Title Expression of FOXO3 and MAPK1 Genes in Patients with Benign Salivary Gland Tumors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Collection of Samples
2.3. Total RNA Extraction
2.4. Reverse Transcription
2.5. Real-Time PCR
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quer, M.; Hernandez-Prera, J.C.; Silver, C.E.; Casasayas, M.; Simo, R.; Vander Poorten, V.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Bradley, P.J.; Tong-Ng, W.; Rodrigo, J.P.; et al. Current Trends and Controversies in the Management of Warthin Tumor of the Parotid Gland. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeslet, A.S. Pleomorphic Adenoma: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2020, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, R.; Misra, S.; Misra, N.; Ashik, R.; Hussain, N.; Nayak, N.; Singh, P.R. Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Orbital Ectopic Lacrimal Gland: An Extremely Rare Occurrence with Review of Literature. Neurol. India 2022, 70, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Prera, J.C.; Skálová, A.; Franchi, A.; Rinaldo, A.; Vander Poorten, V.; Zbären, P.; Ferlito, A.; Wenig, B.M. Pleomorphic adenoma: The great mimicker of malignancy. Histopathology 2021, 79, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousra, Z.; Saliha, C. Pleomorphic adenoma of hard palate: A case report. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2021, 38, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Key, S.; Chia, C.; Hasan, Z.; Sundaresan, P.; Dwivedi, R.C.; Riffat, F. Systematic review of prognostic factors in carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma. Oral Oncol. 2022, 133, 106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obsil, T.; Obsilova, V. Structure/function relationships underlying regulation of FOXO transcription factors. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2263–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.T.D. Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 2479–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, B.J.; Willcox, D.C.; Donlon, T.A.; Willcox, B.J. FOXO3: A Major Gene for Human Longevity—A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2015, 61, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Ohuchida, K.; Fei, S.; Zheng, B.; Guan, W.; Feng, H.; Kibe, S.; Ando, Y.; Koikawa, K.; Abe, T.; et al. Inhibition of ERK1/2 in cancer-associated pancreatic stellate cells suppresses cancer-stromal interaction and metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Zong, C.S.; Xia, W.