A Comprehensive Characterization of Patients with Spinal Cord Neurosarcoidosis: A Single Center Cross-Sectional Study of Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Patient Information
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Clinical Presentation
3.3. Diagnostic Assessment
4. Clinical Findings
5. Discussion
Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rybicki, B.A.; Major, M.; Popovich, J.; Maliarik, M.J.; Iannuzzi, M.C. Racial differences in sarcoidosis incidence: A 5-year study in a health maintenance organization. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannuzzi, M.; Rybicki, B.; Teirstein, A. Review Article Medical Progress Sarcoidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, T.S.; Campellone, J.V.; Maldonado, I.; Huang, N.; Usmani, Q.; Reginato, A.J. Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging manifestations of neurosarcoidosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 34, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.F.; Yandora, K.; Valeri, A.; Chieffe, C.; Schramke, C. Aggressive therapy for neurosarcoidosis: Long-term follow-up of 48 treated patients. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawate, S.; Moses, H.; Sriram, S. Presentations and outcomes of neurosarcoidosis: A study of 54 cases. QJM 2009, 102, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajicek, J.P.; Scolding, N.J.; Foster, O.; Rovaris, M.; Evanson, J.; Moseley, I.F.; Scadding, J.W.; Thompson, E.J.; Chamoun, V.; Miller, D.H.; et al. Central nervous system sarcoidosis-diagnosis and management. QJM 1999, 92, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.; Wellik, K.E.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Wingerchuk, D.M. Cerebrospinal fluid angiotensin-converting enzyme for diagnosis of central nervous system sarcoidosis. Neurologist 2009, 15, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, B.J.; Royal, W.; Gelfand, J.M.; Clifford, D.B.; Tavee, J.; Pawate, S.; Berger, J.R.; Aksamit, A.J.; Krumholz, A.; Pardo, C.A.; et al. Definition and Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Neurosarcoidosis: From the Neurosarcoidosis Consortium Consensus Group. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, M.J.; Pawate, S.; Koth, L.L.; Cho, T.A.; Gelfand, J.M. Neurosarcoidosis: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affan, M.; Mahajan, A.; Rehman, T.; Kananeh, M.; Schultz, L.; Cerghet, M. The effect of race on clinical presentation and outcomes in neurosarcoidosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 417, 117073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzke. Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS). In A Compendium of Tests, Scales and Questionnaires; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Van Swieten, J.C.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Visser, M.C.; Schouten, H.; Van Gijn, J. Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 1988, 19, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, O.C.; Salazar-Camelo, A.; Jimenez, J.A.; Barreras, P.; Reyes, M.I.; Garcia, M.A.; Moller, D.R.; Chen, E.S.; Pardo, C.A. Clinical and MRI phenotypes of sarcoidosis-associated myelopathy. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, M.; Culver, D.A.; Judson, M.A.; Scott, T.F.; Tavee, J.; Nozaki, K. Spinal cord neurosarcoidosis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 347, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakushima, K.; Yabe, I.; Nakano, F.; Yoshida, K.; Tajima, Y.; Houzen, H.; Maruo, Y.; Sasaki, H. Clinical features of spinal cord sarcoidosis: Analysis of 17 neurosarcoidosis patients. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 2163–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakai, Y.; Matsuyama, Y.; Imagam, S. Spinal cord sarcoidosis accompanied with compressive cervical myelopathy. In Sarcoidosis Diagnosis and Management; Kalantar Motamedi, M.H., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, R.M.; Babatunde, V.D.; Schmitt, J.E.; Berger, J.R.; Mohan, S. Spinal cord sarcoidosis occuring at sites od spondylotic stenosis, mimicking spondylotic myelopathy: A case series and review of the literature. AJNR Am. Neuroradiol. 2023, 43, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridel, C.; Courvoisier, D.S.; Vuilleumier, N.; Lalive, P.H. Cerebrospinal fluid angiotensin-converting enzyme for diagnosis of neurosarcoidosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 285, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, B.; Chapelon-Abric, C.; Biard, L.; Saadoun, D.; Demeret, S.; Dormont, D.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Cacoub, P. association of prognostic factors and immunosuppressive treatment with long-term outcomes in neurosarcoidosis. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitoun, S.; Bouvry, D.; Borie, R.; Mahevas, M.; Sacre, K.; Haroche, J.; Psimaras, D.; Pottier, C.; Mathian, A.; Hie, M.; et al. Treatment of neurosarcoidosis: A comparative study of methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil. Neurology 2016, 87, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen Aubart, F.; Bouvry, D.; Galanaud, D.; Dehais, C.; Mathey, G.; Psimaras, D.; Haroche, J.; Pottier, C.; Hie, M.; Mathian, A.; et al. Long-term outcomes of refractory neurosarcoidosis treated with infliximab. J. Neurol. 2017, 265, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambon, P.; Sellimi, A.; Kozyreff, A.; Gheysens, O.; Pothen, L.; Yildiz, H.; van Pesch, V. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, treatment, and outcome of neurosarcoidosis: A mono-centric retrospective study and literature review. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 970168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


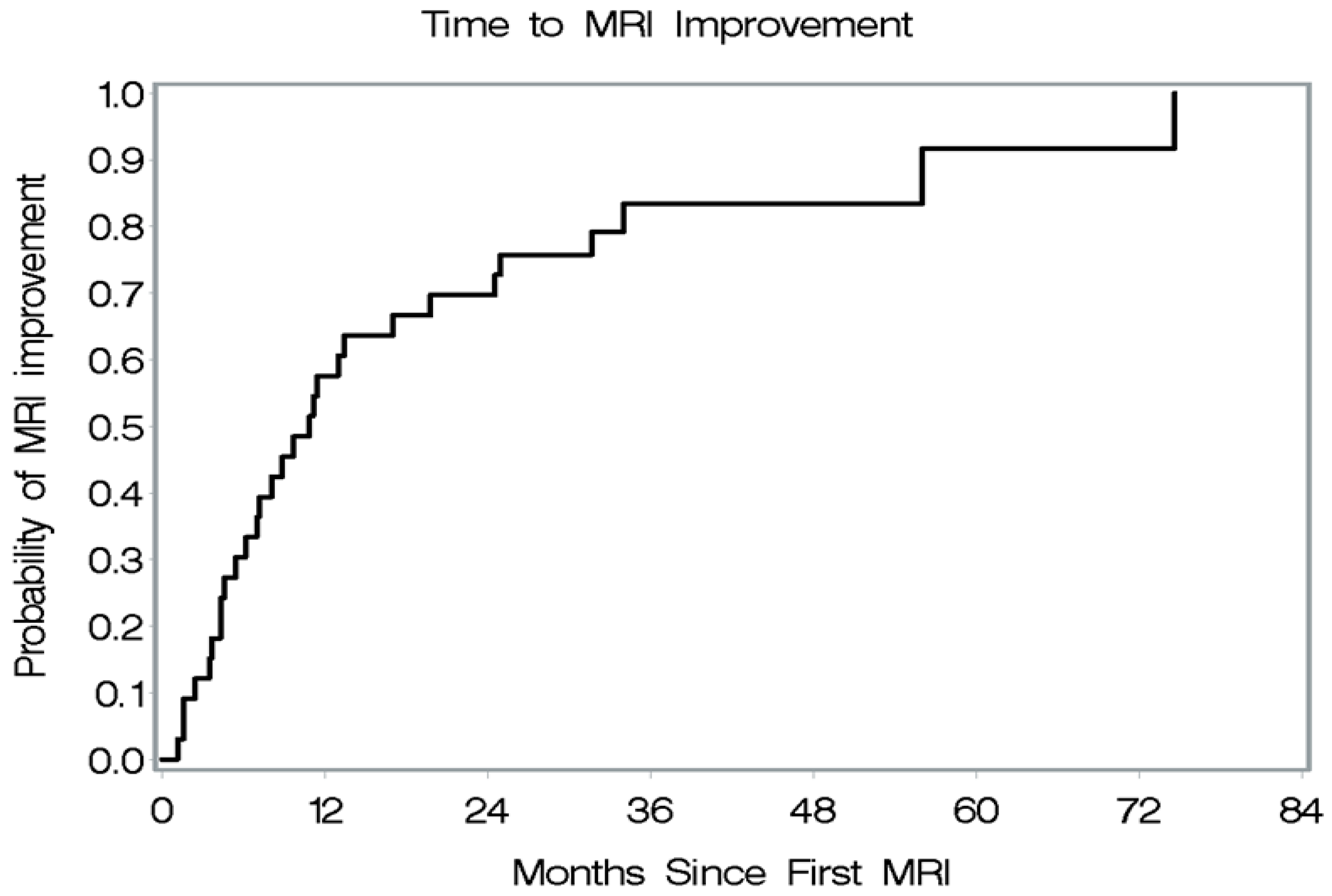
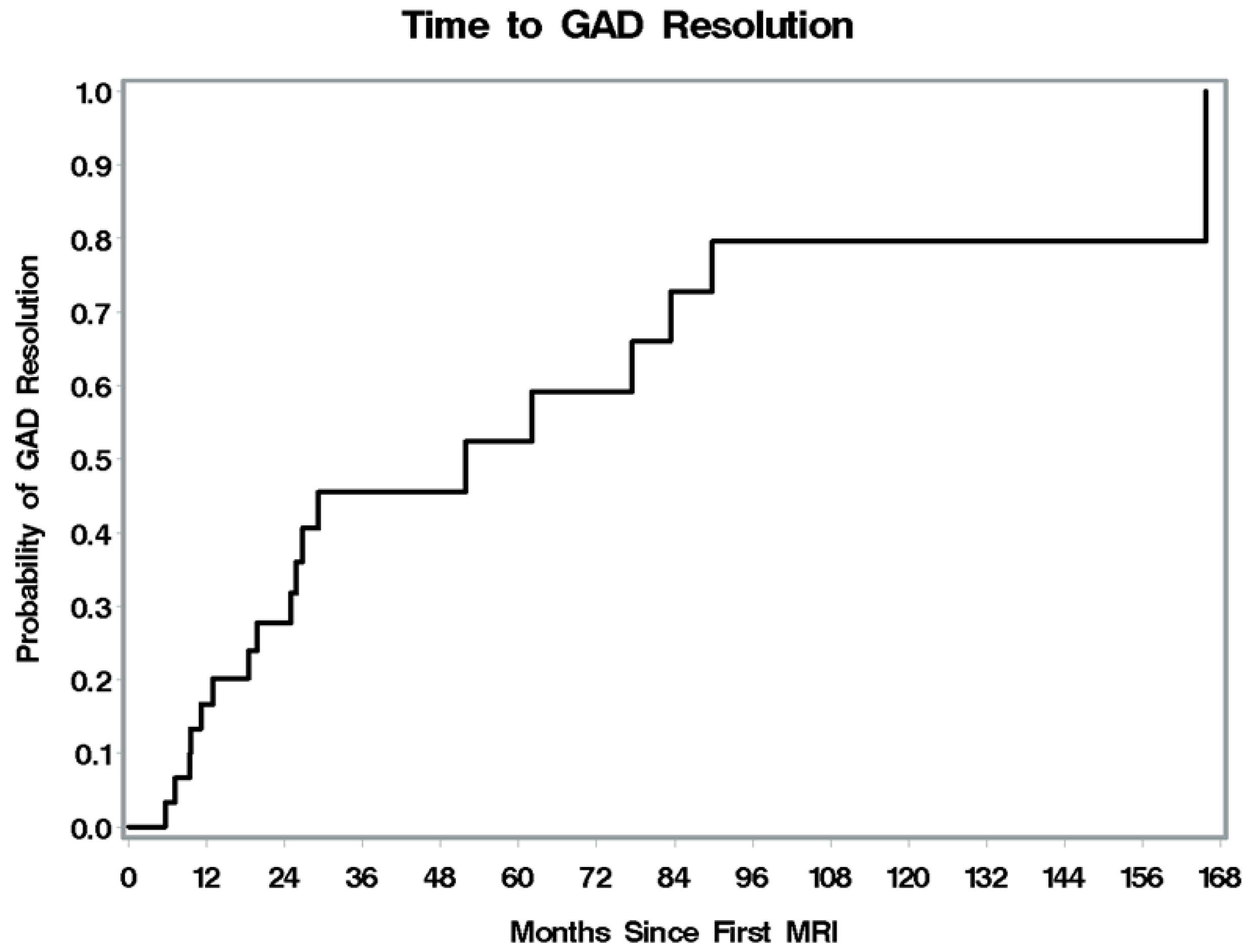
| Characteristic | Result n (%) n = (39) |
|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis, years, mean (SD) | 46.4 (10.2) |
| Sex | |
| Female | 16/39 (41) |
| Male | 23/39 (59) |
| Race | |
| Black | 27/39 (69) |
| White | 11/39 (28) |
| Other | 1/39 (3) |
| Duration of spinal cord neurosarcoidosis, years, mean (SD) | 9.8 (6.3) |
| Diagnosis | |
| Definite | 7/39 (18) |
| Probable | 28/39 (72) |
| Possible | 4/39 (10) |
| Symptoms at presentation | |
| Balance problems | 1/39 (3) |
| Headache | 1/39 (3) |
| Loss of consciousness | 1/39 (3) |
| Paresthesia/neuropathic pain | 20/39 (51) |
| Spasticity | 1/39 (3) |
| Weakness of extremities | 15/39 (38) |
| Degenerative disease of the spine | 32/38 (84) |
| Sarcoidosis before spinal cord involvement | |
| CNS involvement only | 7/39 (18) |
| Extra CNS involvement | 14/39 (36) |
| Other sarcoidosis involvement (before and after spinal cord diagnosis), n (%) | |
| Abdominal mass | 1/39 (3) |
| Bone | 2/39 (5) |
| Brain | 19/39 (49) |
| Cranial nerve | 8/39 (21) |
| Ear | 1/39 (3) |
| Joints | 2/39 (5) |
| Liver | 3/39 (8) |
| Lung | 24/39 (62) |
| Lymphadenopathy/lymph nodes | 10/39 (26) |
| Optic neuritis | 1/39 (3) |
| PNS | 2/39 (5) |
| Skin | 5/39 (13) |
| Uveitis | 2/39 (5) |
| Clinical Finding | n (%) (n = 39) |
|---|---|
| Laboratory tests | |
| 25-hydroxy vitamin D low | 19/26 (73) |
| 25-hydroxy vitamin D elevated | 4/15 (27) |
| C-Reactive Protein elevated | 13/16 (81) |
| Calcium elevated | 8/35 (23) |
| Serum ACE elevated | 17/35 (49) |
| Cerebrospinal fluid | |
