Incomplete Lead Removal During the Extraction Procedure: Predisposing Factors and Impact on Long-Term Survival in Infectious and Non-Infectious Cases: Analysis of 3741 Procedures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Lead Extraction Procedure
2.3. Extraction of Distal Fragments of the Lead
2.4. Dataset and Statistical Methods
2.5. Approval of the Bioethics Committee
3. Results
Results Summary
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Non-removable lead fragments are encountered in about 4.2% of lead extraction procedures.
- (2)
- CIED infection has no influence on partial radiographic success but younger patient age at first CIED implantation, multiple CIED-related procedures and higher complexity of lead extraction were independent risk factors for retention of non-removable lead fragments.
- (3)
- Extraction of defibrillation (ICD) leads seems to be associated with a lower probability of retaining lead fragments.
- (4)
- Retention of an irremovable fragment of the lead (<4 cm) or even the lead tip does not affect survival time either in non-infectious patients or in patients with various types of CIED infections.
- (5)
- “Better survival” in patients with retained lead fragments following TLE is not a result of their presence but is related to the factors predisposing to the occurrence of remnants, especially younger patient age at first CIED implantation and better health status.
Study Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilkoff, B.L.; Love, C.J.; Byrd, C.L.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Carrillo, R.G.; Crossley, G.H., 3rd; Epstein, L.M.; Friedman, R.A.; Kennergren, C.E.; Mitkowski, P.; et al. Transvenous lead extraction: Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus on facilities, training, indications, and patient management: This document was endorsed by the American Heart Association (AHA). Heart Rhythm. 2009, 6, 1085–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumoto, F.M.; Schoenfeld, M.H.; Wilkoff, B.; Berul, C.I.; Birgersdotter-Green, U.M.; Carrillo, R.; Cha, Y.M.; Clancy, J.; Deharo, J.C.; Ellenbogen KAExner, D.; et al. 2017 HRS expert consensus statement on cardiovascular implantable electronic device lead management and extraction. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, e503–e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorni, M.G.; Burri, H.; Deharo, J.C.; Starck, C.; Kennergren, C.; Saghy, L.; Rao, A.; Tascini, C.; Lever, N.; Kutarski, A.; et al. 2018 EHRA expert consensus statement on lead extraction: Recommendations on definitions, endpoints, research trial design, and data collection requirements for clinical scientific studies and registries: Endorsed by APHRS/HRS/LAHRS. Europace 2018, 20, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.J.; Fearnot, N.E.; Byrd, C.L.; Wilkoff, B.L.; Love, C.J.; Sellers, T.D. Five-years’ experience with intravascular lead extraction. U.S. Lead Extraction Database. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1994, 17, 2016–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, C.L.; Wilkoff, B.L.; Love, C.J.; Sellers, T.D.; Turk, K.T.; Reeves, R.; Young, R.; Crevey, B.; Kutalek, S.P.; Freedman, R.; et al. Intravascular extraction of problematic or infected permanent pacemaker leads: 1994–1996. U.S. Extraction Database, MED Institute. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1999, 22, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, C.L.; Wilkoff, B.L.; Love, C.J.; Sellers, T.D.; Reiser, C. Clinical study of the laser sheath for lead extraction: The total experience in the United States. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2002, 25, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorni, M.G.; Giannola, G.; Arena, G.; Soldati, E.; Bartoli, C.; Lapira, F.; Zucchelli, G.; Di Cori, A. Pacing and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator transvenous lead extraction. Ital. Heart J. 2005, 6, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roux, J.F.; Pagé, P.; Dubuc, M.; Thibault, B.; Guerra, P.G.; Macle, L.; Roy, D.; Talajic, M.; Khairy, P. Laser lead extraction: Predictors of success and complications. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2007, 30, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusanov, A.; Spotnitz, H.M. A 15-year experience with permanent pacemaker and defibrillator lead and patch extractions. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 89, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diemberger, I.; Migliore, F.; Biffi, M.; Cipriani, A.; Bertaglia, E.; Lorenzetti, S.; Massaro, G.; Tanzarella, G.; Boriani, G. The “Subtle” connection between development of cardiac implantable electrical device infection and survival after complete system removal: An observational prospective multicenter study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 250, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, J.; Yamaji, K.; Nagashima, M.; Kondo, Y.; Sadohara, Y.; Hirokami, J.; Kuji, R.; Korai, K.; Fukunaga, M.; Hiroshima, K.; et al. Predictors of lead break during transvenous lead extraction. J. Arrhythm. 2021, 37, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvagna, G.M.; Romeo, P.; Ceresa, F.; Valsecchi, S. Transvenous retrieval of foreign objects lost during cardiac device implantation or revision: A 10-year experience. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2013, 36, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutarski, A.; Pietura, R.; Czajkowski, M. Breakage of extracted leads: Another management option. Kardiol. Pol. 2012, 70, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kutarski, A.; Malecka, B.; Zabek, A.; Pietura, R. Broken leads with proximal endings in the cardiovascular system: Serious consequences and extraction difficulties. Cardiol. J. 2013, 20, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanczyk, P.; Polewczyk, A.; Nowosielecka, D.; Tulecki, L.; Miszczak-Knecht, M.; Jachec, W.; Kleinrok, A.; Bieganowska, K.; Kutarski, A. Lead Extraction and Re-Extractions—Inherent Parts of Permanent Pacing in Children and Young Adults. J. Biomed. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 3, 221–226. Available online: https://www.jelsciences.com/articles/jbres1426.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Stefańczyk, P.; Borzęcki, W.; Tułecki, Ł.; Tomków, K.; Nowosielecka, D.; Kleinrok, A.; Kutarski, A. To replace or to abandon and implant a new lead? Conservative approach creates new challenges (and risks) for the patients in future. Should we still wait for class 1 indications? Case report and discussion of the problem. Heart Beat. 2019, 4, 16–192019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanawuttiwat, T.; Cheng, A.; Rickard, J.; Chow, G.V.; Sciortino, C.M.; Brinker, J. Successful extraction of right ventricular lead remnants using the FlexCath® steerable sheath. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2016, 45, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raatikainen, M.J.; Perälä, J.; Lahtinen, J. Successful defibrillator lead remnant extraction from right ventricle using a steerable transseptal sheath and a basket retriever. Europace 2009, 11, 1238–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutarski, A.; Chudzik, M.; Tomaszewski, A.; Pietura, R.; Oszczygiel, A.; Czajkowski, M.; Wranicz, J.K. Difficult dual-stage transcutaneous multiple lead extraction with loss of external silicone tube of broken lead. Cardiol. J. 2013, 20, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, S.; Cranney, G.; Bennett, M.; Giles, R. Long-term outcomes following transvenous lead extraction. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 39, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, S.; Cranney, G.; Bennett, M.; Giles, R. Lead Extraction for Treatment of Cardiac Device Infection: A 20-Year Single Centre Experience. Heart Lung Circ. 2017, 26, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nof, E.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Auricchio, A.; Butter, C.; Dagres, N.; Deharo, J.C.; Rinaldi, C.A.; Maggioni, A.P.; Kutarski, A.; ELECTRa Investigators; et al. Comparison of outcomes in infected cardiovascular implantable electronic devices between complete, partial, and failed lead removal: An ESC-EHRA-EORP ELECTRa (European Lead Extraction ConTrolled) registry. Europace 2019, 21, 1876–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golzio, P.G.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Giuggia, M.; Vinci, M.; Gazzera, C.; Breatta, A.D. Retrieval of pacemaker lead tip embolized into the distal pulmonary arterial bed during extraction procedure. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2007, 30, 1558–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.; Oliver, J.; Sheridan, P.; Sahu, J.; Bowes, R. Fragmentation and embolization of pacemaker leads as a complication of lead extraction. Europace 2010, 12, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Baek, Y.S.; Lee, M.; Uhm, J.S.; Pak, H.N.; Lee, M.H.; Joung, B. Remnant Pacemaker Lead Tips after Lead Extractions in Pacemaker Infections. Korean Circ. J. 2016, 46, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutarski, A.; Polewczyk, M.; Pietura, M. A rare complication of transvenous lead extraction—Pulmonary embolization with a broken distal lead fragment. Heart Beat. 2016, 1, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchelli, G.; Di Cori, A.; Segreti, L.; Laroche, C.