Midseptal and Anteroseptal Accessory Pathway Ablation in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pilcher, T.A.; Saarel, E.V. Anatomic challenges in pediatric catheter ablation. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2014, 7, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, M.A.; Gonzalez, C.M.; Uzun, O.J.; McMahon, C.J.; Sadagopan, S.N.; Yue, A.M.; Seller, N.; Hares, D.L.; Bhole, V.; Till, J.; et al. Outcomes From Pediatric Ablation: A Review of 20 Years of National Data. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, R.; Franke, M.; Gawałko, M.; Lodziński, P.; Balsam, P.; Grabowski, M.; Werner, B. Success rate and safety of catheter ablation in preexcitation syndrome: A comparison between adult and pediatric patients. Cardiol. J. 2022, 29, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, P.G.; Patel, S.M.; Bisco, S.E.; Asirvatham, S.J. Septal Accessory Pathway Anatomy, Causes for Difficulty, and an Approach to Ablation. Indian. Pacing Electrophysiol. J. 2010, 10, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Marcus, F.; Poquet, F.; Gencel, L.; Metayer, P.L.; Clementy, J. Electrocardiographic Characteristics and Catheter Ablation of Parahissian Accessory Pathways. Circulation 1994, 90, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T.; Kiani, S.; Black, G.B.; Lu, M.L.R.; Lloyd, M.; Leon, A.R. Ablation of manifest septal accessory pathways: A single-center experience. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2020, 61, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhou, G.; Liu, X.; Wei, H.; Xie, H.-Y.; Ma, J. Outcomes of Different Ablation Approaches for Para-Hisian Accessory Pathway and Ablation Safety at Each Site. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8, 821988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.T.; Chen, S.A.; Chiang, C.E.; Chang, M.S. Characteristics and radiofrequency catheter ablation of septal accessory atrioventricular pathways. PACE—Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1999, 22, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip Saul, J.; Kanter, R.J.; Abrams, D.; Asirvatham, S.; Bar-Cohen, Y.; Blaufox, A.D.; Cannon, B.; Clark, J.; Dick, M.; Freter, A.; et al. PACES/HRS expert consensus statement on the use of catheter ablation in children and patients with congenital heart disease. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13, e251–e289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandapati, R.; Berul, C.I.; Triedman, J.K.; Alexander, M.E.; Walsh, E.P. Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Septal Accessory Pathways in the Pediatric Age Group. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 92, 947–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutanzi, K.R.; Lumen, A.; Koturbash, I.; Miousse, I.R. Pediatric Exposures to Ionizing Radiation: Carcinogenic Considerations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, W.C.; Wu, M.H.; Lu, C.W.; Wu, K.L.; Wang, J.K.; Lin, M.T.; Chen, C.-A.; Chiu, S.-N. Zero fluoroscopy during ablation of right-sided supraventricular tachycardia substrates in a pediatric population—Initial experience in Taiwan. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2019, 35, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karadeniz, C.E.M.; Akdeniz, C.; Turan, O.; Tuzcu, V. Cryoablation of Septal Accessory Pathways in Children: Midterm Results. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2014, 37, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C.H.; Schueler, B.A. Calculation of effective dose. Med. Phys. 2000, 27, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovach, J.R.; Mah, D.Y.; Abrams, D.J.; Alexander, M.E.; Cecchin, F.; Triedman, J.K.; Walsh, E.P. Outcomes of catheter ablation of anteroseptal and midseptal accessory pathways in pediatric patients. Heart Rhythm 2020, 17, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, X. Cryoablation of the right anteroseptal or midseptal accessory pathways in children: A 2-year single-center experience. PACE—Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swissa, M.; Birk, E.; Dagan, T.; Fogelman, M.; Einbinder, T.; Bruckheimer, E.; Goldenberg, I.; Klempfner, R.; Kirsh, J.A.; Fogelman, R. Cryo-therapy Ablation of Para-Hisian Accessory Pathways in Children. Heart Rhythm 2015, 12, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, A.; Blaufox, A.D.; Fairbrother, D.L.; Saul, J.P.; Carolina, S. Cryo-Ablation for Septal Tachycardia Substrates in Pediatric Patients Mid-Term Results. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergul, Y.; Tahsin Tola, H.; Kiplapinar, N.; Akdeniz, C.; Saygi, M.; Tuzcu, V. Cryoablation of anteroseptal accessory pathways in children with limited fluoroscopy exposure. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2013, 34, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansaran Tanidir, I.; Ergul, Y.; Ozturk, E.; Dalgic, F.; Kiplapinar, N.; Tola, H.T.; Akdeniz, C.; Tuzcu, V. Cryoablation with an 8-mm-Tip Catheter for Right-Sided Accessory Pathways in Children. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 39, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, L.; Spar, D.S.; Nash, M.C.; Silver, E.S. Cryoablation of anteroseptal accessory pathways with a his bundle electrogram on the ablation catheter. Indian. Pacing Electrophysiol. J. 2014, 14, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubin, A.M.; Jorgensen, N.W.; Radbill, A.E.; Bradley, J.; Silva, J.N.; Tsao, S.; Kanter, R.J.; Tanel, R.E.; Trivedi, B.; Young, M.-L.; et al. What have we learned in the last 20 years? A Comparison of a Modern Era Pediatric and Congenital Catheter Ablation Registry to Prior Pediatric Ablation Registries. Heart Rhythm 2018, 16, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne, A.; Gauvreau, K.; O’Leary, E.; Mah, D.Y.; Abrams, D.J.; Alexander, M.E.; DeWitt, E.S.; Bezzerides, V.J.; Triedman, J.K.; Walsh, E.P. Risk Factors for Early Recurrence Following Ablation for Accessory Pathways: The Role of Consolidation Lesions. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, M.; Dello Russo, A.; Pelargonio, G.; Del Greco, M.; Zingarini, G.; Piacenti, M.; Di Cori, A.; Casula, V.; Marini, M.; Pizzamiglio, F.; et al. Near zerO fluoroscopic exPosure during catheter ablAtion of supRavenTricular arrhYthmias: The NO-PARTY multicentre randomized trial. Europace 2016, 18, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, R.H.; Gates, G.G.; Gellis, L.A.; Nappo, L.; Ceresnak, S.R. Reducing patient radiation exposure during paediatric SVT ablations: Use of CARTO® 3 in concert with “ALARA” principles profoundly lowers total dose. Cardiol. Young 2015, 25, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangeli, P.; Proietti, R.; Di Biase, L.; Bai, R.; Natale, A. Cryoablation versus radiofrequency ablation of atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2014, 39, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanninen, M.; Yeung-lai-wah, N.; Massel, D.; Gula, L.J.; Sc, M.; Skanes, A.C.; Yee, R.; Klein, G.J.; Manlucu, J.; Leong-Sit, P. Cryoablation Versus RF Ablation for AVNRT: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2013, 24, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, X.M.; Li, M.T.; Zheng, X.C.; Liu, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, H.Y. 3D electronic anatomy mapping guided radiofrequency catheter ablation in 95 children with atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi = Chin. J. Pediatr. 2018, 56, 674–679. [Google Scholar]
- Sumitomo, N.; Tateno, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Ushinohama, H.; Taniguchi, K.; Ichikawa, R.; Fukuhara, J.; Abe, O.; Miyashita, M.; Kanamaru, H.; et al. Clinical importance of Koch’s triangle size in children—A study using 3-dimensional electroanatomical mapping. Circ. J. 2007, 71, 1918–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-L.; Chiu, S.-N.; Lu, C.-W.; Tseng, W.-C.; Wu, M.-H. Acute Outcomes for Cryoablation in Pediatric Patients with Perinodal Tachyarrhythmia: Single Center Report. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2019, 35, 134–143. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, K.; Kapa, S.; Mulpuru, S.K.; Deshmukh, A.J.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Munger, T.M.; Friedman, P.A.; Packer, D.L.; Miyamoto, K.; Kapa, S.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Cryoablation in Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias Originating from the Para-Hisian Region. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 4, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Heald, S.C.; Bashir, Y.; Camm, A.J.; Ward, D.E. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of septal accessory atrioventricular pathways. Br. Heart J. 1994, 72, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugada, J.; Puigfel, M.; Mont, L.S.; Garcia-bolao, I.; Figueiredo, M.; Matas, M.; Navarro-López, F. Radiofrequency Ablation of Anteroseptal, Para-Hisian, and Mid-Septal Accessory Pathways Using a Simplified Femoral Approach. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1998, 21 Pt 1, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
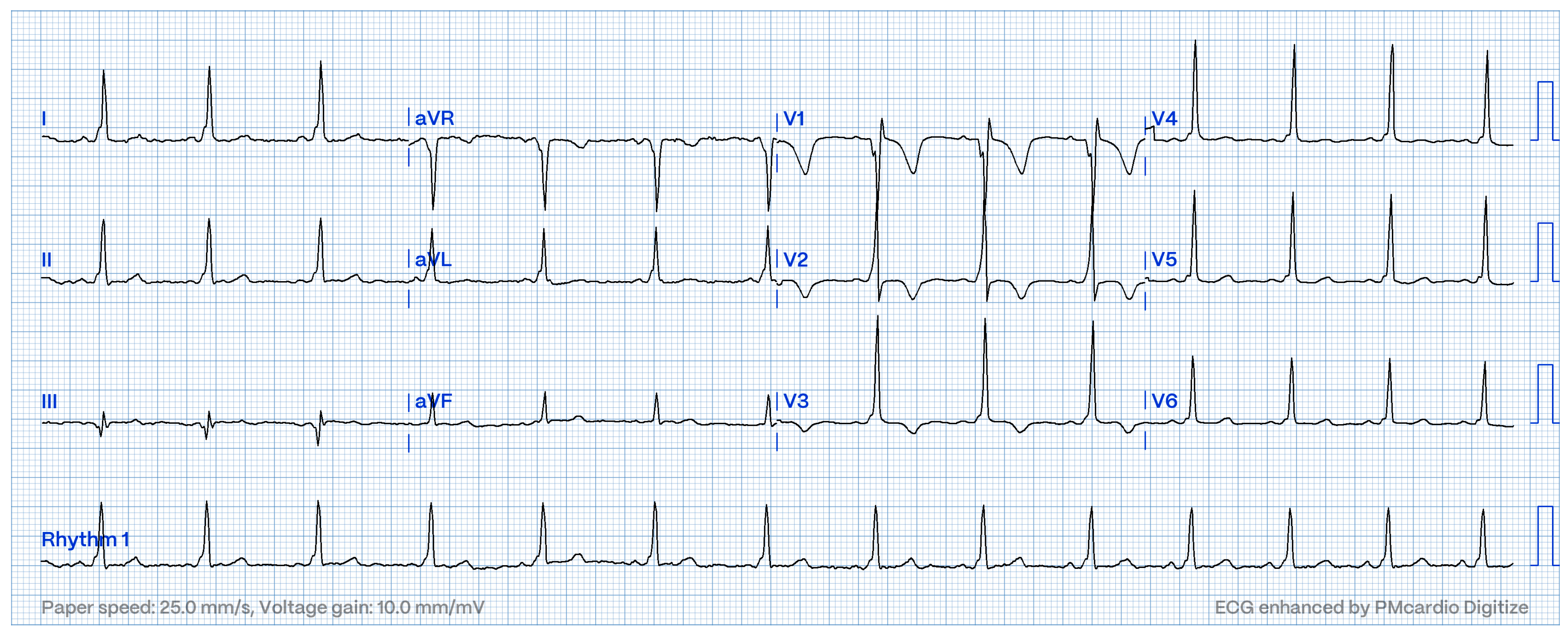
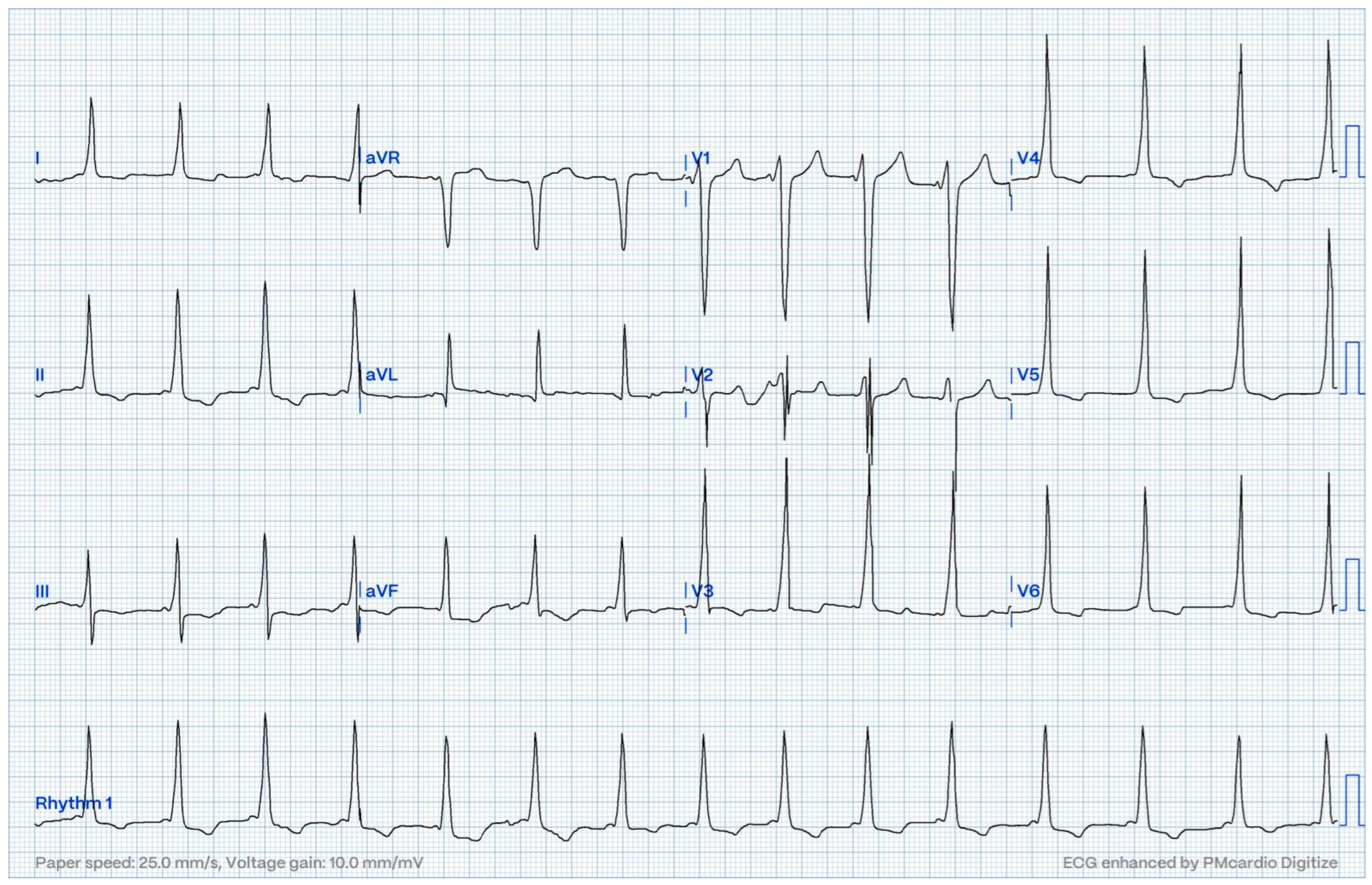
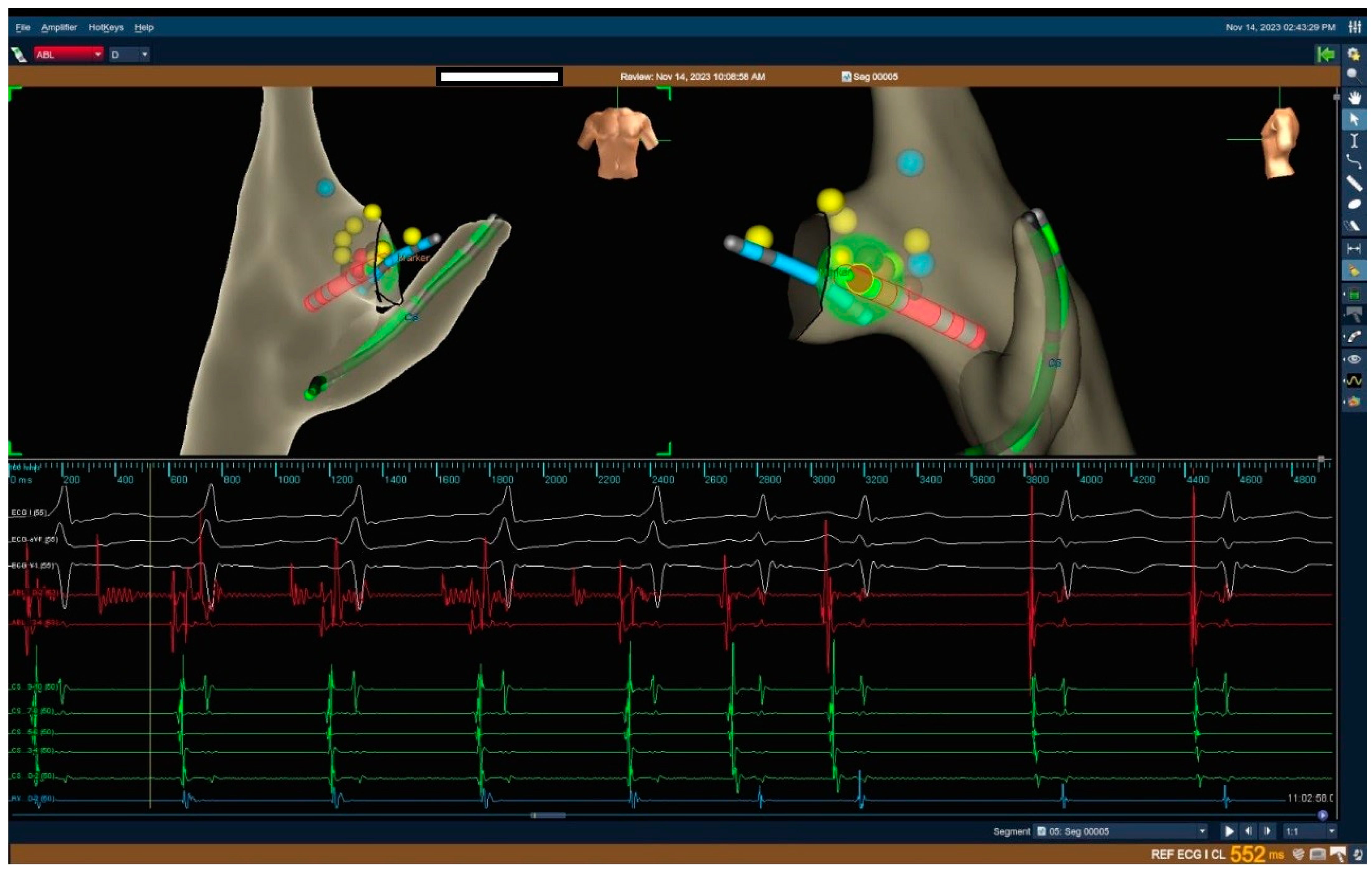
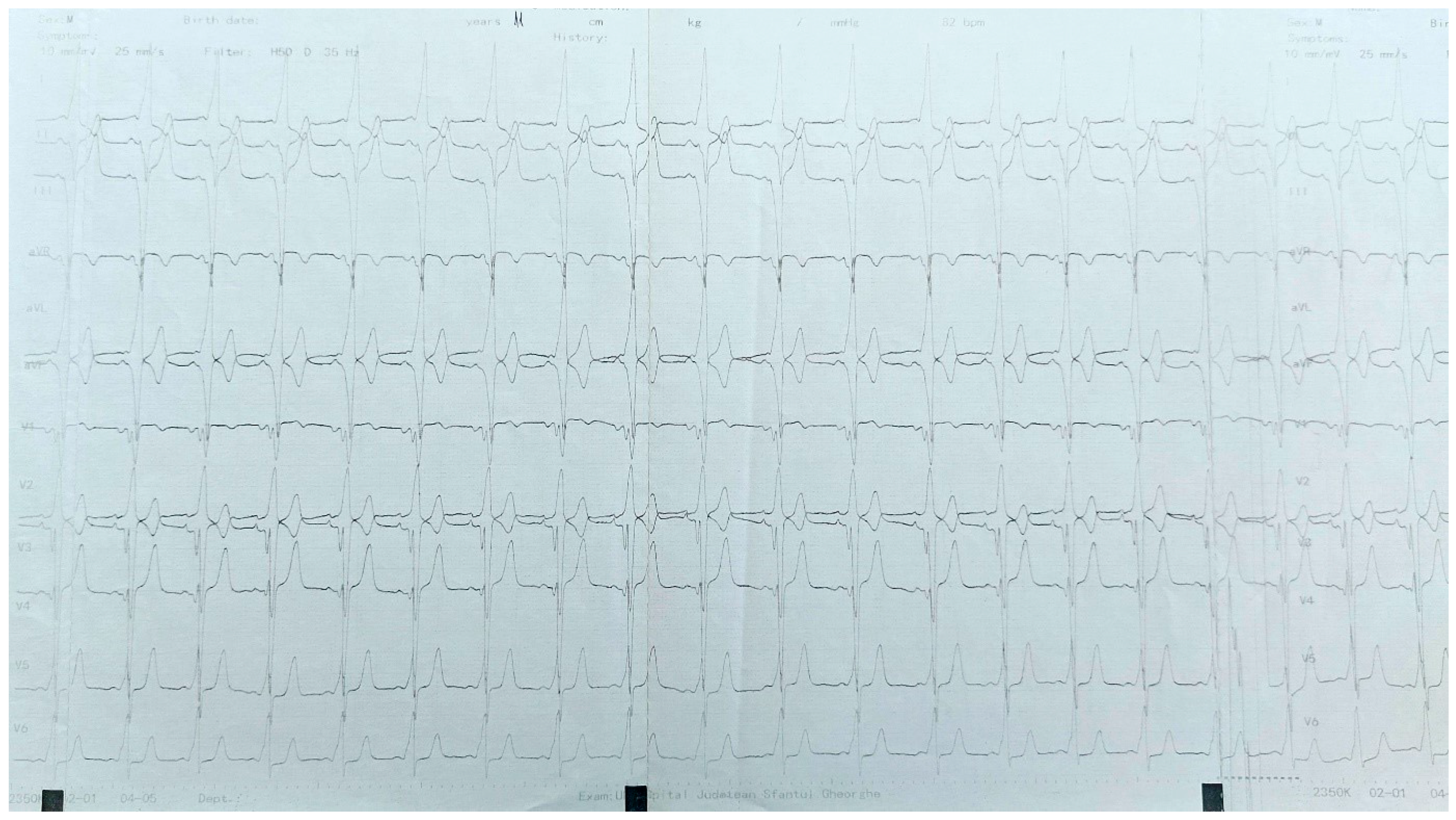
| Procedures | N = 128 |
|---|---|
| Age median (range), years | 13.53 (2.21–18.27) |
| Male/Female (%) | 76 (59.4)/52 (40.6) |
| Height median (range), cm (n = 118) | 162.5 (91–188) |
| Weight median (range), kg (n = 127) | 51.8 (12.5–124.8) |
| Symptomatic before procedure | 75 (58.6%) |
| MS symptomatic (n = 54) | 34 (63.0%) |
| AS symptomatic (n = 74) | 41 (55.4%) |
| Indication for EP study: | |
| Asymptomatic preexcitation | 27 (21.1) |
| Palpitations | 19 (14.8) |
| Documented SVT | 16 (12.5) |
| WPW syndrome | 66 (51.6) |
| Procedures by chronology: | |
| First procedure | 109 (85.2) |
| Redo procedure | 19 (14.8) * |
| Arrhythmia substrate: | |
| AS AP | 74 (57.8) |
| MS AP | 54 (42.2) |
| Type of ablation: | |
| Cryoablation | 93 (72.7) |
| RF ablation | 35 (27.3) |
| Recurrence rate: | |
| After the primary procedure (n = 109) | 19 (17.4) |
| After the redo procedure (n = 19) | 3 (15.8) |
| Procedure time median (range) (n = 118) | 2 h 5 min 0 s (1–6 h) |
| Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Procedure Type (n) | Mean | SD | p-Value |
| First (101) | 2 H 22 M | 1 H 2 M | 0.61 |
