Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index as Predictors of Disability Progression in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Standard Protocol, Approvals, and Registration
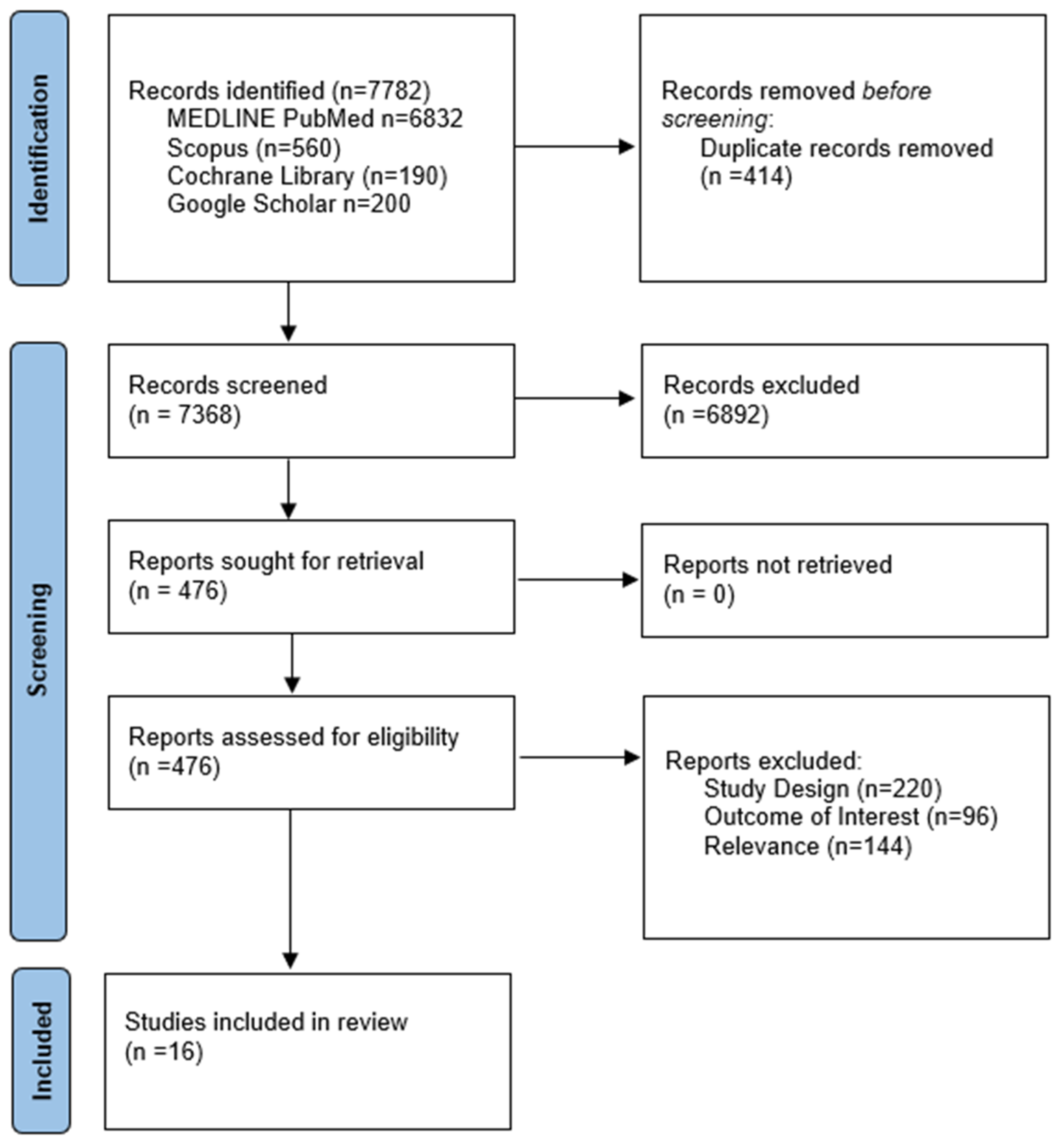
2.2. Data Sources, Search, and Study Selection
2.3. Quality Control, Bias Assessment, and Data Extraction
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Data Availability Statement
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Included Studies
3.2. Quality Control
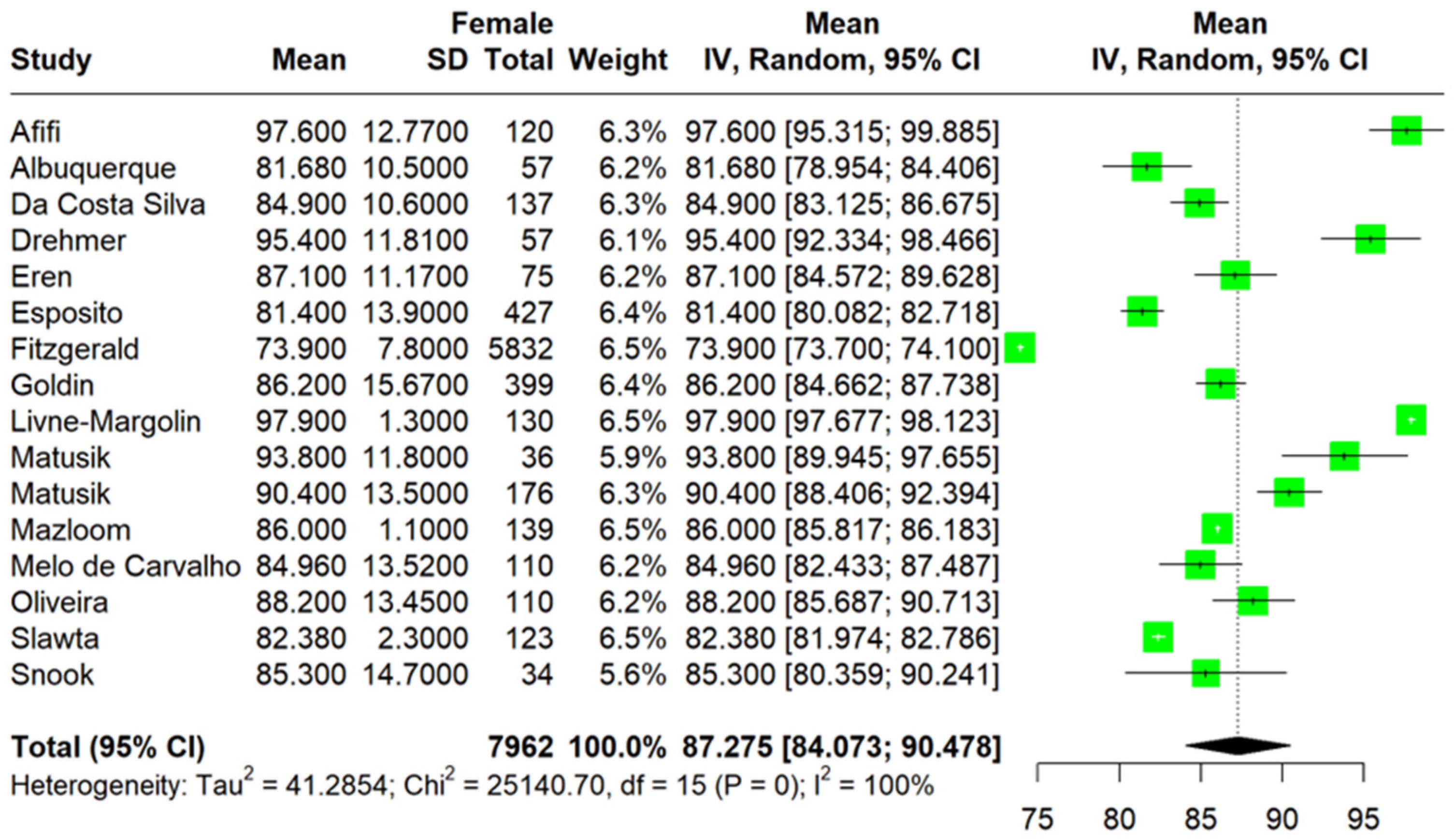
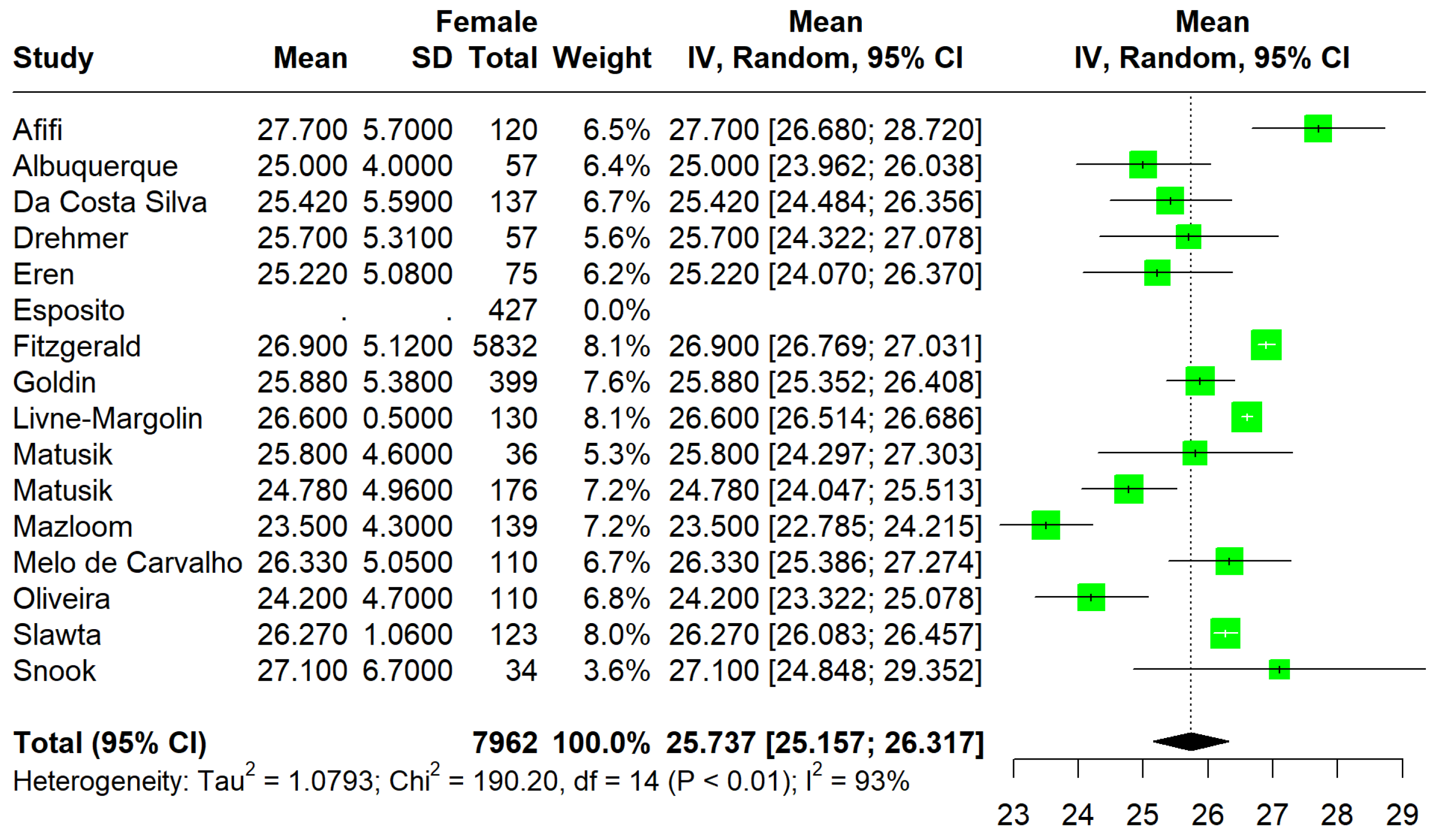
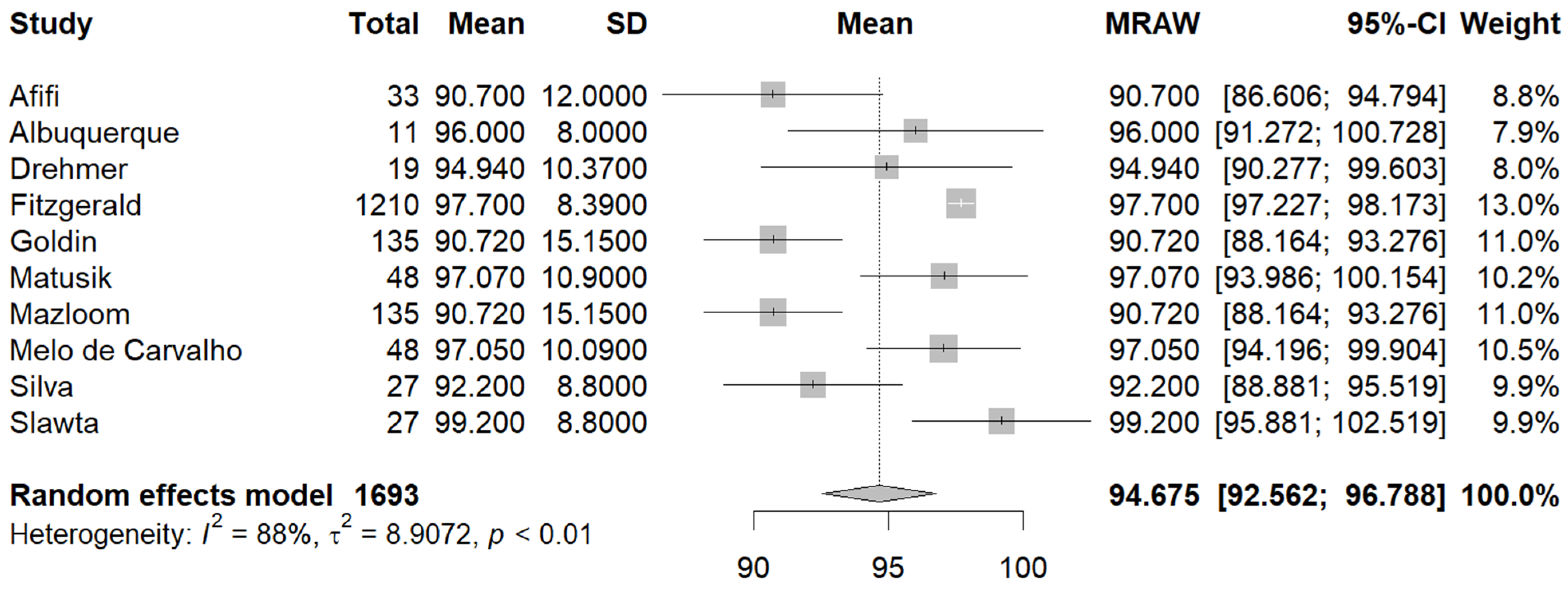
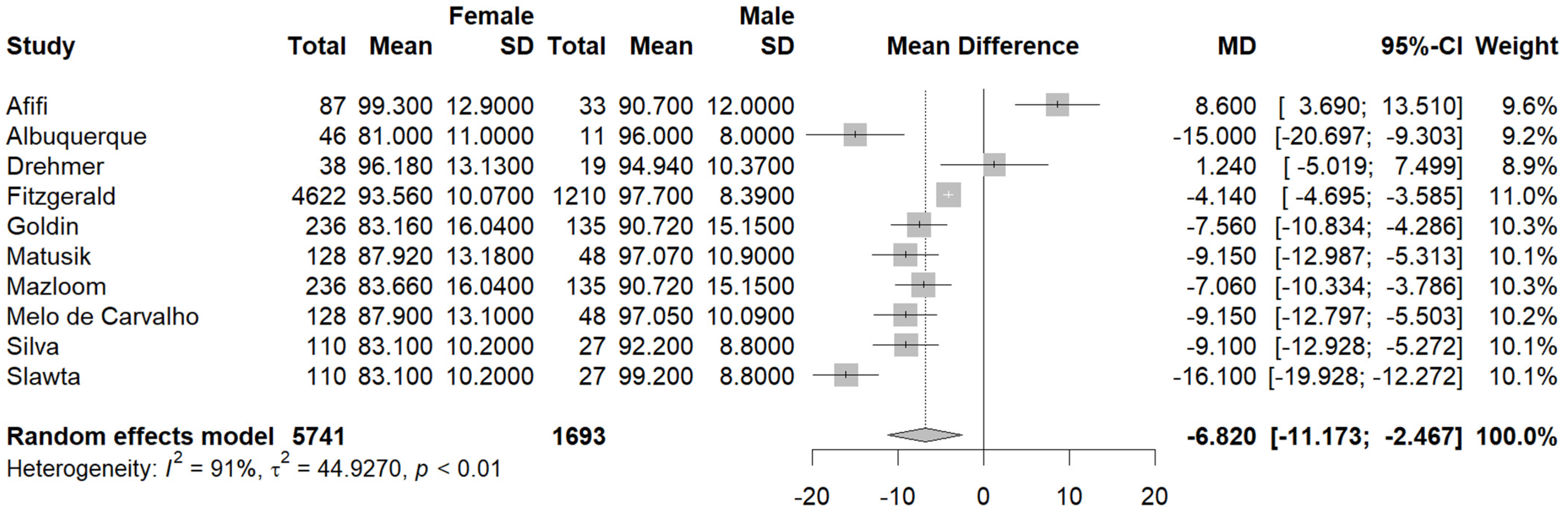
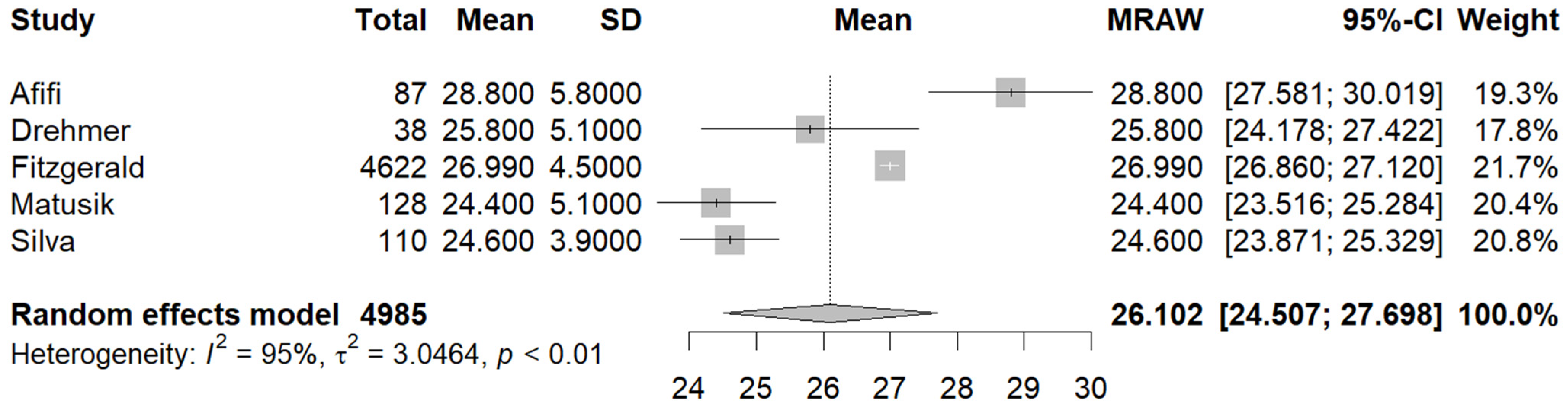
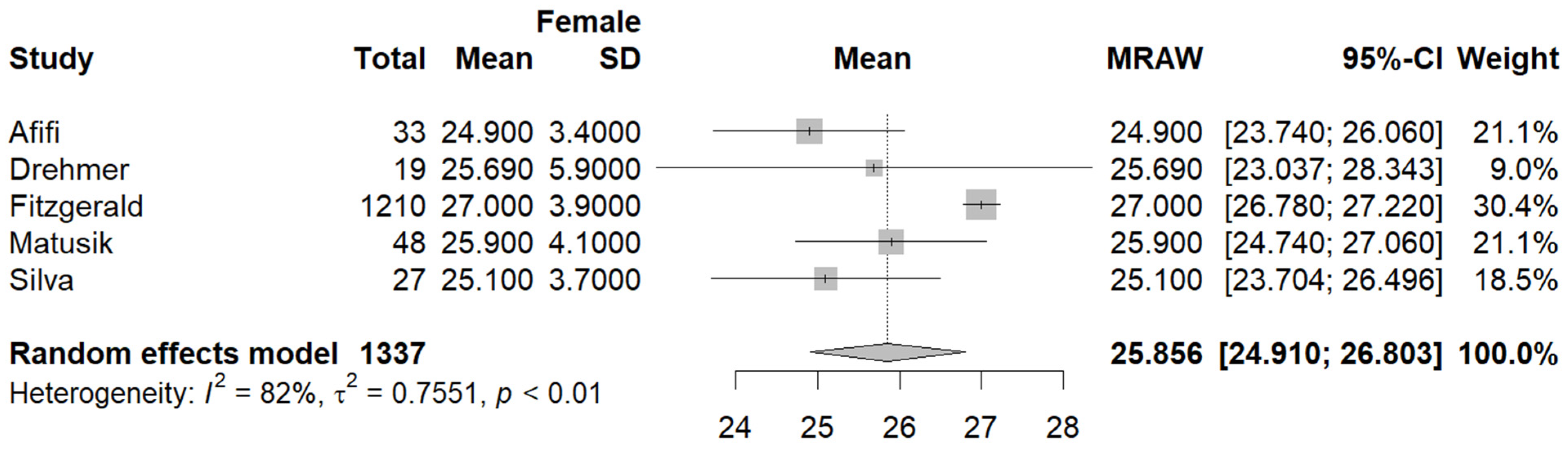
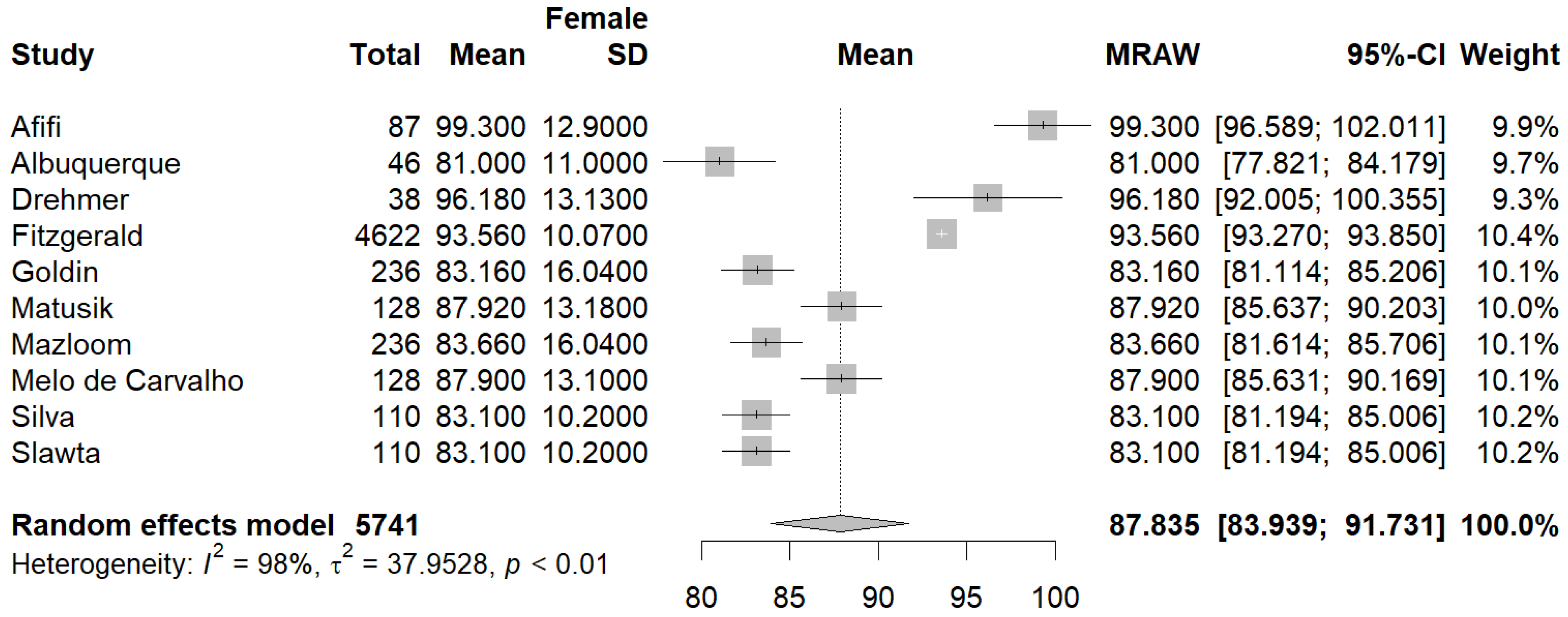
3.3. Quantitative Analysis
3.3.1. Primary Outcomes
3.3.2. Secondary Outcomes
3.3.3. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Issues to Be Addressed
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis—A review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, D.S.; Thompson, N.R.; Cohen, J.A. Influence of hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and obstructive lung disease on multiple sclerosis disease course. Mult. Scler. J. 2017, 23, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannopapas, V.; Stavrogianni, K.; Christouli, N.; Kitsos, D.; Sideri, E.; Bakalidou, D.; Voumvourakis, K.; Papagiannopoulou, G.; Tzartos, J.; Paraskevas, G.; et al. Do cardiovascular disease comorbidities affect the cognitive function of Multiple Sclerosis patients? J. Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 112, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zoubi, S.A.; Esam, H.; Elzawi, E. Impact of Dyslipidemia on Progression of Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 71, 104367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Dubey, P.; Cistola, D.P.; Reddy, S.Y. Association Between Obesity and Cardiovascular Outcomes: Updated Evidence from Meta-analysis Studies. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedström, A.K.; Olsson, T.; Alfredsson, L. High body mass index before age 20 is associated with increased risk for multiple sclerosis in both men and women. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 1334–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokry, L.E.; Ross, S.; Timpson, N.J.; Sawcer, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Richards, J.B. Obesity and Multiple Sclerosis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Muraro PA, editor. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002053. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Larsson, S.C. An atlas on risk factors for multiple sclerosis: A Mendelian randomization study. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harroud, A.; Mitchell, R.E.; Richardson, T.G.; A Morris, J.; Forgetta, V.; Smith, G.D.; E Baranzini, S.; Richards, J.B. Childhood obesity and multiple sclerosis: A Mendelian randomization study. Mult. Scler. J. 2021, 27, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mraz, M.; Haluzik, M. The role of adipose tissue immune cells in obesity and low-grade inflammation. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 222, R113–R127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smotkin-Tangorra, M.; Purushothaman, R.; Gupta, A.; Nejati, G.; Anhalt, H.; Ten, S. Prevalence of Vitamin D Insufficiency in Obese Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 20, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, M.S.; Iezzi, E.; Buttari, F.; Gilio, L.; Simonelli, I.; Carbone, F.; Micillo, T.; De Rosa, V.; Sica, F.; Furlan, R.; et al. Obesity worsens central inflammation and disability in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, W.-Y.; Kalron, A. The Association between Body Mass Index and Leisure-Time Physical Activity in Adults with Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, H.L.; Stevenson, C.E.; Mannan, H.R.; Abdullah, A.; Reid, C.M.; McNeil, J.J.; Peeters, A. Comparing Trends in BMI and Waist Circumference. Obesity 2011, 19, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Chou, R.; Moher, D.