Abstract
Background/Objectives: Researchers have proposed two novel impedance-pH parameters, mean nocturnal baseline impedance (MNBI) and the post-reflux swallow-induced peristaltic wave (PSPW) index, to enhance the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and enable better predictions of the effectiveness of anti-reflux therapies. This systematic review aims to synthesize the available evidence on the utility of the PSPW index and MNBI as diagnostic tools for pediatric GERD. Methods: A systematic search of studies reporting PSPW index and MNBI values in patients with GERD was performed in PubMed, Embase, Clarivate, Scopus, Cochrane and Google Scholar databases from their beginning until April 2024. The following terms were used: GERD, children, pediatric, PSPW and MNBI. Results: Eight studies were included, describing 479 patients ranging from 2 months to 17 years old over an 8-year period in 12 pediatric centers. Four studies demonstrated that children with pathological acid exposure have a significantly lower MNBI, with a good discriminatory ability to diagnose GERD. The PSPW index showed lower values in patients with reflux hypersensitivity (RH) compared to those with functional heartburn (FH). Conclusions: Patients with pathological acid exposure tend to exhibit lower MNBI and PSPW index values compared to those with normal acid exposure. MNBI and the PSPW index show promise as diagnostic tools in distinguishing between different GERD phenotypes. Further research is needed to establish standardized diagnostic criteria and optimize the clinical applicability in GERD diagnosis and management.
1. Introduction
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) represents a prevalent gastrointestinal disorder in pediatric populations and is characterized by the abnormal reflux of gastric content into the esophagus, leading to a spectrum of symptoms and potential complications [1,2,3]. Conventional diagnostic methods for pediatric GERD, such as pH monitoring and endoscopy, have inherent limitations, particularly in capturing non-acid reflux events and assessing the reflux phenotype [4,5].
Multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH (MII-pH) monitoring is currently established as the foremost diagnostic modality for detecting gastroesophageal reflux (GER), as it enables the quantification and description of all reflux events and their potential association with symptoms, delineating several GERD phenotypes, as categorized in the Rome IV esophageal criteria. Non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) is a condition in which patients experience GERD symptoms and have no esophagitis on endoscopy but abnormal acid exposure during MII-pH monitoring. Reflux hypersensitivity (RH) is characterized by a negative endoscopy and normal acid exposure of the esophagus but a positive association between symptoms and reflux episodes. Functional heartburn (FH), on the other hand, is associated with the typical GERD symptoms but a negative endoscopy, normal esophageal acid exposure, and no association between symptoms and reflux episodes during MII-pH monitoring [6,7,8,9].
Researchers have proposed two novel impedance-pH parameters: mean nocturnal baseline impedance (MNBI) and the post-reflux swallow-induced peristaltic wave (PSPW) index [10]. These metrics are believed to provide a more precise evaluation of the GERD phenotype [11], enhance the diagnostic process [12,13], and enable better predictions of the effectiveness of anti-reflux therapies [14].
PSPW, characterized by an antegrade esophageal contraction following reflux events, reflects the effectiveness of the esophageal peristaltic response in clearing refluxed material from the esophagus [12]. MNBI, on the other hand, provides a measure of the baseline electrical conductivity of the esophageal mucosa during periods with no reflux episodes, serving as a surrogate marker for mucosal integrity and reflux burden [15,16].
Studies in adult patients have shown that MNBI correlates with symptom outcomes, especially when the acid exposure time is inconclusive, indicating its utility in cases where traditional metrics fall short [17]. Additionally, MNBI has been proposed as a marker for laryngopharyngeal reflux, further expanding its diagnostic applications [18]. The PSPW index is crucial for evaluating esophageal chemical clearance and mucosal integrity, providing a comprehensive assessment of GERD [19]. These novel impedance parameters have been found to increase the diagnostic yield of impedance-pH monitoring, differentiating between NERD, RH, and FH [12,15,20].
Furthermore, MNBI and the PSPW index have been suggested to be valuable in identifying proton pump inhibitor-refractory reflux disease, highlighting their importance in challenging cases [21,22]. These parameters have also been shown to link proton pump inhibitor (PPI)-responsive heartburn to reflux better than traditional metrics like the acid exposure time, emphasizing their superiority in certain diagnostic scenarios [21]. Overall, the inclusion of MNBI and the PSPW index in impedance monitoring protocols has significantly improved the diagnostic capabilities available for GERD, providing clinicians with valuable tools to enhance patient care and treatment outcomes [23,24].
