The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Metformin Use on Outcomes After Endovascular Aneurysm Repair
Abstract
:1. Introduction
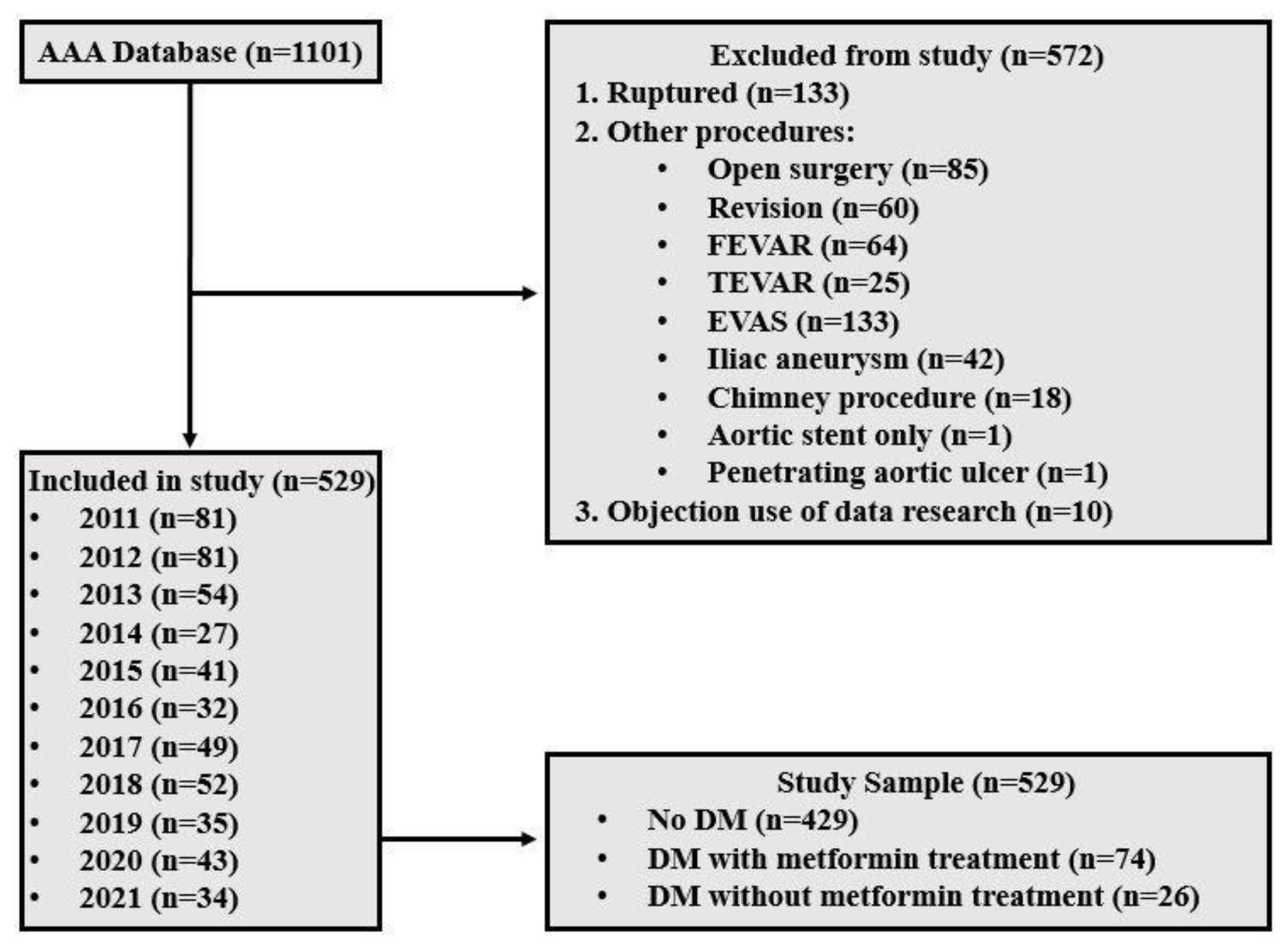
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Definitions
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient and AAA Characteristics
3.2. Procedure, Hospitalization, and 30-Day Complications
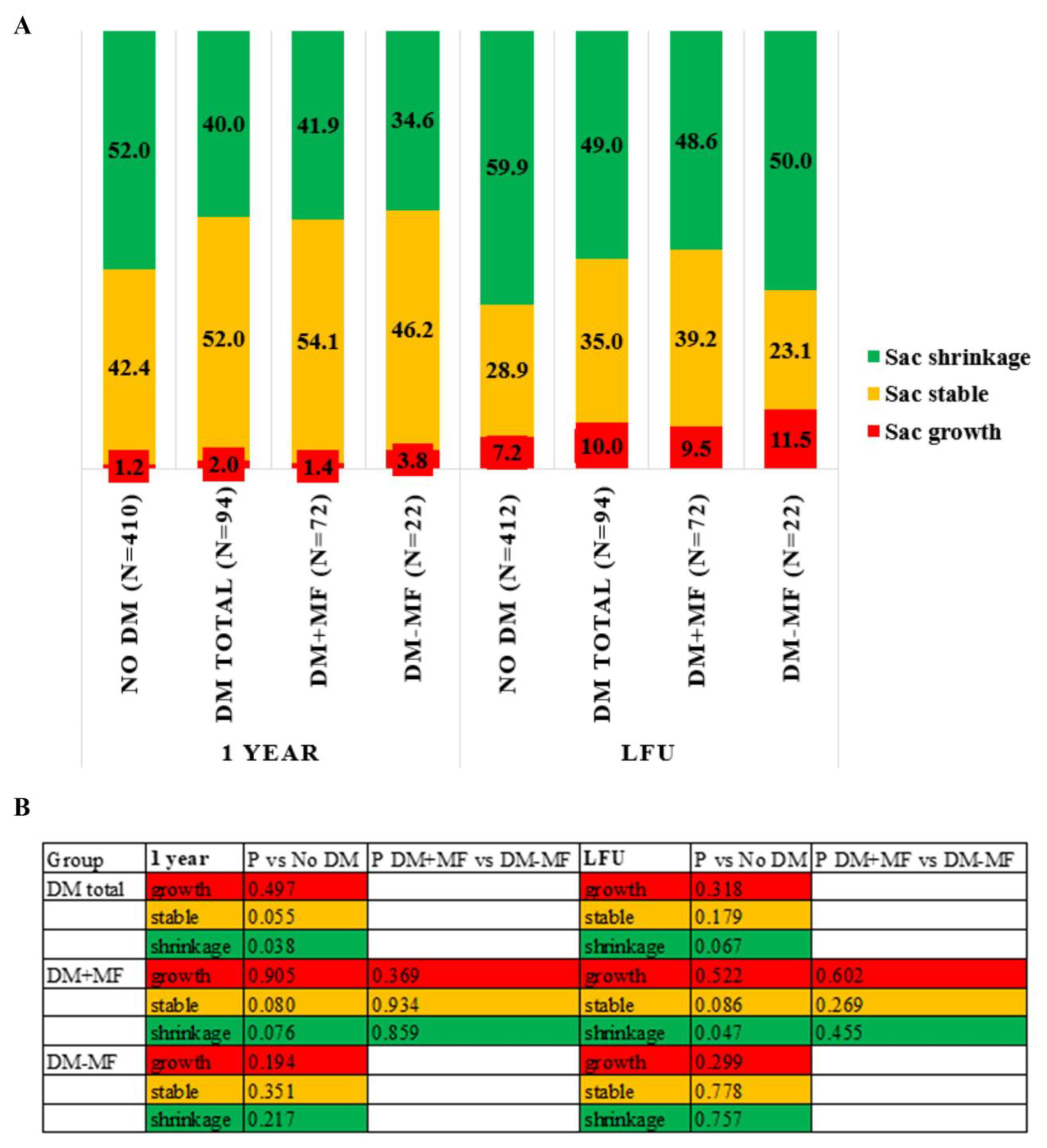
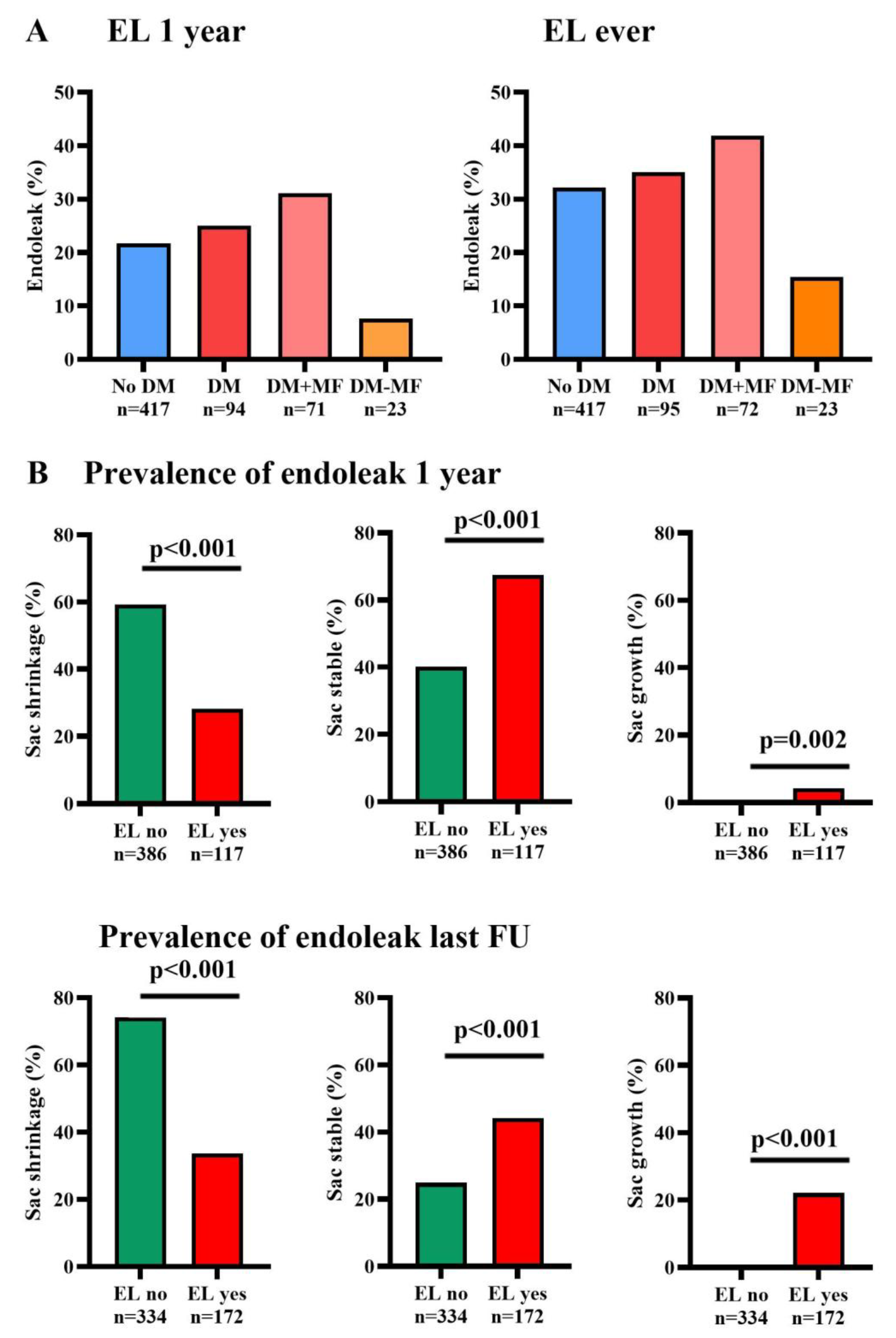
3.3. Sac Remodeling
3.4. Secondary Endpoints
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lalys, F.; Daoudal, A.; Gindre, J.; Goksu, C.; Lucas, A.; Kaladji, A. Influencing factors of sac shrinkage after endovascular aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 65, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos Goncalves, F.; Baderkhan, H.; Verhagen, H.J.; Wanhainen, A.; Bjorck, M.; Stolker, R.J.; Hoeks, S.E.; Mani, K. Early sac shrinkage predicts a low risk of late complications after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rijswijk, R.E.; Jebbink, E.G.; Zeebregts, C.J.; Reijnen, M. A systematic review of anatomic predictors of abdominal aortic aneurysm remodeling after endovascular repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 75, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederle, F.A. The Strange Relationship between Diabetes and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. 2012, 43, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Zafar, M.A.; Ziganshin, B.A.; Elefteriades, J.A. Diabetes Mellitus: Is It Protective against Aneurysm? A Narrative Review. Cardiology 2018, 141, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dattani, N.; Sayers, R.D.; Bown, M.J. Diabetes mellitus and abdominal aortic aneurysms: A review of the mechanisms underlying the negative relationship. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2018, 15, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golledge, J.; Moxon, J.; Pinchbeck, J.; Anderson, G.; Rowbotham, S.; Jenkins, J.; Bourke, M.; Bourke, B.; Dear, A.; Buckenham, T.; et al. Association between metformin prescription and growth rates of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoga, N.K.; Rothenberg, K.A.; Suarez, P.; Ho, T.V.; Mell, M.W.; Xu, B.; Curtin, C.M.; Dalman, R.L. Metformin prescription status and abdominal aortic aneurysm disease progression in the U.S. veteran population. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 69, 710–716.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skovbo Kristensen, J.S.; Krasniqi, L.; Obel, L.M.; Kavaliunaite, E.; Liisberg, M.; Lindholt, J.S. Exploring Drug Re-Purposing for Treatment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2024, 67, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Shen, L.; Gao, P.; Li, G.; He, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhou, H.; Yuan, H.; Jin, X.; Wu, X. Effect of AMPK signal pathway on pathogenesis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 92827–92840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, N.; Xiong, J.; Kettler, E.B.; Xuan, H.J.; Glover, K.J.; Mell, M.W.; Xu, B.H.; Dalman, R.L. Metformin treatment status and abdominal aortic aneurysm disease progression. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 46–54.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Merrienboer, T.A.R.; Rombouts, K.B.; Bogunovic, N.; Mieremet, A.; Meekel, J.P.; Balm, R.; de Waard, V.; Yeung, K.K. Metformin Improves the Function of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Patient-Derived Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanhainen, A.; Unosson, J.; Mani, K.; Gottsater, A.; Investigators, M.T. The Metformin for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Growth Inhibition (MAAAGI) Trial. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2021, 61, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golledge, J.; Arnott, C.; Moxon, J.; Monaghan, H.; Norman, R.; Morris, D.; Li, Q.; Jones, G.; Roake, J.; Bown, M.; et al. Protocol for the Metformin Aneurysm Trial (MAT): A placebo-controlled randomised trial testing whether metformin reduces the risk of serious complications of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Trials 2021, 22, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limiting AAA With Metformin (LIMIT) Trial (LIMIT). 2020. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04500756 (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Metformin Therapy in Non-Diabetic AAA Patients (MetAAA) 2018. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03507413 (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Chaikof, E.L.; Blankensteijn, J.D.; Harris, P.L.; White, G.H.; Zarins, C.K.; Bernhard, V.M.; Matsumura, J.S.; May, J.; Veith, F.J.; Fillinger, M.F.; et al. Reporting standards for endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2002, 35, 1048–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikof, E.L.; Dalman, R.L.; Eskandari, M.K.; Jackson, B.M.; Lee, W.A.; Mansour, M.A.; Mastracci, T.M.; Mell, M.; Murad, M.H.; Nguyen, L.L.; et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 2–77.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oderich, G.S.; Forbes, T.L.; Chaer, R.; Davies, M.G.; Lindsay, T.F.; Mastracci, T.; Singh, M.J.; Timaran, C.; Woo, E.Y. Reporting standards for endovascular aortic repair of aneurysms involving the renal-mesenteric arteries. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 73, 4s–52s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Su, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y. Double-edged sword of diabetes mellitus for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1095608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taimour, S.; Avdic, T.; Franzén, S.; Zarrouk, M.; Acosta, S.; Nilsson, P.; Miftaraj, M.; Eliasson, B.; Svensson, A.M.; Gottsäter, A. Survival, cardiovascular morbidity, and reinterventions after elective endovascular aortic aneurysm repair in patients with and without diabetes: A nationwide propensity-adjusted analysis. Vasc. Med. 2019, 24, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Png, C.Y.M.; Tadros, R.O.; Kang, M.; Beckerman, W.E.; Tardiff, M.L.; Vouyouka, A.G.; Marin, M.L.; Faries, P.L. The Protective Effects of Diabetes Mellitus on Post-EVAR AAA Growth and Reinterventions. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 43, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez Marcos, F.; Llaneza Coto, J.M.; Camblor Santervas, L.A.; Zanabili Al-Sibbai, A.A.; Alonso Perez, M. Five Year Post Endovascular Aneurysm Repair Aneurysmal Sac Evolution in the GREAT Registry: An Insight in Diabetics Using Propensity Matched Controls. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2023, 67, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tongeren, O.; Rastogi, V.; Vecht, D.E.; Ultee, K.H.J.; Hoeks, S.E.; Verhagen, H.J.M.; de Bruin, J.L. Metformin Use and Long-term Outcomes Including Aneurysm Sac Dynamics Following EVAR for Infrarenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: “A Retrospective Study”. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2024, 15266028241268500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rango, P.; Farchioni, L.; Fiorucci, B.; Lenti, M. Diabetes and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. 2014, 47, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climent, E.; Benaiges, D.; Chillarón, J.J.; Flores-Le Roux, J.A.; Pedro-Botet, J. Diabetes mellitus as a protective factor of abdominal aortic aneurysm: Possible mechanisms. Clin. Investig. Arterioscler. 2018, 30, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, V.; Summers, S.P.; Yadavalli, S.D.; Perrier, J.; Allievi, S.; Jabbour, G.; Stangenberg, L.; de Bruin, J.L.; Jones, D.; Ferran, C.J.; et al. Association between Diabetes Status and Long-term Outcomes Following Open and Endovascular Repair of Infrarenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2024, 80, 1685–1696.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Yang, H.; Hu, M.; Chen, X.; Qin, X. Effect of Diabetes on Long-term Mortality following Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair: A Systemic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 64, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanhainen, A.; Bergqvist, D.; Bjorck, M. Measuring the abdominal aorta with ultrasonography and computed tomography—Difference and variability. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2002, 24, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanhainen, A.; Van Herzeele, I.; Bastos Goncalves, F.; Bellmunt Montoya, S.; Berard, X.; Boyle, J.R.; D’Oria, M.; Prendes, C.F.; Karkos, C.D.; Kazimierczak, A.; et al. Editor’s Choice—European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2024 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Abdominal Aorto-Iliac Artery Aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2024, 67, 192–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No DM (n = 429) | DM Total (n = 100) | p | DM + MF (n = 74) | p | DM-MF (n = 26) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 72.8 ± 8.1 | 73.0 ± 0.82 | 0.852 | 72.2 ± 7.7 | 0.551 | 75.2 ± 9.3 | 0.164 |
