Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation: To Anticoagulate or Not?
Abstract
1. Introduction
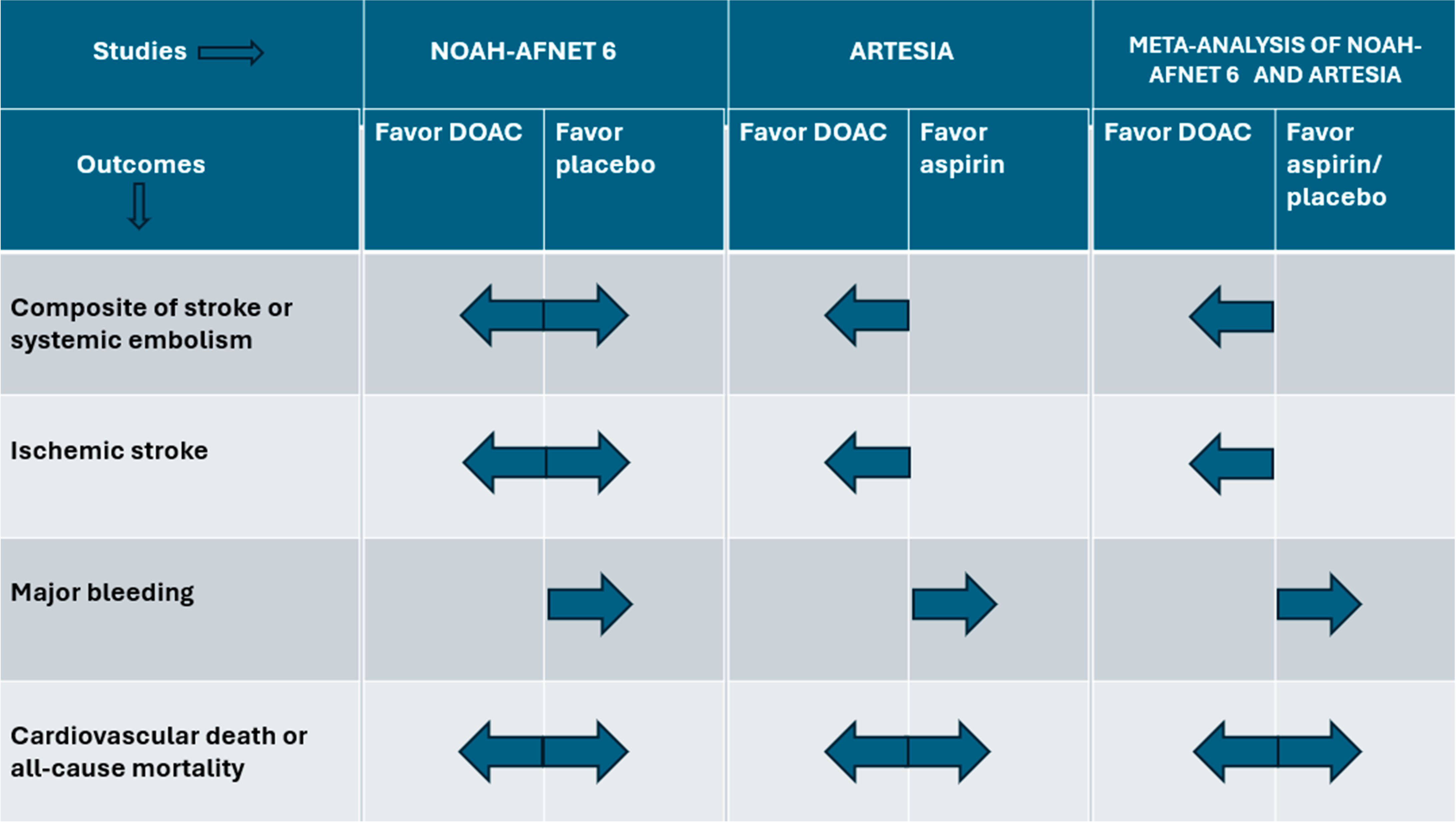
2. Results of the Studies
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Stark, B.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Roth, G.A.; Bisignano, C.; Abady, G.G.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abedi, V.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccini, J.P.; Fonarow, G.C. Preventing Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation—A Steep Climb away from Achieving Peak Performance. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noseworthy, P.A.; Kaufman, E.S.; Chen, L.Y.; Chung, M.K.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Joglar, J.A.; Leal, M.A.; McCabe, P.J.; Pokorney, S.D.; Yao, X.; et al. Subclinical and Device-Detected Atrial Fibrillation: Pondering the Knowledge Gap: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, e944–e963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rojo-Martinez, E.; Sandín-Fuentes, M.; Calleja-Sanz, A.I.; Cortijo-García, E.; García-Bermejo, P.; Ruiz-Piñero, M.; Rubio-Sanz, J.; Arenillas-Lara, J.F. High performance of an implantable Holter monitor in the detection of concealed paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke and a suspected embolic mechanism. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 57, 251–257. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanna, T.; Diener, H.C.; Passman, R.S.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Bernstein, R.A.; Morillo, C.A.; Rymer, M.M.; Thijs, V.; Rogers, T.; Beckers, F.; et al. Cryptogenic stroke and underlying atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2478–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, A.C.; Banki, N.M.; Ren, X.; Rao, V.A.; Go, A.S. Detection of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation by 30-day event monitoring in cryptogenic ischemic stroke: The Stroke and Monitoring for PAF in Real Time (SMART) Registry. Stroke 2012, 43, 2788–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brachmann, J.; Morillo, C.A.; Sanna, T.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Diener, H.C.; Bernstein, R.A.; Rymer, M.; Ziegler, P.D.; Liu, S.; Passman, R.S. Uncovering atrial fibrillation beyond short-term monitoring in cryptogenic stroke patients: Three-year results from the cryptogenic stroke and underlying atrial fibrillation trial. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2016, 9, e003333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayal, A.H.; Tian, M.; Kelly, K.M.; Jones, S.C.; Wright, D.G.; Singh, D.; Jarouse, J.; Brillman, J.; Murali, S.; Gupta, R. Atrial fibrillation detected by mobile cardiac outpatient telemetry in cryptogenic TIA or stroke. Neurology 2008, 71, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladstone, D.J.; Spring, M.; Dorian, P.; Panzov, V.; Thorpe, K.E.; Hall, J.; Vaid, H.; O’Donnell, M.; Laupacis, A.; Côté, R.; et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2024, 