Clinical Predictors of Mood Disorders and Prevalence of Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample
2.2. Psychiatric Assessment
2.3. Clinical Assessment of Lupus Patients
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Autoimmune Clinical Predictors of Presenting a Mood Disorder
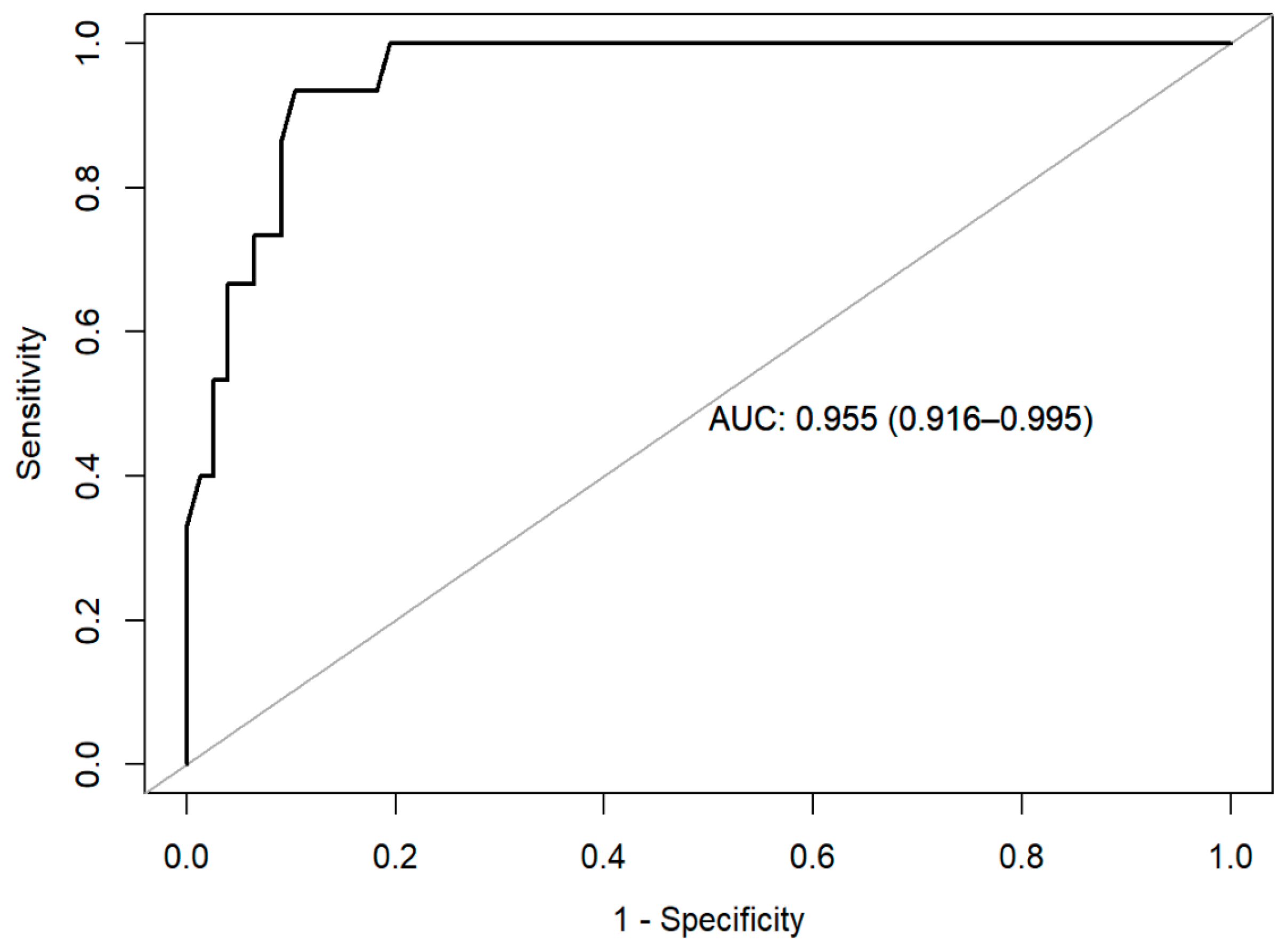
3.2. Psychiatric Predictors of Mood Disorder in SLE Patients
| Total Sample (n = 92) | Patients without a Mood Disorder (n = 77) | Patients with Mood Disorders (n = 15) | N | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender—female | 84 (91.3%) | 71 (92.2%) | 13 (86.7%) | 92 | 0.612 |
| Ethnicity Caucasian Hispanic Arabic | 86 (93.5%) 5 (5.4%) 1 (1.1%) | 74 (96.1%) 2 (2.6%) 1 (1.3%) | 12 (80%) 3 (20%) - | 92 | 0.053 |
| Age at inclusion, Mean (SD): | 44.04 (11.87) | 43.23 (11.89) | 48.20 (11.23) | 92 | 0.136 |
| Disease duration, Median [25th;75th]: | 11.00 [6.00;18.00] | 11.00 [6.00;18.00] | 9.00 [7.00;21.50] | 92 | 0.966 |
| Main clinical manifestations Articular Cutaneous Serosal Hematological Renal Antiphospholipid syndrome | 65 (71.4%) 46 (50.5%) 17 (18.7%) 11 (12.1%) 19 (20.9%) 8 (8.7%) | 54 (21.1%) 40 (52.6%) 15 (19.7%) 10 (13.2%) 14 (18.4%) 8 (10.4%) | 11 (73.3%) 6 (40%) 2 (13.3%) 1 (6.7%) 5 (33.3%) 0 (0%) | 92 | 1.000 0.410 0.728 0.684 0.294 0.345 |
| SLEDAI-2K, Mean (SD): | 1.59 (2.44) | 1.64 (2.60) | 1.31 (1.49) | 92 | 0.995 |
| SDI, Mean (SD): | 0.33 (0.84) | 0.32 (0.84) | 0.38 (0.89) | 92 | 0.802 |
| Positive anti-dsDNA | 25 (27.2%) | 19 (24.7%) | 6 (40%) | 92 | 0.224 |
| C3 (mg/dL), Mean (SD): | 99.34 (21.31) | 98.29 (20.83) | 105.07 (25.50) | 92 | 0.397 |
| C4 (mg/dL), Mean (SD): | 20.38 (8.13) | 20.33 (8.24) | 20.64 (7.78) | 92 | 0.721 |
| Anti-ribosomal p positive, N (%) | 9 (9.8%) | 7 (9.1%) | 2 (13.3%) | 92 | 0.637 |
| Prednisone dose (mg/day), Mean (SD): | 1.94 (1.94) | 1.92 (1.97) | 2.03 (1.88) | 92 | 0.553 |
| Cumulative prednisone dose in 1 year (mg), Mean (SD): | 671.12 (615.34) | 659.61 (626.47) | 725.78 (575.24) | 92 | 0.513 |
| Hydroxychloroquine drug therapy (yes), N (%): | 90 (97.8%) | 77 (100%) | 14 (93.3%) | 92 | 0.163 |
| Other immunosuppressive drug therapy (yes), N (%): | 34 (36.96%) | 26 (33.77%) | 8 (53.33%) | 92 | 0.253 |
| Psychiatric family history (yes), N (%) | 50 (54.95%) | 36 (47.37%) | 14 (93.33%) | 92 | 0.003 |
| Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HARS), Median [25th;75th]: | 2.00 [1.00;6.00] | 1.00 [0.00;4.00] | 9.00 [6.00;18.50] | 92 | <0.001 |
| Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), Median [25th;75th]: | 2.00 [0.00;7.00] | 1.00 [0.00;4.00] | 12.00 [8.50;22.50] | 92 | <0.001 |
| Young Mania Rating Scale (YMRS), Median [25th;75th]: | 0.00 [0.00;0.00] | 0.00 [0.00;0.00] | 0.00 [0.00;3.00] | 92 | <0.001 |
| Plutchik Suicide Risk Scale, Median [25th;75th]: | 2.00 [1.00;4.25] | 1.00 [1.00;3.00] | 5.00 [3.00;7.00] | 92 | <0.001 |
| Global Clinical Impression (CGI), N (%): 1. Normal, not ill | 65 (70.65%) | 64 (83.12%) | 1 (7.14%) | 91 | <0.001 |
| 2. Borderline mental ill | 8 (8.70%) | 6 (7.79%) | 2 (14.29%%) | ||
| 3. Mildly ill | 12 (13.19%) | 5 (6.49%) | 7 (50.00%) | ||
| 4. Moderately ill | 5 (5.43%) | 2 (2.60%) | 3 (21.43%) | ||
| 5. Markedly ill | 1 (1.09%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (7.14%) | ||
| Traumatic Experiences Screening Questionnaire (ExpTra-S), Median [25th;75th] Frequency | 0.00 [0.00;2.00] | 0.00 [0.00;2.00] | 1.00 [0.50;6.00] | 87 | 0.031 |
| Distress | 0.00 [0.00;3.00] | 0.00 [0.00;2.00] | 3.00 [1.00;6.00] | 87 | 0.006 |
