A New Methodology to Determine the Orifice for Root Canal Configurations in First Permanent Molar Root and Canal Morphologies Using Micro-Computed Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Method and Approval
2.2. Sample Selection
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Scanning Procedure
2.5. Scan Alignment
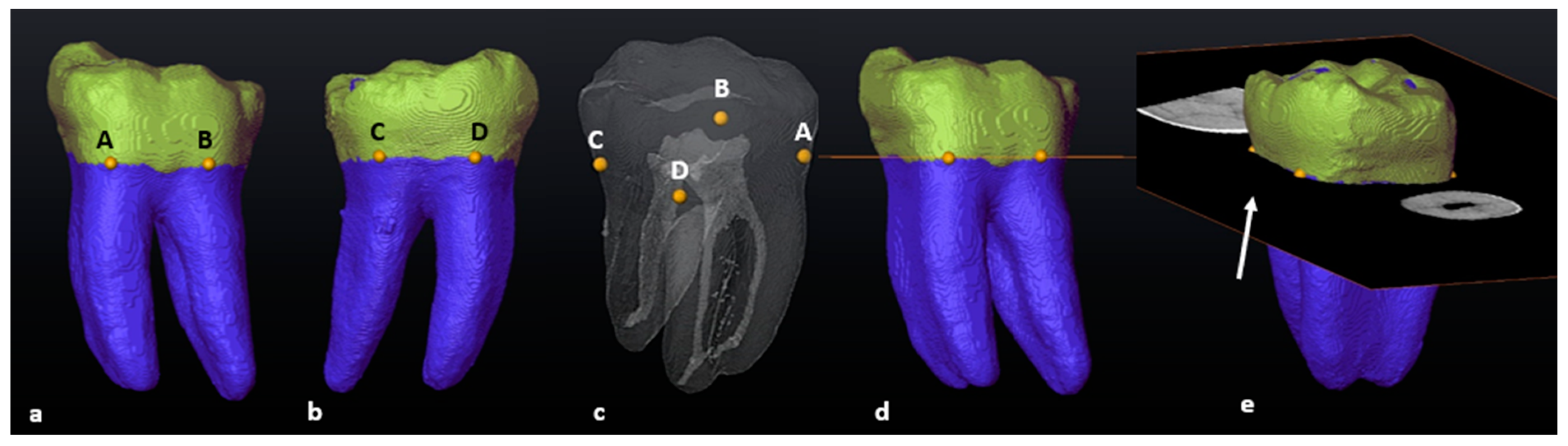
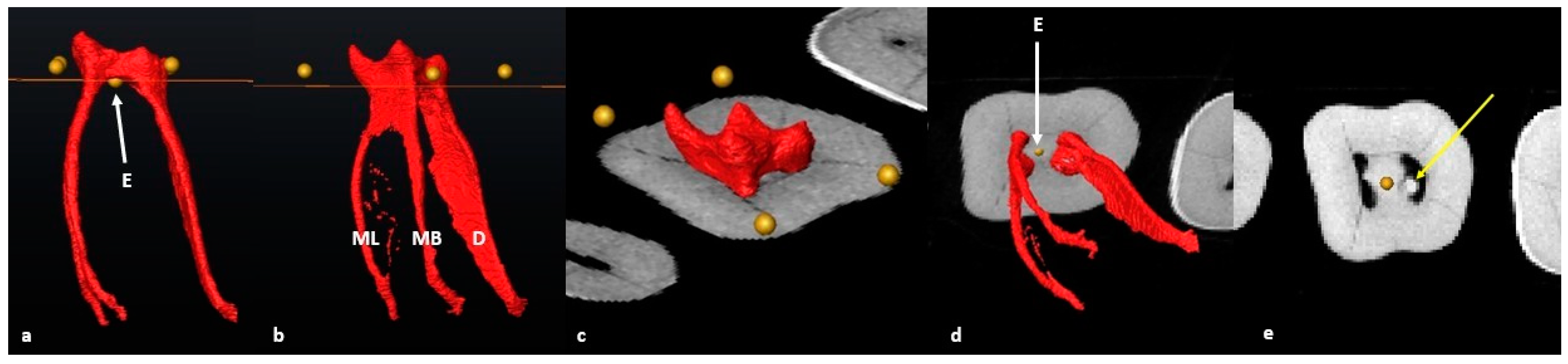
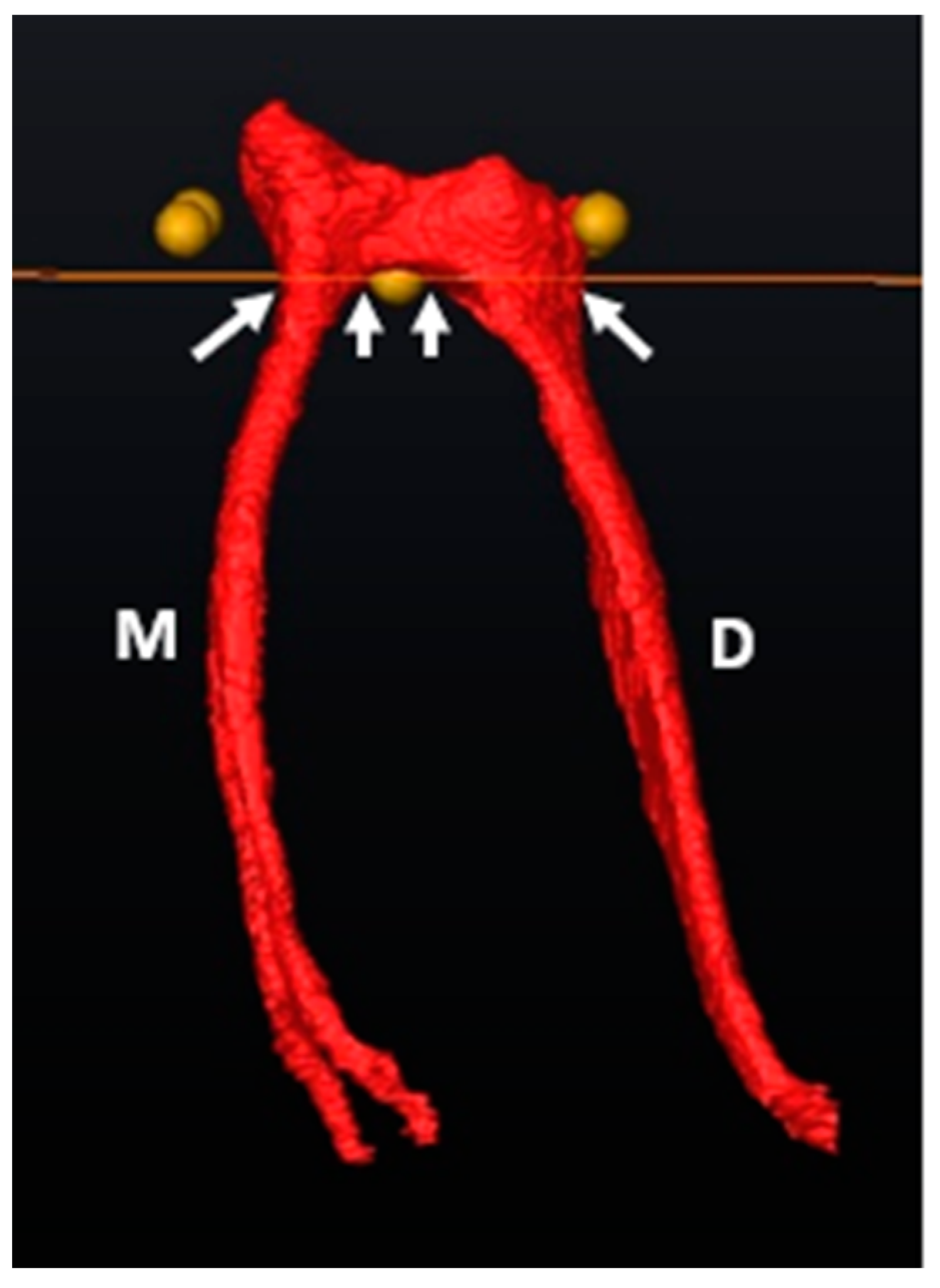
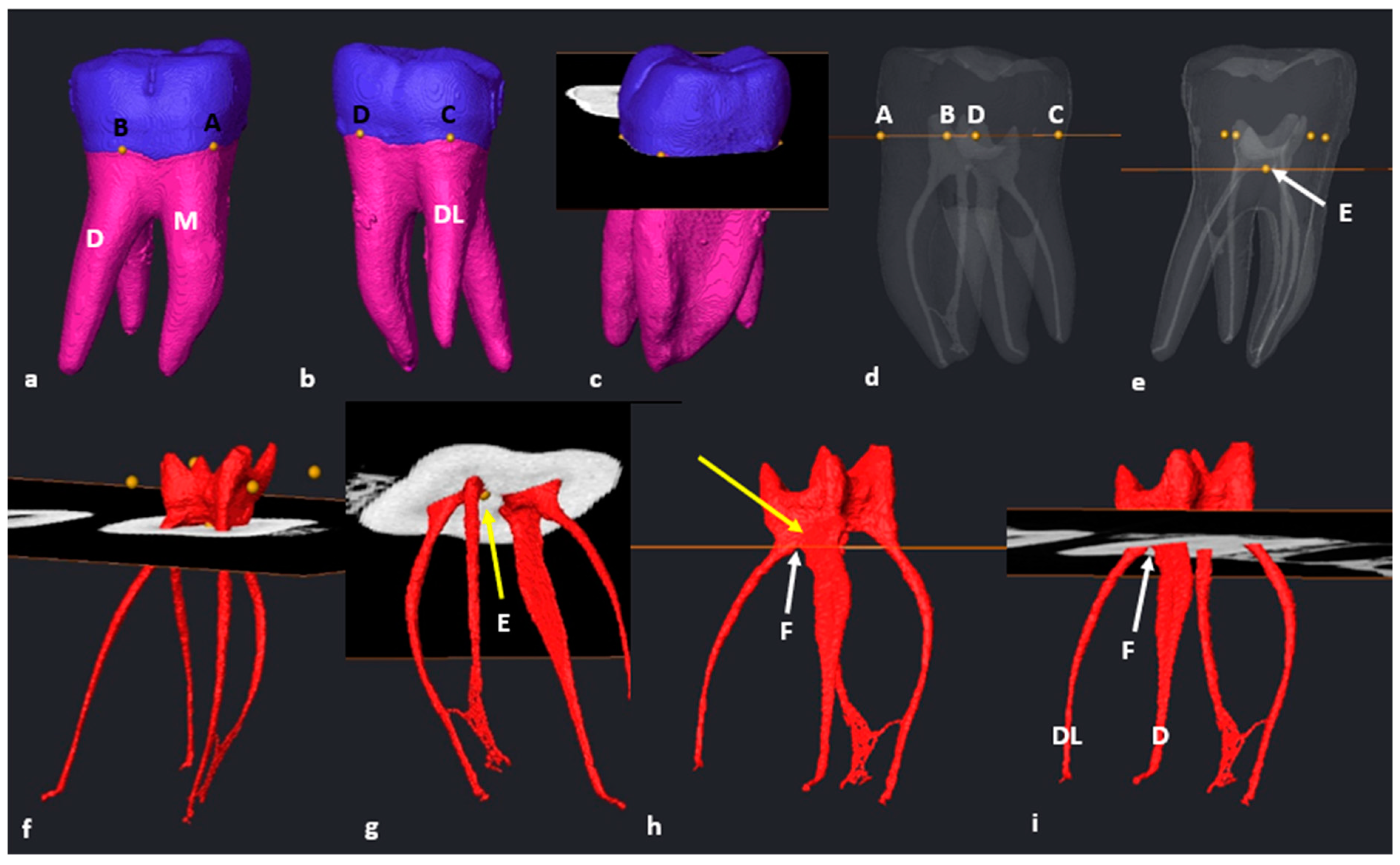
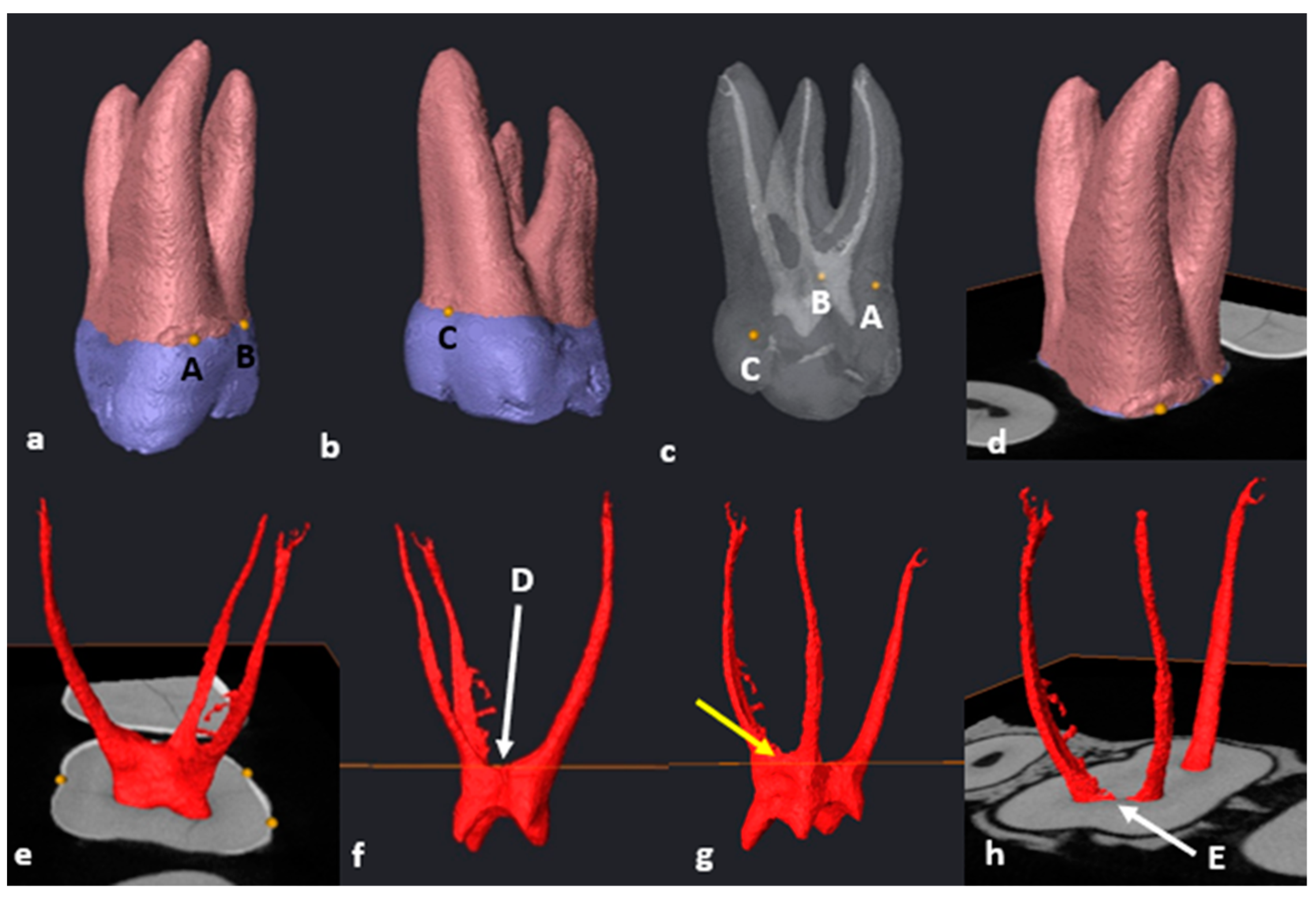
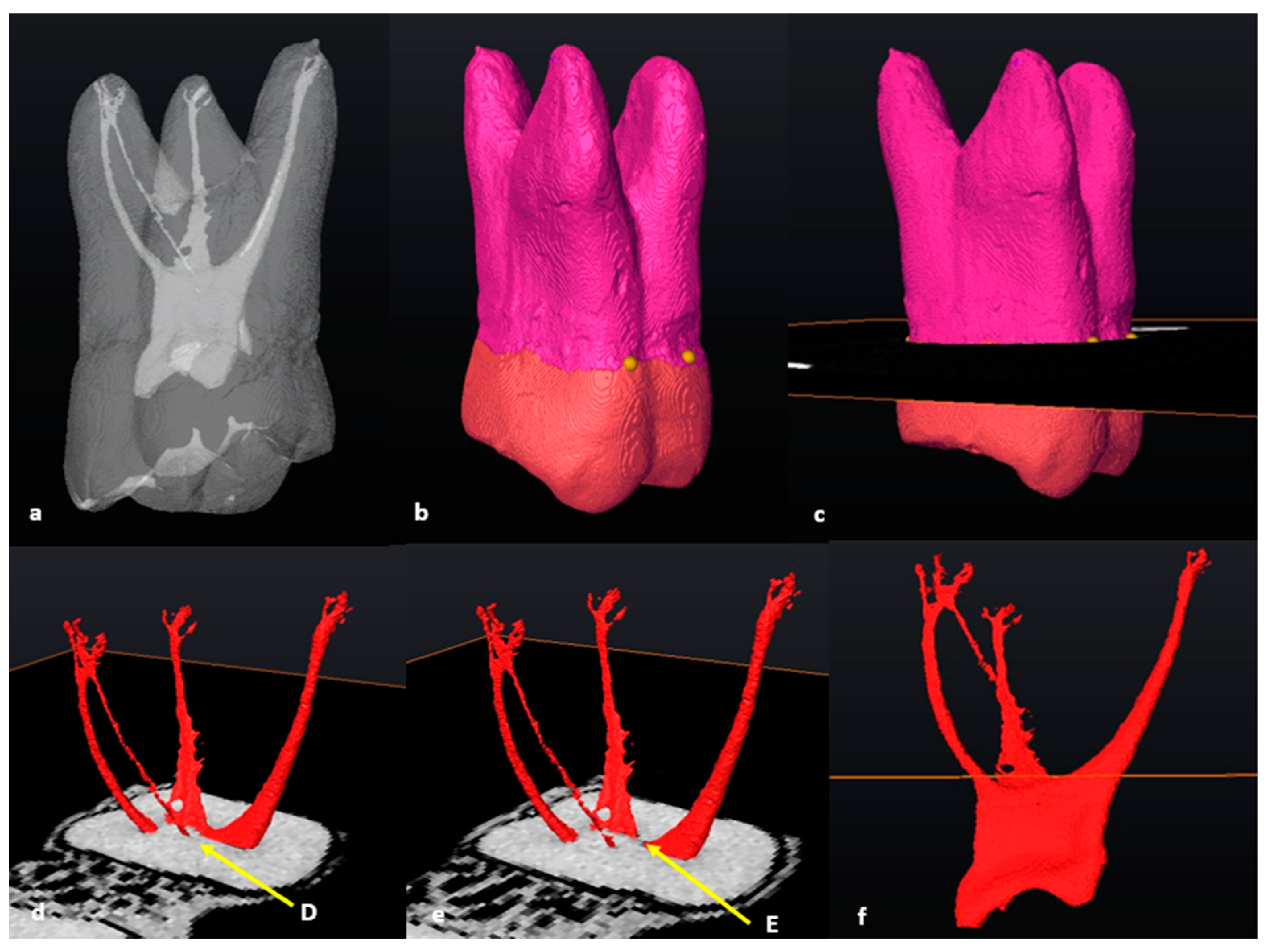
2.6. Segmentation and Landmark Identification
3. Results
3.1. Mandibular First Molars: Two Rooted
3.2. Mandibular First Molars: Three Rooted
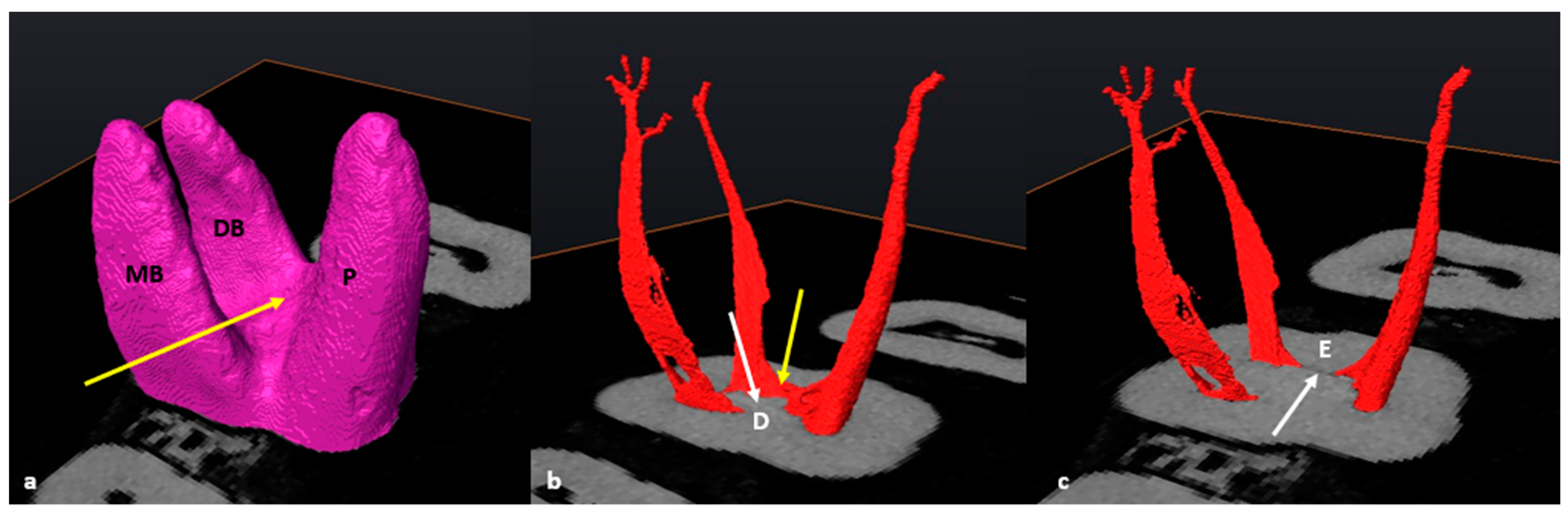
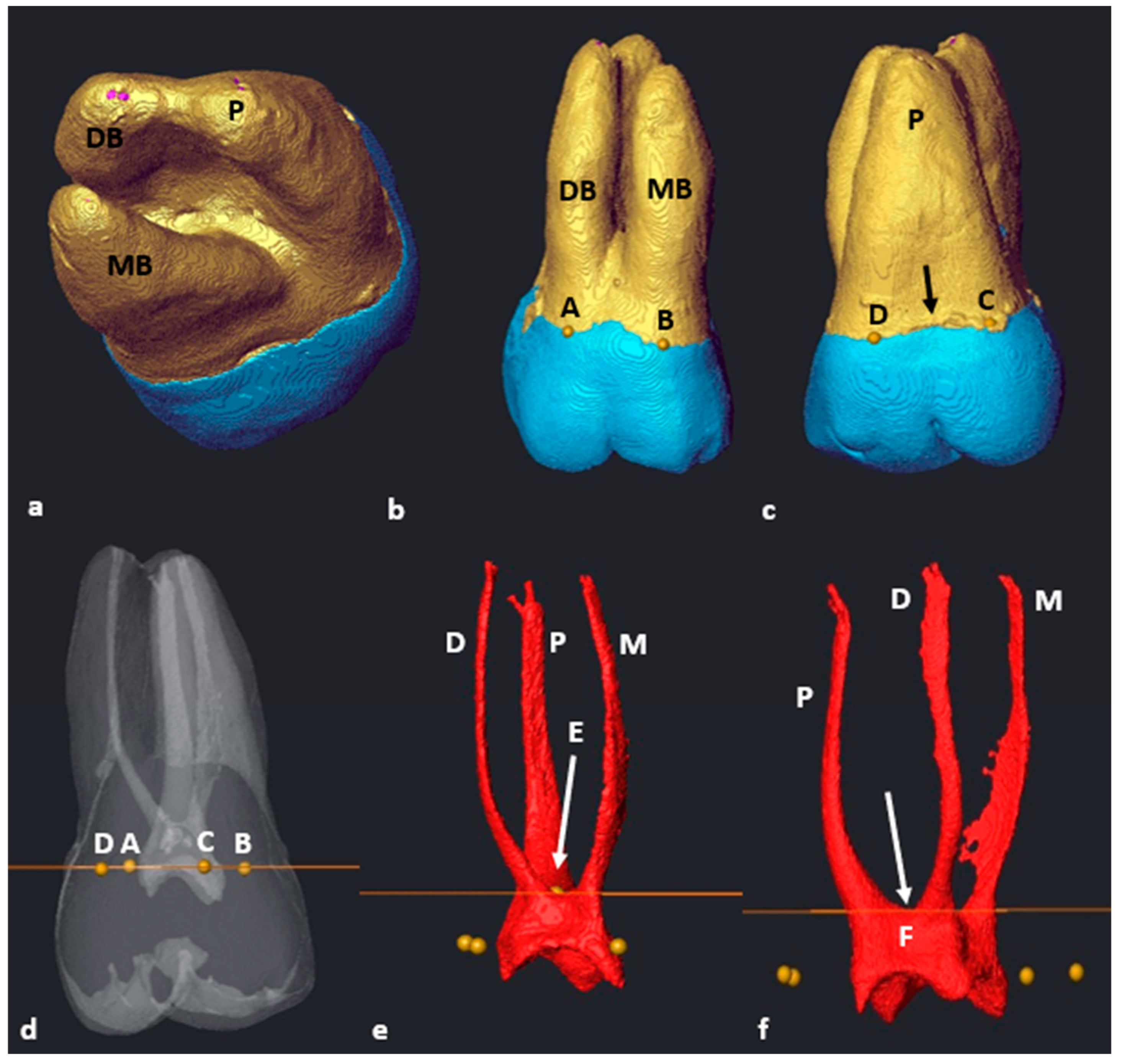
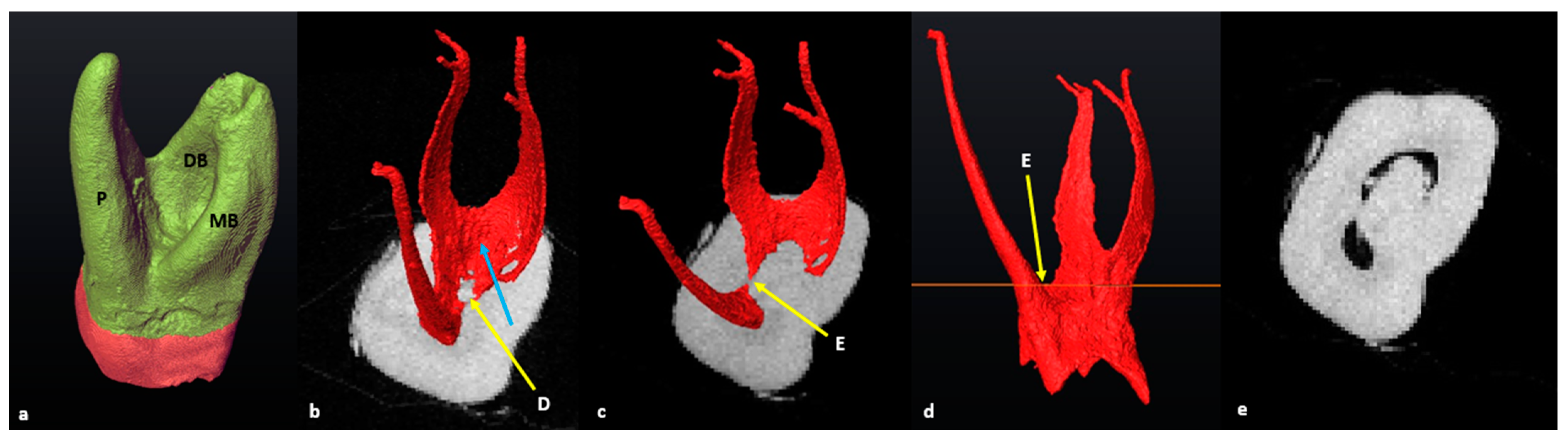
3.3. Maxillary First Molars: Three Separate Roots
3.4. Maxillary Molars: Variants in Mesial or Distal Bifurcations
3.5. Fused Roots
3.6. C-Shaped Canals
3.7. Taurodontism
3.8. Number of Roots
4. Discussion
4.1. Mandibular Molars
4.2. Maxillary Molars
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, B.; Shen, Y.; Cheung, G.S.P.; Xia, T.J. Defects in ProTaper S1 Instruments after Clinical Use: Longitudinal Examination. Int. Endod. J. 2005, 38, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vertucci, F.J. Root Canal Morphology and Its Relationship to Endodontic Procedures. Endod. Topics. 2005, 10, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourasia, H.R.; Meshram, G.K.; Warhadpande, M.; Dakshindas, D. Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Permanent Molars in an Indian Population. Int. J. Dent. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabinejad, M.; Fouad, A.; Shabahang, S. Endodontics E-Book: Principles and Practice, 6th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: London, UK, 2021; pp. 471–493. [Google Scholar]
- Versiani, M.A.; Sousa-Neto, M.D.; Basrani, B. The Root Canal Dentition in Permanent Dentition, 1st ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 89–240. [Google Scholar]
