Surgical Management of Complex Ankle Fractures in Patients with Diabetes: A National Retrospective Multicentre Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting
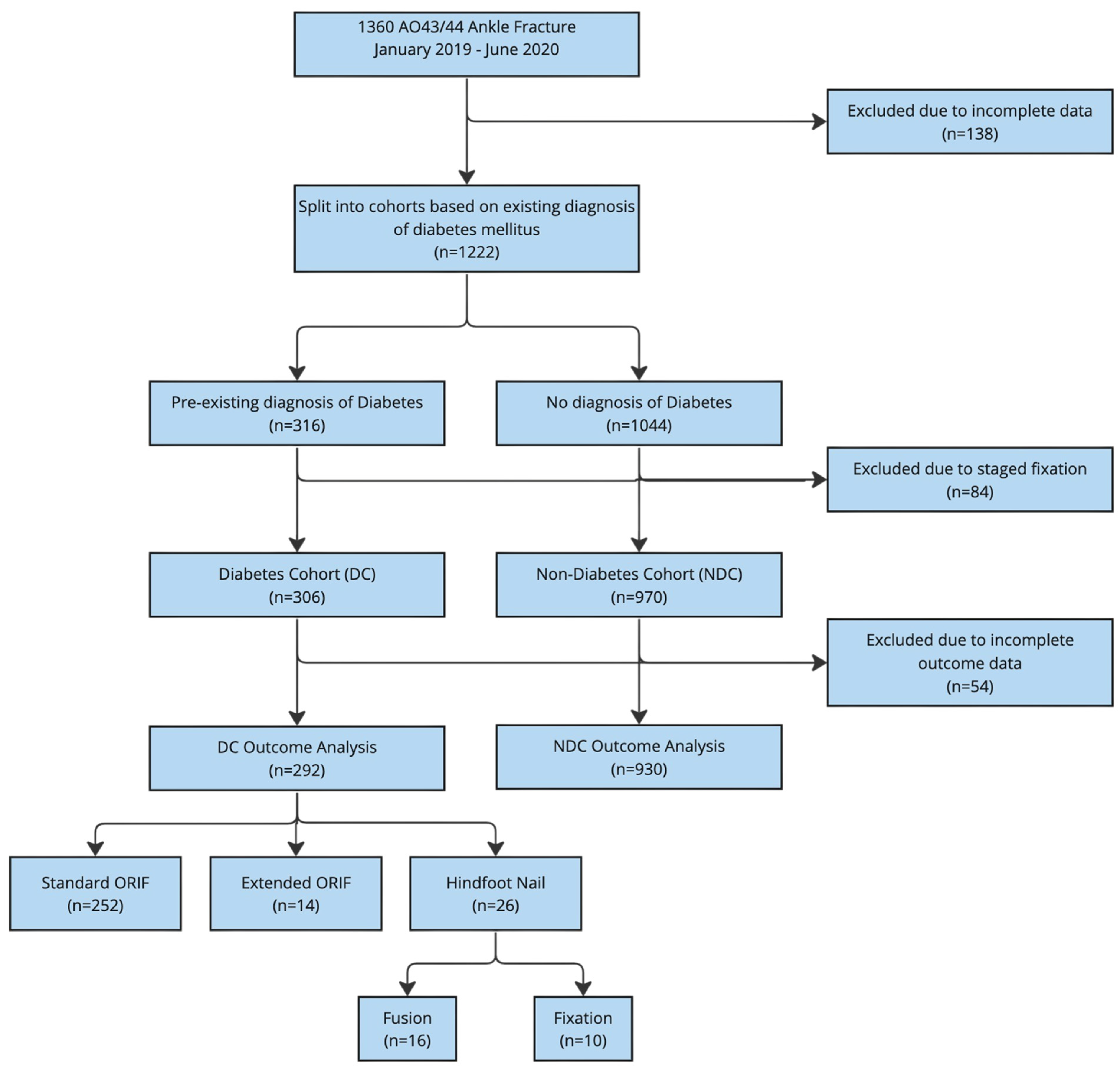
2.3. Participants
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Data Sources
2.6. Bias
2.7. Study Size
2.8. Ethical Approval and Funding
2.9. Statistical Methods
3. Results
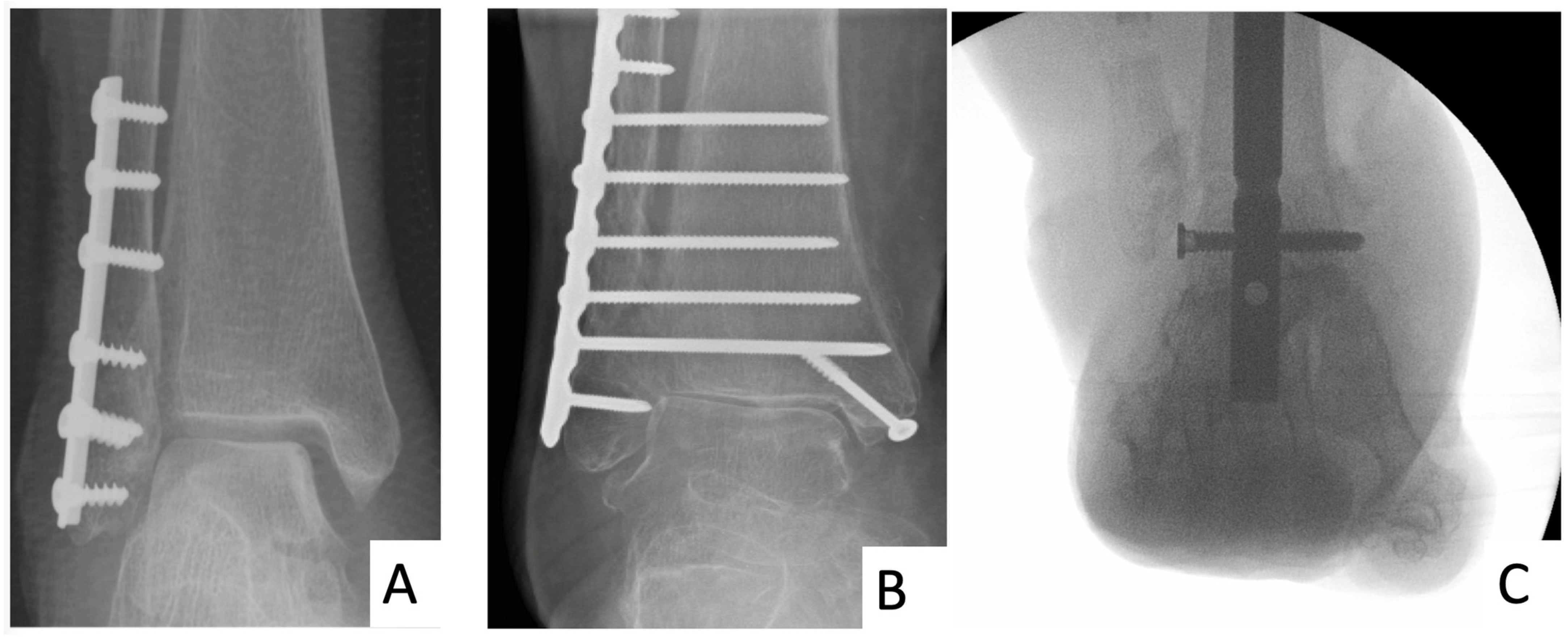
3.1. Standard ORIF
3.2. HFN
4. Discussion
4.1. The Significance of Diabetes in the Surgical Management of Ankle Fractures
4.2. The Need for a Multi-Disciplinary Approach
4.3. Quantifying the Extent of Diabetes Complications
4.4. Challenging Surgical Dogma: The Potential of HFN and Extended ORIF in Limiting Post-Operative Immobilisation/Non-Weightbearing in Diabetes
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gougoulias, N.; Oshba, H.; Dimitroulias, A.; Sakellariou, A.; Wee, A. Ankle Fractures in Diabetic Patients. EFORT Open Rev. 2020, 5, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, E.M.; Polachek, W.S.; Hynes, K. Ankle Fractures in Diabetic Patients: A Critical Analysis. JBJS Rev. 2023, 11, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchanda, K.; Nakonezny, P.; Sathy, A.K.; Sanders, D.T.; Starr, A.J.; Wukich, D.K. A Systematic Review of Ankle Fracture Treatment Modalities in Diabetic Patients. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 16, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, W.J.; Hester, T.; Ha, J. Current Concepts and Challenges in Managing Ankle Fractures in the Presence of Diabetes: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 17, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebraheim, N.; Dammeyer, K.; Paull, D. Treatment of Ankle Fractures in Diabetic Patients. Curr. Orthop. Pract. 2018, 29, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisk, V.R.; Wukich, D.K. Ankle Fractures in Diabetics. Foot Ankle Clin. 2006, 11, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, S.B.; Liporace, F.A.; Gandhi, A.; Donley, B.G.; Pinzur, M.S.; Lin, S.S. Complications of Ankle Fracture in Patients with Diabetes. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2008, 16, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavery, L.A.; Lavery, D.C.; Green, T.; Hunt, N.; Malone, M.; Wukich, D. Incidence of Complications and Risk Factors for Nonunion after Ankle Fracture in Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2022, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polachek, W.S.; Baker, H.P.; Dahm, J.S.; Strelzow, J.A.; Hynes, K.K. Diabetic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Increased Complications Following Operative Management of Ankle Fractures. