Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Postoperative Infection Rates of Blood Transfusion in Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Database
2.2. Study Sample, Definitions, and Outcomes
2.3. Confounding Factors (Potential Risk Factors)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overall Outcome
3.2. Risk Factors for Blood Transfusion
3.3. Prevalence of Postoperative Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.C.; Kim, Y.; Soh, J.W.; Shin, B.J. Risk factors of adjacent segment disease requiring surgery after lumbar spinal fusion: Comparison of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion. Spine 2014, 39, E339–E345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkweather, A. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion: An old concept with new techniques. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2006, 38, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumalla, K.; Yarbrough, C.K.; Pugely, A.J.; Koester, L.; Dorward, I.G. Spinal fusion for pediatric neuromuscular scoliosis: National trends, complications, and in-hospital outcomes. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 25, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, H.; Yoneoka, D. National trends in spinal fusion for pediatric patients with idiopathic scoliosis: Demographics, blood transfusions, and in-hospital outcomes. Spine 2014, 39, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnusamy, K.E.; Kim, T.J.; Khanuja, H.S. Perioperative blood transfusions in orthopaedic surgery. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2014, 96, 1836–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.G.; Patel, J.Y.; Asati, S.; Mewara, N. “Spine Surgery Checklist”: A Step towards Perfection through Protocols. Asian Spine J. 2021, 16, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seicean, A.; Seicean, S.; Alan, N.; Schiltz, N.K.; Rosenbaum, B.P.; Jones, P.K.; Kattan, M.W.; Neuhauser, D.; Weil, R.J. Preoperative anemia and perioperative outcomes in patients who undergo elective spine surgery. Spine 2013, 38, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.; Muller, M.M.; Lauscher, P.; Sireis, W.; Seifried, E.; Zacharowski, K. Perioperative Red Blood Cell Transfusion: Harmful or Beneficial to the Patient? Transfus. Med. Hemother 2012, 39, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, N. Allogeneic transfusion and infection: Economic and clinical implications. Semin. Hematol. 1997, 34, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Basques, B.A.; Anandasivam, N.S.; Webb, M.L.; Samuel, A.M.; Lukasiewicz, A.M.; Bohl, D.D.; Grauer, J.N. Risk Factors for Blood Transfusion With Primary Posterior Lumbar Fusion. Spine 2015, 40, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisahn, C.; Schmidt, C.; Schroeder, J.E.; Vialle, E.; Lieberman, I.H.; Dettori, J.R.; Schildhauer, T.A. Blood Transfusion and Postoperative Infection in Spine Surgery: A Systematic Review. Glob. Spine J. 2018, 8, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.J.; Fiani, B.; Jarrah, R.; Momin, A.A.; Rasouli, J. Surgical Site Infection Prophylaxis and Wound Management in Spine Surgery. Asian Spine J. 2021, 16, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engoren, M.; Habib, R.H.; Hadaway, J.; Zacharias, A.; Schwann, T.A.; Riordan, C.J.; Durham, S.J.; Shah, A. The effect on long-term survival of erythrocyte transfusion given for cardiac valve operations. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 88, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Rogers, C.A.; Rizvi, S.I.; Culliford, L.; Angelini, G.D. Increased mortality, postoperative morbidity, and cost after red blood cell transfusion in patients having cardiac surgery. Circulation 2007, 116, 2544–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahn, D.R.; Moch, H.; Hofmann, A.; Isbister, J.P. Patient blood management: The pragmatic solution for the problems with blood transfusions. Anesthesiology 2008, 109, 951–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greinacher, A.; Weitmann, K.; Schonborn, L.; Alpen, U.; Gloger, D.; Stangenberg, W.; Stupmann, K.; Greger, N.; Kiefel, V.; Hoffmann, W. A population-based longitudinal study on the implication of demographic changes on blood donation and transfusion demand. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.P.; Kleinman, S.H.; Nemo, G.J. Current and emerging infectious risks of blood transfusions. JAMA 2003, 289, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, G.A.; Horlocker, T.T.; Santrach, P.J.; Oliver, W.C., Jr.; Dekutoski, M.B.; Bryant, S. Predictors of blood transfusions in spinal instrumentation and fusion surgery. Spine 2000, 25, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenholtz, S.M.; Pronovost, P.J.; Mullany, D.; Garrett, E.; Ness, P.M.; Dorman, T.; Klag, M.J. Predictors of transfusion for spinal surgery in Maryland, 1997 to 2000. Transfusion 2002, 42, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Claramunt, R.; Ramirez, M.; Lopez-Soques, M.; Salo, G.; Molina-Ros, A.; Llado, A.; Caceres, E. Predictors of blood transfusion in patients undergoing elective surgery for degenerative conditions of the spine. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2012, 132, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosco, M.; Di Fiore, M. Factors predicting blood transfusion in different surgical procedures for degenerative spine disease. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Wass, C.T.; Long, T.R.; Faust, R.J.; Yaszemski, M.J.; Joyner, M.J. Changes in red blood cell transfusion practice during the past two decades: A retrospective analysis, with the Mayo database, of adult patients undergoing major spine surgery. Transfusion 2007, 47, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morcos, M.W.; Jiang, F.; McIntosh, G.; Johnson, M.; Christie, S.; Wai, E.; Ouellet, J.; Bailey, C.; Ahn, H.; Paquet, J.; et al. Predictors of Blood Transfusion in Posterior Lumbar Spinal Fusion: A Canadian Spine Outcome and Research Network Study. Spine 2018, 43, E35–E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, F.; Sethna, N. Blood loss in pediatric spine surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2004, 13 (Suppl. 