Prognostic Nomogram Predicting Survival and Propensity Score Matching with Demographics and Comparative Analysis of Prostate Small Cell and Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
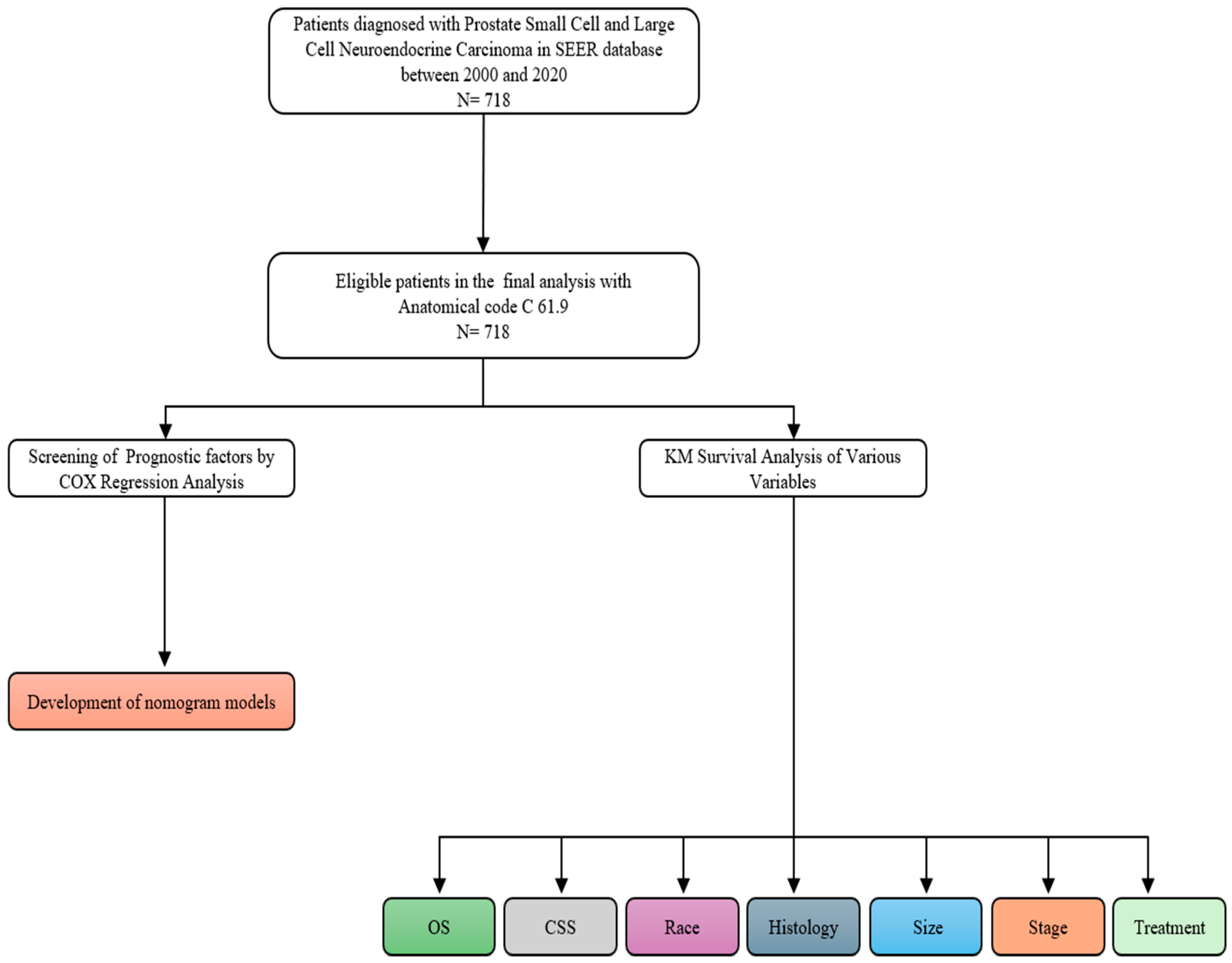
2. Methods
Nomogram Creation and Propensity Score Matching
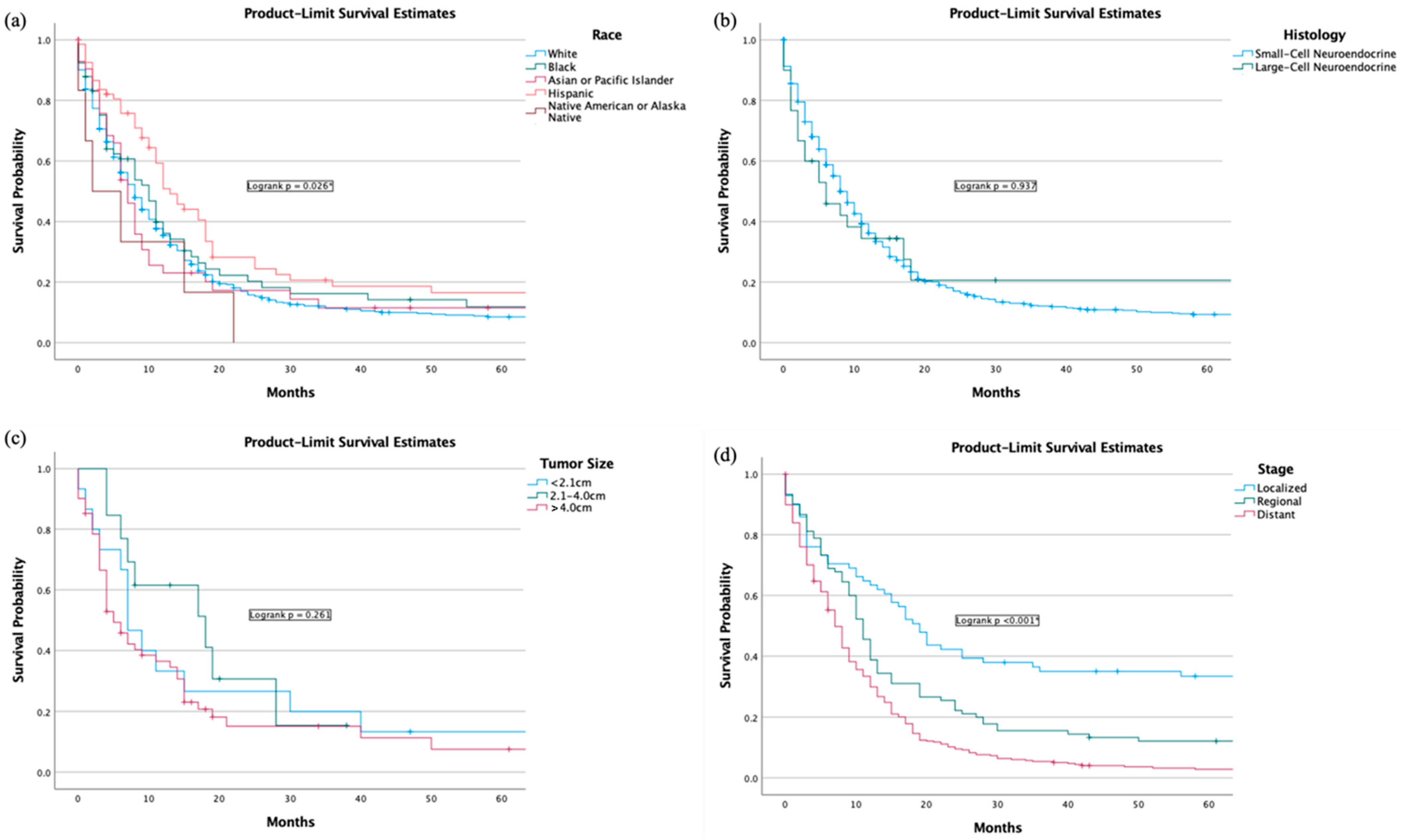
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
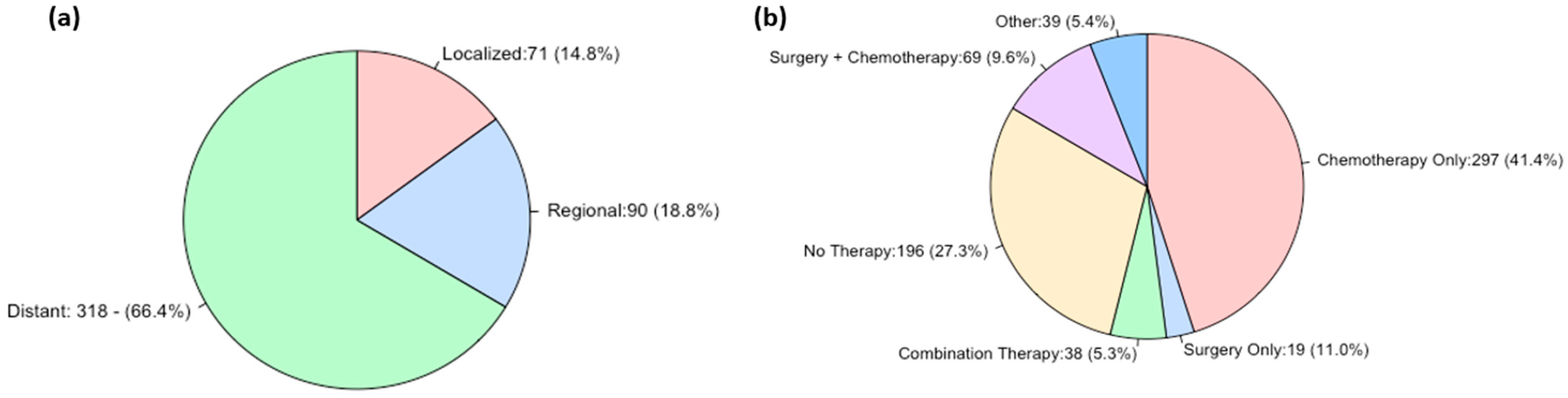
3.2. Tumor Characteristics
3.3. Treatment Modality
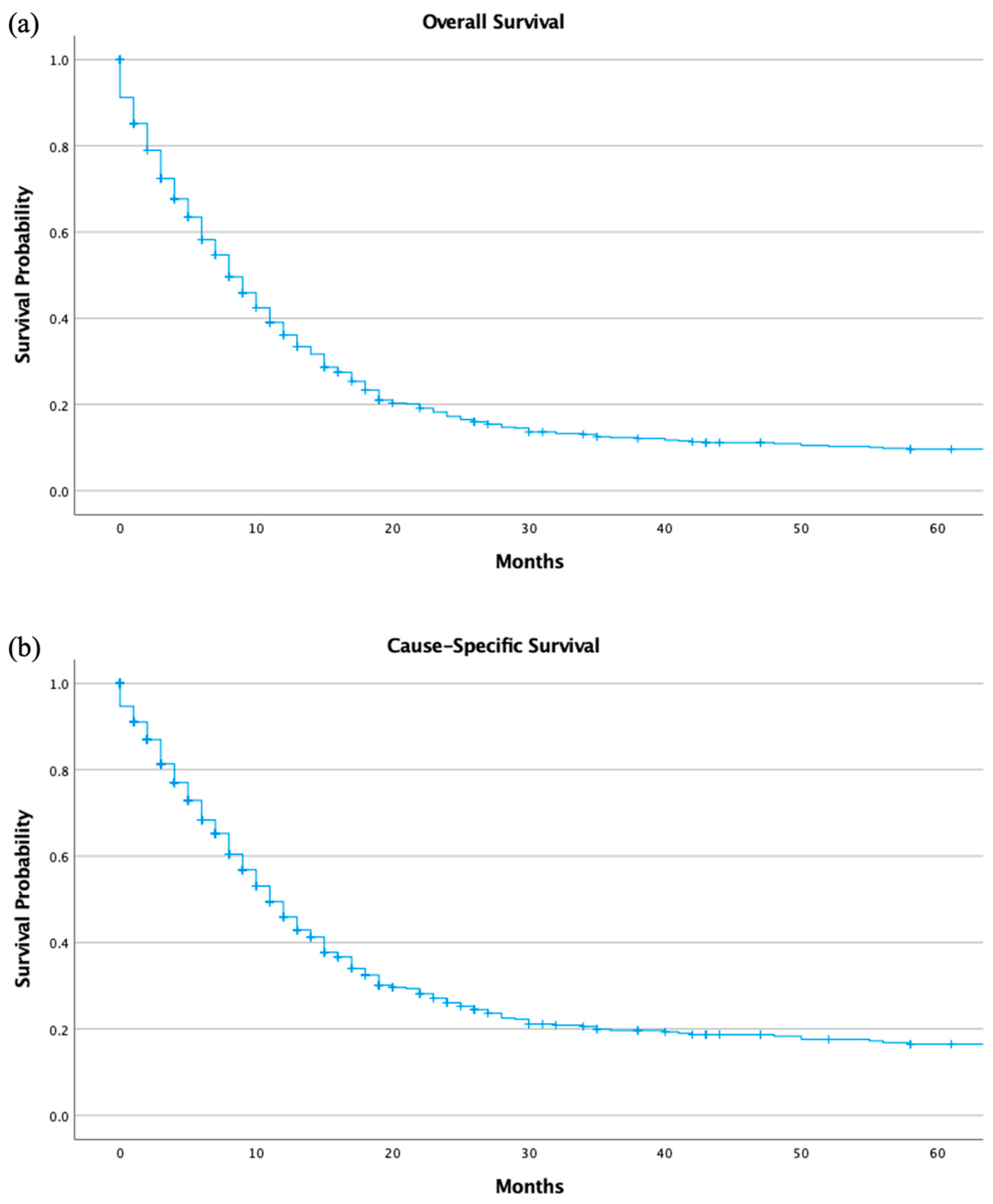
3.4. Outcomes and Survival Analysis of Overall and Cause-Specific Survival
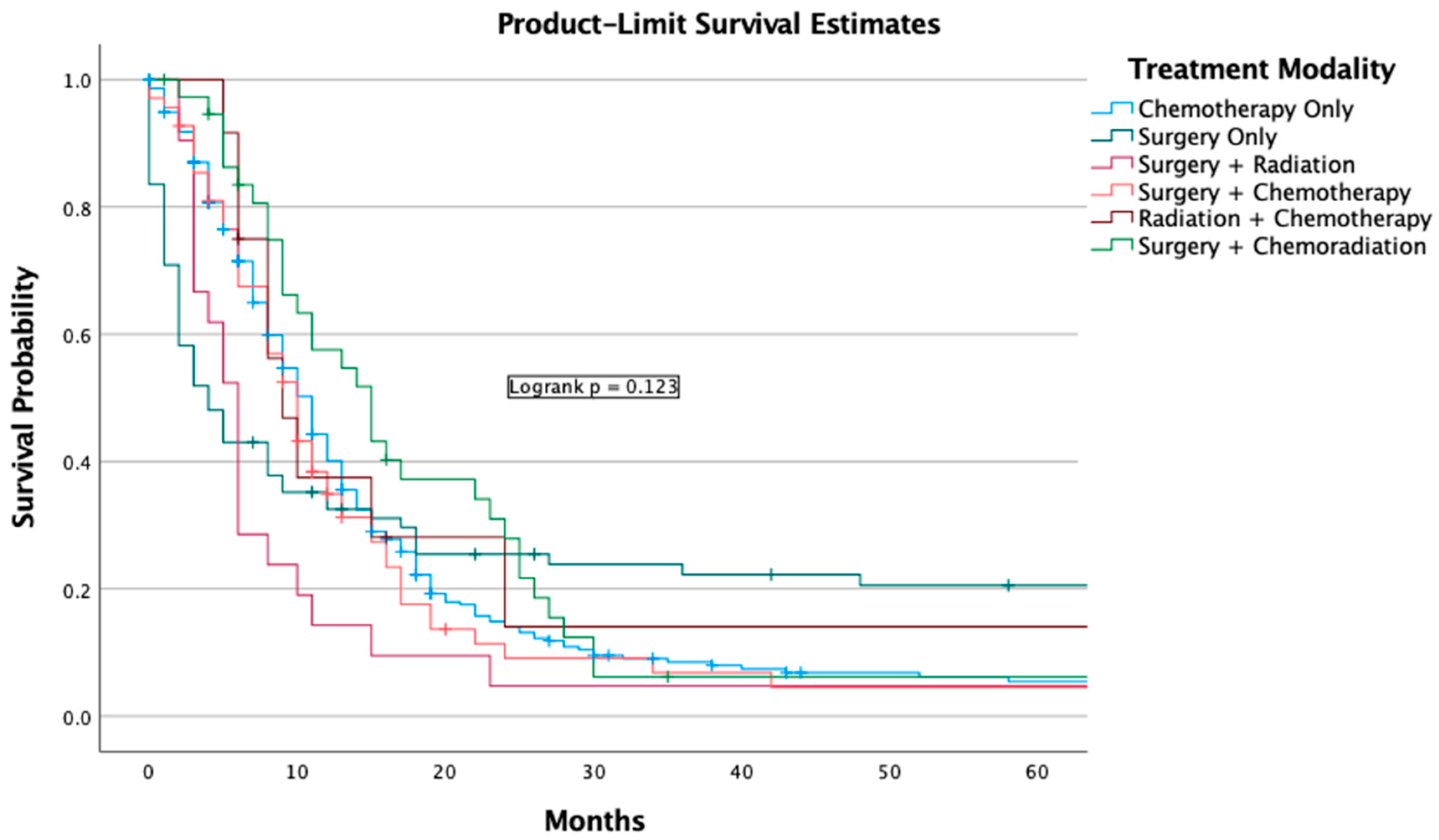
3.5. Outcomes and Overall Survival of Different Treatment Modalities
3.6. Outcomes and Overall Survival of Demographic Factors
3.7. Outcomes and Overall Survival of Tumor Characteristics
3.8. Propensity Score Matching for Large and Small Cell Carcinoma
3.9. Prognostic Nomogram Construction
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Disclosure
References
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giona, S. The Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. In Prostate Cancer; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fine, S. Neuroendocrine tumors of the prostate. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31 (Suppl. S1), 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasim, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J. Complexities of Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priemer, D.S.; Montironi, R.; Wang, L.; Williamson, S.R.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Cheng, L. Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Prostate: Emerging Insights from Molecular Data and Updates to the 2016 World Health Organization Classification. Endocr. Pathol. 