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2022, 7, 24730114221112106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddix, K.P.; Clement, R.C., 3rd; Tennant, J.N.; Ostrum, R.F. Complications Following Operatively Treated Ankle Fractures in Insulin- and Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetic Patients. Foot Ankle Spec. 2018, 11, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, M.M.; Stuart, A.; Ramsey, K.L.; Friess, D.; Working, Z.M. Outcomes of Fracture Surgery in Patients with Escalating Hemoglobin A1C in the Setting of Unmanaged Diabetes. J. Orthop. Trauma 2022, 37, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loder, R.T. The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on the Healing of Closed Fractures. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1988, 232, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazarov, I.; Peace, R.A.; Lagaay, P.M.; Patel, S.B.; Lyon, L.L.; Schuberth, J.M. Early Protected Weightbearing after Ankle Fractures in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2017, 56, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutico, A.G.; Nasser, E.M.; Brutico, J.M. Operative Ankle Fractures in Complicated Diabetes: Outcomes of Prolonged Non-Weightbearing. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2022, 61, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriacou, H.; Mostafa, A.M.H.A.M.; Davies, B.M.; Khan, W.S. Principles and Guidelines in the Management of Ankle Fractures in Adults. J. Perioper. Pract. 2021, 31, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, A.J.; Dellenbaugh, S.G.; Dipreta, J.A.; Uhl, R.L. The Management of Ankle Fractures in Diabetics: Results of a Survey of the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society Membership. Foot Ankle Spec. 2013, 6, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wukich, D.K.; Kline, A.J. The Management of Ankle Fractures in Patients with Diabetes. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2008, 90, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arangio, G.A. Fractures of the Ankle and Foot in the Diabetic Population. Curr. Opin. Orthop. 2007, 18, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinats, D.J.; Kooner, S.; Johal, H. Acute Hindfoot Nailing for Ankle Fractures: A Systematic Review of Indications and Outcomes. J. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 35, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringfellow, T.D.; Coffey, D.; Wek, C.; Tan, S.P.; Reichert, I.; Ahluwalia, R. Epidemiology & Management of Complex Ankle Fractures in the United Kingdom: A Multicentre Cohort Study. Injury 2023, 55, 111037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. BMJ 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwood, K.; Song, X.; MacKnight, C.; Bergman, H.; Hogan, D.B.; McDowell, I.; Mitnitski, A. A