Prophylactic Treatment with Vedolizumab in the Prevention of Postoperative Recurrence (POR) in High-Risk Crohn’s Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Procedures
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Evaluation and Disease Activity at the End of Follow Up
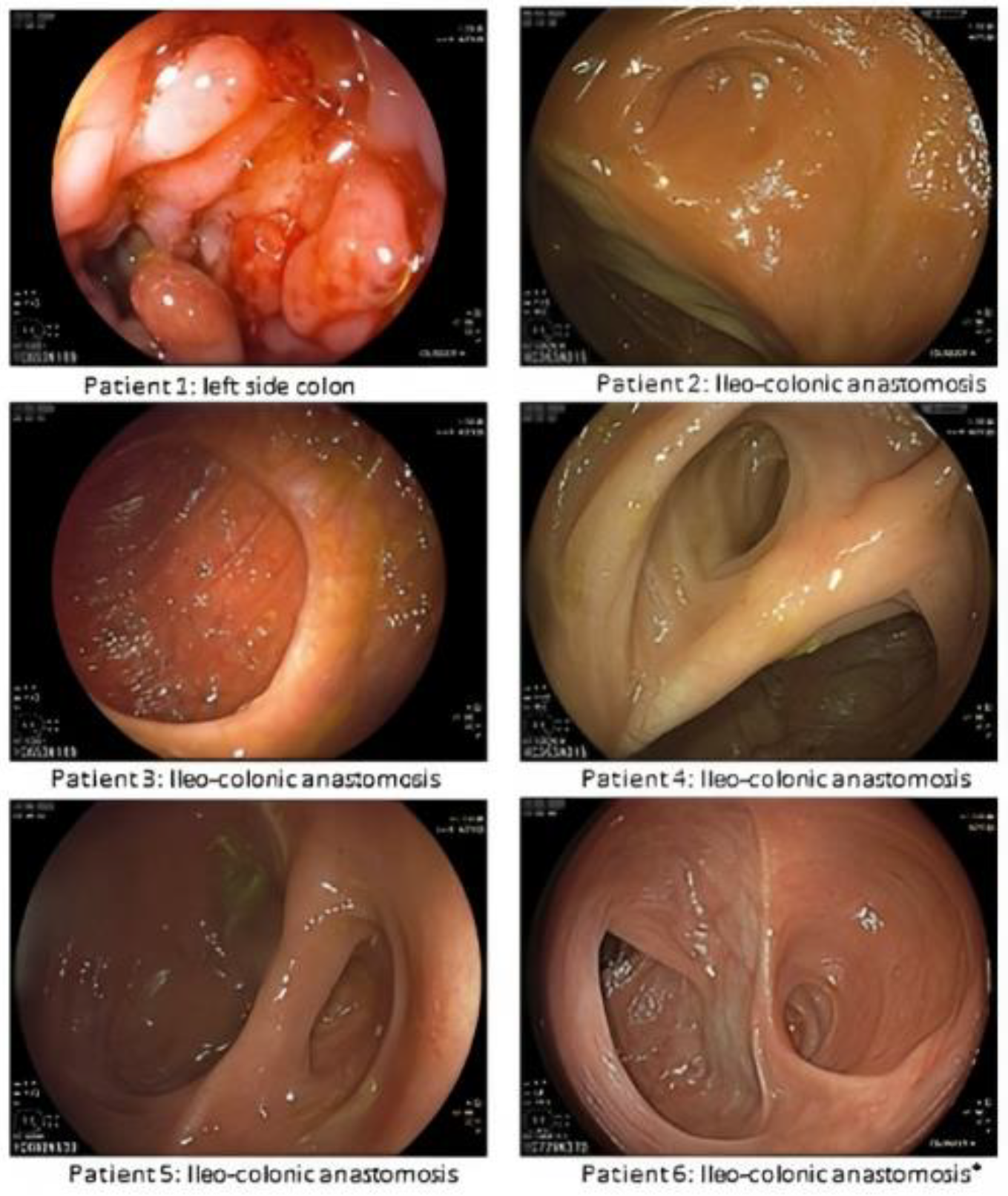
3.2. Endoscopic and Histological Evaluation
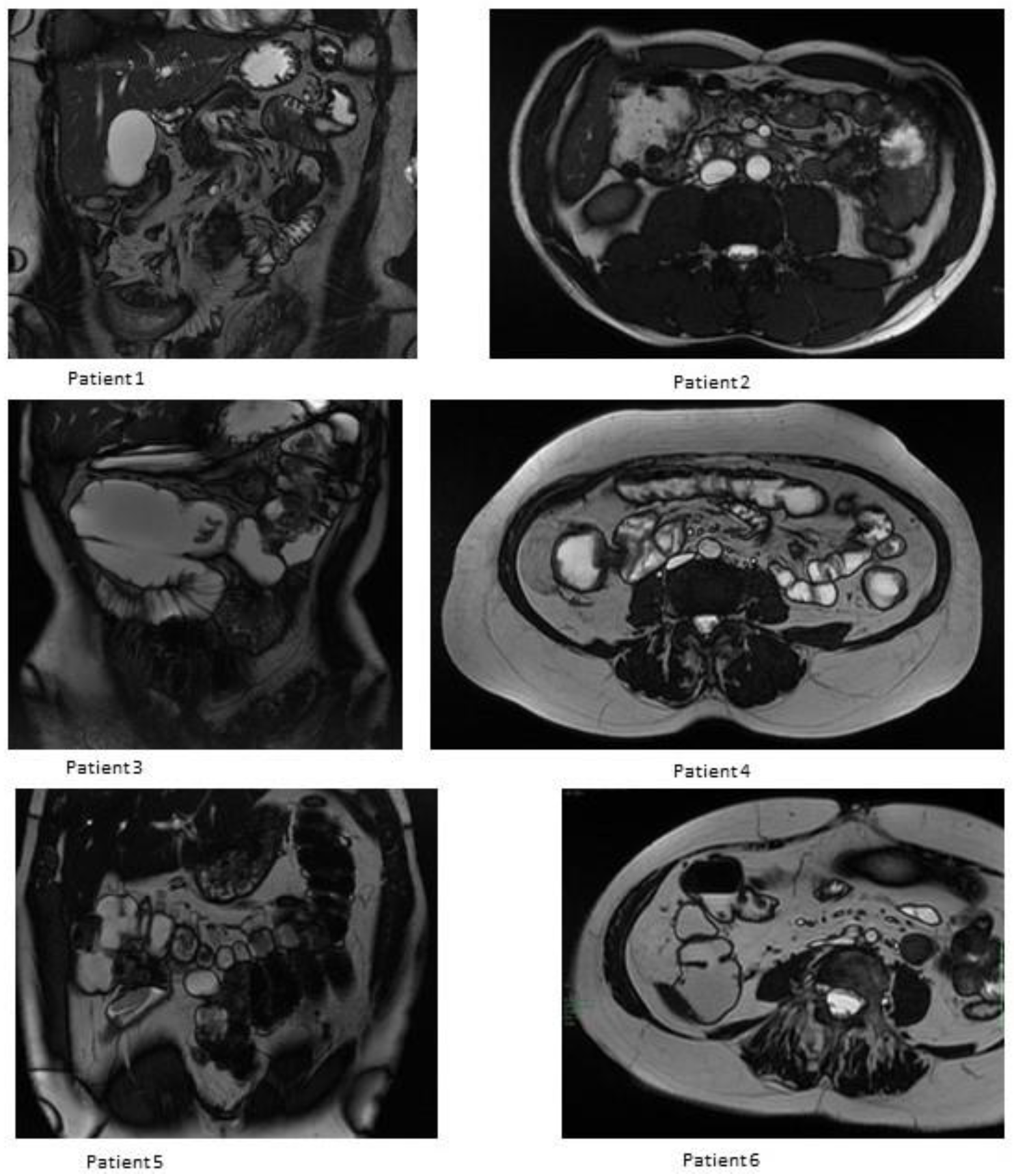
3.3. MRE Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latella, G.; Caprilli, R.; Travis, S. In favour of early surgery in Crohn’s disease: A hypothesis to be tested. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2011, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponsioen, C.Y.; de Groof, E.J.; Eshuis, E.J.; Gardenbroek, T.J.; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; Hart, A.; Warusavitarne, J.; Buskens, C.J.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; Brink, M.A.; et al. Laparoscopic ileocaecal resection versus infliximab for terminal ileitis in Crohn’s disease: A randomised controlled, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Mehandru, S.; Colombel, J.-F.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöss, C.; Berlet, M.; Reischl, S.; Nitsche, U.; Weber, M.C.; Friess, H.; Wilhelm, D.; Neumann, P.A. Crohn’s disease: A population-based study of surgery in the age of biological therapy. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2021, 36, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolkis, A.D.; Dykeman, J.; Negrón, M.E.; DeBruyn, J.; Jette, N.; Fiest, K.M.; Frolkis, T.; Barkema, H.W.; Rioux, K.P.; Panaccione, R.; et al. Risk of Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Has Decreased Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Population-Based Studies. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolkis, A.D.; Lipton, D.S.; Fiest, K.M.; Negrón, M.E.; Dykeman, J.; Debruyn, J.; Jette, N.; Frolkis, T.; Rezaie, A.; Seow, C.H.; et al. Cumulative incidence of second intestinal resection in Crohn’s disease: A systematic review and meta-Analysis of population-based studies. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamina, M.; Bonovas, S.; Raine, T.; Spinelli, A.; Warusavitarne, J.; Armuzzi, A.; Bachmann, O.; Bager, P.; Biancone, L.; Bokemeyer, B.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Surgical Treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gionchetti, P.; Dignass, A.; Danese, S.; Dias, F.J.M.; Rogler, G.; Lakatos, P.L.; Adamina, M.; Ardizzone, S.; Buskens, C.J.; Sebastian, S.; et al. 3rd European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease 2016: Part 2: Surgical management and special situations. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, N.E.; Hall, B.; Hamlin, P.J.; Selinger, C.P.; Ford, A.C.; O’Connor, A. Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Medical Therapies to Prevent Recurrence of Post-Operative Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro, M.; Schraut, W.; Baidoo, L.; Kip, K.E.; Sepulveda, A.R.; Pesci, M.; Harrison, J.; Plevy, S.E. Infliximab Prevents Crohn’s Disease Recurrence After Ileal Resection. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 441–450.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, D.; Terrosu, G.; Paviotti, A.; Geraci, M.; Avellini, C.; Zoli, G.; Fries, W.; Danese, S.; Occhipinti, P.; Croatto, T.; et al. Early diagnosis and treatment of postoperative endoscopic recurrence of Crohn’s disease: Partial benefit by infiximab-A pilot study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, E.; Bodini, G.; Dulbecco, P.; Assandri, L.; Bruzzone, L.; Mazza, F.; Frigo, A.C.; Fazio, V.; Marabotto, E.; Savarino, V. Adalimumab is more effective than azathioprine and mesalamine at preventing postoperative recurrence of Crohn’s disease: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, D. State-of-the-art medical prevention of postoperative recurrence of Crohn’s disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, A.; Komaki, Y.; Patel, N.; Komaki, F.; Pekow, J.; Dalal, S.; Cohen, R.D.; Cannon, L.; Umanskiy, K.; Smith, R.; et al. The Use of Vedolizumab in Preventing Postoperative Recurrence of Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañosa, M.; Fernández-Clotet, A.; Nos, P.; Martín-Arranz, M.D.; Manceñido, N.; Carbajo, A.; Hinojosa, E.; Hernández-Camba, A.; Muñoz-Pérez, R.; Boscá-Watts, M.; et al. Ustekinumab and vedolizumab for the prevention of postoperative recurrence of Crohn’s disease: Results from the ENEIDA registry. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 55, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Kagramanova, A.; Knyazev, O.; Sabino, J.; Haenen, S.; Mantzaris, G.J.; Mountaki, K.; Armuzzi, A.; Pugliese, D.; Furfaro, F.; et al. Endoscopic Postoperative Recurrence in Crohn’s Disease After Curative Ileocecal Resection with Early Prophylaxis by Anti-TNF, Vedolizumab or Ustekinumab: A Real-World Multicentre European Study. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cruz, P.; Kamm, M.A.; Hamilton, A.L.; Ritchie, K.J.; Krejany, E.O.; Gorelik, A.; Liew, D.; Prideaux, L.; Lawrance, I.C.; Andrews, J.M.; et al. Crohn’s disease management after intestinal resection: A randomised trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battat, R.; Dulai, P.S.; Jairath, V.; Vande Casteele, N. A product review of vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 2482–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Feagan, B.G.; Rutgeerts, P.; Hanauer, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Sands, B.E.; Lukas, M.; Fedorak, R.N.; Lee, S.; Bressler, B.; et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, B.E.; Feagan, B.G.; Rutgeerts, P.; Colombel, J.F.; Sandborn, W.J.; Sy, R.; D’Haens, G.; Ben-Horin, S.; Xu, J.; Rosario, M.; et al. Effects of vedolizumab induction therapy for patients with Crohn’s disease in whom tumor necrosis factor antagonist treatment failed. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 618–627.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaser, C.; Sturm, A.; Vavricka, S.R.; Kucharzik, T.; Fiorino, G.; Annese, V.; Calabrese, E.; Baumgart, D.C.; Bettenworth, D.; Borralho Nunes, P.; et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, C.; East, J.; Radaelli, F.; Spada, C.; Benamouzig, R.; Bisschops, R.; Bretthauer, M.; Dekker, E.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Ferlitsch, M.; et al. Bowel preparation for colonoscopy: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline–Update 2019. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 775–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, R.V.; Winer, S.; Travis SPL; Riddell, R.H. Systematic review: Histological remission in inflammatory bowel disease. Is ‘complete’ remission the new treatment paradigm? An IOIBD initiative. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2014, 8, 1582–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, A.; Maaser, C.; Calabrese, E.; Annese, V.; Fiorino, G.; Kucharzik, T.; Vavricka, S.R.; Verstockt, B.; Van Rheenen, P.; Tolan, D.; et al. Ecco-esgar guideline for diagnostic assessment in ibd part 2: Ibd scores and general principles and technical aspects. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13, 273–284E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, T.; Bonovas, S.; Burisch, J.; Kucharzik, T.; Adamina, M.; Annese, V.; Bachmann, O.; Bettenworth, D.; Chaparro, M.; Czuber-Dochan, W.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Ulcerative Colitis: Medical Treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Bonovas, S.; Doherty, G.; Kucharzik, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Raine, T.; Adamina, M.; Armuzzi, A.; Bachmann, O.; Bager, P.; et al. ECCO guidelines on therapeutics in Crohn’s disease: Medical treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.; Ricciuto, A.; Lewis, A.; D’Amico, F.; Dhaliwal, J.; Griffiths, A.M.; Bettenworth, D.; Sandborn, W.J.; Sands, B.E.; Reinisch, W.; et al. STRIDE-II: An Update on the Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE) Initiative of the International Organization for the Study of IBD (IOIBD): Determining Therapeutic Goals for Treat-to-Target strategies in IBD. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscido, A.; Valvano, M.; Stefanelli, G.; Capannolo, A.; Castellini, C.; Onori, E.; Ciccone, A.; Vernia, F.; Latella, G. Systematic review and meta-analysis: The advantage of endoscopic Mayo score 0 over 1 in patients with ulcerative colitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Zundler, S.; Atreya, R.; Rath, T.; Voskens, C.; Hirschmann, S.; López-Posadas, R.; Watson, A.; Becker, C.; Schuler, G.; et al. Differential effects of α4β7 and GPR15 on homing of effector and regulatory T cells from patients with UC to the inflamed gut in vivo. Gut 2016, 65, 1642–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotan, I.; Allez, M.; Danese, S.; Keir, M.; Tole, S.; McBride, J. The role of integrins in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: Approved and investigational anti-integrin therapies. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macaluso, F.S.; Cappello, M.; Crispino, F.; Grova, M.; Privitera, A.C.; Piccillo, G.; Magnano, A.; Ferracane, C.; Belluardo, N.; Giangreco, E.; et al. Vedolizumab may be an effective option for the treatment of postoperative recurrence of Crohn’s disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Haens, G.; Taxonera, C.; Lopez-Sanroman, A.; Nos Mateu, P.; Danese, S.; Armuzzi, A.; Roblin, X.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; West, R.; Witteman, B.; et al. OP14 Prevention of postoperative recurrence of Crohn’s disease with vedolizumab: First results of the prospective placebo-controlled randomised trial REPREVIO. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2023, 17, i19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.; de Hertogh, G.; Hlavaty, T.; D’Haens, G.; Penninckx, F.; D’Hoore, A.; Vermeire, S.; Rutgeerts, P.; Geboes, K.; van Assche, G. The Value of Myenteric Plexitis to Predict Early Postoperative Crohn’s Disease Recurrence. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decousus, S.; Boucher, A.-L.; Joubert, J.; Pereira, B.; Dubois, A.; Goutorbe, F.; Déchelotte, P.J.; Bommelaer, G.; Buisson, A. Myenteric plexitis is a risk factor for endoscopic and clinical postoperative recurrence after ileocolonic resection in Crohn’s disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Malhi, G.; Abdali, D.; Pogue, E.; Marshall, J.K.; de Buck van Overstraeten, A.; Riddell, R.; Narula, N. Active Margins, Plexitis, and Granulomas Increase Postoperative Crohn’s Recurrence: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sex Gender | Age at Diagnosis | Surgery-Free Survival (Years) | Indication to Surgery | Montreal Classification | Previous Medical Treatment | Previous Surgery | Age at Surgery | Weeks to VEDO Induction | First Colonoscopic Evaluation (Rutgeerts) (Months) | Second Colonoscopic Evaluation (Rutgeerts) (Months) | MRE (Months) | End of Follow-Up (Months) | Loss of Response (HBI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 41 | 9 | Inflammatory stenosis; Active penetrating disease | A3/L3/B3p | ADA | No | 50 | 4 | 0 (10) | i4 (32) | T+: i, lc; E+: i, lc (19) | 33 | Yes (10) |
