Cerebrovascular, Cognitive and Cardiac Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Global Federated Health Network Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Follow-Up and Clinical Outcomes
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
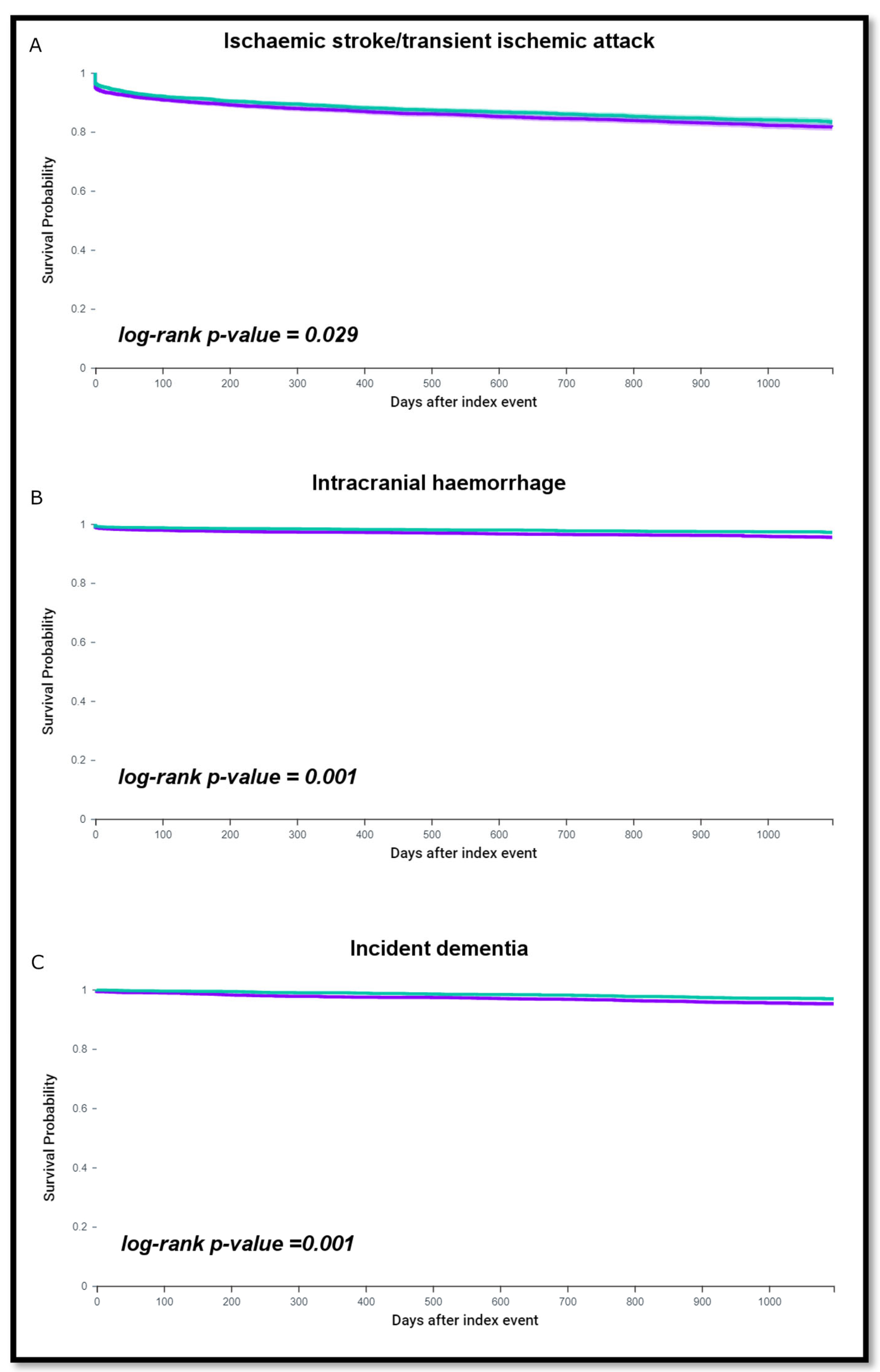
3.1. Cerebrovascular Events and Incident Dementia According to SGLT2i Therapy
3.2. Incident Heart Failure and Mortality
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, E.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Wilding, J.P.H. SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists: Established and emerging indications. Lancet 2021, 398, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, A.; Vickneson, K.; Singh, J.S. SGLT2-inhibitors; more than just glycosuria and diuresis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2021, 26, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jardine, M.J.; Li, Q.; Neuen, B.L.; Cannon, C.P.; de Zeeuw, D.; Edwards, R.; Levin, A.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Perkovic, V.; et al. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on stroke and atrial fibrillation in diabetic kidney disease: Results from the CREDENCE trial and meta-analysis. Stroke 2021, 52, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Bonaca, M.P.; Furtado, R.H.M.; Mosenzon, O.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; Bhatt, D.L.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Wilding, J.P.H.; et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Insights from the DECLARE-TIMI 58 Trial. Circulation 2020, 141, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukoos, J.S.; Lewis, R.J. The propensity score. JAMA 2015, 314, 1637–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantarian, S.; Ruskin, J.N. Atrial Fibrillation and Cognitive Decline. Cardiol. Clin. 2016, 34, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangeli, P.; Di Biase, L.; Bai, R.; Mohanty, S.; Pump, A.; Brantes, M.C.; Horton, R.; Burkhardt, J.D.; Lakkireddy, D.; Reddy, Y.M.; et al. Atrial fibrillation and the risk of incident dementia: A meta-analysis. Heart Rhythm. 2012, 9, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, R.; Alturki, A.; Vio, R.; Licchelli, L.; Rivezzi, F.; Marafi, M.; Russo, V.; Potpara, T.S.; Kalman, J.M.; De Villers-Sidani, E.; et al. The association between atrial fibrillation and Alzheimer’s disease: Fact or fallacy? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 21, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Li, G.; Rexrode, K.M.; Gurol, M.E.; Yuan, X.; Hui, Y.; Ruan, C.; Vaidya, A.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. Prospective study of fasting blood glucose and intracerebral hemorrhagic risk. Stroke 2018, 49, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterline, R.; Oscarsson, J.; Burns, J. A role for sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease? Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2020, 155, 113–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, J.W.; Lundkvist, P.; Jansson, P.A.; Johansson, L.; Kvarnström, M.; Moris, L.; Miliotis, T.; Forsberg, G.B.; Risérus, U.; Lind, L.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin and n-3 carboxylic acids on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in people with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind randomised placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1923–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Lindley, R.I.; Rådholm, K.; Jenkins, B.; Watson, J.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Shaw, W.; et al. Canagliflozin and Stroke in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from the Randomized CANVAS Program Trials. Stroke 2019, 50, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Feng, Q.; Fei, Y.; Tse, Y.K.; Wu, Z.M.; Wen, R.Q.; Tse, H.F.; Cheung, B.M.Y.; Yiu, K.H. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and cardiac arrhythmias: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; McMurray, J.J.V. SGLT2 inhibitors and mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit: A state-of-the-art review. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2108–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterline, R.L.; Vaag, A.; Oscarsson, J.; Vora, J. SGLT2 inhibitors: Clinical benefits by restoration of normal diurnal metabolism? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, R113–R125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Pocock, S.J.; Carson, P.; Januzzi, J.; Verma, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Brueckmann, M.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.-P.; Choi, D.-J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Initial Populations | Propensity Score Matched Populations | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | Patients not on SGLT2 Inhibitors n = 84,295 | Patients on SGLT2 Inhibitors n = 5061 | p-Value | SMD | Patients not on SGLT2 Inhibitors n = 5049 | Patients on SGLT2 Inhibitors n = 5049 | p-Value | SMD | ||||
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 71.8 | 11.3 | 66.6 | 9.92 | <0.001 | 0.490 | 66.7 | 11.3 | 66.7 | 9.91 | 0.727 | 0.007 |
| Female sex, n (%) | 33,708 | 33.99 | 1415 | 27.96 | <0.001 | 0.256 | 1445 | 28.62 | 1413 | 27.99 | 0.480 | 0.014 |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | ||||||||||||
| Hispanic or Latino | 4832 | 5.73 | 309 | 6.11 | 0.268 | 0.016 | 297 | 5.88 | 309 | 6.12 | 0.615 | 0.010 |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 65,725 | 77.97 | 4171 | 82.42 | <0.001 | 0.112 | 4190 | 82.99 | 4161 | 82.41 | 0.445 | 0.015 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | ||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 77,654 | 92.12 | 4761 | 94.07 | 0.457 | 0.077 | 4728 | 93.64 | 4749 | 94.06 | 0.384 | 0.017 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 45,790 | 54.32 | 3004 | 59.36 | <0.001 | 0.102 | 3595 | 71.20 | 3593 | 71.16 | 0.965 | 0.001 |