| Redo (17) | 2 H 14 M | 1 H 0 M | |
| Type of Ablation (n) | |||
| RF ablation (30) | 1 H 53 M | 45 M | 0.00 |
| Cryoablation (88) | 2 H 30 M | 1 H 3 M | |
| 25. Centile | Median | 75. Centile | Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluoroscopy time (n = 13) (H M S) | 0 H 0 M 16 S | 0 H 1 M 19 S | 0 H 5 M 16 S | 0 H 3 M 46 S | 0 H 4 M 41 S |
| DAP (n = 18) (cGycm2) | 1.05 | 7.18 | 21.28 | 22.01 | 41.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Környei, L.; Jan, M.; Ebrahim, M.; Radeljić, V.; Rode, M.; Delić-Brkljačić, D.; Kralik, I.; Kocsis, F.; Krmek, N. Midseptal and Anteroseptal Accessory Pathway Ablation in Children. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6885. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13226885
Környei L, Jan M, Ebrahim M, Radeljić V, Rode M, Delić-Brkljačić D, Kralik I, Kocsis F, Krmek N. Midseptal and Anteroseptal Accessory Pathway Ablation in Children. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(22):6885. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13226885
Chicago/Turabian StyleKörnyei, László, Matevž Jan, Mohammad Ebrahim, Vjekoslav Radeljić, Mirta Rode, Diana Delić-Brkljačić, Ivana Kralik, Flóra Kocsis, and Nikola Krmek. 2024. "Midseptal and Anteroseptal Accessory Pathway Ablation in Children" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 22: 6885. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13226885
APA StyleKörnyei, L., Jan, M., Ebrahim, M., Radeljić, V., Rode, M., Delić-Brkljačić, D., Kralik, I., Kocsis, F., & Krmek, N. (2024). Midseptal and Anteroseptal Accessory Pathway Ablation in Children. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(22), 6885. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13226885