1), S6–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovsky, M.A.; Whitaker, B.; Arnold, N.L. Severe outcomes of allogeneic and autologous blood donation: Frequency and characterization. Transfusion 1995, 35, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Park, S.Y.; Nam, J.J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Suh, S.W. Patient Blood Management During Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2019, 130, e566–e572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, G.; Hasegawa, T.; Yamato, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Oe, S.; Banno, T.; Mihara, Y.; Arima, H.; Ushirozako, H.; Yasuda, T.; et al. Predicting Perioperative Complications in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery Using a Simple Sliding Scale. Spine 2018, 43, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shander, A.; Hofmann, A.; Ozawa, S.; Theusinger, O.M.; Gombotz, H.; Spahn, D.R. Activity-based costs of blood transfusions in surgical patients at four hospitals. Transfusion 2010, 50, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Ha, J.W. Comparison of one-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion performed with a minimally invasive approach or a traditional open approach. Spine 2007, 32, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neradi, D.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Sodavarapu, P.; Goni, V.; Dhatt, S.S. Minimally Invasive Surgery versus Open Surgery for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Asian Spine J. 2021, 16, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, G.A.; Santrach, P.J.; Oliver, W.C., Jr.; Horlocker, T.T.; Shaughnessy, W.J.; Cabanela, M.E.; Bryant, S. The predictors of red cell transfusions in total hip arthroplasties. Transfusion 1996, 36, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, H.; Yoneoka, D. Predictors of allogeneic blood transfusion in spinal fusion for pediatric patients with idiopathic scoliosis in the United States, 2004–2009. Spine 2014, 39, 1860–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.S.; Burke, J.P.; Dolan, R.T.; Fitzpatrick, P.; O'Byrne, J.M.; McCormack, D.; Synnott, K.; Poynton, A.R. Risk analysis of blood transfusion requirements in emergency and elective spinal surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boachie-Adjei, O.; Bradford, D.S. Vertebral column resection and arthrodesis for complex spinal deformities. J. Spinal Disord. 1991, 4, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, S.I.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, S.M.; Chung, E.R.; Nah, K.H. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe spinal deformities. Spine 2002, 27, 2374–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchill, W.H.; McGurk, S.; Chapman, R.H.; Wallace, E.L.; Bertholf, M.F.; Goodnough, L.T.; Kao, K.J.; Olson, J.D.; Woodson, R.D.; Surgenor, D.M. The Collaborative Hospital Transfusion Study: Variations in use of autologous blood account for hospital differences in red cell use during primary hip and knee surgery. Transfusion 1998, 38, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.J.; Braun, Y.; Wood, K.B.; Cha, T.D.; Schwab, J.H. Allogeneic blood transfusions and postoperative infections after lumbar spine surgery. Spine J. 2015, 15, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoude, A.; Nooh, A.; Fortin, M.; Aldebeyan, S.; Jarzem, P.; Ouellet, J.; Weber, M.H. Incidence, Predictors, and Postoperative Complications of Blood Transfusion in Thoracic and Lumbar Fusion Surgery: An Analysis of 13,695 Patients from the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Database. Glob. Spine J. 2016, 6, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triulzi, D.J.; Vanek, K.; Ryan, D.H.; Blumberg, N. A clinical and immunologic study of blood transfusion and postoperative bacterial infection in spinal surgery. Transfusion 1992, 32, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzkopf, R.; Chung, C.; Park, J.J.; Walsh, M.; Spivak, J.M.; Steiger, D. Effects of perioperative blood product use on surgical site infection following thoracic and lumbar spinal surgery. Spine 2010, 35, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
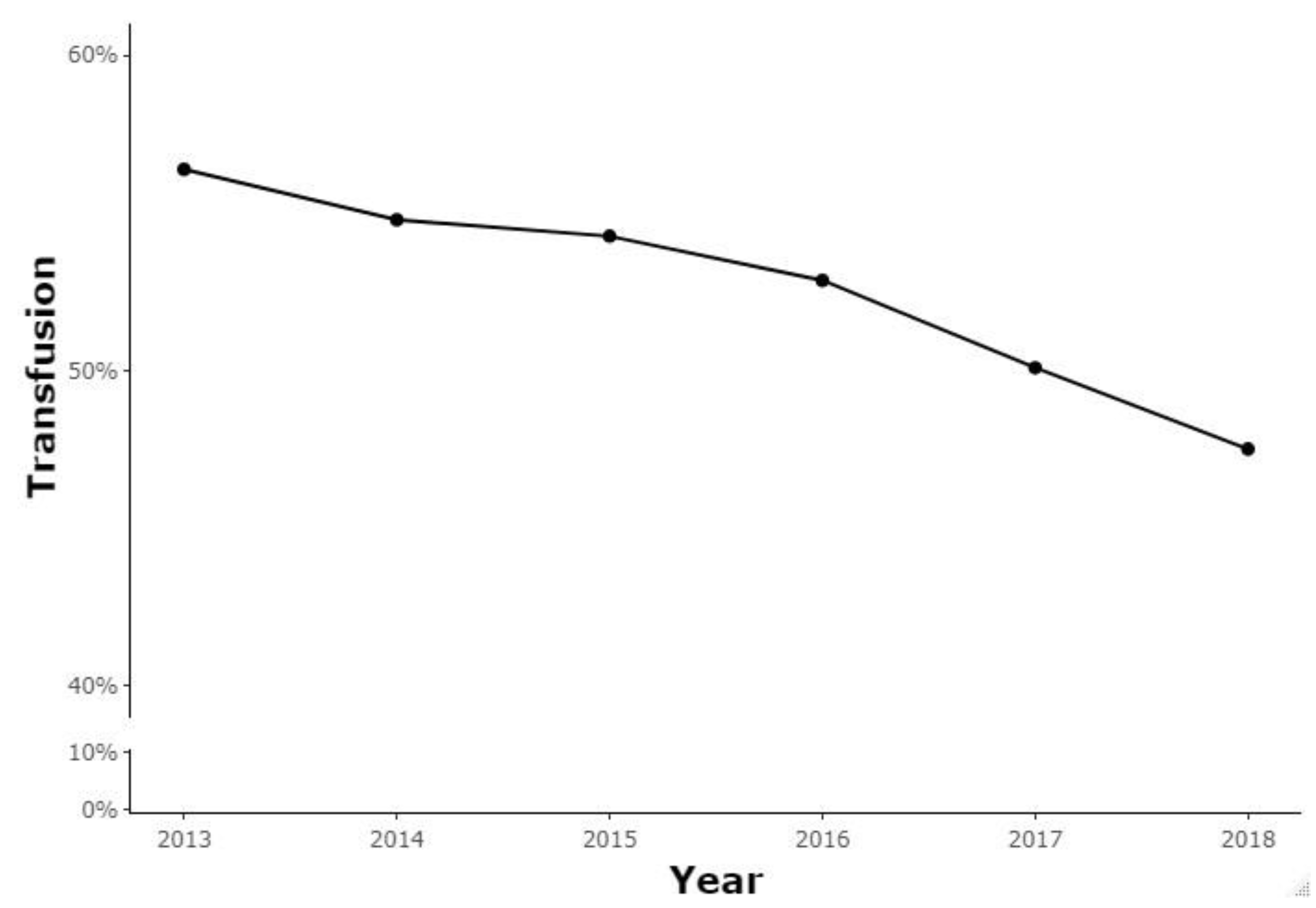
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 31,339 | 30,816 | 30,778 | 32,562 | 31,385 | 31,701 | 188,581 |
| Transfusion (%) | 17,669 (56.38%) | 16,881 (54.78%) | 16,701 (54.26%) | 17,213 (52.86%) | 15,721 (50.09%) | 15,062 (47.51%) | 99,247 |
| Surgical approach | |||||||
| Anterior | 293 | 326 | 287 | 324 | 281 | 275 | 1786 |
| Posterior | 16,333 | 15,468 | 15,294 | 15,615 | 14,210 | 13,547 | 90,467 |
| Anterior and posterior | 1043 | 1087 | 1120 | 1274 | 1230 | 1240 | 6994 |
| All Patients | Transfusion | p-Value * | Surgical Approach | p-Value * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transfusion | No Transfusion | Anterior | Posterior | Anterior and Posterior | ||||
| Total | 188,581 | 99,247 (52.63) | 89,334 (47.37) | 4677 (2.48) | 163,678 (86.79) | 20,226 (10.73) | ||
| Age, n (%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| <40 | 6208 (3.29) | 2341 (2.36) | 3867 (4.33) | 493 (10.54) | 5306 (3.24) | 409 (2.02) | ||
| 40–49 | 11,938 (6.33) | 4590 (4.62) | 7348 (8.23) | 685 (14.65) | 10,011 (6.12) | 1242 (6.14) | ||
| 50–59 | 41,049 (21.77) | 17,557 (17.69) | 23,492 (26.3) | 1067 (22.81) | 35,203 (21.51) | 4779 (23.63) | ||
| 60–69 | 64,993 (34.46) | 33,802 (34.06) | 31,191 (34.92) | 1232 (26.34) | 56,360 (34.43) | 7401 (36.59) | ||
| ≥70 | 64,393 (34.15) | 40,957 (41.27) | 23,436 (26.23) | 1200 (25.66) | 56,798 (34.70) | 6395 (31.62) | ||
| Gender, n (%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Male | 74,222 (39.36) | 32,788 (33.04) | 41,434 (46.38) | 1948 (41.65) | 65,753 (40.17) | 6521 (32.24) | ||
| Female | 114,359 (60.64) | 66,459 (66.96) | 47,900 (53.62) | 2729 (58.35) | 97,925 (59.83) | 13,705 (67.76) | ||