| Current Psychiatric Diagnoses According to ICD-10 (n = 32) | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Mood disorders Major depressive disorder Persistent depressive disorder Trauma and Stress-Related Disorders Adjustment disorder Other disorders Organic depressive disorder—in remission Generalized anxiety disorder Eating disorder Psychosocial conditions not attributable to a mental disorder Code Z63. Problems related to primary support group Code Z73. Problems related to life management difficulty | 13 (40.6%) 2 (6.3%) 5 (15.6%) 1 (3.1%) 1 (3.1%) 1 (3.1%) 4 (12.5%) 5 (15.6%) |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaul, A.; Gordon, C.; Crow, M.K.; Touma, Z.; Urowitz, M.B.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Hughes, G. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, F.; Doherty, M.; Grainge, M.J.; Lanyon, P.; Zhang, W. The worldwide incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1945–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, N.; Stock, A.D.; Putterman, C. Neuropsychiatric lupus: New mechanistic insights and future treatment directions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Hanly, J.; Urowitz, M.; Gordon, C.; Bae, S.-C.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Sanchez-Guerrero, J.; Bernatsky, S.; Clarke, A.E.; Wallace, D.J.; et al. Remission and low disease activity (LDA) prevent damage accrual in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Results from the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) inception cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, A.; Cheung, M.W.-L.; Chiew, H.J.; Liu, Y.; Ho, R.C.-M. Global trend of survival and damage of systemic lupus erythematosus: Meta-analysis and meta-regression of observational studies from the 1950s to 2000s. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 41, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, A.; Isenberg, D.A.; Lau, C.-S. Global trends, potential mechanisms and early detection of organ damage in SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 9, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, S.B.; Beck, C.A.; Williams, J.V.; Barbui, C.; Metz, L.M. Major depression in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2003, 61, 1524–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benros, M.E.; Eaton, W.W.; Mortensen, P.B. The epidemiologic evidence linking autoimmune diseases and psychosis. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benros, M.E.; Waltoft, B.L.; Nordentoft, M.; Østergaard, S.D.; Eaton, W.W.; Krogh, J.; Mortensen, P.B. Autoimmune diseases and severe infections as risk factors for mood disorders: A nationwide study. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Fang, F.; Tomasson, G.; Arnberg, F.K.; Mataix-Cols, D.; de la Cruz, L.F.; Almqvist, C.; Fall, K.; Valdimarsdóttir, U.A. Association of Stress-Related Disorders With Subsequent Autoimmune Disease. JAMA 2018, 319, 2388–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govoni, M.; Hanly, J.G. The management of neuropsychiatric lupus in the 21st century: Still so many unmet needs? Rheumatology 2020, 59, v52–v62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivity, S.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Zandman-Goddard, G.; Chapman, J.; Shoenfeld, Y. Neuropsychiatric lupus: A mosaic of clinical presentations. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 599–608. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, T.; Yin, R.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, B. Prevalence of depression and anxiety in systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.T.; Moazzami, M.; Engel, L.; Bangert, E.; Hassanein, M.; Marzouk, S.; Kravtsenyuk, M.; Fung, W.; Eder, L.; Su, J.; et al. Prevalence and metric of depression and anxiety in systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieta, E.; Alonso, J.; Pérez-Sola, V.; Roca, M.; Hernando, T.; Sicras-Mainar, A.; Sicras-Navarro, A.; Herrera, B.; Gabilondo, A. Epidemiology and costs of depressive disorder in Spain: The EPICO study. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 50, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santomauro, D.F.; Herrera, A.M.M.; Shadid, J.; Zheng, P.; Ashbaugh, C.; Pigott, D.M.; Abbafati, C.; Adolph, C.; Amlag, J.O.; Aravkin, A.Y.; et al. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Arruza, I.; Lozano, J.; Cabezas-Rodriguez, I.; Medina, J.A.; Ugarte, A.; Erdozain, J.G.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G. Restrictive Use of Oral Glucocorticoids in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Prevention of Damage Without Worsening Long-Term Disease Control: An Observational Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgens, K.A. Structured Clinical Interview For DSM-IV (SCID-I/SCID-II). In Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology; Kreutzer, J.S., DeLuca, J., Caplan, B., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10), 10th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lobo, A.; Chamorro, L.; Luque, A.; Dal-Ré, R.; Badia, X.; Baró, E.; Grupo de Validación en Español de Escalas Psicométricas (GVEEP). Validación de las versiones en español de la Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale y la Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale para la evaluación de la depresión y de la ansiedad [Validation of the Spanish versions of the Montgomery-Asberg depression and Hamilton anxiety rating scales]. Med. Clin. 2002, 118, 493–499. [Google Scholar]
- Colom, F.; Vieta, E.; Martinez-Arán, A.; García, M.; Reinares, M.; Torrent, C.; Goikolea, J.M.; Banús, S.; Salamero, M. Versión española de una escaña de evaluación de la manía: Validez y fiabilidad de la Escala de Manía de Young. Med. Clin. 2002, 119, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, G.; Montero, J.; Jáuregui, J.; Villanueva, R.; Casado, M.A.; Marín, J.; Santo-Domingo, J. Validación de la escala de riesgo suicida de Plutchik en población española. Arch. Neurobiol. 1998, 61, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ordóñez Camblor, N.; Fonseca Pedrero, E.; Paino Piñeiro, M.D.; García Alvarez, L.; Pizarro Ruiz, J.P.; Lemos Giráldez, S. Evaluación de experiencias traumáticas tempranas en adultos. Papeles Psicol. 2016, 37, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Busner, J.; Targum, S.D. The clinical global impressions scale: Applying a research tool in clinical practice. Psychiatry 2007, 4, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gladman, D.D.; Ibañez, D.; Urowitz, M.B. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 288–291. [Google Scholar]
- Fortin, P.R.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Clarke, A.E.; Neville, C.; Du Berger, R.; Fraenkel, L.; Liang, M.H. Do lupus disease activity measures detect clinically important change? J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Gladman, D.D.; Urowitz, M.B.; Goldsmith, C.H.; Fortin, P.; Ginzler, E.; Gordon, C.; Hanly, J.G.; Isenberg, D.A.; Kalunian, K.; Nived, O.; et al. The reliability of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Subirana, I.; Sanz, H.; Vila, J. Building Bivariate Tables: The compare Groups Package for R. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 57, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; SAGE: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A. Ggcorrplot: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix Using ’Ggplot2’. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggcorrplot (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Brey, R.L.; Holliday, S.L.; Saklad, A.R.; Navarrete, M.G.; Hermosillo–Romo, D.; Stallworth, C.L.; Valdez, C.R.; Escalante, A.; del Rincón, I.; Gronseth, G.; et al. Neuropsychiatric syndromes in lupus: Prevalence using standardized definitions. Neurology 2002, 58, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, F.G.; Borba, E.F.; Viana, V.S.; Hatch, J.P.; Soares, J.C.; Bonfá, E.; Neto, F.L. Prevalence of depressive and anxiety disorders in systemic lupus erythematosus and their association with anti-ribosomal P antibodies. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, E.J.; Lindner, H.; Lederman, L. Relationship of illness perceptions with depression among individuals diagnosed with lupus. Depress. Anxiety 2009, 26, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanly, J.G.; Su, L.; Urowitz, M.B.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Gordon, C.; Bae, S.; Bernatsky, S.; Clarke, A.E.; Wallace, D.J.; Merrill, J.T.; et al. Mood Disorders in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Results From an International Inception Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx). Discover the World’s Health Data. Prevalence of Depression. 2017. Available online: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Monahan, R.C.; de Voorde, L.J.J.B.-V.; Steup-Beekman, G.M.; Magro-Checa, C.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Hoekman, J.; A Kaptein, A. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in systemic lupus erythematosus: Impact on quality of life. Lupus 2017, 26, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Ruiz-Estevez, B.; Lazaro, E.; Ruiz-Arruza, I.; Duffau, P.; Martin-Cascon, M.; Richez, C.; Ugarte, A.; Blanco, P. Prolonged remission in SLE is possible by using reduced doses of prednisone: An observational study from the Lupus-Cruces and Lupus-Bordeaux in-ception cohorts. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, J.M.; Midwinter, M.J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Belli, A.; Brohi, K.; Kovacs, E.J.; Koenderman, L.; Kubes, P.; Lilford, R.J. The systemic immune response to trauma: An overview of pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet 2014, 384, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwenspoek, M.M.; Kuehn, A.; Muller, C.P.; Turner, J.D. The effects of early life adversity on the immune system. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 82, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| MADRS total score | 1.373 | 1.180 to 1.679 | <0.001 |
| YMRS total score | 3.009 | 1.202 to 10.56 | 0.022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Recio-Barbero, M.; Cabezas-Garduño, J.; Varona, J.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Horrillo, I.; Meana, J.J.; Santos-Zorrozúa, B.; Segarra, R. Clinical Predictors of Mood Disorders and Prevalence of Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185423
Recio-Barbero M, Cabezas-Garduño J, Varona J, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Horrillo I, Meana JJ, Santos-Zorrozúa B, Segarra R. Clinical Predictors of Mood Disorders and Prevalence of Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(18):5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185423
Chicago/Turabian StyleRecio-Barbero, María, Janire Cabezas-Garduño, Jimena Varona, Guillermo Ruiz-Irastorza, Igor Horrillo, J. Javier Meana, Borja Santos-Zorrozúa, and Rafael Segarra. 2024. "Clinical Predictors of Mood Disorders and Prevalence of Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 18: 5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185423
APA StyleRecio-Barbero, M., Cabezas-Garduño, J., Varona, J., Ruiz-Irastorza, G., Horrillo, I., Meana, J. J., Santos-Zorrozúa, B., & Segarra, R. (2024). Clinical Predictors of Mood Disorders and Prevalence of Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(18), 5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185423