Despite their promise, the utility of the PSPW index and MNBI in pediatric GERD remains incompletely understood. While studies in adult populations have demonstrated their potential diagnostic value, the pediatric population presents unique challenges and considerations that may influence the applicability and interpretation of these metrics [25]. As such, a comprehensive evaluation of the existing literature is warranted to assess the evidence supporting the use of the PSPW index and MNBI in diagnosing GERD in children.
This systematic review aims to synthesize the available evidence on the utility of the PSPW index and MNBI as diagnostic tools for pediatric GERD. By critically appraising the existing literature and identifying gaps in the knowledge, this review will reveal the current state of evidence and highlight areas for future investigation in pediatric GERD diagnosis and management.
2. Materials and Methods
An extended search was conducted using the standard methodology published by the Cochrane Collaboration [26,27] in multiple databases, including PubMed, Embase, Clarivate, Scopus, Cochrane, and Google Scholar, from their inception until April 2024. The following terms were used: GERD, children, pediatric, PSPW and MNBI. The review was not registered. The findings were documented in alignment with the guidelines provided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [28].
We included observational studies (retrospective and prospective) that evaluated the gastroesophageal reflux disease spectrum in which PSPW and MNBI were measured. We reviewed studies that involved populations consisting of neonates, infants, children, and adolescents. Studies that included pediatric patients with GERD but did not evaluate them through esophageal pH-impedance monitoring were excluded. Animal studies were also eliminated.
Two reviewers were used for the research. The interrater agreement reached 97% when identifying articles for inclusion in the review. In cases where the raters disagreed on a particular article, that article was excluded from consideration.
Patient characteristics such as age, the gastroesophageal reflux disease spectrum, endoscopic and histologic diagnosis, the duration of impedance monitoring, the type of novel impedance parameter measured, the statistical conclusion, and the clinical results were extracted from each publication.
To synthesize the data, we utilized Microsoft Excel version 2019. The results are presented as either mean with standard deviation or median with interquartile range, depending on the data provided in each article.
3. Results
The systematic literature search identified 355 publications, which underwent thorough screening based on their titles and abstracts. Following the removal of non-relevant articles and duplicates, 23 studies were deemed pertinent and evaluated. Ultimately, eight suitable articles were included in this systematic literature review. Details of the selection process can be found in Figure 1.
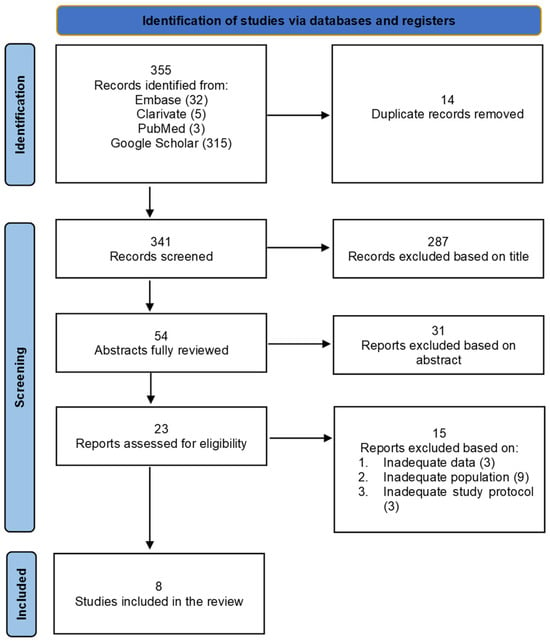
Figure 1.
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for new systematic review: study selection process.
In the studies analyzed, a cohort of 479 patients ranging from 2 months to 17 years old were assessed over an 8-year period, from 2014 until 2022. The studies were conducted in a total of 12 pediatric centers across four continents. Patients with a diverse clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux phenotypes were included, covering suspected GERD, diagnosed GERD, NERD, RH, and FH, as shown in Table 1. Table 2 summarizes the characteristics of the included studies. In the majority of studies, endoscopic and histologic confirmation of the GERD spectrum was established. Patients were off treatment at the time of impedance monitoring in all studies.

Table 1.
