Abstract
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have become the cornerstone of treatment in renal cell carcinoma (RCC), for both metastatic disease and in an adjuvant setting. However, an adaptive resistance from cancer cells may arise during ICI treatment, therefore many studies are focusing on additional immune checkpoint inhibitor pathways. Promising targets of immunotherapeutic agents under investigation include T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT), immunoglobulin-like transcript 4 (ILT4), lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3), vaccines, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 (TIM-3), and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. In this review of the literature, we recollect the current knowledge of the novel treatment strategies in the field of immunotherapy that are being investigated in RCC and analyze their mechanism of action, their activity and the clinical studies that are currently underway.
Keywords:
renal cell carcinoma; RCC; immunotherapy; immune checkpoint inhibitors; ICI; TIGIT; ILT4; LAG-3; TIM-3; vaccine 1. Introduction
In recent years, there has been a progressive increase in the incidence of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), which is associated with a five-year survival rate that has increased from 50% in 1975 to 77% in 2019 [1]. Worldwide, there are over 400,000 new cases of RCC and over 170,000 deaths annually [2].
RCC is divided into two main subtypes, with different clinical and prognostic characteristics: clear cell RCC (ccRCC), which represents the most common histology (75–80% of all cases) and non-clear cell RCC (nccRCC), accounting for 25–20% of RCC and composed of several different histologies, the most common being papillary (15%) and chromophobe (3–5%) RCC [3].
Currently, prognostic factors based on the evaluation of clinical and laboratory values are used to stratify patients with metastatic RCC and therefore define the best therapeutic strategy [4]. However, no validated biomarkers are yet available as predictors of efficacy for current first-line therapies in metastatic RCC (mRCC) [5]. Nowadays, the most used prognostic score for mRCC is the International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium (IMDC) risk score, based on clinical and laboratory criteria, and which stratifies patients into three prognostic groups (favorable, intermediate, and poor risk), each with a different median overall survival (mOS) [6].
In recent years, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have become the cornerstone of RCC systemic treatment in both metastatic disease and adjuvant settings.
Immuno-based combinations, consisting of an ICI in combination with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) or with another ICI, have yielded unprecedented results in several phase III trials conducted on treatment-naive patients with metastatic disease [7].
In the phase III Checkmate-214 trial, the first-line immunotherapy combination of nivolumab (3 mg per kilogram of body weight) plus ipilimumab (1 mg per kilogram) every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab (3 mg per kilogram) every 2 weeks, demonstrated a greater overall survival (OS) benefit than 50 mg sunitinib delivered orally once daily in patients with intermediate/poor risk advanced ccRCC [8].
Keynote-426 is an open-label, phase III randomized trial, that demonstrates superiority in terms of OS and progression-free survival for advanced ccRCC (PFS) (co-primary endpoints) of first-line pembrolizumab 200 mg delivered intravenously (IV) every 3 weeks, in combination with 5 mg axitinib delivered orally twice daily, when compared with sunitinib [9].
The CheckMate 9ER phase III study confirmed the efficacy, in terms of PFS (primary endpoint), OS and objective response rate (ORR)—secondary endpoints—of the combination of nivolumab 240 mg IV every 2 weeks and cabozantinib 40 mg orally once daily, versus sunitinib [10].
Lastly, the phase III Clear study demonstrated an advantage in OS and PFS for the use of 20 mg lenvatinib delivered orally once daily in combination with 200 mg pembrolizumab IV every 3 weeks, when compared with sunitinib in advanced ccRCC [11].
The outcomes of first-line immune-based combination phase III trials with a positive OS in mRCC are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Outcomes of first-line immune-based combinations trials.
The outstanding outcomes of these studies led to the approval of the ICI–TKI combination for all IMDC risk class patients or the ICI–ICI combination for the intermediate/poor risk class patients as the standards of care for patients with previously untreated mRCC.
However, adaptive resistance from cancer cells may arise during ICI treatment. Most important is the loss of response to IFNγ and the secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines like IL-6, IL-12 or TGFβ. These cytokines upregulate PD-L1 and create a T cell dysfunction [12]. Moreover, loss of neoantigen expressions leading to evasion from cytotoxic T cell attack have been described in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) [13]. Further potential mechanisms of resistance to ICIs consist of the overexpression of oncogenes and in the gathering of immunosuppressive cell populations inside the tumor microenvironment (TME), such as tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), and regulatory T cells (Treg). These last two, in particular, seem to be increased in tumor patients and to inhibit T cells activation and function [14,15].
Similarly, resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy may arise specifically due to the increased production of pro-angiogenic factors, endothelial cell variability and cancer cell crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment [16].
After progression on ICI-based first-line treatment, cabozantinib is the most widely used TKI, demonstrating efficacy and safety in several studies as a second-line therapy [17,18]; this is also the case for patients treated with first-line ICI or primary refractory TKI [19].
As an alternative to the use of cabozantinib as a second-line treatment, there are phase II trials and retrospective evidence that show that the combination of lenvatinib plus everolimus leads to a benefit in terms of PFS with an acceptable toxicity profile [20,21].
Furthermore, other molecules are being studied on the angiogenic side, such as the hypoxia-inducible factor-2α (HIF-2α) inhibitor belzutifan [22,23].
