Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy’s Influence on Alpha-Synuclein and Inflammatory Marker Levels: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
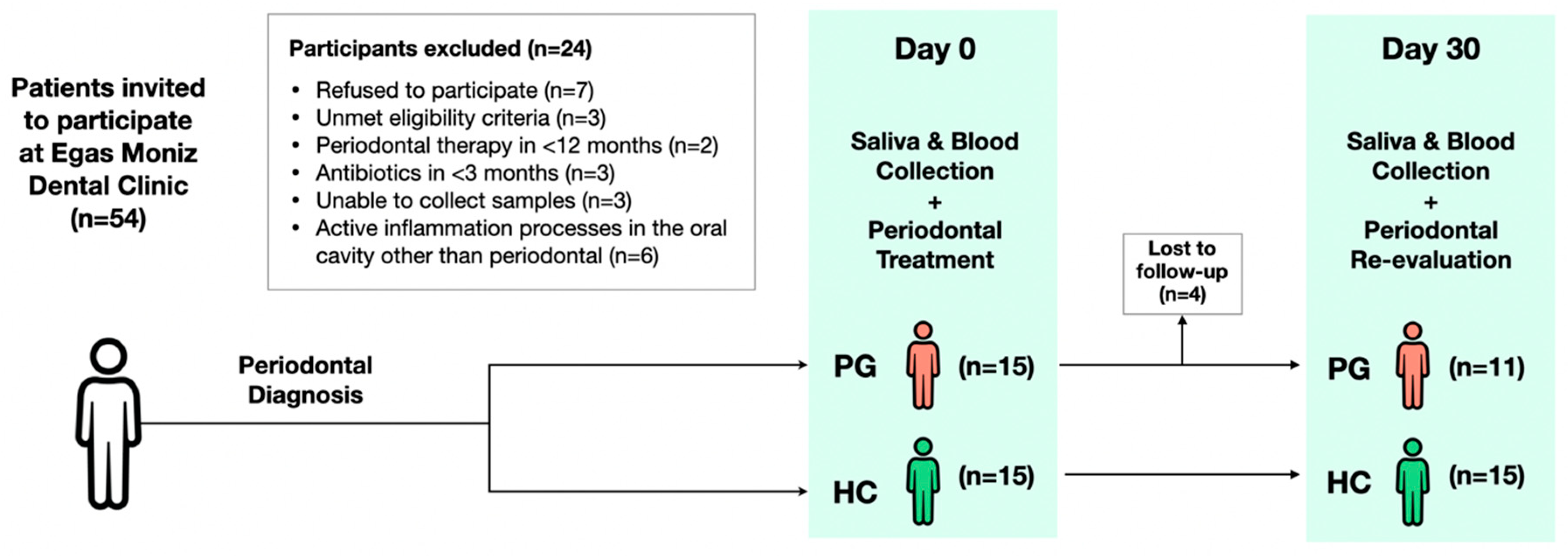
2.1. Study Setting, Eligibility Criteria and Sample Size
2.2. Demographics Characteristics
2.3. Periodontal Clinical Examination and Diagnosis
2.4. Saliva Collection Protocol
2.5. Blood Collection Protocol
2.6. Periodontal Treatment
2.7. Salivary and Blood Circulating Markers
2.8. Data Management and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants/Sample Description/Population
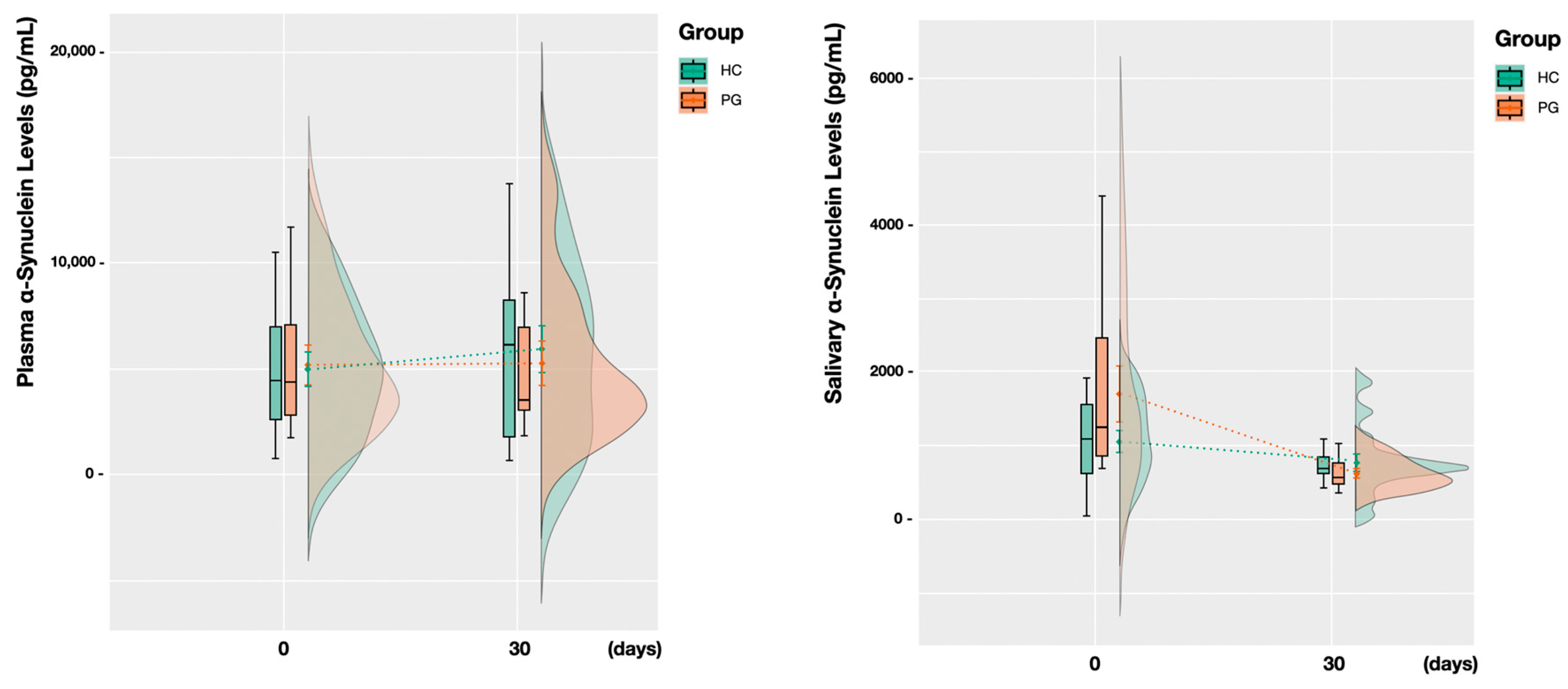
3.2. Plasma and Saliva Levels before and after Treatment
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kramer, M.L.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. Presynaptic α-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with lewy bodies. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, N.; Swallow, D.; Grosset, K.A.; Anichtchik, O.; Spillantini, M.; Grosset, D.G. Alpha-synuclein in peripheral tissues and body fluids as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease—A systematic review. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 130, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra, P.; Machado, V.; Rota, S.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Botelho, J.; Mendes, J.J. Revisiting Alpha-Synuclein Pathways to Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelsson, M. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers—Neurotoxic Molecules in Parkinson’s Disease and Other Lewy Body Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijaz, B.A.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.A. Initiation and propagation of α-synuclein aggregation in the nervous system. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peelaerts, W.; Bousset, L.; Van Der Perren, A.; Moskalyuk, A.; Pulizzi, R.; Giugliano, M.; Van Den Haute, C.; Melki, R.; Baekelandt, V. α-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration. Nature 2015, 522, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-W.; Yang, S.-Y.; Yang, C.-C.; Chang, C.-W.; Wu, Y.-R. Plasma and Serum Alpha-Synuclein as a Biomarker of Diagnosis in Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2020, 10, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougea, A.; Koros, C.; Stefanis, L. Salivary alpha-synuclein as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review. J. Neural Transm. 2019, 126, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Chen, W.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, F.