Reconstructive Techniques Following Malignant Eyelid Tumour Excision—Our Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zgolli, H.; Choura, R.; Elzarrug, H.K.H.; Abdelhedi, C.; Chebbi, A. Management of eyelids’ primary malignancies. Libyan J. Med. 2023, 18, 2258668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sand, J.P.; Zhu, B.Z.; Desai, S.C. Surgical Anatomy of the Eyelids. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 24, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghoul, M.S.; Kearney, A.M.; Pacella, S.J.; Purnell, C.A. Eyelid Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yan, Y.; Fu, R.; Ji, Q.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Yin, X.; Oranges, C.M.; Li, Q. Surgical Strategies for Eyelid Defect Reconstruction: A Review on Principles and Tech-niques. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2022, 11, 1383–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zollino, I.; Riberti, C.; Candiani, M.; Candotto, V.; Carinci, F. Eyelid Reconstruction Following Excision of Cutaneous Malignancy. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 25, e13–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushker, N.; Modaboyina, S.; Meel, R.; Agrawal, S. Auricular skin-cartilage sandwich graft technique for full-thickness eyelid reconstruction. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 70, 1404–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yamamoto, N.; Ogi, H.; Yanagibayashi, S.; Yoshida, R.; Takikawa, M.; Nishijima, A.; Kiyosawa, T. Eyelid Reconstruction Using Oral Mucosa and Ear Cartilage Strips as Sandwich Grafting. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2017, 5, e1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sharma, V.; Benger, R.; Martin, P.; Pa, M. Techniques of periocular reconstruction. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 54, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawati, Y.; Paramita, C.; Daniel, H. Challenging eyelid reconstruction in malignancies: Case reports. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 71, 102987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balchev, G. Complications and Recurrences after Excision and Reconstruction of Eyelid Tumours. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 1713–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiali, L.K.; Patel, P.; Levine, J.P.; Gold, K.G.; Lisman, R.D. Microvascular Free Flap for Total Eyelid Reconstruction With a Visually Useful Eye. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 32, e109–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gąsiorowski, K.; Iwulska, K.; Zapała, J.; Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G. Periocular basal cell carcinoma: Recurrence risk factors/when to reoperate? Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2020, 37, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gąsiorowski, K.; Gontarz, M.; Marecik, T.; Szczurowski, P.; Bargiel, J.; Zapała, J.; Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G. Risk Factors for Orbital Invasion in Malignant Eyelid Tumors, Is Orbital Exenteration Still Necessary? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tan, P.H.; Eng, K.; Agilinko, J.; Khalil, A.S. The Use of a Hemi Glabellar Flap for Reconstruction of Medial Canthus Defects. Cureus 2022, 14, e21880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bertelmann, E.; Rieck, P.; Guthoff, R. Medial Canthal Reconstruction by a Modified Glabellar Flap. Ophthalmologica 2006, 220, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgut, G.; Özcan, A.; Yeşiloğlu, N.; Baş, L. A New Glabellar Flap Modification for the Reconstruction of Medial Canthal and Nasal Dorsal Defects. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2009, 20, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, J.; Nakajima, T.; Nagasao, T.; Konno, E.; Okabe, K.; Tanaka, T.; Fujii, S.; Kobayashi, H. Full-thickness reconstruction of the eyelid with rotation flap based on orbicularis oculi muscle and palatal mucosal graft: Long-term results in 12 cases. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2009, 62, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shope, C.M.; Gonzalez-Parrilla, L.; Atherton, K.M.; Eiseman, A.; Patel, K. The Utility of the Paramedian Forehead Flap in Lower Eyelid Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2023, 91, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, T.W.; Juniat, V.; O’rourke, M.; Slattery, J.; O’donnell, B.; McNab, A.A.; Hardy, T.G.; Caplash, Y.; Selva, D. The use of the paramedian forehead flap alone or in combination with other techniques in the reconstruction of periocular defects and orbital exenterations. Eye 2022, 37, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundridge, W.L.D.; Sismanis, D.N.; Altman, A.H.; DeBacker, C.M.M.; Holck, D.E.M. Single-staged Tunneled Forehead Flap for Medial Canthal and Eyelid Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gupta, R.B.; John, J.B.; Hart, J.D.; Chaiyasate, K. Medial Canthus Reconstruction with the Paramedian Forehead Flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Balchev, G.; Balabanov, C.; Murgova, S. Glabellar flap technique in oculoplastic surgery. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 70, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cespedes, R.A.D.; Evangelio, L.O.; Oprisan, A.; Perez, A.O. Utility of the Glabellar Flap in the Reconstruction of Medial Canthal Tumors after Mohs Surgery. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 51, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koch, C.A.; Archibald, D.J.; Friedman, O. Glabellar Flaps in Nasal Reconstruction. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 19, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Song, B.; Ha, Y.; Kim, S.; Oh, S.-H.; Seo, Y.-J.; Song, S.H. Customized Reconstruction of Lower Eyelid Defects. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2023, 35, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgun, D.; Hayashi, A.; Yoshizawa, H.; Shimizu, A.; Horiguchi, M.; Mochizuki, M.; Kamimori, T.; Aiba-Kojima, E.; Mizuno, H. Oncoplastic Lower Eyelid Reconstruction Analysis. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 30, 2396–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, R.; Maeda, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Funayama, E.; Murao, N.; Osawa, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Ikeda, M.; Hayashi, T. Advancement Flap Using Excess Skin for Upper Eyelid Full-Thickness Defects. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 30, 2614–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vathulya, M. Commentary: Dynamic Upper Eyelid Reconstruction for Total Periorbital Soft Tissue Loss. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2022, 49, V2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wilcsek, G.; Leatherbarrow, B.; Halliwell, M.; Francis, I. The ‘RITE’ use of the Fricke flap in periorbital reconstruction. Eye 2004, 19, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durairaj, V.D.; Allard, F.D. Current techniques in surgical correction of congenital ptosis. Middle East Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 17, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rubino, C.; Farace, F.; Puddu, A.; Canu, V.; Posadinu, M. Total upper and lower eyelid replacement following thermal burn using an ALT flap—A case report. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2008, 61, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, K.N.; Billmire, D.A.; Yakuboff, K.P. Total eyelid reconstruction with free dorsalis pedis flap after deep facial burn. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 104, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sol, S.; Boncimino, F.; Todorova, K.; Waszyn, S.E.; Mandinova, A. Therapeutic Approaches for Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: Standard of Care and Emerging Modalities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.; Nadaf, A.; Imran, M.; Jiba, U.; Sheikh, A.; Almalki, W.H.; Almujri, S.S.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Kesharwani, P.; Ahmad, F.J. Skin cancer: Understanding the journey of transformation from conventional to advanced treatment approaches. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferro, M.; Deodato, F.; Macchia, G.; Gentileschi, S.; Cilla, S.; Torre, G.; Padula, G.D.A.; Nuzzo, M.; Massaccesi, M.; Valentini, V.; et al. Short-Course Radiotherapy in Elderly Patients with Early Stage Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: A Phase II Study. Cancer Investig. 2014, 33, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
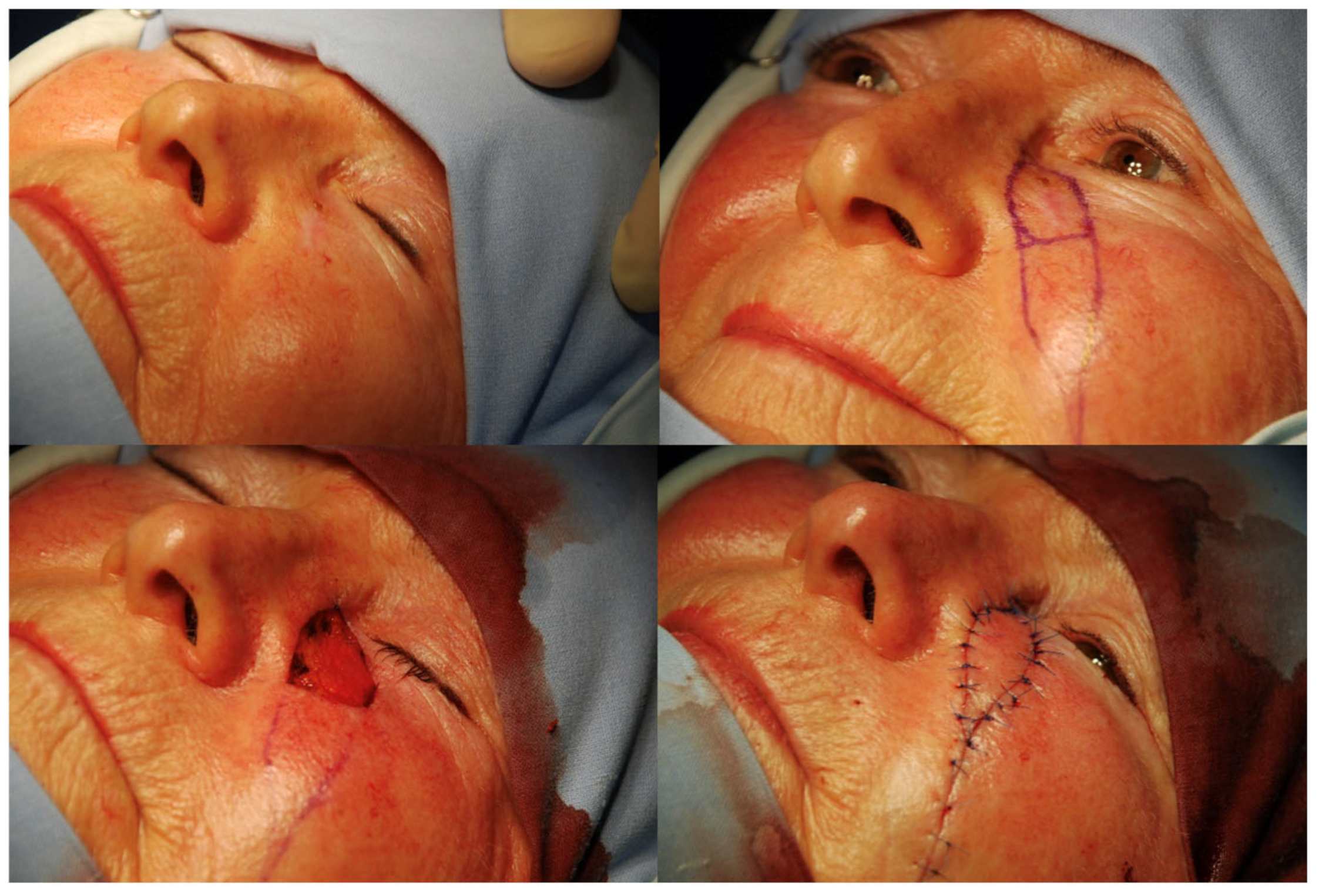
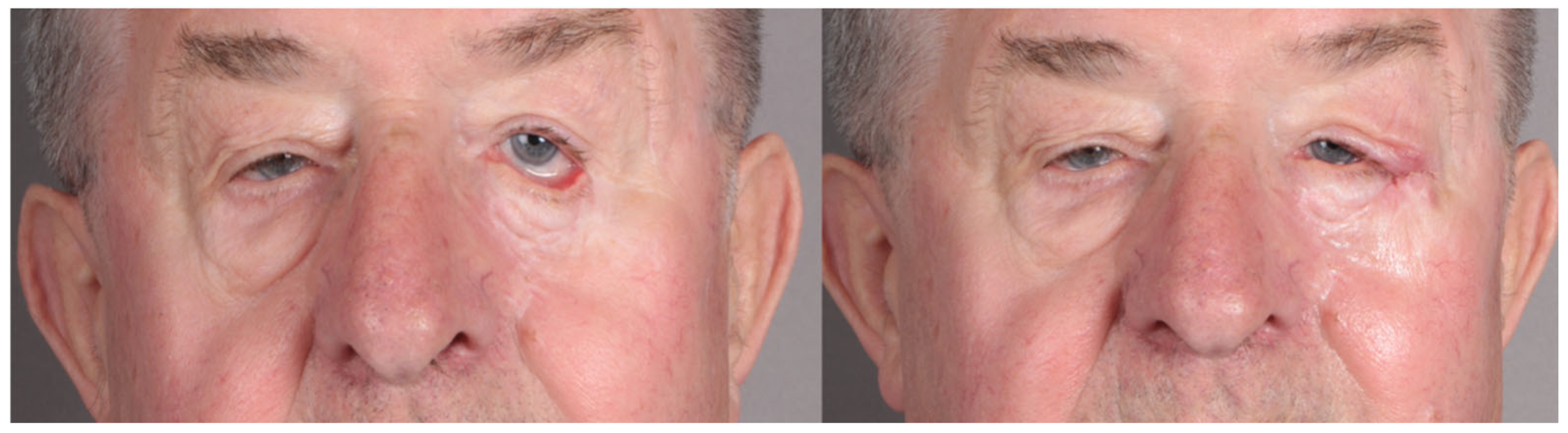
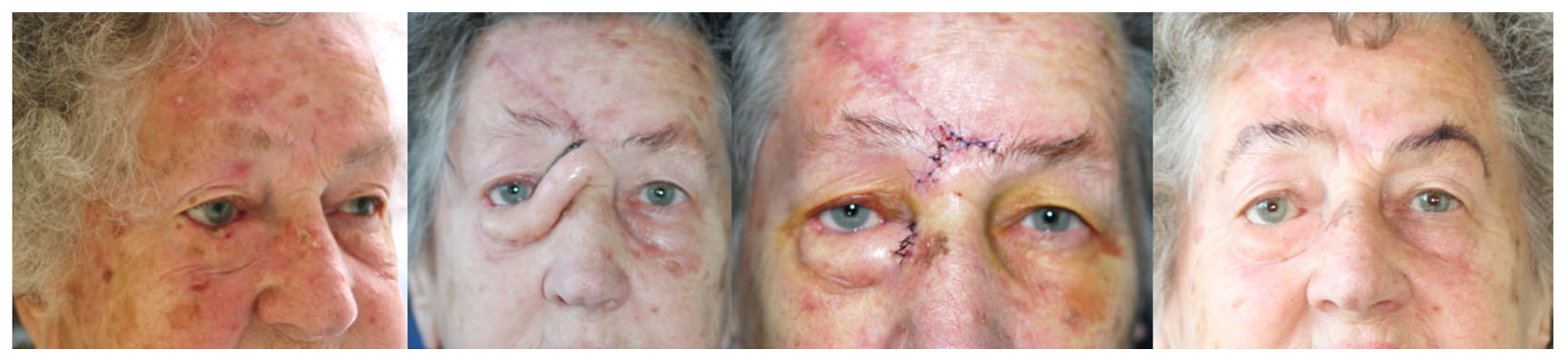
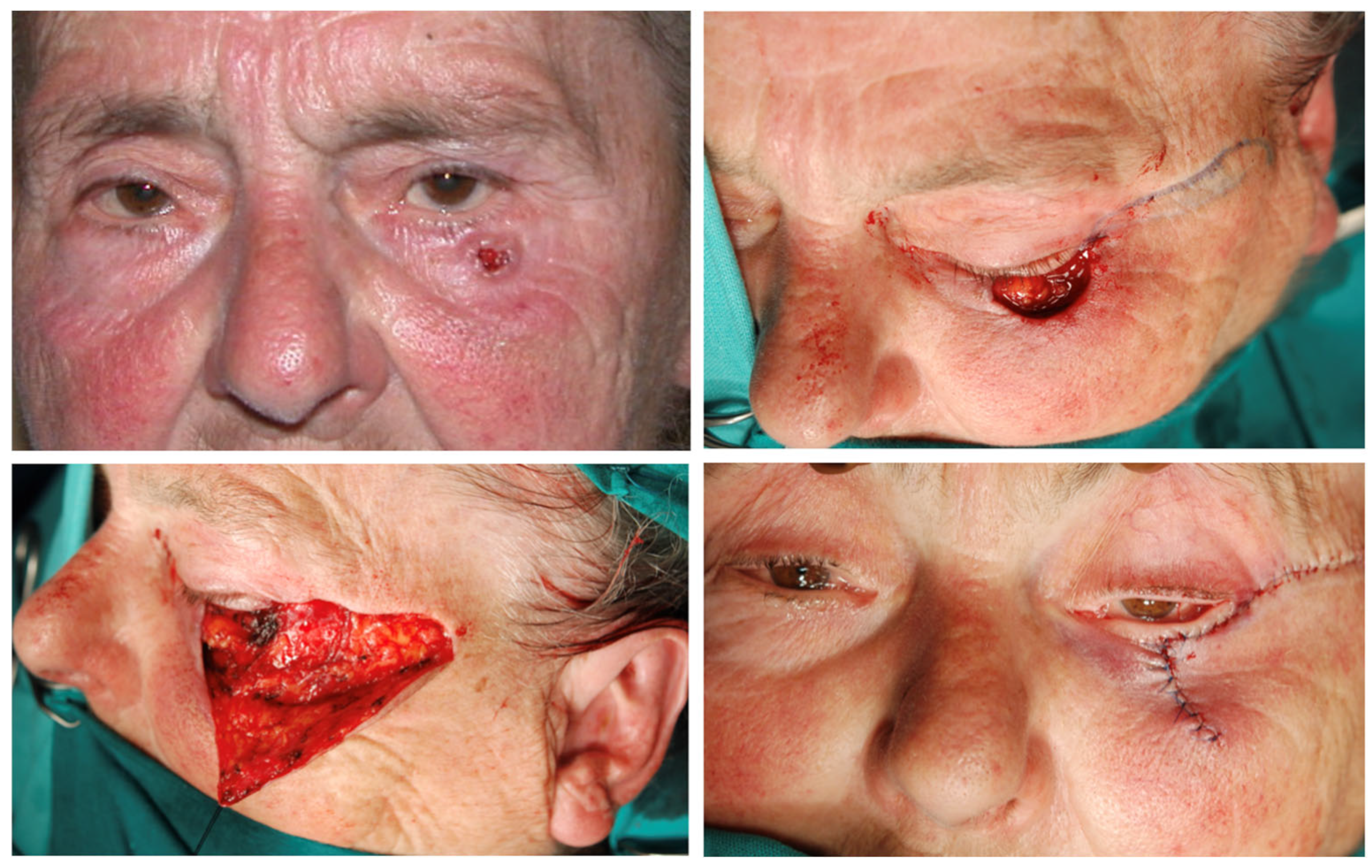
| Types of Reconstruction Methods Used | No of Patients |
|---|---|
| Forehead flap | 59 |
| Simple excision with cantholysis | 38 |
| Skin graft | 11 |
| Mustarde cheek flap | 16 |
| Frontotemporal flap | 10 |
| Cutler-Beard bridge flap | 1 |
| S-plasty | 7 |
| V-Y advancement flap | 5 |
| Glabellar flap | 19 |
| Converse flap | 1 |
| Tumour location | |
| Medial canthus | 78 |
| Lower eyelid | 56 |
| Upper eyelid | 11 |
| Lateral canthus | 8 |
| Medial canthus and lower eyelid | 10 |
| Medial canthus and both eyelids | 2 |
| Medial canthus and upper eyelid | 1 |
| Lateral canthus and upper eyelid | 1 |
| Complications Observed | |
| Tearing | 4 |
| Suppuration | 1 |
| Extropion | 7 |
| Deformation | 2 |
| Flap necrosis | 4 |
| Tearing and ectropion | 2 |
| Ectropion and deformation | 1 |
| Tearing and flap necrosis | 1 |
| Method of Reconstruction | Primary Tumour (T) | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a (n = 7) | 1b (n = 6) | 2a (n = 33) | 2b (n = 48) | 3a (n = 32) | 3b, 4a (n = 10) | ||
