Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus: Dangerous Liaisons or Innocent Bystanders?
Abstract
:1. Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus
1.1. Epidemiologic Interaction of Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes
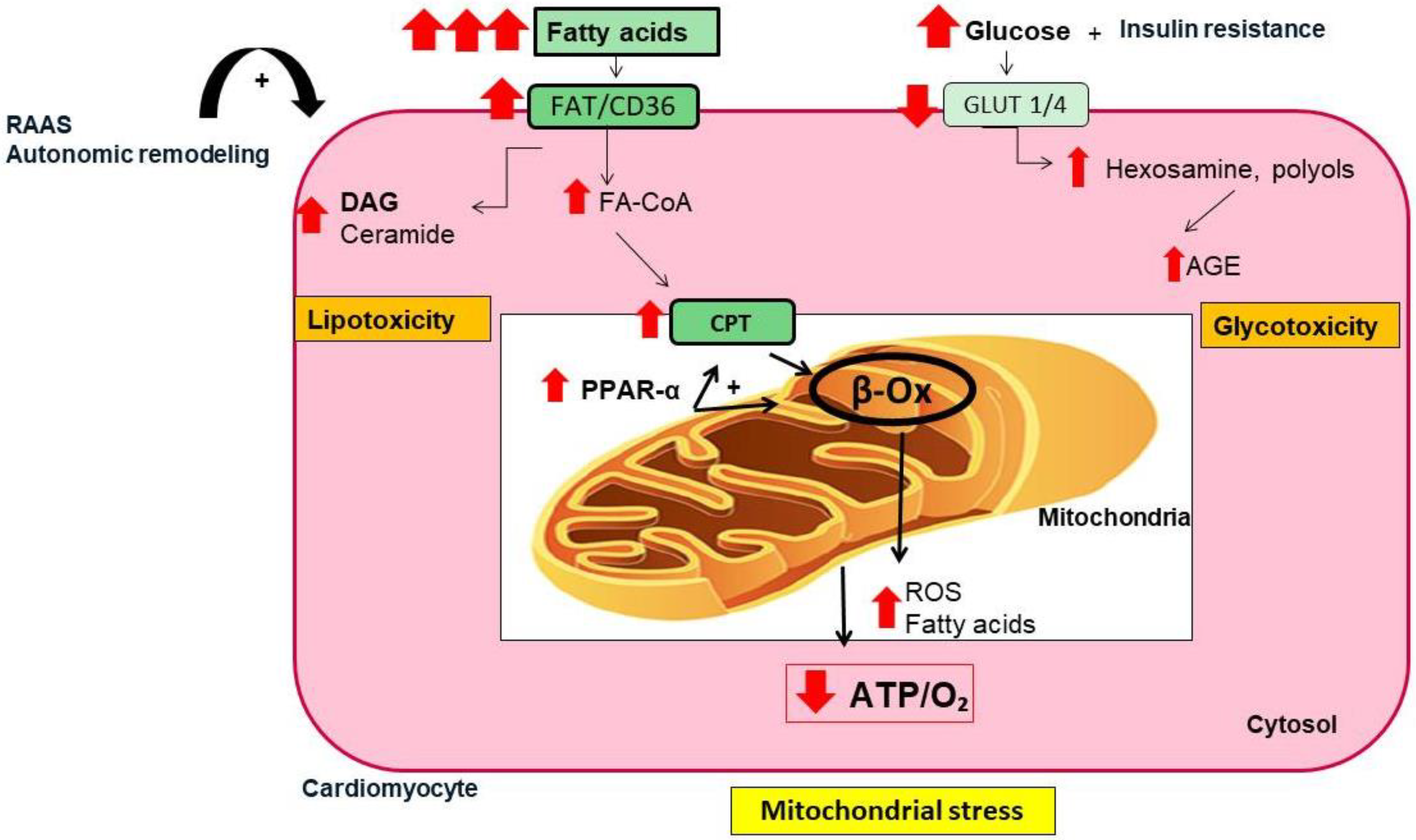
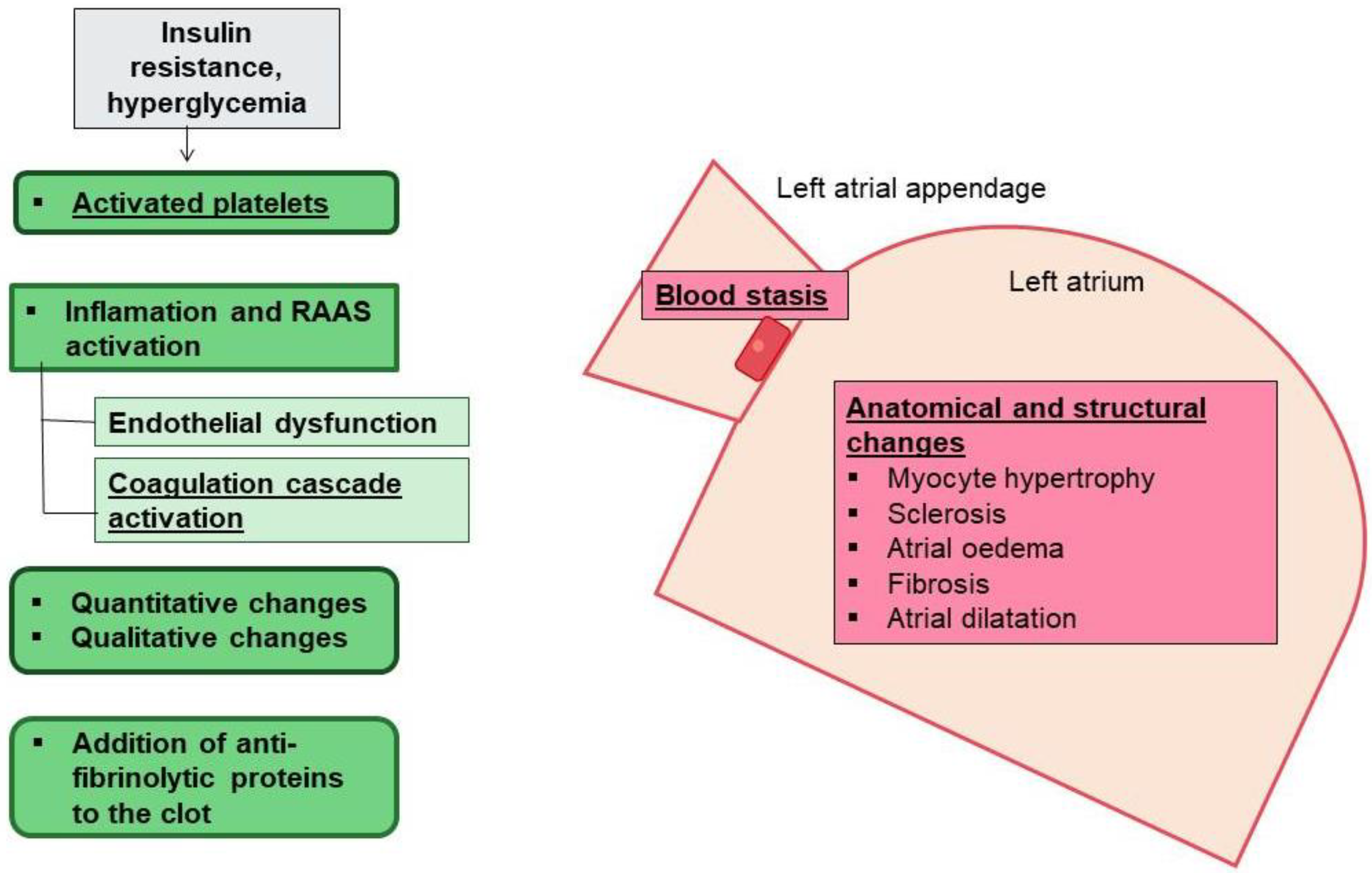
1.2. Interactive Mechanisms of Cardiac Diabetes and Atrial Fibrillation
- (i)
- Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress
- (ii)
- Inflammation and fibrosis
- (iii)
- Calcium disruption
- (iv)
- Fatty acid accumulation and infiltration
- (v)
- Autonomic remodeling
- (vi)
- Thrombogenesis
1.3. Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Thrombotic, and Atrial Fibrillation (Table 1)
| Anti-Diabetic Drug | Beneficial Effect in AF | Neutral Effect in AF | Deletereous Effect in AF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin | ✓ | ||
| Glitazones | ✓ | ||
| Sulfonylurea | ✓ | ||
| DPP-IV inhibitors | ✓ | ||
| GLP-1 RA * | ✓ | ||
| SGLT2 inhibitors | ✓ | ||
| Insulin | ✓ |
2. Future Perspectives
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 1, 373–498. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, F.; Kwan, G.F.; Benjamin, E.J. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabauer, M.; Oeff, M.; Gerth, A.; Wegscheider, K.; Buchholz, A.; Haeusler, K.G.; Hanrath, P.; Meinertz, T.; Ravens, U.; Sprenger, C.; et al. Prognostic markers of all-cause mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation: Data from the prospective long-term registry of the German Atrial Fibrillation NETwork (AFNET). Europace 2021, 23, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e139–e596. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Wolf, P.A.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Silbershatz, H.; Kannel, W.B.; Levy, D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1998, 98, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambatti, M.; Connolly, S.J.; Gold, M.R.; Morillo, C.A.; Capucci, A.; Muto, C.; Lau, C.P.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Carlson, M.; et al. Temporal relationship between subclinical atrial fibrillation and embolic events. Circulation 2014, 129, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.A.; Skjøth, F.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Larsen, T.B.; Kotecha, D. Temporal Trends in Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of Atrial Fibrillation in Primary Care. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, D. The link between diabetes and atrial fibrillation: Cause or correlation? J. Cardiovasc. Dis. Res. 2010, 1, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruff, C.T.; Giugliano, R.P.; Braunwald, E.; Hoffman, E.B.; Deenadayalu, N.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Camm, A.J.; Weitz, J.I.; Lewis, B.S.; Parkhomenko, A.; et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 383, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Shrader, P.; Thomas, L.; Gersh, B.J.; Kowey, P.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Singer, D.E.; Hylek, E.M.; Go, A.S.; Peterson, E.D.; et al. Care Patterns and Outcomes in Atrial Fibrillation Patients With and Without Diabetes: ORBIT-AF Registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes-Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D.; Vaziri, S.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Belanger, A.J.; Wolf, P.A. Independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in a population-based cohort. The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA 1994, 271, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxley, R.R.; Filion, K.B.; Konety, S.; Alonso, A. Meta-analysis of cohort and case-control studies of type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 108, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Feng, T.; Schlesinger, S.; Janszky, I.; Norat, T.; Riboli, E. Diabetes mellitus, blood glucose and the risk of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrachatis, D.A.; Papathanasiou, K.A.; Kossyvakis, C.; Giotaki, S.G.; Raisakis, K.; Iliodromitis, K.E.; Reimers, B.; Stefanini, G.G.; Cleman, M.; Sianos, G.; et al. Atrial fibrillation risk in patients suffering from type I diabetes mellitus. A review of clinical and experimental evidence. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 174, 108724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Fan, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.F.; Wang, C.Q. Impact of long-term glycemic variability on development of atrial fibrillation in type 2 diabetic patients. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2017, 18, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Teshima, Y.; Fukui, A.; Kondo, H.; Nishio, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Saikawa, T.; Takahashi, N. Glucose fluctuations increase the incidence of atrial fibrillation in diabetic rats. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 104, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dublin, S.; Glazer, N.L.; Smith, N.L.; Psaty, B.M.; Lumley, T.; Wiggins, K.L.; Page, R.L.; Heckbert, S.R. Diabetes mellitus, glycemic control, and risk of atrial fibrillation. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2010, 25, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxley, R.R.; Alonso, A.; Lopez, F.L.; Filion, K.B.; Agarwal, S.K.; Loehr, L.R.; Soliman, E.Z.; Pankow, J.S.; Selvin, E. Type 2 diabetes, glucose homeostasis and incident atrial fibrillation: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Heart 2012, 98, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattel, S.; Burstein, B.; Dobrev, D. Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: Mechanisms and implications. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2008, 1, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şerban, R.C.; Scridon, A. Data Linking Diabetes Mellitus and Atrial Fibrillation-How Strong Is the Evidence? From Epidemiology and Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Implications. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, B.S.; Chavez-Moreno, A.; Koh, W.; Akar, J.G.; Akar, F.G. Oxidative stress and inflammation as central mediators of atrial fibrillation in obesity and diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opacic, D.; van Bragt, K.A.; Nasrallah, H.M.; Schotten, U.; Verheule, S. Atrial metabolism and tissue perfusion as determinants of electrical and structural remodelling in atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 109, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, W.C.; Recchia, F.A.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Myocardial substrate metabolism in the normal and failing heart. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 1093–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihm, M.J.; Yu, F.; Carnes, C.A.; Reiser, P.J.; McCarthy, P.M.; Van Wagoner, D.R.; Bauer, J.A. Impaired myofibrillar energetics and oxidative injury during human atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2001, 104, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M. HFpEF Is the Substrate for Stroke in Obesity and Diabetes Independent of Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maack, C.; Lehrke, M.; Backs, J.; Heinzel, F.R.; Hulot, J.S.; Marx, N.; Paulus, W.J.; Rossignol, P.; Taegtmeyer, H.; Bauersachs, J.; et al. Heart failure and diabetes: Metabolic alterations and therapeutic interventions: A state-of-the-art review from the Translational Research Committee of the Heart Failure Association-European Society of Cardiology. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 4243–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoun, G.; McMurray, F.; Thrush, A.B.; Patten, D.A.; Peixoto, A.C.; Slack, R.S.; McPherson, R.; Dent, R.; Harper, M.E. Impaired mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and supercomplex assembly in rectus abdominis muscle of diabetic obese individuals. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarmohammadi, F.; Hayes, A.W.; Karimi, G. Possible protective effect of resolvin D1 on inflammation in atrial fibrillation: Involvement of ER stress mediated the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S.; Guasch, E.; Savelieva, I.; Cosio, F.G.; Valverde, I.; Halperin, J.L.; Conroy, J.M.; Al-Khatib, S.M.; Hess, P.L.; Kirchhof, P.; et al. Early management of atrial fibrillation to prevent cardiovascular complications. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, M. The failing heart--an engine out of fuel. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertero EMaack, C. Metabolic remodelling in heart failure. Nat. RevCardiol. 2018, 15, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Almorós, A.; Cepeda-Rodrigo, J.M.; Lorenzo, Ó. Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2020, 222, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Almorós, A.; Tuñón, J.; Orejas, M.; Cortés, M.; Egido, J.; Lorenzo, Ó. Diagnostic approaches for diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Xie, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Tse, G.; Li, G.; Xu, G.; et al. Activation of NADPH oxidase mediates mitochondrial oxidative stress and atrial remodeling in diabetic rabbits. Life Sci. 2021, 272, 119240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Santulli, G.; Reiken, S.R.; Yuan, Q.; Osborne, B.W.; Chen, B.X. Marks ARMitochondrial oxidative stress promotes atrial fibrillation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabit, C.E.; Chung, W.B.; Hamburg, N.M.; Vita, J.A. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2010, 11, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaan, G.N.; Patten, D.A.; Redpath, C.J.; Harper, M.E. Atrial Fibrillation Is Associated With Impaired Atrial Mitochondrial Energetics and Supercomplex Formation in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2019, 43, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Yuan, M.; Meng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tse, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Liang, X.; Fan, G.; et al. Wenxin Keli Regulates Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress and Homeostasis and Improves Atrial Remodeling in Diabetic Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 2468031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smorodinova, N.; Blaha, M.; Melenovský, V.; Rozsivalova, K.; Přidal, J.; Ďurišová, M. Analysis of immune cell populations in atrial myocardium of patients with atrial fibrillation or sinus rhythm. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chelu, M.G.; Dobrev, D.; Li, N. Cardiomyocyte Inflammasome Signaling in Cardiomyopathies and Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Implications. Front. Physiol. 2018, 13, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajoolabady, A.; Nattel, S.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Ren, J. Inflammasome Signaling in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 2349–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.H.; Schroder, K. Inflammasome signaling and regulation of interleukin-1 family cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, 20190314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Lip, G.Y.; Apostolakis, S. Inflammation in atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.; Persaud, S.J. Cardiac oxidative stress in diabetes: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 172, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Veleva, T.; Scott, L., Jr.; Cao, S.; Li, L.; Chen, G.; Jeyabal, P.; Pan, X.; Alsina, K.M.; Abu-Taha, I.; et al. Enhanced Cardiomyocyte NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Promotes Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2018, 138, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Tu, D.; Liu, X. Role of NLRP3- inflammasome/caspase-1/galectin-3 pathway on atrial remodeling in diabetic rabbits. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2020, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijman, J.; Voigt, N.; Nattel, S.; Dobrev, D. Cellular and molecular electrophysiology of atrial fibrillation initiation, maintenance, and progression. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1483–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, S.; Schenke-Layland, K. Cardiac fibrosis—A short review of causes and therapeutic strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffee, N.; Moore-Morris, T.; Jagla, B.; Mougenot, N.; Dilanian, G.; Berthet, M.; Proukhnitzky, J.; Le Prince, P.; Tregouet, D.A.; Pucéat, M.; et al. Reactivation of the Epicardium at the Origin of Myocardial Fibro-Fatty Infiltration during the Atrial Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1330–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Kneller, J.; Leon, L.J.; Nattel, S. Substrate size as a determinant of fibrillatory activity maintenance in a mathematical model of canine atrium. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1002–H1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambini, E.; Perrucci, G.L.; Bassetti, B.; Spaltro, G.; Campostrini, G.; Lionetti, M.C.; Pilozzi, A.; Martinelli, F.; Farruggia, A.; DiFrancesco, D.; et al. Preferential myofibroblast differentiation of cardiac mesenchymal progenitor cells in the presence of atrial fibrillation. Transl. Res. 2018, 192, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Fu, H.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Cheng, L.; Liu, T.; Li, G. Hyperglycemia aggravates atrial interstitial fibrosis, ionic remodeling and vulnerability to atrial fibrillation in diabetic rabbits. Anadolu. Kardiyol. Derg. 2012, 12, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, L.; Xie, J.; Nattel, S. Molecular determinants of cardiac fibroblast electrical function and therapeutic implications for atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, B.; Comtois, P.; Michael, G.; Nishida, K.; Villeneuve, L.; Yeh, Y.H.; Nattel, S. Changes in connexin expression and the atrial fibrillation substrate in congestive heart failure. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziolo, M.T.; Mohler, P.J. Defining the role of oxidative stress in atrial fibrillation and diabetes. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2015, 26, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Green, J.B.; Halperin, J.L.; Piccini, J.P., Sr. Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakili, R.; Voigt, N.; Kääb, S.; Dobrev, D.; Nattel, S. Recent advances in the molecular pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2955–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S.; Dobrev, D. The multidimensional role of calcium in atrial fibrillation pathophysiology: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic opportunities. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 1870–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Y.; Yeh, Y.H.; Xiao, L.; Burstein, B.; Maguy, A.; Chartier, D.; Villeneuve, L.R.; Brundel, B.J.; Dobrev, D.; Nattel, S. Cellular signaling underlying atrial tachycardia remodeling of L-type calcium current. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S.; Harada, M. Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: Recent advances and translational perspectives. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Y.; Diness, J.G.; Brundel, B.J.; Zhou, X.B.; Naud, P.; Wu, C.T.; Huang, H.; Harada, M.; Aflaki, M.; Dobrev, D.; et al. Role of small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in atrial electrophysiology and fibrillation in the dog. Circulation 2014, 129, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, T.J.; Ehrlich, J.R.; Chartier, D.; Qi, X.Y.; Xiao, L.; Nattel, S. Kir3-based inward rectifier potassium current: Potential role in atrial tachycardia remodeling effects on atrial repolarization and arrhythmias. Circulation 2006, 113, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, N.; Uslu, S.; Ozdemir, S. Diabetes-induced changes in cardiac voltage-gated ion channels. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Yokoshiki, H.; Mitsuyama, H.; Mizukami, K.; Ono, T.; Tsutsui, H. Conduction and refractory disorders in the diabetic atrium. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 303, H86–H95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, T.; Finet, J.E.; Takeuchi, A.; Fujino, Y.; Strom, M.; Greener, I.D.; Rosenbaum, D.S.; Donahue, J.K. Connexin gene transfer preserves conduction velocity and prevents atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2012, 125, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayhan, S.; Ozturk, S.; Alcelik, A.; Ozlu, M.F.; Erdem, A.; Memioglu, T.; Ozdemir, M.; Yazici, M. Atrial conduction time and atrial mechanical function in patients with impaired fasting glucose. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2012, 35, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzardi, M.A.; Iozzo, P. Fatty heart, cardiac damage, and inflammatio. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2011, 8, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouwens, D.M.; Diamant, M.; Fodor, M.; Habets, D.D.J.; Pelsers, M.M.A.L.; El Hasnaoui, M.; Dang, Z.C.; van den Brom, C.E.; Vlasblom, R.; Rietdijk, A.; et al. Cardiac contractile dysfunction in insulin-resistant rats fed a high-fat diet is associated with elevated CD36-mediated fatty acid uptake and esterification. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandoy-Fieiras, N.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; Eiras, S. Myocardium Metabolism in Physiological and Pathophysiological States: Implications of Epicardial Adipose Tissue and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M. The epicardial adipose inflammatory triad: Coronary atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, and heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1567–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. Disease-treatment interactions in the management of patients with obesity and diabetes who have atrial fibrillation: The potential mediating influence of epicardial adipose tissue. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platonov, P.G.; Mitrofanova, L.B.; Orshanskaya, V.; Ho, S.Y. Structural abnormalities in atrial walls are associated with presence and persistency of atrial fibrillation but not with age. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernault, A.C.; Meijborg, V.M.F.; Coronel, R. Modulation of Cardiac Arrhythmogenesis by Epicardial Adipose Tissue: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 1730–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, E.M.; Erande, A.S.; Le, C.; Salcedo, J.; Hoang, K.C.; Kumar, S.; Mohar, D.S.; Saremi, F.; Im, J.; Agrawal, Y.; et al. Comparison of epicardial adipose tissue volume and coronary artery disease severity in asymptomatic adults with versus without diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, R.; Nelson, A.; Pathak, R.K.; Middeldorp, M.E.; Wong, C.X.; Twomey, D.J.; Carbone, A.; Teo, K.; Agbaedeng, T.; Linz, D.; et al. Electroanatomical Remodeling of the Atria in Obesity: Impact of Adjacent Epicardial Fat. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 4, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venteclef, N.; Guglielmi, V.; Balse, E.; Gaborit, B.; Cotillard, A.; Atassi, F.; Amour, J.; Leprince, P.; Dutour, A.; Clément, K.; et al. Human epicardial adipose tissue induces fibrosis of the atrial myocardium through the secretion of adipo-fibrokines. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 795–805a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Knowlton, A.A. Mitochondria and heart failure: New insights into an energetic problem. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2010, 58, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Bakker, J.M.; van Capelle, F.J.; Janse, M.J.; Tasseron, S.; Vermeulen, J.T.; de Jonge, N.; Lahpor, J.R. Slow conduction in the infarcted human heart. “Zigzag” course of activation. Circulation 1993, 88, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, K.; Maeda, M.; Maimaituxun, G.; Yamaguchi, S.; Arasaki, O.; Fukuda, D.; Yagi, S.; Hirata, Y.; Nishio, S.; Iwase, T.; et al. Effect of the Epicardial Adipose Tissue Volume on the Prevalence of Paroxysmal and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 1778–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quisi, A.; Şentürk, S.E.; Harbalıoğlu, H.; Baykan, A.O. The relationship between echocardiographic epicardial adipose tissue, P-wave dispersion, and corrected QT interval. Turk Kardiyol. Dern. Ars. 2018, 46, 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, D.; Vernooij, M.W.; Shahzad, R.; Kavousi, M.; Hofman, A.; van Walsum, T.; Deckers, J.W.; Ikram, M.A.; Heeringa, J.; Franco, O.H.; et al. Epicardial Fat Volume and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation in the General Population Free of Cardiovascular Disease. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 1405–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.Y.; Lee, W.H.; Hsu, P.C.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, H.H.; Chiu, C.A.; Lin, T.H.; Lee, C.S.; Yen, H.W.; Voon, W.C.; et al. Association of Increased Epicardial Adipose Tissue Thickness With Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Medicine 2016, 95, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitropoulos, G.; Tahrani, A.A.; Stevens, M.J. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coumel, P. Autonomic influences in atrial tachyarrhythmias. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 1996, 7, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Po, S.S.; Wang, H.; Scherlag, B.J.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hou, Y. Autonomic Remodeling: How Atrial Fibrillation Begets Atrial Fibrillation in the First 24 Hours. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzer, C.; Lauer, M.S.; Brieke, A.; Blackstone, E.; Hoogwerf, B. Association of fasting plasma glucose with heart rate recovery in healthy adults: A population-based study. Diabetes 2002, 51, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, K.; Seicean, S.; Negishi, T.; Yingchoncharoen, T.; Aljaroudi, W.; Marwick, T.H. Relation of heart-rate recovery to new onset heart failure and atrial fibrillation in patients with diabetes mellitus and preserved ejection fraction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.R.; Sasso, F.C.; Marfella, R.; Siniscalchi, M.; Paolisso, P.; Carbonara, O.; Capoluongo, M.C.; Lascar, N.; Pace, C.; Sardu, C.; et al. Autonomic dysfunction is associated with brief episodes of atrial fibrillation in type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhauser, V.; Schwertfeger, E.; Rutz, T.; Beyersdorf, F.; Rump, L.C. Acetylcholine release inhuman heart atrium: Influence of muscarinicautoreceptors, diabetes, and age. Circulation 2001, 103, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabe, A.M.; Hoover, D.B. Remodeling of cardiac cholinergic innervation and control of heart rate in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Auton. Neurosci. 2011, 162, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.K.; Shen, M.J.; Han, S.; Kim, D.; Hwang, S.; Sayfo, S.; Piccirillo, G.; Frick, K.; Fishbein, M.C.; Hwang, C.; et al. Intrinsic cardiac nerve activity and paroxysmal atrial tachyarrhythmia in ambulatory dogs. Circulation 2010, 121, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masawa, N.; Yoshida, Y.; Yamada, T.; Joshita, T.; Ooneda, G. Diagnosis of cardiac thrombosis in patients with atrial fibrillation in the absence of macroscopically visible thrombi. Virchows Arch. A Pathol Anat. Histopathol. 1993, 422, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, T.; Shantsila, E.; Lip, G.Y. Mechanisms of thrombogenesis in atrial fibrillation: Virchow’s triad revisited. Lancet 2009, 373, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lip, G.Y. Does atrial fibrillation confer a hypercoagulable state? Lancet 1995, 346, 1313–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furui, H.; Taniguchi, N.; Yamauchi, K.; Sotobata, I.; Saito, H.; Inagaki, H. Effects of treadmill exercise on platelet function, blood coagulability and fibrinolytic activity in patients with atrial fibrillation. Jpn. Heart J. 1987, 28, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollick, C.; Taylor, D. Assessment of left atrial appendage function by transesophageal echocardiography. Implications for the development of thrombus. Circulation 1991, 84, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanfilippo, A.J.; Abascal, V.M.; Sheehan, M.; Oertel, L.B.; Harrigan, P.; Hughes, R.A.; Weyman, A.E. Atrial enlargement as a consequence of atrial fibrillation. A prospective echocardiographic study. Circulation 1990, 82, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, S.; Chin, B.S.; Blann, A.D.; Lip, G.Y. A study of platelet activation in paroxysmal, persistent and permanent atrial fibrillation. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2002, 13, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.I.; Erbas, T.; Park, T.S.; Nolan, R.; Pittenger, G.L. Platelet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davì, G.; Patrono, C. Platelet activation and atherothrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthikonda, S.; Lev, E.I.; Patel, R.; DeLao, T.; Bergeron, A.L.; Dong, J.F.; Kleiman, N.S. Reticulated platelets and uninhibited COX-1 and COX-2 decrease the antiplatelet effects of aspirin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechlivani, N.; Ajjan, R.A. Thrombosis and Vascular Inflammation in Diabetes: Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davì, G.; Gennaro, F.; Spatola, A.; Catalano, I.; Averna, M.; Montalto, G.; Amato, S.; Notarbartolo, A. Thrombin-antithrombin III complexes in type II diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complicat. 1992, 6, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, S.A. Cytokines, platelet production and hemostasis. Platelets 1997, 8, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrani, D.L. Regulation of fibrinogen biosynthesis: Glucocorticoid and interleukin-6 control. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1990, 1, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, S.A.; Peng, J.; Friese, P.; Wolf, R.F.; Harrison, P.; Downs, T.; Hamilton, K.; Comp, P.; Dale, G.L. Cytokine-induced alteration of platelet and hemostatic function. Stem Cells 1996, 14 (Suppl. 1), 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.S.; Buggins, P.; Hughes, E.; Lip, G.Y. Relationship of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein to the prothrombotic state in chronic atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; García-Cardeña, G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Alp, N.J.; Cai, S.; Lygate, C.A.; Neubauer, S.; Eigenthaler, M.; Bauersachs, J.; Channon, K.M. Reduced vascular NO bioavailability in diabetes increases platelet activation in vivo. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneni, F.; Beckman, J.A.; Creager, M.A.; Cosentino, F. Diabetes and vascular disease: Pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: Part I. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, K.; Tomlinson, D.; Smith, K.; Ajjan, R. Hypofibrinolysis in diabetes: A therapeutic target for the reduction of cardiovascular risk. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemkes, B.A.; Hermanides, J.; Devries, J.H.; Holleman, F.; Meijers, J.C.; Hoekstra, J.B. Hyperglycemia: A prothrombotic factor? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajjan, R.A.; Gamlen, T.; Standeven, K.F.; Mughal, S.; Hess, K.; Smith, K.A.; Dunn, E.J.; Anwar, M.M.; Rabbani, N.; Thornalley, P.J.; et al. Diabetes is associated with posttranslational modifications in plasminogen resulting in reduced plasmin generation and enzyme-specific activity. Blood 2013, 122, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, M.; van Zyl, D.G.; Rheeder, P.; Jerling, J.C.; Loots du, T.; van der Westhuizen, F.H.; Gottsche, L.T.; Weisel, J.W. Glycation of fibrinogen in uncontrolled diabetic patients and the effects of glycaemic control on fibrinogen glycation. Thromb. Res. 2007, 120, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lados-Krupa, A.; Konieczynska, M.; Chmiel, A.; Undas, A. Increased Oxidation as an Additional Mechanism Underlying Reduced Clot Permeability and Impaired Fibrinolysis in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 456189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, S.; Song, C.; Gray, W.A.; Furie, K.L.; Elkind, M.S.; Kamel, H. Left Atrial Appendage Function and Stroke Risk. Stroke 2015, 46, 3554–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.; Cavallari, I.; Andreotti, F.; Calabrò, P.; Cirillo, P.; Denas, G.; Galli, M.; Golia, E.; Maddaloni, E.; Marcucci, R.; et al. Prevention of atherothrombotic events in patients with diabetes mellitus: From antithrombotic therapies to new-generation glucose-lowering drugs. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calenda, B.W.; Fuster, V.; Halperin, J.L.; Granger, C.B. Stroke risk assessment in atrial fibrillation: Risk factors and markers of atrial myopathy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Wu, L.S.; Chiou, M.J.; Liu, J.R.; Yu, K.H.; Kuo, C.F.; Wen, M.S.; Chen, W.J.; Yeh, Y.H.; See, L.C. Association of metformin with lower atrial fibrillation risk among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A population-based dynamic cohort and in vitro studies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostropolets, A.; Elias, P.A.; Reyes, M.V.; Wan, E.Y.; Pajvani, U.B.; Hripcsak, G.; Morrow, J.P. Metformin Is Associated With a Lower Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Ventricular Arrhythmias Compared With Sulfonylureas: An Observational Study. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2021, 14, e009115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, O.; Takahashi, N.; Wakisaka, O.; Nagano-Torigoe, Y.; Teshima, Y.; Nakagawa, M.; Yufu, K.; Hara, M.; Saikawa, T.; Yoshimatsu, H. Pioglitazone attenuates inflammatory atrial fibrosis and vulnerability to atrial fibrillation induced by pressure overload in rats. Heart Rhythm. 