Impact of Vision Defects on Tooth Shade Selection: A Comparative of Spectrophotometry and Shade Guides in a Cross-Sectional Clinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient Selection
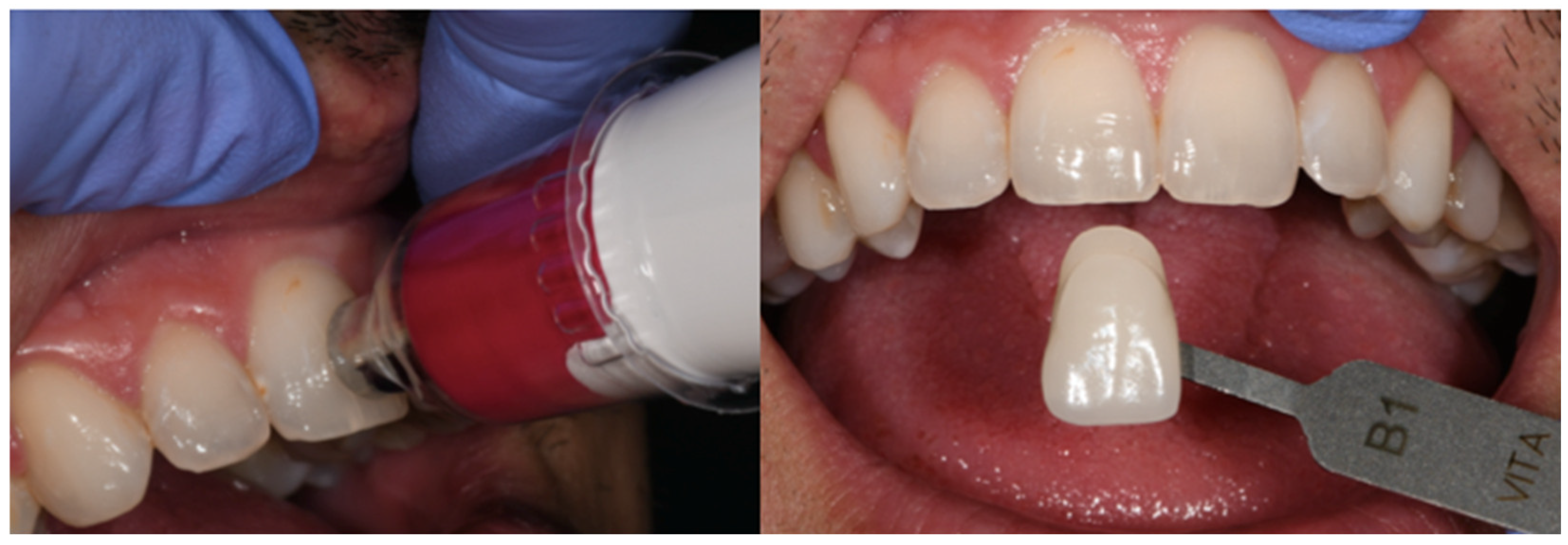
2.3. Measurement Process
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dudkiewicz, K.; Łacinik, S.; Jedliński, M.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Grocholewicz, K. Dental color matching instruments and systems. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 27, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.J.; Devigus, A.; Paravina, R.D.; Mieleszko, A.J. Fundamentals of Color: Shade Matching and Communication in Esthetic Dentistry, 2nd ed.; Quintessence: Chicago, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Joiner, A.; Luo, W. Tooth colour and whiteness: A review. J. Dent. 2017, 67S, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSaleh, S.; Labban, M.; AlHariri, M.; Tashkandi, E. Evaluation of self-shade matching ability of dental students using visual and instrumental means. J. Dent. 2012, 40, e82–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanini, L. Light and color in anterior composite restorations. Pract. Periodont. Aesthet. Dent. 1996, 8, 673–682. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, W.M. Review of Translucency Determinations and Applications to Dental Materials: Translucency of Dental Materials. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2014, 26, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, B.G.; Gaidarji, B.; Righes, D.Z.; Pecho, O.E.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Durand, L.B. Masking ability of resin composites: A scoping review. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2023, 35, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Yu, B. Measurement of opalescence of tooth enamel. J. Dent. 2007, 35, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öngül, D.; Şermet, B.; Balkaya, M.C. Visual and instrumental evaluation of color match ability of 2 shade guides on a ceramic system. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2012, 108, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitel, M.L. Optimizing Your Shade-Matching Success: Tips, Tools, and Clinical Techniques. Dent. Today 2015, 34, 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Rondón, L.F.; Ramírez, R.; Pecho, O.E. Comparison of visual shade matching and photographic shade analysis. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2022, 34, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, A.G.; Meyer, A.; Wu, W.; Wichman, C.S. Lighting conditions used during visual shade matching in private dental offices. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaei, M.; Ghanbarzadeh, J.; Keyvanloo, S.; Alavi, S.; Jafarzadeh, H. Shade Matching Performance of Dental Students with Three Various Lighting Conditions. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2013, 14, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terry, D.A.; Geller, W.; Tric, O.; Anderson, M.J.; Tourville, M.; Kobashigawa, A. Anatomical form defines color: Function, form, and aesthetics. Pract. Proced. Aesthetic Dent. 2002, 14, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-López, J.; Perez, M.M.; Lucena, C.; Pulgar, R.; López-Toruño, A.; Tejada-Casado, M.; Ghinea, R. Visual and instrumental coverage error of two dental shade guides: An in vivo study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 5961–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayed, M.A.; Alnasyan, A.S.; Aljutayli, A.A.; Alzaben, M.M.; Alrusayni, W.M.; Al Hujaylan, A.A. Considerations and Implications in Shade Selection for Dental Restorations: A Review. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2021, 13 (Suppl. S2), S898–S902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greţa, D.C.; Gasparik, C.; Colosi, H.A.; Dudea, D. Color matching of full ceramic versus metal-ceramic crowns—A spectrophotometric study. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2020, 93, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurema, A.L.; Claudino, E.S.; Torres, C.R.; Bresciani, E.; Caneppele, T.M. Effect of Over-the-counter Whitening Products associated or Not with 10% Carbamide Peroxide on Color Change and Microhardness: In vitro Study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2018, 19, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiliagkou, A.; Diamantopoulou, S.; Papazoglou, E.; Kakaboura, A. Evaluation of reliability and validity of three dental color-matching devices. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2016, 11, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lakhanpal, S.; Neelima, M. Accuracy of Three Shade-matching Devices in Replicating the Shade of Metal Ceramic Restorations: An in vitro Study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2016, 17, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrea, J.; Gurrea, M.; Bruguera, A.; Sampaio, C.; Janal, M.; Bonfante, E. Evaluation of Dental Shade Guide Variability Using Cross-Polarized Photography. Int. J. Periodont. Restor. Dent. 2016, 36, e76–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiefer, U.; Kraus, C.; Baumbach, P.; Ungewiß, J.; Michels, R. Refractive errors: Epidemiology, effects and treatment options. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2016, 113, 693. [Google Scholar]
- Harb, E.N.; Wildsoet, C.F. Origins of Refractive Errors: Environmental and Genetic Factors. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2019, 5, 47–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswini, K.K.; Ramanarayanan, V.; Rejithan, A.; Sajeev, R.; Suresh, R. The effect of gender and clinical experience on shade perception. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2019, 31, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosla, A.; Maini, A.; Wangoo, A.; Singh, S.; Mehar, D. Prevalence of Colour Vision Anomalies Amongst Dental Professionals and its Effect on Shade Matching of Teeth. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, ZC33–ZC36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsy, N.; Holiel, A.A. Color difference for shade determination with visual and instrumental methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2023, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohlen, B.; Hawlina, M.; Pompe, M.T.; Kopač, I. Do Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Color-Vision Deficiencies Influence Shade-Matching Ability? Int. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 31, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlen, B.; Hawlina, M.; Kopač, I. The Influence of the Extent of Color-Vision Deficiency on Shade-Matching Ability. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2019, 53, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, K.; Devigus, A.; Wentaschek, S.; Igiel, C.; Scheller, H.; Paravina, R. Comparison of visual shade matching and electronic color measurement device. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2017, 12, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaju, R.; Nagai, S.; Karimbux, N.; Da Silva, J. Evaluating tooth color matching ability of dental students. J. Dent. Educ. 2010, 74, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecho, O.; Ghinea, R.; Perez, M.; Della Bona, A. Influence of Gender on Visual Shade Matching in Dentistry. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2017, 29, E15–E23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samra, A.P.B.; Moro, M.G.; Mazur, R.F.; Vieira, S.; De Souza, E.M.; Freire, A. Performance of Dental Students in Shade Matching: Impact of Training. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2017, 29, E24–E32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahn, E.; Tortora, S.; Olate, B.; Cacciuttolo, F.; Kernitsky, J.; Jorquera, G. Comparison of visual analog shade matching, a digital visual method with a cross-polarized light filter, and a spectrophotometer for dental color matching. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 125, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberato, W.; Barreto, I.; Costa, P.; de Almeida, C.; Pimentel, W.; Tiossi, R. A comparison between visual, intraoral scanner, and spectrophotometer shade matching: A clinical study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitrarsu, V.; Chidambaranathan, A.; Balasubramaniam, M. Analysis of Shade Matching in Natural Dentitions Using Intraoral Digital Spectrophotometer in LED and Filtered LED Light Sources. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, e68–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igiel, C.; Lehmann, K.M.; Ghinea, R.; Weyhrauch, M.; Hangx, Y.; Scheller, H. Reliability of visual and instrumental color matching. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2017, 29, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameswaran, V.; Anilkumar, S.; Lylajam, S.; Rajesh, C.; Narayan, V. Comparison of accuracies of an intraoral spectrophotometer and conventional visual method for shade matching using two shade guide systems. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2016, 16, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohlen, B.; Hawlina, M.; Šober, K.; Kopač, I. Tooth Shade-Matching Ability Between Groups of Students with Different Color Knowledge. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 29, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfouzan, A.F.; Alqahtani, H.M.; Tashkandi, E.A. The Effect of Color Training of Dental Students’ on Dental Shades Matching Quality: Effect of color training. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2017, 29, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Jain, V.; Yadav, N. Dental students’ tooth shade selection ability in relation to years of dental education. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 4010–4014. [Google Scholar]
- Śmielecka, M.; Dorocka-Bobkowska, B. Effects of different light sources on tooth shade selection. Dent. Med. Probl. 2020, 57, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralur, S.; Al-Shehri, K.; Assiri, H.; Al-Qahtani, M. Influence of personality on tooth shade selection. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2016, 11, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alkhudairy, R.; Tashkandi, E. The Effectiveness of a Shade-Matching Training Program on the Dentists’ Ability to Match Teeth Color. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2017, 29, E33–E43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udiljak, Z.; Illeš, D.; Knezović Zlatarić, D.; Ćelić, R. Effect of Clinical Experience on the Shade Matching Accuracy in Different Dental Occupational Groups. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2018, 52, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Polo, C.; Gómez-Polo, M.; Celemin-Viñuela, A.; Martínez Vázquez De Parga, J.A. Differences between the human eye and the spectrophotometer in the shade matching of tooth colour. J. Dent. 2014, 42, 742–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| n | % | ||
| Gender | Men | 123 | 41.8 |
| Women | 171 | 58.2 | |
| Vision disorders | Myopia | 139 | 48.8 |
| Astigmatism | 86 | 29.6 | |
| Hyperopia | 20 | 7 | |
| Prescription lenses | With lenses | 154 | 53.8 |
| Without lenses | 140 | 46.2 | |
| Tooth Type | With Lenses n = 154 | Without Lenses n = 140 |
|---|---|---|
| Upper central incisor | 0.65 * | 0.47 * |
| Lower central incisor | 0.47 * | 0.52 * |
| Upper lateral incisor | 0.43 * | 0.44 * |
| Lower lateral incisor | 0.50 * | 0.54 * |
| Upper canine | 0.55 * | 0.60 * |
| Lower canine | 0.54 * | 0.55 * |
| 1st upper premolar | 0.37 * | 0.46 * |
| 1st lower premolar | 0.59 * | 0.47 * |
| 2nd upper premolar | 0.36 * | 0.37 * |
| 2nd lower premolar | 0.31 * | 0.44 * |
| Lenses | Mean | Student’s t-Test | Significance Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper central incisor | Yes | 12.35 | 1.41 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 11.85 | |||
| Lower central incisor | Yes | 10.96 | 1.48 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 10.32 | |||
| Upper lateral incisor | Yes | 11.46 | 1.71 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 10.84 | |||
| Lower lateral incisor | Yes | 9.90 | 0.90 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 9.49 | |||
| Upper canine | Yes | 7.09 | 1.57 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.65 | |||
| Lower canine | Yes | 6.36 | 1.60 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 5.69 | |||
| 1st upper premolar | Yes | 8.57 | 0.68 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 8.28 | |||
| 1st lower premolar | Yes | 6.80 | 0.38 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.65 | |||
| 2nd upper premolar | Yes | 8.43 | −0.49 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 8.65 | |||
| 2nd lower premolar | Yes | 6.68 | −0.46 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.87 |
| Tooth Type | Myopic | Mean | Student’s t | Significance Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper central incisor | Yes | 12.48 | 1.88 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 11.82 | |||
| Lower central incisor | Yes | 11.23 | 2.63 | p < 0.05 * |
| No | 10.11 | |||
| Upper lateral incisor | Yes | 11.66 | 2.42 | p < 0.05 * |
| No | 10.81 | |||