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Quinn, T.J.; et al. Salivary total α-synuclein, oligomeric α-synuclein and SNCA variants in Parkinson’s disease patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivacqua, G.; Latorre, A.; Suppa, A.; Nardi, M.; Pietracupa, S.; Mancinelli, R.; Fabbrini, G.; Colosimo, C.; Gaudio, E.; Berardelli, A. Abnormal salivary total and oligomeric alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, P.; Lashuel, H.A. Opportunities and challenges of alpha-synuclein as a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Bloem, B.R. The Parkinson pandemic—A call to action. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, D.F.; Rodrigues, E.F.; Langohr, R.; Shahpasandzadeh, H.; Ribeiro, T.; Guerreiro, P.; Gerhardt, E.; Kröhnert, K.; Klucken, J.; Pereira, M.D.; et al. Systematic Comparison of the Effects of Alpha-synuclein Mutations on Its Oligomerization and Aggregation. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuko, S.; Akiko, K.; Ruberu, N.N.; Hideo, F.; Shunichi, K.; Motoji, S.; Tomio, A.; Hiroshi, N.; Hiroshi, Y.; Masato, H.; et al. Accumulation of phosphorylated α-synuclein in aging human brain. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 62, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, E.; Murphy, S.; Martinson, H.A. Alpha-synuclein pathology and the role of the microbiota in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 446582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Jepsen, S.; Jin, L.; Otomo-Corgel, J. Impact of the global burden of periodontal diseases on health, nutrition and wellbeing of mankind: A call for global action. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, J.; Machado, V.; Leira, Y.; Proença, L.; Chambrone, L.; Mendes, J.J. Economic burden of periodontitis in the United States and Europe—An updated estimation. J. Periodontol. 2021, 93, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könönen, E.; Gursoy, M.; Gursoy, U. Periodontitis: A Multifaceted Disease of Tooth-Supporting Tissues. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Chavakis, T. Local and systemic mechanisms linking periodontal disease and inflammatory comorbidities. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebersole, J.L.; Al-Sabbagh, M.; Gonzalez, O.A.; Dawson, D.R. Ageing effects on humoral immune responses in chronic periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, J.; Leira, Y.; Viana, J.; Machado, V.; Lyra, P.; Aldrey, J.M.; Pías-Peleteiro, J.M.; Blanco, J.; Sobrino, T.; Mendes, J.J. The Role of Inflammatory Diet and Vitamin D on the Link between Periodontitis and Cognitive Function: A Mediation Analysis in Older Adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra, P.; Machado, V.; Proença, L.; Domingos, J.; Godinho, C.; Mendes, J.J.; Botelho, J. Parkinson’s disease, periodontitis and patient-related outcomes: A cross-sectional study. Medicina 2020, 56, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominy, S.S.; Lynch, C.; Ermini, F.; Benedyk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Konradi, A.; Nguyen, M.; Haditsch, U.; Raha, D.; Griffin, C.