Patterns of Cognitive Impairment in Hemodialysis Patients and Related Factors including Depression and Anxiety
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cognitive Function Evaluation
2.2. Anxiety and Depression Evaluation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kramer, A.; Pippias, M.; Noordzij, M.; Stel, V.S.; Andrusev, A.M.; Aparicio-Madre, M.I.; Arribas Monzón, F.E.; Åsberg, A.; Barbullushi, M.; Beltrán, P.; et al. The European Renal Association - European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) Registry Annual Report 2016: A summary. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 702–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canaud, B.; Chazot, C.; Koomans, J.; Collins, A. Fluid and hemodynamic management in hemodialysis patients: Challenges and opportunities. J. Bras. Nefrol. 2019, 41, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, S.; Horton, E.J.; Renshaw, D.; Jimenez, A.; Krishnan, N.; McGregor, G. Hemodynamic Instability during Dialysis: The Potential Role of Intradialytic Exercise. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8276912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, K.; Fukiyama, K. Predictors of stroke in patients receiving chronic hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 1672–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, T.; Takemoto, Y.; Shoji, T.; Shima, H.; Ishimura, E.; Okamura, M.; Nakatani, T. Factors associated with cerebral white matter hyperintensities in haemodialysis patients. Nephrology 2012, 17, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zwieten, A.; Wong, G.; Ruospo, M.; Palmer, S.C.; Barulli, M.R.; Iurillo, A.; Saglimbene, V.; Natale, P.; Gargano, L.; Murgo, M.; et al. Prevalence and patterns of cognitive impairment in adult hemodialysis patients: The COGNITIVE-HD study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakizlis, H.; Bohl, K.; Ziemek, J.; Dodel, R.; Hoyer, J. Assessment of cognitive impairment and related risk factors in hemodialysis patients. J. Nephrol. 2022, 35, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorr, M.; Zalitach, M.; House, C.; Gomes, J.; Wild, C.J.; Salerno, F.R.; McIntyre, C. Cognitive Impairment Early After Initiating Maintenance Hemodialysis: A Cross Sectional Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 719208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.M.; Tupper, D.E.; Knopman, D.S.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Pederson, S.L.; Li, S.; Smith, G.E.; Hochhalter, A.K.; Collins, A.J.; Kane, R.L. Cognitive impairment in hemodialysis patients is common. Neurology 2006, 67, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Lai, S.; He, X.; Masembe, N.P.; Yuan, H.; Yong, Z.; Zhu, B.; Wu, J.; Zhao, W. Mild cognitive impairment in maintenance hemodialysis patients: A cross-sectional survey and cohort study. Clin. Interv. Aging. 2018, 14, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, K.; Quinn, T.J.; Mark, P.B.; Findlay, M.D. “Is It Removed During Dialysis?”