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Kutarski, A.; Regoli, F.; Butter, C.; Defaye, P.; ELECTRa Investigators; et al. Major cardiac and vascular complications after transvenous lead extraction: Acute outcome and predictive factors from the ESC-EHRA ELECTRa (European Lead Extraction ConTRolled) registry. Europace 2019, 21, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, A.F.; Wazni, O.M.; Tarakji, K.; Saliba, W.I.; Nimri, N.; Rickard, J.; Brunner, M.; Bhargava, M.; Kanj, M.; Baranowski, B.; et al. Transvenous lead extraction at the time of cardiac implantable electronic device upgrade: Complexity, safety, and outcomes. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, 1807–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bontempi, L.; Vassanelli, F.; Cerini, M.; Inama, L.; Salghetti, F.; Giacopelli, D.; Gargaro, A.; Raweh, A.; Curnis, A. Predicting the difficulty of a transvenous lead extraction procedure: Validation of the LED index. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 28, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontempi, L.; Curnis, A.; Della Bella, P.; Cerini, M.; Radinovic, A.; Inama, L.; Melillo, F.; Salghetti, F.; Marzi, A.; Gargaro, A.; et al. The MB score: A new risk stratification index to predict the need for advanced tools in lead extraction procedures. Europace 2020, 22, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, P.; Tsiachris, D.; Marzi, A.; Ciconte, G.; Paglino, G.; Sora, N.; Sala, S.; Vergara, P.; Gulletta, S.; Della Bella, P. Predictors of advanced lead extraction based on a systematic stepwise approach: Results from a high volume center. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2013, 36, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutarski, A.; Polewczyk, M.; Polewczyk, A.M.; Polewczyk, A. A relevant Byrd dilator sheath damage during transvenous lead extraction—The rare phenomenon with potentially serious consequences. Heart Beat. 2017, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutarski, A.; Jacheć, W.; Tułecki, Ł.; Czajkowski, M.; Nowosielecka, D.; Stefańczyk, P.; Tomków, K.; Polewczyk, A. Disparities in transvenous lead extraction in young adults. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCanta, A.C.; Tanel, R.E.; Gralla, J.; Runciman, D.M.; Collins, K.K. The fate of nontargeted endocardial leads during the extraction of one or more targeted leads in pediatrics and congenital heart disease. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2014, 37, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tułecki, Ł.; Czajkowski, M.; Targońska, S.; Polewczyk, A.; Jacheć, W.; Tomków, K.; Karpeta, K.; Nowosielecka, D.; Kutarski, A. The role of cardiac surgeon in transvenous lead extraction: Experience from 3462 procedures. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowosielecka, D.; Jacheć, W.; Polewczyk, A.; Tułecki, Ł.; Tomków, K.; Stefańczyk, P.; Tomaszewski, A.; Brzozowski, W.; Szcześniak-Stańczyk, D.; Kleinrok, A.; et al. Transesophageal Echocardiography As a Monitoring Tool During Transvenous Lead Extraction-Does It Improve Procedure Effectiveness? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oszczygieł, E.; Kutarski, A.; Oszczygieł, A.; Mańkowska-Załuska, B.; Chudzik, M.; Wranicz, J.K.; Cygankiewicz, I. Risk score to assess mortality risk in patients undergoing transvenous lead extraction. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 40, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckx, S.; Marynissen, T.; Rega, F.; Ector, J.; Nuyens, D.; Heidbuchel, H.; Willems, R. Predictors of 30-day and 1-year mortality after transvenous lead extraction: A single-centre experience. Europace 2014, 16, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diemberger, I.; Biffi, M.; Lorenzetti, S.; Martignani, C.; Raffaelli, E.; Ziacchi, M.; Rapezzi, C.; Pacini, D.; Boriani, G. Predictors of long-term survival free from relapses after extraction of infected CIED. Europace 2018, 20, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemberger, I.; Segreti, L.; Rinaldi, C.A.; Svendsen, J.H.; Kutarski, A.; Younis, A.; Laroche, C.; Leclercq, C.; Małecka, B.; Mitkowski, P.; et al. Transvenous Lead Extraction in Patients with Cardiac Implantable Device: The Impact of Systemic and Local Infection on Clinical Outcomes-An ESC-EHRA ELECTRa (European Lead Extraction Controlled) Registry Substudy. Biology 2022, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maytin, M.; Jones, S.O.; Epstein, L.M. Long-term mortality after transvenous lead extraction. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2012, 5, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, V.S.; Elliott, M.K.; Sidhu, B.S.; Gould, J.; Kemp, T.; Vergani, V.; Kadiwar, S.; Shetty, A.K.; Blauth, C.; Gill, J.; et al. Long-term survival following transvenous lead extraction: Importance of indication and comorbidities. Heart Rhythm. 2021, 18, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polewczyk, A.; Jacheć, W.; Tomaszewski, A.; Brzozowski, W.; Czajkowski, M.; Opolski, G.; Grabowski, M.; Janion, M.; Kutarski, A. Lead-related infective endocarditis: Factors influencing early and long-term survival in patients undergoing transvenous lead extraction. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narducci, M.L.; Di Monaco, A.; Pelargonio, G.; Leoncini, E.; Boccia, S.; Mollo, R.; Perna, F.; Bencardino, G.; Pennestrì, F.; Scoppettuolo, G.; et al. Presence of ‘ghosts’ and mortality after transvenous lead extraction. Europace 2017, 19, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutarski, A.; Czajkowski, M.; Pietura, R.; Obszanski, B.; Polewczyk, A.; Jachec, W.; Polewczyk, M.; Młynarczyk, K.; Grabowski, M.; Opolski, G. Effectiveness, safety, and long-term outcomes of non-powered mechanical sheaths for transvenous lead extraction. Europace 2018, 20, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
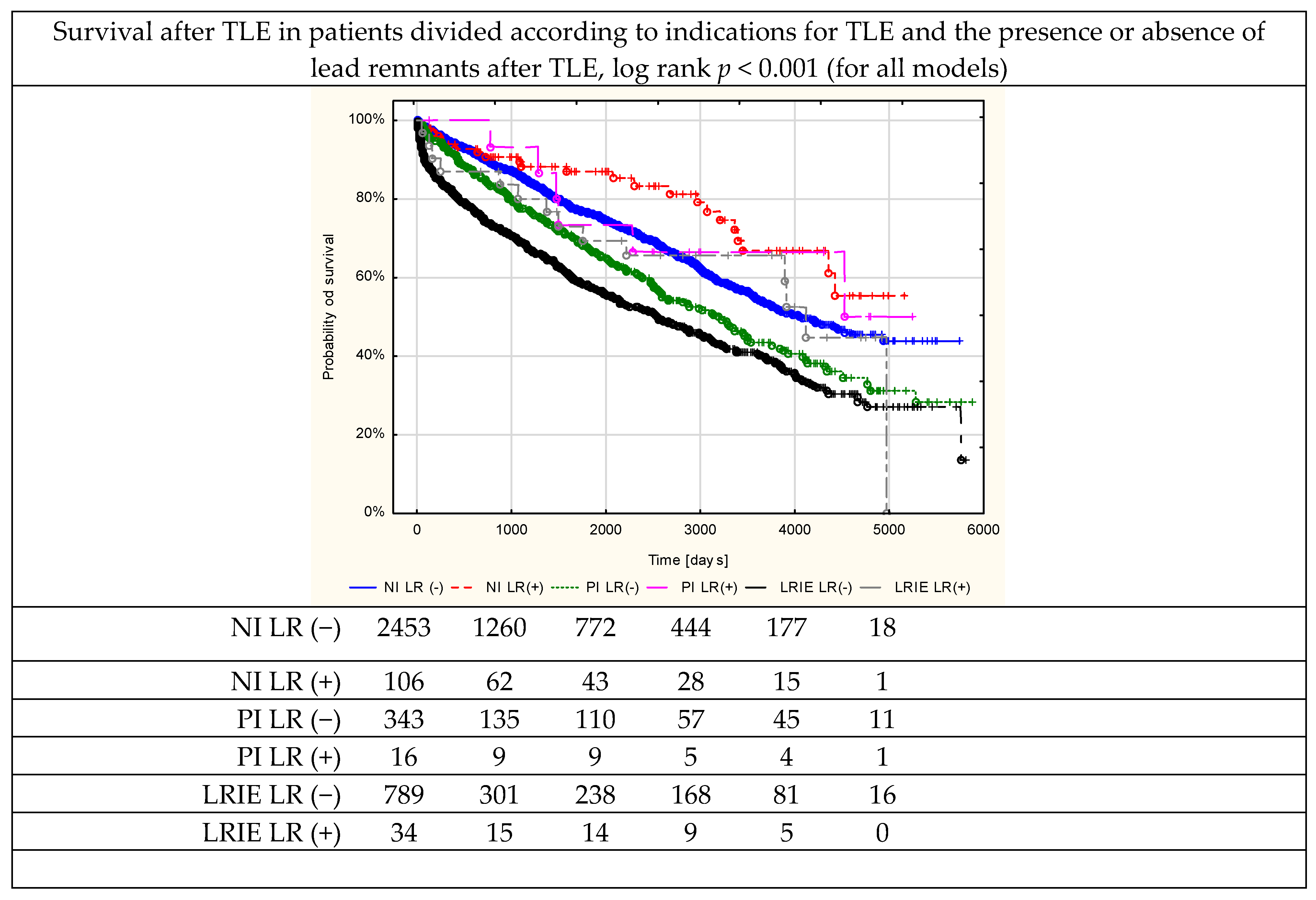
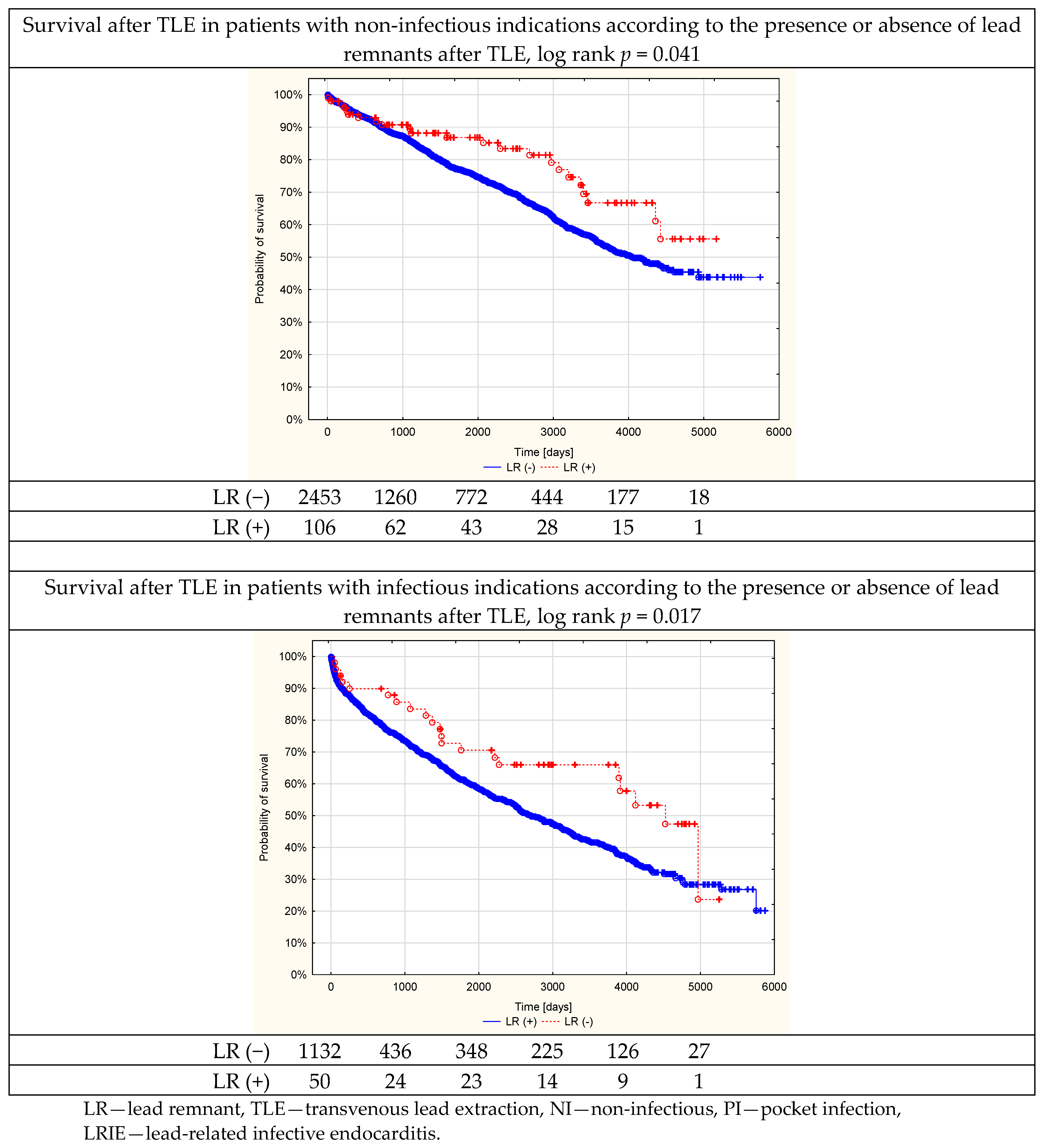
| Non-Infectious Indications | Pocket Infection | Lead-Related Infective Endocarditis | All Infectious Indications | All Patients | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | |
| n = 2453 | n = 106 | n = 343 | n = 16 | n = 789 | n = 34 | n = 1132 | n = 50 | n = 3585 | n = 156 | |
| Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | ||||||
| Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | ||||||
| Clinical data | ||||||||||
| Patient age during TLE [years] | 61.14 ± 16.00 | 54.62 ± 22.59 p < 0.001 | 69.87 ± 13.00 | 64.00 ± 15.93 p = 0.157 | 68.47 ± 13.58 | 64.74 ± 15.23 p = 0.171 | 68.89 ± 13.42 | 64.50 ± 15.29 p = 0.051 | 66.32 ± 15.33 | 57.79 ± 21.00 p < 0.001 |
| Patient age at first CIED implantation [years] | 56.59 ± 17.42 | 40.48 ± 23.29 p < 0.001 | 62.27 ± 13.55 | 52.81 ± 18.10 p = 0.025 | 60.99 ± 14.81 | 50.03 ± 19.26 p < 0.001 | 61.38 ± 14.44 | 50.88 ± 18.77 p < 0.001 | 58.10 ± 16.68 | 43.91 ± 22.39 p < 0.001 |
| Female | 1041 (42.44) | 41 (38.68) p = 0.445 | 92 (26.82) | 5 (31.25) p = 0.919 | 232 (29.40) | 14 (41.18) p = 0.171 | 324 (28.62) | 19 (38.00) p = 0.169 | 1365 (38.08) | 60 (38.46) p = 0.876 |
| Ischemic aetiology | 1396 (56.91) | 40 (37.74) p < 0.001 | 201 (58.60) | 10 (62.50) p = 0.905 | 428 (54.25) | 15 (44.11) p = 0.477 | 629 (55.56) | 25 (50.00) p = 0.715 | 2025 (56.48) | 65 (41.67) p < 0.001 |
| NYHA class [I–IV] | 1.83 ± 0.67 | 1.68 ± 0.70 p = 0.018 | 1.79 ± 0.65 | 1.38 ± 0.50 p = 0.022 | 1.90 ± 0.75 | 1.75 ± 0.73 p = 0.346 | 1.86 ± 0.72 | 1.63 ± 0.69 p = 0.047 | 1.84 ± 0.69 | 1.66 ± 0.69 p = 0.002 |
| LVEF [%] | 48.84 ± 15.45 | 54.09 ± 12.97 p = 0.005 | 49.17 ± 14.70 | 55.88 ± 12.18 p = 0.085 | 47.37 ± 15.04 | 53.86 ± 10.56 p = 0.007 | 47.83 ± 15.02 | 54.49 ± 11.01 p = 0.001 | 49.20 ± 15.33 | 54.22 ± 12.31 p < 0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure (symptomatic) | 480 (19.57) | 15 (14.15) p = 0.363 | 55 (16.04) | 0 (0.00) p = 0.166 | 153 (19.39) | 1 (2.94) p = 0.063 | 208 (18.38) | 1 (2.00) p = 0.013 | 688 (19.19) | 16 (10.26) p = 0.006 |
| Renal failure (any) | 457 (18.63) | 10 (9.43) p = 0.048 | 76 (22.16) | 2 (12.50) p = 0.516 | 241 (30.55) | 5 (14.71) p = 0.122 | 317 (28.00) | 7 (14.00) p = 0.068 | 774 (21.59) | 17 (10.90) p = 0.006 |
| Diabetes t.2 | 444 (18.14) | 10 (9.43) p = 0.022 | 72 (20.99) | 3 (18.75) p = 0.852 | 211 (26.81) | 5 (13.89) p = 0.118 | 283 (25.04) | 8 (15.39) p = 0.157 | 727 (20.28) | 18 (11.54) p = 0.008 |
| Charlson comorbidity index [points] | 4.52 ± 3.62 | 3.07 ± 3.20 p < 0.001 | 4.99 ± 3.46 | 3.94 ± 3.64 p = 0.136 | 5.49 ± 3.87 | 3.82 ± 3.24 p < 0.001 | 5.34 ± 3.76 | 3.86 ± 3.34 p = 0.002 | 4.78 ± 3.68 | 3.32 ± 2.26 p < 0.001 |
| Indications for lead extraction | ||||||||||
| Non-infectious | 2453 (100.0) | 106 (100.0) p = 1.000 | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 2453 (68.42) | 106 (67.95) p = 0.972 |
| Infectious | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 343 (100.0) | 16 (100.0) p = 1.000 | 789 (100.0) | 34 (100.0) p = 1.000 | 1132 (100.0) | 50 (100.0) p = 1.000 | 1132 (31.58) | 50 (32.05) p = 0.783 |