149, e1–e156, Erratum in Circulation 2024, 149, e167; Erratum in Circulation 2024, 149, e936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, W.M.; Simmons, J.D.; Interian, A., Jr.; Atapattu, S.A.; Castellanos, A.; Myerburg, R.J.; Mitrani, R.D. Clinical utility of intraatrial pacemaker stored electrograms to diagnose atrial fibrillation and flutter. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2001, 24 Pt 1, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healey, J.S.; Connolly, S.J.; Gold, M.R.; Israel, C.W.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Capucci, A.; Lau, C.P.; Fain, E.; Yang, S.; Bailleul, C.; et al. Subclinical atrial fibrillation and the risk of stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 120–129, Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toennis, T.; Bertaglia, E.; Brandes, A.; Dichtl, W.; Fluschnik, N.; de Groot, J.R.; Marijon, E.; Mont, L.; Lundqvist, C.B.; Cabanelas, N.; et al. The influence of atrial high-rate episodes on stroke and cardiovascular death: An update. Europace 2023, 25, euad166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaufman, E.S.; Israel, C.W.; Nair, G.M.; Armaganijan, L.; Divakaramenon, S.; Mairesse, G.H.; Brandes, A.; Crystal, E.; Costantini, O.; Sandhu, R.K.; et al. Positive predictive value of device-detected atrial high-rate episodes at different rates and durations: An analysis from ASSERT. Heart Rhythm. 2012, 9, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, P.; Toennis, T.; Goette, A.; Camm, A.J.; Diener, H.C.; Becher, N.; Bertaglia, E.; Lundqvist, C.B.; Borlich, M.; Brandes, A.; et al. Anticoagulation with Edoxaban in Patients with Atrial High-Rate Episodes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healey, J.S.; Lopes, R.D.; Granger, C.B.; Alings, M.; Rivard, L.; McIntyre, W.F.; Atar, D.; Birnie, D.H.; Boriani, G.; Camm, A.J.; et al. Apixaban for Stroke Prevention in Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, W.F.; Benz, A.P.; Becher, N.; Healey, J.S.; Granger, C.B.; Rivard, L.; Camm, A.J.; Goette, A.; Zapf, A.; Alings, M.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Patients with Device-Detected Atrial Fibrillation: A Study-Level Meta-Analysis of the NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESiA Trials. Circulation 2024, 149, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svendsen, J.H.; Diederichsen, S.Z.; Højberg, S.; Krieger, D.W.; Graff, C.; Kronborg, C.; Olesen, M.S.; Nielsen, J.B.; Holst, A.G.; Brandes, A.; et al. Implantable loop recorder detection of atrial fibrillation to prevent stroke (The LOOP Study): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 1507–1516, Erratum in Lancet 2021, 398, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glotzer, T.V.; Daoud, E.G.; Wyse, D.G.; Singer, D.E.