-Cognitive Dysfunction in Advanced Kidney Failure-A Review Article. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 787370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukor, D.; Coplan, J.; Brown, C.; Friedman, S.; Cromwell-Smith, A.; Peterson, R.A.; Kimmel, P.L. Depression and anxiety in urban hemodialysis patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek, B.; Ilkowska, Z.; Kropinska, S.; Tobis, S.; Krzyminska-Siemaszko, R.; Kaluzniak-Szymanowska, A.; Wieczorowska-Tobis, K. Applying ACE-III, M-ACE and MMSE to Diagnostic Screening Assessment of Cognitive Functions within the Polish Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelland, I.; Dahl, A.A.; Haug, T.T.; Neckelmann, D. The validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. An updated literature review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Amer. Stat. Ass. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, T. An Introduction to ROC Analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 28, 61–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheskin, D.J. Handbook of Parametric and Nonparametric Statistical Procedures; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Fadili, W.; Al Adlouni, A.; Louhab, N.; Habib Allah, M.; Kissani, N.; Laouad, I. Prevalence and risk factors of cognitive dysfunction in chronic hemodialysis patients. Aging Ment Health. 2014, 18, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Kitamura, M.; Hayashida, M.; Tamaki, A.; Tomura, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nishino, T.; Funakoshi, S. Survival and cognitive deterioration in elderly patients undergoing hemodialysis. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2023, 23, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Janse, E.; Visser, K.; Meyer, A.S. What do verbal fluency tasks measure? Predictors of verbal fluency performance in older adults. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnak, M.J.; Tighiouart, H.; Scott, T.M.; Lou, K.V.; Sorensen, E.P.; Giang, L.M.; Drew, D.A.; Shaffi, K.; Strom, J.A.; Singh, A.K.; et al. Frequency of and risk factors for poor cognitive performance in hemodialysis patients. Neurology 2013, 80, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurella, M.; Chertow, G.M.; Luan, J.; Yaffe, K. Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, G.C. Vascular dementia: Distinguishing characteristics, treatment, and prevention. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51 (Suppl. S5), S296–S304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geldmacher, D.S.; Whitehouse, P.J. Evaluation of dementia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, D.A.; Bhadelia, R.; Tighiouart, H.; Novak, V.; Scott, T.M.; Lou, K.V.; Shaffi, K.; Weiner, D.E.; Sarnak, M.J. Anatomic brain disease in hemodialysis patients: A cross-sectional study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 61, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglinas, M.; Cesniene, U.; Janusaite, M.M.; Vinikovas, A. Cerebrovascular Disease and Cognition in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCarli, C. The role of cerebrovascular disease in dementia. Neurologist 2003, 9, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, T.A. Neuroanatomical substrates of age-related cognitive decline. Psychol. Bull. 2011, 137, 753–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouten, R.W.; Haverkamp, G.L.; Loosman, W.L.; Chandie Shaw, P.K.; van Ittersum, F.J.; Smets, Y.F.C.; Vleming, L.J.; Dekker, F.W.; Honig, A.; Siegert, C.E.H. Anxiety Symptoms, Mortality, and Hospitalization in Patients Receiving Maintenance Dialysis: A Cohort Study. Am. J. Kidney. Dis. 2019, 74, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, F.; Di Giacomo, D.; Ranieri, J.; Tunno, M.; Piscitani, L.; Ferri, C. Chronic Kidney Disease and Its Relationship with Mental Health: Allostatic Load Perspective for Integrated Care. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Eberle, J.; Messelhäuser, U.; Schiffmann, L.; Nies, C.; Schabram, J.; Zielke, A.; Holzer, K.; Rottler, E.; Henne-Bruns, D.; et al. Parathyroidectomy, elevated depression scores, and suicidal ideation in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism: Results of a prospective multicenter study. JAMA Surg. 2013, 148, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
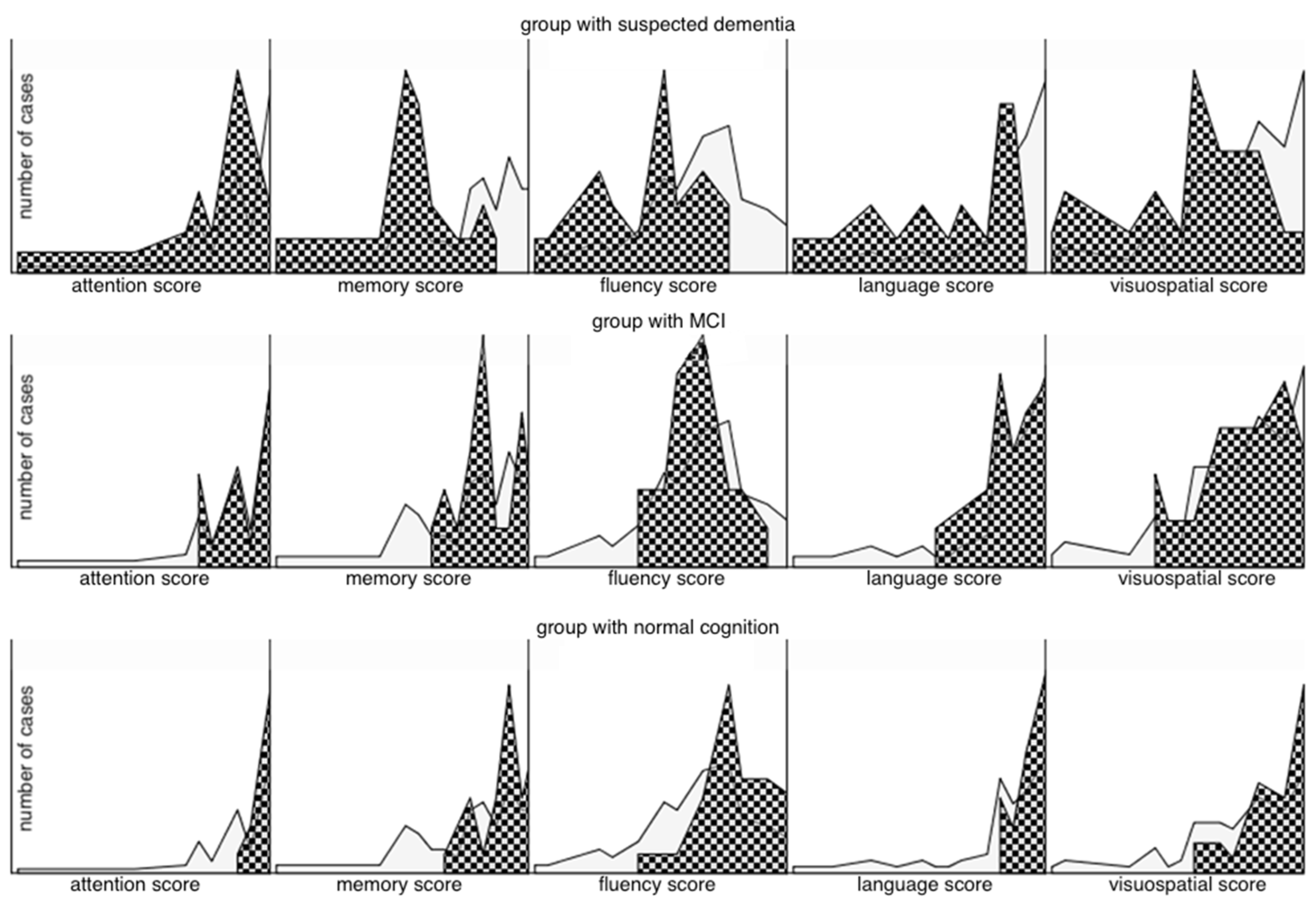
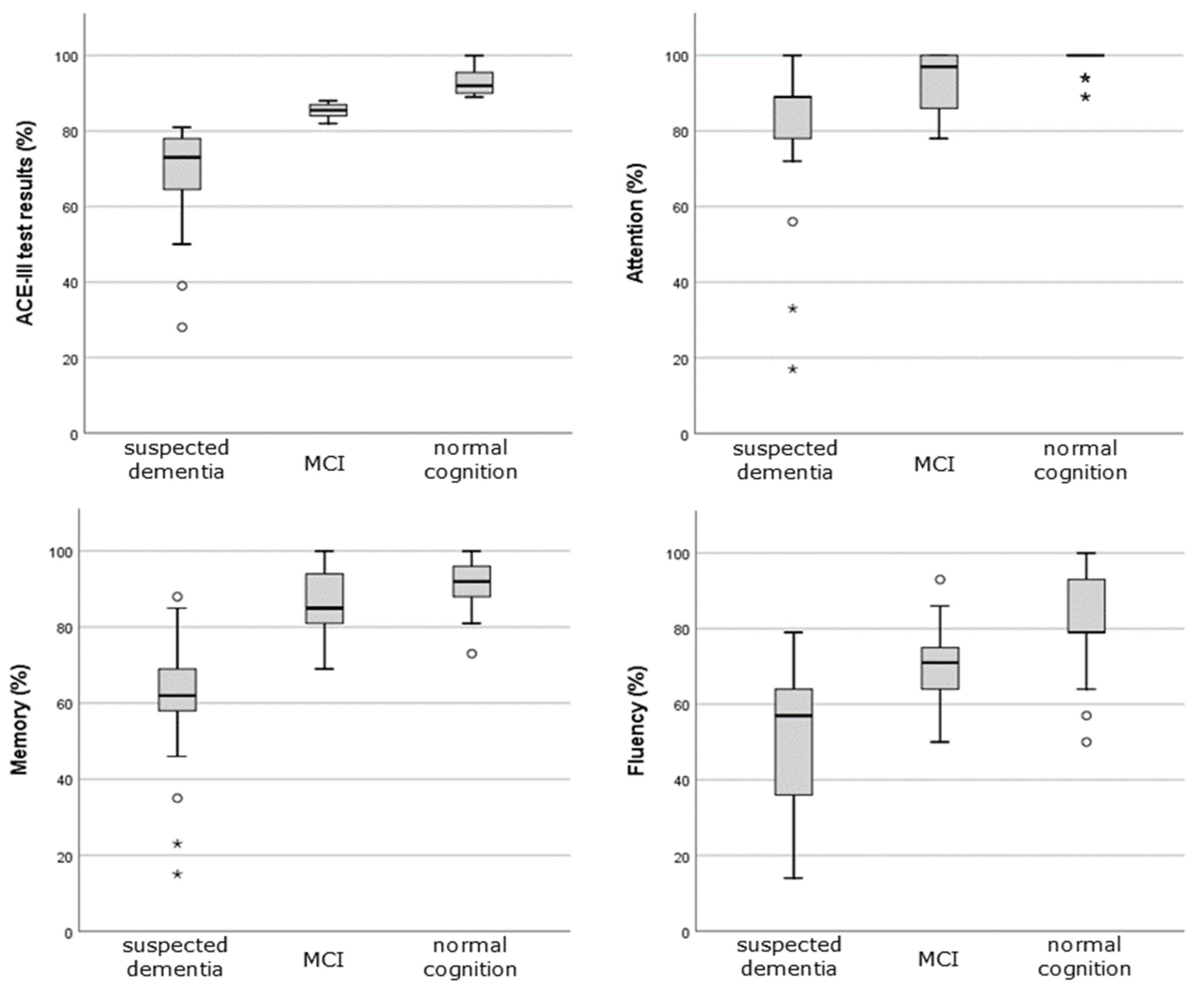
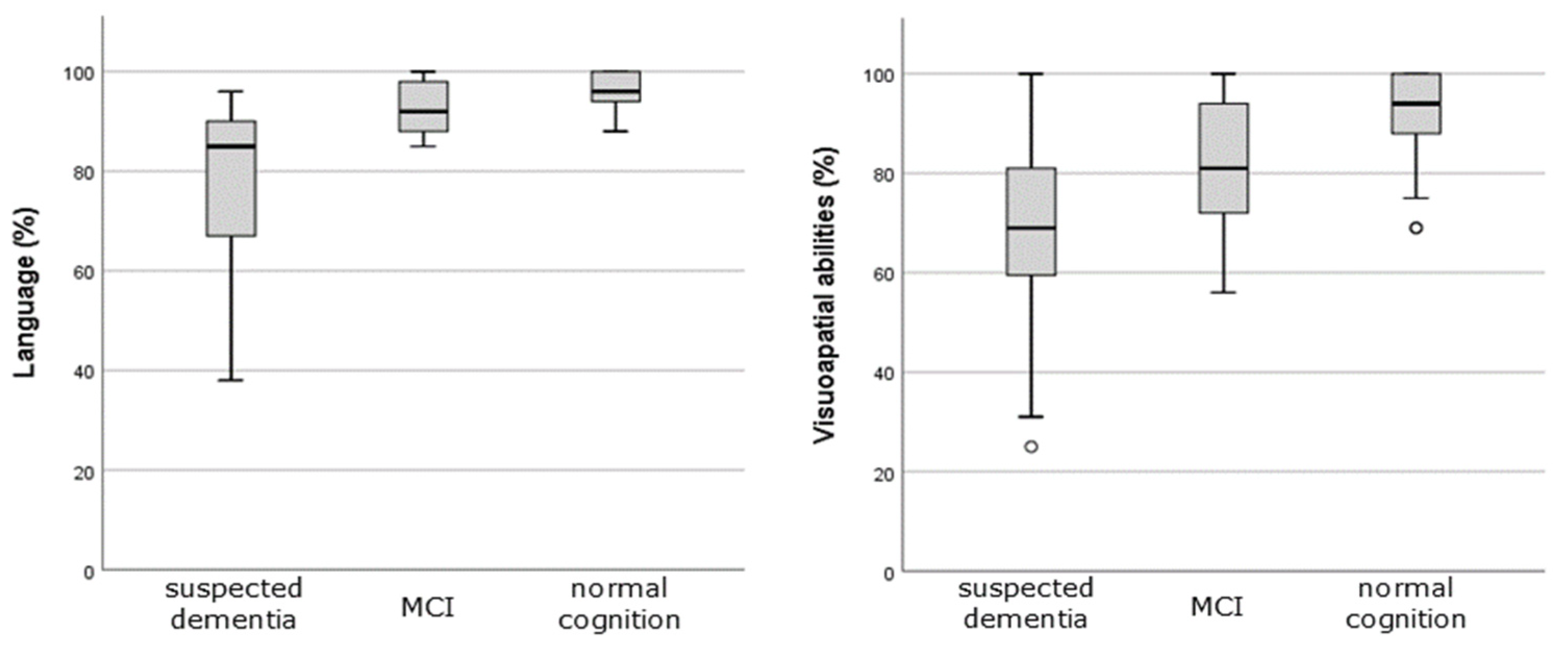