| Pocket infection (isolated) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 343 (100.0) | 16 (100.0) p = 1.000 | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 343 (30.30) | 16 (32.00) p = 0.938 | 343 (9.57) | 16 (10.26) p = 0.935 |
| LRIE + PI | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 441 (55.89) | 12 (35.29) p = 0.014 | 441 (38.96) | 12 (24.00) p = 0.032 | 441 (12.30) | 12 (7.69) p = 0.103 |
| LRIE (isolated) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 348 (44.11) | 22 (64.71) p = 0.029 | 348 30.74) | 22 (44.00) p = 0.019 | 348 (9.71) | 22 (14.10) p = 0.096 |
| LRIE all | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00 | 789 (100.0) | 34 (100.0) p = 1.000 | 789 (69.58) | 34 (68.00) p = 0.938 | 789 (22.01) | 34 (21.79) p = 0.878 |
| Main pathogen | ||||||||||
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 24 (7.96) | 1 (6.67) p = 0.885 | 105 (13.89) | 2 (5.88) p = 0.276 | 129 (12.08) | 3 (6.12) p = 0.285 | 129 (12.01) | 3 (6.12) p = 0.315 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 63 (20.19) | 3 (20.00) p = 0.776 | 196 (25.93) | 7 (20.59) p = 0.571 | 259 (24.25) | 10 (20.48) p = 0.633 | 259 (24.12) | 10 (20.41) p = 0.697 |
| Staphylococcus (other) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 45 (14.42) | 1 (6.67) p = 0.878 | 107 (14.15) | 7 (20.59) p = 0.678 | 152 (14.23) | 8 (16.33) p = 0.844 | 152 (14.15) | 8 (16.33) p = 0.814 |
| Other bacteria | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 13 (4.17) | 1 (6.67) p = 0.863 | 62 (8.20) | 2 (5.88) p = 0.956 | 75 (7.02) | 3 (6.12) p = 0.876 | 75 (6.98) | 3 (6.12) p = 0.829 |
| Culture negative | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 112 (35.90) | 7 (46.68) p = 0.538 | 175 (23.15) | 11 (32.35) p = 0.172 | 287 (26.87) | 18 (36.74) p = 0.106 | 292 (27.19) | 18 (36.74) p = 0.106 |
| Lack of culture result | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 55 (17.63) | 2 (13.33) p = 0.863 | 111 (14.68) | 5 (14.71) p = 0.978 | 166 (15.54) | 7 (14.29) p = 0.830 | 167 (15.55) | 7 (14.29) p = 0.663 |
| Non-Infectious Indications | Pocket Infection | Lead-Related Infectious Endocarditis | All Infectious Indications | All Patients | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | |
| n = 2453 | n = 106 | n = 343 | n = 16 | n = 789 | n = 34 | n = 1132 | n = 50 | n = 3585 | n = 156 | |
| Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | ||||||
| Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | ||||||
| System and history of pacing | ||||||||||
| ICD—all | 575 (23.44) | 9 (8.49) p = 0.002 | 70 (20.41) | 0 (0.00) p = 0.091 | 168 (21.29) | 3 (8.82) p = 0.209 | 238 (21.03) | 3 (6.00) p = 0.031 | 813 (22.68) | 12 (7.69) p < 0.001 |
| CRT-D pacing system | 140 (5.71) | 3 (2.83) p = 0.490 | 29 (8.46) | 0 (0.00) p = 0.457 | 88 (11.15) | 1 (2.94) p = 0.188 | 117 (10.34) | 1 (2.00) p = 0.080 | 257 (7.17) | 4 (2.56) p = 0.037 |
| Presence of abandoned lead before TLE | 202 (8.24) | 23 (21.70) p < 0.001 | 45 (13.12) | 3 (18.75) p = 0.719 | 127 (16.10) | 13 (38.24) p = 0.004 | 172 (15.19) | 16 (32.00) p = 0.013 | 374 (10.43) | 39 (25.00) p < 0.001 |
| Number of procedures before lead extraction | 1.70 ± 0.93 | 2.38 ± 1.33 p < 0.001 | 2.14 ± 1.15 | 2.67 ± 0.82 p = 0.007 | 2.06 ± 1.23 | 3.24 ± 1.79 p < 0.001 | 2.09 ± 1.21 | 3.06 ± 1.56 p < 0.001 | 1.83 ± 1.05 | 2.61 ± 1.44 p < 0.001 |
| PADIT score [points] | 3.53 ± 2.82 | 4.49 ± 2.02 p < 0.001 | 3.90 ± 3.00 | 4.06 ± 2.57 p = 0.481 | 4.13 ± 3.02 | 4.79 ± 2.79 p = 0.186 | 4.06 ± 3.01 | 4.56 ± 2.72 p = 0.133 | 3.70 ± 2.89 | 4.51 ± 2.92 p < 0.001 |
| Dwell time of oldest lead per patient before TLE [months] | 103.4 ± 73.31 | 178.1 ± 94.04 p < 0.001 | 89.28 ± 68.91 | 134.3 ± 49.25 p < 0.001 | 89.72 ± 68.19 | 168.8 ± 80.43 p < 0.001 | 89.57 ± 68.40 | 157.8 ± 73.23 p < 0.001 | 99.04 ± 74.17 | 171.6 ± 88.19 p < 0.001 |
| Global (cumulative) implant duration per patient [years] | 15.25 ± 12.80 | 26.71 ± 15.24 p < 0.001 | 12.91 ± 10.80 | 22.57 ± 7.98 p < 0.001 | 14.39 ± 12.61 | 30.55 ± 15.55 p < 0.001 | 13.94 ± 12.10 | 28.00 ± 14.02 p < 0.001 | 14.84 ± 12.60 | 27.12 ± 14.82 p < 0.001 |
| Procedure-related risk factors for major complications and complexity of TLE | ||||||||||
| Number of extracted leads per patient | 1.48 ± 0.64 | 1.75 ± 0.79 p < 0.001 | 1.88 ± 0.67 | 2.19 ± 0.40 p = 0.033 | 2.05 ± 0.80 | 2.41 ± 0.70 p < 0.003 | 2.00 ± 0.77 | 2.34 ± 0.63 p < 0.001 | 1.64 ± 0.72 | 1.94 ± 0.79 p < 0.001 |
| Three or more leads extracted | 152 (6.20) | 17 (16.04) p < 0.001 | 44 (12.83) | 16 (100.0) p < 0.001 | 164 (20.79) | 14 (41.18) p < 0.001 | 208 (18.38) | 17 (34.00) p = 0.0.10 | 360 (10.04) | 34 (21.80) p < 0.001 |
