Impact of Baseline Anti-ABO Antibody Titer on Biliary Complications in ABO-Incompatible Living-Donor Liver Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Desensitization Protocols and Immunosuppressants
2.3. Surgical Procedure
2.4. Diagnosis and Definition of Biliary Complication
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Recipients and Donors
3.2. Operative Findings and Postoperative Outcomes
3.3. Biliary Complications
3.4. Risk Factors for Biliary Complication-Free Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, J.; Zeng, R.W.; Lim, W.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Yong, J.N.; Fu, C.E.; Tay, P.; Syn, N.; Ong, C.E.Y.; Ong, E.Y.H.; et al. The incidence of adverse outcome in donors after living donor liver transplantation: A meta-analysis of 60,829 donors. Liver Transpl. 2024, 30, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, G.P.; De Bruyere, M.; Squifflet, J.P.; Moriau, M.; Latinne, D.; Pirson, Y. Human ABO-incompatible living donor renal homografts. Neth. J. Med. 1985, 28, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, M.; Kawachi, S.; Obara, H.; Shinoda, M.; Hibi, T.; Kitagawa, Y.; Wakabayashi, G.; Shimazu, M.; Kitajima, M. Current progress in ABO-incompatible liver transplantation. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 40, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.K.; Hua, Y.F.; Bai, X.; Lou, J.; Que, R.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xie, Q.; Edoo, M.I.A.; et al. ABO-Incompatible Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation in the Era of Rituximab: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 8589402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.C.; Kim, S.H.; Park, S.J. Outcomes after liver transplantation in accordance with ABO compatibility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6516–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ye, S.; Xu, X.; Xie, H.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Recipient outcomes after ABO-incompatible liver transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, H.; Teramukai, S.; Haga, H.; Tanabe, M.; Fukushima, M.; Shimazu, M. Present status of ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation in Japan. Hepatology 2008, 47, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeva, I.; Karagyozov, P.I.; Tishkov, I. Post-liver transplant biliary complications: Current knowledge and therapeutic advances. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Rammohan, A.; Gunasekaran, V.; Hong, S.; Chih-Yi Chen, I.; Kim, J.; Hervera Marquez, K.A.; Hsu, S.C.; Kirimker, E.O.; Akamatsu, N.; et al. Biliary complications after adult-to-adult living-donor liver transplantation: An international multicenter study of 3633 cases. Am. J. Transplant. 