The clinical spectrum of the gastroesophageal reflux phenotypes in the included articles and the impedance parameters (PSPW index, MNBI).

Table 2.
Overview of the key characteristics found in the eligible studies.
The types of impedance parameters that were determined were the PSPW index in six out of eight studies and MNBI in eight out of eight studies. In the majority of studies, data were reported as mean ± standard deviation, so an overall mean ± standard derivation was calculated for the principal gastroesophageal reflux disease phenotypes (GERD, NERD, RH, and FH), as can be seen in Table 3. One study [29] reported the impedance parameters as the median and interquartile rate, so its results were reported exactly and not included in the overall score.

Table 3.
Impedance parameters (PSPW index, MNBI) for the main gastroesophageal reflux phenotypes.
4. Discussion
Emerging evidence indicates the existence of different phenotypes in GERD, underscored by multifaceted underlying mechanisms, contributing to varying symptom perception and potential treatment outcomes [36]. Non-erosive reflux disease stands as the predominant type of GERD across all age groups, delineated recently into three distinct phenotypes based on the Rome IV esophageal criteria: NERD, RH, and FH, [1,24,37]. Blasi et al. [29] suggest that FH is the most prevalent pediatric non-erosive esophageal phenotype at 38.2%, followed by NERD at 26.5% and RH at 20.6%, confirming the accuracy of the existing data [37].
Understanding the mechanism implicated in the spectrum of GERD phenotypes in children is essential to tailor the treatment.
Acid exposure of the esophageal mucosa is known to disrupt intercellular junctional complexes, leading to a subsequent leak between cells and the dilation of intercellular spaces in the epithelium. This damaged epithelium exhibits lower electrical resistance compared to healthy tissue, resulting in decreased impedance in pH-MII [38,39,40,41,42].
4.1. MNBI
Four studies included in this review [29,30,31,35] demonstrated that patients with pathological acid exposure have significantly lower MNBI values compared to those with normal acid exposure. This inverse correlation between acid exposure and MNBI has also been observed in adults [16,17,19].
Eiamkulbutr et al. [25] described MNBI as having a good discriminatory ability to diagnose GERD, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.726 (95% CI: 0.581–0.870). The study identified a cutoff value of 1466 ohms for MNBI, yielding a sensitivity of 50.0% and a specificity of 33.33%. In adult studies, MNBI was used to diagnose GERD, with an AUC of 0.876 (95% CI: 0.833–0.918). The best cutoff value identified was 2292 ohms [12]. Another study [13] reported a cutoff of 2061 ohms, with an AUC of 0.792. This cutoff yielded a sensitivity of 74.9% and a specificity of 67.4% [13]. Further research and validation are necessary to establish standardized diagnostic criteria and optimize the clinical utility of MNBI in GERD diagnosis.
Rosado-Arias et al. [33] showed that children presenting severe esophagitis have a lower MNBI compared to patients with non-severe esophagitis, suggesting that the measurement of nocturnal baseline impedance may serve as a valuable diagnostic tool, potentially obviating the necessity for upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in the assessment of esophagitis. Blasi et al. [29] demonstrated a reduced MNBI among children diagnosed with NERD compared to those diagnosed with RH and FH. In addition, Tortoriello et al. [30] revealed a significantly lower MNBI in pediatric patients with GERD compared to those with RH and FH, and Sabban et al. [32] showed statistically significantly lower values in children with RH compared to the group diagnosed with FH (p = 0.001).
These observations are consistent with the results described in adults, where MNBI has been shown to be useful in assessing GERD phenotypes accurately, especially when conventional metrics provide ambiguous results [11,22,43,44,45]. Studies have demonstrated that a low MNBI is associated with an abnormal reflux burden, fragmented peristalsis, and ineffective esophageal motility, such as erosive esophagitis; this is compared to those with less severe mucosal damage, such as non-erosive reflux disease and FH [12,45]. Additionally, MNBI has been shown to be lower in patients with RH and NERD compared to those with FH and healthy individuals [46]. Furthermore, MNBI has been found to distinguish patients with NERD from patients with FH with high accuracy [22,47].
In children, low MNBI values may serve as a useful predictor of endoscopically confirmed reflux esophagitis, offering the advantage of being less invasive and not requiring fasting or sedation.
