Differential Expression of LMNA/C and Insulin Receptor Transcript Variants in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Leukemia Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data of Subjects
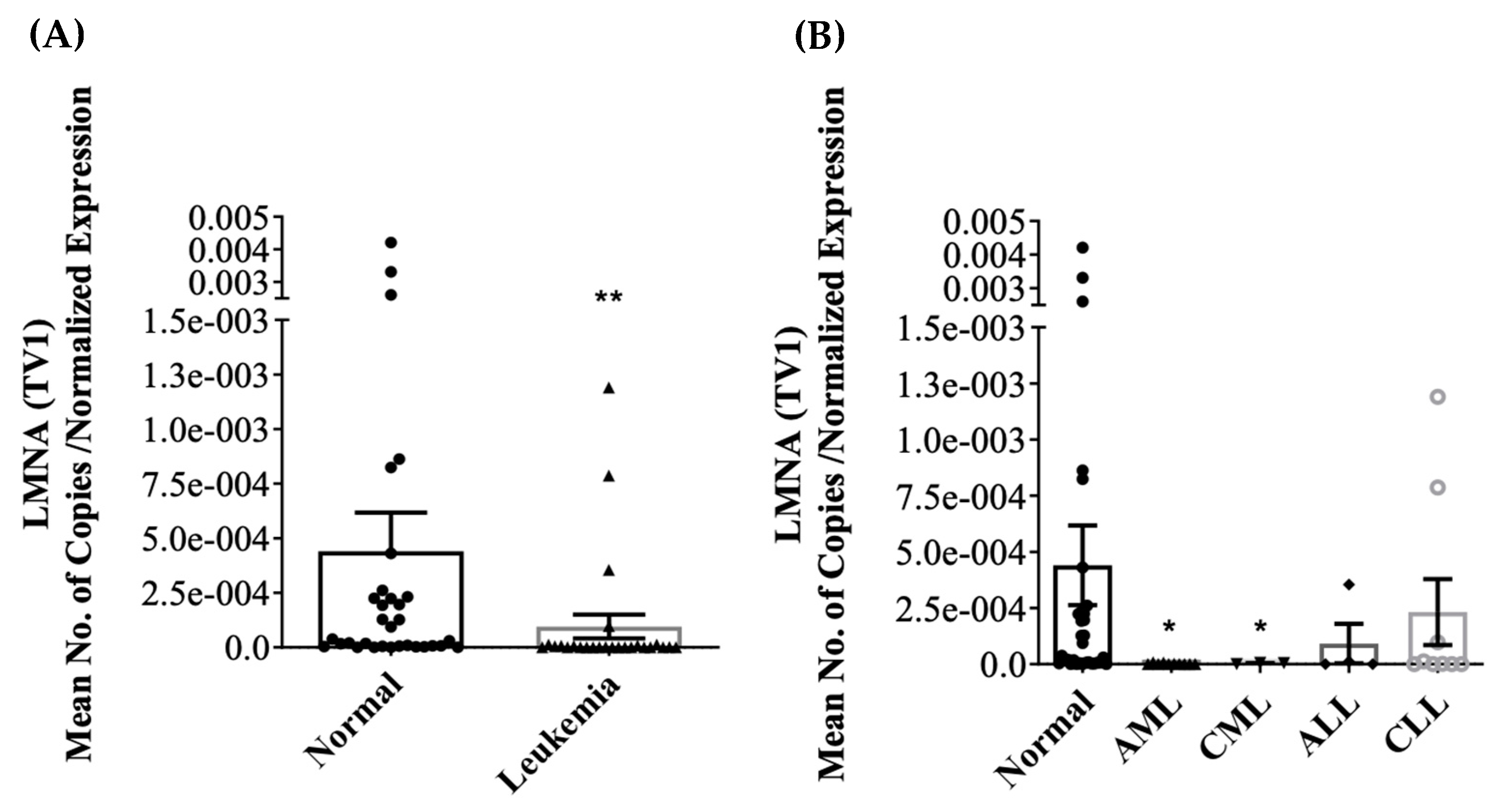
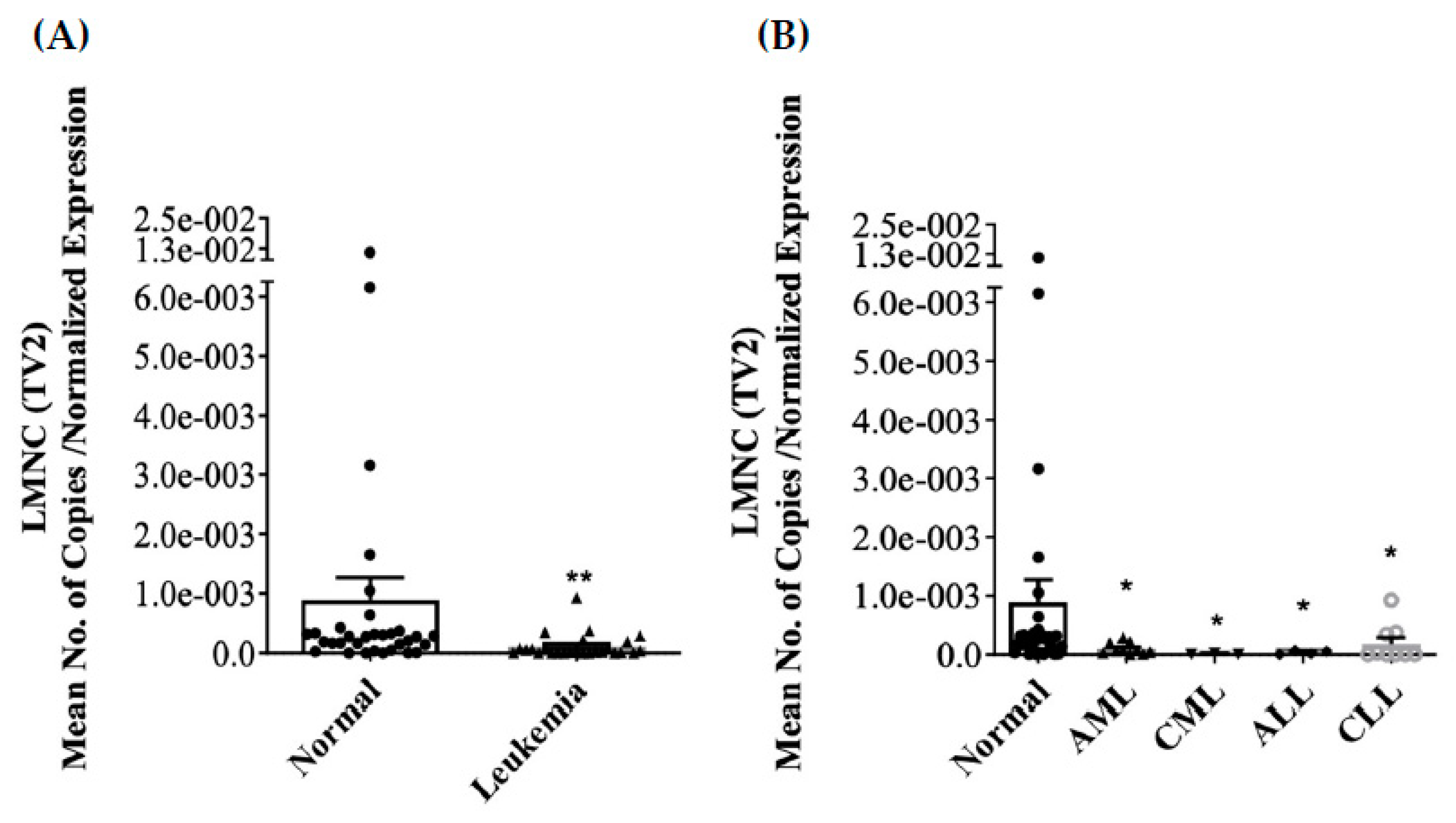
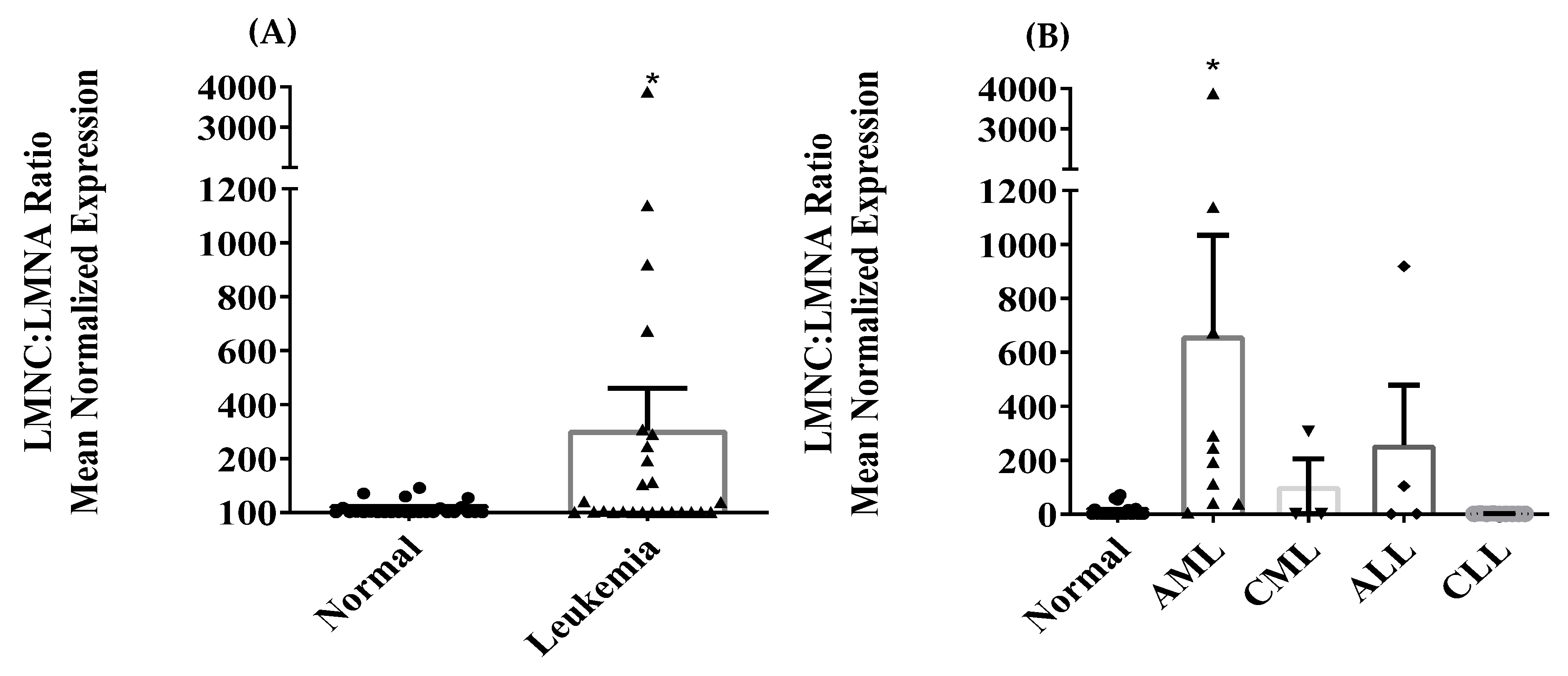
3.2. Differential Expression of LMNA/C mRNA Expression in PBMC
3.3. Inhibition of INSR (IR-A) mRNA Expression in PBMC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamid, G.A. Classification of acute leukemia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 87, 740–753. [Google Scholar]
- Laosai, J.; Chamnongthai, K. Classification of acute leukemia using medical-knowledge-based morphology and CD marker. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 44, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckenna, R.W. Multifaceted approach to the diagnosis and classification of acute leukemias. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46 Pt 2, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.G.; Stasi, R.; Bastianelli, C.; Venditti, A.; del Poeta, G.; Amadori, S.; Sargent, J.M. Diagnosis and classification of the acute leukemias: Recent advances and controversial issues. Hematop. Mol. Hematol. 1996, 10, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, R.J.; Chang, C.-C.J.; Herrick, J.; Zu, Y.; Ehsan, A. Acute leukemia immunohistochemistry: A systematic diagnostic approach. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2008, 132, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foon, K.A.; Gale, R.P.; Todd, R.F. Recent advances in the immunologic classification of leukemia. Semin. Hematol. 1986, 23, 257–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sobol, R.E.; Royston, I.; Lebien, T.W.; Minowada, J.; Anderson, K.; Davey, F.R.; Cuttner, J.; Schiffer, C.A.; Ellison, R.R.; Bloomfield, C.D. Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia phenotypes defined by monoclonal antibodies. Blood 1985, 65, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, C.-H.; Carroll, W.L.; Meshinchi, S.; Arceci, R.J. Biology, risk stratification, and therapy of pediatric acute leukemias: An update. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yohe, S.L. Molecular Genetic Markers in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 460–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Flotho, C.; Downing, J.R. Genomic Assessment of Pediatric Acute Leukemia. Cancer J. 2005, 11, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Dewald, G.W.; Litzow, M.; Cortes, J.E.; Mauro, M.J.; Talpaz, M.; Kantarjian, H.M. Chronic myeloid leukemia: Current application of cytogenetics and molecular testing for diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2005, 80, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechat, T.; Adam, S.A.; Taimen, P.; Shimi, T.; Goldman, R.D. Nuclear