| Insurance, n (%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Health insurance | 174,142 (92.34) | 89,932 (90.61) | 84,210 (94.26) | 4423 (94.57) | 150,535 (91.97) | 19,184 (94.85) | ||
| Medical Aid | 14,439 (7.66) | 9315 (9.39) | 5124 (5.74) | 254 (5.43) | 13,143 (8.03) | 1042 (5.15) | ||
| Hospital size, n (%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Tertiary referral hospital | 48,249 (25.59) | 25,302 (25.49) | 22,947 (25.69) | 1075 (22.98) | 44,076 (26.93) | 3098 (15.32) | ||
| General hospital | 50,935 (27.01) | 28,595 (28.81) | 22,340 (25.01) | 651 (13.92) | 45,862 (28.02) | 4422 (21.86) | ||
| Hospital | 88,171 (46.75) | 44,358 (44.69) | 43,813 (49.04) | 2941 (62.88) | 72,533 (44.31) | 12,697 (62.78) | ||
| Private clinic | 1226 (0.65) | 992 (1.00) | 234 (0.26) | 10 (0.21) | 1207 (0.74) | 9 (0.04) | ||
| Hospital region, n (%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Metropolitan | 119,419 (63.33) | 60,360 (60.82) | 59,059 (66.11) | 2558 (54.69) | 99,889 (61.03) | 16,972 (83.91) | ||
| Urban | 68,820 (36.49) | 38,617 (38.91) | 30,203 (33.81) | 2118 (45.29) | 63,459 (38.77) | 3243 (16.03) | ||
| Rural | 342 (0.18) | 270 (0.27) | 72 (0.08) | 1 (0.02) | 330 (0.20) | 11 (0.05) | ||
| Osteotomy, n (%) | 432 (0.23) | 419 (0.42) | 13 (0.01) | <0.0001 | 164 (3.51) | 204 (0.12) | 64 (0.32) | <0.0001 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | ||||||||
| Myocardial infarction | 4310 (2.29) | 2580 (2.60) | 1730 (1.94) | <0.0001 | 91 (1.95) | 3818 (2.33) | 401 (1.98) | 0.0021 |
| Congestive heart failure | 19,006 (10.08) | 11,557 (11.64) | 7449 (8.34) | <0.0001 | 399 (8.53) | 16,638 (10.17) | 1969 (9.73) | 0.0003 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 68,943 (36.56) | 38,516 (38.81) | 30,427 (34.06) | <0.0001 | 1354 (28.95) | 59,864 (36.57) | 7725 (38.19) | <0.0001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 36,678 (19.45) | 21,391 (21.55) | 15,287 (17.11) | <0.0001 | 746 (15.95) | 32,105 (19.61) | 3827 (18.92) | <0.0001 |
| Dementia | 7321 (3.88) | 4466 (4.50) | 2855 (3.20) | <0.0001 | 146 (3.12) | 6395 (3.91) | 780 (3.86) | 0.0229 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 103,938 (55.12) | 55,845 (56.27) | 48,093 (53.84) | <0.0001 | 2425 (51.85) | 89,854 (54.90) | 11,659 (57.64) | <0.0001 |
| Rheumatologic disease | 32,304 (17.13) | 18,379 (18.52) | 13,925 (15.59) | <0.0001 | 719 (15.37) | 27,850 (17.02) | 3735 (18.47) | <0.0001 |
| Peptic ulcer disease | 104,009 (55.15) | 55,844 (56.27) | 48,165 (53.92) | <0.0001 | 2411 (51.55) | 89,795 (54.86) | 11,803 (58.36) | <0.0001 |
| Mild liver disease | 87,983 (46.66) | 46,747 (47.10) | 41,236 (46.16) | <0.0001 | 2104 (44.99) | 76,065 (46.47) | 9814 (48.52) | <0.0001 |
| Diabetes | 78,273 (41.51) | 43,946 (44.28) | 34,327 (38.43) | <0.0001 | 1635 (34.96) | 68,448 (41.82) | 8190 (40.49) | <0.0001 |
| Diabetes complications | 32,444 (17.20) | 19,092 (19.24) | 13,352 (14.95) | <0.0001 | 621 (13.28) | 28,691 (17.53) | 3132 (15.49) | <0.0001 |
| Hemiplegia or paraplegia | 4326 (2.29) | 2604 (2.62) | 1722 (1.93) | <0.0001 | 129 (2.76) | 3804 (2.32) | 393 (1.94) | 0.0003 |