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochran, W.G. The Comparison of Percentages in Matched Samples. Biometrika 1950, 37, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhning, D.; Lerdsuwansri, R.; Holling, H. Some general points on the I2—Measure of heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Metrika 2017, 80, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chu, H. Quantifying Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. Biometrics 2018, 74, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, S.; Zhao, X.; Steele, R.; Thombs, B.D.; Benedetti, A.; Levis, B.; Riehm, K.E.; Saadat, N.; Levis, A.W.; Azar, M.; et al. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from commonly reported quantiles in meta-analysis. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2020, 29, 2520–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balduzzi, S.; Rücker, G.; Schwarzer, G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: A practical tutorial. Évid. Based Ment. Health 2019, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slawta, J.N.; Mccubbin, J.A.; Wilcox, A.R.; Fox, S.D.; Nalle, D.J.; Anderson, G. Coronary heart disease risk between active and inactive women with multiple sclerosis. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snook, E.M.; Mojtahedi, M.C.; Evans, E.M.; McAuley, E.; Motl, R.W. Physical Activity and Body Composition Among Ambulatory Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. MS Care 2005, 7, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.R.; Simão, A.N.; Kallaur, A.P.; de Almeida, E.R.; Morimoto, H.K.; Lopes, J.; Dichi, I.; Kaimen-Maciel, D.R.; Reiche, E.M. Disability in patients with multiple sclerosis: Influence of insulin resistance, adiposity, and oxidative stress. Nutrition 2014, 30, 268–273. [Google Scholar]
- Mazloom, Z.; Razmjouei, N.; Hejazi, N.; Sanjarian Dehaghani, F. Food Insecurity in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis and Its Association with Anthropometric Measurements. Int. J. Nutr. Sci. 2017, 2, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa Silva, B.Y.; De Carvalho Sampaio, H.A.