With regard to ICI therapy, rechallenge with anti PD-1/PD-L1 therapy did not demonstrate significant benefits [24,25], therefore recent research has been seeking to explore new immune checkpoint targets.
In this review of the literature, we recollect the current knowledge on novel treatment strategies in the field of immunotherapy that are being investigated in RCC and analyze their mechanism of action, their activity and the clinical studies that are underway.
2. Methods
We performed a search on Pubmed/Medline, using the following keywords: “renal cell carcinoma” OR “kidney cancer” OR “RCC” AND “immunotherapy” OR “immune check-point inhibitors” OR “ICI” OR “CPI” OR “anti-PD1” OR “anti-PD-L1“. We also searched the words “TIGIT” OR “ILT4” OR “CAR-T” OR “LAG-3” OR “TIM-3” OR “vaccines” AND “renal cell carcinoma,” to address the biochemical nature of the novel targets and their role in the RCC treatment paradigm or its future perspectives. We selected pivotal registration studies and the most relevant studies in terms of how they were conducted, innovation, outcomes, statistical analysis and number of patients enrolled. We then performed a search on the Clinicaltrials.gov database for ongoing studies, both recruiting and not recruiting, using the keywords “renal cell carcinoma” AND “TIGIT” OR “ILT4” OR “CAR-T” OR “LAG-3” OR “TIM-3” OR “vaccines.” The search was carried out between 11 March and 31 May of the current year.
3. New Immune Pathways
Novel immune pathways are being studied as related to resistance to currently used ICIs and are being targeted with novel immune-related therapies. Herein, we discuss promising fields of research in the context of RCC.
3.1. T Cell Immunoglobulin and ITIM Domain (TIGIT)
T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT) is an inhibitory immunoglobulin receptor expressed on lymphocytes, consisting of an extracellular immunoglobulin variable domain, a type I transmembrane portion, and a short intracellular region with an inhibitory motif based on immunoreceptor tyrosine (ITIM) and an immunoglobulin tyrosine tail-like domain (ITT). First identified in 2009, TIGIT directly inhibits the proliferation of T cells and the action of natural killer (NK) cells [26,27].
TIGIT is a competitive ligand of the immune activator receptor CD226 or the DNAX-1 accessory molecule (DNAM-1) for CD155 and CD112 adhesion molecules, which are nectin receptors whose binding increases the activity of T and NK cells [28,29].
Jhonston et al. identified a highly specific 15-gene signature associated with tumor-infiltrating T cells with several co-inhibitors within TIGIT and programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) using gene expression data from the Cancer Genome Atlas collection of lung squamous carcinoma [30]. Similarly, this upregulation has been observed in ccRCC, colon, endometrial and breast cancers [31], for which several clinical trials are ongoing [32].
In particular, TIGIT has been shown to be mainly expressed in ccRCC tissue as compared with adjacent normal tissue [33].
3.2. Immunoglobulin-like Transcript 4 (ILT4)
Immunoglobulin-like transcript 4 (ILT4)—also named monocyte/macrophage immunoglobulin-like receptor 10 (MIR-10), lymphocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor (LIR) 2, or CD85d—is a type I transmembrane receptor with 4 extracellular tandem Ig-like domains, a transmembrane region of 23 amino acids and a cytoplasmic tail with 3 immunoreceptor tyrosine inhibitory motifs. Its main ligands are major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and human leukocyte antigens (HLAs) [34].
ILT4 belongs to a family of inhibitory and activating immunoglobulin-like transcripts which modulates activation of immune cells. It is predominantly expressed in innate immune cells, including macrophages, monocytes, granulocytes and dendritic cells. Furthermore, ILT4 is expressed in hematopoietic stem cells, osteoclast precursor cells, platelets and other neurons, being involved in their biological and functional regulation.
ILT4 has been shown to be overexpressed in malignant tumor cells from both hematopoietic and solid tumors and in the tumor stroma cell microenvironment, favoring tumor progression and metastasis [35].
Therefore, anti-ILT4 agents, in combination with other ICIs, could enhance the immune response against tumor cells.
Siu et al. have demonstrated that a novel first-in-class human IgG4 monoclonal antibody targeting ILT4 (MK-4830), as monotherapy or in combination with pembrolizumab, triggered antitumor activity in patients with pretreated advanced solid tumors, including those whose disease had previously progressed during ICI while also maintaining a good safety profile [36].
3.3. Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T (CAR-T)
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) are chimeric receptor proteins designed to give T cells the ability to target a specific antigen. CAR-T is therefore a single receptor that combines both the antigen binding and T cell activation functions.
Thus, CAR-T cells are used in genetically modified immunotherapy, now widely used in the hematological field to treat some cancers, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, acute lymphoblastic leukemia and multiple myeloma. The standard approach is to collect T cells from patients, genetically alter them so they can recognize tumor cells, then infuse the resulting CAR-T cells back into patients (autologous transplant) or use those from a donor (allogeneic transplant).
Engineered CARs program T cells to recognize antigens expressed on cancer cells [37]. Therefore, the T cell linked to the antigen expressed on the tumor cell is active and exerts a cytotoxic action [38].
CD70 is highly expressed in RCC, making it a promising target for CAR-T cells.
Several phase I and phase II trials with CAR-T cells are ongoing for solid tumors, including RCC.