- Rwenyonyi, C.M.; Kutesa, A.M.; Muwazi, L.M.; Buwembo, W. Root and Canal Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Permanent Molar Teeth in a Ugandan Population. Int. Endod. J. 2007, 40, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelakantan, P.; Subbarao, C.; Ahuja, R.; Subbarao, C.V.; Gutmann, J.L. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study of Root and Canal Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars in an Indian Population. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Woo, J. Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars Analyzed by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in a Korean Population: Variations in the Number of Roots and Canals and the Incidence of Fusion. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, J.N.; Mata, A.; Marques, D.; Caramês, J. Prevalence of Root Fusions and Main Root Canal Merging in Human Upper and Lower Molars: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Vivo Study. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Yang, X.; Qian, L.; Wei, B.; Gong, Y. Analysis of the Root and Canal Morphologies in Maxillary First and Second Molars in a Chinese Population Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tredoux, S.; Warren, N.; Buchanan, G.D. Root and Canal Configurations of Mandibular First Molars in a South African Subpopulation. J. Oral Sci. 2021, 63, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Fan, B.; Fan, W.; Gutmann, J.L. Root and Root Canal Morphology in Maxillary Second Molar with Fused Root from a Native Chinese Population. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weine, F.S.; Healey, H.J.; Gerstein, H.L. Evanson Canal Configuration in the Mesiobuccal Root of the Maxillary First Molar and Its Endodontic Significance. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1969, 28, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vertucci, F.; Seelig, A.; Gillis, R. Root Canal Morphology of the Human Maxillary Second Premolar. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1974, 38, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weine, F.S. Endodontic Therapy, 3rd ed.; CV Mosby: St. Louis, MI, USA, 1982; pp. 288–306. [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque, D.V.; Kottoor, J.; Velmurugan, N. A New Anatomically Based Nomenclature for the Roots and Root Canals—Part 2: Mandibular Molars. Int. J. Dent. 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kottoor, J.; Albuquerque, D.V.; Velmurugan, N. A New Anatomically Based Nomenclature for the Roots and Root Canals—Part 1: Maxillary Molars. Int. J. Dent. 2012, 2012, 120565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.M.A.; Ibrahim, N.; Mohamad, N.S.; Nambiar, P.; Muhammad, R.F.; Yusoff, M.; Dummer, P.M.H. Application of a New System for Classifying Root and Canal Anatomy in Studies Involving Micro-computed Tomography and Cone Beam Computed Tomography: Explanation and Elaboration. Int. Endod. J. 2021, 54, 1056–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.M.A.; Dummer, P.M.H. Advantages and Applications of a New System for Classifying Roots and Canal Systems in Research and Clinical Practice. Eur. Endod. J. 2018, 3, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.M.A. A Critical Analysis of Laboratory and Clinical Research Methods to Study Root and Canal Anatomy. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55, 229–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAE. American Association of Endodontists. Glossary of Endodontic Terms. 2020. Available online: https://www.aae.org/specialty/clinical-resources/glossary-endodontic-terms/ (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Ahmed, H.M.A.; Versiani, M.A.; De-Deus, G.; Dummer, P.M.H. A New System for Classifying Root and Root Canal Morphology. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanci, A. Ten Cate’s Oral Histology. Development, structure, and function 2013, 8, 79–289. [Google Scholar]
