Comparative Analysis of Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis and Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Serum Samples
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Instrumentation and Conditions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
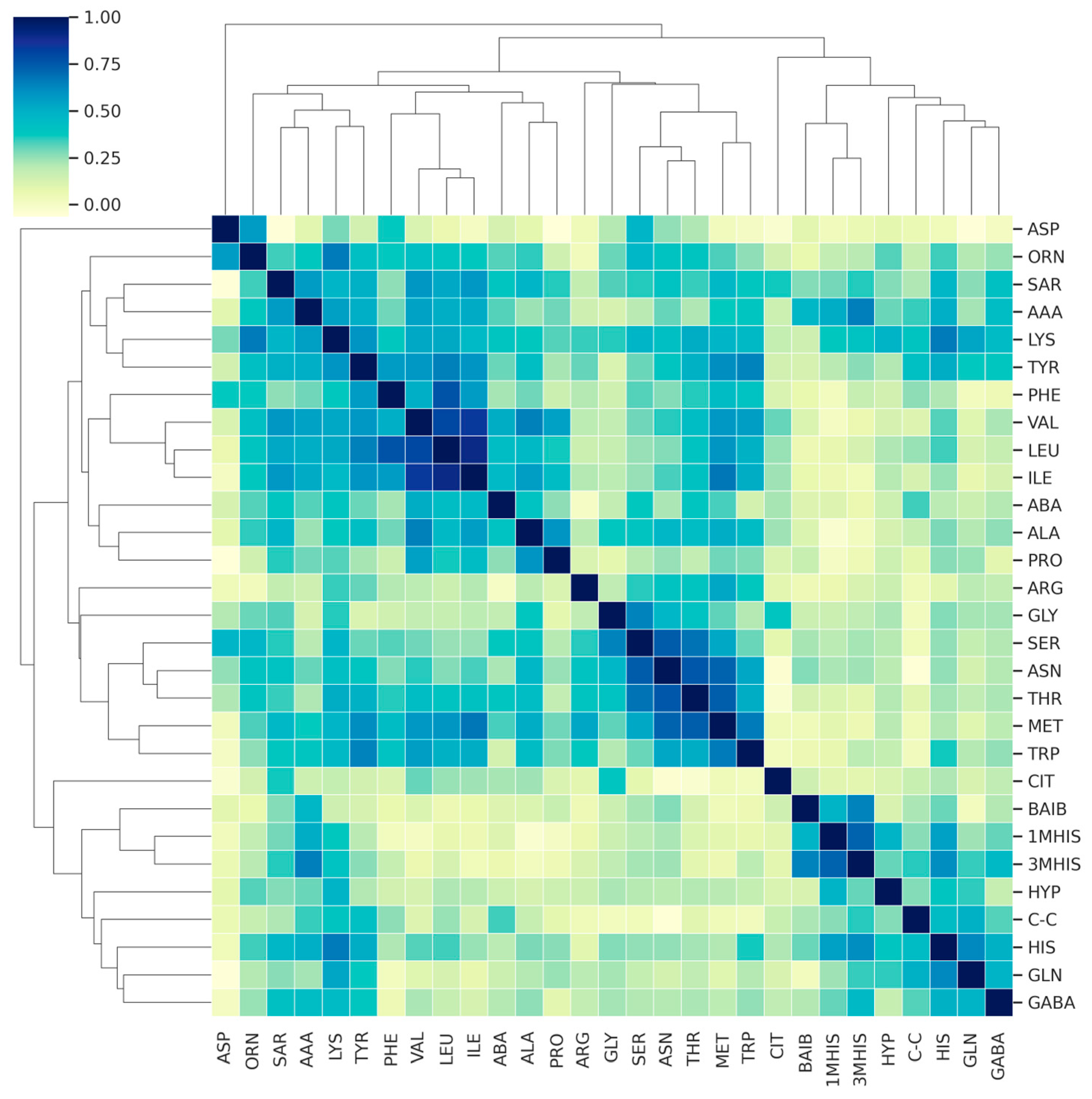
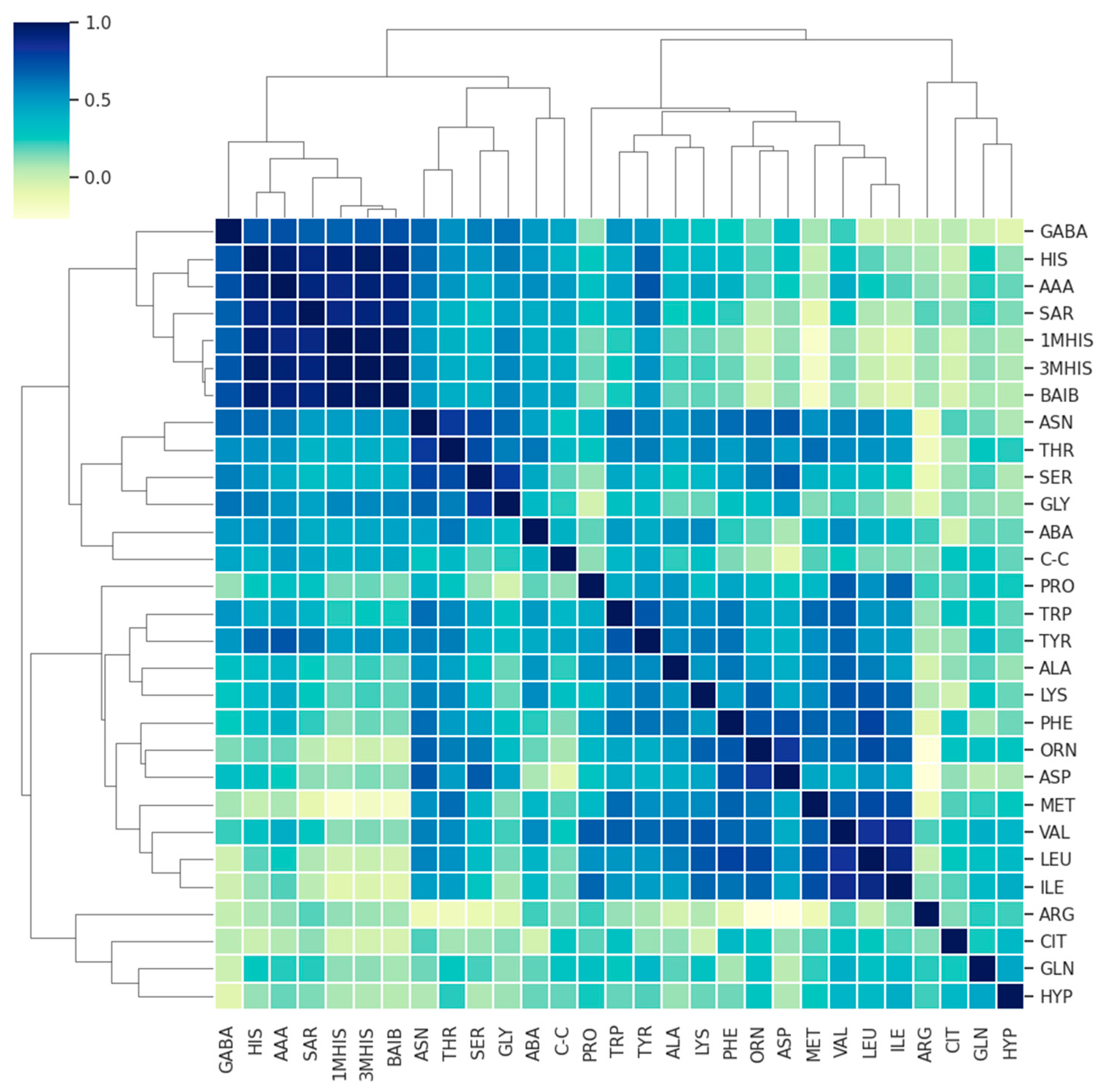
3. Results
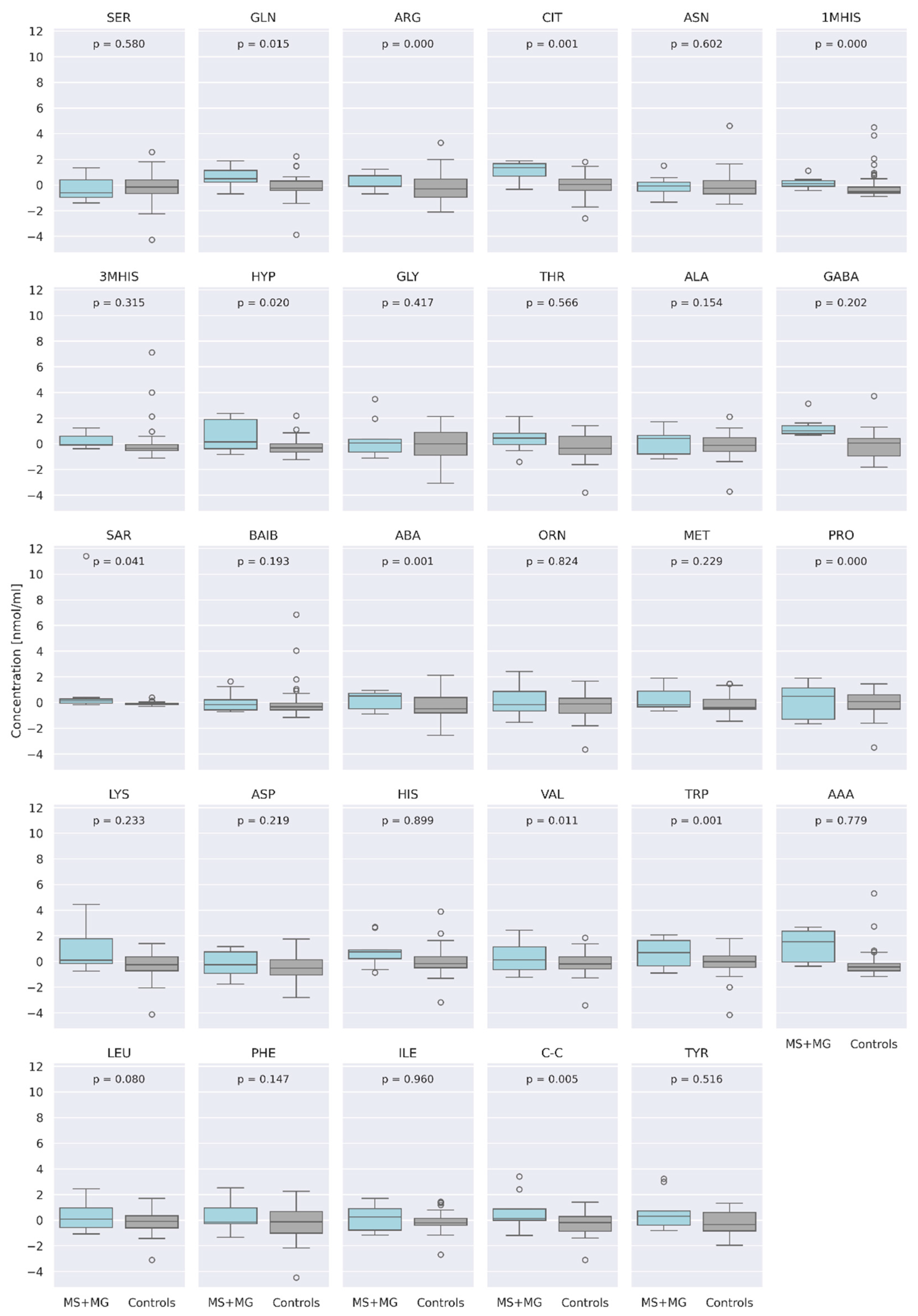
3.1. Comparison of AA Concentration between a Group of Patients (MS + MG Patients) and a Control Group of Healthy People
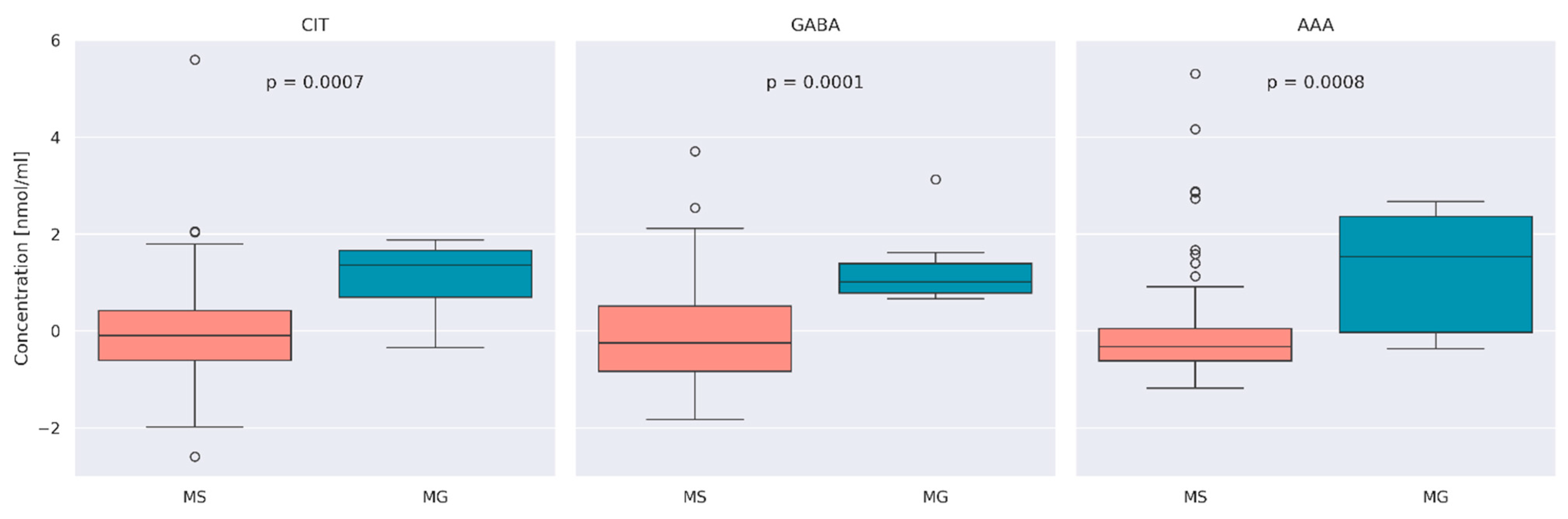
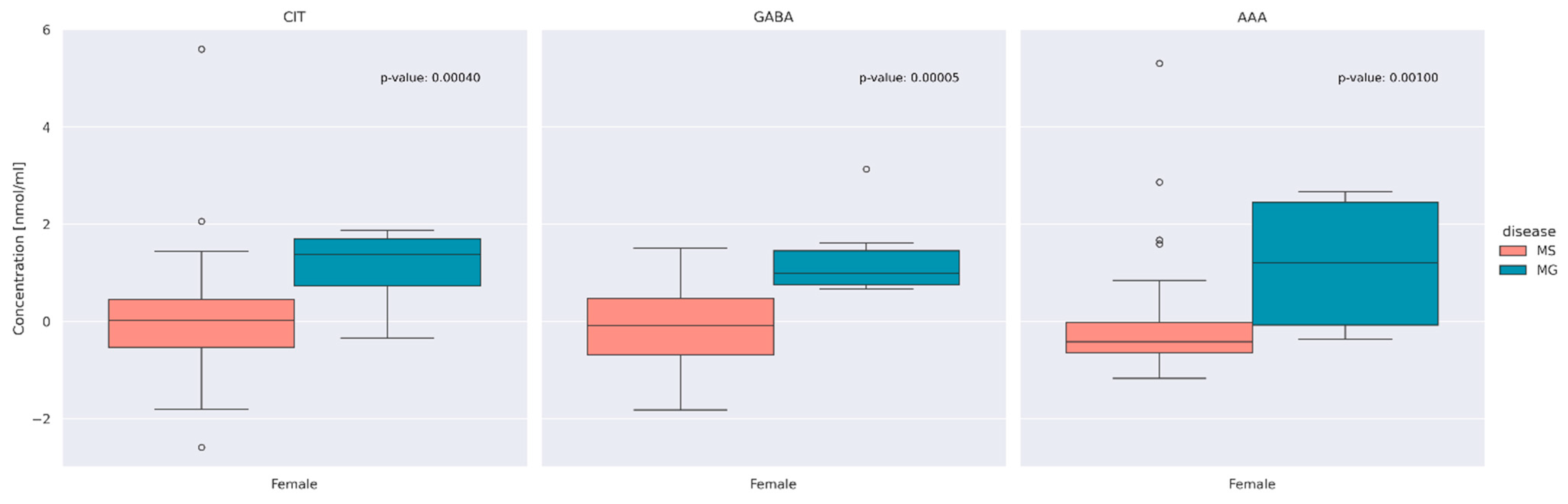
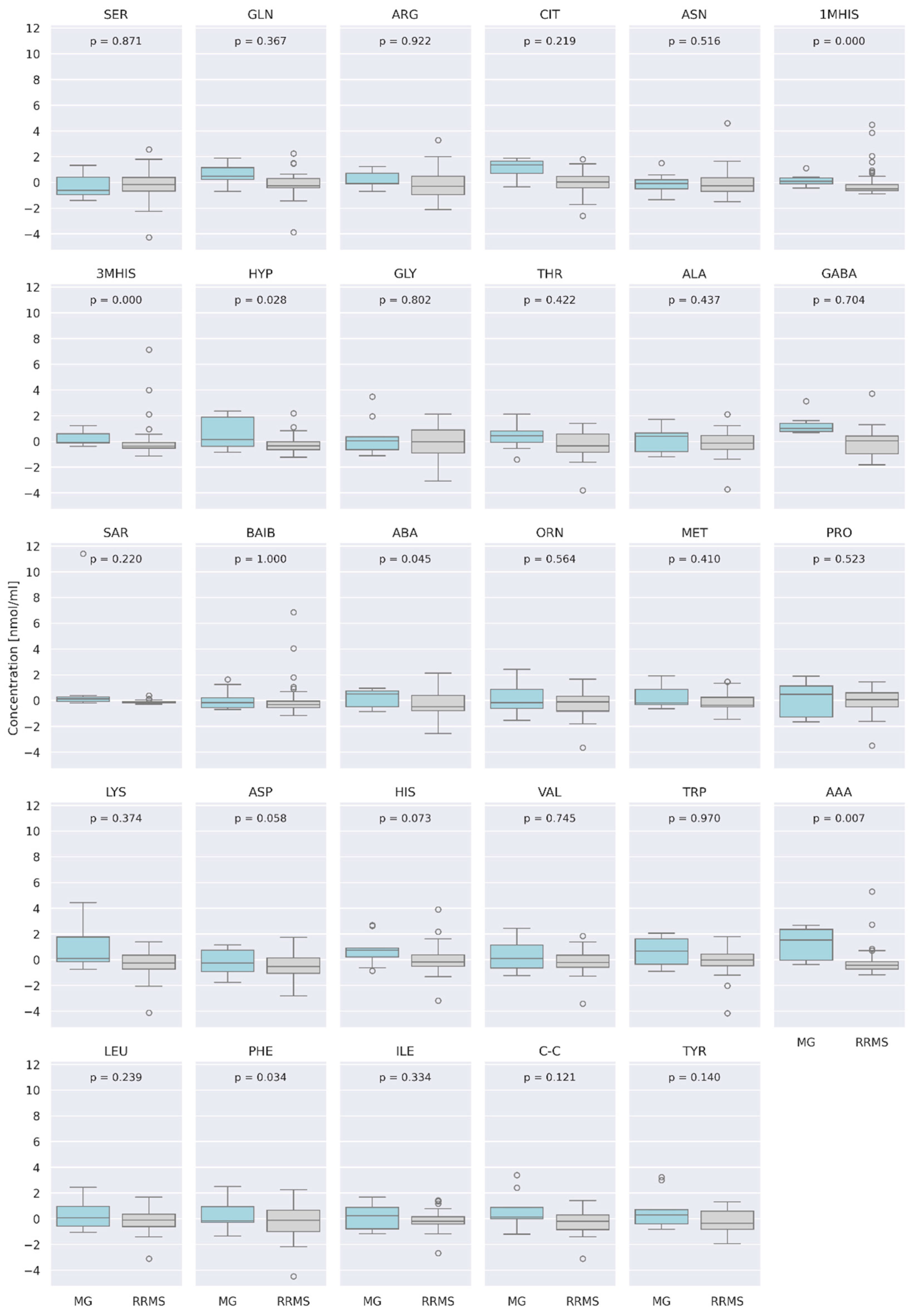
3.2. Comparison of AA Concentration between MS and MG Patients
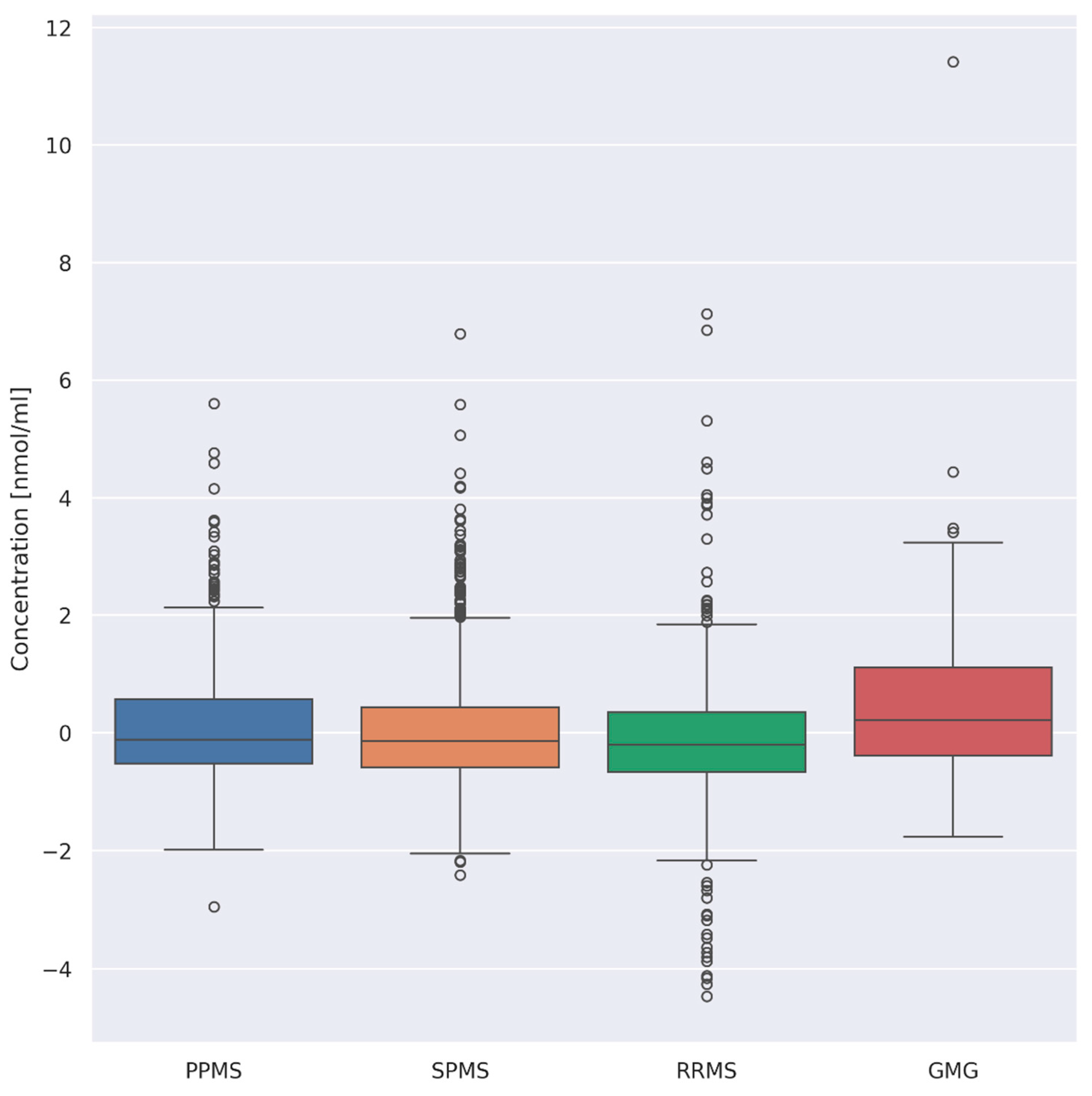
3.3. Evaluation of Differences between Overall AA Concentrations according to the Type of Disease
- (i)
- PPMS (n = 26) and RRMS (n = 41) (p = 0.008)
- (ii)
- PPMS (n = 26) and GMG (n = 25) (p = 0.03)
- (iii)
- RRMS (n = 41) and GMG (n = 25) (p = 0.00001)
- (iv)
- SPMS (n = 55) and GMG (n = 25) (p = 0.0008)
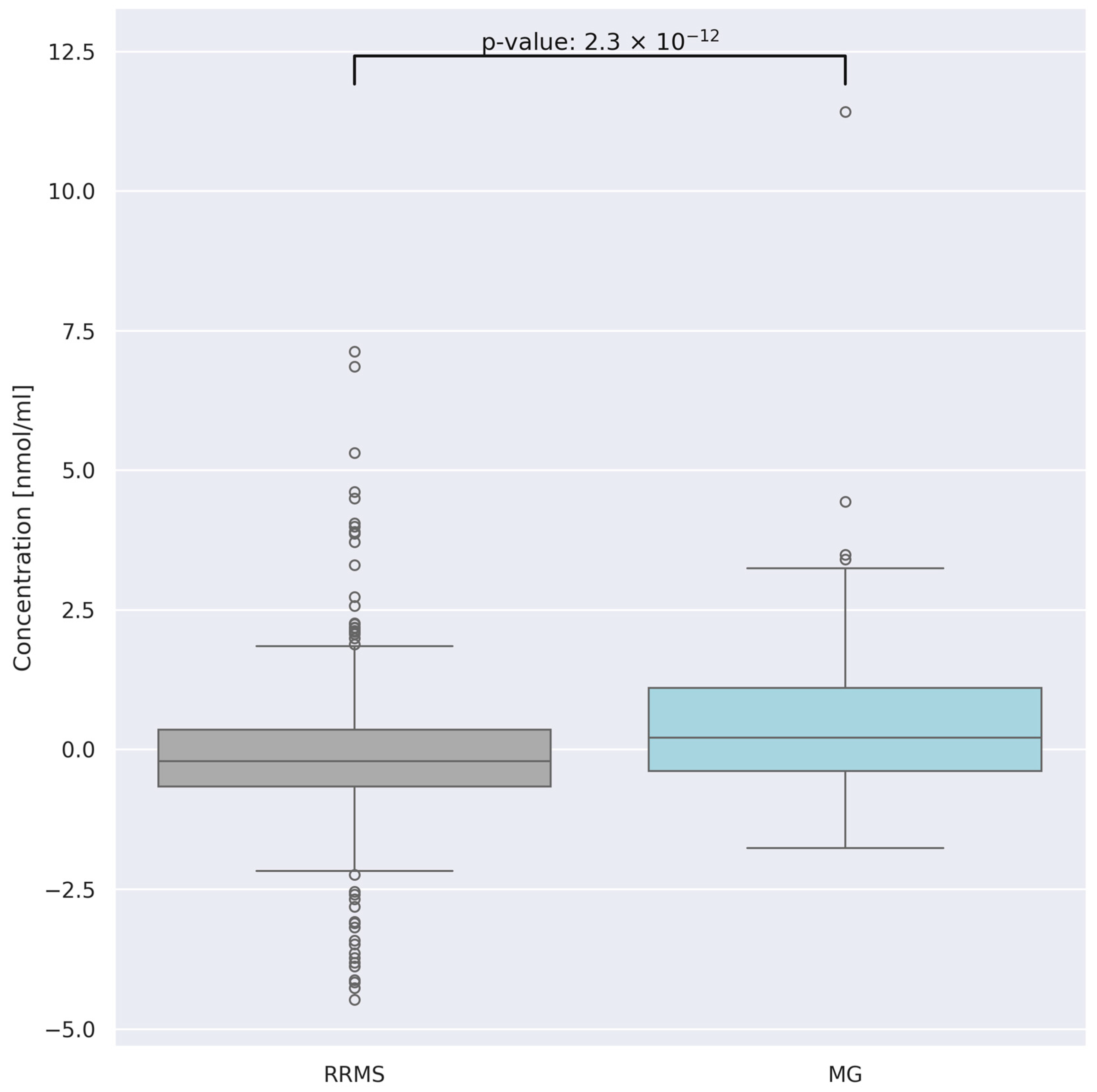
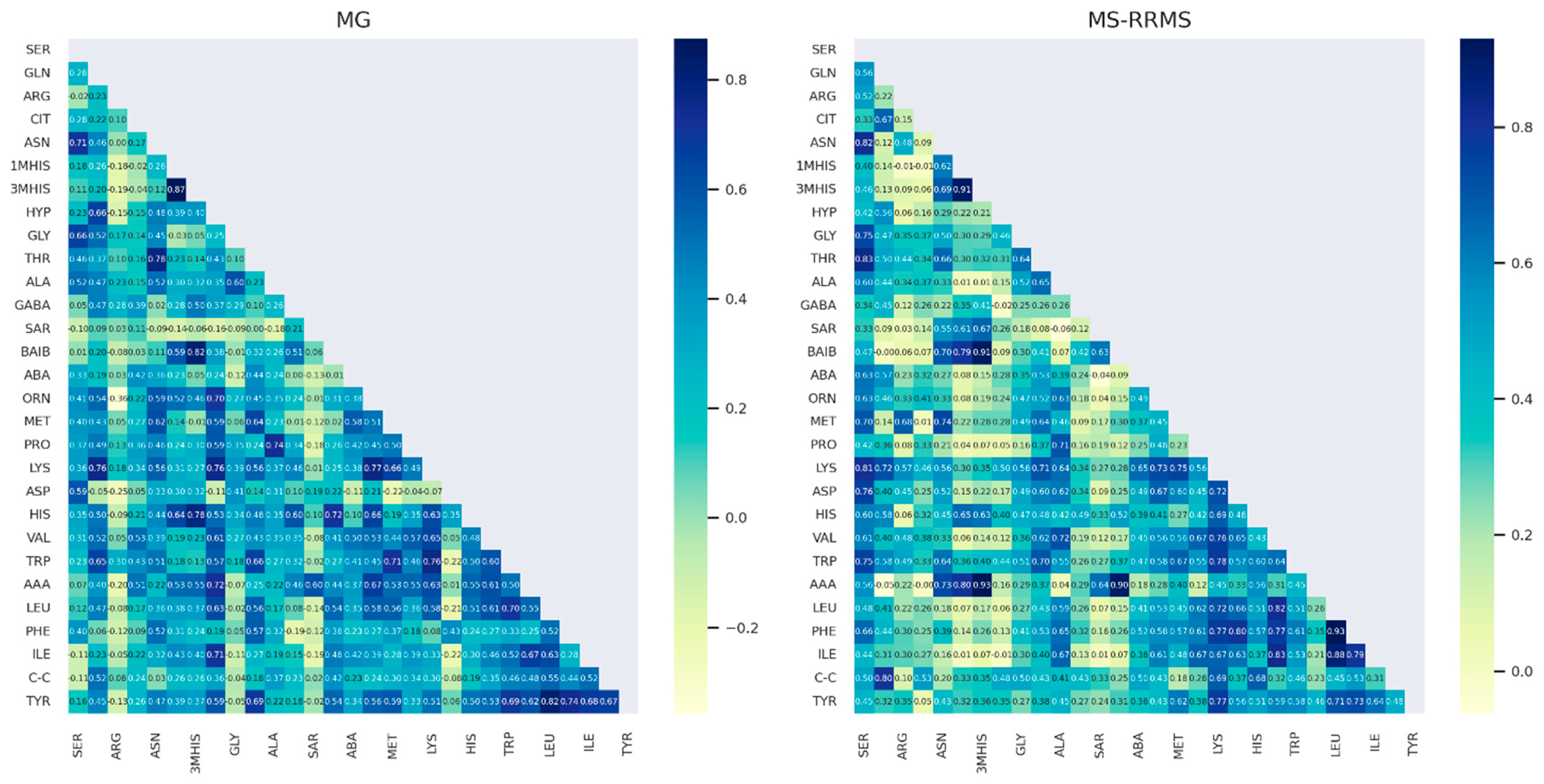
3.4. Comparison of AA Concentration between Two Groups of Patients: RRMS (n = 41) and MG (n = 28)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeMaio, A.; Mehrotra, S.; Sambamurti, K.; Husain, S. The Role of the Adaptive Immune System and T Cell Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.C.; Richman, D.P. Myasthenia Gravis and Related Disorders: Pathology and Molecular Pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, N.; Razavi, S.; Nikzad, E. Multiple Sclerosis: Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Diagnoses and Cell-Based Therapy. Cell J. 2017, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, D.; Chong, M.K.C.; Wu, Y.; Kaminski, H.; Cutter, G.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Yin, J.; Yu, S.; et al. Gender Differences in Quality of Life among Patients with Myasthenia Gravis in China. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbo, H.F.; Gold, R.; Tintora, M. Sex and Gender Issues in Multiple Sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2013, 6, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danikowski, K.M.; Jayaraman, S.; Prabhakar, B.S. Regulatory T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis and Myasthenia Gravis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, I.; Verhoeven, A.; Derks, R.J.; Giera, M. Analytical Pitfalls and Challenges in Clinical Metabolomics. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 1509–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Kwan, Y.; Lin, H.; Ngai, S. Serum Metabolomics for the Diagnosis and Classification of Myasthenia Gravis. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmore, D.; Siddiqi, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, N.; Maksymowych, W. Beyond the Antibodies: Serum Metabolomic Profiling of Myasthenia Gravis. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rispoli, M.G.; Valentinuzzi, S.; De Luca, G.; Del Boccio, P.; Federici, L.; Di Ioia, M.; Digiovanni, A.; Grasso, E.A.; Pozzilli, V.; Villani, A.; et al. Contribution of Metabolomics to Multiple Sclerosis Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.N.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ru, J.N.; Lu, J.H.; Ding, B.; Wu, J. Amino Acid Metabolism in Health and Disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, H.; Soriano-Baguet, L.; Brenner, D. Regulatory T Cell Metabolism at the Intersection between Autoimmune Diseases and Cancer. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 1626–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, I.R.; Wong, B.H.S.; Kelleher, D.; Verma, N.K. Maladaptive T-Cell Metabolic Fitness in Autoimmune Diseases. Cells 2023, 12, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socha, E.; Koba, M.; Kośliński, P. Amino Acid Profiling as a Method of Discovering Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corso, G.; Cristofano, A.; Sapere, N.; La Marca, G.; Angiolillo, A.; Vitale, M.; Fratangelo, R.; Lombardi, T.; Porcile, C.; Intrieri, M.; et al. Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Normal Subjects and in Patients with or at Risk of Alzheimer Dementia. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. Extra 2017, 7, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figura, M.; Kuśmierska, K.; Bucior, E.; Szlufik, S.; Koziorowski, D.; Jamrozik, Z.; Janik, P. Serum Amino Acid Profile in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, M.; Yoshida, N.; Tsokos, G.C. Amino Acid Metabolism in