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis in Alzheimer’s disease brains: Evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vitola, P.; Balducci, C.; Baroni, M.; Artioli, L.; Santamaria, G.; Castiglioni, M.; Cerovic, M.; Colombo, L.; Caldinelli, L.; Pollegioni, L.; et al. Peripheral inflammation exacerbates α-synuclein toxicity and neuropathology in Parkinson’s models. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2021, 47, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.M.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, H.; Kam, W.; Wilson, B.; Hong, J.S. Neuroinflammation and α-synuclein dysfunction potentiate each other, driving chronic progression of neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzenberg, E.; Berry, D.; Yang, D.; Lee, E.Y.; Kroemer, A.; Kaufman, S.; Wong, G.C.L.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Sen, S.; Fishbein, T.; et al. A Role for Neuronal Alpha-Synuclein in Gastrointestinal Immunity. J. Innate Immun. 2017, 9, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kang, W.; Hwang, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, K.W.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, H.; Yoon, H.J.; Park, Y.K.; Chalita, M.; et al. Oral and gut dysbiosis leads to functional alterations in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermini, F.; Low, V.F.; Song, J.J.; Tan, A.Y.S.; Faull, R.L.M.; Dragunow, M.; Curtis, M.A.; Dominy, S.S. Ultrastructural localization of Porphyromonas gingivalis gingipains in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s disease brains. NPJ Park. Dis. 2024, 10, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbrouckef, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizzi, A.; Tirabassi, G.; Aspriello, S.D.; Piemontese, M.; Rubini, C.; Lucarini, G. Gingival advanced glycation end-products in diabetes mellitus-associated chronic periodontitis: An immunohistochemical study. J. Periodontal Res. 2013, 48, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, N.H.; Acharya, A.B.; Patil, V.S.; Trivedi, D.J.; Setty, S.; Thakur, S.L. Resistin Levels in Gingival Crevicular Fluid of Patients With Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISCED-P 2011; International Standard Classification of Education: Education Programmes 2011. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: London, UK, 2011.