Global Clinical Measure of Fitness and Frailty in Elderly People. CMAJ 2005, 173, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NHS. Health Research Authority and Medical Research Council Decison Tool. Available online: https://www.hra-decisiontools.org.uk/research/ (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Wukich, D.K.; Crim, B.E.; Frykberg, R.G.; Rosario, B.L. Neuropathy and Poorly Controlled Diabetes Increase the Rate of Surgical Site Infection after Foot and Ankle Surgery. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2014, 96, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SooHoo, N.F.; Krenek, L.; Eagan, M.J.; Gurbani, B.; Ko, C.Y.; Zingmond, D.S. Complication Rates Following Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Ankle Fractures. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NICE. Diabetic Foot Problems: Prevention and Management; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2023; ISBN 9781473149458. [Google Scholar]
- Yee, J.; Pillai, A.; Ferris, L. Diabetic Ankle Fractures: A Review of the Literature and an Introduction to the Adelaide Fracture in the Diabetic Ankle Algorithm and Score. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 153146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buggy, A.; Moore, Z. The Impact of the Multidisciplinary Team in the Management of Individuals with Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Systematic Review. J. Wound Care 2017, 26, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Y.; Wilkins, C.J.; Evans, D.R.; Ammar, T.; Deane, C.; Vas, P.R.; Rashid, H.; Sidhu, P.S.; Edmonds, M.E. The Diabetic Foot: The Importance of Coordinated Care. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 31, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Ashe, H.A.; Parnell, L.N.; Fernando, D.J.; Tsigos, C.; Young, R.J.; Ward, J.D.; Boulton, A.J. The Prevalence of Foot Ulceration and Its Correlates in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Population-Based Study. Diabet. Med. 1994, 11, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, W.; Thordarson, D.B.; Debnath, U.K. Operative Management of Ankle Fractures in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Foot Ankle Int. 2007, 28, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourbault, L.J.; Fennelly, J.T.; Stedman, T.; Price, M.J.; Ward, A.E.; AUGMENT Collaborative. The Current UK Consensus on the Management of Weber B and Posterior Ankle Fractures: A Questionnaire Study as Part of the Acute Management of Ankle Fractures (AUGMENT) Audit. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2021, 60, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ludwig, T.; Ebraheim, N.A. Effect of the Blood HbA1c Level on Surgical Treatment Outcomes of Diabetics with Ankle Fractures. Orthop. Surg. 2013, 5, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, A.R.; Kantar, R.S.; Ramly, E.P.; Daar, D.A.; Rifkin, W.J.; Levine, J.P.; Ceradini, D.J. Diabetes Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Wound Complications and Readmission in Patients with Surgically Managed Pressure Ulcers. Wound Repair Regen. 2019, 27, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, A.A.; Davis, M.W.; Rubenach, S.E.; Sivakumaran, S.; Smith, P.N.; Budge, M.M. Outcomes for Older Patients with Hip Fractures: The Impact of Orthopedic and Geriatric Medicine Cocare. J. Orthop. Trauma 2006, 20, 172–178; discussion 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, R.G.; Leith, J.M. Ankle Fractures in Diabetics. Complications of Surgical Management. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1998, 80, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, E.W.; Gu, Q.; Williams, D.; de Rekeneire, N.; Cheng, Y.J.; Geiss, L.; Engelgau, M. Prevalence of Lower Extremity Diseases Associated with Normal Glucose Levels, Impaired Fasting Glucose, and Diabetes among U.S. Adults Aged 40 or Older. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 77, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuckett, P.; Hope, M.; Tetsworth, K.; Van De Pol, J.; McDougall, C. Transarticular Tibiotalocalcaneal Nailing versus Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for Treatment of the Elderly Ankle Fracture: Protocol for a Multicentre, Prospective, Randomised Controlled Trial. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e026360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toole, W.P.; Elliott, M.; Hankins, D.; Rosenbaum, C.; Harris, A.; Perkins, C. Are Low-Energy Open Ankle Fractures in the Elderly the New Geriatric Hip Fracture? J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2015, 54, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeeing, D.P.J.; Houwert, R.M.; Briet, J.P.; Groenwold, R.H.H.; Lansink, K.W.W.; Leenen, L.P.H.; van der Zwaal, P.; Hoogendoorn, J.M.; van Heijl, M.; Verleisdonk, E.J.; et al. Weight-Bearing or Non-Weight-Bearing after Surgical Treatment of Ankle Fractures: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2020, 46, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Large, T.M.; Kaufman, A.M.; Frisch, H.M.; Bankieris, K.R. High-Risk Ankle Fractures in High-Risk Older Patients: To Fix or Nail? Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2023, 143, 3725–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, V.; Tennyson, M.; Zhou, A.; Patel, R.; Fortune, M.D.; Thahir, A.; Krkovic, M. Retrograde Tibiotalocalcaneal Nailing for the Treatment of Acute Ankle Fractures in the Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. EFORT Open Rev. 2022, 7, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diabetes Cohort (N = 306) | Non-Diabetes Cohort (N = 970) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Mean ± SD) | 63.89 ± 15.27 | 49.37 ± 19.61 | <0.001 | |