Lupus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 623844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, E.L.; Nguyen, T.; Rhyne, S.; Kim, J. Amino Acids in Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrotto, L.; Correale, J. Amino Acid Catabolism in Multiple Sclerosis Affects Immune Homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1900–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzepiński, Ł.; Kośliński, P.; Kowalewski, M.; Koba, M.; Maciejek, Z. Serum Amino Acid Profiling in Differentiating Clinical Outcomes of Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol. I Neurochir. Pol. 2023, 57, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashaei, S.; Yarani, R.; Mohammadi, P.; Emami Aleagha, M.S. The Potential Roles of Amino Acids and Their Major Derivatives in the Management of Multiple Sclerosis. Amino Acids 2022, 54, 841–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kośliński, P.; Rzepiński, Ł.; Daghir-Wojtkowiak, E.; Koba, M.; Maciejek, Z. Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis. Amino Acids 2023, 55, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzepiński, Ł.; Kośliński, P.; Gackowski, M.; Koba, M.; Maciejek, Z. Amino Acid Levels as Potential Biomarkers of Multiple Sclerosis in Elderly Patients: Preliminary Report. J. Clin. Neurol. 2022, 18, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L. Python 3 Reference Manual; CreateSpace: Scotts Valley, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rzepiński, Ł.; Zawadka-Kunikowska, M.; Newton, J.L.; Zalewski, P. Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction in Myasthenia Gravis and Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis—A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehbashi, S.; Hamouda, D.; Shanina, E. Co-Occurrence of Multiple Sclerosis and Myasthenia Gravis: A Case Report and Review of Immunological Theories. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 34, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, H.C.; Salmond, R.J. The Role of Non-Essential Amino Acids in T Cell Function and Anti-Tumour Immunity. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2021, 69, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröer, S.; Bröer, A. Amino Acid Homeostasis and Signalling in Mammalian Cells and Organisms. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1935–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellebjerg, F.; Giovannoni, G.; Hand, A.; Madsen, H.O.; Jensen, C.V.; Garred, P. Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Nitric Oxide Metabolites Predict Response to Methylprednisolone Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis and Optic Neuritis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 125, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virarkar, M.; Alappat, L.; Bradford, P.G.; Awad, A.B. L-Arginine and Nitric Oxide in CNS Function and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desine, S.; Gabriel, C.L.; Smith, H.M.; Antonetti, O.R.; Wang, C.; Calcutt, M.W.; Doran, A.C.; Silver, H.J.; Nair, S.; Terry, J.G.; et al. Association of Alpha-Aminoadipic Acid with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Healthy and High-Risk Individuals. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1122391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.C.; Amaral, A.U.; Cecatto, C.; Wajner, A.; dos Santos Godoy, K.; Ribeiro, R.T.; de Mello Gonçalves, A.; Zanatta, Â.; da Rosa, M.S.; Loureiro, S.O.; et al. α-Ketoadipic Acid and α-Aminoadipic Acid Cause Disturbance of Glutamatergic Neurotransmission and Induction of Oxidative Stress In Vitro in Brain of Adolescent Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 32, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyver, M.V.; Beelen, R.; De Keyser, J.; Nagels, G.; Van Binst, A.M.; Verborgh, C.; D’haeseleer, M. Plasma Citrulline Levels Are Increased in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 387, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crenn, P.; Coudray-Lucas, C.; Thuillier, F.; Cynober, L.; Messing, B. Postabsorptive Plasma Citrulline Concentration Is a Marker of Absorptive Enterocyte Mass and Intestinal Failure in Humans. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuillard, C.; Cynober, L.; Moinard, C. Citrulline and Nitrogen Homeostasis: An Overview. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Maernura, K.; Kanbara, K.; Tamayama, T.; Hayasaki, H. GABA and GABA Receptors in the Central Nervous System and Other Organs. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2002, 213, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Yin, X.; Edden, R.A.E.; Evans, A.C.; Xu, J.; Cao, G.