2024, 24, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Kim, J.M. Immunologic strategies and outcomes in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.S.; Yu, Y.D.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, D.S. Left liver graft in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation with an optimal portal flow modulation strategy to overcome the small-for-size syndrome—A retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2022, 106, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadaun, S.S.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, S.; Saigal, S. Strategies for ABO Incompatible Liver Transplantation. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2023, 13, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, S.C.; Choi, J.; Kim, I.; Wu, G.; Toyoda, M.; Shin, B.; Vo, A. Interleukin-6, A Cytokine Critical to Mediation of Inflammation, Autoimmunity and Allograft Rejection: Therapeutic Implications of IL-6 Receptor Blockade. Transplantation 2017, 101, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.W.; Lee, S.G.; Hwang, S.; Kim, K.H.; Ahn, C.S.; Moon, D.B.; Ha, T.Y.; Jung, D.H.; Park, G.C.; Kim, W.J.; et al. ABO-Incompatible Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation Under the Desensitization Protocol With Rituximab. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Suh, K.S.; Shin, W.Y.; Cho, E.H.; Yi, N.J.; Lee, J.M.; Han, J.K.; Lee, K.U. Classification and prognosis of intrahepatic biliary stricture after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2007, 13, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.W.; Lee, S.G.; Hwang, S.; Kim, K.H.; Ahn, C.S.; Moon, D.B.; Ha, T.Y.; Jung, D.H.; Park, G.C.; Kang, S.H.; et al. Biliary stricture is the only concern in ABO-incompatible adult living donor liver transplantation in the rituximab era. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasullo, M.; Patel, M.; Khanna, L.; Shah, T. Post-transplant biliary complications: Advances in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2022, 9, e000778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, D.H.; Ikegami, T.; Balci, D.; Bhangui, P. Biliary reconstruction and complications in living donor liver transplantation. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 82, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaldas, F.M.; Korayem, I.M.; Russell, T.A.; Agopian, V.G.; Aziz, A.; DiNorcia, J.; Farmer, D.G.; Yersiz, H.; Hiatt, J.R.; Busuttil, R.W. Assessment of Anastomotic Biliary Complications in Adult Patients Undergoing High-Acuity Liver Transplant. JAMA Surg. 2019, 154, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; Huang, Z.Y.; Chen, X.P. Biliary complications after living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2011, 17, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.