Do Ultrasound Lung Abnormalities Correlate to Biomarkers and Male Gender in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients? A Monocentric Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Measurements
- PLUS 1, non-linear and non-homogeneous, thickened pleural line;
- PLUS 2, disrupted pleural line (“fragmented”);
- PLUS 3, subpleural consolidation (subpleural echo-poor region or “tissue-like”);
- PAUS 1, discrete divergent B lines;
- PAUS 2, confluent B lines;
- PAUS 3, dense confluent areas (“whiteout”) that persist during the respiratory cycle.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Correlation of LUS Parameters with Demographic, Clinical, and Laboratory Biomarkers: Predictivity of Risks Factors for LUS Score
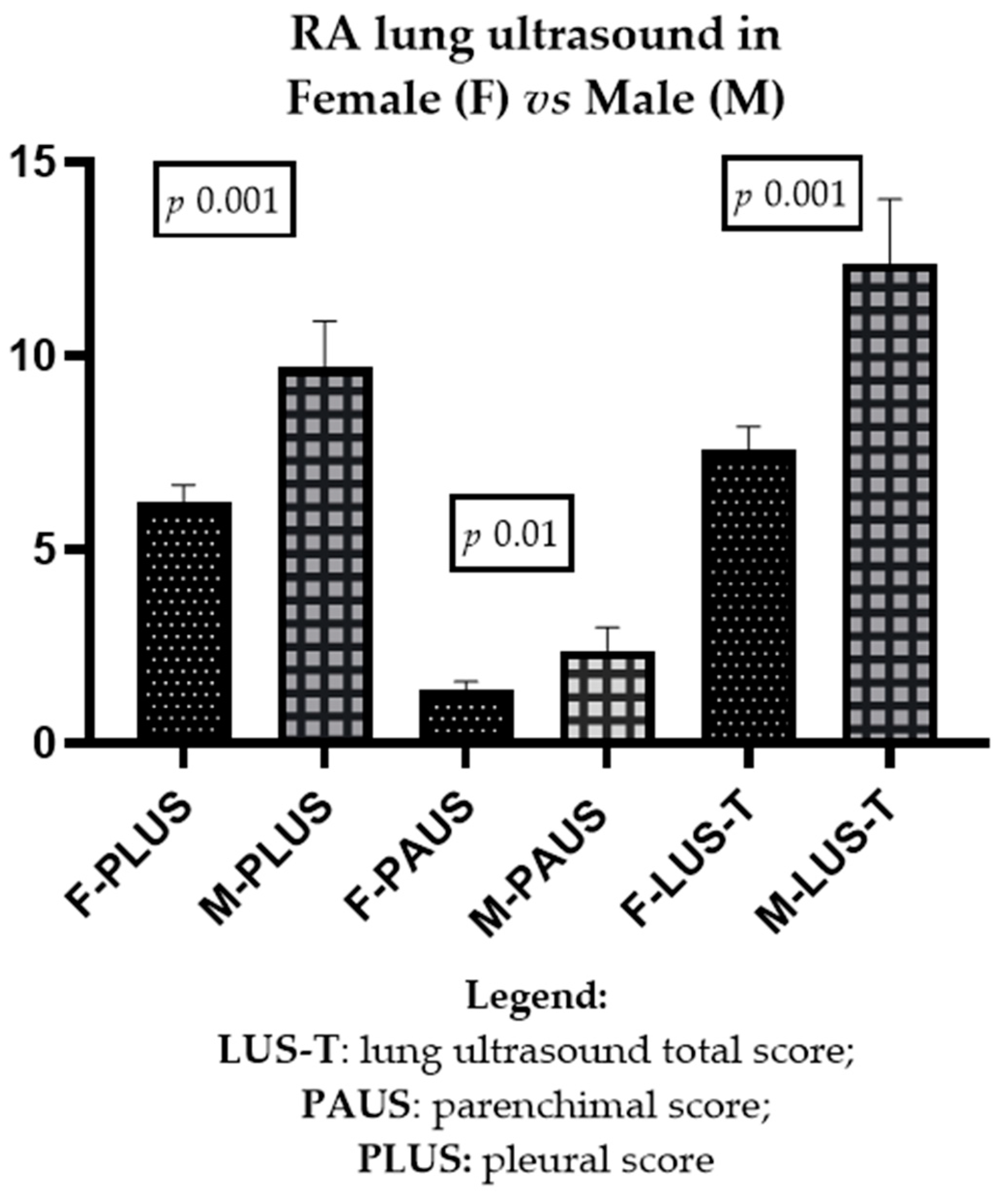
3.2. Difference in LUS between Genders
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandinelli, F.; Benucci, M.; Salaffi, F.; Manetti, M.; Infantino, M.; Damiani, A.; Manfredi, M.; Grossi, V.; Matucci, A.; Li Gobbi, F.; et al. Do New and Old Biomarkers of Early Undifferentiated Arthritis Correlate with Arthritis Impact Measurement Scales? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benucci, M.; Damiani, A.; Li Gobbi, F.; Bandinelli, F.; Infantino, M.; Grossi, V.; Manfredi, M.; Noguier, G.; Meacci, F. Correlation between HLA haplotypes and the development of antidrug antibodies in a cohort of patients with rheumatic diseases. Biologics 2018, 12, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwaka, Y.; Chikashi, T. The Impact of Cigarette Smoking on Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Narrative Review. Cells 2020, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laria, A.; Lurati, A.M.; Zizzo, G.; Zaccara, E.; Mazzocchi, D.; Re, K.A.; Marrazza, M.; Faggioli, P.; Mazzone, A. Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Practical Review. Front. Med. 2022, 13, 837133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, J.; Lama, S.; Knapp, K.; Gutierrez, C.; Lovett, K.; Thai, S.; Craig, G.L. Epidemiology, and clinical characteristics of interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis from the JointMan database. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Zhu, C.; Ye, Y. Incidence, risk factors, and prognosis of acute exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.; Oelzner, P.; Teichgräber, U.; Franz, M.; Gaßler, N.; Kroegel, C.; Wolf, G.; Pfeil, A. Diagnosing lung involvement in inflammatory rheumatic diseases—Where do we currently stand? Front. Med. 2023, 9, 1101448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoruelle, C.K.; Solomon, J.J.; Fischer, A.; Deane, K.D. The lung may play a role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Clin. Rheumtol. 2014, 9, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, H.M.; Purokivi, M.K.; Kärkkäinen, M.S.; Kettunen, H.-P.; Selander, T.A.; Kaarteenaho, R.L. Variable course of disease of rheumatoid arthritis-associated usual interstitial pneumonia compared to other subtypes. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.; Collins, B.F.; Ho, L.A.; Raghu, G. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chansakul, T.; Dellaripa, P.F.; Doyle, T.J.; Madan, R. Intra-thoracic rheumatoid arthritis: Imaging spectrum of typical findings and treatment related complications. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, T.J.; Weis, J.M.; Baran, T.M.; Kan, J.; Meng, S.; Yeo, A.; Zhao, Y.T.; Ambrosini, R.; Cleary, S.; Rubens, D.; et al. Lung ultrasound volume sweep imaging for respiratory illness: A new horizon in expanding imaging access. BMJ Open Resp. Res. 2021, 8, e000919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, H.; Ogura, T.; Kameda, H.; Kishaba, T.; Iwasawa, T.; Takemura, T.; Kuwano, K. Decision-Making Strategy for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (RA-ILD). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Itoh, H.; Nagahara, K.; Hata, H.; Mitsui, K. Relationships of Radiation Dose Indices with Body Size Indices in Adult Body Computed Tomography. Tomography 2023, 9, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, D.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Wu, N.; Ye, Q. Progression of radiographic fibrosis in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1265355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, H.K.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.-R. Risk factors for interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: A cohort study from the KOBIO registry. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2024, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinache, G.; Popescu, C.C.; Mogos, C.; Enache, L.; Agache, M.; Codreanu, C. Lung Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis—A Retrospective Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Yin, J.; Zhang, X. Factors associated with interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assayag, D.; Elicker, B.M.; Urbania, T.H.; Colby, T.V.; Kang, B.H.; Ryu, J.H.; King, T.E.; Collard, H.R.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, J.S. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: Radiologic identification of usual interstitial pneumonia pattern. Radiology 2014, 270, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, F.; Manfredi, A.; Faverio, P.; Andersen, M.B.; Bono, F.; Pagni, F.; Salvarani, C.; Bendstrup, E.; Sebastiani, M. The usual Interstitial pneumonia pattern in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, I.I.; Khouqeer, G.A.; Nada, A.; Abuzaid, M.M.; Sulieman, A. Low-Dose Chest CT Protocols for Imaging COVID-19 Pneumonia: Technique Parameters and Radiation Dose. Life 2023, 13, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, M.; Devkota, S.; Prabhakar, N.; Debi, U.; Kaur, M.; Sehgal, I.S.; Dhooria, S.; Bhalla, A.; Sandhu, M.S. Ultra-Low Dose CT Chest in Acute COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Pilot Study from India. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, M.K.; Maher, M.M.; Rizzo, S.; Kanarek, D.; Shepard, J.-A.O. Radiation exposure from chest CT: Issues and strategies. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2004, 19, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzessere, C.; von Garnier, C.; Beigelman-Aubry, C. Radiation Exposure to Low-Dose Computed Tomography for Lung Cancer Screening: Should We Be Concerned? Tomography 2023, 9, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargani, L.; Bruni, C.; Romei, C.; Frumento, P.; Moreo, A.; Agoston, G.; Guiducci, S.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Lepri, G.; Belloli, L.; et al. Prognostic Value of Lung Ultrasound B-Lines in Systemic Sclerosis. Chest 2020, 158, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delle Sedie, A.; Doveri, M.; Frassi, F.; Gargani, L.; D’Errico, G.; Pepe, P.; Bazzichi, L.; Riente, L.; Caramella, D.; Bombardieri, S. Ultrasound lung comets in systemic sclerosis: A useful tool to detect lung interstitial fibrosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2010, 28, S54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, M.; Soto-Fajardo, C.; Pineda, C.; Alfaro-Rodriguez, A.; Terslev, L.; Bruyn, G.A.; Iagnocco, A.; Bertolazzi, C.; D’Agostino, M.A.; Delle Sedie, A. Ultrasound in the Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Literature Review by the OMERACT Ultrasound Group. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Buonsenso, D.; Perrone, T.; Briganti, D.F.; Perlini, S.; Torri, E.; Mariani, A.; Mossolani, E.E.; et al. Proposal for International Standardization of the Use of Lung Ultrasound for Patients With COVID-19: A Simple, Quantitative, Reproducible Method. J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attanasi, M.; Sferrazza Papa, S.; Porreca, A.; Sferrazza Papa, G.F.; Di Filippo, P.; Piloni, F.; Dodi, G.; Sansone, F.; Di Pillo, S.; Chiarelli, F. Use of lung ultrasound school aged children with weezing. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 10, 926252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gargani, L.; Barskova, T.; Furst, D.E.; Matucci Cerinic, M. Usefulness of lung ultrasound B-lines in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: A literature review. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zheng, S.; Lin, J.; Hu, S.; Zhuang, J.; Lin, Q.; Xie, X.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, W.; et al. The role of lung ultrasound B-lines and serum KL-6 in the screening and follow-up of rheumatoid arthritis patients for an identification of interstitial lung disease: Review of the literature, proposal for a preliminary algorithm, and clinical application to cases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofíudóttir, B.K.; Harders, S.M.W.; Lage-Hansen, P.R.; Christensen, R.; Munk, H.L.; Sorensen, G.L.; Davidsen, J.R.; Ellingsen, T. Using thoracic ultrasound to detect interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A protocol for the diagnostic test accuracy AURORA study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e067434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Moreno, P.; Linares-Contreras, M.F.; Rodríguez-Vargas, G.S.; Rodríguez-Linares, P.; Mata-Hurtado, A.; Ibatá, L.; Martínez, S.; Rojas-Villarraga, A.; Diaz, M.; Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; et al. Usefulness of Lung Ultrasound as a Method for Early Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Open Access Rheumatol. 