| Gender | Male | 111 (36.3%) | 499 (51.4%) | <0.001 |
| Female | 195 (63.7%) | 471 (48.6%) | ||
| Anatomic Descriptor | AO43 | 25 (8.2%) | 336 (34.6%) | <0.001 |
| AO44 | 281 (91.8%) | 634 (65.4%) | ||
| Clinical Frailty (Score > 4) | 100 (32.7%) | 146 (15%) | <0.001 | |
| ASA Grade | Median [IR] | 3 [2–3] | 2 [1–2] | <0.001 |
| I | 7 (2.3%) | 334 (34.4%) | <0.001 | |
| II | 132 (43.1%) | 397 (40.9%) | 0.363 | |
| III | 157 (51.3%) | 192 (19.7%) | <0.001 | |
| IV | 10 (3.3%) | 39 (4.2%) | 0.006 | |
| V | 0 | 10 (1.0%) | ||
| Pre-Operative Status | Rheumatoid Arthritis | 3 (1%) | 16 (1.6%) | 0.338 |
| Alcoholism | 23 (7.5%) | 169 (17.4%) | <0.001 | |
| Peripheral neuropathy | 23 (7.5%) | 22 (2.3%) | <0.001 | |
| Mental health | 12 (3.9%) | 103 (10.6%) | 0.01 | |
| Dementia | 9 (2.9%) | 34 (3.6%) | 0.574 | |
| Smoker | 43 (14.1%) | 245 (25.2%) | <0.001 | |
| Pre-Operative Mobility | Unaided mobilisation | 232 (75.8%) | 835 (86.1%) | <0.001 |
| Walks with one stick | 47 (15.3%) | 45 (4.6%) | <0.001 | |
| Two walking sticks or walking/Zimmer frame | 27 (8.8%) | 54 (5.6%) | 0.054 | |
| Non-weightbearing/wheelchair | 11 (3.6%) | 8 (0.8%) | 0.001 | |
| Fixation Type and Diabetes Group | Standard ORIF | Extended ORIF | HFN (Fixation) | HFN (Fusion) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC (n = 252) | NDC (n = 816) | DC (n = 14) | NDC (n = 29) | DC (n = 10) | NDC (n = 62) | DC (n = 16) | NDC (n = 23) | ||
| Post-operative weightbearing status | Non-weightbearing | 216 (85.7%) | 724 (88.7%) | 13 (92.9%) | 24 (82.8%) | 14 (53.4%) ** | 18 (29%) | 8 (50%) * | 6 (26.1%) |
| Partially weightbearing | 20 (7.9%) | 61 (7.5%) | 1 (7.1%) | 4 (13.8%) | 3 (11.5%) | 20 (32.3%) | 2 (12.5%) | 10 (43.5%) ** | |
| Fully weightbearing | 16 (6.3%) | 31 (7.5%) | 0 | 1 (3.4%) | 9 (34.6%) | 23 (37.1%) | 6 (37.5%) | 7 (30.4%) | |
| Post-operative Complications | Wound complication | 38 (15.1%) | 71 (8.7%) * | 2 (14.3%) | 3 (10.3%) | 1 (10%) | 2 (3.3%) | 5 (33.3%) | 3 (13%) |
| Wound breakdown | 24 (9.1%) * | 40 (5.3%) * | 0 | 3 (10.3%) | 0 | 0 | 5 (31.3%) | 3 (13%) ** | |
| Wound infection | 31 (12.3%) * | 58 (7.6%) * | 2 (14.3%) | 3 (10.3%) | 1 (10%) | 2 (3.3%) | 3 (18.8%) | 4 (17.4%) | |
| DVT | 0 | 4 (0.6%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (6.3%) | 0 | |
| PE | 2 (0.8%) | 4 (0.5%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (6.3%) | 1 (4.3%) | |