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.; Silva Albuquerque, L.D.; Ferreira Carioca, A.A.; D’Almeida, J.A.C.; Costa Maia, C.S.; Luisa Pereira De Melo, M. Interactions between dietary inflammatory index, nutritional state and Multiple Sclerosis clinical condition. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 26, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matusik, E.; Augustak, A.; Durmala, J. Functional Mobility and Basic Motor Skills in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis and Its Relation to the Anthropometrical Status and Body Composition Parameters. Medicina 2019, 55, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drehmer, E.; Platero, J.L.; Carrera-Juliá, S.; Moreno, M.L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Navarro, M.; López-Rodríguez, M.M.; Ortí, J.E.d.l.R. The Relation between Eating Habits and Abdominal Fat, Anthropometry, PON1 and IL-6 Levels in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.C.; Salter, A.; Tyry, T.; Fox, R.J.; Cutter, G.; Marrie, R.A. Measures of general and abdominal obesity and disability severity in a large population of people with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Sparaco, M.; Maniscalco, G.; Signoriello, E.; Lanzillo, R.; Russo, C.; Carmisciano, L.; Cepparulo, S.; Lavorgna, L.; Gallo, A.; et al. Lifestyle and Mediterranean diet adherence in a cohort of Southern Italian patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 47, 102636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livne-Margolin, M.; Latzer, I.T.; Pinhas-Hamiel, O.; Harari, G.; Achiron, A. Bodyweight Measures and Lifestyle Habits in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis and Moderate to Severe Disability. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eren, F.; Ozkan, B.; Demir, A. The relationship between dysphagia, respiratory functions and anthropometry in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 55, 103192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, L.d.S.; Damasceno, N.R.T.; Maia, F.N.; de Carvalho, B.M.; Maia, C.S.C.; D’Almeida, J.A.C.; de Melo, M.L.P. Cardiovascular risk estimated in individuals with multiple sclerosis: A case-control