4.2. PSPW
Two studies [30,35] showed that the PSPW index was significantly lower in children with a conclusive GERD diagnosis compared to non-erosive phenotypes, revealing an inverse association between the PSPW index and acid exposure time. Blasi et al. [29] observed that the PSPW index was lower in NERD children compared to other non-erosive phenotypes. While no statistically significant variances were identified among various non-erosive reflux phenotypes, their study unveiled an inverse correlation between the PSPW index and acid exposure time, indicating a potential link between a lower PSPW index and a prolonged exposure to acid.
In a study conducted by Sabban et al. [32], the PSPW index showed statistically significant lower values in patients with the RH phenotype compared to those with FH (p = 0.01). The same group conducted a two-center cohort study [34] that revealed differences in the PSPW index in children according to their clinical presentation. Those with the respiratory symptoms of GERD had a lower PSPW index and a higher MNBI compared to those with gastrointestinal symptoms.
These results are consistent with adult studies that have strong data supporting the use of the PSPW index in investigating GERD patients. The PSPW index has been found to be lower in acid reflux-predominant GERD phenotypes, such as erosive esophagitis (EE) and non-erosive reflux disease (NERD), compared to esophageal hypersensitivity-predominant phenotypes [48].
A retrospective analysis involving adult GERD patients resistant to PPI treatment showed significantly lower PSPW index values in those with esophagitis who did not respond to treatment compared to those with healed esophagitis or non-erosive reflux disease (p = 0.003). This suggests that the PSPW index is a good measure of the effectiveness of clearing both acidic and weakly acidic refluxes [49].
Another study highlighted a strong negative relationship (r = −0.889) between the bolus clearance time and PSPW index, emphasizing the importance of esophageal clearance mechanisms [50]. Moreover, there was a positive correlation (r = 0.623) between the PSPW index and baseline impedance values, indicating the role of chemical clearance in maintaining mucosal integrity. The PSPW index also correlated directly (r = 0.626) with the esophageal contractile reserve, which inversely correlates with the acid exposure time, suggesting that acid exposure has an impact on esophageal muscle contractility [51].
In a prospective multi-center study [52], among the MII-pH parameters, only the PSPW index independently predicted resistance to GERD treatment (OR 1.082, 95% CI 1.022–1.146, p = 0.007).
Furthermore, the diagnostic value of the PSPW index has been highlighted in adult studies evaluating its performance in identifying patients with reflux disease, with high AUC values observed, indicating its potential ability to perform accurate disease identification [11,12,20,45].
Limitations: The constraints of this systematic review stem from the limitations inherent in the studies that were included. Overall, a small number of patients, around four hundred (479), were included in the analysis due to the fact that some studies had small samples of cases (defined as fewer than 50 patients). Different definitions were used for pathological AET. Some studies used the British Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition BSPGHAN Motility Working Group criteria [53] (>7% in children aged ≥1 year, and >10% in children aged <1 year, or if reflux episodes occur ≥70 times in children aged ≥1 year, and ≥100 times in children aged <1 year or positive symptoms). Other studies [31] considered the pathologic AET as >5% in patients >1 year or >10% in those <1 year. Extended follow-up periods are necessary to enhance the assessment of the significance of these innovative parameters. Only one study [29] followed the patients in the long term (follow-up duration: 28.8 ± 21.8 months).
In summary, the studies reviewed provide valuable insights into the utility of the PSPW index and MNBI in children with GERD. They underscore the potential use of these parameters as diagnostic markers and emphasize the need for tailored approaches in pediatric GERD management. However, further research with a high number of patients is warranted to establish standardized protocols and guidelines for the use of the novel pH-impedance parameters in pediatric populations.