2024, 17, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triggianese, P.; Conigliaro, P.; De Martino, E.; Monosi, B.; Chimenti, M.S. Overview on the Link Between the Complement System and Auto-Immune Articular and Pulmonary Disease. Open Access Rheumatol. 2023, 15, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqalyoobi, S.; Adegunsoye, A.; Linderholm, A.; Hrusch, C.; Cutting, C.; Ma, S.-F.; Sperling, A.; Noth, I.; Strek, M.E.; Oldham, J.M. Circulating Plasma Biomarkers of Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena-Vázquez, N.; Rojas-Gimenez, M.; Romero-Barco, C.M.; Manrique-Arija, S.; Francisco, E.F.; Aguilar-Hurtado, M.C.; Añón-Oñate, I.; Pérez-Albaladejo, L.; Ortega-Castro, R.; Godoy-Navarrete, F.J.; et al. Predictors of Progression and Mortality in Patients with Prevalent Rheumatoid Arthritis and Interstitial Lung Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.K.; Quah, E.; Earnshaw, B.; Amoasii, C.; Mudawi, T.; Spencer, L.G. Does methotrexate cause progressive fibrotic interstitial lung disease? A systematic review. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juge, P.A.; Lee, J.S.; Lau, J.; Kawano-Dourado, L.; Rojas Serrano, J.; Sebastiani, M.; Koduri, G.; Eric Matteson, E.; Karina Bonfiglioli, K.; Sawamura, M.; et al. Methotrexate and rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2000337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco Cubero, C.; Chamizo Carmona, E.; Vela Casasempere, P. Systematic review of the impact of drugs on diffuse interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatol. Clin. 2021, 17, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, K.; Lehto, J.T.; Sutinen, E.; Kautiainen, H.; Myllärniemi, M.; Saarto, T. mMRC dyspnoea scale indicates impaired quality of life and increased pain in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. ERJ Open Res 2017, 3, 00084–02017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandinelli, F.; Pagano, M.; Vallecoccia, M.S. Post-COVID-19 and Post-COVID-19 Vaccine Arthritis, Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Horton’s Arteritis: A Single-Center Assessment of Clinical, Serological, Genetic, and Ultrasonographic Biomarkers. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.C.; Murthy, S.; Diaz, J.; Adhikari, N.; Angus, D.C.; Arabi, Y.M.; Baillie, K.; Bauer, M.; Berry, S.; Blackwood, B. A Minimal Common Outcome Measure Set for COVID-19 Clinical Research. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e192–e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, P.; Cascella, M. Diffusing Capacity of The Lungs for Carbon Monoxide; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, E.K.; von Mühlen, C.A.; Fritzler, M.J.; Damoiseaux, J.; Infantino, M.; Klotz, W.; Satoh, M.; Musset, L.; García-De La Torre, I.; Carballo, O.G. The International Consensus on ANA Patterns (ICAP) in 2021—The 6th Workshop and Current Perspectives. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2022, 7, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, E.A.; Minami, T.; Ma, I.W.Y.; Yasukawa, K. Lung Ultrasound for Pleural Line Abnormalities, Confluent B-Lines, and Consolidation, Expert Reproducibility and a Method of Standardization. J Ultrasound Med 2022, 41, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazedi-Fuerst, F.C.; Kielhauser, S.M.; Scheidl, S.; Tripolt, N.J.; Lutfi, A.; Yazdani-Biuki, B.; Dejaco, C.; Graninger, W.B. Ultrasound screening for interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2014, 32, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cuschieri, S. The STROBE Guidelines. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2019, 13, S31–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otaola, M.; Paulin, F.; Rosemffet, M.; Balcazar, J.; Perandones, M.; Orausclio, P.; Cazenave, T.; Rossi, S.; Marciano, S.; Schneeberger, E.; et al. Lung ultrasound is a promising screening tool to rule out interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Respirology 2024, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruaro, B.; Baratella, E.; Confalonieri, P.; Confalonieri, M.; Vassallo, F.G.; Wade, B.; Geri, P.; Pozzan, R.; Caforio, G.; Marrocchio, C.; et al. High-Resolution Computed Tomography and Lung Ultrasound in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Which One to Choose? Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloescu, C.; Rucki, A.A.; Chen, A.; Zahiri, M.; Ghoshal, G.; Wang, J.; Chew, R.; Kessler, D.; Chan, D.K.I.; Hicks, B.; et al. Machine Learning Algorithm Detection of Confluent B-Lines. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2023, 49, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, F.; Delle Sedie, A. The use of ultrasound for assessing interstitial lung involvement in connective tissue diseases. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Yang, Y.; Han, X. Machine Learning and Single-Cell Analysis Identify Molecular Features of IPF-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes and Their Implications on IPF Prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Di Carlo, M.; Tardella, M.; Giovagnoni, A. High-resolution computed tomography of the lung in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Prevalence of interstitial lung disease involvement and determinants of abnormalities. Medicine 2019, 98, e17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yang, H.I.; Kim, K.-S. Etiology and Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Interstitial Lung Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, L.; Song, S.; Hu, Y.; Liang, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. Predictors of long-term prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutolo, M.; Straub, R.H. Sex steroids and autoimmune rheumatic diseases: State of the art. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Card, J.W.; Zeldin, D.C. Hormonal influences on lung function and response to environmental agents: Lessons from animal models of respiratory disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2009, 6, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morani, A.; Barros, R.P.; Imamov, O.; Hultenby, K.; Arner, A.