Contralateral Snare Cannulation vs. Retrograde Gate Cannulation during Endovascular Aortic Repair in Difficult Iliac Artery Anatomy: A Single Center Experience
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
Surgical Technique
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wanhainen, A.; Verzini, F.; Van Herzeele, I.; Allaire, E.; Bown, M.; Cohnert, T.; Dick, F.; van Herwaarden, J.; Karkos, C.; Koelemay, M.; et al. Editor’s Choice—European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Abdominal Aorto-iliac Artery Aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019, 57, 8–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachat, M.; Pfammatter, T.; Witzke, H.; Bettex, D.; Künzli, A.; Wolfensberger, U.; Turina, M. Reprinted Article “Endovascular Repair with Bifurcated Stent-Grafts under Local Anaesthesia to Improve Outcome of Ruptured Aortoiliac Aneurysms”. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 42, S86–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecoraro, F.; Pakeliani, D.; Dinoto, E.; Bajardi, G. Endovascular treatment of large and wide aortic neck: Case report and literature review. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 65, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.Y.; Chen, P.L.; Shih, C.C.; Chen, I.M. Cross-wire technique for difficult contralateral limb cannulation during endovascular abdominal aneurysm repair for tortuous proximal aortic neck. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 28, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rancic, Z.; Pfammatter, T.; Lachat, M.; Hechelhammer, L.; Oberkofler, C.; Veith, F.; Mayer, D. Pull-Down Technique to Allow Complete Endovascular Relining of Failed AAA Vanguard Endografts with Excluder Bifurcated Endografts. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2009, 38, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titus, J.M.; Cragg, A.; Alden, P.; Alexander, J.; Manunga, J., Jr.; Stephenson, E.; Skeik, N.; Sullivan, T. A prospective randomized comparison of contralateral snare versus retrograde gate cannulation in endovascular aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 66, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikof, E.L.; Fillinger, M.F.; Matsumura, J.S.; Rutherford, R.B.; White, G.H.; Blankensteijn, J.D.; Bernhard, V.M.; Harris, P.L.; Kent, K.; May, J.; et al. Identifying and grading factors that modify the outcome of endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2002, 35, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, J.; Palmaz, J.; Barone, H. Transfemoral Intraluminal Graft Implantation for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 1991, 5, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moise, M.A.; Alvarez-Tostado, J.A.; Clair, D.G.; Greenberg, R.K.; Lyden, S.P.; Srivastava, S.D.; Eagleton, M.; Sarac, T.S.; Kashyap, V.S. Endovascular Management of Chronic Infrarenal Aortic Occlusion. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2009, 16, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaiah, V.G.; Thompson, C.S.; Shafique, S.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Ravi, R.; DiMugno, L.; Diethrich, E.B. Crossing the limbs: A useful adjunct for successful deployment of the aneurx stent-graft. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2002, 9, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, F.; Ambreen, T.; Park, C.W.; Kim, D.-I. Comparative evaluation of ballet-type and conventional stent graft configurations for endovascular aneurysm repair: A CFD analysis. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2021, 78, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shek, T.L.T.; Tse, L.W.; Nabovati, A.; Amon, C.H. Computational Fluid Dynamics Evaluation of the Cross-Limb Stent Graft Configuration for Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. J. Biomech. Eng. 2012, 134, 121002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, N.J.; Calligaro, K.D.; Zheng, H.; Troutman, D.A.; Dougherty, M.J. Outcomes of Brachial Artery Access for Endovascular Interventions. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 56, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternbergh, W.C., III. Technique: Endovascular aneurysm repair. In Rutherford’s Vascular Surgery, 8th ed.; Cronenwett, J.L., Johnston, K.W., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 1338–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaccaro, D.; Sciarrini, M.; Nano, G. The challenge of gate cannulation during endovascular aortic repair: A hypothesis of simplification. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 94, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

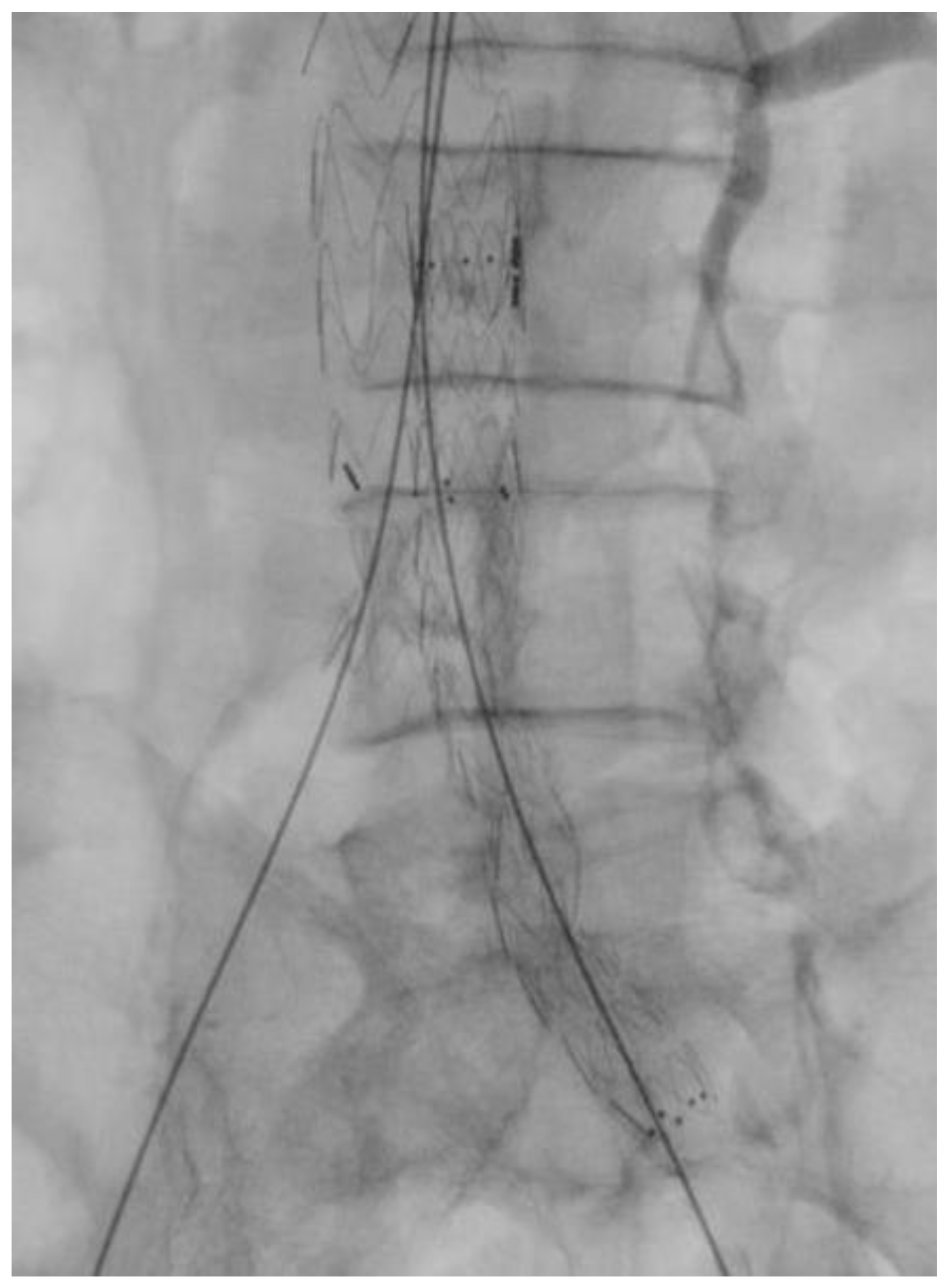
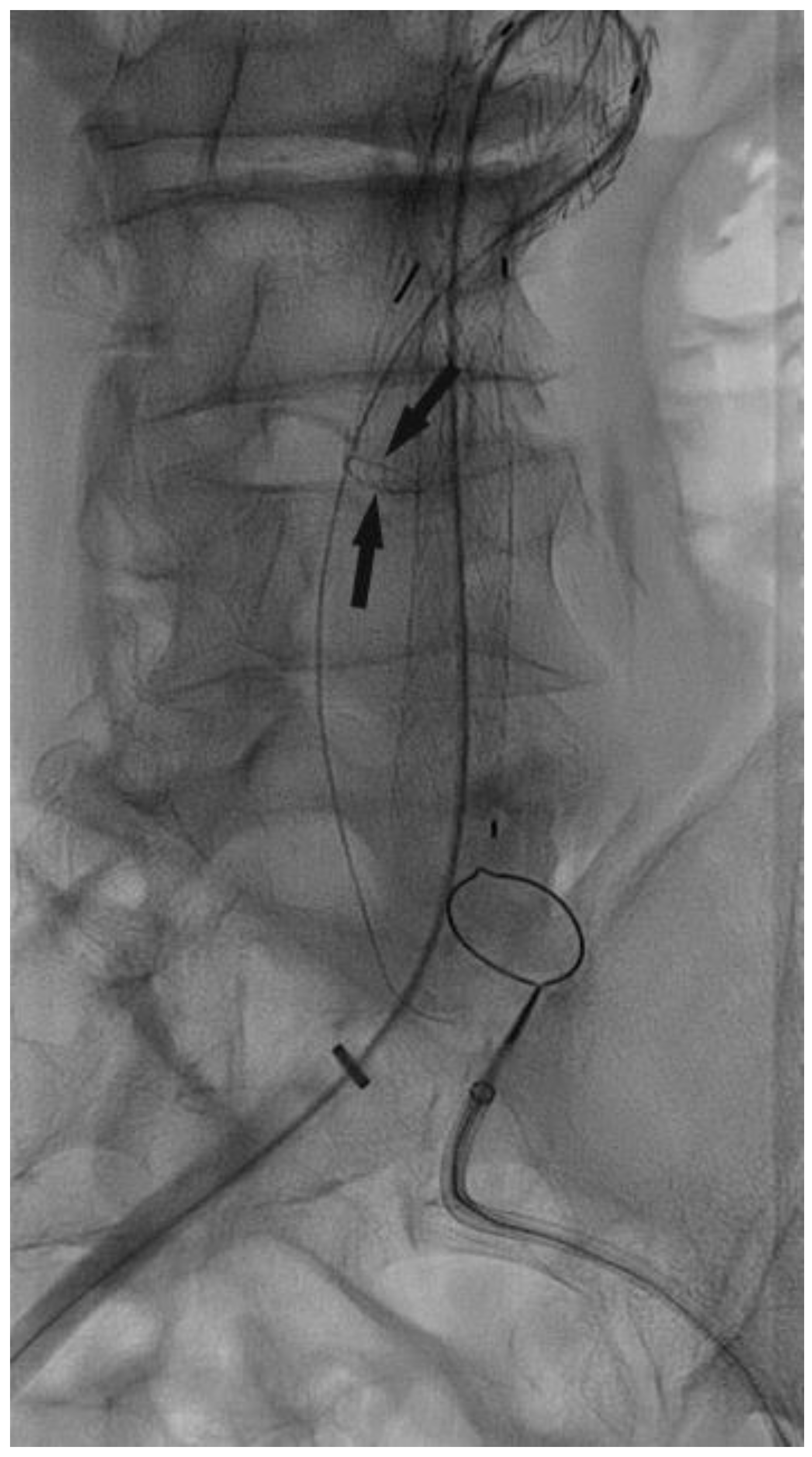
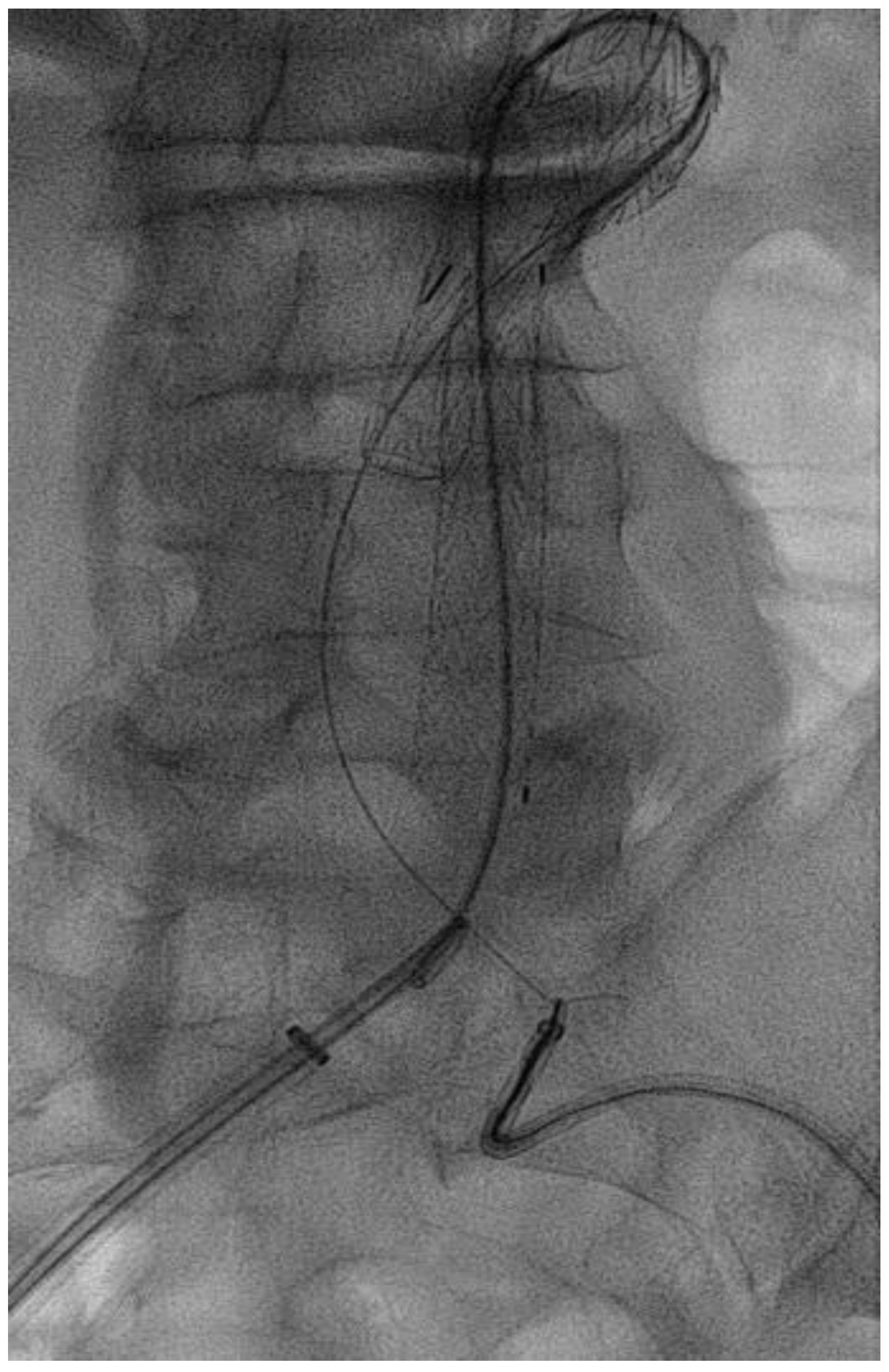
| Grade | |
|---|---|
| Absent = 0 | <1.25 |
| Mild = 1 | 1.25–1.5 |
| Moderate = 2 | 1.5–1.6 |
| Severe = 3 | >1.6 |
| All Patients (148) | Retrograde (116) | Snare (32) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Age (y) | 73.4 | 75.7 | 73.5 | 0.68 |
| Male (%) | 81 (54.7) | 62 (53.4) | 19 (59.3) | 0.67 |
| Neck Length > 10 mm (%) | 142 (95.9) | 110 (94.8) | 32 (100) | 0.77 |
| Iliac Tortuosity Index (%) | ||||
| 0 | 43 (29.0) | 41 (35.3) | 2 (6.25%) | 0.011 |
| 1 | 42 (28.3) | 38 (32.7) | 4 (12.5) | 0.11 |
| 2 | 40 (27.0) | 29 (25) | 11 (34.3) | 0.37 |
| 3 | 34 (22.9) | 18 (15.5) | 16 (50) | 0.001 |
| Aortic diameter at gate (Cm) | 4.49 (3.7–5.7) | 4.55 (3–5.5) | 4.3 (3.1–5.7) | 0.18 |
| Aortic lumen at gate (Cm) | 3.07 (2–4.5) | 3.07 (2–4.5) | 3.13 (2.4–4.2) | 0.73 |