| All (n = 74) | Normal Cognition (n = 31) | MCI (n = 20) | Suspected Dementia (n = 23) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, mean ± SD (range) | 65.69 ± 13.9 (28, 94) | 60.19 ± 13.242 (28, 75) | 64.3 ± 12.96 (31, 86) | 74.3 ± 11.57 (50, 94) |
| Female, n (%) | 27 (36) | 10 (37) | 6 (22) | 11 (41) |
| Years of education, mean ± SD (range) | 13.64 ± 3.4 (7, 23) | 15.23 ± 3.19 (10, 23) | 13 ± 3.18 (8, 18) | 12.04 ± 2.98 (7, 18) |
| Hemodialysis vintage, months, mean ± SD (range) | 36.62 ± 47.5 (1, 297) | 22.55 ± 23 (1, 120) | 56 ± 68.52 (1, 297) | 38.74 ± 45.76 (1, 180) |
| Cardiovascular disease, n (%) | 31 (41.9) | 11 (35.5) | 8 (40) | 12 (52.2) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 63 (85.1) | 28 (90.3) | 15 (75) | 20 (87) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 24 (32.4) | 10 (32.3) | 3 (15) | 11 (47.8) |
| Nonsmoking, n (%) | 57 (77) | 24 (77.4) | 15 (75) | 18 (78.3) |
| ACE-III test results, % ± SD, (range) | 83.04 ± 13.4 (28, 100) | 92.81 ± 3.26 (89, 100) | 85.35 ± 1.84 (82, 88) | 67.87 ± 14.04 (28, 81) |
| Attention, % ± SD (range) | 90.69 ± 14.5 (17, 100) | 98.32 ± 3.34 (89, 100) | 92.25 ± 9.01 (78, 100) | 79.04 ± 19.66 (17, 100) |
| Fluency, % ± SD (range) | 68.93 ± 19.2 (14, 100) | 81.94 ± 12.29 (50, 100) | 69.15 ± 11.5 (50, 93) | 51.22 ± 18.29 (14, 79) |
| Language, % ± SD (range) | 89.2 ± 13.3 (38, 100) | 96.26 ± 4.49 (88, 100) | 92.15 ± 6.97 (73, 100) | 77.13 ± 17 (38, 96) |
| Memory, % ± SD (range) | 80.23 ± 18.0 (15, 100) | 91.55 ± 6.99 (73, 100) | 85.45 ± 6.64 (69, 100) | 60.43 ± 18.27 (15, 88) |