-Y.; Ho, C.-M.; Wu, Y.-M.; Ho, M.-C.; Hu, R.-H.; Lee, P.-H. Management of early hepatic artery occlusion after liver transplantation with failed rescue. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacha, S.; Barad, A.; Martin, J.; Levitsky, J. Association of hepatic artery stenosis and biliary strictures in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transplant. 2011, 17, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| ABOc Group (n = 116) | ABOi-L Group (n = 29) | ABOi-H Group (n = 14) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recipients | ||||
| Age & | 54 (33–73) | 55 (34–68) | 56 (47–61) | 0.862 |
| Sex (male) | 85 (73.3%) | 16 (55.2%) | 11 (78.6%) | 0.126 |
| BMI (kg/m2) * | 23.9 (17.0–40.4) | 24.12 (15.5–29.5) | 23.73 (20.3–33.2) | 0.730 |
| Baseline anti-ABO antibody titer ¶ | 32 (8–64) | 256 (128–1024) | <0.001 | |
| TPE (number) ¶ | 2 (0–4) | 4 (2–11) | <0.001 | |
| Diagnosis (multiple) | ||||
| HBV | 72 (62.1%) | 16 (55.2%) | 9 (64.3%) | 0.766 |
| HCV # | 14 (12.1%) | 3 (10.3%) | 2 (14.3%) | 0.922 |
| Alcohol-related cirrhosis | 31 (26.7%) | 8 (27.6%) | 3 (21.4%) | 0.902 |
| Autoimmune liver disease # | 2 (1.7%) | 4 (13.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.022 |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 71 (61.2%) | 19 (65.5%) | 10 (71.4%) | 0.718 |
| HTN | 21 (18.1%) | 9 (31.0%) | 3 (21.4%) | 0.307 |
| DM | 25 (21.6%) | 9 (31.0%) | 5 (35.7%) | 0.339 |
| MELD score at the time of transplantation * | 12 (6–40) | 11 (6–32) | 10 (7–21) | 0.288 |
| Child–Pugh Score * | 7 (5–14) | 7 (5–13) | 7 (5–12) | 0.632 |
| Platelet (×103) * | 70 (18–243) | 79 (17–548) | 63 (25–144) | 0.826 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) * | 1.49 (0.29–38.64) | 1.54 (0.27–10.49) | 1.29 (0.39–5.88) | 0.227 |
| PT (INR) * | 1.28 (0.92–3.89) | 1.23 (0.94–2.37) | 1.27 (0.96–1.85) | 0.794 |
| Donors | ||||
| Age * | 30 (16–54) | 30 (19–53) | 28 (20–55) | 0.494 |
| Sex (male) | 85 (73.3%) | 20 (69.0%) | 13 (92.9%) | 0.222 |
| BMI (kg/m2) * | 24.1 (16.7–37.2) | 23.8 (19.0–30.3) | 22.7 (19.6–34.6) | 0.775 |
| ICG-R15 (%) & | 9.0 (0.2–18.5) | 8.4 (0.3–12.5) | 7.4 (1.8–15.3) | 0.197 |
| Macrosteatosis (≥20%) # | 8 (7.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (7.1%) | 0.416 |
| Graft type # | ||||
| right | 93 (80.2%) | 17 (58.6%) | 11 (78.6%) | 0.101 |
| left | 18 (15.5%) | 11 (37.9%) | 3 (21.4%) | |
| right posterior | 5 (4.3%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Operation type of donor (laparoscopic) | 13 (11.2%) | 6 (20.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.131 |
| GRWR * | 0.98 (0.60–1.89) | 0.94 (0.70–1.94) | 1.05 (0.73–1.32) | 0.052 |