Author Contributions
R.S.P. had the idea for the article and wrote the manuscript. R.S.P. and L.E.C. performed the literature search and data analysis. D.F. and D.L.D. drafted and critically revised the work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rosen, R.; Vandenplas, Y.; Singendonk, M.; Cabana, M.; DiLorenzo, C.; Gottrand, F.; Gupta, S.; Langendam, M.; Staiano, A.; Thapar, N.; et al. Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice Guidelines: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 516–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, A.; Pesce, M.; Thapar, N.; Borrelli, O. Gastro-Esophageal Reflux in Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Hauser, B. An Updated Review on Gastro-Esophageal Reflux in Pediatrics. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 9, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojsak, I.; Ivković, L.; Trbojević, T.; Pavić, I.; Jadrešin, O.; Mišak, Z.; Kolaček, S. The Role of Combined 24-h Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance-PH Monitoring in the Evaluation of Children with Gastrointestinal Symptoms Suggesting Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilic, D.; Fröhlich, T.; Nöh, F.; Pappas, A.; Schmidt-Choudhury, A.; Köhler, H.; Skopnik, H.; Wenzl, T.G. Detection of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children Using Combined Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance and PH Measurement: Data from the German Pediatric Impedance Group. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 650–654.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wijk, M.P.; Benninga, M.A.; Omari, T.I. Role of the Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance Technique in Infants and Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 48, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singendonk, M.M.J.; Benninga, M.A.; van Wijk, M.P. Reflux Monitoring in Children. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzl, T.G.; Benninga, M.A.; Loots, C.M.; Salvatore, S.; Vandenplas, Y. Indications, Methodology, and Interpretation of Combined Esophageal Impedance-PH Monitoring in Children: ESPGHAN EURO-PIG Standard Protocol. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quitadamo, P.; Tambucci, R.; Mancini, V.; Cristofori, F.; Baldassarre, M.; Pensabene, L.; Francavilla, R.; Di Nardo, G.; Caldaro, T.; Rossi, P.; et al. Esophageal PH-Impedance Monitoring in Children: Position Paper on Indications, Methodology and Interpretation by the SIGENP Working Group. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1522–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzoni, M.; de Bortoli, N.; Frazzoni, L.; Tolone, S.; Savarino, V.; Savarino, E. Impedance-PH Monitoring for Diagnosis of Reflux Disease: New Perspectives. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sararu, E.R.; Peagu, R.; Fierbinteanu-Braticevici, C. Association between Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance (MNBI) and Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index (PSPW) in GERD Patients. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazzoni, M.; Savarino, E.; de Bortoli, N.; Martinucci, I.; Furnari, M.; Frazzoni, L.; Mirante, V.G.; Bertani, H.; Marchi, S.; Conigliaro, R.; et al. Analyses of the Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index and Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Parameters Increase the Diagnostic Yield of Impedance-PH Monitoring of Patients with Reflux Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Guo, Z.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, C. Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance: Influencing Factors and Diagnostic Value in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Technol. Health Care 2023, 31, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribolsi, M.; De Bortoli, N.; Frazzoni, M.; Marchetti, L.; Savarino, E.; Cicala, M. Proximal Esophageal Impedance Baseline Increases the Yield of Impedance-PH and Is Associated with Response to PPIs in Chronic Cough Patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2024, 36, e14775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzoni, M.; de Bortoli, N.; Frazzoni, L.; Furnari, M.; Martinucci, I.; Tolone, S.; Farioli, A.; Marchi, S.; Fuccio, L.; Savarino, V.; et al. Impairment of Chemical Clearance and Mucosal Integrity Distinguishes Hypersensitive Esophagus from Functional Heartburn. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Wang, D.; Sainani, N.; Sayuk, G.S.; Gyawali, C.P. Distal Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance on PH-Impedance Monitoring Predicts Reflux Burden and Symptomatic Outcome in Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengarajan, A.; Savarino, E.; Della Coletta, M.; Ghisa, M.; Patel, A.; Gyawali, C.P. Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Correlates With Symptom Outcome When Acid Exposure Time Is Inconclusive on Esophageal Reflux Monitoring. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.N.; Wang, C.