| Renal disease | 7281 (3.86) | 4635 (4.67) | 2646 (2.96) | <0.0001 | 146 (3.12) | 6509 (3.98) | 626 (3.10) | <0.0001 |
| Any malignancy including leukemia and lymphoma | 14,540 (7.71) | 8149 (8.21) | 6391 (7.15) | <0.0001 | 291 (6.22) | 12,851 (7.85) | 1398 (6.91) | <0.0001 |
| Severe liver disease | 1529 (0.81) | 945 (0.95) | 584 (0.65) | <0.0001 | 38 (0.81) | 1341 (0.82) | 150 (0.74) | 0.509 |
| Metastatic solid tumor | 1683 (0.89) | 1154 (1.16) | 529 (0.59) | <0.0001 | 46 (0.98) | 1495 (0.91) | 142 (0.70) | 0.0085 |
| OR | CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical approach | |||
| Anterior | 0.511 | (0.48, 0.545) | <0.0001 |
| Posterior | ref | ||
| Anterior and posterior | 0.426 | (0.412, 0.44) | <0.0001 |
| Age | |||
| <40 | ref | ||
| 40–49 | 0.948 | (0.888, 1.012) | 0.1067 |
| 50–59 | 1.082 | (1.022, 1.145) | 0.0069 |
| 60–69 | 1.541 | (1.457, 1.63) | <0.0001 |
| ≥70 | 2.391 | (2.258, 2.531) | <0.0001 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | ref | ||
| Female | 1.772 | (1.737, 1.807) | <0.0001 |
| Insurance | |||
| Health insurance | ref | ||
| Medical Aid | 1.534 | (1.478, 1.592) | <0.0001 |
| Hospital size | |||
| Tertiary referral hospital | ref | ||
| General hospital | 1.115 | (1.086, 1.146) | <0.0001 |
| Hospital | 1.03 | (1.005, 1.055) | 0.0166 |
| Private clinic | 4.148 | (3.583, 4.801) | <0.0001 |
| Hospital region | |||
| Metropolitan | ref | ||
| Urban | 1.211 | (1.186, 1.236) | <0.0001 |
| Rural | 3.506 | (2.682, 4.582) | <0.0001 |
| Osteotomy | 37.019 | (21.227, 64.558) | <0.0001 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Myocardial infarction | 1.149 | (1.076, 1.226) | <0.0001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 1.119 | (1.082, 1.157) | <0.0001 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 1.001 | (0.98, 1.023) | 0.8932 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 1.032 | (1.005, 1.058) | 0.0173 |
| Dementia | 1.016 | (0.966, 1.069) | 0.538 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 0.93 | (0.911, 0.949) | <0.0001 |
| Rheumatologic disease | 1.08 | (1.053, 1.109) | <0.0001 |
| Peptic ulcer disease | 0.951 | (0.932, 0.971) | <0.0001 |
| Mild liver disease | 0.957 | (0.937, 0.977) | <0.0001 |
| Diabetes | 1.032 | (1.01, 1.056) | 0.0048 |
| Diabetes complications | 1.101 | (1.071, 1.133) | <0.0001 |
| Hemiplegia or paraplegia | 1.308 | (1.226, 1.396) | <0.0001 |
| Renal disease | 1.323 | (1.257, 1.393) | <0.0001 |
| Any malignancy including leukemia and lymphoma | 1.009 | (0.972, 1.048) | 0.6226 |
| Severe liver disease | 1.387 | (1.244, 1.546) | <0.0001 |
| Metastatic solid tumor | 2.166 | (1.937, 2.421) | <0.0001 |
| OR | CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transfusion | |||
| Transfusion | 1.876 | (1.815, 1.939) | <0.0001 |
| No transfusion | ref | ||
| Surgical approach | |||
| Anterior | 1.28 | (1.164, 1.408) | <0.0001 |
| Posterior | ref | ||
| Anterior and posterior | 1.118 | (1.062, 1.177) | <0.0001 |
| Age | |||
| <40 | ref | ||
| 40–49 | 0.879 | (0.795, 0.973) | 0.0126 |
| 50–59 | 0.843 | (0.772, 0.921) | 0.0001 |