| ABOc Group (n = 116) | ABOi-L Group (n = 29) | ABOi-H Group (n = 14) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operative variables | ||||
| Operation time (min) * | 813 (545–1430) | 770 (590–1041) | 738 (540–1190) | 0.101 |
| Graft’s bile duct features | ||||
| Number # | 1.000 | |||
| 1 | 80 (69.0%) | 21 (72.4%) | 10 (71.4%) | |
| 2 | 33 (28.4%) | 8 (27.6%) | 4 (28.6%) | |
| 3 | 3 (2.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Ductoplasty | 24 (20.7%) | 7 (24.1%) | 3 (21.4%) | 0.921 |
| Maximum size (mm) * | 5 (1–13) | 4 (2–8) | 5 (2–10) | 0.990 |
| Minimum size (mm) * | 4 (1–13) | 4 (2–8) | 5 (2–10) | 0.909 |
| Multiple hepatic arterial anastomosis # | 6 (5.2%) | 2 (6.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.840 |
| Reconstruction type # | 0.803 | |||
| Duct to duct with internal stent | 101 (87.1%) | 27 (93.1%) | 14 (100%) | |
| Duct to duct without internal stent | 7 (6.0%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Hepaticojejunostomy | 8 (6.9%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Duct to duct with internal stent and hepaticojejunostomy | 2 (1.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Warm ischemic time (min) * | 5 (0–91) | 6 (0–15) | 6 (0–41) | 0.180 |
| Cold ischemic time (min) * | 153 (15–273) | 149 (36–228) | 142 (98–252) | 0.560 |
| Transfused RBC (unit) * | 8 (0–117) | 10 (0–36) | 7 (0–28) | 0.936 |
| Postoperative outcomes | ||||
| Complication (CD ≥ IIIa) | 58 (50.0%) | 14 (48.3%) | 9 (64.3%) | 0.571 |
| Hepatic artery complication # | 1 (0.9%) | 2 (6.9%) | 1 (7.1%) | 0.084 |
| Portal vein complication # | 5 (4.3%) | 2 (6.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.807 |
| Hepatic vein complication # | 12 (10.3%) | 2 (6.9%) | 2 (14.3%) | 0.675 |
| Rejection # | 7 (6.0%) | 1 (3.4%) | 1 (7.1%) | 1.000 |
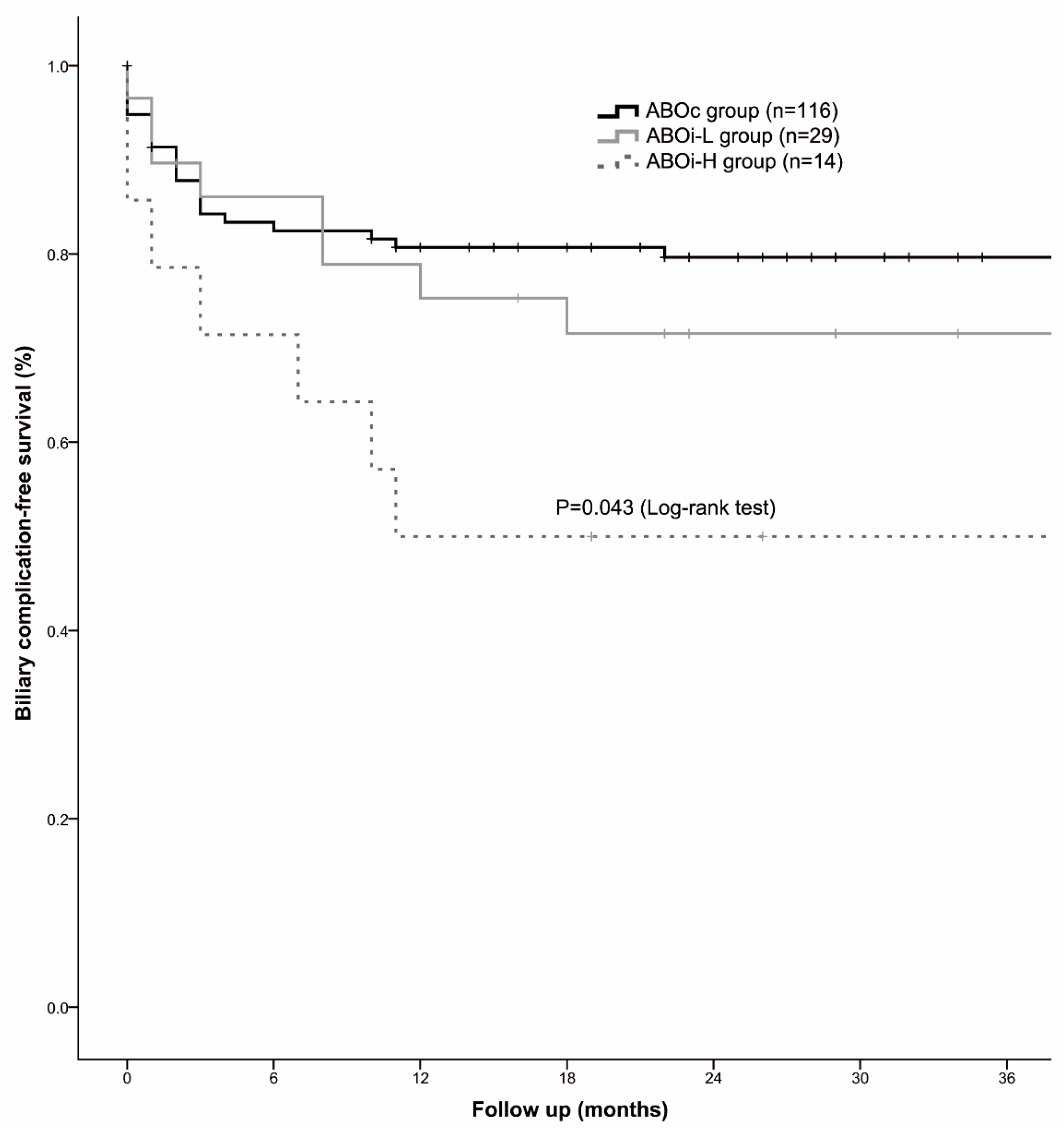
| Biliary complication | 24 (20.7%) | 8 (27.6%) | 7 (50.0%) | 0.041 |
| Hospital days ¶ | 20 (1–154) | 30 (9–336) | 25 (16–50) | 0.825 |
| 30-day mortality # | 1 (0.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.000 |
| 90-day mortality # | 3 (2.6%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.000 |
| Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Donors | ||||
| Age (≥40 years) | 0.892 (0.348–2.284) | 0.811 | ||
| Sex (male) | 0.952 (0.464–1.955) | 0.894 | ||
| BMI (≥30 kg/m2) | 1.092 (0.263–4.535) | 0.904 | ||
| Macrosteatosis (≥20%) | 0.454 (0.062–3.312) | 0.436 | ||
| Graft types | ||||
| Right graft | Ref. | — | ||
| Left graft | 0.304 (0.093–0.991) | 0.048 | 0.430 (1.121–1.537) | 0.194 |
| Right posterior graft | 2.291 (0.701–7.489) | 0.170 | ||
| GRWR (<0.8) | 1.566 (0.556–4.409) | 0.396 | ||
| Operation type of donor (laparoscopic) | 0.922 (0.328–2.595) | 0.878 | ||
| Graft bile duct opening (multiple) | 2.041 (1.083–3.847) | 0.027 | 1.092 (0.396–3.008) | 0.865 |