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Hilker, C.; Miller, C.; Qi, D.; Ziegler, P.D. The relationship between daily atrial tachyarrhythmia burden from implantable device diagnostics and stroke risk: The TRENDS study. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, G.D.; Lowenstern, A.; Borre, E.; Chatterjee, R.; Goode, A.; Sharan, L.; Lapointe, N.A.; Raitz, G.; Shah, B.; Yapa, R.; et al. Stroke Prevention in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review Update [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 October (Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 214) Introduction. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534135/ (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Israel, C.W.; Ehrlich, J.R.; Grönefeld, G.; Klesius, A.; Lawo, T.; Lemke, B.; Hohnloser, S.H. Prevalence, characteristics and clinical implications of regular atrial tachyarrhythmias in patients with atrial fibrillation: Insights from a study using a new implantable device. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 38, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Trial Name | Study Design and Location | Study Duration | Test Drug (n)/Control (N) | Mean Age | CHA2DS2-VASc Score | Arrhythmia | Stroke or Systemic Embolism | Ischemic Stroke HR (95% CI) | Major Bleeding HR (95% CI) | Cardiovascular Death HR (95% CI) | All-Cause Mortality HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOAH-AFNET6 trial. Kirchhof et al. (2023) [15] | Investigator-initiated, DB, double-dummy, RCT. Multicenter. | 5 years | Edoxaban (1270)/Placebo (1266) | 77.5 ± 6.7 | 4 ± 1 (Median) | AHRE * | 0.65 (0.39 to 1.07) | 0.79 (0.45 to 1.39) | 2.10 (1.30 to 3.38) | 0.90 (CI, 0.62 to 1.31) | 1.16 (0.88 to 1.53) |
| ARTESIA trial. Healey et al. (2023) [16] | DB, double-dummy randomized trial. Multicenter | 6 years | Apixaban (2015)/Aspirin (1997) | 76.8 ± 7.6 | 3.9 ± 1.1 (Mean) | SCAF # | 0.63 (0.45 to 0.88) | 0.62 (0.43 to 0.91) | 1.36 (1.01 to 1.82) | 0.96 (0.73 to 1.25) | 1.04 (0.90 to 1.21) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kommu, S.; Sharma, P.P. Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation: To Anticoagulate or Not? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113236
Kommu S, Sharma PP. Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation: To Anticoagulate or Not? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(11):3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113236
Chicago/Turabian StyleKommu, Sharath, and Param P. Sharma. 2024. "Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation: To Anticoagulate or Not?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 11: 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113236
APA StyleKommu, S., & Sharma, P. P. (2024). Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation: To Anticoagulate or Not? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(11), 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113236