- Schied, R.; Weiss, G. Woelfel’s Dental Anatomy, 8th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 3–41. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, S.J.; Ash, M.M. Wheeler’s Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion, 9th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MI, USA, 2010; pp. 111–112. [Google Scholar]
- Nusstein, J.M. Application of Root and Pulp Morphology Related to Endodontic Therapy. In Woelfel’s Dental Anatomy; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 231–249. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.M.A.; Che Ab Aziz, Z.A.; Azami, N.H.; Farook, M.S.; Khan, A.A.; Mohd Noor, N.S.; Ayoub, A.A.; Imran, Z.A.; Halim, M.S.; Pai, A.R.V. Application of a New System for Classifying Root Canal Morphology in Undergraduate Teaching and Clinical Practice: A National Survey in Malaysia. Int. Endod. J. 2020, 53, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.B.; Alyassin, A.M.; Peters, D.D.; Carnes, D.L.; Lancaster, J. Microcomputed Tomography: An Advanced System for Detailed Endodontic Research. J. Endod. 1995, 21, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, N.M.; Plotino, G.; Gambarini, G.; Testarelli, L.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Pecci, R.; Bedini, R. Present and Future in the Use of Micro-CT Scanner 3D Analysis for the Study of Dental and Root Canal Morphology. Ann. Dell’istituto Super. Sanita 2012, 48, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Briseño-Marroquín, B.; Paqué, F.; Maier, K.; Willershausen, B.; Wolf, T.G. Root Canal Morphology and Configuration of 179 Maxillary First Molars by Means of Micro–Computed Tomography: An Ex Vivo Study. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 2008–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, O.A.; Laib, A.; Rüegsegger, P.; Barbakow, F. Three-Dimensional Analysis of Root Canal Geometry by High-Resolution Computed Tomography. J. Dent. Res. 2000, 79, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Cristancho, A.; González-Osuna, L.; Poblete, D.; Cafferata, E.A.; Carvajal, P.; Lozano, C.P.; Vernal, R. Micro-Tomographic Characterization of the Root and Canal System Morphology of Mandibular First Premolars in a Chilean Population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versiani, M.A.; Pécora, J.D.; Sousa-Neto, M.D. The Anatomy of Two-rooted Mandibular Canines Determined Using Micro-computed Tomography. Int. Endod. J. 2011, 44, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versiani, M.A.; Pécora, J.D.; de Sousa-Neto, M.D. Root and Root Canal Morphology of Four-Rooted Maxillary Second Molars: A Micro–Computed Tomography Study. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versiani, M.A.; Pécora, J.D.; Sousa-Neto, M.D. Microcomputed Tomography Analysis of the Root Canal Morphology of Single-rooted Mandibular Canines. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Abbé, E.N.; Loots, M.; Meiring, J.H. The Pretoria Bone Collection: A Modern South African Skeletal Sample. HOMO 2005, 56, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Abbé, E.N.; Krüger, G.C.; Theye, C.E.; Hagg, A.C.; Sapo, O. The Pretoria Bone Collection: A 21st Century Skeletal Collection in South Africa. J. Forensic. Sci. 2021, 1, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.W.; De Beer, F.C. Characteristics of the Micro-Focus X-Ray Tomography Facility (MIXRAD) at Necsa in South Africa. In Proceedings of the 18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, Durban, South Africa, 16–20 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Krasner, P.; Rankow, H.J. Anatomy of the Pulp-Chamber Floor. J. Endod. 2004, 30, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westenberger, P. Avizo—Three-Dimensional Visualization Framework. In Proceedings of the Geoinformatics—Data to Knowledge Conference, Potsdam, Germany, 11–13 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, F.; Beucher, S. Morphological Segmentation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 1990, 1, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerdink, J.B.T.M.; Meijster, A. The Watershed Transform: Definitions, Algorithms and Parallelization Strategies. Fundam. Inform. 