However, in solid tumors, unlike hematologic cancers, CAR-T cells have reduced efficacy due to their difficulty in penetrating the tumor. Moreover an immunosuppressive microenvironment restricts the efficacy [39].
Different toxicities are associated with CAR-T. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is one of the most important due to the secretion of multiple cytokines like IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 that cause fever, arthralgia and myalgia. Similarly, endothelial activation driven by cytokines results in disruption of the blood–brain barrier (BBB), while a temporary leakage of cytokines into the cerebrospinal fluid and brain causes neurotoxicity [40]. Many other toxicities, like graft-versus-host disease, are observed in CAR-T therapy [41].
Chimeric antigen receptor natural killer (CAR-NK) is a new frontier of immunotherapy that promises to improve efficacy while reducing toxicity. Unlike T lymphocytes, NK cells have the ability to be transplanted into a new environment with different MHC expression patterns while maintaining their functionality and without triggering graft-versus-host disease or other toxicities, like CRS and neurotoxicity. With advancements in genetic modification technologies, NK cells can be further engineered, including the introduction of CARs and the knockout of inhibitory genes [42].
3.4. Lymphocytes Activation Gene 3 (LAG3)
Lymphocytes activation gene 3 (LAG3), also known as CD223, is an inhibitory receptor, a structural homolog of CD4, and is highly expressed on exhausted T cells and many other lymphocytic and non-lymphocytic cells. Its activity has been largely related to downregulating the immune response in both tumors and infections, but a thorough understanding of its ligands and its role in the immune pathways is still lacking [43].
Following the evidence that LAG3 tends to be overexpressed on exhausted T cells, the idea that T cell activity could be restored by inhibiting LAG3 has arisen, leading to anti-LAG3 immunotherapeutics. The association between anti-LAG3 relatlimab and anti-PD1 nivolumab in previously untreated advanced melanoma patients was studied in the randomized phase II/III RELATIVITY-047 trial, achieving a 12-month PFS rate of 47%, compared with 36% with nivolumab monotherapy [44]. Furthermore, the abovementioned association proved to be active and safe in heavily pretreated advanced melanoma patients who had progressed to a prior anti-PD(L)-1-containing regimen in the phase I/II RELATIVITY-020 trial [45].
In 2022, these results led the FDA to approve opdualag, an association between relatlimab and nivolumab, for the treatment of advanced melanoma [46].
Regarding RCC, an interesting study by Schoenfeld et al. investigated how LAG3 expression levels are, on average, lower at metastatic sites than those at primary RCC sites, and how this difference was more enhanced in patients with high-risk clinical features, such as those presenting with a larger primary tumor; with grade 4, IMDC poor-risk disease; or with brain metastases [47]. The authors further showed that higher LAG3 levels at metastatic sites may predict a greater response to immunotherapy and better survival outcomes after the development of metastatic disease.
The purpose of the open-label, randomized phase 2 FRACTION-RCC platform trial (NCT02996110) is to test the efficacy and safety of various combinations of nivolumab compared with nivolumab and ipilimumab in participants with advanced RCC that has progressed on or after ICI (participants undergoing anti-CTLA-4 therapy were eligible). This study uses an adaptive design to test different combination therapies: one arm consists of nivolumab and ipilimumab, another of nivolumab and relatlimab, another of nivolumab and BMS-986205, and the last consists of nivolumab and BMS-813160. This trial aims to recruit 200 patients with advanced RCC. The primary outcomes are ORR, PFS and duration of response (DOR). The results of the arm with patients treated with nivolumab plus ipilimumab were published in November 2022 and show that, with a median follow-up of 33.8 months, the ORR was 17.4% (entire population n = 46) with 8 patients achieving partial response and 19 patients achieving stable disease. The PFS rate at 24 weeks was 43.2%, mOS was 23.8 months and median DOR was 16.4 months.
3.5. T Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin Domain 3 (TIM-3)
T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (TIM-3) is a protein that is part of the TIM family and is identified by type 1 T helper cells (Th1) surface and then on other cell types such as type 17 T helper cells (Th17), monocytes, and macrophages. TIM-3 targets its ligand galectin-9 (Gal-9), inducing the depletion of Th1, resulting in peripheral immune tolerance and negative regulation of immune response. TIM-3 inhibition has been shown to be related to the blocking of tolerance induction in Th1 cells [48]. In addition, TIM-3 seems to be involved in the negative regulation of the production of IFN-Ɣ in CD8+ Tc1 cells [49]. TIM-3 overexpression has been observed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and appears to be related to poor prognosis, as the bond between TIM-3/Gal-9 promotes the depletion of T cells in HBV-related HCC [50]. A study by Yuan et al. assessed the prognostic role of TIM-3 overexpression ccRCC by analyzing 137 ccRCC tumor samples [51].
TIM-3 expression appears to be higher in tumoral tissue than in the adjacent normal renal tissue, and the short interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knockdown of TIM-3 inhibited proliferation and invasion in ccRCC cell lines. Furthermore, TIM-3 expression was found to be related to both cancer-specific survival and PFS and to be associated with poor prognosis.