| Further procedure | 24 (9.5%) | 66 (8.7%) | 3 (21.4%) | 4 (13.8%) | 0 | 3 (4.9%) | 5 (31.3%) | 3 (13%) | |
| Failure of construct | 13 (5.3%) | 25 (3.3%) ** | 1 (7.1%) | 2 (6.9%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (6.3%) | 2 (9.1%) | |
| Removal of metalwork | 25 (10.3%) | 62 (8.5%) | 3 (21.4%) | 4 (13.8%) | 0 | 2 (3.5%) | 3 (18.8%) | 4 (18.2%) | |
| Standard ORIF (n = 252) | Extended ORIF (n = 14) | HFN Fixation (n = 10) | HFN Fusion (n = 16) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-operative Weightbearing Status | Non-weightbearing | 216 (85.7%) | 13 (92.9%) | 6 (60%) | 8 (50%) |
| Partially weightbearing | 20 (7.9%) | 1 (7.1%) | 1 (10%) | 2 (12.5%) | |
| Fully weightbearing | 16 (6.3%) | 0 | 3 (30%) | 6 (37.5%) | |
| Complication | Wound complication | 38 (15.1%) | 2 (14.3%) | 1 (10%) | 6 (37.5%) |
| DVT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (6.3%) | |
| PE | 2 (0.8%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (6.3%) | |
| Further procedure | 24 (9.5%) | 3 (21.4%) | 0 | 5 (31.3%) | |
| Failure of construct | 13 (5.3%) | 1 (7.1%) | 0 | 1 (6.3%) | |
| Removal of metalwork | 25 (10.3%) | 3 (21.4%) | 0 | 3 (18.8%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahluwalia, R.; Wek, C.; Lewis, T.L.; Stringfellow, T.D.; Coffey, D.; Tan, S.P.; Edmonds, M.; Meloni, M.; Reichert, I.L.H., on behalf of The HARnT Collaborative King’s College Hospital, London. Surgical Management of Complex Ankle Fractures in Patients with Diabetes: A National Retrospective Multicentre Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133949
Ahluwalia R, Wek C, Lewis TL, Stringfellow TD, Coffey D, Tan SP, Edmonds M, Meloni M, Reichert ILH on behalf of The HARnT Collaborative King’s College Hospital, London. Surgical Management of Complex Ankle Fractures in Patients with Diabetes: A National Retrospective Multicentre Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133949
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhluwalia, Raju, Caeser Wek, Thomas Lorchan Lewis, Thomas David Stringfellow, Duncan Coffey, Sze Ping Tan, Michael Edmonds, Marco Meloni, and Ines L. H. Reichert on behalf of The HARnT Collaborative King’s College Hospital, London. 2024. "Surgical Management of Complex Ankle Fractures in Patients with Diabetes: A National Retrospective Multicentre Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133949
APA StyleAhluwalia, R., Wek, C., Lewis, T. L., Stringfellow, T. D., Coffey, D., Tan, S. P., Edmonds, M., Meloni, M., & Reichert, I. L. H., on behalf of The HARnT Collaborative King’s College Hospital, London. (2024). Surgical Management of Complex Ankle Fractures in Patients with Diabetes: A National Retrospective Multicentre Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133949