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Chuang, C.Y.; Tsou, Y.A.; Fu, J.C.; Yang, S.S.; Chang, C.S.; Lien, H.C. Distal Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Predicts Pathological Reflux of Isolated Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Symptoms. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 29, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, B.D.; Rengarajan, A.; Ribolsi, M.; Ghisa, M.; Quader, F.; Penagini, R.; de Bortoli, N.; Mauro, A.; Cicala, M.; Savarino, E.; et al. Postreflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index from PH-Impedance Monitoring Associates with Esophageal Body Motility and Esophageal Acid Burden. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e13973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.M.; Gao, Y.; Gao, F. Role of Esophageal Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance and Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index in Discriminating Chinese Patients with Heartburn. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzoni, L.; Frazzoni, M.; de Bortoli, N.; Tolone, S.; Furnari, M.; Martinucci, I.; Bertani, H.; Marchi, S.; Conigliaro, R.; Fuccio, L.; et al. Postreflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index and Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Can Link PPI-Responsive Heartburn to Reflux Better than Acid Exposure Time. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e13116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, B.; Wang, M.; Lin, L.; Jiang, L. Esophageal Nocturnal Baseline Impedance and Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index in Identifying Proton Pump Inhibitor-Refractory Non-Erosive Reflux Disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Lu, C.L.; Tseng, P.H.; Lin, L.; Hou, X.; Li, Y.; Zou, D.; Lv, B.; Xiang, X.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Esophageal Ambulatory Reflux Monitoring in Chinese Adults. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash Gyawali, C.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Savarino, E.; Zerbib, F.; Mion, F.; Smout, A.J.P.M.; Vaezi, M.; Sifrim, D.; Fox, M.R.; Vela, M.F.; et al. Modern Diagnosis of GERD: The Lyon Consensus. Gut 2018, 67, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiamkulbutr, S.; Dumrisilp, T.; Sanpavat, A.; Sintusek, P. Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children with Extraesophageal Manifestations Using Combined-Video, Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance-PH Study. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2023, 12, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Group, P.-P. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and Explanation. BMJ 2015, 350, g7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, S.; Bethel, A.; Rogers, M. Conduct and Reporting of Citation Searching in Cochrane Systematic Reviews: A Cross-Sectional Study. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 11, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Mckenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, E.; Stefanelli, E.; Tambucci, R.; Salvatore, S.; De Angelis, P.; Quitadamo, P.; Pacchiarotti, C.; Di Nardo, G.; Crocco, F.; Felici, E.; et al. Prevalence of Non-Erosive Esophageal Phenotypes in Children: A European Multicenter Study. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 29, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortoriello, A.Q.; Morán, E.S.; Zárate-Mondragón, F.; Monjaraz, E.T.; Castillejos, P.G.; Osorio, G.M.; Berumen, L.E. Novel Impedance Ph Monitoring Parameters in the Categorization of the Clinical Spectrum of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 77, S337–S338. [Google Scholar]
- Rosado-Arias, Y.; Toro-Monjaraz, E.M.; Cervantes-Bustamante, R.; Zarate-Mondragon, F.; Cadena-Leon, J.; Ignorosa-Arellano, K.; Loredo-Mayer, A.; Ramírez-Mayans, J. Low Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Is Associated with a Pathological Acid Exposure Time in Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2022, 74, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabban, J.C.; Ursino, F.; Micheletti, E.; De La Iglesia, P.; Orsi, M. Postreflux Swallow Induced Peristaltic Wave (PSPW) and Nocturnal Baseline Impedance (MNBI) in Children with Different Reflux Phenotypes? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, 567. [Google Scholar]
- Rosado-Arias, Y.M.R.; Monjaraz, E.M.T.; Mayans, J.A.R.; Mondragón, F.E.Z.; Arellano, K.R.I.; Barrios, E.M.; León, J.F.C.; Mayer, A.L.; Bustamante, R.C. Baseline Impedance and Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Values in Children with Erosive Oesophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Sabban, J.C.; Ursino, F.; Weinschelbaum, R.; Micheletti, E.; Romero, A.; Pagotto, V.; Orsi, M. Are There Differences in the Postreflux Swallow Induced Peristaltic Wave or in the Nocturnal Baseline Impedance in Children According to Symptom Presentation? A Two-Center Study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 73, S103–S104. [Google Scholar]