| Male sex | 361 (84.1) | 89 (89.0) | 0.220 | 65 (87.8) | 0.416 | 24 (92.3) | 0.263 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.8 (23.8; 28.4) | 27.81 (24.6; 31.0) | <0.001 | 27.8 (24.8; 31.0) | <0.001 | 27.6 ± 4.5 | 0.058 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 143.0 (127; 156.5) | 143.06 (127.5; 160.0) | 0.596 | 143.0 (125.0; 160.0) | 0.761 | 143.0 (130.0; 156.0) | 0.557 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 81.0 (74; 89) | 81.06 (73.0; 87.0) | 0.348 | 81.0 (74.0; 87.0) | 0.410 | 82.0 (70.0; 87.0) | 0.599 |
| Heart Rate (bpm) | 72.5 (64; 84.5) | 74 (66.0; 85.0) | 0.188 | 73.0 (66.0; 85.0) | 0.471 | 78.0 (70.0; 85.0) | 0.134 |
| ASA classification ≤ 2 | 195 (46.9) | 26 (26.0) | <0.001 | 22 (29.7) | 0.025 | 4 (15.4) | 0.002 |
| ASA classification ≥ 3 | 221 (53.1) | 73 (73.0) | 51 (68.9) | 22 (84.6) | |||
| Hypertension | 293 (69.3) | 86 (86) | <0.001 | 62 (83.8) | 0.011 | 24 (92.3) | 0.012 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 295 (76.8) | 80 (87.0) | 0.033 | 59 (79.7) | 0.011 | 21 (80.8) | 0.105 |
| Cardiac history | 176 (46.0) | 56 (60.2) | 0.014 | 43 (58.1) | 0.017 | 13 (50.0) | 0.324 |
| Pulmonary history | 79 (21.1) | 24 (26.4) | 0.279 | 20 (27.0) | 0.115 | 4 (15.4) | 0.602 |
| Renal history | 110 (26.3) | 34 (35.4) | 0.073 | 23 (31.1) | 0.321 | 11 (42.3) | 0.037 |
| Tobacco use a | 142 (35.0) | 36 (37.1) | 0.692 | 27 (36.5) | 0.680 | 9 (34.6) | 0.917 |
| DM type 2, controlled by diet or oral agents | - | 77 (77.0) | 60 (81.1) | 17 (65.4) | |||
| DM type 2, insulin-controlled b | - | 21 (21.0) | 14 (18.9) | 7 (26.9) | |||
| DM type 1 | - | 2 (2.0) | - | 2 (7.7) | |||
| Glucose (mmol/L) c | 5.7 (5.2; 6.3) | 9.1 (6.5; 11.0) | <0.001 | 9.2 (6.5; 11.4) | <0.001 | 8.8 (6.7; 10.4) | <0.001 |
| Metformin | - | 74 (76.0) | <0.001 | 74 (100) | <0.001 | - | - |
| Other Oral DM medication d | - | 60 (66.7) | <0.001 | 49 (66.2) | <0.001 | 10 (38.5) | <0.001 |