3.6. Vaccines
Therapeutic cancer vaccines are based on the premise that a vaccine targets tumor-associated antigens through a cytotoxic immune response to these agents, inducing long-lasting immune responses by both establishing memory against tumor antigens and minimizing toxicity related to an off-target immune system. MHC molecules present peptide fragments derived from internal cellular proteins on the cell surface, thus allowing T cells to discriminate between healthy cells and diseased cells, including virus-infected and tumor cells [52].
Peptides that are predominantly present on tumor cells (and less so on healthy cells) are called tumor-associated peptides (TUMAPs). Vaccination with TUMAPs is believed to activate the immune system against cancer [53].
IMA901 is the first therapeutic vaccine developed for RCC. It is a vaccine consisting of ten selected TUMAPs that are naturally present in tumors.
IMA901 was evaluated in an early clinical trial with a single dose of cyclophosphamide (to deplete regulatory T cells), demonstrating that immune response to TUMAPs is associated with longer OS [54]. In contrast, the phase III IMPRINT trial, comparing sunitinib plus IMA901 versus sunitinib alone in first-line therapy for patients with metastatic ccRCC, showed no benefit in OS [55].
An alternative personalized vaccine approach is AGS-003. This is based on amplified tumor RNA, which was incorporated into autologous monocyte-derived dendritic cells (called rocapuldencel-T or AGS-003) and administered as a therapeutic vaccine. In a phase III trial, ASG-003 was combined with sunitinib versus sunitinib alone in intermediate or poor-risk metastatic ccRCC. No significant differences in PFS or OS were demonstrated [56].
The most recent approach targets tumor neoantigens. These are a specific class of tumor antigen and originate from somatic alteration. In many tumor types, neoantigen loads are correlated with response to ICI therapy [57]. In ccRCC, neoantigen load is lower than other immunotherapy sensitive cancer, like melanoma or lung cancer, but does not correlate with the response to ICI therapy [58].
Generating a personalized neoantigen vaccine is a feasible strategy that is achieved by sequencing a patient’s tumor genome and predicting which mutations generate peptides that might bind to specific HLA class I alleles.
3.7. Immunosuppressive Cells and Resistance
As already mentioned, immunosuppressive cells, such as TAM, MDSC, and Tregs, can contribute to a resistance to ICIs and have consequently become an important potential target with which to increase the efficacy of immunotherapy. TAMs have been thought to be involved in tumor development, proliferation and spread, with their high representation in TME appearing to be related to the poor prognosis of a broad spectrum of tumors. TAMs can undermine immune response by reducing T cells and NK activity, expressing proteins or releasing soluble factors, and by recruiting other immunosuppressive cells, such as Tregs [59]. Many studies have demonstrated the role of TAMs in immunotherapy resistance, thus the specific mechanism is still unknown [60]. MDSCs are a broad population of immature myeloid cells which massively increase during tumor development and proliferation. These cells both promote immune evasion, for example increasing PD-L1 expression to promote T cell anergy, and contribute directly to tumor proliferation via angiogenesis and by facilitating metastatization [61]. Lastly, Tregs, which present CD25 and CTLA-4 on their surface, play key roles in preventing autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. However, their increase in the TME suppresses anti-tumor immune response. Many preclinical studies have demonstrated that circulating Treg depletion can enhance anti-cancer immune response [62]. Immunosuppressive cells represent future potential targets for the development of new immunotherapeutics.
The discussed immune pathways are depicted in Figure 1.
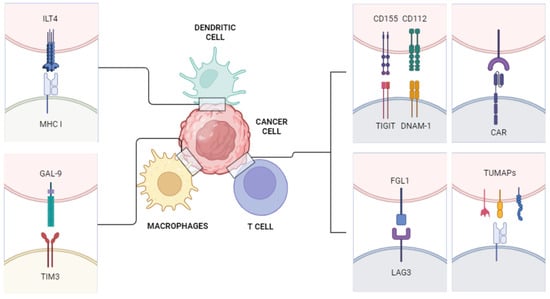
Figure 1.
Novel immune pathways. ILT4: immunoglobulin-like transcript 4, which modulates activation of immune cells and appears to be overexpressed on the surface of solid and hematopoietic tumor cells; MHC I: major histocompatibility complex class I; GAL-9: galectin-9, a widely expressed receptor involved in immune response and tumor proliferation; TIM3: T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3; CD155: cluster of differentiation 115, often upregulated on tumor cells, contributing to proliferation; CD112: cluster of differentiation 112, a nectin receptor which, if activated, enhances the efficacy of T and NK cells; TIGIT: T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain, an immunoglobulin receptor expressed on lymphocytes, which directly inhibits the proliferation of T cells and the action of natural killer (NK) cells; DNAM-1: DNAX accessory molecule, one of the main NK cell-activating receptors; CAR: Chimeric antigen receptor; FGL1: fibrinogen-like protein 1; LAG3: lymphocyte activation gene-3, an inhibitory receptor which downregulates immune response in both tumors and infections; TUMAPs: multiple tumor-associated peptides.
4. Trials Ongoing
4.1. Phase I–II Targeting TIGIT
Numerous studies on anti-TIGIT drugs are ongoing in RCC patients.