| Local flap | 4 (57.14%) | 5 (83.33%) | 16 (48.48%) | 17 (35.42%) | 3 (9.38%) | 0 (0.00%) | p < 0.001 |
| Regional flap | 3 (42.86%) | 0 (0.00%) | 14 (42.42%) | 28 (58.33%) | 28 (87.50%) | 10 (100.00%) | |
| Skin graft | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (16.67%) | 3 (9.09%) | 3 (6.25%) | 1 (3.12%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| Complications | Localization of Tumour | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medial Canthus (n = 78) | Lower Eyelid (n = 56) | Upper Eyelid (n = 11) | Lateral Canthus (n = 8) | Medial Canthus and Lower Eyelid (n = 10) | Other (n = 4) | ||
| No | 69 (88.46%) | 46 (82.14%) | 10 (90.91%) | 8 (100.00%) | 9 (90.00%) | 3 (75.00%) | p = 0.674 |
| Yes | 9 (11.54%) | 10 (17.86%) | 1 (9.09%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (10.00%) | 1 (25.00%) | |
| Complications | Methods of Reconstruction | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local Flap (n = 55) | Regional Flap (n = 102) | Skin Graft (n = 8) | ||
| No | 50 (91.11%) | 82 (80.72%) | 7 (87.50%) | p = 0.289 |
| Yes | 5 (8.89%) | 20 (19.28%) | 1 (12.50%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gąsiorowski, K.; Gontarz, M.; Bargiel, J.; Marecik, T.; Szczurowski, P.; Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G. Reconstructive Techniques Following Malignant Eyelid Tumour Excision—Our Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206120
Gąsiorowski K, Gontarz M, Bargiel J, Marecik T, Szczurowski P, Wyszyńska-Pawelec G. Reconstructive Techniques Following Malignant Eyelid Tumour Excision—Our Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(20):6120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206120
Chicago/Turabian StyleGąsiorowski, Krzysztof, Michał Gontarz, Jakub Bargiel, Tomasz Marecik, Paweł Szczurowski, and Grażyna Wyszyńska-Pawelec. 2024. "Reconstructive Techniques Following Malignant Eyelid Tumour Excision—Our Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 20: 6120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206120
APA StyleGąsiorowski, K., Gontarz, M., Bargiel, J., Marecik, T., Szczurowski, P., & Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G. (2024). Reconstructive Techniques Following Malignant Eyelid Tumour Excision—Our Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(20), 6120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206120