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ding, Q.; Xie, X.; Cheng, Y.; Muller, W.J.; Sahin, A.A.; Yu, D.; et al. ERK promotes tumorigenesis by inhibiting FOXO3a via MDM2-mediated degradation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Hung, M.C. A new fork for clinical application: Targeting forkhead transcription factors in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potente, M.; Urbich, C.; Sasaki, K.I.; Hofmann, W.K.; Heeschen, C.; Aicher, A.; Kollipara, R.; DePinho, R.; Zeiher, A.; Dimmeler, S.; et al. Involvement of Foxo transcription factors in angiogenesis and postnatal neovascularization. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2382–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, W.-Z.; Liu, T.; Feng, X.; Yang, N. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2015, 35, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handra-Luca, A.; Bilal, H.; Bertrand, J.C.; Fouret, P. Extracellular signal-regulated ERK-1/ERK-2 pathway activation in human salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma: Association to aggressive tumor behavior and tumor cell proliferation. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Shankar, S. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways causes activation of FOXO transcription factor, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. J. Mol. Signal. 2010, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Yu, D. Akt-FOXO3a signaling axis dysregulation in human oral squamous cell carcinoma and potent efficacy of FOXO3a-targeted gene therapy. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ma, J.; Xue, W.; Cheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ke, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; et al. The expression and prognosis of FOXO3a and Skp2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2009, 15, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Ma, X.; Li, H.Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, Q.; Zhang, P.; Song, E.-L.; Huang, Q.-B.; et al. Downregulation of FOXO3a promotes tumor metastasis and is associated with metastasis-free survival of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röijer, E.; Nordkvist, A.; Ström, A.-K.; Ryd, W.; Behrendt, M.; Bullerdiek, J.; Mark, J.; Stenman Mattias, K.G.; Andersson, G.S. Translocation, Deletion/Amplification, and Expression of HMGIC and MDM2 in a Carcinoma ex Pleomorphic Adenoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.C.T.; Lee, D.F.; Xia, W.; Golfman, L.S.; Ou-Yang, F.; Yang, J.Y.; Zou, Y.; Bao, S.; Saso, H.; Hung, M.