2016, 27, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Beltran, H. Clinical and Biological Features of Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, G. Current trend of worsening prognosis of prostate small cell carcinoma: A population-based study. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6799–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffuto, E.; Pompe, R.; Zanaty, M.; Bondarenko, H.D.; Leyh-Bannurah, S.R.; Moschini, M.; Dell’Oglio, P.; Gandaglia, G.; Fossati, N.; Stabile, A.; et al. Contemporary Incidence and Cancer Control Outcomes of Primary Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer: A SEER Database Analysis. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2017, 15, e793–e800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liang, X.; Wu, D.; Chen, S.; Yang, B.; Mao, W.; Shen, D. Clinicopathological characteristics and survival outcomes in neuroendocrine prostate cancer: A population-based study. Medicine 2021, 100, e25237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillejos-Molina, R.A.; Gabilondo-Navarro, F.B. Prostate cancer. Salud Publica Mex. 2016, 58, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, J.W.; Schoots, I.G.; Carlsson, S.V.; Jenster, G.; Roobol, M.J. Prostate Specific Antigen as a Tumor Marker in Prostate Cancer: Biochemical and Clinical Aspects. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 867, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.H.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K.; Yong, E.L. Androgen receptor: Structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansen, I.; Stephan, C.; Jung, K.; Dietel, M.; Rieger, A.; Tolkach, Y.; Kristiansen, G. Sensitivity of HOXB13 as a Diagnostic Immunohistochemical Marker of Prostatic Origin in Prostate Cancer Metastases: Comparison to PSA, Prostein, Androgen Receptor, ERG, NKX3.1, PSAP, and PSMA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conteduca, V.; Oromendia, C.; Eng, K.W.; Bareja, R.; Sigouros, M.; Molina, A.; Faltas, B.M.; Sboner, A.; Mosquera, J.M.; Elemento, O.; et