2000, 41, 187–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Fan, B.; Gutmann, J.L.; Cheung, G.S. Identification of C-Shaped Canal in Mandibular Second Molars. Part I: Radiographic and Anatomical Features Revealed by Intraradicular Contrast Medium. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melton, D.C.; Krell, K.V.; Fuller, M.W. Anatomical and Histological Features of C-Shaped Canals in Mandibular Second Molars. J. Endod. 1991, 17, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M. Taurodontism Part 1: History, Aetiology and Molecular Signalling, Epidemiology and Classification. Dent. Update. 2019, 46, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.C.; Consolaro, A. Anthropological and Clinical Importance of Distolingual Root in the Permanent Lower Molars. Endodoncia 1997, 15, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.M.A.; Neelakantan, P.; Dummer, P.M.H. A New System for Classifying Accessory Canal Morphology. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolk, L. Bemerkungen Über Wurzelvariationen Am Menschlichen Unteren Molaren. Z. Morphol. Anthropol. 1915, 17, 605–610. [Google Scholar]
- Sperber; Moreau Study of the Number of Roots and Canals in Senegalese First Permanent Mandibular Molars. Int. Endod. J. 1998, 31, 117–122. [CrossRef]
- Rwenyonyi, C.M.; Kutesa, A.; Muwazi, L.M.; Buwembo, W. Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular First and Second Permanent Molar Teeth in a Ugandan Population. Odontology 2009, 97, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirbuga, S.; Sekerci, A.; Dincer, A.; Cayabatmaz, M.; Zorba, Y. Use of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography to Evaluate Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular First and Second Molars in Turkish Individuals. Med. Oral. 2013, e737–e744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calberson, F.L.; De Moor, R.J.; Deroose, C.A. The Radix Entomolaris and Paramolaris: Clinical Approach in Endodontics. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irhaim, A.A. Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary First Molars Cone Beam Computed Tomography in a Sample of Patients Treated at the Wits Oral Health Centre. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, 16 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mashyakhy, M.; Chourasia, H.R.; Jabali, A.; Almutairi, A.; Gambarini, G. Analysis of Fused Rooted Maxillary First and Second Molars with Merged and C-Shaped Canal Configurations: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Correlations in a Saudi Arabian Population. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsesis, I.; Shifman, A.; Kaufman, A.Y. Taurodontism: An Endodontic Challenge. Report of a Case. J. Endod. 2003, 29, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayashankara, C.M.; Shivanna, A.K.; Sridhara, K.S.; Kumar, P.S. Taurodontism: A Dental Rarity. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 17, 478. [Google Scholar]
- De-Deus, G.; Belladonna, F.G.; Silva, E.J.N.L.; Marins, J.R.; Souza, E.M.; Perez, R.; Lopes, R.T.; Versiani, M.A.; Paciornik, S.; Neves, A. de A. Micro-CT Evaluation of Non-Instrumented Canal Areas with Different Enlargements Performed by NiTi Systems. Braz. Dent. J. 2015, 26, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versiani, M.A.; Ordinola-Zapata, R. Root Canal Anatomy: Implications in Biofilm Disinfection. In Root Canal Anatomy: Implications in Biofilm Disinfection. In The Root Canal Biofilm, 1st ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 23–52. [Google Scholar]
