Periprosthetic Hip Fractures around the Stem: Can the Stem Design Affect Fracture Features?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Learmonth, I.D.; Young, C.; Rorabeck, C. The operation of the century: Total hip replacement. Lancet 2007, 370, 1508–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2007, 89-A, 780–785. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Kieser, D.; Wyatt, M.; Stringer, M.; Frampton, C.; Hooper, G. Risk factors for periprosthetic femoral fractures around total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. ANZ J. Surg. 2020, 90, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsiogiannis, N.; Kanakaris, N.K.; Giannoudis, P.V. Periprosthetic hip fractures: An update into their management and clinical outcomes. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, A.V.; Negus, J.J.; Haddad, F.S. Periprosthetic femoral fractures and trying to avoid them. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99-B, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, A.I.; Hume, E.L.; Pezzin, L.E.; McGinley, E.L.; Dillingham, T.R. The impact of femoral component cementation on fracture and mortality risk in elective total hip arthroplasty: Analysis from a national Medicare sample. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2022, 104, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.P.; Chan, P.H.; Prentice, H.A.; Paxton, E.W.; Hinman, A.D.; Khatod, M. Cause-specific stem revision risk in primary total hip arthroplasty using cemented vs cementless femoral stem fixation in a US cohort. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 89–96.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.S.A.; Dillman, D.; Wilson, D.; Dunbar, M.; Richardson, G. Higher periprosthetic fracture rate associated with use of modern uncemented stems compared to cemented stems in femoral neck fractures. Hip Int. 2019, 29, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savio, D.; Bagno, A. When the Total Hip Replacement Fails: A Review on the Stress-Shielding Effect. Processes 2022, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, P.C.; Alexander, J.W.; Lindahl, L.J.; Yew, D.T.; Granberry, W.M.; Tullos, H.S. The anatomic basis of femoral component design. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1988, 235, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissinger, M.; Helmreich, C.; Pöll, G. Periprosthetic fractures of the hip. Acta Chir. Orthop. Traumatol. Cech. 2009, 76, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, C.P.; Masri, B.A. Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr. Course Lect. 1995, 44, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dorr, L.D.; Faugere, M.C.; Mackel, A.M.; Gruen, T.A.; Bognar, B.; Malluche, H.H. Structural and cellular assessment of bone quality of proximal femur. Bone 1993, 14, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkerson, J.; Fernando, N.D. Classifications in Brief: The Dorr Classification of Femoral Bone. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1939–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karachalios, T.S.; Koutalos, A.A.; Komnos, G.A. Total hip arthroplasty in patients with osteoporosis. Hip Int. 2020, 30, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, M.; Leone, L.; Carrani, E.; Di Benedetto, C.; Manno, V.; Luzi, I.; Masciocchi, M. Progetto Registro Italiano ArtroProtesi (RIAP): Risultati della Fase Pilota sugli Interventi di Protesi D’anca; Rapporti ISTISAN; Istituto Superiore di Sanità: Rome, Italy, 2012; 12/32; Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/it/document/view/27991936/progetto-riap-risultati-della-fase-pilota-sugli-interventi-oer-puglia (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Rivière, C.; Grappiolo, G.; Engh, C.A., Jr.; Vidalain, J.P.; Chen, A.F.; Boehler, N.; Matta, J.; Vendittoli, P.A. Long-term bone remodelling around ‘legendary’ cementless femoral stems. EFORT Open Rev. 2018, 3, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.A.; Achten, J.; Parsons, N.; Griffin, X.L.; Png, M.E.; Gould, J.; McGibbon, A.; Costa, M.L. Cemented or Uncemented Hemiarthroplasty for Intracapsular Hip Fracture. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draenert, K.D.; Draenert, Y.I.; Krauspe, R.; Bettin, D. Strain adaptive bone remodelling in total joint replacement. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 430, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatem, M.A.; Ferreira da Luz, B.; Nishi, R.N.; Cimbalista de Alencar, P.G. Evaluation of the results from proximal fixation of uncemented conical femoral components in Dorr type C femurs. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2014, 49, 260–266. [Google Scholar]