| Visuospatial abilities, % ± SD (range) | 81.95 ± 17.7 (25, 100) | 92.48 ± 9.7 (69, 100) | 80.7 ± 14.01 (56, 100) | 68.83 ± 19.96 (25, 100) |
| Anxiety, n (%) | 16 (21.6) | 5 (16.1) | 5 (25) | 6 (26) |
| Depression, n (%) | 21 (28.4) | 7 (22.6) | 6 (30) | 8 (34.8) |
| Creatinine clearance (ml/min/1.73 m2), mean ± SD (range) | 6.32 ±2.8 (3, 18) | 6.45 ± 2.85 (3, 18) | 5.6 ± 2.84 (4, 17) | 6.78 ± 2.61 (3, 13) |
| Creatinine level (mg/dL), mean ± SD (range) | 8.11 ± 2.3 (3.29, 14.79) | 8.3 ± 2.45 (3.29, 14.79) | 8.88 ± 2.07 (3.56, 12.74) | 7.19 ± 2.2 (4.13, 11.01) |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL), mean ± SD (range) | 10.757 ±1.4 (7.4, 13.8) | 10.62 ± 1.29 (8.3, 13) | 10.7 ± 0.88 (8.6, 11.9) | 11 ± 1.78 (7.4, 13.8) |
| Parathyroid hormone (pg/mL), mean ± SD (range) | 450.65 ± 382.8 (42.8, 2484.0) | 412.53 ± 299.98 (42.8, 1208) | 482.22 ± 331.82 (86.3, 1126) | 473.95 ± 517.71 (70.8, 2484) |
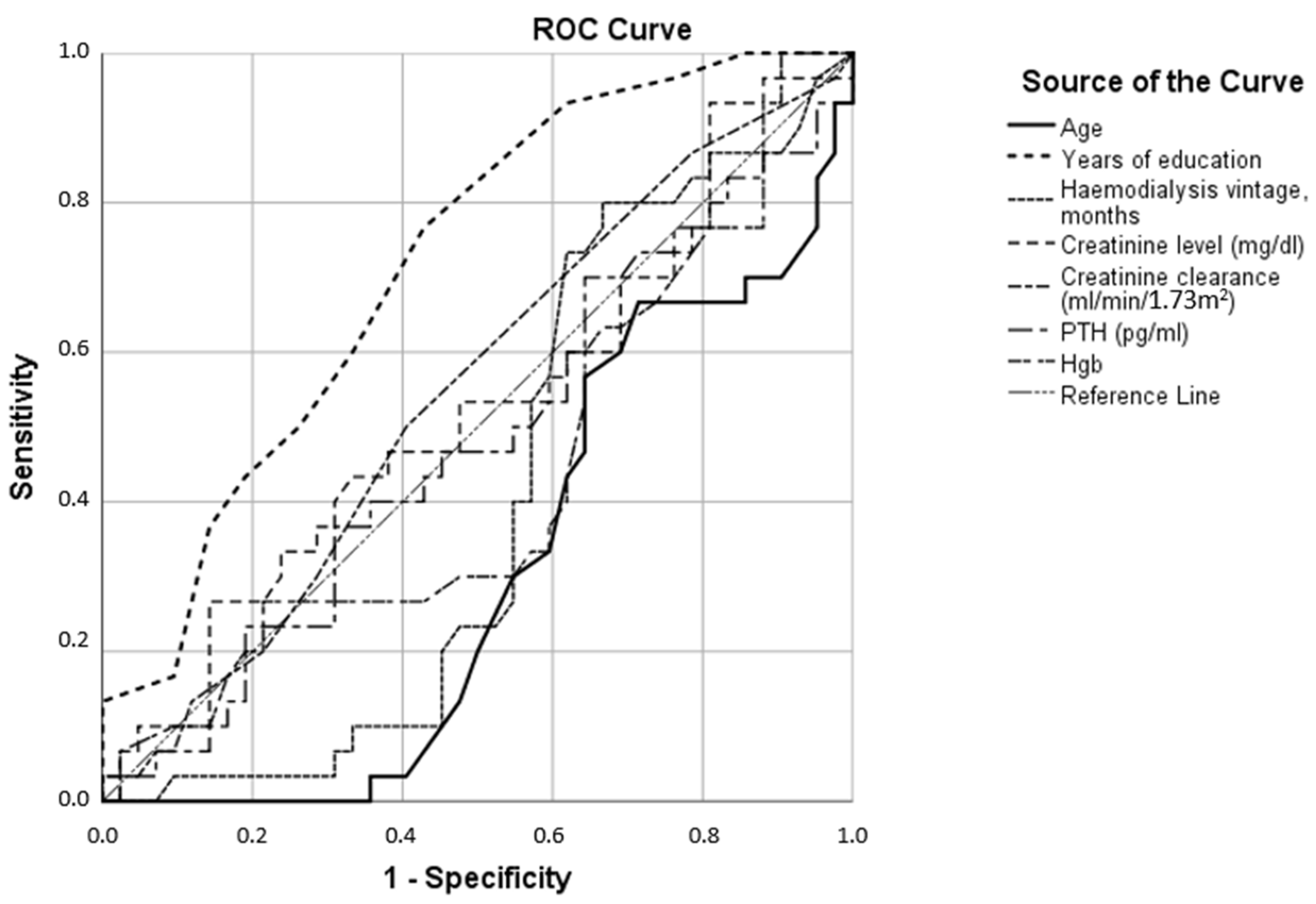
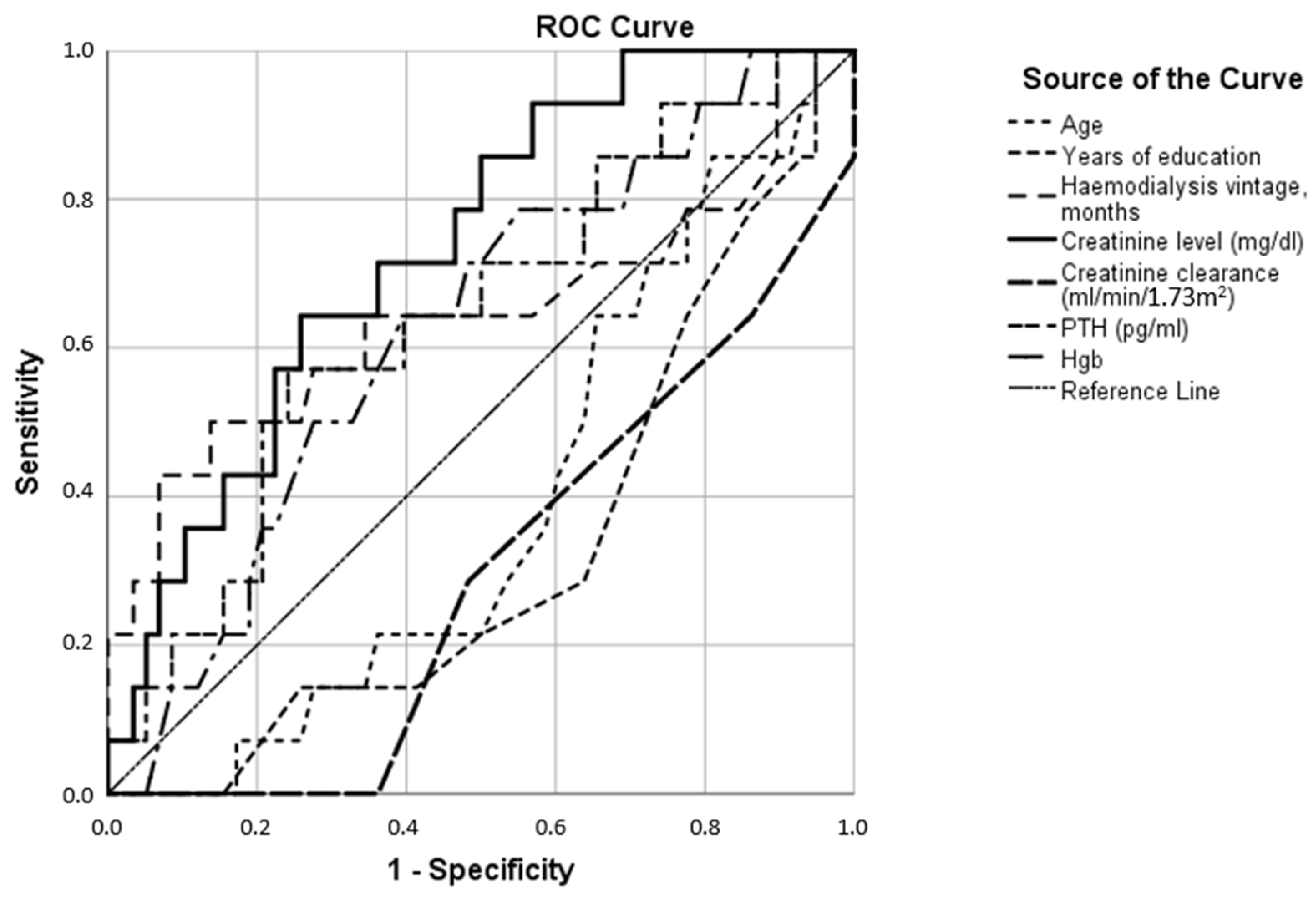
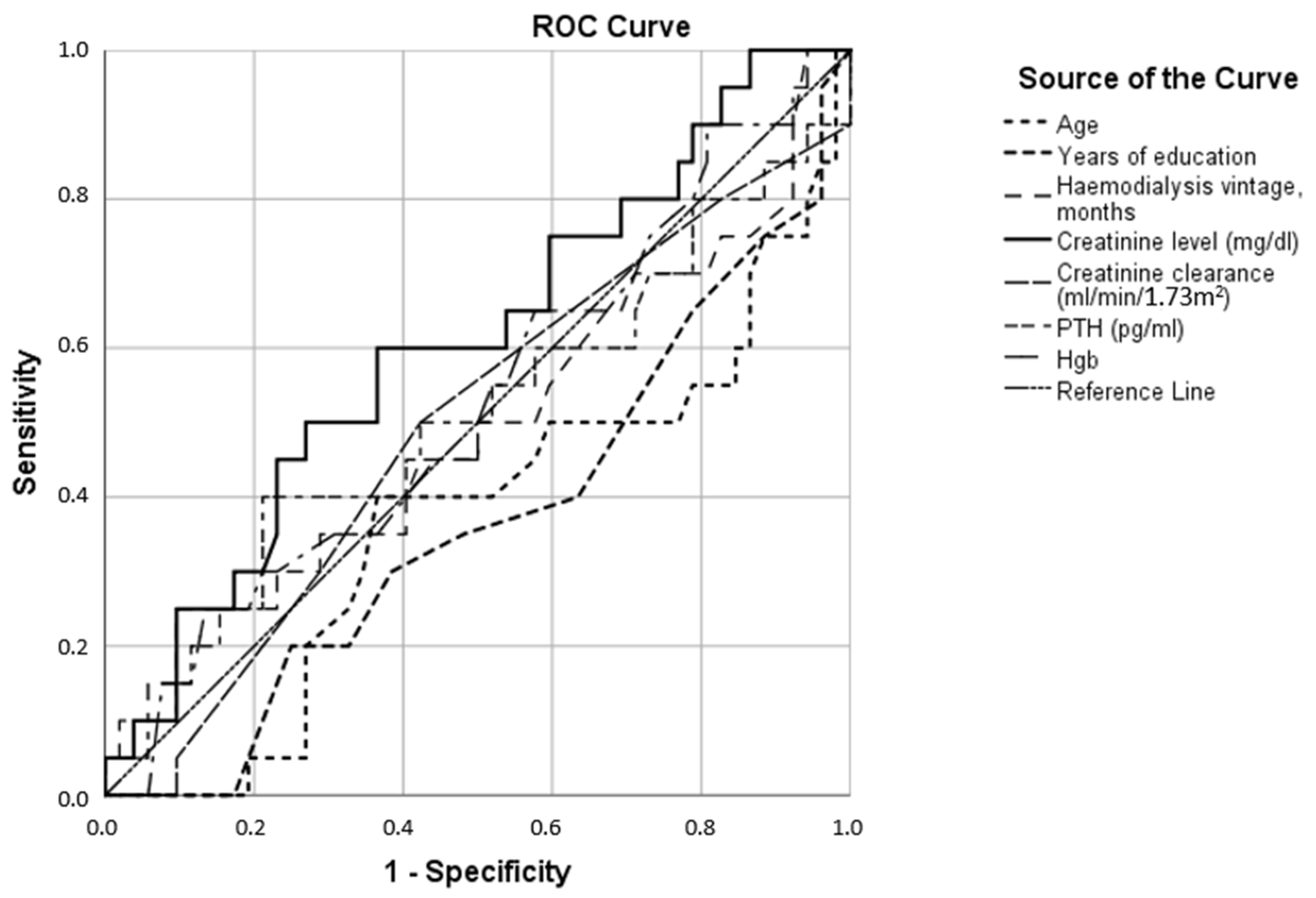
| Anxiety Test Result Variables | AUC |
|---|---|
| Age | 0.390 |
| Years of education | 0.328 |
| Hemodialysis vintage, months | 0.646 |
| Creatinine level (mg/dL) | 0.735 |
| Creatinine clearance (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 0.297 |
| Parathyroid hormone (pg/mL) | 0.644 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0.627 |
| Cramer’s V | ||
|---|---|---|
| Value | Significance (=Chi-Squared) | |
| Gender | 0.159 | 0.391 |
| Education category | 0.273 | 0.087 |
| Depression | 0.116 | 0.606 |
| Anxiety | 0.114 | 0.620 |
| Hypertension | 0.178 | 0.310 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.267 | 0.072 |
| Vascular disease | 0.145 | 0.460 |
| Smoking | 0.096 | 0.852 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golenia, A.; Żołek, N.; Olejnik, P.; Żebrowski, P.; Małyszko, J. Patterns of Cognitive Impairment in Hemodialysis Patients and Related Factors including Depression and Anxiety. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3119. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093119
Golenia A, Żołek N, Olejnik P, Żebrowski P, Małyszko J. Patterns of Cognitive Impairment in Hemodialysis Patients and Related Factors including Depression and Anxiety. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(9):3119. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093119
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolenia, Aleksandra, Norbert Żołek, Piotr Olejnik, Paweł Żebrowski, and Jolanta Małyszko. 2023. "Patterns of Cognitive Impairment in Hemodialysis Patients and Related Factors including Depression and Anxiety" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 9: 3119. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093119
APA StyleGolenia, A., Żołek, N., Olejnik, P., Żebrowski, P., & Małyszko, J. (2023). Patterns of Cognitive Impairment in Hemodialysis Patients and Related Factors including Depression and Anxiety. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(9), 3119. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093119