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.A. Lung dysfunction causes systemic hypoxia in estrogen receptor beta knockout (Erbeta−/−) mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, S.; Periera-Simon, S.; Xia, X.; Catanuto, P.; Rubio, G.; Shahzeidi, S.; El Salem, F.; Shapiro, J.; Briegel, K.; Korach, K.S.; et al. MicroRNA let-7 Downregulates Ligand-Independent Estrogen Receptor-mediated Male-Predominant Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1246–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
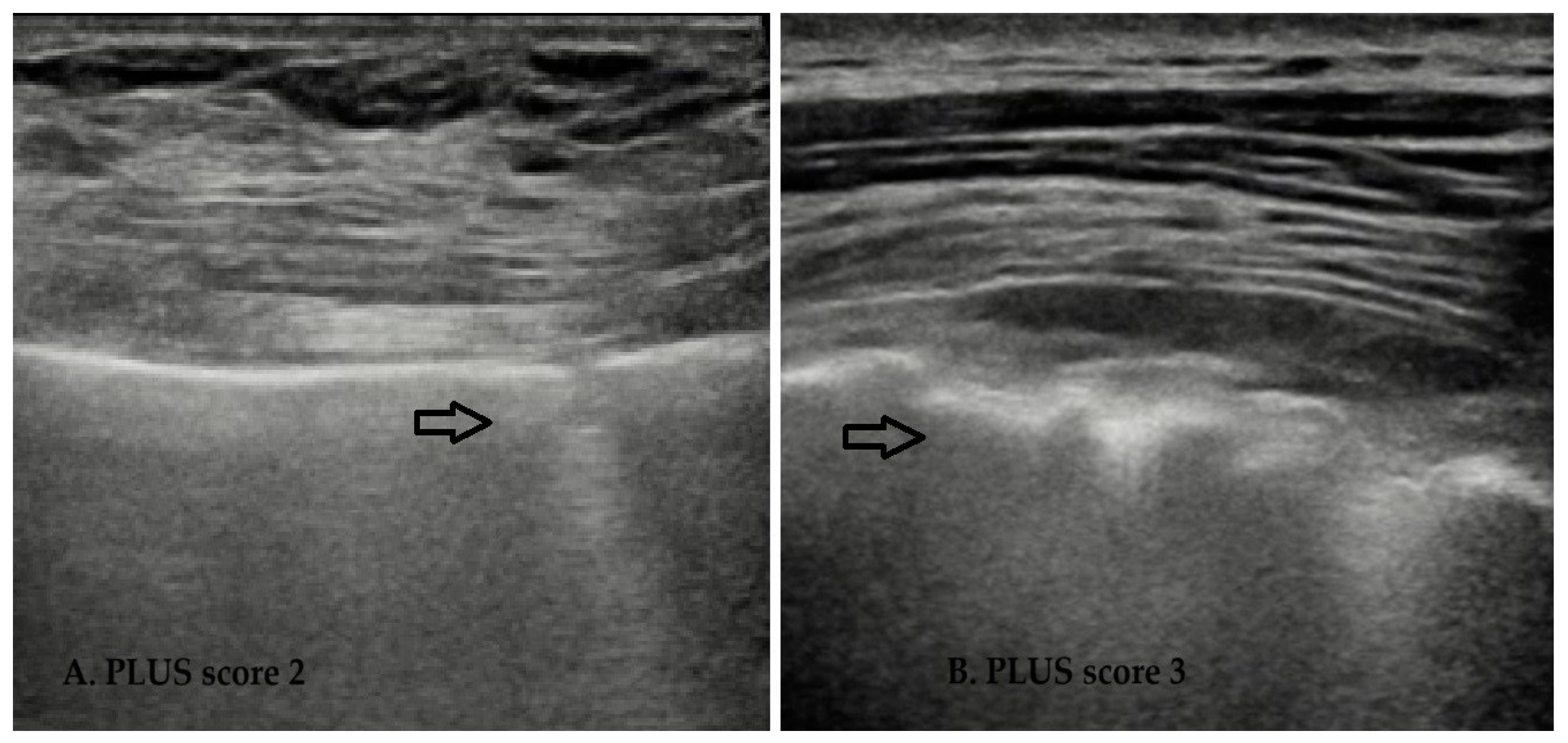
| RA Patients (n= 155) | Correlation of LUS and RA Biomarkers and Difference in LUS for Single Parameter Examined | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (median, IQR) | 67 (56–76) | PLUS (*) PAUS LUS-T | <0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 |
| Disease duration (median, IQR, N, %) | 12 (5–20) years; early-RA (<1 year) (9.7%) vs. late RA | All LUS parameters | NS |
| LUS score (median, IQR) | PLUS: 6 (3–10) PAUS: 1 (0.5–2) LUS-T: 7 (4–12) | NA | NA |
| Smoking (N, %) | 33 (26.4%) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| Male gender (N, %) | 30 (24%) | PLUS (**) PAUS LUS-T | 0.001 0.05 0.001 |
| Connective disease overlap | 9 (5.8%) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| DAS28(ESR) (median, IQR) | 2.6 (2–3.4) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| DAS28 (CRP) (median, IQR) | 2 (1.5–3.1) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| COVID-19 (WHO > 3) past infection and latent tuberculosis (N, %) | 10 (8%) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| Previous and concomitant treatments | |||
| Methotrexate and anti-jak (respectively) | 99 (65.9%), 37 (29.6%) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| Biologic anti-TNF-alpha and non-anti-TNF-alpha (respectively) | 57 (45.6%), 68 (54.4%) | PLUS (**) PAUS LUS-T | 0.04, 0.01 NS, NS 0.03, 0.01 |
| Laboratory tests | |||
| CRP (mg/dL) (median, IQR) | 0.21 (0.06–0.8) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| ESR (mm/h) (median, IQR) | 17.5 (6–32.2) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| RF IgM (U/mL) (median, IQR) | 73 (20–222) | PLUS (*) PAUS LUS-T | 0.0006 0.02 0.001 |
| RF IgA (U/mL) (median, IQR) | 20 (6.3–43) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| RF IgG (U/mL) (median, IQR) | 20 (8.9–29) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| ACPA (U/mL) (median, IQR) | 129 (20–1600) | PLUS (*) PAUS LUS-T | 0.001 0.006 0.001 |
| IL6 (pg/mL) (median, IQR) | 2.9 (2.9–9.6) | PLUS (*) PAUS LUS-T | 0.02 NS 0.02 |
| Classic, BML, alternative complement (median, IQR) | 111 (87.4–123), 34 (9.8–71), 86.5 (67–96.7) | All LUS parameters | NS |
| Female (N = 125) | Male (N 30) | p-Value (*) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (median, IQR) | 66.00 (53.5–76.00) | 69 (63.5–75.00) | NS |
| Disease duration (median, IQR) | 5 (12–20) | 9 (3–15) | NS |
| DAS28 (ESR); DAS28 (CRP) | 2.6 (2–3.4); 1.04 (1.5–3) | 2.5 (1.7–3.4); 1.8 (1.5–3.2) | NS |
| LUS scores (median, IQR) | PLUS: 5 (3–9) PAUS: 0.1 (0–2) LUS-T: 6 (3–10.2) | PLUS: 9.5 (5–13.25) PAUS: 1.5 (0.1–3) LUS-T: 11.5 (6–16.2) | 0.001 0.01 0.001 |