| Heart failure | 38,334 | 45.48 | 2243 | 44.32 | 0.108 | 0.023 | 2941 | 58.25 | 2967 | 58.76 | 0.599 | 0.010 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 12,778 | 15.16 | 735 | 14.52 | 0.220 | 0.018 | 842 | 16.68 | 832 | 16.48 | 0.789 | 0.005 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 64,318 | 76.30 | 4388 | 86.70 | <0.001 | 0.270 | 4365 | 86.45 | 4376 | 86.67 | 0.748 | 0.006 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 23,948 | 28.41 | 1191 | 23.53 | <0.001 | 0.111 | 1163 | 23.03 | 1190 | 23.57 | 0.525 | 0.013 |
| Cerebral infarction | 13,832 | 16.41 | 711 | 14.05 | <0.000 | 0.066 | 811 | 16.06 | 794 | 15.73 | 0.644 | 0.009 |
| Pulmonary embolism | 5752 | 6.82 | 325 | 6.42 | 0.270 | 0.016 | 783 | 15.51 | 734 | 14.54 | 0.172 | 0.027 |
| Other venous embolism and thrombosis | 14,134 | 16.77 | 834 | 16.48 | 0.594 | 0.008 | 1163 | 23.03 | 1190 | 23.57 | 0.525 | 0.013 |
| Overweight/obesity | 35,938 | 42.63 | 2976 | 58.80 | <0.001 | 0.328 | 2978 | 58.98 | 2993 | 59.28 | 0.761 | 0.006 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 20,224 | 23.99 | 950 | 18.77 | <0.001 | 0.128 | 1872 | 37.08 | 1862 | 36.88 | 0.837 | 0.004 |
| Acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease | 40,477 | 48.02 | 1866 | 36.87 | <0.001 | 0.227 | 2118 | 41.95 | 2130 | 42.19 | 0.809 | 0.005 |
| Diseases of the nervous system | 57,720 | 68.47 | 3727 | 73.64 | <0.001 | 0.114 | 3684 | 72.97 | 3717 | 73.62 | 0.458 | 0.015 |
| Diseases of liver | 10,910 | 12.94 | 836 | 16.52 | <0.001 | 0.101 | 957 | 18.95 | 948 | 18.78 | 0.819 | 0.005 |
| Neoplasms | 33,229 | 39.42 | 2136 | 42.21 | <0.001 | 0.057 | 2272 | 45.00 | 2236 | 44.29 | 0.471 | 0.014 |
| Pharmacological therapy, n (%) | ||||||||||||
| Beta blockers | 68,668 | 81.46 | 4466 | 88.24 | <0.000 | 0.190 | 4474 | 88.61 | 4456 | 88.26 | 0.575 | 0.011 |
| ACE inhibitors | 40,021 | 47.48 | 3111 | 61.47 | <0.001 | 0.284 | 3183 | 63.04 | 3103 | 61.46 | 0.101 | 0.033 |
| Angiotensin II inhibitors | 24,733 | 29.34 | 2038 | 40.27 | <0.001 | 0.231 | 2018 | 39.97 | 2030 | 40.21 | 0.807 | 0.005 |
| Antilipemic agents | 63,394 | 75.21 | 4526 | 89.43 | <0.000 | 0.379 | 4587 | 90.85 | 4514 | 89.40 | 0.015 | 0.048 |
| Calcium channel blockers | 45,152 | 53.56 | 2800 | 55.33 | 0015 | 0.035 | 2840 | 56.25 | 2791 | 55.28 | 0.326 | 0.020 |
| Diuretics | 58,526 | 69.43 | 3701 | 73.13 | 0.027 | 0.082 | 3724 | 73.76 | 3692 | 73.12 | 0.471 | 0.014 |
| Antiarrhythmics | 49,402 | 58.61 | 3385 | 66.88 | <0.001 | 0.172 | 3339 | 66.13 | 3376 | 66.87 | 0.435 | 0.016 |
| Antiplatelets | 52,170 | 61.89 | 3510 | 69.35 | <0.001 | 0.158 | 3550 | 70.31 | 3499 | 69.30 | 0.269 | 0.022 |
| Oral anticoagulants | ||||||||||||
| Vitamin K antagonists | 52,399 | 62.16 | 2852 | 56.35 | <0.001 | 0.118 | 2828 | 56.01 | 2847 | 56.39 | 0.703 | 0.008 |
| Non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants | 31,896 | 37.84 | 2209 | 43.65 | <0.001 | 0.165 | 2221 | 43.99 | 2202 | 43.61 | 0.588 | 0.011 |
| Blood glucose regulation agents | ||||||||||||