lamins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuurman, N.; Heins, S.; Aebi, U. Nuclear lamins: Their structure, assembly, and interactions. J. Struct. Biol. 1998, 122, 42–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butin-Israeli, V.; Adam, S.A.; Goldman, A.E.; Goldman, R.D. Nuclear lamin functions and disease. Trends Genet. TIG 2012, 28, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokocimer, M.; Margalit, A.; Gruenbaum, Y. The nuclear lamina and its proposed roles in tumorigenesis: Projection on the hematologic malignancies and future targeted therapy. J. Struct. Biol. 2006, 155, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irianto, J.; Pfeifer, C.R.; Ivanovska, I.L.; Swift, J.; Discher, D.E. Nuclear Lamins in Cancer. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2016, 9, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljada, A.; Doria, J.; Saleh, A.M.; Al-Matar, S.H.; AlGabbani, S.; Shamsa, H.B.; Al-Bawab, A.; Ahmed, A.A. Altered Lamin A/C splice variant expression as a possible diagnostic marker in breast cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2016, 39, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, C.M.; Emanuelli, B.; Kahn, C.R. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin action. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R. Insulin receptor and cancer. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2011, 18, R125–R147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanandhan, S.; Mukhopadhyay, D. Genetic status of KRAS influences Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling: An insight into Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) mediated tumorigenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 54, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal Gupta, S.; Baumann, H.; Wetzler, M. Epigenetic regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2008, 32, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benekli, M.; Baumann, H.; Wetzler, M. Targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway in leukemias. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4422–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Chen, Y.-G. Interplay between TGF-β signaling and receptor tyrosine kinases in tumor development. Sci. China Life Sci. 2017, 60, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Sciacca, L.; Pezzino, V.; Squatrito, S.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R. The role of insulin receptors and IGF-I receptors in cancer and other diseases. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galal, M.A.; Alouch, S.S.; Alsultan, B.S.; Dahman, H.; Alyabis, N.A.; Alammar, S.A.; Aljada, A. Insulin Receptor Isoforms and Insulin Growth Factor-like Receptors: Implications in Cell Signaling, Carcinogenesis, and Chemoresistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, A. The role of insulin receptor isoforms and hybrid insulin/IGF-I receptors in human cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, K.; Rönnstrand, L. Oncogenic signaling from the hematopoietic growth factor receptors c-Kit and Flt3. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P. The insulin receptor isoform A: A mitogenic proinsulin receptor? Endocrinology 2012, 153, 2054–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vella, V.; Milluzzo, A.; Scalisi, N.M.; Vigneri, P.; Sciacca, L. Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljada, A.; Saleh, A.M.; Al-Aqeel, S.M.; Shamsa, H.B.; Al-Bawab, A.; Al Dubayee, M.; Ahmed, A.A. Quantification of insulin receptor mRNA splice variants as a diagnostic tumor marker in breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2015, 15, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciacca, L.; Prisco, M.; Wu, A.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R.; Baserga, R. Signaling differences from the A and B isoforms of the insulin receptor (IR) in 32D cells in the presence or absence of IR substrate-1. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesti, G.; Tullio, A.N.; D’Alfonso, R.; Napolitano, M.; Marini, M.A.; Borboni, P.; Longhi, R.; Albonici, L.; Fusco, A.; Aglianó, A.M.; et al. Tissue-specific expression of two alternatively spliced isoforms of the human insulin receptor protein. Acta Diabetol. 1994, 31, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Morehouse, C.; Streicher, K.; Higgs, B.W.; Gao, J.; Czapiga, M.; Boutrin, A.; Zhu, W.; Brohawn, P.; Chang, Y.; et al. Altered expression of insulin receptor isoforms in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Zhu, W.; Streicher, K.; Morehouse, C.; Brohawn, P.; Ge, X.; Dong, Z.; Yin, X.; Zhu, G.; Gu, Y.; et al. Increased IR-A/IR-B ratio in non-small cell lung cancers associates with lower epithelial-mesenchymal transition signature and longer survival in squamous cell lung carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.; König, I.R.; Schulz-Knappe, P.D.M. Challenges in planning and conducting diagnostic studies with molecular biomarkers. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2013, 138, e14–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajia, M. Limitations of Different PCR Protocols Used in Diagnostic Laboratories: A Short Review. Med. Lab. J. 2018, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggington, J.M.; Bowles, K.R.; Moyes, K.; Manley, S.; Esterling, L.E.; Sizemore, S.; Rosenthal, E.T.; Theisen, A.P.; Saam, J.; Arnell, C.; et al. A comprehensive laboratory-based program for classification of variants of uncertain significance in hereditary cancer genes. Clin. Genet. 2014, 86, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangar, R.C.; Daly, D.S.; White, A.M. ELISA microarray technology as a high-throughput system for cancer biomarker validation. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2006, 3, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatovich, P.L.; Bischoff, R. Current Technological Challenges in Biomarker Discovery and Validation. Eur. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2010, 16, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P. Q-Gene: Processing Quantitative Real-time RT-PCR Data. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1439–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broers, J.L.; Machiels, B.M.; Kuijpers, H.J.; Smedts, F.; van den Kieboom, R.; Raymond, Y.; Ramaekers, F.C. A- and B-type lamins are differentially expressed in normal human tissues. Histochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 107, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, C.J.; Worman, H.J. A-type lamins: Guardians of the soma? Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadelmann, B.; Khandjian, E.; Hirt, A.; Luthy, A.; Weil, R.; Wagner, H.P. Repression of nuclear lamin A and C gene expression in human acute lymphoblastic leukemia and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells. Leuk. Res. 1990, 14, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Worman, H.J. Expression of nuclear lamins in human tissues and cancer cell lines and transcription from the promoters of the lamin A/C and B1 genes. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 236, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrelo, R.; Setien, F.; Espada, J.; Artiga, M.J.; Rodriguez, M.; Perez-Rosado, A.; Sanchez-Aguilera, A.; Fraga, M.F.; Piris, M.A.; Esteller, M. Inactivation of the lamin A/C gene by CpG island promoter hypermethylation in hematologic malignancies, and its association with poor survival in nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3940–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, N.D.; Cox, T.R.; Rahman-Casans, S.F.; Smits, K.; Przyborski, S.A.; van den Brandt, P.; van Engeland, M.; Weijenberg, M.; Wilson, R.G.; de Bruine, A.; et al. Lamin A/C is a risk biomarker in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaffidi, P.; Misteli, T. Reversal of the cellular phenotype in the premature aging disease Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, J.I.; Yang, S.H.; Qiao, X.; Beigneux, A.P.; Gelb, M.H.; Moulson, C.L.; Miner, J.H.; Young, S.G.; Fong, L.G. Blocking protein farnesyltransferase improves nuclear shape in fibroblasts from humans with progeroid syndromes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12873–12878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulson, C.L.; Fong, L.G.; Gardner, J.M.; Farber, E.A.; Go, G.; Passariello, A.; Grange, D.K.; Young, S.G.; Miner, J.H. Increased progerin expression associated with unusual LMNA mutations causes severe progeroid syndromes. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, D.; Ratner, D.; Lokuge, M.; Owens, D.M.; Gordon, L.B.; Collins, F.S.; Djabali, K. The mutant form of lamin A that causes Hutchinson-Gilford progeria is a biomarker of cellular aging in human skin. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landskron, G.; De la Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 149185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perillie, P.E.; Finch, S.C. The local exudative cellular response in leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 1960, 39, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itälä, M.; Vainio, O.; Remes, K. Functional abnormalities in granulocytes predict susceptibility to bacterial infections in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 1996, 57, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, J.O.; Chang, X.; Blaser, B.W.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Zheng, P.; Liu, Y. Tumor growth impedes natural-killer-cell maturation in the bone marrow. Blood 2006, 108, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsten, M.; Baumann, B.C.; Simonsson, M.; Jädersten, M.; Forsblom, A.-M.; Hammarstedt, C.; Bryceson, Y.T.; Ljunggren, H.-G.; Hellström-Lindberg, E.; Malmberg, K.-J. Reduced DNAM-1 expression on bone marrow NK cells associated with impaired killing of CD34+ blasts in myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riches, J.C.; Ramsay, A.G.; Gribben, J.G. Immune Reconstitution in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2012, 7, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Bayona, P.W.; Kim, M.; Chang, J.; Hong, S.; Park, Y.; Budiman, A.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, C.Y.; Kim, W.S.; et al. Macrophage Lamin A/C Regulates Inflammation and the Development of Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goalstone, M.; Carel, K.; Leitner, J.W.; Draznin, B. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation and activity of farnesyltransferase via the Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 5119–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, B.S.; Fong, L.G.; Yang, S.H.; Coffinier, C.; Young, S.G. The posttranslational processing of prelamin A and disease. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan, J.L.; Ingham, R.R.; Dalia, S.; Furman, M.S.; Merhi, B.; Nemr, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Mitri, J.; Castillo, J.J. Association Between Obesity/Overweight and Leukemia: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Blood 2011, 118, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Overweight and obesity and incidence of leukemia: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1418–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galati, P.C.; Ribeiro, C.M.; Pereira, L.T.G.; Amato, A.A. The association between excess body weight at diagnosis and pediatric leukemia prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Rev. 2022, 51, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer. | Sense (5′→3′) | Anti Sense (5′→3′) | Probe | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMNA | TGACTGTGGTTGAGGACGAC | GACACTGGAGGCAGAAGAGC | CGCTGAGTACAACCT | NM_170707.3 |