study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 54, 103133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusik, E.; Durmala, J.; Ksciuk, B.; Matusik, P. Body Composition in Multiple Sclerosis Patients and Its Relationship to the Disability Level, Disease Duration and Glucocorticoid Therapy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldin, K.; Riemann-Lorenz, K.; Daubmann, A.; Pöttgen, J.; Krause, N.; Schröder, H.; Heesen, C. Health behaviors of people with multiple sclerosis and its associations with MS related outcomes: A German clinical cohort. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1172419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afifi, Z.; Hassan, A.; Abdelrahman, N.; El Sayed, A.; Salem, M. Impact of nutrition counseling on anthropometry and dietary intake of multiple sclerosis patients at Kasr Alainy Multiple Sclerosis Unit, Cairo, Egypt 2019–2020: Randomized controlled clinical trial. Arch. Public Health 2023, 81, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, B.M.D.; Silva, R.S.C.; Lima, V.V.M.D.; Almondes, K.G.D.S.; Rodrigues, F.N.S.; D’Almeida, J.A.C.; de Melo, M.L.P. Excess weight increases the risk of sarcopenia in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 79, 105049. [Google Scholar]
- Dardiotis, E.; Tsouris, Z.; Aslanidou, P.; Aloizou, A.-M.; Sokratous, M.; Provatas, A.; Siokas, V.; Deretzi, G.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M. Body mass index in patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A meta-analysis. Neurol. Res. 2019, 41, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.; Neeland, I.J.; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, R.D.; Arsenault, B.; Cuevas, A.; Hu, F.B.; et al. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: A Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilutti, L.A.; Motl, R.W. Body Mass Index Underestimates Adiposity in Persons with Multiple Sclerosis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroff, B.M.; Klaren, R.E.; Motl, R.W. Relationships Among Physical Inactivity, Deconditioning, and Walking Impairment in Persons with Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2015, 39, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feltham, M.G.; Collett, J.; Izadi, H.; Wade, D.; Morris, M.G.; Meaney, A.J.; Howells, K.; Sackley, C.; Dawes, H. Cardiovascular adaptation in people with multiple sclerosis following a twelve week exercise programme suggest deconditioning rather than autonomic dysfunction caused by the disease. Results from a randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 49, 765–774. [Google Scholar]
- Valet, M.; Lejeune, T.; Glibert, Y.; Hakizimana, J.C.; Van Pesch, V.; El Sankari, S.; Detrembleur, C.; Stoquart, G. Fatigue and physical fitness of mildly disabled persons with multiple sclerosis: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2017, 40, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Shin, G.G.; Han, J.A.; Kim, J.W. Association between Abdominal Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Adults with Normal Body Mass Index: Based on the Sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 28, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, S.; Boeing, H.; Pischon, T. Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt. Online 2010, 107, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, P.; Wang, S.-X. Risk for Cardiovascular Death Associated with Waist Circumference and Diabetes: A 9-Year Prospective Study in the Wan Shou Lu Cohort. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 856517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siren, R.; Eriksson, J.G.; Vanhanen, H. Waist circumference a good indicator of future risk for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannopapas, V.; Palaiodimou, L.; Kitsos, D.; Papagiannopoulou, G.; Stavrogianni, K.; Chasiotis, A.; Kosmidou, M.; Tzartos, J.S.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Bakalidou, D.; et al. The Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus Type II (DMII) in the Multiple Sclerosis Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correale, J.; Marrodan, M. Multiple sclerosis and obesity: The role of adipokines. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1038393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breden, M.A.; Smith, B.K.; Harris, M.P.; Gloekner, A.; Burgess, B.; Phillips, M.D.; Wooten, J.S. TACSM Abstract the Effect of Gender on Circulating Adipokines during Weight Loss and Weight Maintenance. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. Conf. Proc. 2016, 8, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Eriks-Hoogland, I.; Hilfiker, R.; Baumberger, M.; Balk, S.; Stucki, G.; Perret, C. Clinical assessment of obesity in persons with spinal cord injury: Validity of waist circumference, body mass index, and anthropometric index. J. Spinal. Cord. Med. 2011, 34, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchholz, A.C.; Bugaresti, J.M. A review of body mass index and waist circumference as markers of obesity and coronary heart disease risk in persons with chronic spinal cord injury. Spinal. Cord. 2005, 43, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfullin, I.; Eveslage, M.; Bittner, S.; Antony, G.; Flaskamp, M.; Luessi, F.; Salmen, A.; Gisevius, B.; Klotz, L.; Korsukewitz, C.; et al. Association of obesity with disease outcome in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Year | Region | Study Design | Sample Size | Mean Age | RRMS | EDSS | Disease Duration | Female/Male |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slawta et al. [23] | 2002 | USA | OBS | 123 | 46.4 | 123/0 | |||
| Snook et al. [24] | 2005 | USA | OBS | 34 | 44.3 | 6.9 | 32/2 | ||
| Oliveira et al. [25] | 2014 | Brazil | RCT | 110 | 38.2 | 64.7 | 3.2 | 6.3 | 75/35 |
| Mazloom et al. [26] | 2017 | Italy | CS | 139 | 26.5 | 118/21 | |||
| (Da Costa) Silva et al. [27] | 2018 | Brazil | CS | 137 | 88.3% | 110/27 | |||
| Matusik et al. [28] | 2019 | Poland | OBS | 36 | 4.4 | 24/12 | |||
| Drehmer et al. [29] | 2020 | Spain | OBS | 57 | 49.7 | 3.8 | 38/19 | ||
| Fitzgerald et al. [30] | 2020 | USA | OBS | 5832 | 54.6 | 4622/1210 | |||
| Esposito et al. [31] | 2020 | Italy | CS | 427 | 42.4 | 3.6 | 10 | 292/135 | |
| Livne-Margolin et al. [32] | 2021 | Israel | CS | 130 | 55.8 | 5.5 | 18.2 | 94/36 | |