| Insulin e | - | 38 (42.2) | <0.001 | 28 (37.8) | <0.001 | 10 (38.5) | <0.001 |
| Metformin only | - | 20 (22.2) | <0.001 | 20 (27.0) | <0.001 | - | - |
| AAA characteristics | |||||||
| Maximum aneurysm diameter (mm) | 57.0 (53.0; 63.0) | 56.5 (53.2; 62.7) | 0.823 | 57.0 (54.0; 63.0) | 0.794 | 55.0 (53.0; 59.0) | 0.350 |
| Infrarenal aortic neck diameter (mm) | 23.5 (21.0; 25.0) | 24.0 (22.0; 26.0) | 0.320 | 23.0 (21.0; 25.0) | 0.696 | 26.0 (24.0; 28.0) | 0.004 |
| Infrarenal aortic neck length (mm) | 27.5 (19.0; 37.0) | 29.5 (20.0; 40.0) | 0.212 | 30.0 (21.0; 38.0) | 0.232 | 29.0 (16.0; 50.5) | 0.610 |
| Angle between AAA and neck (degrees) | 41.5 (27.0; 60.0) | 35.0 (23.0; 44.5) | 0.052 | 30.0 (23.0; 49.0) | 0.080 | 40.0 (26.0; 40.0) | 0.327 |
| Right CIA diameter (mm) | 16.0 (13.0; 20.0) | 16.0 (13.0; 19.5) | 0.986 | 17.0 (14.0; 22.5) | 0.227 | 14.0 (11.0; 18.0) | 0.050 |
| Left CIA diameter (mm) | 15.0 (13.0; 19.0) | 15.0 (13.0; 18.0) | 0.679 | 16.0 (14.0; 21.0) | 0.099 | 13.05 (12.0; 15.0) | 0.064 |
| Type of aneurysm | 0.749 | 0.618 | 0.831 | ||||
| Saccular | 39 (9.7) | 10 (10.8) | 8 (10.8) | 2 (7.7) | |||
| Fusiform | 365 (90.3) | 83 (89.2) | 61 (82.4) | 22 (84.6) | |||
| Device type | 0.463 | 0.338 | 0.868 | ||||
| Medtronic Endurant | 241 (56.3) | 55 (55.0) | 40 (54.1) | 15 (57.7) | |||
| Gore Excluder | 134 (31.3) | 32 (32.0) | 26 (35.1) | 6 (23.1) | |||
| Endologix AFX | 21 (4.9) | 4 (4.0) | - | 4 (15.4) | |||
| Other | 32 (7.5) | 9 (9.0) | 8 (10.8) | 1 (3.8) |
| No DM (n = 429) | DM Total (n = 100) | p | DM + MF (n = 74) | p | DM-MF (n = 26) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time hospitalization (days) | 3.0 (2.0; 4.0) | 3.0 (2.0; 5.5) | 0.017 | 4.0 (2.0; 6.0) | 0.016 | 3.0 (2.0; 5.0) | 0.425 |
| Blood loss (mL) | 100.0 (0.0; 300.0) | 100.0 (0.0; 250.0) | 0.719 | 150.0 (5.0; 300.0) | 0.371 | 0.0 (0.0; 100.0) | 0.020 |
| Total procedure time (min) | 88.0 (71.5; 112.0) | 100.5 (75.5; 120.0) | 0.039 | 98.0 (76.0; 124.0) | 0.039 | 102.5 (75.0; 114.0) | 0.474 |
| Technical success | 369 (86.0) | 88 (88.0) | 0.602 | 69 (93.2) | 0.087 | 19 (73.1) | 0.071 |
| Assisted technical success | 421 (98.1) | 99 (99.0) | 0.547 | 74 (100.0) | 0.236 | 25 (96.2) | 0.481 |
| Conversion to open repair | 1 (0.2) | 1 (3.0) | 0.632 | 1 (1.4) | 0.683 | 0 (0.0) | 0.812 |
