Augmented Reality in Extratemporal Lobe Epilepsy Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Preoperative Imaging and Planning for Invasive Diagnostics
2.3. Operating Room Setup
2.4. Intraoperative Workflow for Invasive Diagnostics
2.5. Preoperative Imaging and Planning for Resection
2.6. Intraoperative Workflow for Resection of the Epileptogenic Lesion
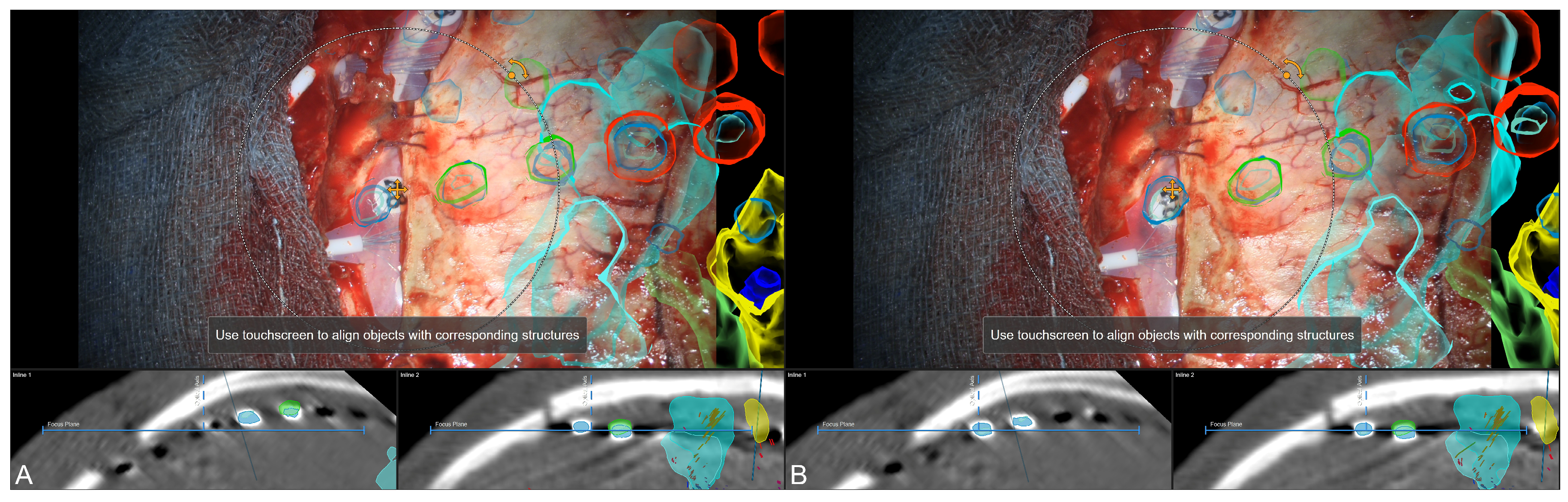
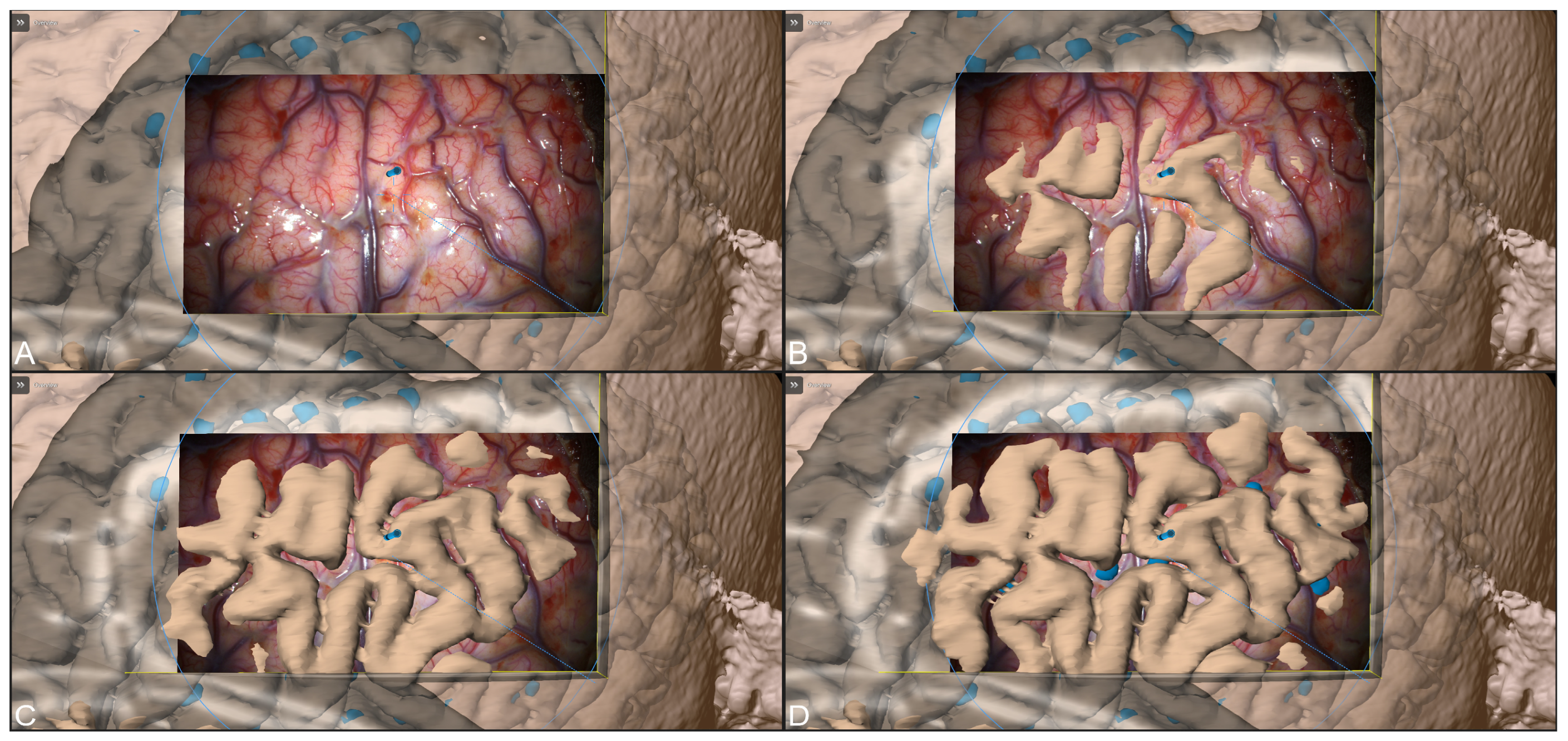
2.7. Augmented Reality
2.8. Surgical and Epileptogenic Outcomes
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Demographic Information
3.2. Surgical and Epileptogenic Outcomes
3.3. Navigation and Augmented Reality Support
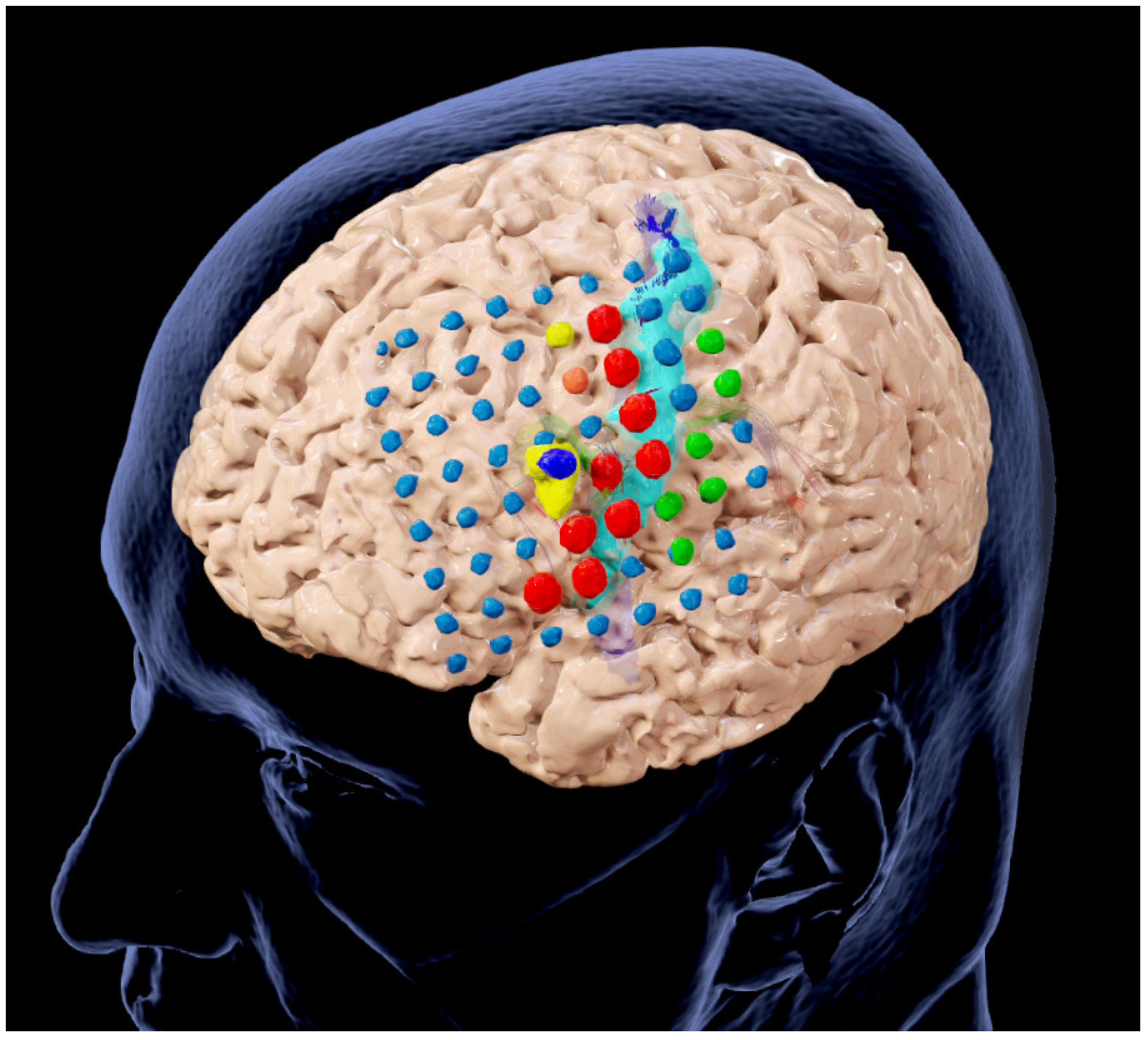
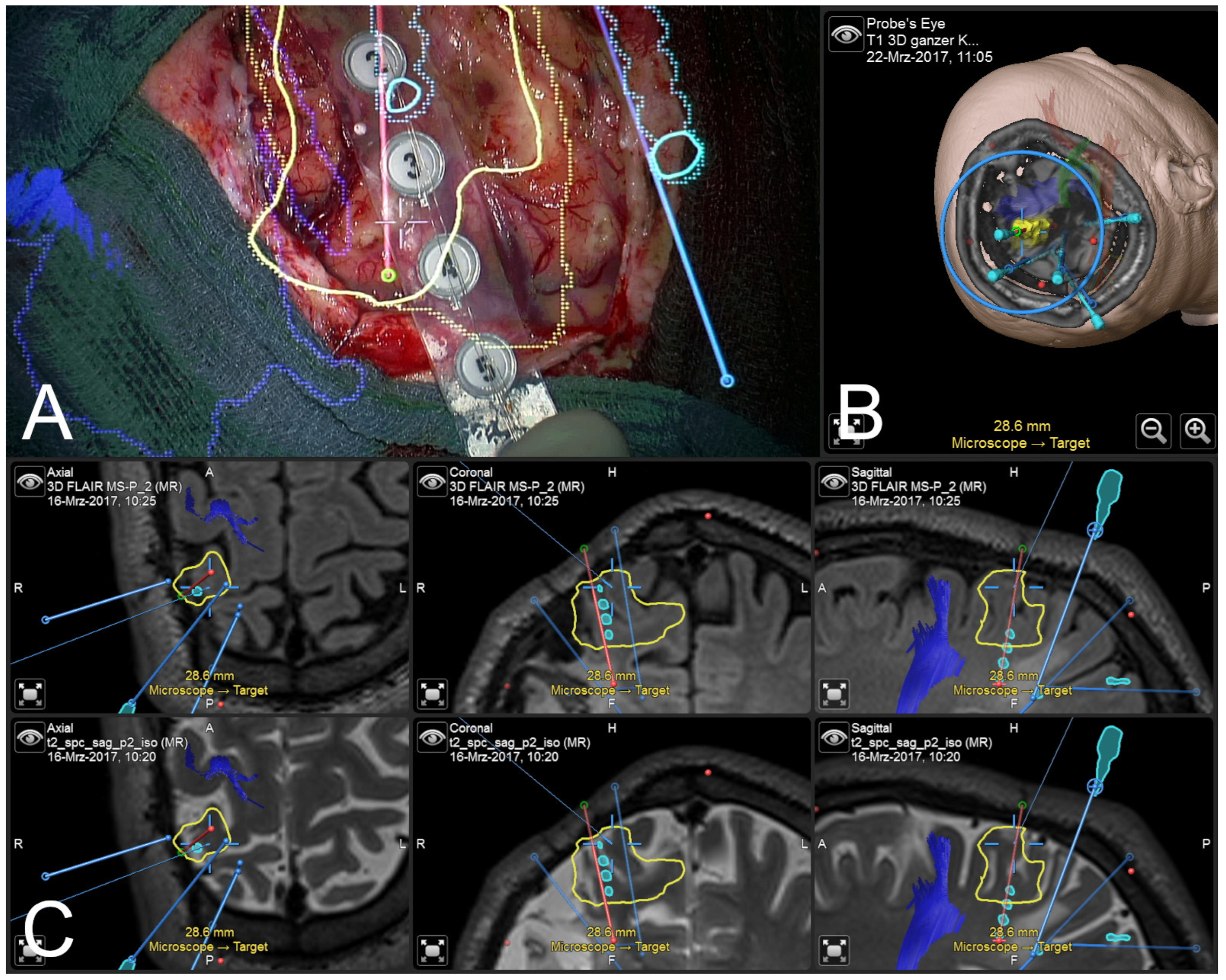
3.4. Illustrative Case (Patient No. 4)
3.5. Illustrative Case (Patient No. 9)
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meola, A.; Cutolo, F.; Carbone, M.; Cagnazzo, F.; Ferrari, M.; Ferrari, V. Augmented reality in neurosurgery: A systematic review. Neurosurg. Rev. 2017, 40, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Alker, G.J., Jr.; Goerss, S. Computer-assisted stereotactic microsurgery for the treatment of intracranial neoplasms. Neurosurgery 1982, 10, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.W.; Strohbehn, J.W.; Hatch, J.F.; Murray, W.; Kettenberger, H. A frameless stereotaxic integration of computerized tomographic imaging and the operating microscope. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 65, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.P.; Edwards, P.J.; Maurer, C.R., Jr.; de Cunha, D.A.; Hawkes, D.J.; Hill, D.L.; Gaston, R.P.; Fenlon, M.R.; Strong, A.J.; Chandler, C.L.; et al. A system for microscope-assisted guided interventions. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 1999, 72, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiya, N.; Dureza, C.; Fukushima, T.; Maroon, J.C. Computer navigational microscope for minimally invasive neurosurgery. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 1997, 40, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrilo, I.; Bijlenga, P.; Schaller, K. Augmented reality in the surgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: Technique assessment and considerations. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 1769–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrilo, I.; Bijlenga, P.; Schaller, K. Augmented reality in the surgery of cerebral aneurysms: A technical report. Neurosurgery 2014, 10 (Suppl. S2), 252–260; discussion 260–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrilo, I.; Schaller, K.; Bijlenga, P. Augmented reality-assisted bypass surgery: Embracing minimal invasiveness. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannizzaro, D.; Zaed, I.; Safa, A.; Jelmoni, A.J.M.; Composto, A.; Bisoglio, A.; Schmeizer, K.; Becker, A.C.; Pizzi, A.; Cardia, A.; et al. Augmented Reality in Neurosurgery, State of Art and Future Projections. A Systematic Review. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 864792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascitelli, J.R.; Schlachter, L.; Chartrain, A.G.; Oemke, H.; Gilligan, J.; Costa, A.B.; Shrivastava, R.K.; Bederson, J.B. Navigation-Linked Heads-Up Display in Intracranial Surgery: Early Experience. Oper. Neurosurg. 2018, 15, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.C.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.L.; Yu, X.G.; Ma, X.D.; Zhou, D.B.; Zhu, R.Y.; Xu, B.N. Impact of Virtual and Augmented Reality Based on Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Functional Neuronavigation in Glioma Surgery Involving Eloquent Areas. World Neurosurg. 2016, 96, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrilo, I.; Sarrafzadeh, A.; Bijlenga, P.; Landis, B.N.; Schaller, K. Augmented reality-assisted skull base surgery. Neurochirurgie 2014, 60, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, B.; Bopp, M.; Benescu, A.; Sass, B.; Nimsky, C. Indocyanine Green Angiography Visualized by Augmented Reality in Aneurysm Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2020, 142, e307–e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, B.; Bopp, M.; Sass, B.; Pojskic, M.; Voellger, B.; Nimsky, C. Spine Surgery Supported by Augmented Reality. Glob. Spine J. 2020, 10, 41S–55S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl, B.; Bopp, M.; Sass, B.; Voellger, B.; Nimsky, C. Implementation of augmented reality support in spine surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 1697–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devinsky, O.; Hesdorffer, D.C.; Thurman, D.J.; Lhatoo, S.; Richerson, G. Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, P.; Brodie, M.J. Early identification of refractory epilepsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, D.J.; Beghi, E.; Begley, C.E.; Berg, A.T.; Buchhalter, J.R.; Ding, D.; Hesdorffer, D.C.; Hauser, W.A.; Kazis, L.; Kobau, R.; et al. Standards for epidemiologic studies and surveillance of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2011, 52 (Suppl. S7), 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, S.; Blume, W.T.; Girvin, J.P.; Eliasziw, M. Effectiveness and Efficiency of Surgery for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Study. Group A randomized, controlled trial of surgery for temporal-lobe epilepsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, A.M.; Averill, C.A.; Kalnins, R.M.; Mitchell, L.A.; Fabinyi, G.C.; Jackson, G.D.; Berkovic, S.F. Long-term seizure outcome and risk factors for recurrence after extratemporal epilepsy surgery. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delev, D.; Oehl, B.; Steinhoff, B.J.; Nakagawa, J.; Scheiwe, C.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Zentner, J. Surgical Treatment of Extratemporal Epilepsy: Results and Prognostic Factors. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascino, G.D. Surgical Treatment for Extratemporal Epilepsy. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2004, 6, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, S.N. Surgical treatment of the extratemporal epilepsies. Epilepsia 2009, 50 (Suppl. S8), 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, G.; Ringler, H.; Knogler, F.; Schnizer, M. Evaluation of neuronavigation in lesional and non-lesional epilepsy surgery. Comput. Aided Surg. 2003, 8, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellmer, J.; von der Groeben, F.; Klarmann, U.; Weber, C.; Elger, C.E.; Urbach, H.; Clusmann, H.; von Lehe, M. Risks and benefits of invasive epilepsy surgery workup with implanted subdural and depth electrodes. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenow, F.; Luders, H. Presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Brain 2001, 124, 1683–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, T.; Clusmann, H.; Urbach, J.; Schramm, J.; Elger, C.E.; Kurthen, M.; Grunwald, T. Preoperative evaluation for epilepsy surgery (Bonn Algorithm). Zentralbl. Neurochir. 2002, 63, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.K.; Mittal, S. Invasive electroencephalography monitoring: Indications and presurgical planning. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2014, 17, S89–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamoun, R.B.; Nayar, V.V.; Yoshor, D. Neuronavigation applied to epilepsy monitoring with subdural electrodes. Neurosurg. Focus. 2008, 25, E21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamida, T.; Anan, M.; Shimotaka, K.; Abe, T.; Fujiki, M.; Kobayashi, H. Visualization of subdural electrodes with fusion CT scan/MRI during neuronavigation-guided epilepsy surgery. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslarova, A.; Zhao, Y.; Rosch, J.; Dorfler, A.; Coras, R.; Blumcke, I.; Lang, J.; Schmidt, M.; Hamer, H.M.; Reindl, C.; et al. Surgical planning, histopathology findings and postoperative outcome in MR-negative extra-temporal epilepsy using intracranial EEG, functional imaging, magnetoencephalography, neuronavigation and intraoperative MRI. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2023, 226, 107603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimsky, C.; Buchfelder, M. Neuronavigation in epilepsy surgery. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2003, 61 (Suppl. S1), 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Roethe, A.L.; Rosler, J.; Misch, M.; Vajkoczy, P.; Picht, T. Augmented reality visualization in brain lesions: A prospective randomized controlled evaluation of its potential and current limitations in navigated microneurosurgery. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leger, E.; Drouin, S.; Collins, D.L.; Popa, T.; Kersten-Oertel, M. Quantifying attention shifts in augmented reality image-guided neurosurgery. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, B.; Bopp, M.; Gjorgjevski, M.; Nimsky, C. Navigation-Supported Stereotaxy by Applying Intraoperative Computed Tomography. World Neurosurg. 2018, 118, e584–e592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl, B.; Bopp, M.; Sass, B.; Nimsky, C. Intraoperative computed tomography as reliable navigation registration device in 200 cranial procedures. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H.G.; Blume, W.T.; Fish, D.; Goldensohn, E.; Hufnagel, A.; King, D.; Sperling, M.R.; Luders, H.; Pedley, T.A.; Commission on Neurosurgery of the International League AgainstEpilepsy. ILAE Commission Report. Proposal for a new classification of outcome with respect to epileptic seizures following epilepsy surgery. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdos, M.; Riha, P.; Kojan, M.; Dolezalova, I.; Mutsaerts, H.; Petr, J.; Rektor, I. Epileptogenic zone detection in MRI negative epilepsy using adaptive thresholding of arterial spin labeling data. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez-Zenteno, J.F.; Hernandez Ronquillo, L.; Moien-Afshari, F.; Wiebe, S. Surgical outcomes in lesional and non-lesional epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Res. 2010, 89, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hader, W.J.; Mackay, M.; Otsubo, H.; Chitoku, S.; Weiss, S.; Becker, L.; Snead, O.C., 3rd; Rutka, J.T. Cortical dysplastic lesions in children with intractable epilepsy: Role of complete resection. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuloh, G.; Bien, C.G.; Clusmann, H.; von Lehe, M.; Schramm, J. Continuous motor monitoring enhances functional preservation and seizure-free outcome in surgery for intractable focal epilepsy. Acta Neurochir. 2010, 152, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delev, D.; Send, K.; Malter, M.; Ormond, D.R.; Parpaley, Y.; von Lehe, M.; Schramm, J.; Grote, A. Role of Subdural Interhemispheric Electrodes in Presurgical Evaluation of Epilepsy Patients. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 1719–1725.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, E.L.; Lee, R.W. Epilepsy surgery in MRI-negative epilepsies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2014, 27, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedegard, E.; Bjellvi, J.; Edelvik, A.; Rydenhag, B.; Flink, R.; Malmgren, K. Complications to invasive epilepsy surgery workup with subdural and depth electrodes: A prospective population-based observational study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonigal, A.; Bartolomei, F.; Regis, J.; Guye, M.; Gavaret, M.; Trebuchon-Da Fonseca, A.; Dufour, H.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Girard, N.; Peragut, J.C.; et al. Stereoelectroencephalography in presurgical assessment of MRI-negative epilepsy. Brain 2007, 130, 3169–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl, B.; Bopp, M.; Sass, B.; Pojskic, M.; Gjorgjevski, M.; Voellger, B.; Nimsky, C. Reliable navigation registration in cranial and spine surgery based on intraoperative computed tomography. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 47, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Fujii, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Kimura, M.; Murai, Y.; Hata, M.; Sugiura, A.; Tsuzaka, M.; Wakabayashi, T. Evaluation of errors influencing accuracy in image-guided neurosurgery. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2009, 2, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieglitz, L.H.; Fichtner, J.; Andres, R.; Schucht, P.; Krahenbuhl, A.K.; Raabe, A.; Beck, J. The silent loss of neuronavigation accuracy: A systematic retrospective analysis of factors influencing the mismatch of frameless stereotactic systems in cranial neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantelhardt, S.R.; Gutenberg, A.; Neulen, A.; Keric, N.; Renovanz, M.; Giese, A. Video-Assisted Navigation for Adjustment of Image-Guidance Accuracy to Slight Brain Shift. Oper. Neurosurg. 