| 60–69 | 0.819 | (0.751, 0.893) | <0.0001 |
| ≥70 | 0.876 | (0.802, 0.956) | 0.0029 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | ref | ||
| Female | 0.72 | (0.698, 0.743) | <0.0001 |
| Insurance | |||
| Health insurance | ref | ||
| Medical Aid | 1.05 | (0.994, 1.109) | 0.0835 |
| Hospital size | |||
| Tertiary referral hospital | ref | ||
| General hospital | 1.185 | (1.137, 1.236) | <0.0001 |
| Hospital | 0.875 | (0.841, 0.91) | <0.0001 |
| Private clinic | 2.235 | (1.943, 2.572) | <0.0001 |
| Hospital region | |||
| Metropolitan | ref | ||
| Urban | 0.98 | (0.948, 1.012) | 0.217 |
| Rural | 1.189 | (0.871, 1.622) | 0.2749 |
| Osteotomy | 1.256 | (0.969, 1.629) | 0.0846 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Myocardial infarction | 1.006 | (0.912, 1.109) | 0.9097 |
| Congestive heart failure | 1.062 | (1.009, 1.117) | 0.0207 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 1.001 | (0.968, 1.036) | 0.9361 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 0.977 | (0.938, 1.017) | 0.2583 |
| Dementia | 0.97 | (0.896, 1.05) | 0.4467 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 0.984 | (0.953, 1.017) | 0.3493 |
| Rheumatologic disease | 1.021 | (0.98, 1.064) | 0.3234 |
| Peptic ulcer disease | 0.987 | (0.955, 1.02) | 0.4245 |
| Mild liver disease | 1.099 | (1.063, 1.136) | <0.0001 |
| Diabetes | 1.075 | (1.037, 1.114) | <0.0001 |
| Diabetes complications | 1.077 | (1.031, 1.124) | 0.0008 |
| Hemiplegia or paraplegia | 1.247 | (1.139, 1.364) | <0.0001 |
| Renal disease | 1.002 | (0.929, 1.081) | 0.9501 |
| Any malignancy including leukemia and lymphoma | 0.929 | (0.875, 0.986) | 0.0157 |
| Severe liver disease | 0.907 | (0.768, 1.07) | 0.2462 |
| Metastatic solid tumor | 0.883 | (0.748, 1.043) | 0.1433 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.Y.; Kang, T.; Jeong, W.K.; Song, J.E. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Postoperative Infection Rates of Blood Transfusion in Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4867. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164867
Park SY, Kang T, Jeong WK, Song JE. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Postoperative Infection Rates of Blood Transfusion in Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(16):4867. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164867
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Si Young, Taewook Kang, Woong Kyo Jeong, and Ji Eun Song. 2024. "Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Postoperative Infection Rates of Blood Transfusion in Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Nationwide Population-Based Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 16: 4867. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164867
APA StylePark, S. Y., Kang, T., Jeong, W. K., & Song, J. E. (2024). Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Postoperative Infection Rates of Blood Transfusion in Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(16), 4867. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164867