al. Clinical features of neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, W.; Karray, O.; Abi Abdallah, M.; Bleichner-Perez, S.; Kourda, J.; Cosma-Opris, M.; Assouad, S.; Riffaud, J.C.; Bart, S.; Coloby, P. Large-cell neuroendocrine tumor of the prostate: A case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Joseph, C.T.; Guo, M.; Zhang, M.; Sun, X.; Gong, Y. Utility of NKX3.1 Immunostaining in the Detection of Metastatic Prostatic Carcinoma on Fine-Needle Aspiration Smears. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 152, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, P.D.; Huber, A.R.; Agostini-Vulaj, D. Clinicopathologic features of metastatic small cell carcinoma of the prostate to the liver: A series of four cases. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkens, L.; Sailer, V.; Lessel, D.; Janzen, E.; Greimeier, S.; Kirfel, J.; Perner, S.; Pantel, K.; Werner, S.; von Amsberg, G. Aggressive variants of prostate cancer: Underlying mechanisms of neuroendocrine transdifferentiation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2022, 41, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Luo, J. Detection of androgen receptor (AR) and AR-V7 in small cell prostate carcinoma: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Asian J. Urol. 2019, 6, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, S.; Aiken, W.; Morrison, B.; Valentine, H.; Bryan, S.; Gachii, A.; Ragin, C. Disparities in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates: Solvable or not? Prostate 2020, 80, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.; Satturwar, S.; Van der Kwast, T. Young-age prostate cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 68, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.A.; O’Neil, M.E.; Richards, T.B.; Dowling, N.F.; Weir, H.K. Prostate Cancer