-C.; et al. IκB kinase promotes tumorigenesis through inhibition of forkhead FOXO3a. Cell 2004, 117, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przezak, A.; Bielka, W.; Sroczyński, T.; Zakład Fizjologii, K. Czynniki transkrypcyjne FOXO-potencjalny punkt uchwytu leczenia chorób cywilizacyjnych. Farm Pol. 2020, 76, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, M.; Song, Y.H.; Yokomizo, A.; Kiyoshima, K.; Tada, Y.; Uchino, H.; Uchiumi, T.; Inokuchi, J.; Oda, Y.; Kuroiwa, K.; et al. Foxo3a suppression of urothelial cancer invasiveness through twist1, Y-box-binding protein 1, and E-cadherin regulation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5654–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzi, L.; Combes, E.; Vié, N.; Ayrolles-Torro, A.; Tosi, D.; Desigaud, D.; Perez-Gracia, E.; Larbouret, L.; Montagut, C.; Jarlier, M.; et al. FOXO3a and the MAPK p38 are activated by cetuximab to induce cell death and inhibit cell proliferation and their expression predicts cetuximab efficacy in colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Matsui, M.; Yoshimori, T.O.Y. In vivo analysis of autophagy in response to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammucari, C.; Milan, G.; Romanello, V.; Masiero, E.; Rudolf, R.; Del Piccolo, P.; Burden, S.J.; Di Lisi, R.; Sandri, C.; Zhao, J.; et al. FoxO3 controls autophagy in skeletal muscle in vivo. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijkelenboom, A.; Burgering, B.M. FOXOs: Signalling integrators for homeostasis maintenance. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, V.M.; Rafalski, V.A.; Morgan, A.A.; Salih, D.A.M.; Brett, J.O.; Webb, A.E.; Villeda, S.A.; Thekkat, P.U.; Guillerey, C.; Denko, N.C.; et al. FoxO3 regulates neural stem cell homeostasis. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Hron, J.D.; Peng, S.L. Regulation of NF-kappaB, Th activation, and autoinflammation by the forkhead transcription factor Foxo3a. Immunity 2004, 21, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.H.; Kollipara, R.; Chu, G.; Ji, H.; Xiao, Y.; Ding, Z.; Tothova, Z.; Horner, J.W.; Carrasco, D.R.; Jiang, S.; et al. FoxOs are lineage-restricted redundant tumor suppressors and regulate endothelial cell homeostasis. Cell 2007, 128, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
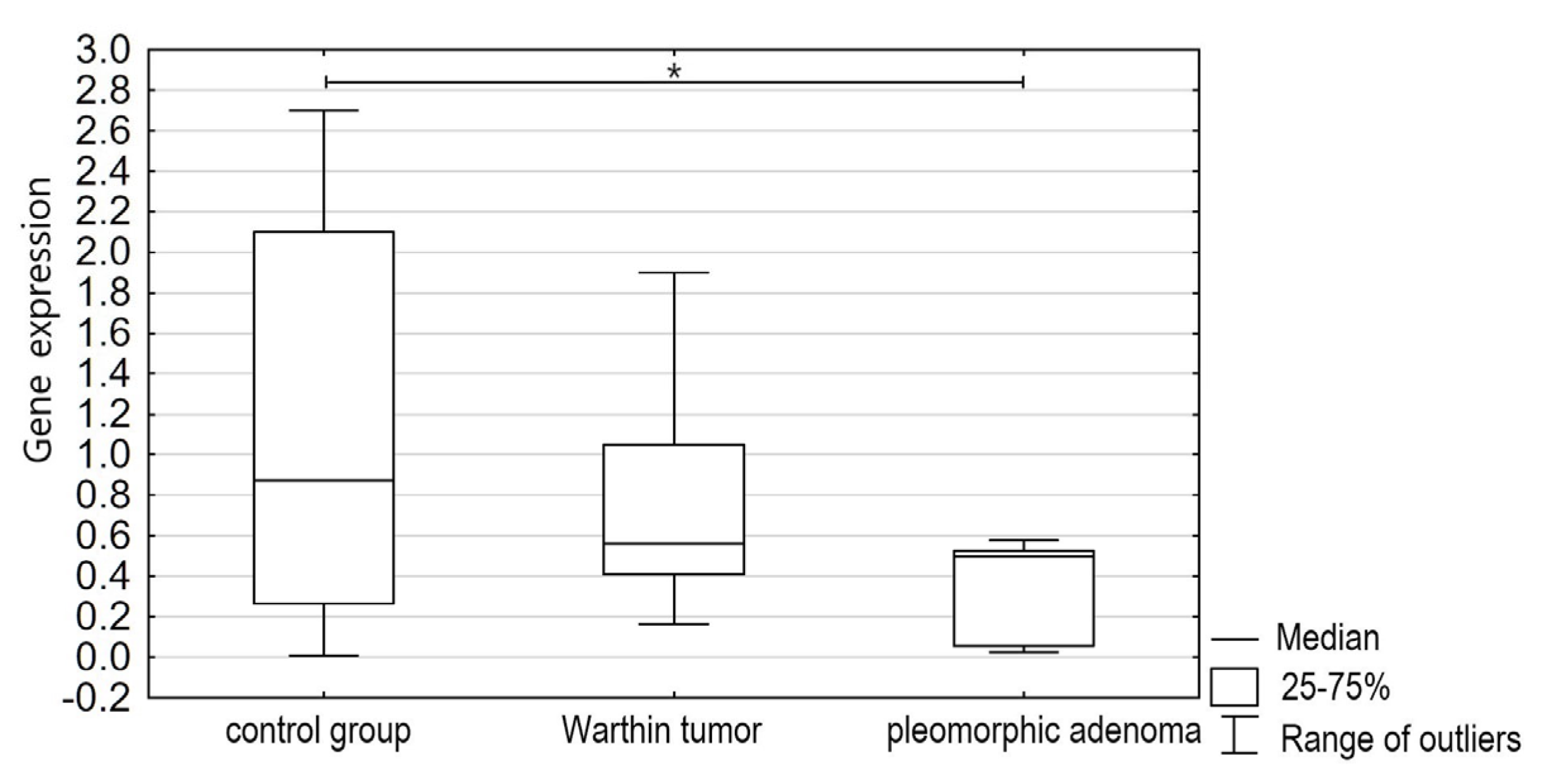
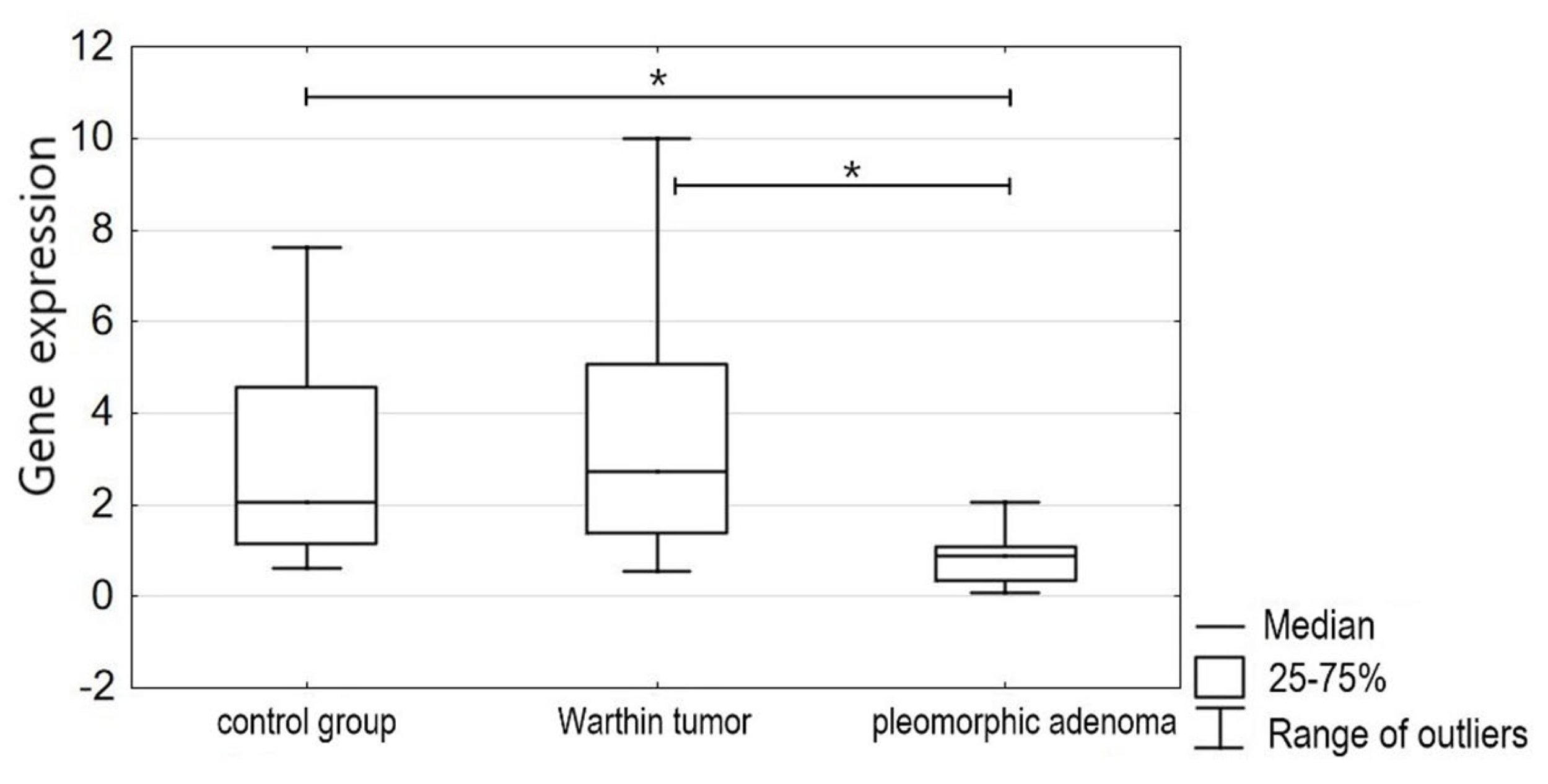
| Analyzed Trait | Warthin Tumor n = 25 | Pleomorphic Adenoma n = 25 | p-Value (<0.05) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.8621 | ||
| Female | 9 F | 16 F | |
