Homograft Aortic Root Replacement for Destructive Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis: Results in the Current Era
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Operative Technique
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
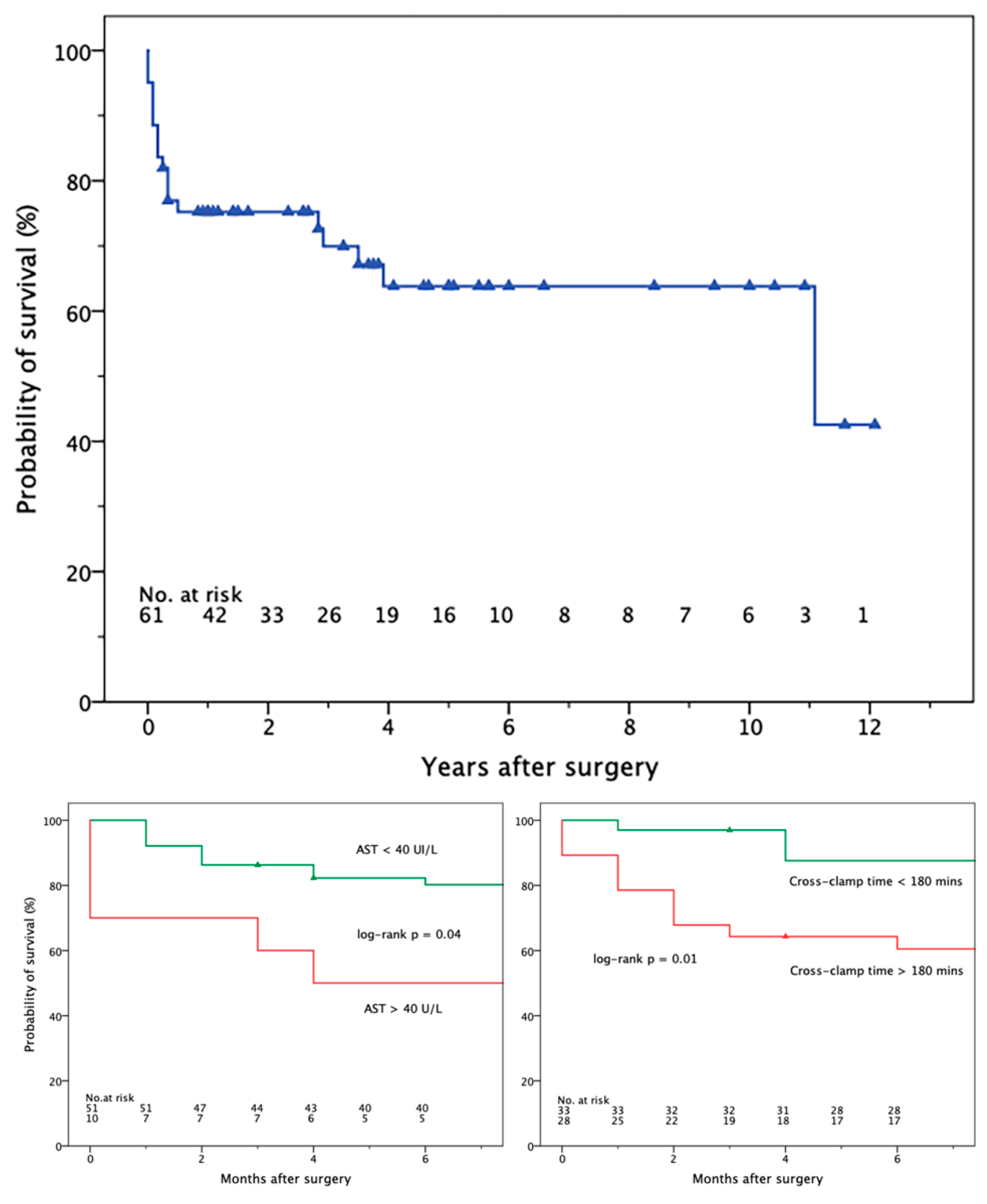
3.1. Early Mortality and Adverse Events
3.2. Late Mortality and Adverse Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Survival and Perioperative Complications
4.2. Reoperation
4.3. Biohumoral Outcome Predictors
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalil, H.; Soufi, S. Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567731/ (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Wang, A.; Athan, E. Contemporary clinical profile and outcome of prosthetic valve endocarditis. JAMA 2007, 36, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, N.; Jackson, V. Aortic valve replacement with mechanical vs. biological prostheses in patients aged 50–69 years. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantha-Narayanan, M.; Reddy, Y.N.V. Endocarditis risk with bioprosthetic and mechanical valves: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart 2020, 106, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, J.H.; Ihlemann, N. Long-term risk of infective endocarditis after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, G.; Lancellotti, P. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: The Task Force for the Management of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 3075–3128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delgado, V.; Ajmone Marsan, N.L.J.; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3948–4042, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 4780; Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.; Blanca-Lopez, N. Definition, clinical profile, microbiological spectrum, and prognostic factors of early-onset prosthetic valve endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahesh, B.; Angelini, G. Prosthetic valve endocarditis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 80, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, G.; Derumeaux, G. Value and limitations of the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999, 33, 2023–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, C.; Pocar, M. Minimally invasive surgery: Standard of care for mitral valve endocarditis. Medicina 2023, 59, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, C.; Pocar, M. Surgical treatment for isolated tricuspid valve disease: A less invasive approach for better outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeone, A.; Trojan, D. Cryopreserved aortic homografts for complex aortic valve or root endocarditis: A 28-year experience. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 62, ezac193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, J.C.; Durbak, E. Performance and durability of cryopreserved allograft aortic valve replacements. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2021, 111, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.B.; Ejiofor, J.I. Are homografts superior to conventional prosthetic valves in the setting of infective endocarditis involving the aortic valve? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 151, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, I.; Bianco, V. Aortic root replacement with cryopreserved homograft for infective endocarditis in the modern North American opioid epidemic. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 157, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotta, S.; Aljassim, O. Survival and quality of life after aortic root replacement with homografts in acute endocarditis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 90, 1862–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinda, J.M.; Mainardi, J.L. Cryopreserved aortic viable homograft for active aortic endocarditis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 79, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirklin, J.K.; Kirklin, J.W. Aortic valve endocarditis with aortic root abscess cavity: Surgical treatment with aortic valve homograft. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1988, 45, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuna, I.C.; Orszulak, T.A. Results of homograft aortic valve replacement for active endocarditis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1990, 49, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preventza, O.; Mohamed, A.S. Homograft use in reoperative aortic root and proximal aortic surgery for endocarditis: A 12-year experience in high-risk patients. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Musci, M.; Weng, Y. Homograft aortic root replacement in native or prosthetic active infective endocarditis: Twenty-year single-center experience. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 139, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagl, C.; Galla, J.D. Replacing the ascending aorta and aortic valve for acute prosthetic valve endocarditis: Is using prosthetic material contraindicated? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 74, S1781–S1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, S.; Mastrobuoni, S. Over 20 years experience with aortic homograft in aortic valve replacement during acute infective endocarditis. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 50, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamabe, T.; Pearsall, C.A. Incidence, cause, and outcome of reinterventions after aortic root replacement. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 113, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etz, C.D.; von Aspern, K. Long-term survival after composite mechanical aortic root replacement: A consecutive series of 448 cases. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 145 (Suppl. S3), S41–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogami, T.; Serna-Gallegos, D. The impact of reoperative surgery on aortic root replacement in the United States. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2024, 167, 1185–1193.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canabal, J.M.; Kramer, D.J. Management of sepsis in patients with liver failure. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2008, 14, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yin, Y. Advances in sepsis-associated liver dysfunction. Burns Trauma 2014, 2, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Acar, U.; Gökkaya, Z. Impact of cytokine adsorption treatment in liver failure. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 2420–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, V.; Streja, E. Association of aspartate aminotransferase with mortality in hemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobashi, H.; Toshimori, J. Sepsis-associated liver injury: Incidence, classification and the clinical significance. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 43, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No./Median | (%) [IQR] | Alive | Dead | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 53) | (n = 8) | ||||
| Age (yrs) | 68 | [54–76] | 68 | 71 | 0.15 |
| Female | 13 | (21) | 11 | 2 | 0.55 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 25.0 | [22.8–26.8] | 24.8 | 25.8 | 0.84 |
| Hypertension | 42 | (69) | 37 | 5 | 0.45 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 14 | (23) | 12 | 2 | 0.25 |
| Smoking | 34 | (56) | 31 | 3 | 0.23 |
| Drug addiction | 8 | (13) | 8 | 0 | 0.30 |
| EuroSCORE II | 13 | [9–25] | 12 | 25 | 0.07 |
| Urgent operation | 19 | (31) | 15 | 4 | 0.20 |
| Third operation or more | 12 | (20) | 10 | 2 | 0.50 |
| Mechanical aortic prosthesis | 18 | (30) | 17 | 1 | 0.25 |
| Prior aortic root replacement | 9 | (15) | 7 | 2 | 0.34 |
| Prior mitral operation | 9 | (15) | 7 | 2 | 0.34 |
| Coronary artery disease | 13 | (21) | 10 | 3 | 0.22 |
| Dialysis | 4 | (7) | 4 | 0 | 0.56 |
| Ejection fraction | 60 | [55–61] | 60 | 60 | 0.45 |
| Aortic regurgitation > 2+ | 29 | (48) | 25 | 4 | 0.59 |