2015, 11, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmeier, R.; Rachinger, J.; Kaus, M.; Ganslandt, O.; Huk, W.; Fahlbusch, R. Factors influencing the application accuracy of neuronavigation systems. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2000, 75, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimsky, C.; Ganslandt, O.; Cerny, S.; Hastreiter, P.; Greiner, G.; Fahlbusch, R. Quantification of, visualization of, and compensation for brain shift using intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 1070–1079; discussion 1079–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggi, S.; Pallotta, S.; Russo, S.; Gallina, P.; Torresin, A.; Bucciolini, M. Neuronavigation accuracy dependence on CT and MR imaging parameters: A phantom-based study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2003, 48, 2199–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastreiter, P.; Rezk-Salama, C.; Soza, G.; Bauer, M.; Greiner, G.; Fahlbusch, R.; Ganslandt, O.; Nimsky, C. Strategies for brain shift evaluation. Med. Image Anal. 2004, 8, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimsky, C.; Ganslandt, O.; Hastreiter, P.; Fahlbusch, R. Intraoperative compensation for brain shift. Surg. Neurol. 2001, 56, 357–364; discussion 364–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oertel, J.; Gaab, M.R.; Runge, U.; Schroeder, H.W.; Wagner, W.; Piek, J. Neuronavigation and complication rate in epilepsy surgery. Neurosurg. Rev. 2004, 27, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, R.S.; Yacubian, E.M.; Sakamoto, A.C.; Ferraz, A.F.; Junior, H.C.; Cavalheiro, S. Pre-surgical evaluation and surgical treatment in children with extratemporal epilepsy. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2006, 22, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, B.; Grummich, P.; Coras, R.; Kasper, B.S.; Blumcke, I.; Hamer, H.M.; Stefan, H.; Buchfelder, M.; Roessler, K. Integration of functional neuronavigation and intraoperative MRI in surgery for drug-resistant extratemporal epilepsy close to eloquent brain areas. Neurosurg. Focus 2013, 34, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, B.; Roessler, K.; Rampp, S.; Hamer, H.M.; Blumcke, I.; Stefan, H.; Buchfelder, M. Magnetoencephalography-guided surgery in frontal lobe epilepsy using neuronavigation and intraoperative MR imaging. Epilepsy Res. 2016, 126, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bien, C.G.; Szinay, M.; Wagner, J.; Clusmann, H.; Becker, A.J.; Urbach, H. Characteristics and surgical outcomes of patients with refractory magnetic resonance imaging-negative epilepsies. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.Y.; Lee, W.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Chen, C.C.; Tso, M. Application of neuronavigator coupled with an operative microscope and electrocorticography in epilepsy surgery. Surg. Neurol. 