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Zhao, B.; Wang, J.; et al. Altered Hippocampal GABA and Glutamate Levels and Uncoupling from Functional Connectivity in Multiple Sclerosis. Hippocampus 2018, 28, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nantes, J.C.; Proulx, S.; Zhong, J.; Holmes, S.A.; Narayanan, S.; Brown, R.A.; Hoge, R.D.; Koski, L. GABA and Glutamate Levels Correlate with MTR and Clinical Disability: Insights from Multiple Sclerosis. NeuroImage 2017, 157, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, T.; Yoshizawa, F.; Nishizawa, N. Plasma N-Methylhistidine Concentration Is a Sensitive Index of Myofibrillar Protein Degradation during Starvation in Rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 501–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjijlin, J.; Hjort, G.; Friman, G.; Hambraeus, L. Urinary Excretion of L-Methylhistidine: A Qualitative Indicator of Exogenous 3-Methylhistidine and Intake of Meats From Various Sources. Metabolism 1987, 36, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, P.; Servais, L.; Vialle, R. Neuromuscular Diseases: Diagnosis and Management. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2018, 104, S89–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MS | MG | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects (n) | 121 | 28 |
| Sex (male/female) | 42/80 (34%/66%) | 3/25 (10.7%/89.3%) |
| Age, years | 52.5 ± 11.61 Min–Max: 23–77 | 48.92 ± 12.61 Min–Max: 29–75 |
| Disease duration (years) [range] | 16 ± 8.4 | 7.85 ± 6.53 |
