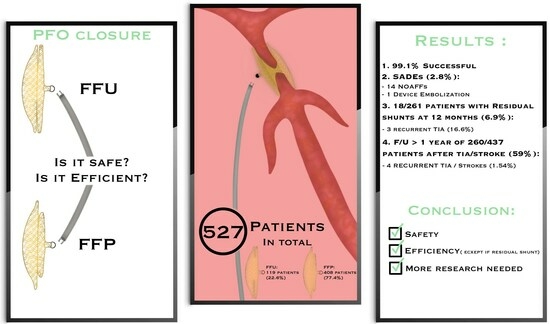
The RISE Study: Retrospective Registry for the International Safety and Efficacy Results of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure with Figulla Flex Il PFO and UNI Occluders
Abstract
1. Introduction
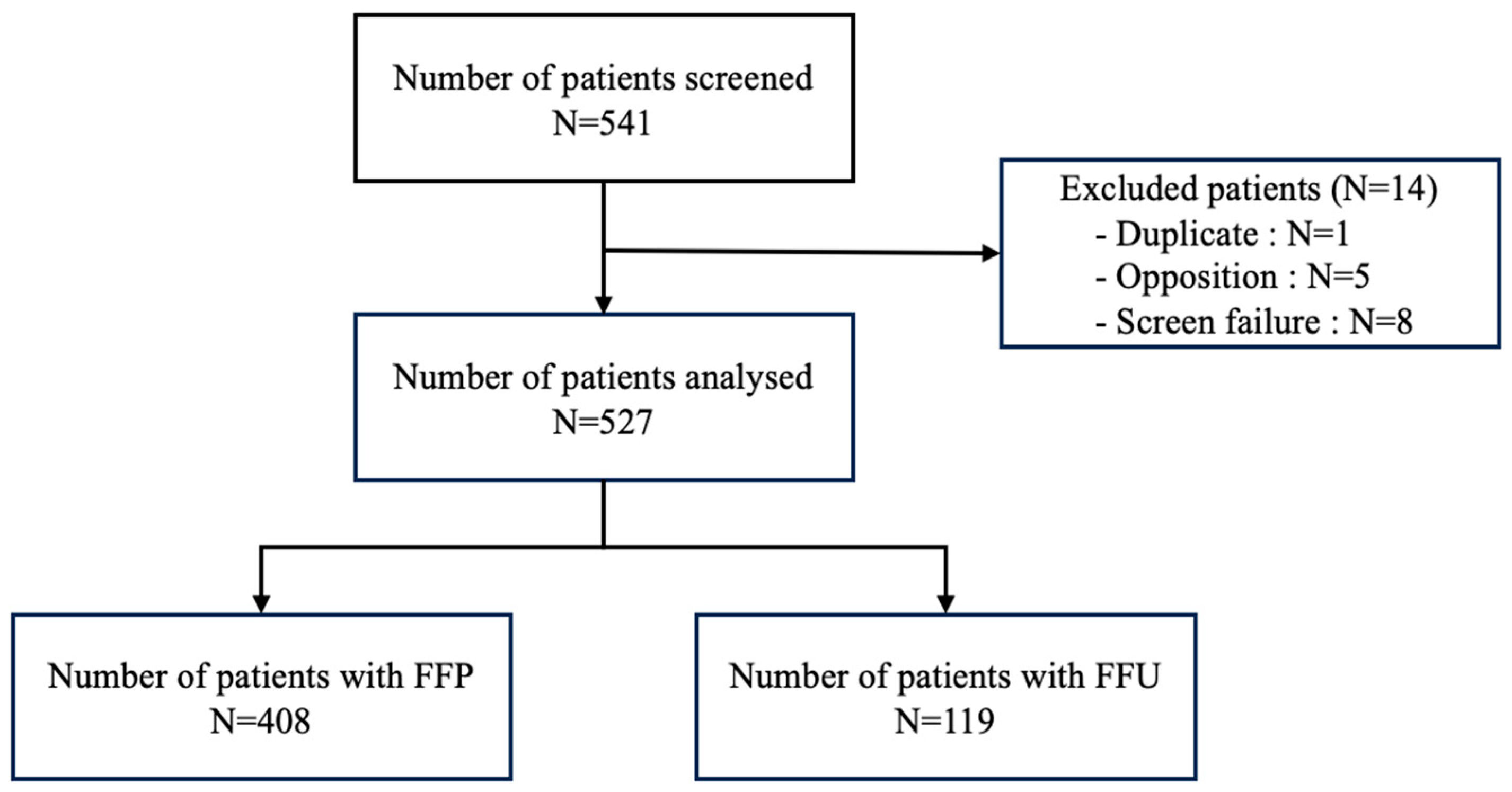
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Eligibility
2.2. Data Collection/Follow Up
2.3. Objectives
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics and Procedure (Table 1)
| Baseline Characteristics | Patient Population—Nb (%) or Mean (± SD) |
|---|---|
| Female | 247 (46.9) |
| Age (years) | 48.9 (±13.8) |
| Height (cm) | 171.2 (±9.3) |
| Weight (kg) | 73.8 (±16.2) |
| No smoking history | 389 (74.0) |
| Hypertension | 134 (25.5) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 120 (22.9) |
| Diabetes | 25 (4.8) |
| Renal dysfunction | 8 (1.5) |
| Cardiac surgery | 20 (3.8) |
| Coronary angiogram | 10 (1.9) |
| Any other cardiac event | 37 (7.0) |
| Indication for PFO closure | |
| Stroke | 302 (57.3) |
| TIA | 155 (29.4) |
| Peripheral embolic event | 10 (1.9) |
| Migraine | 81 (15.4) |
| Hypoxemia | 21 (4.0) |
| Decompression illness | 5 (0.9) |
| Professional scuba divers without decompression illness | 1 (0.2) |
| Other | 21 (4.0) |
3.2. SADE and Outcome (Table 2)
| Follow Up | Patient Population (n = 527)—Nb (%) |
|---|---|
| 1 month | 424 (80.5) |
| 6 months | 322 (61.1) |
| 12 months | 279 (52.9) |
| 5 years or last follow-up | 192 (36.4) |
| SADEs following implantation. | |
| Cardiac erosion | 0 (0) |
| Endocarditis | 0 (0) |
| Thrombus formation on the device | 0 (0) |
| Cardiac tamponade | 0 (0) |
| NOAFF within 6 months after implantation | 14 (2.7) |
| Device embolization | 1 (0.2) |
| Neuro events after PFO closure for stroke/TIA | Population >1 y F/U (n = 260)—Nb (%) |
| Recurrent TIA | 2 (0.76) |
| Recurrent stroke | 2 (0.76) |
3.3. Comparison of FFP with FFU Devices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hagen, P.T.; Scholz, D.G.; Edwards, W.D. Incidence and size of patent foramen ovale during the first 10 decades of life: An autopsy study of 965 normal hearts. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1984, 59, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, J.L.; Derumeaux, G.; Guillon, B.; Massardier, E.; Hosseini, H.; Mechtouff, L.; Arquizan, C.; Béjot, Y.; Vuillier, F.; Detante, O.; et al. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Anticoagulation vs. Antiplatelets after Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, L.; Kasner, S.E.; Rhodes, J.F.; Andersen, G.; Iversen, H.K.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Settergren, M.; Sjöstrand, C.; Roine, R.O.; Hildick-Smith, D.; et al. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Antiplatelet Therapy for Cryptogenic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saver, J.L.; Carroll, J.D.; Thaler, D.E.; Smalling, R.W.; MacDonald, L.A.; Marks, D.S.; Tirschwell, D.L. Long-Term Outcomes of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Medical Therapy after Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardt, S.E.; Eicken, A.; Berger, F.; Schubert, S.; Carminati, M.; Butera, G.; Grohmann, J.; Höhn, R.