- Di Chio, T.; Chanpong, A.; Savarino, E.; Thapar, N.; Salliakellis, E.; Peroni, D.; Lindley, K.J.; De Bortoli, N.; Borrelli, O. Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance and Esophageal Chemical Clearance in a Pediatric Population of Patients with Suspected GERD: The Real Add on Value. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, L.B.L.B.; Rosen, R. The Spectrum of Reflux Phenotypes. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 15, 646–654. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, L.B.; Nurko, S.; Rosen, R. The Prevalence of Rome IV Nonerosive Esophageal Phenotypes in Children. J. Pediatr. 2017, 189, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Duan, L.; Wang, K.; Xu, Z.; Ge, Y.; Yang, C.; Han, Y. Esophageal Intraluminal Baseline Impedance Is Associated with Severity of Acid Reflux and Epithelial Structural Abnormalities in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, S.; Salvatoni, A.; Van Steen, K.; Ummarino, D.; Hauser, B.; Vandenplas, Y. Behind the (Impedance) Baseline in Children. Dis. Esophagus 2014, 27, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabban, J.C.; Bertoldi, G.D.; Ussher, F.; Christiansen, S.; Lifschitz, C.; Orsi, M.; Cohen Sabban, J.; Bertoldi, G.D.; Ussher, F.; Christiansen, S.; et al. Low-Impedance Baseline Values Predict Severe Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couselo, M.; Ibáñez, V.; Lluna, J.; Vila, J.J. Role of Intraluminal Esophageal Impedance Baseline in the Diagnosis of Esophagitis in Children. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 27, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilic, D.; Hankel, S.; Koerner-Rettberg, C.; Hamelmann, E.; Schmidt-Choudhury, A. The Role of Baseline Impedance as a Marker of Mucosal Integrity in Children with Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribolsi, M.; Gyawali, C.P.; Savarino, E.; Rogers, B.; Rengarajan, A.; Della Coletta, M.; Ghisa, M.; Cicala, M. Correlation between Reflux Burden, Peristaltic Function, and Mucosal Integrity in GERD Patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshikawa, Y.; Sawada, A.; Sonmez, S.; Nikaki, K.; Woodland, P.; Yazaki, E.; Sifrim, D. Measurement of Esophageal Nocturnal Baseline Impedance: A Simplified Method. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 26, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visaggi, P.; Mariani, L.; Svizzero, F.B.; Tarducci, L.; Sostilio, A.; Frazzoni, M.; Tolone, S.; Penagini, R.; Frazzoni, L.; Ceccarelli, L.; et al. Clinical Use of Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance and Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index for the Diagnosis of Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease. Esophagus 2022, 19, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.; Sullivan, B.; Charles, K.; McIntosh, T.; Davis, A.; Gellad, Z.; Shimpi, R.; Gyawali, C.P.; Patel, A. Esophageal Baseline Impedance from High-Resolution Impedance Manometry Correlates with Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance from PH-Impedance Monitoring. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 26, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimine, T.; Funaki, Y.; Kawamura, Y.; Tamura, Y.; Izawa, S.; Ebi, M.; Ogasawara, N.; Murotani, K.; Sasaki, M.; Kasugai, K. Convenient Method of Measuring Baseline Impedance for Distinguishing Patients with Functional Heartburn from Those with Proton Pump Inhibitor-Resistant Endoscopic Negative Reflux Disease. Digestion 2019, 99, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, A.; Sifrim, D.; Fujiwara, Y. Esophageal Reflux Hypersensitivity: A Comprehensive Review. Gut Liver 2023, 17, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzoni, M.; Bertani, H.; Manta, R.; Mirante, V.G.; Frazzoni, L.; Conigliaro, R.; Melotti, G. Impairment of Chemical Clearance Is Relevant to the Pathogenesis of Refractory Reflux Oesophagitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bortoli, N.; Martinucci, I.; Savarino, E.V.; Frazzoni, M.; Tutuian, R.; Tolone, S.; Piaggi, P.; Furnari, M.; Russo, S.; Bertani, L.; et al. Manually Calculated Oesophageal Bolus Clearance Time Increases in Parallel with Reflux Severity at Impedance-PH Monitoring. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinucci, I.; De Bortoli, N.; Savarino, E.; Piaggi, P.; Bellini, M.; Antonelli, A.; Savarino, V.; Frazzoni, M.; Marchi, S. Esophageal Baseline Impedance Levels in Patients with Pathophysiological Characteristics of Functional Heartburn. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazzoni, M.; Frazzoni, L.; Tolone, S.; De Bortoli, N.; Savarino, V.; Savarino, E. Lack of Improvement of Impaired Chemical Clearance Characterizes PPI-Refractory Reflux-Related Heartburn. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutalib, M.; Rawat, D.; Lindley, K.; Borrelli, O.; Perring, S.; Auth, M.K.H.; Thapar, N. BSPGHAN Motility Working Group Position Statement: Paediatric Multichannel Intraluminal PH Impedance Monitoring-Indications, Methods and Interpretation. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).