| Median EDSS score (IQR) | 6 (4.0–6.5) | n.a. |
| MS type n (%) | RRMS: 41 (34%) | n.a. |
| SPMS: 55 (45%) | ||
| PPMS: 25 (21%) | ||
| MG type n (%) | GMG: 25 (89.3%) | |
| OMG: 3 (10.7%) | ||
| AChRAb | Yes: 21 (75%) | |
| No: 7 (25%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kośliński, P.; Rzepiński, Ł.; Koba, M.; Maciejek, Z.; Kowalewski, M.; Daghir-Wojtkowiak, E. Comparative Analysis of Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis and Multiple Sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4083. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144083
Kośliński P, Rzepiński Ł, Koba M, Maciejek Z, Kowalewski M, Daghir-Wojtkowiak E. Comparative Analysis of Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis and Multiple Sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(14):4083. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144083
Chicago/Turabian StyleKośliński, Piotr, Łukasz Rzepiński, Marcin Koba, Zdzisław Maciejek, Mariusz Kowalewski, and Emilia Daghir-Wojtkowiak. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis and Multiple Sclerosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 14: 4083. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144083
APA StyleKośliński, P., Rzepiński, Ł., Koba, M., Maciejek, Z., Kowalewski, M., & Daghir-Wojtkowiak, E. (2024). Comparative Analysis of Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis and Multiple Sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(14), 4083. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144083