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Hildick-Smith, D.; et al. Closure of patent foramen ovale defects using GORE® CARDIOFORM septal occluder: Results from a prospective European multicenter study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 90, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, S.; Siebert, E.; Mbroh, J.; Poli, K.; Krumbholz, M.; Mengel, A.; Greulich, S.; Härtig, F.; Müller, K.A.L.; Bocksch, W.; et al. Closure or medical therapy of patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic stroke: Prospective case series. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2021, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spies, C.; Strasheim, R.; Timmermanns, I.; Schraeder, R. Patent foramen ovale closure in patients with cryptogenic thrombo-embolic events using the Cardia PFO occluder. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, L.; Rubbio, A.P.; Squillace, M.; Albano, F.; Cesario, V.; Casenghi, M.; Tarantini, G.; Pagnotta, P.; Ielasi, A.; Popusoi, G.; et al. Patent foramen ovale occlusion with the Cocoon PFO Occluder. The PROS-IT collaborative project. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 9, 1064026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, R.J.R.; Renes, L.E.; Suttorp, M.J.; Ten Berg, J.M.; Post, M.C. Percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure using the Occlutech Figulla device: More than 1300 patient-years of follow up. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 93, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luermans, J.G.; Post, M.C.; Plokker, H.W.; Ten Berg, J.M.; Suttorp, M.J. Complications and mid-term outcome after percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure in patients with cryptogenic stroke. Neth. Heart J. 2008, 16, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.C.; Van Deyk, K.; Budts, W. Percutaneous closure of a patent foramen ovale: Single-centre experience using different types of devices and mid-term outcome. Acta Cardiol. 2005, 60, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornung, M.; Bertog, S.C.; Franke, J.; Id, D.; Taaffe, M.; Wunderlich, N.; Vaskelyte, L.; Hofmann, I.; Sievert, H. Long-term results of a randomized trial comparing three different devices for percutaneous closure of a patent foramen ovale. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3362–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wintzer-Wehekind, J.; Alperi, A.; Houde, C.; Côté, J.-M.; Asmarats, L.; Côté, M.; Rodés-Cabau, J. Long-Term Follow-Up after Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale in Patients with Cryptogenic Embolism. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagianni, A.; Mandalenakis, Z.; Dellborg, M.; Mirzada, N.; Johansson, M.C.; Eriksson, P. Recurrent cerebrovascular events in patients after percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale. J Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabattoni, D.; Gaspardone, A.; Sgueglia, G.; Fabbiocchi, F.; Gioffrè, G.; Montorsi, P.; Calligaris, G.; Iamele, M.; De Santis, A.; Bartorelli, A. AMPLATZER versus Figulla occluder for transcatheter patent foramen ovale closure. EuroIntervention 2017, 12, 2092–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuser, J.; Akin, M.; Bavendiek, U.; Kempf, T.; Bauersachs, J.; Widder, J.D. Mid-term results of interventional closure of patent foramen ovale with the Occlutech Figulla® Flex II Occluder. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2016, 16, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scalise, F.; Auguadro, C.; Sorropago, G.; Sorropago, A.; Novelli, E.; Finizio, M.; Specchia, G. Long-Term Contrast Echocardiography and Clinical Follow-Up after Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale Using Two Different Atrial Septal Occluder Devices. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2016, 29, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, D.; Eicken, A.; Dähnert, I.; Boudjemline, Y.; Sievert, H.; Schneider, M.B.; Gori, T.; Hijazi, Z.M. A randomized, controlled, multi-center trial of the efficacy and safety of the Occlutech Figulla Flex-II Occluder compared to the Amplatzer Septal Occluder for transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 93, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meerhaeghe, T.; Droogmans, S.; Hanon, S.; Sonck, J. Platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome: An unusual presentation of a complex disease. Acta Clin. Belg. 2018, 73, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabattoni, D.; Gili, S.; Calligaris, G.; Teruzzi, G.; Troiano, S.; Ravagnani, P.; Baldi, G.S.; Montorsi, P. Patent foramen ovale closure with the Occlutech Figulla flex II device: A long-term (up to 10-years) follow-up. Int. J. Cardiol. 2023, 387, 131116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjat-Pasos, J.I.; Guedeney, P.; Houde, C.; Alperi, A.; Robichaud, M.; Côté, M.; Montalescot, G.; Rodés-Cabau, J. Transcatheter Patent Foramen Ovale Closure in Patients With Transient Ischemic Attack. Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 187, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Kumar, P.; Mahmoud, A.N.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Shapiro, H.; West, B.; Charles, A.C.; Mattle, H.P.; Sorensen, S.; Meier, B.; et al. Pooled Analysis of PFO Occluder Device Trials in Patients with PFO and Migraine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheiri, B.; Abdalla, A.; Osman, M.; Ahmed, S.; Hassan, M.; Bachuwa, G.; Bhatt, D.L. Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale in Migraine: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, 816–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, T.; Cubeddu, R.J.; Rengifo-Moreno, P.A.; Cruz-Gonzalez, I.; Solis-Martin, J.; Buonanno, F.S.; Inglessis, I.; Palacios, I.F. Management of residual shunts after initial percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure: A single center experience with immediate and long-term follow-up. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 76, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Yin, S.; McMullin, D.; Inglessis-Azuaje, I.; Elmariah, S.; Hung, J.; Lo, E.H.; Palacios, I.F.; Buonanno, F.S.; Ning, M. Residual Shunt after Patent Foramen Ovale Closure and Long-Term Stroke Recurrence: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butera, G.; Sarabia, J.F.; Saracino, A.; Chessa, M.; Piazza, L.; Carminati, M. Residual shunting after percutaneous PFO closure: How to manage and how to close. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 82, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigatelli, G.; Dell’Avvocata, F.; Cardaioli, P.; Braggion, G.; Giordan, M.; Mazza, A.; Fraccaro, C.; Chinaglia, M.; Chen, J.P. Long-term results of the amplatzer cribriform occluder for patent foramen ovale with associated atrial septal aneurysm: Impact on occlusion rate and left atrial functional remodelling. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 2, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silvestry, F.E.; Naseer, N.; Wiegers, S.E.; Hirshfeld, J.W.; Herrmann, H.C. Percutaneous transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale with the Amplatzer Cribriform septal occluder. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2008, 71, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F. Patent foramen ovale closure by using transesophageal echocardiography for cryptogenic stroke: Single center experience in 132 consecutive patients. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scacciatella, P.; Meynet, I.; Giorgi, M.; Biava, L.M.; Matranga, I.; Biasco, L.; Omedè, P.; Orzan, F.; Gaita, F. Angiography vs transesophageal echocardiography-guided patent foramen ovale closure: A propensity score matched analysis of a two-center registry. Echocardiography 2018, 35, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Q.; Gao, L.; Jin, W.; Zhao, T. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects without fluoroscopy: A well-established procedure for alternative use in children. EuroIntervention 2016, 12, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratori, M.; Agostoni, P.; Trabattoni, D. When a patent foramen ovale device is no more in place: Silent patent foramen ovale occluder device migration to the aortic arch. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2018, 3, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Rusheen, J.; Tobis, J.M. A comparison of methods to determine patent foramen ovale size. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 96, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staubach, S.; Steinberg, D.H.; Zimmermann, W.; Wawra, N.; Wilson, N.; Wunderlich, N.; Sievert, H. New onset atrial fibrillation after patent foramen ovale closure. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2009, 74, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z.; Thijs, V.N. Atrial Fibrillation Following Patent Foramen Ovale Closure: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies and Clinical Trials. Stroke 2021, 52, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlinger, C.; Paar, V.; Kheder, S.H. Endothelialization and Inflammatory Reactions after Intracardiac Device Implantation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1401, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diepgen, T.L.; Ofenloch, R.F.; Bruze, M.; Bertuccio, P.; Cazzaniga, S.; Coenraads, P.-J.; Elsner, P.; Goncalo, M.; Svensson, Å.; Naldi, L. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population in different European regions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leger, C.S.; DeSouza, J.F. Migraine Modulation and Debut after Percutaneous Atrial Septal Defect Closure: A Review. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kealaher, A.; Tharindra Dissanayake, P.S.; Thomas, D.E.; Barry, J.; Margulescu, A.D. Hypersensitivity Reactions to Components of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices and Their Treatment: A Systematic Review. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. Rev. 2023, 12, e08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patients’ Characteristics | FFP (n = 408) Nb (%) or Mean (±SD) | FFU (n = 119) Nb (%) or Mean (±SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 191 (46.8) | 56 (47.1) | 0.96 |