NCT05805501 is a randomized, open-label, three-arm phase II trial that evaluates the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of the anti-PD-1 and anti-LAG3 bispecific antibody tobemstomig (also known as RO7247669) in treatment-naive patients with unresectable or metastatic ccRCC. This trial is composed of two experimental arms—an arm A whose participants will receive the combination of tobemstomig and axitinib versus an arm B whose participants will receive the combination of tobemstomig, tiragolumab and axitinib—that are compared with a control arm (arm C) whose patients receive pembrolizumab plus axitinib.
NCT05259319 is a phase I trial that evaluates the safety and efficacy of the combination of the anti-PD-L1 atezolizumab with the anti-TIGIT tiragolumab—associated with concomitant or sequential stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT)—in patients with oligometastatic disease. In this study, one cohort consisted of patients progressing to first-line treatment.
Lastly, the NCT04626479 trial is a substudy of a larger research umbrella study (the phase Ib/II MK-3475-U03 umbrella trial), which aims to evaluate the safety and efficacy of experimental combinations of investigational agents (among which are favezelimab/pembrolizumab) in RCC. The substudy 03A (MK-3475-03A) involves participants with advanced untreated ccRCC (estimated n = 400), including a safety lead-in phase and an efficacy phase. On the other hand, the substudy 03B (MK-3475-03B) focuses on the second-line setting, enrolling pre-treated mRCC patients (estimated n = 370).
MK-3475-03A investigates the addition of vibostolimab (anti-TIGIT) to pembrolizumab in metastatic treatment-naive patients.
4.2. Phase I–II Targeting ILT4
The combination of pembrolizumab and MK-4830 is currently being studied in an umbrella trial that includes RCC (NCT04626518). CDX-585 is another anti-ILT-4 agent under investigation and is an open-label, non-randomized, multicenter, dose escalation and expansion study in patients with selected solid tumors, including RCC. It is currently open and enrolling (NCT05788484).
4.3. Phase I–II of CAR-T
Several phase I and II trials are ongoing to assess the safety and tolerability of CAR-T in patients with advanced RCC (NCT05420519, NCT06182735, NCT04696731, NCT04438083).
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX), a genetic product downstream of the hyperactivation of the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) pathway, is an interesting therapeutic target, being present with greater density in patients with ccRCC. NCT04969354 is a trial that evaluates the safety and efficacy of CAR-T cells targeting CAIX in metastatic RCC patients.
Furthermore, NCT03393936 is a dose escalation and dose expansion clinical study to evaluate the safety, tolerability and anti-tumor activity of the autologous CAR-T cells CCT 301-38 or CCT 301-59 in patients with mRCC. All of these studies are still recruiting and their results are awaited.
Another study investigated the administration of cells transduced with CAR VEGFR2, which inhibited the growth of tumor cells in different mouse strains (NCT01218867). This study is currently complete but final results have not yet been published.
For CAR-NK cells, NCT05703854 is a phase I/II study seeking to evaluate the safety, tolerability and optimal cell dose of CAR-NK in patients with advanced RCC.
4.4. Phase I–II Targeting LAG3
The DUET-4 trial (NCT03849469) is a phase I trial assessing the safety, pharmacokinetics and anti-tumor activity of the new anti-LAG3 drug XmAb22841, in monotherapy and in combination with pembrolizumab, in patients with advanced solid tumors, including RCC. This trial is complete, but results are yet to be reported.
One trial is currently studying the role of anti-LAG3 drugs in different settings of RCC. The STELLAR-002 trial (NCT05176483) aims to assess the activity of a new multi-targeted inhibitor of receptor tyrosine kinases, XL092, in combination with many immunotherapy agents, such as the anti-LAG3 relatlimab, in unresectable advanced solid tumors, including RCC. This trial is currently open and recruiting.
4.5. Phase I–II Targeting TIM-3
Two trials have tested two anti-TIM-3 drugs in advanced solid tumors, as follows: MBG453 (NCT02608268), also known as sabatolimab, and INCAGN02390 (NCT03652077). The first trial (NCT02608268) is a phase I/II trial built to assess the safety, pharmacokinetics and anti-tumor activity of the anti-TIM-3 drug MBG453 in advanced solid tumors, including RCC, administered in monotherapy or in combination with spartalizumab. The second study (NCT03652077) is a phase I trial which aims to investigate the safety and tolerability of INCAGN02390. While both of these studies are complete, their results have not yet been published.
4.6. Phase I–II of Vaccines
The NCT02950766 trial is currently assessing personalized neoantigen vaccines in combination with ipilimumab in ccRCC. Moreover, the NCT05269381 trial is investigating the safety and tolerability of tailored neoantigen vaccines in combination with pembrolizumab in advanced or metastatic malignancies, including RCC. Lastly, the addition of personalized neoantigen vaccines to the standard of care is being studied in the NCT05641545 trial.
We summarized ongoing phase I and phase II trials in Table 2.

Table 2.
Ongoing phase I and phase II trials in metastatic RCC patients.