Incidence and Survival, by Stage and Race/Ethnicity—United States, 2001–2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshmand, S.; Dorff, T.B.; Quek, M.L.; Cai, J.; Pike, M.C.; Nichols, P.W.; Pinski, J. Ethnic differences in neuroendocrine cell expression in normal human prostatic tissue. Urology 2005, 65, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Qi, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Hao, Z.; Meng, J.; Liang, C. Nomogram for predicting the overall survival of patients with early-onset prostate cancer: A population-based retrospective study. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 3260–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, A.; Wen, S.; Ma, Y.; Wei, L.; Liu, A. Clinicopathological analysis on small cell carcinoma of the prostate in chinese patients. J. Cancer 2014, 5, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzou, K.-Y.; Cheng, W.-H.; Lee, W.-H.; Ho, C.-H. Primary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate in a hormone naive patient: A case report from Taiwan. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14 (Suppl. S3), S785–S788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, G.D.; Epstein, J.I.; Piantadosi, S.; Walsh, P.C. Management of stage D1 adenocarcinoma of the prostate: The Johns Hopkins experience 1974 to 1987. J. Urol. 1990, 144, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, W., 3rd; Jackson, J.; Wei, J.T.; Dunn, R.; Baker, E.; Demonner, S.; Wood, D.P. Racial treatment trends in localized/regional prostate carcinoma: 1992–1999. Cancer 2005, 103, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turbat-Herrera, E.A.; Herrera, G.A.; Gore, I.; Lott, R.L.; Grizzle, W.E.; Bonnin, J.M. Neuroendocrine differentiation in prostatic carcinomas. A retrospective autopsy study. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1988, 112, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Beltran, H.; Rickman, D.S.; Park, K.; Chae, S.S.; Sboner, A.; MacDonald, T.Y.; Wang, Y.; Sheikh, K.L.; Terry, S.; Tagawa, S.T.; et al. Molecular characterization of neuroendocrine prostate cancer and identification of new drug targets. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable (n = 718) | Frequency (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | <70 | 305 (42.5%) |
| ≥70 | 413 (57.5%) | |
| Ethnicity | Unknown | 2 (0.3%) |
| White | 534 (74.4%) | |
| Black | 66 (9.2%) | |
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 42 (5.8%) | |
| Hispanic | 68 (9.5%) | |
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 6 (0.8%) | |
| Income (US$/year) | ≤$75,000 | 388 (54.0%) |
| ≥$75,000 | 330 (46.0%) | |
| Rural-Urban Continuum | Metropolitan | 618 (86.1%) |
| Rural | 100 (13.9%) | |
| Variable (n = 718) | Frequency (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Prostate Histological Type | SCNEC | 688 (95.8%) |
| LCNEC | 30 (4.2%) | |
| Tumor Size | When known (n = 89) (B = 0.88) | |
| <2.1 cm | 15 (16.9%) | |
| 2.1–4.0 cm | 13 (14.6%) | |
| >4.1 cm | 61 (68.5%) | |
| Local Lymph Node Status | When Known (n = 58) (B = 0.79) | |
| Positive | 30 (51.7%) | |
| Negative | 28 (48.3%) | |
| Metastasis | Metastasis Status (n = 292) (B = 0.95) | |
| Positive Metastases | 211 (27.7%) | |
| Negative Metastases | 81 (72.3%) | |
| # of Metastasis (n = 211) (B = 0.92) | ||
| Single Site | 169 (57.9%) | |
| Multiple Sites | 123 (42.1%) | |
| Site of Metastases (n = 211) (B = 0.92) | ||
| Bone | 138 (47.3%) | |
| Brain | 14 (4.8%) | |
| Liver | 101 (34.6%) | |
| Lung | 47 (16.1%) | |
| Distant Lymph Node | 75 (25.7%) | |
| Other | 29 (9.9%) | |
| Underwent Treatment Modality | Chemotherapy | 416 (57.9%) * |
| Radiation | 77 (10.7%) | |
| Surgery | 207 (28.8%) | |
| Variables | Bivariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (C.I. 95%) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (C.I. 95%) | p-Value | ||