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hujoel, P.P.; White, B.A.; García, R.I.; Listgarten, M.A. The dentogingival epithelial surface area revisited. J. Periodontal Res. 2001, 36, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesse, W.; Abbas, F.; Van Der Ploeg, I.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Vissink, A. Periodontal inflamed surface area: Quantifying inflammatory burden. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liukkonen, J.; Gürsoy, U.K.; Könönen, E.; Gürsoy, M.; Metso, J.; Salminen, A.; Kopra, E.; Jauhiainen, M.; Mäntylä, P.; Buhlin, K.; et al. Salivary biomarkers in association with periodontal parameters and the periodontitis risk haplotype. Innate Immun. 2018, 24, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; Herrera, D.; Kebschull, M.; Chapple, I.; Jepsen, S.; Berglundh, T.; Sculean, A.; Tonetti, M.S.; Merete Aass, A.; Aimetti, M.; et al. Treatment of stage I–III periodontitis—The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 4–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, P.I.; Wei, L.; Thornton-Evans, G.O.; Borrell, L.N.; Borgnakke, W.S.; Dye, B.; Genco, R.J. Risk Indicators for Periodontitis in US Adults: NHANES 2009 to 2012. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, J.; Machado, V.; Proença, L.; Alves, R.; Cavacas, M.A.; Amaro, L.; Mendes, J.J. Study of Periodontal Health in Almada-Seixal (SoPHiAS): A cross-sectional study in the Lisbon Metropolitan Area. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, V.; Aguilera, E.M.; Botelho, J.; Hussain, S.B.; Leira, Y.; Proença, L.; D’Aiuto, F.; Mendes, J.J. Association between Periodontitis and High Blood Pressure: Results from the Study of Periodontal Health in Almada-Seixal (SoPHiAS). J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behle, J.H.; Sedaghatfar, M.H.; Demmer, R.T.; Wolf, D.L.; Celenti, R.; Kebschull, M.; Belusko, P.B.; Herrera-Abreu, M.; Lalla, E.; Papapanou, P.N. Heterogeneity of systemic inflammatory responses to periodontal therapy. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekeridou, A.; Mombelli, A.; Cancela, J.; Courvoisier, D.; Giannopoulou, C. Systemic inflammatory burden and local inflammation in periodontitis: What is the link between inflammatory biomarkers in serum and gingival crevicular fluid? Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2019, 5, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.N. Changes in inflammatory cytokines in saliva after non-surgical periodontal therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Total (n = 26) | HC (n = 15) | PG (n = 11) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) (Min–Max) | 50.1 (17.8) (19–77) | 43.5 (18.6) (19–70) | 59.1 (12.3) (40–77) | 0.024 * |
| Sex, % (n) | ||||
| Female | 53.8 (14) | 46.7 (7) | 63.6 (7) | 0.391 |
| Male | 46.2 (12) | 53.3 (8) | 36.4 (4) | |
| Educational Level, % (n) | ||||
| Elementary | 15.4 (4) | 13.3 (2) | 18.2 (2) | - |
| Middle | 57.7 (15) | 60.0 (9) | 54.5 (6) | |
| Higher | 26.9 (7) | 26.7 (4) | 27.3 (3) | |
| Marital Status, % (n) | ||||
| Single | 34.6 (9) | 40.0 (6) | 27.3 (3) | - |
| Married/Living with Partner | 46.2 (12) | 53.3 (8) | 36.4 (4) | |
| Divorced/Separated/Widowed | 19.2 (5) | 6.7 (1) | 36.4 (4) | |
| Smoking Habits, % (n) | ||||
| Non-Smoker | 50.0 (13) | 53.3 (8) | 45.5 (5) | - |
| Former Smoker | 26.9 (7) | 26.7 (4) | 27.3 (3) | |
| Active Smoker | 23.1 (6) | 20.0 (3) | 27.3 (3) | |
| Last Dental Visit, % (n) | ||||
| <6 Months | 61.5 (16) | 66.7 (10) | 54.5 (6) | - |
| 6–12 Months | 15.4 (4) | 13.3 (2) | 18.2 (2) | |
| >12 Months | 23.1 (6) | 20.0 (3) | 27.3 (3) | |
| Toothbrushing, % (n) | ||||
| Once a Day | 3.8 (1) | 0.0 (0) | 9.1 (1) | - |
