retat, L.; Garcia Sanchez, J.J.; Hungta, C.; Barone, S. POS300 Patient-reported early stage chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Levey, A.S.; de Jong, P.E.; Coresh, J.; El Nahas, M.; Astor, B.C.; Matsushita, K.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Kasiske, B.L.; Eckardt, K.U. The definition, classification, and prognosis of chronic kidney disease: A KDIGO Controversies Conference report. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E. Summary of KDIGO 2012 CKD Guideline: Behind the scenes, need for guidance, and a framework for moving forward. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Tangri, N.; Stevens, L.A. Classification of chronic kidney disease: A step forward. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 154, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonelli, M.; Muntner, P.; Lloyd, A.; Manns, B.J.; James, M.T.; Klarenbach, S.; Quinn, R.R.; Wiebe, N.; Hemmelgarn, B.R. Using proteinuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate to classify risk in patients with chronic kidney disease: A cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 154, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulware, L.E.; Jaar, B.G.; Tarver-Carr, M.E.; Brancati, F.L.; Powe, N.R. Screening for proteinuria in US adults: A cost-effectiveness analysis. JAMA 2003, 290, 3101–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, K.; White, S.; Salkeld, G.; McDonald, S.; Craig, J.C.; Chadban, S.; Cass, A. Cost-effectiveness of screening and optimal management for diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease: A modeled analysis. Value Health 2010, 13, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.; Yamagata, K.; Hoshi, S.L.; Saito, C.; Asahi, K.; Moriyama, T.; Tsuruya, K.; Yoshida, H.; Iseki, K.; Watanabe, T. Cost-effectiveness of chronic kidney disease mass screening test in Japan. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2012, 16, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlington, O.; Dickerson, C.; Evans, M.; McEwan, P.; Sörstadius, E.; Sugrue, D.; van Haalen, H.; Garcia Sanchez, J.J. Costs and Healthcare Resource Use Associated with Risk of Cardiovascular Morbidity in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Evidence from a Systematic Literature Review. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 994–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnak, M.J.; Levey, A.S.; Schoolwerth, A.C.; Coresh, J.; Culleton, B.; Hamm, L.L.; McCullough, P.A.; Kasiske, B.L.; Kelepouris, E.; Klag, M.J.; et al. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: A statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Hypertension 2003, 42, 1050–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.H.; Gullion, C.M.; Nichols, G.; Keith, D.S.; Brown, J.B. Cost of medical care for chronic kidney disease and comorbidity among enrollees in a large HMO population. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuyun, M.F.; Khaw, K.T.; Luben, R.; Welch, A.; Bingham, S.; Day, N.E.; Wareham, N.J. Microalbuminuria independently predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a British population: The European Prospective Investigation into Cancer in Norfolk (EPIC-Norfolk) population study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 33, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliberté, F.; Bookhart, B.K.; Vekeman, F.; Corral, M.; Duh, M.S.; Bailey, R.A.; Piech, C.T.; Lefebvre, P. Direct all-cause health care costs associated with chronic kidney disease in patients with diabetes and hypertension: A managed care perspective. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2009, 15, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadban, S.; Arıcı, M.; Power, A.; Wu, M.S.; Mennini, F.S.; Arango Álvarez, J.J.; Garcia Sanchez, J.J.; Barone, S.; Card-Gowers, J.; Martin, A.; et al. Projecting the economic burden of chronic kidney disease at the patient level (Inside CKD): A microsimulation modelling study. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 72, 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertow, G.M.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Eckardt, K.U.; Kanda, E.; Karasik, A.; Li, G.; Christiansen, C.F.; Stafylas, P.; Holt, S.G.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. Projecting the clinical burden of chronic kidney disease at the patient level (Inside CKD): A microsimulation modelling study. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 72, 102614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Al-Ghamdi, S.M.G.; Li, G.; Wu, M.S.; Stafylas, P.; Retat, L.; Card-Gowers, J.; Barone, S.; Cabrera, C.; Garcia Sanchez, J.J. Global Economic Burden Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Pragmatic Review of Medical Costs for the Inside CKD Research Programme. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 4405–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangri, N.; Chadban, S.; Cabrera, C.; Retat, L.; Sánchez, J.J.G. Projecting the Epidemiological and Economic Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease Using Patient-Level Microsimulation Modelling: Rationale and Methods of Inside CKD. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covic, A.; Säemann, M.; Filipov, J.; Gellert, R.; Gobin, N.; Jelaković, B.; Kabulbayev, K.; Luman, M.; Miglinas, M.; Mosenzon, O.; et al. The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention in Chronic Kidney Disease: Calls-to-Action from Nephrologists Based Mainly in Central/Eastern Europe. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2024, 49, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangri, N.; Moriyama, T.; Schneider, M.P.; Virgitti, J.B.; De Nicola, L.; Arnold, M.; Barone, S.; Peach, E.; Wittbrodt, E.; Chen, H.; et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed stage 3 chronic kidney disease in France, Germany, Italy, Japan and the USA: Results from the multinational observational REVEAL-CKD study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e067386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuffield Department of Population Health Renal Studies Group; SGLT2 inhibitor Meta-Analysis Cardio-Renal Trialists’ Consortium. Impact of diabetes on the effects of sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors on kidney outcomes: Collaborative meta-analysis of large placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 2022, 400, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, G.M.C.; Tamargo, J.; Kjeldsen, K.P.; Lainscak, M.; Agewall, S.; Anker, S.D.; Ceconi, C.; Coats, A.J.S.; Drexel, H.; Filippatos, G.; et al. Expert consensus document on the management of hyperkalaemia in patients with cardiovascular disease treated with renin angiotensin aldosterone system inhibitors: Coordinated by the Working Group on Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2018, 4, 180–188. [Google Scholar]
- Countries with Declining Population 2024. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/countries-with-declining-population (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Statistics Poland. The Situation of Older People in Poland in 2020. 2021. Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/files/gfx/portalinformacyjny/en/defaultaktualnosci/3618/1/3/1/the_situation_of_older_people_in_poland_in_2020.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Chesnaye, N.C.; Ortiz, A.; Zoccali, C.; Stel, V.S.; Jager, K.J. The impact of population ageing on the burden of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawłowicz-Szlarska, E.; Vanholder, R.; Sever, M.S.; Tuğlular, S.; Luyckx, V.; Eckardt, K.U.; Gallego, D.; Ivanov, D.; Nistor, I.; Shroff, R.; et al. Distribution, preparedness and management of Ukrainian adult refugees on dialysis-an international survey by the Renal Disaster Relief Task Force of the European Renal Association. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Rutkowski, B.; Jagodziński, P.; Rutkowski, P.; Przygoda, J.; Lewandowska, D.; Czerwiński, J.; Kamiński, A.; Gellert, R. Aktualny stan dializoterapii w polsce—2020. Nefrol. Dial. Pol. 2021, 25, 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- Król, E.; Rutkowski, B.; Czarniak, P.; Kraszewska, E.; Lizakowski, S.; Szubert, R.; Czekalski, S.; Sułowicz, W.; Wiecek, A. Early detection of chronic kidney disease: Results of the PolNef study. Am. J. Nephrol. 2009, 29, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdrojewski, Ł.; Król, E.; Rutkowski, B.; Piotrowski, W.; Pająk, A.; Drygas, W.; Zdrojewski, T. Chronic kidney disease in Polish elderly population aged 75+: Results of the WOBASZ Senior Survey. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, P.; Khunti, K.; Cebrián, A.; Deed, G. Early Identification and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Narrative Review of the Crucial Role of Primary Care Practitioners. Adv. Ther. 2024, 41, 3757–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Baseline Characteristic | Total Population (n = 37,739,779) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male, n (%) | 18,283,212 (48.4) |
| Age groups, years, n (%) | |
| 0–17 | 6,849,708 (18.1) |
| 18–34 | 7,426,902 (19.7) |
| 35–64 | 15,909,721 (42.2) |
| ≥65 | 7,553,448 (20.0) |
| CKD stage, n (%) | |
| Stage 1 | 773,400 (2.0) |
| Stage 2 | 960,191 (2.5) |
| Stage 3a | 1,724,862 (4.6) |
| Stage 3b | 500,306 (1.3) |
| Stage 4 | 81,463 (0.2) |
| Stage 5 | 9239 (<0.1) |
| CKD, n (%) | |
| Total | 4,049,462 (10.7) |
| Diagnosed | 1,211,948 (3.2) |
| Comorbidities, n (%) * | |
| Heart failure | 692,603 (17.1) |
| Hypertension | 2,319,040 (57.3) |
| Type 2 diabetes | 809,364 (20.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masajtis-Zagajewska, A.; Kurek, R.; Modrzyńska, K.; Coker, T.; Nowicki, M. The Clinical and Economic Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease in Poland: Inside Patient-Level Microsimulation Modelling of CKD. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010054
Masajtis-Zagajewska A, Kurek R, Modrzyńska K, Coker T, Nowicki M. The Clinical and Economic Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease in Poland: Inside Patient-Level Microsimulation Modelling of CKD. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasajtis-Zagajewska, Anna, Renata Kurek, Katarzyna Modrzyńska, Timothy Coker, and Michał Nowicki. 2025. "The Clinical and Economic Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease in Poland: Inside Patient-Level Microsimulation Modelling of CKD" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010054
APA StyleMasajtis-Zagajewska, A., Kurek, R., Modrzyńska, K., Coker, T., & Nowicki, M. (2025). The Clinical and Economic Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease in Poland: Inside Patient-Level Microsimulation Modelling of CKD. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010054