- Meding, J.B.; Galley, M.R.; Ritter, M.A. High survival of uncemented proximally porous-coated titanium alloy femoral stems in osteoporotic bone. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-J.; Park, C.-W.; Cho, K.; Jeong, J.; Lim, S.-J.; Park, Y.-S. Rectangular Taper Stem Designs Are Associated with a Higher Risk for Periprosthstic Femoral Fractures after Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, 2379–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, M.; Barbera, L.; Anticonome, A.; Ottardi, C.; Tanaka, A.; Villa, T. Periprosthetic femoral fractures in sideways fall configuration: Comparative numerical analysis of the influence of femoral stem design. Hip Int. 2020, 30, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windell, L.; Kulkarni, A.; Alabort, E.; Barba, D.; Reed, R.; Singh, H.P. Biomechanical Comparison of Periprosthetic Femoral Fracture Risk in Three Femoral Components in a Sawbone Model. J. Arthroplasty 2021, 36, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konow, T.; Baetz, J.; Melsheimer, O.; Grimberg, A.; Morlock, M. Factors influencing periprosthetic femoral fracture risk: A German registry study. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sershon, R.A.; McDonald, J.F., 3rd; Ho, H.; Hamilton, W.G. Periprosthetic Femur Fracture Risk: Influenced by Stem Choice, Not Surgical Approach. J. Arthroplasty 2021, 36, S363–S366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottino, U.; Dettoni, F.; Caputo, G.; Bonasia, D.E.; Rossi, P.; Rossi, R. Incidence and pattern of periprosthetic hip fractures around the stem in different stem geometry. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luger, M.; Feldler, S.; Pisecky, L.; Klasan, A.; Gotterbarm, T.; Schopper, C. Periprosthetic femoral fractures in cementless short versus straight stem total hip arthroplasty: A propensity score matched analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Martín, D.; Hernández-Castillejo, L.E.; Herrera-Pérez, M.; Pais-Brito, J.L.; González-Casamayor, S.; Garrido-Miguel, M. Osteosynthesis versus revision arthroplasty in Vancouver B2 periprosthetic hip fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Trauma Emergy Surg. 2023, 49, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, H.; Malchau, H.; Herberts, P.; Garellick, G. Periprosthetic femoral fractures. J. Arthroplast. 