| Alternative approach | 65 (2.65) | 17 (16.04) p < 0.001 | 8 (2.33) | 1 (6.25) p = 0.872 | 34 (4.31) | 10 (29.41) p < 0.001 | 42 (2.65) | 11 (22.00) p = 0.001 | 107 (2.99) | 28 (17.95) p < 0.001 |
| Extraction of abandoned lead(s) (any) | 180 (7.34) | 20 (18.87) p < 0.001 | 42 (12.25) | 2 (12.50) p = 0.719 | 122 (15.460 | 13 (38.24) p = 0.001 | 164 (14.49) | 15 (30.00) p = 0.005 | 344 (9.60) | 35 (22.44) p < 0.001 |
| ICD lead extraction | 652 (26.58) | 11 (10.38) p < 0.001 | 99 (28.86) | 0 (0.00) p = 0.025 | 255 (32.32) | 4 (11.77) p < 0.001 | 354 (31.27) | 4 (8.00) p < 0.001 | 1006 (28.06) | 15 (9.62) p < 0.001 |
| Dwell time of oldest extracted lead per patient before TLE (months) | 101.1 ± 75.07 | 177.7 ± 94.13 p < 0.001 | 87.94 ± 67.69 | 134.3 ± 49.25 p = 0.001 | 89.21 (67.74) | 167.4 ± 78.67 p < 0.001 | 88.83 (67.70) | 156.8 ± 71.79 p = 0.001 | 97.20 ± 73.04 | 171.0 ± 87.90 p < 0.001 |
| Global (cumulative) age of extracted leads per patient (in years) | 12.98 ± 12.49 | 23.37 ± 15.63 p < 0.001 | 12.57 ± 10.50 | 22.56 ± 7.98 p = 0.001 | 14.17 (12.44) | 28.81 ± 14.44 p < 0.001 | 13.69 ± 11.90 | 26.81 ± 12.98 p = 0.001 | 13.21 ± 12.31 | 25.15 ± 14.83 p < 0.001 |
| Non-Infectious Indications | Pocket Infection | Lead-Related Infectious Endocarditis | All Infectious Indications | All Patients | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | LR(−) | LR(+) | |
| n = 2453 | n = 106 | n = 343 | n = 16 | n = 789 | n = 34 | n = 1132 | n = 50 | n = 3585 | n = 156 | |
| Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | Mann–Whitney U test Chi2 test | ||||||
| Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | Mean ± SD Count (%) | ||||||
| Procedure complexity and outcomes | ||||||||||
| Procedure duration (sheath-to-sheath) [minutes] | 13.08 ± 18.41 | 50.13 ± 62.44 p < 0.001 | 13.07 ± 19.05 | 26.00 ± 22.00 p < 0.001 | 16.02 ± 23.38 | 36.71 ± 31.05 p < 0.001 | 15.12 ± 22.19 | 33.28 ± 28.68 p < 0.001 | 13.73 ± 19.70 | 44.73 ± 54.44 p < 0.001 |
| Average time of single lead extraction * [minutes] | 8.70 ± 11.62 | 28.38 ± 32.81 p < 0.001 | 6.87 ± 8.91 | 12.07 ± 10.20 p = 0.009 | 7.51 ± 9.33 | 15.11 ± 11.83 p < 0.001 | 7.32 ± 9.20 | 14.14 ± 11.32 p < 0.001 | 8.26 ± 10.93 | 23.76 ± 28.47 p < 0.001 |
| Unexpected procedure difficulty (any) | 460 (18.75) | 69 (65.09) p < 0.001 | 42 (12.54) | 10 (62.50) p < 0.001 | 109 (13.82) | 18 (52.94) p < 0.001 | 151 (13.34) | 28 (56.00) p < 0.001 | 611 (17.04) | 97 (62.18) p < 0.001 |
| Need to change venous approach | 57 (2.32) | 17 (16.04) p < 0.001 | 8 (2.33) | 2 (12.50) p = 0.101 | 33 (4.18) | 10 (29.41) p < 0.001 | 41 (3.62) | 12 (24.00) p < 0.001 | 98 (2.73) | 29 (18.95) p < 0.001 |
| Fracture of extracted lead | 57 (2.32) | 45 (42.45) p < 0.001 | 7 (2.04) | 7 (43.75) p < 0.001 | 15 (1.90) | 13 (38.24) p < 0.001 | 22 (1.94) | 20 (40.00) p < 0.001 | 79 (2.20) | 65 (41.67) p < 0.001 |
| Two or more technical problems | 122 (4.79) | 47 (44.34) p < 0.001 | 15 (4.37) | 5 (32.25) p < 0.001 | 35 (4.44) | 13 (38.24) p < 0.001 | 50 (4.42) | 18 (36.00) p < 0.001 | 172 (4.80) | 65 (41.67) p < 0.001 |
| Use of second line/advanced tools | ||||||||||
| Evolution (old and new) or TightRail | 28 (1.14) | 14 (13.21) p < 0.001 | 4 (1.17) | 1 (6.25) p = 0.545 | 6 (0.76) | 2 (5.88) p = 0.046 | 10 (0.88) | 3 (6.00) p = 0.010 | 38 (1.06) | 17 (10.90) p < 0.001 |
| Metal sheath | 209 (8.52) | 32 (30.19) p < 0.001 | 17 (4.96) | 2 (12.50) p = 0.455 | 41 (5.20) | 3 (8.82) p = 0.664 | 58 (5.12) | 5 (10.00) p = 0.278 | 267 (7.45) | 37 (23.72) p < 0.001 |
| Lasso catheter/snare/basket catheter | 96 (3.92) | 36 (33.96) p < 0.001 | 7 (2.04) | 6 (37.50) p < 0.001 | 26 (3.30) | 9 (26.47) p < 0.001 | 33 (2.92) | 15 (30.00) p < 0.001 | 129 (3.60) | 51 (32.69) p < 0.001 |
| TLE efficacy and complications | ||||||||||
| Major complications (any) | 46 (1.88) | 10 (9.43) p < 0.001 | 3 (0.88) | 2 (12.50) p = 0.005 | 12 (1.52) | 4 (11.77) p < 0.001 | 15 (1.33) | 6 (12.00) p < 0.001 | 61 (1.70) | 16 (10.26) p < 0.001 |
| Haemopericardium | 30 (1.22) | 8 (7.55) p = 0.002 | 2 (0.58) | 1 (6.25) p = 0.303 | 6 (0.76) | 3 (8.82) p < 0.001 | 7 (0.62) | 2 (4.00) p < 0.001 | 36 (1.00) | 12 (7.69) p < 0.001 |
| Tricuspid valve damage during TLE (severe) | 14 (0.57) | 2 (1.89) p = 0.308 | 0 (0.00) | 1 (6.25) p = 0.027 | 5 (0.63) | 0 (0.00) p = 0.508 | 5 (0.44) | 1 (2.00) p = 0.639 | 19 (0.53) | 3 (1.92) p = 0.095 |
| Emergent cardiac surgery | 25 (1.02) | 7 (6.60) p = 0.042 | 2 (0.58) | 1 (6.25) p = 0.159 | 5 (0.63) | 3 (8.82) p < 0.001 | 7 (0.62) | 3 (6.00) p = 0.002 | 32 (0.893) | 10 (6.41) p < 0.001 |
| Complete clinical success | 2436 (99.31) | 101 (95.28) p < 0.001 | 342 (99.71) | 1 (6.25) p < 0.001 | 779 (98.73) | 4 (11.77) p < 0.001 | 1121 (99.03) | 5 (10.00) p < 0.001 | 3557 (99.22) | 105 (67.31) p < 0.001 |