| Age | 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | <0.001 * | 1.02 (0.98–1.07) | 0.365 | |
| Ethnicity # | |||||
| Non-Hispanic White | 869 (83.6%) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Non-Hispanic Black | 52 (5.0%) | 0.86 (0.65–1.15) | 0.306 | 1.10 (0.11–11.06) | 0.936 |
| Non-Hispanic Asian/PI | 42 (4.0%) | 1.07 (0.76–1.50) | 0.706 | 0.69 (0.05–9.02) | 0.776 |
| Hispanic (All Races) | 75 (7.2%) | 0.67 (0.50–0.88) | 0.005 + | 0.52 (0.14–1.97) | 0.335 |
| Stage | |||||
| Localized | 440 (42.3%) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Regional | 184 (17.7%) | 1.70 (1.21–2.39) | 0.002 * | 0.60 (0.45–7.83) | 0.693 |
| Distant | 154 (14.8%) | 2.63 (2.00–3.53) | <0.001 * | 0.39 (0.03–5.61) | 0.487 |
| Nodal Status | |||||
| Negative | 164 (15.8%) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Positive | 53 (5.1%) | 2.81 (1.49–5.30) | 0.001 * | 3.03 (0.79–11.52) | 0.105 |
| Chemotherapy Only | |||||
| No | 714 (86.7%) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Yes | 326 (31.3%) | 0.91 (0.77–1.07) | 0.244 | 0.7 (0.00–1.43) | 0.084 |
| Surgery Only | |||||
| No | 714 (86.7%) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Yes | 326 (31.3%) | 0.93 (0.72–1.20) | 0.575 | 0.02 (0.00–1.17) | 0.059 |
| Surgery + Chemotherapy | |||||
| No | 394 (62.1%) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Yes | 394 (37.9%) | 0.98 (0.75–1.29) | 0.881 | 0.02 (0.00–1.19) | 1.88 |
| Radiation + Chemotherapy | |||||
| No | 394 (62.1%) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Yes | 394 (37.9%) | 0.79 (0.41–1.52) | 0.473 | 0.03 (0.00–2.29) | 0.113 |
| Combination | |||||
| No | 841 (80.9%) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Yes | 199 (19.1%) | 0.75 (0.52–1.07) | 0.107 | 0.02 (0.00–1.92) | 0.093 |
| Systemic Therapy | |||||