| Age (years) | 48.2 (+13.2) | 51.5 (+15.3) | 0.03 |
| Height (cm) | 171.1 (+9.2) | 171.6 (+9.8) | 0.47 |
| Weight (kg) | 72.8 (+15.3) | 77.1 (+18.7) | 0.05 |
| No smoking history | 309 (75.9) | 80 (67.2) | 0.04 |
| Hypertension | 98 (24.0) | 36 (30.8) | 0.14 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 92 (22.5) | 28 (23.9) | 0.75 |
| Diabetes | 15 (3.7) | 10 (8.5) | 0.03 |
| Renal dysfunction | 6 (1.5) | 2 (1.7) | 1.00 |
| Other cardiac surgery | 13 (3.2) | 7 (6.0) | 0.17 |
| Other cardiac events | 25 (6.1) | 12 (10.3) | 0.12 |
| Indication for PFO closure | |||
| Stroke | 227 (55.6) | 75 (63.0) | 0.15 |
| TIA | 133 (32.6) | 22 (18.5) | 0.003 |
| Peripheral embolic event | 6 (1.5) | 4 (3.4) | 0.24 |
| Migraine | 73 (17.9) | 8 (6.7) | 0.003 |
| Hypoxemia | 14 (3.4) | 7 (5.9) | 0.28 |
| Decompression illness | 2 (0.5) | 3 (2.5) | 0.08 |
| Professional scuba divers without decompression illness | 0 (0) | 1 (0.8) | 0.23 |
| Other | 7 (1.7) | 14 (11.8) | <0.001 |
| Procedural data | |||
| General anesthesia | 162 (39.7) | 29 (24.4) | 0.002 |
| Fluoroscopy time (min) | 3.9 (+4.1) | 4.6 (+3.7) | 0.002 |
| Procedural time (min) | 32.1 (+18.4) | 46.2 (+21.3) | <0.001 |
| TTE | 105 (25.7) | 80 (67.2) | <0.001 |
| TEE | 167 (40.9) | 26 (21.8) | <0.001 |
| ICE | 136 (33.3) | 13 (10.9) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pioch, N.; Trabattoni, D.; Bouvaist, H.; Vautrin, E.; Teruzzi, G.; Dollinger, C.; Rioufol, G.; Godart, F.; Fraisse, A. The RISE Study: Retrospective Registry for the International Safety and Efficacy Results of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure with Figulla Flex Il PFO and UNI Occluders. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061681
Pioch N, Trabattoni D, Bouvaist H, Vautrin E, Teruzzi G, Dollinger C, Rioufol G, Godart F, Fraisse A. The RISE Study: Retrospective Registry for the International Safety and Efficacy Results of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure with Figulla Flex Il PFO and UNI Occluders. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(6):1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061681
Chicago/Turabian StylePioch, Nicolas, Daniela Trabattoni, Helene Bouvaist, Estelle Vautrin, Giovanni Teruzzi, Cecile Dollinger, Gilles Rioufol, François Godart, and Alain Fraisse. 2024. "The RISE Study: Retrospective Registry for the International Safety and Efficacy Results of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure with Figulla Flex Il PFO and UNI Occluders" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 6: 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061681
APA StylePioch, N., Trabattoni, D., Bouvaist, H., Vautrin, E., Teruzzi, G., Dollinger, C., Rioufol, G., Godart, F., & Fraisse, A. (2024). The RISE Study: Retrospective Registry for the International Safety and Efficacy Results of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure with Figulla Flex Il PFO and UNI Occluders. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(6), 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061681