2005, 20, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidler-Maier, C.C.; Waddell, J.P. Incidence and predisposing factors of periprosthetic proximal femoral fractures: A literature review. Int. Orthop. 2015, 39, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learmonth, I.D. The management of periprosthetic fractures around the femoral stem. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2004, 86, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
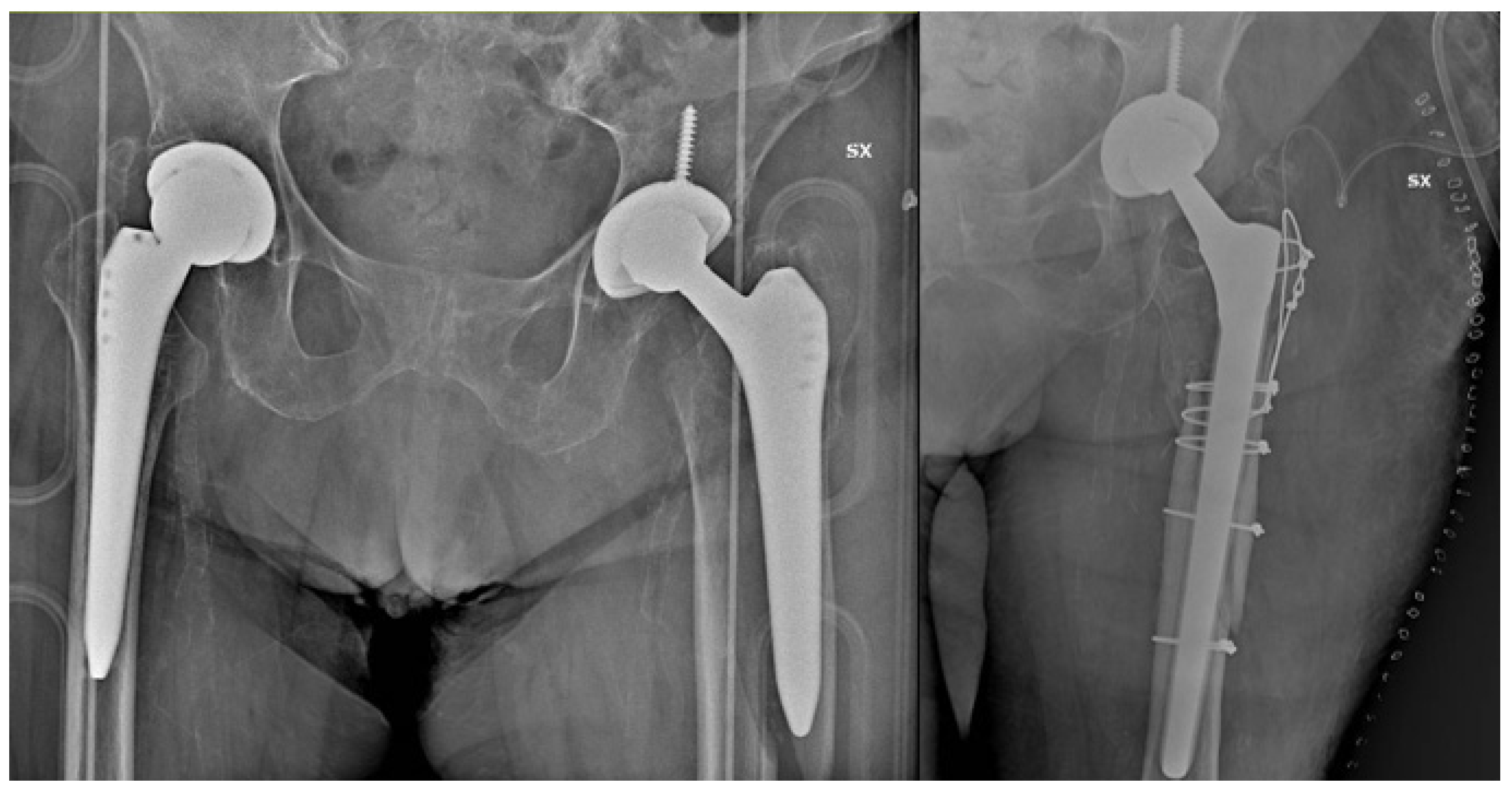
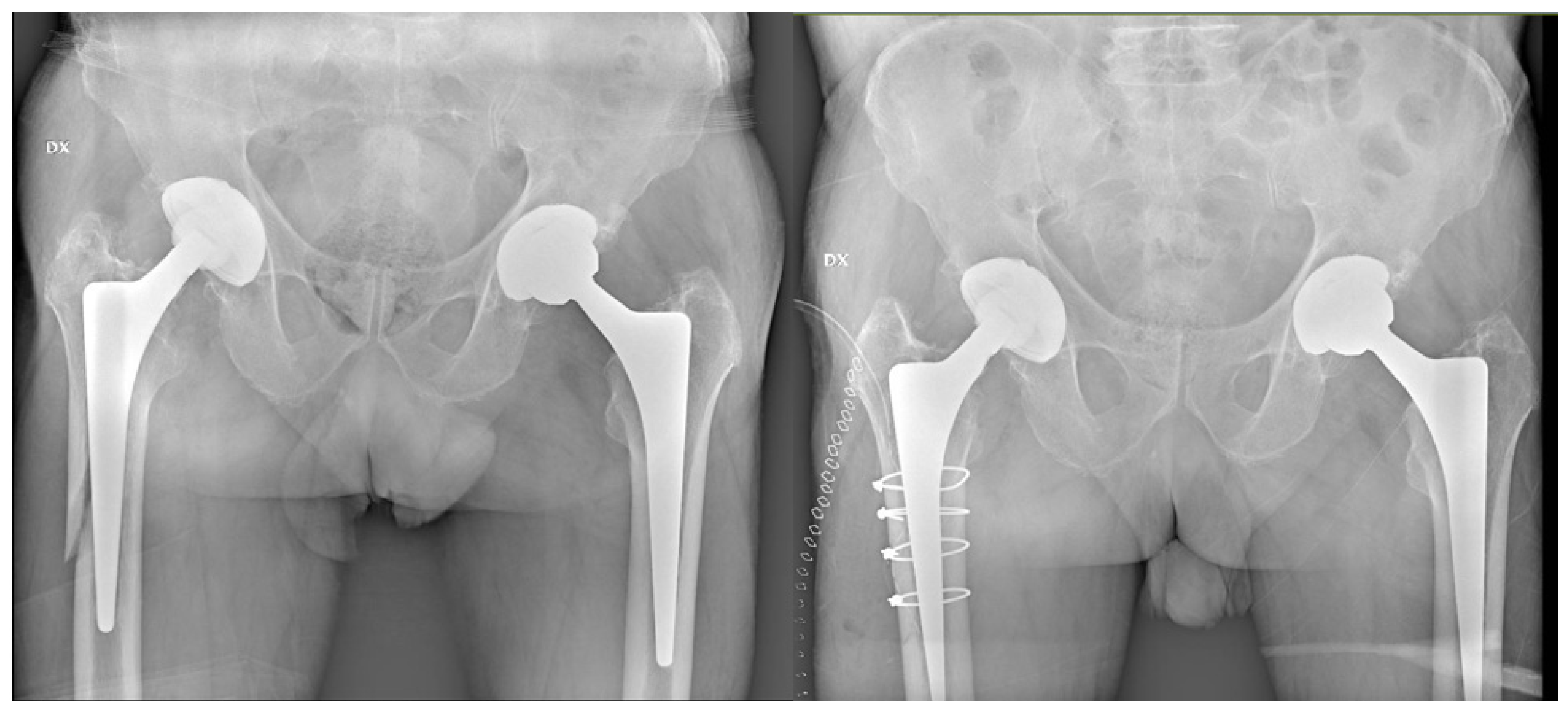
| Patients, n | Alloclassic (A) | CLS (B) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, n | 55 | 42 | |
| Sex (male/female), n | 13/42 | 24/18 | p = 0.0014 |
| Mean age | 81 (51–96) | 81 (65–96) | p > 0.05 |
| Alloclassic (A) | CLS (B) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dorr A | 4 | 18 | p = 0.000095 |
| Dorr B | 35 | 21 | p > 0.05 |
| Dorr C | 16 | 3 | p = 0.009 |
| Vancouver | Alloclassic (A) | CLS (B) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 6 | 4 | p > 0.05 |
| B1 | 19 | 21 | p > 0.05 |
| B2 | 17 | 12 | p > 0.05 |
| B3 | 9 | 5 | p > 0.05 |
| C | 4 | 0 | p > 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Comba, L.C.; Gagliardi, L.; Onorato, F.; Rivera, F. Periprosthetic Hip Fractures around the Stem: Can the Stem Design Affect Fracture Features? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092627
Comba LC, Gagliardi L, Onorato F, Rivera F. Periprosthetic Hip Fractures around the Stem: Can the Stem Design Affect Fracture Features? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(9):2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092627
Chicago/Turabian StyleComba, Luca Costanzo, Luca Gagliardi, Francesco Onorato, and Fabrizio Rivera. 2024. "Periprosthetic Hip Fractures around the Stem: Can the Stem Design Affect Fracture Features?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 9: 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092627
APA StyleComba, L. C., Gagliardi, L., Onorato, F., & Rivera, F. (2024). Periprosthetic Hip Fractures around the Stem: Can the Stem Design Affect Fracture Features? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(9), 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092627