| DAS28 (ESR); DAS28 (CRP) (median, IQR) | 2.6 (2–3.4); 1.04 (1.5–3) | 2.5 (1.7–3.4); 1.8 (1.5–3.2) | NS |
| Biomarkers | |||
| RF IgM, IgA, IgG U/mL (median, IQR) | 62 (20–182), 20 (5.3–39), 20 (8.4–30) (*) | 112 (20–457), 21 (18.5–151), 20 (11–27.5) | NS IgM and IgG 0.02 IgA |
| ACPA U/mL (median, IQR) | 105. 5 (12.7–504.4) | 239.5 (36.5–665.6) | NS |
| IL6 pG/mL (median, IQR) | 2.9 (2.9–8.6) | 4.4 (2.9–15.4) | NS |
| Lung involvement and factor of risk | |||
| HRCT ILD N (%) | 21 (16.8%) (**) | 11 (36.6%) | 0.01 |
| DLCO reduction (<60% or <75% with association of FVC reduction) N (%) | 2 (1.6%) (**) | 4 (13.3%) | 0.001 |
| Smoking | 22 (17.6%) | 11 (36.6%) | NS |
| COVID-19 hospitalization and latent tuberculosis (treated with prophylaxis) N (%) | 7 (5.6%) | 4 (13%) | NS |
| Concomitant treatments | |||
| Hydroxychloroquine, N (%) | 17 (13.6%) | 4 (13.3%) | NS |
| Methotrexate, N (%) | 44 (35.2%) | 12 (40%) | NS |
| Sulfasalazine, N (%) | 1 (0.8%) | 0 (0%) | NS |
| Leflunomide, N (%) | 9 (7.2%) | 1 (3.3%) | NS |
| Anti-TNF-alpha, N (%) | 18 (35.2%) | 4 (13.3%) | NS |
| Anti-jak inhibitors, N (%) | 25 (20%) | 5 (16.6%) | NS |
| Tocilizumab, N (%) | 33 (26.4%) | 10 (33.3%) | NS |
| Sarilumab, N (%) | 7 (5.6%) | 2 (6.6%) | NS |
| Rituximab, N (%) | 3 (2.4%) | 1 (3.3%) | NS |
| Abatacept, N (%) | 33 (26.4%) | 4 (13.3%) | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bandinelli, F.; Benucci, M.; Mallia, I.; Mauro, I.; Pecani, N.; Li Gobbi, F.; Manfredi, M.; Guiducci, S.; Lari, B.; Grossi, V.; et al. Do Ultrasound Lung Abnormalities Correlate to Biomarkers and Male Gender in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients? A Monocentric Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123534
Bandinelli F, Benucci M, Mallia I, Mauro I, Pecani N, Li Gobbi F, Manfredi M, Guiducci S, Lari B, Grossi V, et al. Do Ultrasound Lung Abnormalities Correlate to Biomarkers and Male Gender in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients? A Monocentric Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(12):3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123534
Chicago/Turabian StyleBandinelli, Francesca, Maurizio Benucci, Ilenia Mallia, Ilaria Mauro, Nikita Pecani, Francesca Li Gobbi, Mariangela Manfredi, Serena Guiducci, Barbara Lari, Valentina Grossi, and et al. 2024. "Do Ultrasound Lung Abnormalities Correlate to Biomarkers and Male Gender in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients? A Monocentric Cross-Sectional Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 12: 3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123534
APA StyleBandinelli, F., Benucci, M., Mallia, I., Mauro, I., Pecani, N., Li Gobbi, F., Manfredi, M., Guiducci, S., Lari, B., Grossi, V., Infantino, M., & Giannasi, G. (2024). Do Ultrasound Lung Abnormalities Correlate to Biomarkers and Male Gender in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients? A Monocentric Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(12), 3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123534