| Male | 26 | 1 | Inflammatory stenosis | A2/L3/B3 | IFX | No | 27 | 6 | i1 (12) | i0(26) | T−; E+: i (13) | 58 | No (1) |
| Female | 31 | 6 (1st resection) 16 (2nd resection) | Inflammatory stenosis; Active penetrating disease | A2/L3/B3p | IFX; AZA | Yes | 57 | 10 | 0 (8) | 0 (32) | T−; E− (17) | 62 | No (1) |
| Female | 52 | 11 | Inflammatory stenosis | A3/L1/B2 | ADA | No | 63 | 6 | 0 (12) | i0(33) | T+: lc, sc E+: lc (52) | 64 | No (1) |
| Male | 53 | 2 | Fibrotic stenosis | A3/L1/B2 | IFX | No | 54 | 12 | 0 (8) | i1 (25) | T−; E− (14) | 45 | No (4) |
| Female | 62 | 2 | Inflammatory stenosis; | A3/L3/B2 | ADA | No | 64 | 6 | 0 (8) | n.a. | T−; E+: i (29) | 39 | No (2) |
| Sex Gender | Perianal Localization | Active Smoking | Penetrating Disease at Index Surgery | Prior Intestinal Surgery | Granulomas | Myenteric Plexitis | Previous Loss of Response to Anti-TNFα |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | yes | yes | No | no | n.a. | n.a. | yes |
| Male | no | yes | No | no | n.a. | n.a. | yes |
| Female | yes | no | No | yes | n.a. | n.a. | yes |
| Female | no | no | yes | no | n.a. | n.a. | yes |
| Male | no | no | yes | no | n.a. | n.a. | yes |
| Female | no | yes | No | no | n.a. | n.a. | yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frieri, G.; Valvano, M.; Frassino, S.; Faenza, S.; Cesaro, N.; Amicucci, G.; Manetta, R.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. Prophylactic Treatment with Vedolizumab in the Prevention of Postoperative Recurrence (POR) in High-Risk Crohn’s Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093130
Frieri G, Valvano M, Frassino S, Faenza S, Cesaro N, Amicucci G, Manetta R, Viscido A, Latella G. Prophylactic Treatment with Vedolizumab in the Prevention of Postoperative Recurrence (POR) in High-Risk Crohn’s Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(9):3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093130
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrieri, Giuseppe, Marco Valvano, Sara Frassino, Susanna Faenza, Nicola Cesaro, Gianfranco Amicucci, Rosa Manetta, Angelo Viscido, and Giovanni Latella. 2023. "Prophylactic Treatment with Vedolizumab in the Prevention of Postoperative Recurrence (POR) in High-Risk Crohn’s Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 9: 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093130
APA StyleFrieri, G., Valvano, M., Frassino, S., Faenza, S., Cesaro, N., Amicucci, G., Manetta, R., Viscido, A., & Latella, G. (2023). Prophylactic Treatment with Vedolizumab in the Prevention of Postoperative Recurrence (POR) in High-Risk Crohn’s Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(9), 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093130