- Cleghorn, B.M.; Christie, W.H.; Dong, C.C.S. Root and Root Canal Morphology of the Human Permanent Maxillary First Molar: A Literature Review. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moor, R.J.G. C-Shaped Root Canal Configuration in Maxillary First Molars. Int. Endod. J. 2002, 35, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-P.; Yang, S.-F.; Lee, G. The Root and Root Canal Anatomy of Maxillary Molars in a Chinese Population. Dent. Traumatol. 1988, 4, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Yang, J.; Gutmann, J.L.; Fan, M. Root Canal Systems in Mandibular First Premolars with C-Shaped Root Configurations. Part I: Microcomputed Tomography Mapping of the Radicular Groove and Associated Root Canal Cross-Sections. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, D.S.; Câmara, A.C.; Aguiar, C.M.; Do Nascimento, M.D.C.C.; De Araujo, L.F. A C-Shaped Canal in a Maxillary Second Molar: Prexion 3D Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Analysis. Acta. Stomatol. Croat. 2016, 50, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jonker, C.H.; Lambourn, G.; Oettlé, A.C.; Foschi, F.; Theye, C.; L’Abbé, E.N. A New Methodology to Determine the Orifice for Root Canal Configurations in First Permanent Molar Root and Canal Morphologies Using Micro-Computed Tomography. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010071
Jonker CH, Lambourn G, Oettlé AC, Foschi F, Theye C, L’Abbé EN. A New Methodology to Determine the Orifice for Root Canal Configurations in First Permanent Molar Root and Canal Morphologies Using Micro-Computed Tomography. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleJonker, Casper Hendrik, Guy Lambourn, Anna Catherina Oettlé, Federico Foschi, Charlotte Theye, and Ericka Noelle L’Abbé. 2024. "A New Methodology to Determine the Orifice for Root Canal Configurations in First Permanent Molar Root and Canal Morphologies Using Micro-Computed Tomography" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010071
APA StyleJonker, C. H., Lambourn, G., Oettlé, A. C., Foschi, F., Theye, C., & L’Abbé, E. N. (2024). A New Methodology to Determine the Orifice for Root Canal Configurations in First Permanent Molar Root and Canal Morphologies Using Micro-Computed Tomography. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010071