| Lower lateral incisor | Yes | 10.30 | 2.34 | p < 0.05 * |
| No | 9.25 | |||
| Upper canine | Yes | 7.34 | 1.77 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.59 | |||
| Lower canine | Yes | 6.62 | 2.64 | p < 0.05 * |
| No | 5.51 | |||
| 1st upper premolar | Yes | 8.73 | 1.18 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 8.20 | |||
| 1st lower premolar | Yes | 6.81 | 0.60 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.57 | |||
| 2nd upper premolar | Yes | 8.52 | −0.31 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 8.66 | |||
| 2nd lower premolar | Yes | 6.68 | −0.32 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.82 |
| Tooth Type | Astigmatism | Mean | Student’s t-Test | Significance Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper central incisor | Yes | 12.14 | 0.20 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 12.06 | |||
| Lower central incisor | Yes | 10.68 | 0.09 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 10.64 | |||
| Upper lateral incisor | Yes | 11.27 | 0.45 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 11.08 | |||
| Lower lateral incisor | Yes | 9.67 | −0.06 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 9.70 | |||
| Upper canine | Yes | 6.99 | 0.31 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.84 | |||
| Lower canine | Yes | 6.16 | 0.44 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 5.96 | |||
| 1st upper premolar | Yes | 8.21 | −0.63 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 8.53 | |||
| 1st lower premolar | Yes | 6.40 | −0.92 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.81 | |||
| 2nd upper premolar | Yes | 8.25 | −0.82 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 8.65 | |||
| 2nd lower premolar | Yes | 6.09 | −2.01 | p < 0.05 * |
| No | 7.00 |
| Tooth Type | Hypermetropia | Mean | Student’s t-Test | Signification Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper central incisor | Yes | 12.65 | 0.86 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 12.06 | |||
| Lower central incisor | Yes | 10.40 | −0.33 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 10.67 | |||
| Upper lateral incisor | Yes | 11.68 | 0.78 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 11.13 | |||
| Lower lateral incisor | Yes | 9.95 | 0.30 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 9.69 | |||
| Upper canine | Yes | 7.45 | 0.72 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.86 | |||
| Lower canine | Yes | 6.15 | 0.17 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.01 | |||
| 1st upper premolar | Yes | 9.42 | 1.26 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 8.35 | |||
| 1st lower premolar | Yes | 6.84 | 0.22 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 6.67 | |||
| 2nd upper premolar | Yes | 9.55 | 1.31 | p > 0.05 |
| No | 8.46 | |||
| 2nd lower premolar | Yes | 7.42 | 0.95 | p > 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarado-Lorenzo, M.; Lozano-Garcia, E.; Colino-Gallardo, P.; Pellicer Castillo, L.D.; Díaz-Flores García, V.; Alvarado-Lorenzo, A. Impact of Vision Defects on Tooth Shade Selection: A Comparative of Spectrophotometry and Shade Guides in a Cross-Sectional Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010293
Alvarado-Lorenzo M, Lozano-Garcia E, Colino-Gallardo P, Pellicer Castillo LD, Díaz-Flores García V, Alvarado-Lorenzo A. Impact of Vision Defects on Tooth Shade Selection: A Comparative of Spectrophotometry and Shade Guides in a Cross-Sectional Clinical Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(1):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010293
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarado-Lorenzo, Mario, Eva Lozano-Garcia, Pedro Colino-Gallardo, Luis Daniel Pellicer Castillo, Victor Díaz-Flores García, and Alfonso Alvarado-Lorenzo. 2025. "Impact of Vision Defects on Tooth Shade Selection: A Comparative of Spectrophotometry and Shade Guides in a Cross-Sectional Clinical Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 1: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010293
APA StyleAlvarado-Lorenzo, M., Lozano-Garcia, E., Colino-Gallardo, P., Pellicer Castillo, L. D., Díaz-Flores García, V., & Alvarado-Lorenzo, A. (2025). Impact of Vision Defects on Tooth Shade Selection: A Comparative of Spectrophotometry and Shade Guides in a Cross-Sectional Clinical Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(1), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010293