2005, 64, 411–417; discussion 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, T.; Arango, G.; Kaminsky, J.; Samii, A.; Thorns, U.; Vorkapic, P.; Samii, M. An experimental approach to image guided skull base surgery employing a microscope-based neuronavigation system. Acta Neurochir. 1998, 140, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajiwara, K.; Nishizaki, T.; Ohmoto, Y.; Nomura, S.; Suzuki, M. Image-guided transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary lesions using Mehrkoordinaten Manipulator (MKM) navigation system. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2003, 46, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meola, A.; Chang, S.D. Letter: Navigation-Linked Heads-Up Display in Intracranial Surgery: Early Experience. Oper. Neurosurg. 2018, 14, E71–E72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, P.J.; Johnson, L.G.; Hawkes, D.J.; Fenlon, M.R.; Strong, A.J.; Gleeson, M.J. Clinical Experience and Perception in Stereo Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hosny, M.; Gao, W.; Fu, Y. Facial landmark-guided surface matching for image-to-patient registration with an RGB-D camera. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2022, 18, e2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.B.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Toms, S.A.; Maurer, C.R., Jr.; Maciunas, R.J. Fiducial point placement and the accuracy of point-based, rigid body registration. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 810–816; discussion 816–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, T.; Fujii, M.; Tsuzaka, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Asahina, Y.; Wakabayashi, T. Skin shift and its effect on navigation accuracy in image-guided neurosurgery. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2011, 4, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfisterer, W.K.; Papadopoulos, S.; Drumm, D.A.; Smith, K.; Preul, M.C. Fiducial versus nonfiducial neuronavigation registration assessment and considerations of accuracy. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachinger, J.; von Keller, B.; Ganslandt, O.; Fahlbusch, R.; Nimsky, C. Application accuracy of automatic registration in frameless stereotaxy. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2006, 84, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letteboer, M.M.; Willems, P.W.; Viergever, M.A.; Niessen, W.J. Brain shift estimation in image-guided neurosurgery using 3-D ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinertsen, I.; Lindseth, F.; Askeland, C.; Iversen, D.H.; Unsgard, G. Intra-operative correction of brain-shift. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saß, B.; Carl, B.; Pojskic, M.; Nimsky, C.; Bopp, M. Navigated 3D Ultrasound in Brain Metastasis Surgery: Analyzing the Differences in Object Appearances in Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopp, M.H.A.; Grote, A.; Gjorgjevski, M.; Pojskic, M.; Sass, B.; Nimsky, C. Enabling Navigation and Augmented Reality in the Sitting Position in Posterior Fossa Surgery Using Intraoperative Ultrasound. Cancers 2024, 16, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, S.; Atsumi, H.; Kikinis, R.; Moriarty, T.M.; Metcalf, D.C.; Jolesz, F.A.; Black, P.M. Use of cortical surface vessel registration for image-guided neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 1201–1208; discussion 1208–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bopp, M.H.A.; Corr, F.; Sass, B.; Pojskic, M.; Kemmling, A.; Nimsky, C. Augmented Reality to Compensate for Navigation Inaccuracies. Sensors 2022, 22, 9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavarajasingam, S.G.; Vardanyan, R.; Arjomandi Rad, A.; Thavarajasingam, A.; Khachikyan, A.; Mendoza, N.; Nair, R.; Vajkoczy, P. The use of augmented reality in transsphenoidal surgery: A systematic review. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 36, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopp, M.H.A.; Sass, B.; Pojskic, M.; Corr, F.; Grimm, D.; Kemmling, A.; Nimsky, C. Use of Neuronavigation and Augmented Reality in Transsphenoidal Pituitary Adenoma Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojskic, M.; Bopp, M.; Sass, B.; Nimsky, C. Single-Center Experience of Resection of 120 Cases of Intradural Spinal Tumors. World Neurosurg. 2024, 187, e233–e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojskic, M.; Bopp, M.H.A.; Sass, B.; Nimsky, C. Single-Center Experience in Microsurgical Resection of Acoustic Neurinomas and the Benefit of Microscope-Based Augmented Reality. Medicina 2024, 60, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadipour, Y.; Lemonas, E.; Maslehaty, H.; Goericke, S.; Stuck, B.A.; El Hindy, N.; Sure, U.; Mueller, O. Critical analysis of anatomical landmarks within the sphenoid sinus for transsphenoidal surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 3929–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Patient No. | Age | Sex | Epileptogenic Zone | MRI Assessment | Invasive Diagnostics | Histopathology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23.82 | Female | FLE, left | negative | SEEG + grid | DNH |
| 2 | 47.43 | Male | FLE, left | FCD | SEEG | FCD type IIa |
| 3 | 30.92 | Male | FLE, right | FLAIR/T2 hyperintensity | SEEG + grid | FCD type IIb + ganglioglioma |
| 4 | 30.82 | Male | PLE, right | gliosis along resection cavity | SEEG | FCD type IIa |
| 5 | 34.15 | Male | FLE, right | negative | grid | FCD type IIb + DNH |
| 6 | 47.63 | Female | left hemisphere | ischemia | grid | Hypoxia |
| 7 | 29.08 | Male | F(T)LE, right | negative | grid | FCD type IIa |
| 8 | 54.29 | Male | FLE, left | negative | SEEG, grid | DNH |
| 9 | 23.52 | Male | FLE, left | FCD | SEEG, grid | DNH |
| 10 | 16.65 | Female | FLE, left/bilateral | T2 hyperintensity | SEEG | gliotic scar |
| Patient No. | Seizure Frequency | Seizure Type | Antiepileptic Drugs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ineffective Medication | Current Medication | |||
| 1 | 3/week | aura, FIAS, sleep related | BRV, CBZ, LTG, LEV, PER | LCM, ZNS |
| 2 | 5–10/day | aura, FIAS | BRV, LCM | CBZ, LEV, TPM |
| 3 | 3–4/month | G, TCS | CBZ, PB, OXC, VPA | LTG, LEV, TPM |
| 4 | 2/week | aura, TCS | LEV, ZNS | BRV, CBZ, LCM |