| No | 332 (40.0%) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Yes | 497 (60.0%) | 0.78 (0.63–0.96) | 0.021 + | 1.21 (0.10–15.17) | 0.882 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, A.; Yasinzai, A.Q.K.; Lee, K.T.; Chaudhury, T.; Chaudhury, H.; Chandasir, A.; Wali, A.; Waheed, A.; Tareen, B.; Khan, M.; et al. Prognostic Nomogram Predicting Survival and Propensity Score Matching with Demographics and Comparative Analysis of Prostate Small Cell and Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164874
Ullah A, Yasinzai AQK, Lee KT, Chaudhury T, Chaudhury H, Chandasir A, Wali A, Waheed A, Tareen B, Khan M, et al. Prognostic Nomogram Predicting Survival and Propensity Score Matching with Demographics and Comparative Analysis of Prostate Small Cell and Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(16):4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164874
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Asad, Abdul Qahar Khan Yasinzai, Kue Tylor Lee, Tristin Chaudhury, Hannah Chaudhury, Abdullah Chandasir, Agha Wali, Abdul Waheed, Bisma Tareen, Marjan Khan, and et al. 2024. "Prognostic Nomogram Predicting Survival and Propensity Score Matching with Demographics and Comparative Analysis of Prostate Small Cell and Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 16: 4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164874
APA StyleUllah, A., Yasinzai, A. Q. K., Lee, K. T., Chaudhury, T., Chaudhury, H., Chandasir, A., Wali, A., Waheed, A., Tareen, B., Khan, M., Goyal, A., Iqbal, A., Sohail, A. H., Maan, S., Sheikh, A. B., Ghafouri, S. A. R., Khan, I., Del Rivero, J., & Karki, N. R. (2024). Prognostic Nomogram Predicting Survival and Propensity Score Matching with Demographics and Comparative Analysis of Prostate Small Cell and Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(16), 4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164874