2011, 8, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Letsas, K.P.; Tse, G.; Gong, M.; Meng, L.; Li, G.; Liu, T. Thiazolidinedione use and atrial fibrillation in diabetic patients: A meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2017, 17, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Yeh, Y.H.; Chan, Y.H.; Liu, J.R.; Chang, S.H.; Lee, H.F.; Wu, L.S.; Yen, K.C.; Kuo, C.T.; See, L.C. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor decreases the risk of atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide cohort study in Taiwan. Cardiovasc. Diabetol 2017, 16, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scirica, B.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Braunwald, E.; Steg, P.G.; Davidson, J.; Hirshberg, B.; Ohman, P.; Frederich, R.; Wiviott, S.D.; Hoffman, E.B.; et al. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, Y.S.; Yang, F.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Jong, G.P. Antihyperglycemic drugs use and new-onset atrial fibrillation: A population-based nested case control study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Cannon, C.P.; Heller, S.R.; Nissen, S.E.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Bakris, G.L.; Perez, A.T.; Fleck, P.R.; Mehta, C.R.; Kupfer, S.; et al. Alogliptin after acute coronary syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Ren, G.; Wang, P.; Gao, L.; Chen, H.; Ding, C. Comparison of the effect of glucose-lowering agents on the risk of atrial fibrillation: A network meta-analysis. Heart Rhythm. 2021, 18, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monami, M.; Nreu, B.; Scatena, A.; Giannini, S.; Andreozzi, F.; Sesti, G.; Mannucci, E. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.; Petrie, M.C.; Ambery, P.D.; Donaldson, J.; Ye, J.; McMurray, J.J. Cardiovascular safety of albiglutide in the Harmony programme: A meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ORIGIN Trial Investigators; Gerstein, H.C.; Bosch, J.; Dagenais, G.R.; Díaz, R.; Jung, H.; Maggioni, A.P.; Pogue, J.; Probstfield, J.; Ramachandran, A.; et al. Basal insulin and cardiovascular and other outcomes in dysglycemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Hanefeld, M.; Frier, B.M.; Pistrosch, F. Hypoglycemia and Cardiovascular Risk: Is There a Major Link? Diabetes Care 2016, 39 (Suppl. 2), S205–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, M.; Slawik, J.; Brueckmann, M.; Mattheus, M.; George, J.T.; Ofstad, A.P.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Fitchett, D.; Anker, S.D.; Marx, N.; et al. Efficacy of empagliflozin on heart failure and renal outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation: Data from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.C.; Fernandes, A.; Cardoso, R.; Penalver, J.; Knijnik, L.; Mitrani, R.D.; Myerburg, R.J.; Goldberger, J.J. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in patients with type 2 diabetes or heart failure: A meta-analysis of 34 randomized controlled trials. Heart Rhythm. 2021, 18, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, A.W.; Chan, C.C.; Chen, S.W.; Kao, Y.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Chan, Y.H.; Chu, P.H. The risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Hidru, T.H.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, K.H.C.; Tang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Tse, G.; et al. Protective Effects of Sodium-Glucose Transporter 2 Inhibitors on Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 619586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Bonaca, M.P.; Furtado, R.H.M.; Mosenzon, O.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; Bhatt, D.L.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Wilding, J.P.H.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin on Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Insights From the DECLARE-TIMI 58 Trial. Circulation 2020, 141, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, J.H.; Docherty, K.F.; Jhund, P.S.; de Boer, R.A.; Böhm, M.; Desai, A.S.; Howlett, J.G.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and atrial fibrillation in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Insights from DAPA-HF. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 24, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okunrintemi, V.; Mishriky, B.M.; Powell, J.R.; Cummings, D.M. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors and atrial fibrillation in the cardiovascular and renal outcome trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Meng, L.; Lee, S.; Tse, G.; Gong, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, T. Empagliflozin, a sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, alleviates atrial remodeling and improves mitochondrial function in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Aizawa, Y.; Yuasa, S.; Kishi, S.; Fuse, K.; Fujita, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Kitazawa, H.; Takahashi, M.; Sato, M.; et al. The effect of dapagliflozin treatment on epicardial adipose tissue volume. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Mazer, C.D.; Yan, A.T.; Mason, T.; Garg, V.; Teoh, H.; Zuo, F.; Quan, A.; Farkouh, M.E.; Fitchett, D.H.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Left Ventricular Mass in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Artery Disease: The EMPA-HEART CardioLink-6 Randomized Clinical Trial. Circulation 2019, 140, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, L.; Yuan, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X. SGLT2i: Beyond the glucose-lowering effect. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, R.E.; Mende, C.; Vijapurkar, U.; Sha, S.; Davies, M.J.; Desai, M. Effects of Canagliflozin on Serum Magnesium in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Post Hoc Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Lubitz, S.A.; Sullivan, L.M.; Sun, J.X.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Magnani, J.W.; Ellinor, P.T.; Benjamin, E.J.; Wang, T.J. Low serum magnesium and the development of atrial fibrillation in the community: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2013, 127, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamariz, L.; Hernandez, F.; Bush, A.; Palacio, A.; Hare, J.M. Association between serum uric acid and atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.J. Uric acid and the cardio-renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraakman, M.J.; Lee, M.K.; Al-Sharea, A.; Dragoljevic, D.; Barrett, T.J.; Montenont, E.; Basu, D.; Heywood, S.; Kammoun, H.L.; Flynn, M.; et al. Neutrophil-derived S100 calcium-binding proteins A8/A9 promote reticulated thrombocytosis and atherogenesis in diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2133–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.; Lynn, H.S.; Rong, F.; Zhang, W. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of the new anticoagulants versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 64, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauchier, L.; Boriani, G.; de Groot, J.R.; Kreutz, R.; Rossing, P.; Camm, A.J. Medical therapies for prevention of cardiovascular and renal events in patients with atrial fibrillation and diabetes mellitus. Europace 2021, 23, 1873–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Varughese, G.I. Diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation: Perspectives on epidemiological and pathophysiological links. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 105, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawałko, M.; Agbaedeng, T.A.; Saljic, A.; Müller, D.N.; Wilck, N.; Schnabel, R.; Penders, J.; Rienstra, M.; van Gelder, I.; Jespersen, T.; et al. Gut microbiota, dysbiosis and atrial fibrillation. Arrhythmogenic mechanisms and potential clinical implications. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 2415–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Luo, Y.; Gong, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhuo, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis promotes age-related atrial fibrillation by lipopolysaccharide and glucose-induced activation of NLRP3-inflammasome. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daios, S.; Savopoulos, C.; Kanellos, I.; Goudis, C.A.; Nakou, I.; Petalloti, S.; Hadjidimitriou, N.; Pilalas, D.; Ziakas, A.; Kaiafa, G. Circadian Pattern of Acute Myocardial Infarction and Atrial Fibrillation in a Mediterranean Country: A study in Diabetic Patients. Medicina 2021, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorenzo-Almorós, A.; Casado Cerrada, J.; Álvarez-Sala Walther, L.-A.; Méndez Bailón, M.; Lorenzo González, Ó. Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus: Dangerous Liaisons or Innocent Bystanders? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082868
Lorenzo-Almorós A, Casado Cerrada J, Álvarez-Sala Walther L-A, Méndez Bailón M, Lorenzo González Ó. Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus: Dangerous Liaisons or Innocent Bystanders? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(8):2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082868
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorenzo-Almorós, Ana, Jesús Casado Cerrada, Luis-Antonio Álvarez-Sala Walther, Manuel Méndez Bailón, and Óscar Lorenzo González. 2023. "Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus: Dangerous Liaisons or Innocent Bystanders?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 8: 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082868
APA StyleLorenzo-Almorós, A., Casado Cerrada, J., Álvarez-Sala Walther, L.-A., Méndez Bailón, M., & Lorenzo González, Ó. (2023). Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus: Dangerous Liaisons or Innocent Bystanders? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(8), 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082868








