Cytokine Dynamics in Acute Pancreatitis: The Quest for Biomarkers from Acute Disease to Disease Resolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Sample Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Serum Concentrations for Evaluated Cytokines
3.2. Cytokine Correlation Analyses in AP Patients and Controls
3.3. Cytokine Concentrations According to Severity and Clinical Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iannuzzi, J.P.; King, J.A.; Leong, J.H.; Quan, J.; Windsor, J.W.; Tanyingoh, D.; Coward, S.; Forbes, N.; Heitman, S.J.; Shaheen, A.-A.; et al. Global Incidence of Acute Pancreatitis Is Increasing Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, M.; Fei, L.W.; Cao, Y.; Hon, Y.L.; Huang, J.; Puneet, P.; Chevali, L. Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2005, 5, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinonquel, P.; Laleman, W.; Wilmer, A. Advances in acute pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care. 2021, 27, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kudo, M.; Strober, W. Immunopathogenesis of pancreatitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.J.; Papachristou, G.I. New insights into acute pancreatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmer, A.P. What’s new in the management of acute pancreatitis? Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2001, 14, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J. Immunomodulatory therapies for acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianliang, Z.; Jieshou, L.; Zhiwei, J.; Baojun, Y. Association of plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and its soluble receptors, two polymorphisms of the TNF gene, with acute severe pancreatitis and early septic shock due to it. Pancreas 2003, 26, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyanarayan, G.; Garg, P.K.; Prasad, H.; Tandon, R.K. Elevated level of interleukin-6 predicts organ failure and severe disease in patients with acute pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, T.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, X. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2011, 31, 187–189. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, K.; Glenn, H.; Delaney, A.; Andersen, C.R.; Sasson, S.C. Fire in the belly: A scoping review of the immunopathological mechanisms of acute pancreatitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1077414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malheiro, F.; Ângelo-Dias, M.; Lopes, T.; Azeredo-Lopes, S.; Martins, C.; Borrego, L.M. B Cells and Double-Negative B Cells (CD27-IgD-) Are Related to Acute Pancreatitis Severity. Diseases 2024, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Kinns, H. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristou, G.I.; Muddana, V.; Yadav, D.; O’Connell, M.; Sanders, M.K.; Slivka, A.; Whitcomb, D.C. Comparison of BISAP, Ranson’s, APACHE-II, and CTSI Scores in Predicting Organ Failure, Complications, and Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 435–441, quiz 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, H.; MacVicar, T.D.; Tellkamp, F.; Krüger, M. Instant Clue: A Software Suite for Interactive Data Visualization and Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternby, H.; Hartman, H.; Thorlacius, H.; Regnér, S. The Initial Course of IL1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, IFN-γ and TNF-α with Regard to Severity Grade in Acute Pancreatitis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Lai, T.; Peng, H.; Gui, L.; He, W. Interleukin-6 is better than C-reactive protein for the prediction of infected pancreatic necrosis and mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Nicolas, A.; Martínez-Chamorro, A.; Jiménez, P.; Matas-Cobos, A.M.; Redondo-Cerezo, E.; Ruiz-Cabello, F. TH1 and TH2 Cytokine Profiles as Predictors of Severity in Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2018, 47, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Lin, T.-L.; Cai, Z.; Yan, C.-H.; Gou, S.-R.; Zhuang, Y.-D. Assessment of acute pancreatitis severity via determination of serum levels of hsa-miR-126-5p and IL-6. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, C.; Lee, P.J.; Paragomi, P.; Greer, P.; Stello, K.; Hart, P.A.; Whitcomb, D.C.; Papachristou, G.I. A Novel 5-Cytokine Panel Outperforms Conventional Predictive Markers of Persistent Organ Failure in Acute Pancreatitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hou, C.; Shi, C.; Huang, D.; Lu, Z.; Miao, Y.; Li, Q. Development an Inflammation-Related Factor-Based Model for Predicting Organ Failure in Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Mediators Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 4906768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Vaz, P.; Abrantes, A.M.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Gouveia, A.; Botelho, M.F.; Tralhão, J.G. Multifactorial Scores and Biomarkers of Prognosis of Acute Pancreatitis: Applications to Research and Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, P.J.; Lee, P.J.; Paragomi, P.; Stello, K.; Phillips, A.; Hart, P.; Speake, C.; Lacy-Hulbert, A.; Whitcomb, D.C.; Papachristou, G.I. Severe acute pancreatitis exhibits distinct cytokine signatures and trajectories in humans: A prospective observational study. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2022, 323, G428–G438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonstra, J.; Rijken, P.; Humbel, B.; Cremers, F.; Verkleij, A.; van Bergen en Henegouwen, P. The epidermal growth factor. Cell Biol. Int. 1995, 19, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhakarmi, K.; Seo, J.-E.; Lamichhane, S.; Thapa, C.; Lee, S. EGF, a veteran of wound healing: Highlights on its mode of action, clinical applications with focus on wound treatment, and recent drug delivery strategies. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2023, 46, 299–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Koh, Y.G.; Lee, W.G.; Seok, J.; Park, K.Y. The use of epidermal growth factor in dermatological practice. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, T.; Takeyama, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Matsumura, N.; Sawa, H.; Nakajima, T.; Kuroda, Y. Vascular endothelial growth factor increases in serum and protects against the organ injuries in severe acute pancreatitis. J. Surg. Res. 2006, 134, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Căluianu, E.I.; Alexandru, D.O.; Târtea, E.A.; Georgescu, M.; MercuŢ, D.; Traşcă, E.T.; Iancău, M. Assessment of T- and B-lymphocytes and VEGF-A in acute pancreatitis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2017, 58, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Niklander, S.; Bordagaray, M.J.; Fernández, A.; Hernández, M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor: A Translational View in Oral Non-Communicable Diseases. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Adamis, A.P. Ten years of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik-Dasthagirisaheb, Y.; Varvara, G.; Murmura, G.; Saggini, A.; Potalivo, G.; Caraffa, A.; Antinolfi, P.; Tetè, S.; Tripodi, D.; Conti, F.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), mast cells and inflammation. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2013, 26, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Hong, Y.J.; Kim, M. Angiogenesis in Chronic Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papachristou, G.I.; Sass, D.A.; Avula, H.; Lamb, J.; Lokshin, A.; Barmada, M.M.; Slivka, A.; Whitcomb, D.C. Is the monocyte chemotactic protein-1 -2518 G allele a risk factor for severe acute pancreatitis? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 3, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Anshita, D.; Ravichandiran, V. MCP-1: Function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapp, J.; Hall, A.G.; Walters, R.W.; Jahann, D.; Kassim, T.; Reddymasu, S. Trends and Outcomes of Hospitalizations Related to Acute Pancreatitis: Epidemiology From 2001 to 2014 in the United States. Pancreas 2019, 48, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mederos, M.A.; Reber, H.A.; Girgis, M.D. Acute Pancreatitis: A Review. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Lin, T.; Zhu, Q.; Wan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lv, S.; Song, J.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Correlation Between Severity of Illness and Levels of Free Triiodothyronine, Interleukin-6, and Interleukin-10 in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e933230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.J.; Chen, J.; Phillips, A.R.J.; Windsor, J.A.; Petrov, M.S. Predictors of severe and critical acute pancreatitis: A systematic review. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-López, F.; Martínez-Cara, J.G.; Redondo-Cerezo, E. Acute pancreatitis. Med. Clin. 2022, 158, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, R.; Pinter, A.; Ferris, L.K.; Gerdes, S.; Rich, P.; Vender, R.; Miller, M.; Shen, Y.-K.; Kannan, A.; Li, S.; et al. An Oral Interleukin-23-Receptor Antagonist Peptide for Plaque Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

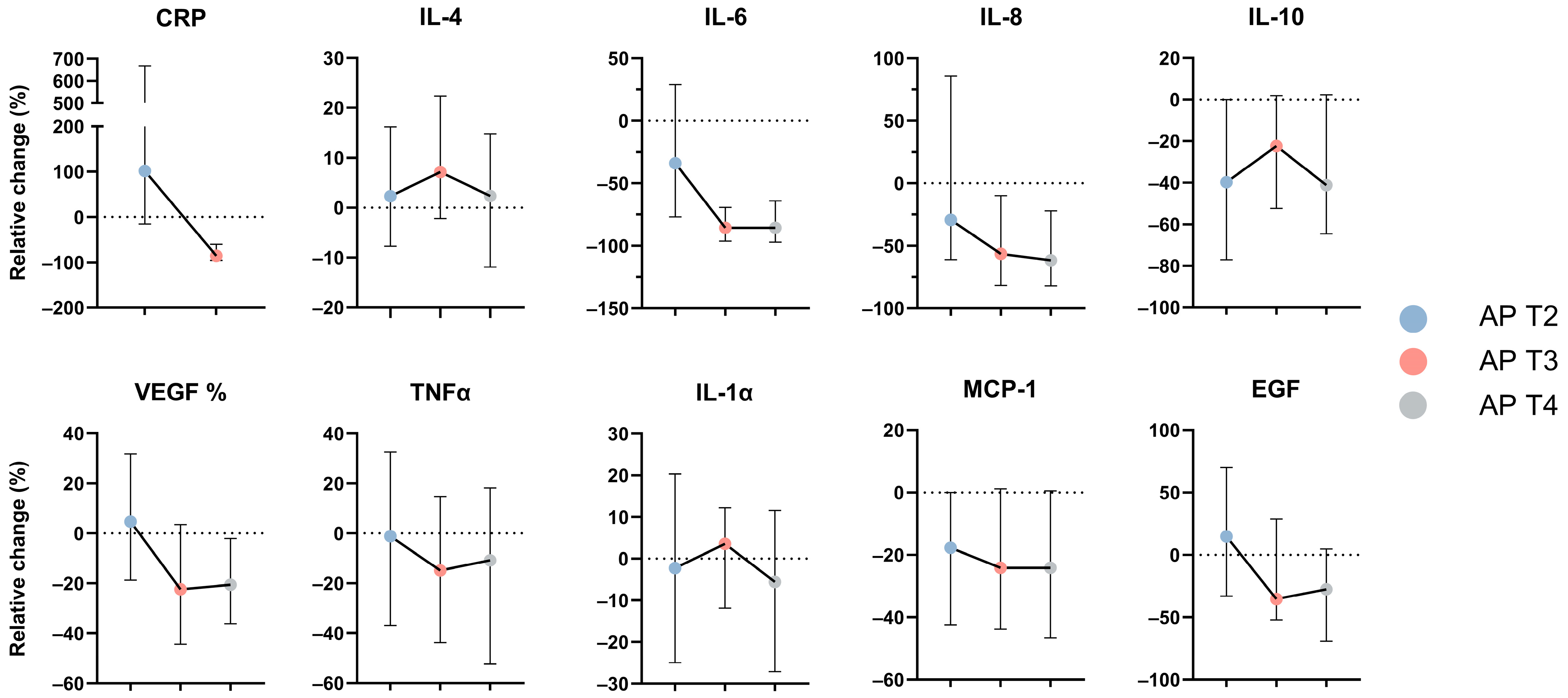


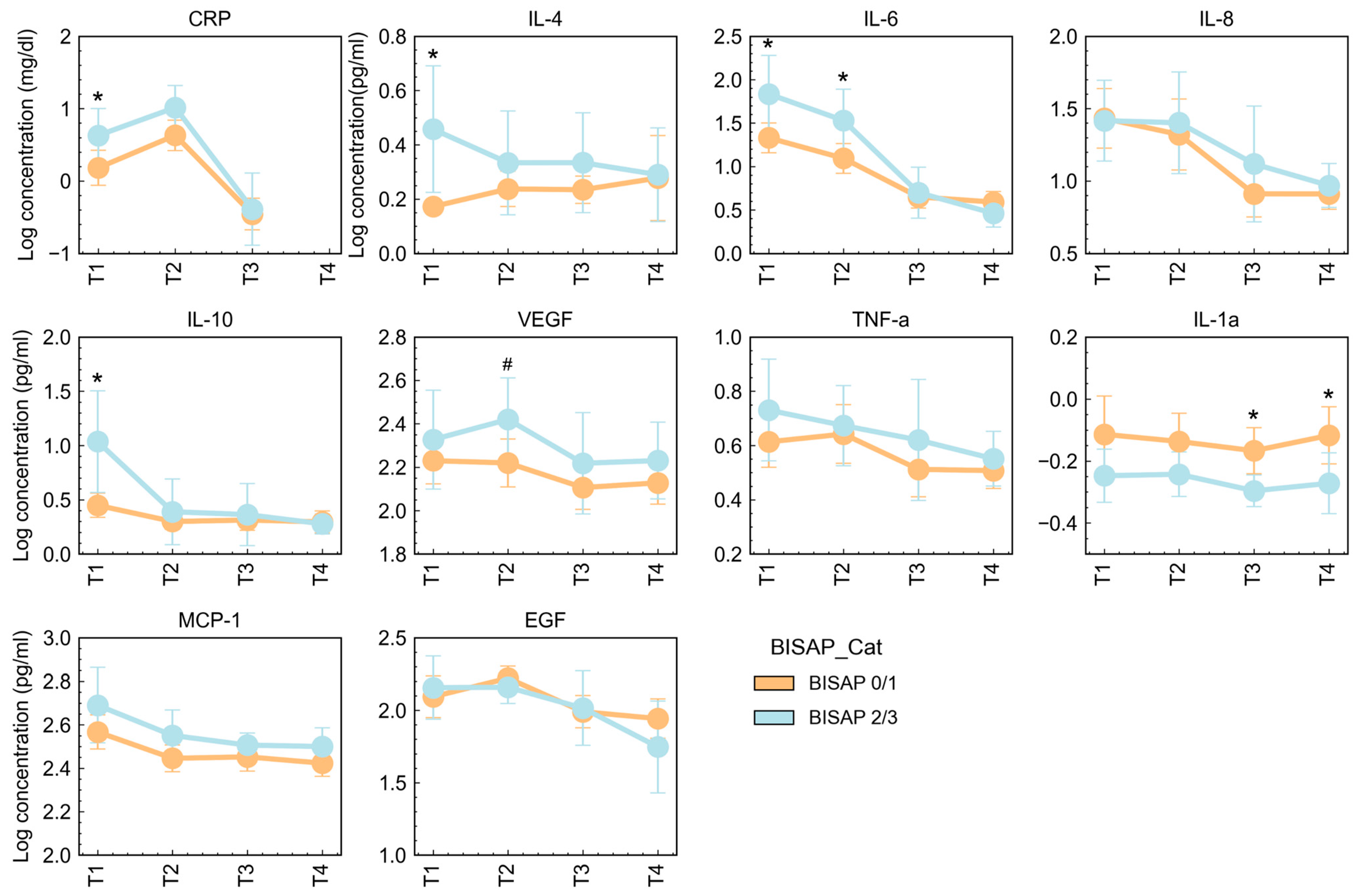

| Characteristics | AP (n = 50) | HC (n = 30) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, mean (SD) | 59.9 (14.6) | 58.1 (16.6) | n.s. a |
| Gender, n (%) | n.s. b | ||
| Male | 23 (46) | 14 (47) | |
| Female | 27 (54) | 16 (53) | |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean (SD) | 29.0 (5.8) | 26.3 (3.5) | n.s. a |
| Cause (%) | - | - | |
| Gallstone | 23 (46) | ||
| Alcoholic | 5 (10) | ||
| Unknown | 21 (42) | ||
| Other | 1 (2) | ||
| Severity, n (%) | - | - | |
| Mild | 34 (66) | ||
| Moderate | 13 (28) | ||
| Severe | 3 (6) | ||
| 30-day mortality, n (%) | 0 (0) | - | - |
| ICU, n (%) | 3 (6) | - | - |
| Mechanical ventilation, n (%) | 1 (2) | - | - |
| BISAP score, n (0) | - | - | |
| 0 | 14 (28) | ||
| 1 | 20 (40) | ||
| 2 | 9 (18) | ||
| 3 | 7 (14) | ||
| AP criteria, n (%) | - | - | |
| 2 | 26 (52) | ||
| 3 | 24 (48) | ||
| LOS, days, median [IQR] | 6 [3–6] | - | - |
| HC | AP T1 | AP T2 | AP T3 | AP T4 | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP | - | 0.32 ± 0.72 (−1.00; 1.40) | 0.75 ± 0.61 (−0.74; 1.6) | −0.44 ± 0.53 (−1.30; 0.58) | - | <0.0001 |