| Complete procedural success | 2436 (99.31) | 0 (0.00) p < 0.001 | 342 (99.71) | 0 (0.00) p < 0.001 | 779 (98.73) | 1 (2.94) p < 0.001 | 1121 (99.03) | 1 (2.00) p < 0.001 | 3557 (99.22) | 1 (0.65) p < 0.001 |
| Death, procedure related (intra-, post-procedural) | 3 (0.12) | 2 (1.89) p = 0.004 | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (2.94) p = 0.021 | 0 (0.00) | 1 (2.00) p = 0.023 | 3 (0.08) | 3 (1.92) p < 0.001 |
| Death, indication-related (intra-, post-procedural) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (0.29) | 0 (0.00) p = 0.835 | 2 (0.25) | 1 (2.94) p = 0.274 | 3 (0.27) | 1 (2.00) p = 0.410 | 3 (0.08) | 1 (0.64) p = 0.404 |
| Survival at follow-up | ||||||||||
| Log rank p for all models | p < 0.001 | |||||||||
| Survivors at follow-up | 1743 (71.06) | 82 (77.34) | 181 (52.77) | 10 (62.50) | 354 (44.87) | 17 (50.00) | 535 (47.26) | 27 (54.00) | 2278 (63.54) | 109 (69.87) |
| <First 2 days after TLE | 3 (0.12) | 1 (0.94) p = 0.404 | 1 (0.29) | 0 (0.00) p = 0.829 | 2 (0.25) | 4 (11.76) p < 0.001 | 3 (0.27) | 4 (8.00) p < 0.001 | 6 (0.17) | 5 (3.21) p < 0.001 |
| One-month mortality after TLE | 18 (0.73) | 2 (1.89) p = 0.455 | 4 (1.17) | 0 (0.00) p = 0.433 | 35 (4.44) | 4 (11.76) p = 0.120 | 39 (3.45) | 4 (8.00) p = 0.196 | 57 (1.59) | 6 (3.85) p = 0.068 |
| One-year mortality after TLE | 131 (5.34) | 7 (6.60) Log rank p = 0.811 | 28 (8.16) | 0 (0.00) Log rank p = 0.244 | 140 (17.74) | 7 (20.59) Log rank p = 0.418 | 168 (14.84) | 7 (14.00) Log rank p = 0.208 | 299 (8.34) | 14 (8.97) Log rank p = 0.461 |
| Three-year mortality after TLE | 211 (8.60) | 11 (10.38) Log rank p = 0.419 | 71 (20.70) | 1 (6.25) Log rank p = 0.132 | 237 (30.04) | 9 (26.47) Log rank p = 0.158 | 308 (27.21) | 10 (20.00) Log rank p = 0.046 | 619 (17.27) | 21 (13.46) Log rank p = 0.054 |
| Total mortality at follow-up | 710 (28.94) | 24 (22.64) Log rank p = 0.012 | 162 (47.23) | 6 (37.50) Log rank p = 0.181 | 435 (55.13) | 17 (50.00) Log rank p = 0.052 | 597 (52.74) | 23 (46.00) Log rank p = 0.010 | 1307 (36.46) | 47 (30.13) Log rank p = 0.041 |
| Univariable Linear Regression | Multivariable Linear Regression | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p | OR | 95% CI | p | |
| The tip of the lead left after TLE | ||||||
| Patient age at first CIED implantation [by 1 year] | 0.977 | 0.966–0.989 | p < 0.001 | 0.984 | 0.972–0.997 | p = 0.013 |
| Number of procedures before lead extraction [by 1] | 1.498 | 1.285–1.747 | p < 0.001 | 1.362 | 1.153–1.609 | p < 0.001 |
| Unexpected procedure difficulty (any) [y/n] | 3.027 | 1.856–4.973 | p < 0.001 | 2.211 | 1.327–3.686 | p = 0.002 |
| Lead or longer fragment of the lead retained after TLE | ||||||
| Patient age at first CIED implantation [by 1 year] | 0.964 | 0.955–0.974 | p < 0.001 | 0.978 | 0.967–0.988 | p < 0.001 |
| ICD lead extraction [y/n] | 0.231 | 0.106–0.502 | p < 0.001 | 0.311 | 0.141–0.685 | p = 0.004 |
| Number of procedures before lead extraction [by 1] | 1.628 | 1.420–1.868 | p < 0.001 | 1.330 | 1.134–1.560 | p < 0.001 |
| Unexpected procedure difficulty (any) [y/n] | 9.815 | 6.192–15.56 | p < 0.001 | 6.319 | 3.903–10.23 | p < 0.001 |
| All remnants present after TLE | ||||||
| Patient age at first CIED implantation [by 1 year] | 0.965 | 0.958–0.972 | p < 0.001 | 0.975 | 0.968–0.983 | p < 0.001 |
| ICD lead extraction [y/n] | 0.303 | 0.182–0.503 | p < 0.001 | 0.393 | 0.234–0.662 | p < 0.001 |
| Number of procedures before lead extraction [by 1] | 1.607 | 1.444–1.789 | p < 0.001 | 1.323 | 1.171–1.494 | p < 0.001 |
| Unexpected procedure difficulty (any) [y/n] | 7.483 | 5.392–10.38 | p < 0.001 | 4.909 | 3.478–6.927 | p < 0.001 |
| Univariable Cox Regression | Multivariable Cox Regression | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire Cohort | ||||||
| HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | |
| Patient age during TLE [by 1 year] | 1.050 | 1.045–1.055 | p < 0.001 | 1.046 | 1.040–1.052 | p < 0.001 |
| Female [y/n] | 0.653 | 0.582–0.733 | p < 0.001 | 0.927 | 0.817–1.051 | p = 0.238 |
| Ischemic aetiology [y/n] | 1.799 | 1.610–2.012 | p < 0.001 | 0.950 | 0.852–1.080 | p = 0.491 |
| NYHA functional class [by 1] | 2.149 | 2.000–2.308 | p < 0.001 | 1.345 | 1.224–1.477 | p < 0.001 |
| LVEF [by 1 %p] | 0.966 | 0.962–0.969 | p < 0.001 | 0.979 | 0.974–0.984 | p < 0.001 |
| Renal failure (any) [y/n] | 3.245 | 2.896–3.635 | p < 0.001 | 1.835 | 1.628–2.068 | p < 0.001 |
| Diabetes t. 2 [y/n] | 1.825 | 1.616–2.061 | p < 0.001 | 1.322 | 1.168–2.068 | p < 0.001 |
| Charlson comorbidity index [by 1 point] | 1.146 | 1.131–1.161 | p < 0.001 | |||