| 5 | 2–4/week | aura, TCS | LTG, LEV, VPA | LCM |
| 6 | 2–7/week | TCS | CBZ, VPA | LEV, ZNS |
| 7 | 3/week | aura, TCS | LCM, LTG, LEV, VPA | BRV, OXC, ZNS |
| 8 | 2–3/week (2/year) | TCS (G) | LCM, TPM, VPA | LEV, PER |
| 9 | 3/day | FIAS, TCS, sleep related | OXC, SUM | BRV, LCM, PER |
| 10 | 2/week | aura, FAS | LCM, LTG, VPA | LEV, OXC |
| Patient No. | Surgical Complications | New Postoperative Neurological Deficits | ILAE Outcome at One Year Follow-Up | ILAE Outcome at Latest Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | dislocation of boneflap, refixation required | - | 1 | 1 (4 years) |
| 2 | - | - | 1 | 1 (7 years) |
| 3 | - | - | 2 | 2 (6 years) |
| 4 | - | slight coordination disturbance of the left side (<1 month) | 1 | 1 (7 years) |
| 5 | - | - | 1 | 1 (1 year) |
| 6 | - | - | 4 | 4 (5 years) |
| 7 | CSF fistula, revision surgery required | - | 1 | 1 (5 years) |
| 8 | - | - | 3 | 3 (2 years) |
| 9 | - | transient sensoric aphasia (<3 weeks) | 3 | 1 (2 years) |
| 10 | - | - | 1 | 1 (4 years) |
| Patient No. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR Visualization | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Lesion | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| SEEG electrodes | x | x | x | x | - | - | - | - | x | x |
| Subdural grid electrodes | x | - | x | - | x | x | x | x | x | - |
| Seizure-related electrode contacts (onset, propagation) | x | - | - | - | x | x | - | x | x | x |
| Motor cortex | - | - | x | - | - | - | - | x | x | - |
| Cerebrum | x | - | - | - | x | - | x | x | x | x |
| CST | x | x | - | x | x | - | - | - | x | - |
| AF | x | x | - | x | - | - | - | - | x | - |
| IFOF | x | x | - | x | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| UF | x | x | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| fMRI language activation | - | x | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | x |
| Acquired subdural grid electrode contacts | x | - | - | - | x | - | x | x | - | - |
| SEEG trajectory | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | x | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grote, A.; Neumann, F.; Menzler, K.; Carl, B.; Nimsky, C.; Bopp, M.H.A. Augmented Reality in Extratemporal Lobe Epilepsy Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195692
Grote A, Neumann F, Menzler K, Carl B, Nimsky C, Bopp MHA. Augmented Reality in Extratemporal Lobe Epilepsy Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(19):5692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195692
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrote, Alexander, Franziska Neumann, Katja Menzler, Barbara Carl, Christopher Nimsky, and Miriam H. A. Bopp. 2024. "Augmented Reality in Extratemporal Lobe Epilepsy Surgery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 19: 5692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195692
APA StyleGrote, A., Neumann, F., Menzler, K., Carl, B., Nimsky, C., & Bopp, M. H. A. (2024). Augmented Reality in Extratemporal Lobe Epilepsy Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(19), 5692. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195692