| IL-4 | 0.25 ± 0.11 (0.12; 0.44) | 0.18 ± 0.07 (0.10; 0.40) | 0.23 ± 0.11 (0.1; 0.51) | 0.26 ± 0.14 (0.10; 0.58) | 0.21 ± 0.11 (0.10; 0.47) | 0.013 |
| IL-6 | 0.41 ± 0.21 (0.14; 0.96) | 1.50 ± 0.66 (0.20; 3.2) | 1.20 ± 0.59 (0.29; 3.00) | 0.67 ± 0.39 (0.16; 1.70) | 0.54 ± 0.30 (0.14; 1.30) | <0.0001 |
| IL-8 | 0.80 ± 0.21 (0.30; 1.20) | 1.40 ± 0.56 (0.26; 3.2) | 1.30 ± 0.67 (0.44; 3.20) | 0.90 ± 0.42 (0.28; 2.2) | 0.93 ± 0.28 (0.26; 1.5) | <0.0001 |
| IL-10 | 0.26 ± 0.10 (0.16; 0.52) | 0.53 ± 0.28 (0.17; 1.10) | 0.24 ± 0.06 (0.17; 0.37) | 0.27 ± 0.11 (0.17; 0.56) | 0.27 ± 0.09 (0.17; 0.47) | <0.0001 |
| VEGF | 1.90 ± 0.34 (1.30; 2.70) | 2.30 ± 0.35 (1.50; 2.90) | 2.30 ± 0.34 (1.40; 3.00) | 2.10 ± 0.33 (1.30; 2.80) | 2.20 ± 0.28 (1.60; 2.60) | <0.0001 |
| TNF-α | 0.42 ± 0.16 (0.18; 0.88) | 0.65 ± 0.30 (0.10; 1.50) | 0.65 ± 0.30 (0.14; 1.50) | 0.49 ± 0.18 (0.10; 1.2) | 0.52 ± 0.18 (0.20; 1.10) | 0.0001 |
| IL-1α | −0.18 ± 0.15 (−0.36; 0.14) | −0.21 ± 0.14 (−0.37; 0.08) | −0.20 ± 0.11 (−0.37; 0.06) | −0.22 ± 0.13 (−0.37; 0.08) | −0.16 ± 0.17 (−0.37; 0.37) | 0.577 |
| MCP-1 | 2.40 ± 0.18 (2.00; 2.70) | 2.60 ± 0.26 (1.90; 3.20) | 2.50 ± 0.13 (2.10; 2.70) | 2.50 ± 0.13 (2.20; 2.80) | 2.4 ± 0.17 (1.9; 2.8) | <0.0001 |
| EGF | 1.60 ± 0.47 (0.56; 2.40) | 2.20 ± 0.20 (1.70; 2.60) | 2.20 ± 0.23 (1.50; 2.60) | 2.00 ± 0.35 (0.93; 2.60) | 1.9 ± 0.44 (0.77; 2.5) | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malheiro, F.; Ângelo-Dias, M.; Lopes, T.; Martins, C.G.; Borrego, L.M. Cytokine Dynamics in Acute Pancreatitis: The Quest for Biomarkers from Acute Disease to Disease Resolution. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082287
Malheiro F, Ângelo-Dias M, Lopes T, Martins CG, Borrego LM. Cytokine Dynamics in Acute Pancreatitis: The Quest for Biomarkers from Acute Disease to Disease Resolution. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(8):2287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082287
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalheiro, Filipa, Miguel Ângelo-Dias, Teresa Lopes, Catarina Gregório Martins, and Luis Miguel Borrego. 2024. "Cytokine Dynamics in Acute Pancreatitis: The Quest for Biomarkers from Acute Disease to Disease Resolution" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 8: 2287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082287
APA StyleMalheiro, F., Ângelo-Dias, M., Lopes, T., Martins, C. G., & Borrego, L. M. (2024). Cytokine Dynamics in Acute Pancreatitis: The Quest for Biomarkers from Acute Disease to Disease Resolution. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(8), 2287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082287