| Pocket infection [y/n] | 1.178 | 1.001–1.386 | p = 0.048 | 1.300 | 1.095–1.545 | p = 0.001 |
| Lead-related infective endocarditis [y/n] | 1.717 | 1.532–1.924 | p < 0.001 | 1.614 | 1.430–1.822 | p < 0.001 |
| ICD VR-DR before TLE [y/n] | 1.182 | 1.043–1.340 | p = 0.009 | 1.126 | 0.969–1.308 | p = 0.123 |
| CRTD before TLE [y/n] | 2.274 | 1.905–2.716 | p < 0.001 | 1.308 | 1.071–1.598 | p = 0.009 |
| 1 Lead remnant after TLE [y/n] | 0.622 | 0.460–0.840 | p = 0.002 | 0.858 | 0.634–1.161 | p = 0.321 |
| Non-infectious indications for lead extraction | ||||||
| Patient age during TLE [by 1 year] | 1.053 | 1.046–1.060 | p < 0.001 | 1.052 | 1.043–1.061 | 0.000 |
| Female [y/n] | 0.632 | 0.543–0.735 | p < 0.001 | 0.877 | 0.738–1.043 | 0.137 |
| Ischemic aetiology [y/n] | 2.027 | 1.738–2.364 | p < 0.001 | 0.921 | 0.779–1.089 | 0.334 |
| NYHA functional class [by 1] | 2.246 | 2.034–2.480 | p < 0.001 | 1.262 | 1.103–1.443 | 0.001 |
| LVEF [by 1 %p] | 0.964 | 0.959–0.968 | p < 0.001 | 0.977 | 0.971–0.984 | 0.000 |
| Renal failure (any) [y/n] | 3.419 | 2.924–3.997 | p < 0.001 | 1.787 | 1.511–2.113 | 0.000 |
| Diabetes t. 2 [y/n] | 1.773 | 1.497–2.099 | p < 0.001 | 1.242 | 1.043–1.478 | 0.015 |
| Charlson comorbidity index [by 1 point] | 1.146 | 1.126–1.167 | p < 0.001 | |||
| ICD VR-DR before TLE [y/n] | 1.166 | 1.001–1.374 | p = 0.049 | 1.187 | 0.982–1.437 | 0.077 |
| CRTD before TLE [y/n] | 2.084 | 1.594–2.723 | p < 0.001 | 1.258 | 0.942–1.681 | 0.120 |
| 2 Lead remnant after TLE [y/n] | 0.643 | 0.429–0.967 | p = 0.034 | 0.983 | 0.653–1.479 | 0.934 |
| Infectious indications for lead extraction | ||||||
| Patient age during TLE [by 1 year] | 1.042 | 1.034–1.049 | p < 0.001 | 1.039 | 1.030–1.048 | p < 0.001 |
| Female [y/n] | 0.833 | 0.696–0.997 | p = 0.047 | 0.971 | 0.804–1.173 | p = 0.760 |
| Ischemic aetiology [y/n] | 1.572 | 1.337–1.852 | p < 0.001 | 0.982 | 0.826–1.168 | p = 0.842 |
| NYHA functional class [by 1] | 2.013 | 1.818–2.229 | p < 0.001 | 1.466 | 1.283–1.674 | p < 0.001 |
| LVEF [by 1 %p] | 0.968 | 0.963–0.973 | p < 0.001 | 0.981 | 0.973–0.989 | p < 0.001 |
| Renal failure (any) [y/n] | 2.751 | 2.331–3.248 | p < 0.001 | 1.881 | 1.583–2.235 | p < 0.001 |
| Diabetes t. 2 [y/n] | 1.727 | 1.449–2.060 | p < 0.001 | 1.407 | 1.178–1.682 | p < 0.001 |
| Charlson comorbidity index [by 1 point] | 1.135 | 1.112–1.157 | p < 0.001 | |||
| ICD VR-DR before TLE [y/n] | 1.332 | 1.096–1.620 | p = 0.004 | 0.981 | 0.763–1.260 | p = 0.878 |
| CRTD before TLE [y/n] | 2.170 | 1.711–2.751 | p < 0.001 | 1.269 | 0.948–1.698 | p = 0.109 |
| 3 Lead remnant after TLE y/n] | 0.605 | 0.391–0.935 | p = 0.024 | 0.777 | 0.499–1.208 | p = 0.262 |
| Staphylococcus aureus [y/n] | 1.324 | 1.051–1.667 | p = 0.017 | 1.211 | 0.950–1.542 | p = 0.122 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis [y/n] | 0.816 | 0.677–0.983 | p = 0.032 | 0.885 | 0.725–1.081 | p = 0.231 |
| Other Staphylococci [y/n] | 1.084 | 0.626–1.878 | p = 0.774 | |||
| Other bacteria [y/n] | 1.760 | 1.331–2.328 | p < 0.001 | 1.463 | 1.093–1.960 | p = 0.011 |
| Culture negative [y/n] | 0.857 | 0.712–1.033 | p = 0.105 | |||
| Lack of culture results [y/n] | 1.137 | 0.907–1.426 | p = 0.265 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kutarski, A.; Jacheć, W.; Polewczyk, A.; Nowosielecka, D. Incomplete Lead Removal During the Extraction Procedure: Predisposing Factors and Impact on Long-Term Survival in Infectious and Non-Infectious Cases: Analysis of 3741 Procedures. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082837
Kutarski A, Jacheć W, Polewczyk A, Nowosielecka D. Incomplete Lead Removal During the Extraction Procedure: Predisposing Factors and Impact on Long-Term Survival in Infectious and Non-Infectious Cases: Analysis of 3741 Procedures. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(8):2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082837
Chicago/Turabian StyleKutarski, Andrzej, Wojciech Jacheć, Anna Polewczyk, and Dorota Nowosielecka. 2023. "Incomplete Lead Removal During the Extraction Procedure: Predisposing Factors and Impact on Long-Term Survival in Infectious and Non-Infectious Cases: Analysis of 3741 Procedures" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 8: 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082837
APA StyleKutarski, A., Jacheć, W., Polewczyk, A., & Nowosielecka, D. (2023). Incomplete Lead Removal During the Extraction Procedure: Predisposing Factors and Impact on Long-Term Survival in Infectious and Non-Infectious Cases: Analysis of 3741 Procedures. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(8), 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082837