| Complications during hospitalization | 99 (23.1) | 38 (38.0) | 0.002 | 27 (36.5) | 0.011 | 11 (42.3) | 0.026 |
| Systemic complications | 31 (31.1) | 8 (21.0) | 4 (14.8) | 4 (36.4) | |||
| Urine tract infection | 2 (2.0) | 1 (2.6) | 1 (3.7) | - | |||
| Renal function deterioration | 7 (7.1) | 1 (2.6) | - | 1 (9.1) | |||
| Fever | 20 (20.2) | 5 (13.2) | 3 (11.1) | 2 (18.2) | |||
| Pulmonary complications | 13 (13.5) | 5 (13.2) | 0.499 | 4 (14.8) | 0.250 | 1 (9.1) | 0.643 |
| Cardiac complications | 19 (19.8) | 7 (18.4) | 0.505 | 6 (23.1) | 0.872 | 1 (9.1) | 0.302 |
| Angina (NYHA class) | 1 (1.0) | - | - | - | |||
| Myocardial infarction | 3 (3.0) | 1 (2.6) | - | 1 (9.1) | |||
| Coronary artery disease | 1 (1.0) | - | - | - | |||
| Atrial fibrillation | 5 (5.1) | - | - | - | |||
| Acute heart failure | 2 (2.0) | 1 (2.6) | 1 (3.7) | - | |||
| Procedure related deaths | 10 (2.3) | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Merrienboer, T.A.R.; Warlich, V.; Holewijn, S.; Driessen, W.; Yeung, K.K.; Reijnen, M.M.P.J. The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Metformin Use on Outcomes After Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010295
van Merrienboer TAR, Warlich V, Holewijn S, Driessen W, Yeung KK, Reijnen MMPJ. The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Metformin Use on Outcomes After Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(1):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010295
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Merrienboer, Tara A. R., Veerle Warlich, Suzanne Holewijn, Wouter Driessen, Kak K. Yeung, and Michel M. P. J. Reijnen. 2025. "The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Metformin Use on Outcomes After Endovascular Aneurysm Repair" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 1: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010295
APA Stylevan Merrienboer, T. A. R., Warlich, V., Holewijn, S., Driessen, W., Yeung, K. K., & Reijnen, M. M. P. J. (2025). The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Metformin Use on Outcomes After Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(1), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010295