| Mitral regurgitation > 2+ | 16 | (26) | 15 | 1 | 0.32 |
| Preoperative inotropes | 4 | (7) | 4 | 0 | 0.56 |
| Periannular abscess | 42 | (69) | 35 | 7 | 0.21 |
| Subaortic involvement | 30 | (49) | 26 | 4 | 0.63 |
| Ventricular septal defect | 6 | (10) | 4 | 2 | 0.17 |
| Embolization | 19 | (31) | 16 | 3 | 0.48 |
| Stroke | 11 | (18) | 10 | 1 | 0.56 |
| Intracerebral hemorrhage | 7 | (11) | 6 | 1 | 0.65 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.2 | [9.7–12] | 11.4 | 10.8 | 0.23 |
| White blood cell count (×109/L) | 9.0 | [6.6–11.1] | 9.0 | 9.8 | 0.81 |
| Platelet count (×109/L) | 196 | [122–226] | 202 | 168 | 0.22 |
| eGFR (mL/min) | 60 | [39–82] | 60 | 44 | 0.14 |
| AST | 22 | [15–32] | 21 | 43 | 0.02 |
| ALT | 19 | [12–28] | 19 | 30 | 0.45 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.1 | [0.9–1.3] | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.21 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 14 | [1–18] | 14 | 19 | 0.18 |
| Procalcitonin (mg/mL) | 0.5 | [0.26–0.80] | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.97 |
| MRSA or MRSE | 13 | (21) | 10 | 3 | 0.22 |
| Other Staphylococci | 11 | (18) | 9 | 2 | 0.37 |
| Streptococci | 14 | (23) | 12 | 2 | 0.29 |
| Enterococci | 3 | (5) | 3 | 0 | 0.43 |
| Gram-negative | 7 | (11) | 6 | 1 | 0.65 |
| Fungus | 4 | (7) | 4 | 0 | 0.56 |
| Culture-negative | 9 | (15) | 9 | 0 | 0.26 |
| Intravenous antibiotics (days) | 16 | [12–21] | 14 | 17 | 0.41 |
| Homograft diameter (mm) | 24 | [23–25] | 24 | 23 | 0.95 |
| Mitral valve surgery | 27 | (44) | 22 | 5 | 0.23 |
| Repair | 20 | (33) | 18 | 2 | 0.47 |
| Replacement | 7 | (11) | 4 | 3 | 0.04 |
| Tricuspid valve repair | 3 | (5) | 2 | 1 | 0.35 |
| Subaortic patch repair | 7 | (11) | 6 | 1 | 0.65 |
| Cardiopulmonary bypass (mins) | 230 | [195–290] | 225 | 293 | 0.03 |
| Aortic cross-clamp (mins) | 180 | [158–204] | 171 | 209 | 0.002 |
| Dobutamine > 5 mcg/kg/min | 41 | (67) | 38 | 3 | 0.07 |
| Epinephrine > 0.05 mcg/kg/min | 12 | (20) | 8 | 4 | 0.04 |
| Norepinephrine > 0.15 mcg/kg/min | 28 | (46) | 23 | 5 | 0.26 |
| ICU stay (days) | 3 | [2–7] | 3 | 11 | 0.02 |
| Mechanical ventilation (days) | 1 | [1–4] | 1 | 10 | 0.001 |
| Postoperative inotropes (days) | 4 | [3–5] | 4 | 8 | 0.06 |
| Stroke | 4 | (7) | 2 | 2 | 0.05 |
| AKI (new-onset dialysis) | 14 | (23) | 11 | 3 | 0.14 |
| Permanent pacemaker | 18 | (30) | 18 | 0 | 0.10 |
| Hospital stay (days) | 15 | [18–26] | 15 | 4 | 0.03 |
| Death | 8 | (13) | – | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pocar, M.; Barbero, C.; Marro, M.; Ferrante, L.; Costamagna, A.; Fazio, L.; La Torre, M.; Boffini, M.; Salizzoni, S.; Rinaldi, M. Homograft Aortic Root Replacement for Destructive Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis: Results in the Current Era. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154532
Pocar M, Barbero C, Marro M, Ferrante L, Costamagna A, Fazio L, La Torre M, Boffini M, Salizzoni S, Rinaldi M. Homograft Aortic Root Replacement for Destructive Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis: Results in the Current Era. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(15):4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154532
Chicago/Turabian StylePocar, Marco, Cristina Barbero, Matteo Marro, Luisa Ferrante, Andrea Costamagna, Luigina Fazio, Michele La Torre, Massimo Boffini, Stefano Salizzoni, and Mauro Rinaldi. 2024. "Homograft Aortic Root Replacement for Destructive Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis: Results in the Current Era" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 15: 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154532
APA StylePocar, M., Barbero, C., Marro, M., Ferrante, L., Costamagna, A., Fazio, L., La Torre, M., Boffini, M., Salizzoni, S., & Rinaldi, M. (2024). Homograft Aortic Root Replacement for Destructive Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis: Results in the Current Era. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(15), 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154532