| Male | 16 M | 9 M | |
| Age (years) | mean 67.7 | mean 54.2 | 0.0032 * |
| BMI 1 | 27.5 | 25.3 | 0.4427 |
| Normal weight | 6 | 7 | 0.4832 |
| Overweight | 14 | 13 | |
| Obesity | 5 | 4 | |
| Metabolic syndrome | 0 | 1 | |
| Smoking status “yes” | 18/25 | 6/25 | 0.006 * |
| Duration smoking (years) | mean 17.2 | mean 9 | 0.04131 * |
| Number of cigarettes per day | 14.5 | 6.5 | 0.0064 * |
| Alcohol drinking | 0.9655 | ||
| <30 j/week | 19/25 | 13/25 | |
| >30 j/week | 2/25 | 1/25 | |
| Diabetes | 0.7236 | ||
| Diabetes type 1 | 1/25 | 0/25 | |
| Diabetes type 2 | 1/25 | 1/25 | |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 5/25 | 4/25 | 0.0542 |
| Hypertension artery | 4/25 | 3/25 | 0.1823 |
| Analyzed Trait | Warthin Tumor n = 25 | Pleomorphic Adenoma n = 25 | p-Value (<0.05) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor location: | N/A | ||
| Parotid | 25/25 | 24/25 | |
| Submandibular | 0/25 | 1/25 | |
| Sublingual | 0/25 | 0/25 | |
| Tumor size | 0.7232 | ||
| >1 cm | 18/25 | 21/25 | |
| <1 cm | 7/25 | 4/25 | |
| Type of surgery | N/A | ||
| Extracapsular dissection | 0/25 | 0/25 | |
| Partial parotidectomy | 25/25 | 24/25 | |
| Total parotidectomy | 0/25 | 0/25 | |
| Removal of submandibular gland | 0/25 | 1/25 | |
| The agreement between FNAB 1 results and postoperative histopathological diagnosis | 81% | 73% | N/A |
| Consistency of the tumor | 0.4421 | ||
| Soft | 18/25 | 16/25 | |
| Taut | 3/25 | 7/25 | |
| Not palpable | 4/25 | 2/25 | |
| Movable tumor in relation to the ground | 21/25 | 23/25 | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolary-Siekierska, K.; Niewiadomski, P.; Namieciński, W.; Miłoński, J. Title Expression of FOXO3 and MAPK1 Genes in Patients with Benign Salivary Gland Tumors. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010215
Kolary-Siekierska K, Niewiadomski P, Namieciński W, Miłoński J. Title Expression of FOXO3 and MAPK1 Genes in Patients with Benign Salivary Gland Tumors. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010215
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolary-Siekierska, Katarzyna, Piotr Niewiadomski, Wojciech Namieciński, and Jarosław Miłoński. 2024. "Title Expression of FOXO3 and MAPK1 Genes in Patients with Benign Salivary Gland Tumors" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010215
APA StyleKolary-Siekierska, K., Niewiadomski, P., Namieciński, W., & Miłoński, J. (2024). Title Expression of FOXO3 and MAPK1 Genes in Patients with Benign Salivary Gland Tumors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010215