| Twice or More a Day | 96.2 (25) | 100.0 (15) | 90.9 (10) | |
| Toothbrush Type, % (n) | ||||
| Manual | 84.6 (22) | 93.3 (14) | 72.7 (8) | 0.279 |
| Electric | 15.4 (4) | 6.7 (1) | 27.3 (3) | |
| Interproximal Cleaning, % (n) | ||||
| No | 76.9 (20) | 73.3 (11) | 81.8 (9) | 0.005 * |
| Often/Yes | 23.1 (6) | 26.7 (4) | 18.2 (2) | |
| Diabetes Mellitus, % (n) | ||||
| Yes | 11.5 (3) | 0.0 (0) | 27.3 (3) | - |
| No | 88.5 (23) | 100.0 (15) | 72.7 (8) |
| Variable | Total (n = 26) | HC (n = 15) | PG (n = 11) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-synuclein (pg/mL), mean (SD) | ||||
| Salivary, T0 | 1365.1 (964.4) | 1090.4 (566.3) | 1739.6 (1268.3) | 0.090 |
| Plasma, T0 | 5067.2 (3091.9) | 4977.9 (3155.6) | 5189.1 (3151.1) | 0.867 |
| Salivary, T30 | 711.0 (369.6) | 772.9 (449.3) | 626.7 (212.9) | 0.329 |
| Plasma, T30 | 5643.1 (3883.3) | 5929.5 (4267.5) | 5252.6 (3451.5) | 0.670 |
| Salivary, (Diff., T30-T0) | −654.0 (1021.6) | −317.5 (452.1) | −1112.8 (1386.3) | 0.093 |
| Plasma, (Diff., T30-T0) | 575.9 (1948.8) | 951.6 (1844.3) | 63.6 (2057.3) | 0.259 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL), mean (SD) | ||||
| Salivary, T0 | 6.0 (7.8) | 4.4 (6.2) | 8.1 (9.4) | 0.240 |
| Plasma, T0 | 6.3 (3.7) | 4.7 (3.8) | 8.4 (2.2) | 0.008 * |
| Salivary, T30 | 6.4 (7.8) | 6.2 (9.2) | 6.6 (5.6) | 0.908 |
| Plasma, T30 | 4.7 (3.0) | 3.6 (3.0) | 6.1 (2.5) | 0.034 * |
| Salivary, (Diff., T30-T0) | 0.4 (7.2) | 1.8 (8.4) | −1.5 (5.1) | 0.256 |
| Plasma, (Diff., T30-T0) | −1.6 (2.0) | −1.1 (1.7) | −2.3 (2.4) | 0.137 |
| IL1-β (pg/mL), mean (SD) | ||||
| Salivary, T0 | 462.3 (318.4) | 502.2 (358.4) | 407.8 (260.7) | 0.466 |
| Plasma, T0 | 162.6 (80.5) | 151.2 (89.5) | 178.0 (67.2) | 0.412 |
| Salivary, T30 | 468.0 (385.4) | 421.3 (398.6) | 531.6 (375.8) | 0.482 |
| Plasma, T30 | 84.4 (52.0) | 77.6 (45.9) | 93.7 (60.3) | 0.447 |
| Salivary, (Diff., T30-T0) | −5.7 (212.1) | −80.9 (169.3) | 123.8 (213.8) | 0.012 * |
| Plasma, (Diff., T30-T0) | −78.2 (52.3) | −73.6 (51.3) | −84.4 (55.7) | 0.614 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyra, P.; Botelho, J.; Rota, S.; Poplawska-Domaszewicz, K.; Machado, V.; Guerreiro, D.; Proença, L.; Barroso, H.; Mendes, J.J.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy’s Influence on Alpha-Synuclein and Inflammatory Marker Levels: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3586. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123586
Lyra P, Botelho J, Rota S, Poplawska-Domaszewicz K, Machado V, Guerreiro D, Proença L, Barroso H, Mendes JJ, Chaudhuri KR. Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy’s Influence on Alpha-Synuclein and Inflammatory Marker Levels: A Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(12):3586. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123586
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyra, Patrícia, João Botelho, Silvia Rota, Karolina Poplawska-Domaszewicz, Vanessa Machado, Daniela Guerreiro, Luís Proença, Helena Barroso, José João Mendes, and Kallol Ray Chaudhuri. 2024. "Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy’s Influence on Alpha-Synuclein and Inflammatory Marker Levels: A Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 12: 3586. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123586
APA StyleLyra, P., Botelho, J., Rota, S., Poplawska-Domaszewicz, K., Machado, V., Guerreiro, D., Proença, L., Barroso, H., Mendes, J. J., & Chaudhuri, K. R. (2024). Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy’s Influence on Alpha-Synuclein and Inflammatory Marker Levels: A Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(12), 3586. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123586











_Chaudhuri_also_Ray-Chaudhuri.png)