| Eren et al. [33] | 2021 | Turkey | RCT | 75 | 38.4 | 70.7% | 2.5 | 7.82 | 50/25 |
| Albuquerque et al. [34] | 2021 | Brazil | CC | 57 | 34.6 | 89.5% | 1 | 6 | 48/9 |
| Matusik et al. [35] | 2022 | Poland | OBS | 176 | 45.7 | 69.8% | 3.3 | 10.9 | 128/48 |
| Goldin et al. [36] | 2023 | German | Cohort | 399 | 41.8 | 236/135 | |||
| Afifi et al. [37] | 2023 | Egypt | RCT | 120 | 33.5 | 3.1 | 7 | 87/33 | |
| Melo de Carvalho et al. [38] | 2023 | Brazil | OBS | 110 | 37.1 | 89.1% | 1.9 | 6.29 | 89/21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannopapas, V.; Stefanou, M.-I.; Smyrni, V.; Kitsos, D.K.; Kosmidou, M.; Stasi, S.; Chasiotis, A.K.; Stavrogianni, K.; Papagiannopoulou, G.; Tzartos, J.S.; et al. Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index as Predictors of Disability Progression in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061739
Giannopapas V, Stefanou M-I, Smyrni V, Kitsos DK, Kosmidou M, Stasi S, Chasiotis AK, Stavrogianni K, Papagiannopoulou G, Tzartos JS, et al. Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index as Predictors of Disability Progression in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(6):1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061739
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannopapas, Vasileios, Maria-Ioanna Stefanou, Vassiliki Smyrni, Dimitrios K. Kitsos, Maria Kosmidou, Sophia Stasi, Athanasios K. Chasiotis, Konstantina Stavrogianni, Georgia Papagiannopoulou, John S. Tzartos, and et al. 2024. "Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index as Predictors of Disability Progression in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 6: 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061739
APA StyleGiannopapas, V., Stefanou, M.-I., Smyrni, V., Kitsos, D. K., Kosmidou, M., Stasi, S., Chasiotis, A. K., Stavrogianni, K., Papagiannopoulou, G., Tzartos, J. S., Paraskevas, G. P., Tsivgoulis, G., & Giannopoulos, S. (2024). Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index as Predictors of Disability Progression in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(6), 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061739