| Metformin | 34,607 | 41.06 | 3970 | 78.44 | <0.001 | 0.825 | 4021 | 79.64 | 3958 | 78.39 | 0.124 | 0.031 |
| Insulin | 49,801 | 59.08 | 3622 | 71.57 | <0.001 | 0.265 | 3632 | 71.94 | 3612 | 71.54 | 0.658 | 0.009 |
| Glipizide | 11,647 | 13.82 | 1325 | 26.18 | <0.001 | 0.313 | 1309 | 25.93 | 1318 | 26.10 | 0.838 | 0.004 |
| Sitagliptin | 7189 | 8.53 | 1342 | 26.52 | <0.001 | 0.487 | 1268 | 25.11 | 1330 | 26.34 | 0.158 | 0.028 |
| Glimepiride | 7615 | 9.03 | 1010 | 19.96 | <0.001 | 0.314 | 972 | 19.25 | 1.003 | 19.87 | 0.437 | 0.015 |
| Pioglitazone | 3341 | 3.96 | 560 | 11.07 | <0.001 | 0.272 | 557 | 11.03 | 554 | 10.97 | 0.924 | 0.002 |
| Linagliptin | 1973 | 2.34 | 429 | 8.48 | <0.001 | 0.274 | 397 | 7.86 | 423 | 8.38 | 0.344 | 0.019 |
| Glyburide | 3221 | 3.82 | 394 | 7.79 | <0.001 | 0.170 | 384 | 7.61 | 392 | 7.76 | 0.765 | 0.006 |
| Saxagliptin | 616 | 0.73 | 138 | 2.73 | <0.001 | 0.154 | 132 | 2.61 | 135 | 2.67 | 0.852 | 0.004 |
| Repaglinide | 679 | 0.81 | 79 | 1.56 | 1.258 | 0.070 | 70 | 1.39 | 78 | 1.55 | 0.508 | 0.013 |
| Nateglinide | 373 | 0.44 | 52 | 1.03 | 0.042 | 0.069 | 53 | 1.05 | 52 | 1.03 | 0.922 | 0.002 |
| Rosiglitazone | 475 | 0.56 | 44 | 0.87 | 0.005 | 0.036 | 45 | 0.89 | 44 | 0.87 | 0.915 | 0.002 |
| Acarbose | 270 | 0.32 | 37 | 0.73 | <0.001 | 0.057 | 31 | 0.61 | 36 | 0.71 | 0.540 | 0.012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Proietti, R.; Rivera-Caravaca, J.M.; López-Gálvez, R.; Harrison, S.L.; Marín, F.; Underhill, P.; Shantsila, E.; McDowell, G.; Vinciguerra, M.; Davies, R.; et al. Cerebrovascular, Cognitive and Cardiac Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Global Federated Health Network Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082814
Proietti R, Rivera-Caravaca JM, López-Gálvez R, Harrison SL, Marín F, Underhill P, Shantsila E, McDowell G, Vinciguerra M, Davies R, et al. Cerebrovascular, Cognitive and Cardiac Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Global Federated Health Network Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(8):2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082814
Chicago/Turabian StyleProietti, Riccardo, José Miguel Rivera-Caravaca, Raquel López-Gálvez, Stephanie L. Harrison, Francisco Marín, Paula Underhill, Eduard Shantsila, Garry McDowell, Manlio Vinciguerra, Rhys Davies, and et al. 2023. "Cerebrovascular, Cognitive and Cardiac Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Global Federated Health Network Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 8: 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082814
APA StyleProietti, R., Rivera-Caravaca, J. M., López-Gálvez, R., Harrison, S. L., Marín, F., Underhill, P., Shantsila, E., McDowell, G., Vinciguerra, M., Davies, R., Giebel, C., Lane, D. A., & Lip, G. Y. H. (2023). Cerebrovascular, Cognitive and Cardiac Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Global Federated Health Network Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(8), 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082814