| Graft ductoplasty | 1.112 (0.528–2.343) | 0.780 | ||
| Minimum diameter of graft bile duct (<4 mm) | 0.047 (0.000–362.906) | 0.503 | ||
| Recipients | ||||
| Age (≥60 years) | 0.868 (0.399–1.888) | 0.721 | ||
| Sex (female) | 3.088 (1.208–7.897) | 0.019 | 3.307 (1.271–8.604) | 0.014 |
| BMI (<18.5 kg/m2) | 21.490 (0.021–22,167.806) | 0.386 | ||
| Baseline anti-ABO-Ab titer | ||||
| ABO-compatible | Ref. | — | ||
| ABO titer < 128 | 1.367 (0.613–3.049) | 0.445 | ||
| ABO titer ≥128 | 2.815 (1.211–6.542) | 0.016 | 3.943 (1.635–9.506) | 0.002 |
| HBV | 1.131 (0.587–2.178) | 0.712 | ||
| HCV | 1.471 (0.615–3.519) | 0.385 | ||
| Alcohol-related cirrhosis | 1.004 (0.489–2.064) | 0.991 | ||
| Autoimmune | 0.046 (0.000–42.068) | 0.377 | ||
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 1.854 (0.903–3.808) | 0.093 | 1.230 (0.563–2.688) | 0.604 |
| MELD score (≥20) | 0.687 (0.269–1.756) | 0.433 | ||
| Hepaticojejunostomy | 1.808 (0.858–3.810) | 0.119 | ||
| Warm ischemic time (≥20 min) | 1.710 (0.902–3.239) | 0.100 | 1.850 (0.946–3.616) | 0.072 |
| Intraoperative transfused RBC (≥20 units) | 1.587 (0.838–3.005) | 0.156 | ||
| Hepatic artery complication | 3.119 (1.214–8.018) | 0.018 | 3.505 (1.313–9.354) | 0.012 |
| Portal vein complication | 1.339 (0.322–5.565) | 0.688 | ||
| Hepatic vein complication | 0.537 (0.191–1.513) | 0.240 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.-H.; Jo, H.-S.; Yu, Y.-D.; Park, P.-J.; Han, H.-J.; Kim, S.-J.; Kamarulzaman, S.H.; Kim, D.-S. Impact of Baseline Anti-ABO Antibody Titer on Biliary Complications in ABO-Incompatible Living-Donor Liver Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164789
Yu S-H, Jo H-S, Yu Y-D, Park P-J, Han H-J, Kim S-J, Kamarulzaman SH, Kim D-S. Impact of Baseline Anti-ABO Antibody Titer on Biliary Complications in ABO-Incompatible Living-Donor Liver Transplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(16):4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164789
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Se-Hyeon, Hye-Sung Jo, Young-Dong Yu, Pyoung-Jae Park, Hyung-Joon Han, Sang-Jin Kim, Syahrul Hadi Kamarulzaman, and Dong-Sik Kim. 2024. "Impact of Baseline Anti-ABO Antibody Titer on Biliary Complications in ABO-Incompatible Living-Donor Liver Transplantation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 16: 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164789
APA StyleYu, S.-H., Jo, H.-S., Yu, Y.-D., Park, P.-J., Han, H.-J., Kim, S.-J., Kamarulzaman, S. H., & Kim, D.-S. (2024). Impact of Baseline Anti-ABO Antibody Titer on Biliary Complications in ABO-Incompatible Living-Donor Liver Transplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(16), 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164789