| ACE elevated | 6/25 (24) |
| Glucose low | 6/31 (19) |
| IgG elevated | 20/28 (71) |
| IgG index elevated | 10/26 (38) |
| Oligoclonal bands | 6/27 (22) |
| Protein elevated | 23/34 (68) |
| WBC elevated | 25/34 (74) |
| Therapies Received, n (%) (n = 39) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic Reagent | Patients Received Treatment n (%) | Patients with Lesion Reduction Observed on MRI While on Treatment | Patients with GAD Resolution While on Treatment |
| Azathioprine | 12 (31) | 5 | 3 |
| Corticosteroids | 37 (95) | 22 | 11 |
| Hydroxychloroquine | 6 (15) | 1 | 1 |
| Infliximab | 5 (13) | 1 | 1 |
| Methotrexate | 19 (49) | 6 | 5 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | 7 (18) | 4 | 2 |
| Time Score Taken, Mean (SD) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presentation | Last Visit | Difference | p-Value | |
| Pyramidal function score (n = 33) | 2.48 (1.23) | 1.88 (1.34) | 0.61 (1.14) | 0.004 |
| Sensory function score (n = 30) | 1.63 (0.96) | 1.27 (0.94) | 0.36 (0.89) | 0.031 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Hader, R.; Nofar, J.; Mohamedelkhair, A.; Affan, M.; Schultz, L.R.; Cerghet, M. A Comprehensive Characterization of Patients with Spinal Cord Neurosarcoidosis: A Single Center Cross-Sectional Study of Clinical Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175069
Al-Hader R, Nofar J, Mohamedelkhair A, Affan M, Schultz LR, Cerghet M. A Comprehensive Characterization of Patients with Spinal Cord Neurosarcoidosis: A Single Center Cross-Sectional Study of Clinical Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(17):5069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175069
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Hader, Rami, Justin Nofar, Ahmed Mohamedelkhair, Muhammad Affan, Lonni R. Schultz, and Mirela Cerghet. 2024. "A Comprehensive Characterization of Patients with Spinal Cord Neurosarcoidosis: A Single Center Cross-Sectional Study of Clinical Outcomes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 17: 5069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175069
APA StyleAl-Hader, R., Nofar, J., Mohamedelkhair, A., Affan, M., Schultz, L. R., & Cerghet, M. (2024). A Comprehensive Characterization of Patients with Spinal Cord Neurosarcoidosis: A Single Center Cross-Sectional Study of Clinical Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(17), 5069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175069