| LMNC | GTGGAAGGCACAGAACACCT | GCGGCGGCTACCACTCAC | AGATGACCTGCTCCATCACC | NM_005572.3 |
| LMNAΔ10 | AACTCCACTGGGGAAGGCTCC | GCTCCTGAGCCGCTGGCAGA | AGTACAACCTGCGCTCGCGC | NM_170708.3 |
| LMNAΔ50 | GCGTCAGGAGCCCTGAGC | GACGCAGGAAGCCTCCAC | AGCATCATGTAATCTGGGACCT | NM_001282626.1 |
| INSR (IR-A) | TATCCGGAACAACCTCACTA | GGAAGAGCAGCAAGTAATCA | CTCTGTCATCGAAGGACACTTG | NM_001079817 |
| INSR (IR-B) | AGGAGTCCTCGTTTAGGAAG | AGGAAGTGTTGGGGAAAG | AGAAAAACCTCTTCAGGCACTG | NM_000208 |
| Ubiquitin C | ACTACAACATCCAGAAAGAGTCCA | CCAGTCAGGGTCTTCACGAAG | CCCACCTCTGAGACGGAGCACCAG | NM_021009.6 |
| RPL13 | AACAAGTTGAAGTACCTGGCTTTC | TGGTTTTGTGGGGCAGCATA | CGCAAGCGGATGAACACCAACCCT | NM_000977.3 |
| Gender | Age (years) | BMI kg/m2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 14M, 18F | 31.9 ± 2.18 | 32.1 ± 2.0 |
| AML | 9M, 8F | 48.2 ± 5.18 * | 26.4 ± 1.28 |
| CML | 4M, 1F | 59.4 ± 6.75 *ɛ | 30.4 ± 1.78 |
| ALL | 5M, 3F | 34.4 ± 5.51 | 25.9 ± 2.38 |
| CLL | 7M, 8F | 66.5 ± 3.42 *ɛ | 28.1 ± 1.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshaalan, K.S.; Albawardi, T.K.; Zhra, M.; Bin Sulaiman, N.; Jnied, O.Y.; Saleem, R.A.; Aljada, A. Differential Expression of LMNA/C and Insulin Receptor Transcript Variants in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Leukemia Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092568
Alshaalan KS, Albawardi TK, Zhra M, Bin Sulaiman N, Jnied OY, Saleem RA, Aljada A. Differential Expression of LMNA/C and Insulin Receptor Transcript Variants in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Leukemia Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(9):2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092568
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshaalan, Khalid Saud, Turki Khalid Albawardi, Mahmoud Zhra, Norah Bin Sulaiman, Osama Yaheia Jnied, Rimah Abdullah Saleem, and Ahmad Aljada. 2024. "Differential Expression of LMNA/C and Insulin Receptor Transcript Variants in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Leukemia Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 9: 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092568
APA StyleAlshaalan, K. S., Albawardi, T. K., Zhra, M., Bin Sulaiman, N., Jnied, O. Y., Saleem, R. A., & Aljada, A. (2024). Differential Expression of LMNA/C and Insulin Receptor Transcript Variants in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Leukemia Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(9), 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092568