4.7. Overview on Ongoing Trials
All of these new treatment combinations could represent a valid alternative to the current standard of care as first-line therapies and beyond in RCC, providing a broader inhibitory profile of multiple immune checkpoint targets. Thus, it has to be underlined that many of these studies involve small patient cohorts and often do not focus exclusively on RCC, needing further future large-scale studies to confirm efficacy and safety across different populations. Furthermore, despite the possible enhanced benefits in survival of targeting multiple immune checkpoints, there remains the relatively unknown potential of synergistics effects, the challenge of new resistance mechanisms and, as with every combination therapy, the possible increase in toxicity. For example, for second-line treatments and beyond, the use of anti-PD1 after progression on first-line ICIs may represent a challenge, considering the use of a similar target beyond progression. Lastly, and especially for CAR-T and vaccines, difficulties regarding manufacturing and costs may undermine the broad adoption of these treatment strategies in clinical practice.
There are currently no ongoing trials involving immunosuppressive cells such as Treg, MDSC, and TAM.
5. Conclusions
In both metastatic and adjuvant settings, immunotherapy is the cornerstone of treatment for RCC. However, an adaptive resistance from cancer cells may arise during ICI treatment. The mechanisms most frequently involved in the progressive resistance to ICI are the loss of response to IFN-gamma, the secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines, the loss of neoantigen expression, and the modifications of the tumor microenvironment related to the overexpression of TAM, MDSC, and Treg.
This has made it necessary to investigate new immune checkpoint inhibitor molecules that are able to overcome these crucial issues.
Drugs directed against TIGIT, ILT4, LAG-3, TIM-3 or therapeutic cancer vaccines are currently being studied in early-phase clinical trials, showing promising results. Additionally, trials are underway on the use of autologous and allogeneic transplants of CAR-engineered T cells and CAR-NK cells. These new immunotherapeutic targets could eventually change the therapeutic landscape of RCC, but the results of larger studies are needed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.M., V.M., M.R. and A.M. (Andrea Marchetti); methodology, F.M., V.M., M.R., A.M. (Andrea Marchetti) and E.T.; investigation, S.C., C.C., L.G., M.R., A.M. (Andrea Marchetti), E.T., P.P., A.M. (Angelo Mottaran) and R.S.; data curation, F.M., V.M. and M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.C., C.C. and L.G.; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, S.C., C.C. and L.G.; supervision, F.M. and V.M.; project administration, F.M. and V.M.; funding acquisition, F.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union—Next Generation EU through the Italian Ministry of University and Research under PNRR—M4C2-11.3 Project PE_00000019 “HEAL ITALIA” to Francesco Massari CUP J33C22002920006. The views and opinions expressed are those of the authors only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Commission. Neither the European Union nor the European Commission can be held responsible for them.
Conflicts of Interest
Francesco Massari (F.M.) has received research support and/or honoraria from Astellas, BMS, Janssen, Ipsen, MSD and Pfizer outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Cancer Observatory. International Agency for Research on Cancer. World Health Organization. 2020. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/ (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- Moch, H.; Amin, M.B.; Berney, D.M.; Compérat, E.M.; Gill, A.J.; Hartmann, A.; Menon, S.; Raspollini, M.R.; Rubin, M.A.; Srigley, J.R.; et al. The 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs—Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccarese, C.; Brunelli, M.; Montironi, R.; Fiorentino, M.; Iacovelli, R.; Heng, D.; Tortora, G.; Massari, F. The prospect of precision therapy for renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 49, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosellini, M.; Marchetti, A.; Mollica, V.; Rizzo, A.; Santoni, M.; Massari, F. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2023, 20, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Warren, M.A.; Golshayan, A.R.; Sahi, C.; Eigl, B.J.; Ruether, J.D.; Cheng, T.; North, S.; et al. Prognostic Factors for Overall Survival in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor–Targeted Agents: Results From a Large, Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5794–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, F.; Rizzo, A.; Mollica, V.; Rosellini, M.; Marchetti, A.; Ardizzoni, A.; Santoni, M. Immune-based combinations for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 154, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Aren Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Plimack, E.R.; Stus, V.; Gafanov, R.; Hawkins, R.; Nosov, D.; Pouliot, F.; Alekseev, B.; Soulières, D.; Melichar, B.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Powles, T.; Burotto, M.; Escudier, B.; Bourlon, M.T.; Zurawski, B.; Oyervides Juárez, V.M.; Hsieh, J.J.; Basso, U.; Shah, A.Y.; et al. Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.; Alekseev, B.; Rha, S.-Y.; Porta, C.; Eto, M.; Powles, T.; Grünwald, V.; Hutson, T.E.; Kopyltsov, E.; Méndez-Vidal, M.J.; et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.S.; Teng, M.W.L.; Smyth, M.J. Cancer immunoediting and resistance to T cell-based immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagchi, S.; Yuan, R.; Engleman, E.G. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer: Clinical Impact and Mechanisms of Response and Resistance. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2021, 16, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanasekaran, R.; Hansen, A.S.; Park, J.; Lemaitre, L.; Lai, I.; Adeniji, N.; Kuruvilla, S.; Suresh, A.; Zhang, J.; Swamy, V.; et al. MYC Overexpression Drives Immune Evasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma That Is Reversible through Restoration of Proinflammatory Macrophages. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haist, M.; Stege, H.; Grabbe, S.; Bros, M. The Functional Crosstalk between Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Regulatory T Cells within the Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2021, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Fu, B.M. Resistance Mechanisms of Anti-angiogenic Therapy and Exosomes-Mediated Revascularization in Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 610661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiges, L.; Schmidinger, M.; Taguieva-Pioger, N.; Perol, D.; Grünwald, V.; Guemas, E. CaboPoint: A phase II study of cabozantinib as second-line treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Futur. Oncol. 2021, 18, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, G.; Claps, M.; Pircher, C.; Porcu, L.; Sepe, P.; Guadalupi, V.; De Giorgi, U.; Bimbatti, D.; Nolè, F.; Carrozza, F.; et al. A multicenter phase 2 single arm study of cabozantinib in patients with advanced or unresectable renal cell carcinoma pre-treated with one immune-checkpoint inhibitor: The BREAKPOINT trial (Meet-Uro trial 03). Tumori J. 2023, 109, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, M.; Massari, F.; Bracarda, S.; Grande, E.; Matrana, M.R.; Rizzo, M.; De Giorgi, U.; Basso, U.; Aurilio, G.; Incorvaia, L.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma Primary Refractory to First-line Immunocombinations or Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Eur. Urol. Focus 2022, 8, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Glen, H.; Michaelson, M.D.; Molina, A.; Eisen, T.; Jassem, J.; Zolnierek, J.; Maroto, J.P.; Mellado, B.; et al. Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buti, S.; Olivari, A.; Masini, C.; Bimbatti, D.; Sartori, D.; Ermacora, P.; Cattrini, C.; Vitale, M.G.; Rossi, E.; Mucciarini, C.; et al. Assessing the effectiveness and safety of lenvatinib and everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: Insights from the RELIEVE study’s analysis of heavily pretreated patients. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2024, 16, 17562872241244574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiges, L.; Rini, B.; Peltola, K.; Oria, G.D.V.; Burotto, M.; Rodriguez, C.S.; Ghatalia, P.; Iacovelli, R.; Lam, E.; Verzoni, E.; et al. LBA88 Belzutifan versus everolimus in participants (pts) with previously treated advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC): Randomized open-label phase III LITESPARK-005 study. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1329–S1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; McDermott, D.F.; Merchan, J.; Bauer, T.M.; Figlin, R.; Heath, E.I.; Michaelson, M.D.; Arrowsmith, E.; D’SOuza, A.; Zhao, S.; et al. Belzutifan plus cabozantinib for patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma previously treated with immunotherapy: An open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.K.; Albiges, L.; Tomczak, P.; Suárez, C.; Voss, M.H.; de Velasco, G.; Chahoud, J.; Mochalova, A.; Procopio, G.; Mahammedi, H.; et al. Atezolizumab plus cabozantinib versus cabozantinib monotherapy for patients with renal cell carcinoma after progression with previous immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment (CONTACT-03): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosellini, M.; Tassinari, E.; Marchetti, A.; Mollica, V.; Massari, F. Re: Atezolizumab Plus Cabozantinib Versus Cabozantinib Monotherapy for Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma After Progression with Previous Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment (CONTACT-03): A Multicentre, Randomised, Open-label, Phase 3 Trial. Eur. Urol. 2024, 85, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joller, N.; Hafler, J.P.; Brynedal, B.; Kassam, N.; Spoerl, S.; Levin, S.D.; Sharpe, A.H.; Kuchroo, V.K. Cutting Edge: TIGIT Has T Cell-Intrinsic Inhibitory Functions. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1338–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjunpää, H.; Guillerey, C. TIGIT as an emerging immune checkpoint. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 200, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, W.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Tian, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, C.; Zheng, J. Immunoreceptor TIGIT inhibits the cytotoxicity of human cytokine-induced killer cells by interacting with CD155. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagumo, Y.; Iguchi-Manaka, A.; Yamashita-Kanemaru, Y.; Abe, F.; Bernhardt, G.; Shibuya, A.; Shibuya, K. Increased CD112 Expression in Methylcholanthrene-Induced Tumors in CD155-Deficient Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.J.; Comps-Agrar, L.; Hackney, J.; Yu, X.; Huseni, M.; Yang, Y.; Park, S.; Javinal, V.; Chiu, H.; Irving, B.; et al. The Immunoreceptor TIGIT Regulates Antitumor and Antiviral CD8 + T Cell Effector Function. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.L.; Garrido-Laguna, I. TIGIT: A novel immunotherapy target moving from bench to bedside. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, A.; Parisi, C.; Barlesi, F. Anti-TIGIT therapies for solid tumors: A systematic review. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X. Correlation of T Cell Immunoglobulin and ITIM Domain (TIGIT) and Programmed Death 1 (PD-1) with Clinicopathological Characteristics of Renal Cell Carcinoma May Indicate Potential Targets for Treatment. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 6861–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuvola, G.; Mollica, V.; Massari, F.; Suárez, C. The Future of Immunotherapy in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Beyond PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors. Immunotherapy 2023, 15, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Sun, Y.; Peng, G. ILT4 functions as a potential checkpoint molecule for tumor immunotherapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2018, 1869, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, L.L.; Wang, D.; Hilton, J.; Geva, R.; Rasco, D.; Perets, R.; Abraham, A.K.; Wilson, D.C.; Markensohn, J.F.; Lunceford, J.; et al. First-in-Class Anti-immunoglobulin–like Transcript 4 Myeloid-Specific Antibody MK-4830 Abrogates a PD-1 Resistance Mechanism in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Riddell, S.R. Engineering CAR-T cells: Design concepts. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Schüßler-Lenz, M.; Bondanza, A.; Buchholz, C.J. Clinical development of CAR T cells—Challenges and opportunities in translating innovative treatment concepts. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.C.; Sterner, R.M. CAR-T cell therapy: Current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrough, A.; Abraham, P.R.; Turer, L.; Kaur, G.; Sannareddy, A.; Hansen, D.K.; Anderson, L.D., Jr. Toxicity of CAR T-Cell Therapy for Multiple Myeloma. Acta Haematol. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, V.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Rezaei, N. The immunologic aspects of cytokine release syndrome and graft versus host disease following CAR T cell therapy. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 41, 649–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wolterink, R.G.J.K.; Wang, J.; Bos, G.M.J.; Germeraad, W.T.V. Chimeric antigen receptor natural killer (CAR-NK) cell design and engineering for cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, C.J.; Dugger, K.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Cutting Edge: Molecular Analysis of the Negative Regulatory Function of Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 5392–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Schadendorf, D.; Lipson, E.J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Matamala, L.; Gutiérrez, E.C.; Rutkowski, P.; Gogas, H.J.; Lao, C.D.; De Menezes, J.J.; et al. Relatlimab and Nivolumab versus Nivolumab in Untreated Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Lipson, E.J.; Dummer, R.; Larkin, J.; Long, G.V.; Sanborn, R.E.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Dréno, B.; Dalle, S.; Schadendorf, D.; et al. Nivolumab and Relatlimab in Patients With Advanced Melanoma That Had Progressed on Anti–Programmed Death-1/Programmed Death Ligand 1 Therapy: Results From the Phase I/IIa RELATIVITY-020 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2724–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Hodi, F.S.; Lipson, E.J.; Schadendorf, D.; Ascierto, P.A.; Matamala, L.; Salman, P.; Gutiérrez, E.C.; Rutkowski, P.; Gogas, H.J.; et al. Overall Survival and Response with Nivolumab and Relatlimab in Advanced Melanoma. NEJM Evid. 2023, 2, EVIDoa2200239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, D.A.; Merkin, R.D.; Moutafi, M.; Martinez, S.; Adeniran, A.; Kumar, D.; Jilaveanu, L.; Hurwitz, M.; Rimm, D.L.; Kluger, H.M. Location matters: LAG3 levels are lower in renal cell carcinoma metastatic sites compared to primary tumors, and expression at metastatic sites only may have prognostic importance. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 990367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, W.D.; Anderson, D.E.; Kassam, N.; Koguchi, K.; Greenfield, E.A.; Kent, S.C.; Zheng, X.X.; Strom, T.B.; Hafler, D.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. TIM-3 is expressed on activated human CD4+ T cells and regulates Th1 and Th17 cytokines. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikawa, T.; Kamimura, Y.; Akiba, H.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K.; Takahashi, H.; Zeniya, M.; Tajiri, H.; Azuma, M. Preferential Involvement of Tim-3 in the Regulation of Hepatic CD8+ T Cells in Murine Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4281–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, K.; Tao, K.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Q.; Lu, X.; Liu, J.; Shi, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, G.; et al. Tim-3/galectin-9 signaling pathway mediates T-cell dysfunction and predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, H.; Huang, Q. Prognostic implication of TIM-3 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Neoplasma 2014, 61, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammensee, H.G.; Falk, K.; Rötzschke, O. Peptides naturally presented by MHC class I molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1993, 11, 213–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirner, A.; Mayer-Mokler, A.; Reinhardt, C. IMA901: A multi-peptide cancer vaccine for treatment of renal cell cancer. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2014, 10, 3179–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.; Weinschenk, T.; Stenzl, A.; Zdrojowy, R.; Pluzanska, A.; Szczylik, C.; Staehler, M.; Brugger, W.; Dietrich, P.-Y.; Mendrzyk, R.; et al. Multipeptide immune response to cancer vaccine IMA901 after single-dose cyclophosphamide associates with longer patient survival. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Stenzl, A.; Zdrojowy, R.; Kogan, M.; Shkolnik, M.; Oudard, S.; Weikert, S.; Bracarda, S.; Crabb, S.J.; Bedke, J.; et al. IMA901, a multipeptide cancer vaccine, plus sunitinib versus sunitinib alone, as first-line therapy for advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma (IMPRINT): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figlin, R.A. Personalized immunotherapy (AGS-003) when combined with sunitinib for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2015, 15, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, D.A.; Bakouny, Z.; Hirsch, L.; Flippot, R.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wu, C.J.; Choueiri, T.K. Beyond conventional immune-checkpoint inhibition—Novel immunotherapies for renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, H.; Sato, Y.; Karasaki, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Kume, H.; Ogawa, S.; Homma, Y.; Kakimi, K. Neoantigen Load, Antigen Presentation Machinery, and Immune Signatures Determine Prognosis in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, D.; Xu, X. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages to synergize tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Lu, D.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, X. Heterogeneous responses in hepatocellular carcinoma: The achilles heel of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 1085–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Shi, H.; Zhang, B.; Ou, X.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shu, P.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as immunosuppressive regulators and therapeutic targets in cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.; Tanaka, A.; Sakaguchi, S. Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells as targets of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).