| Distance from Bifurcation to gate orifice (Cm) | 2.69 (2–4.5) | 2.58 (2.7–3.5) | 3.14 (2–4.5) | <0.0001 |
| Graft Device (%) | ||||
| Endurant II | 41 (7,4) | 31 (26.7) | 10 (32.2) | 0.65 |
| Treo | 44 (29.7) | 35 (30.1) | 9 (28.1) | 0.87 |
| Zenith | 62 (41.8) | 50 (43.1) | 12 (37.5) | 0.68 |
| Iliac Tortuosity Index | All Patients | Retrograde | Snare | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.76 min. | 2.71 min. | 3.85 min. | 0.0001 |
| 1 | 2.69 min. | 2.74 min. | 2.8 min. | 0.63 |
| 2 | 2.87 min. | 3.01 min. | 2.71 min. | 0.01 |
| 3 | 4.08 min. | 4.93 min. | 3.28 min. | 0.0001 |
| Overall Times | 2.98 min. | 2.94 min. | 3.15 min. | 0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sena, G.; Montemurro, R.; Pezzo, F.; Gioffrè, R.; Gallelli, G.; Rubino, P. Contralateral Snare Cannulation vs. Retrograde Gate Cannulation during Endovascular Aortic Repair in Difficult Iliac Artery Anatomy: A Single Center Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010175
Sena G, Montemurro R, Pezzo F, Gioffrè R, Gallelli G, Rubino P. Contralateral Snare Cannulation vs. Retrograde Gate Cannulation during Endovascular Aortic Repair in Difficult Iliac Artery Anatomy: A Single Center Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010175
Chicago/Turabian StyleSena, Giuseppe, Rossella Montemurro, Francesco Pezzo, Rosario Gioffrè, Giuseppe Gallelli, and Paolo Rubino. 2024. "Contralateral Snare Cannulation vs. Retrograde Gate Cannulation during Endovascular Aortic Repair in Difficult Iliac Artery Anatomy: A Single Center Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010175
APA StyleSena, G., Montemurro, R., Pezzo, F., Gioffrè, R., Gallelli, G., & Rubino, P. (2024). Contralateral Snare Cannulation vs. Retrograde Gate Cannulation during Endovascular Aortic Repair in Difficult Iliac Artery Anatomy: A Single Center Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010175







