Clinical and Forensic Signs Resulting from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Other Chemical Elements of the Periodic Table
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
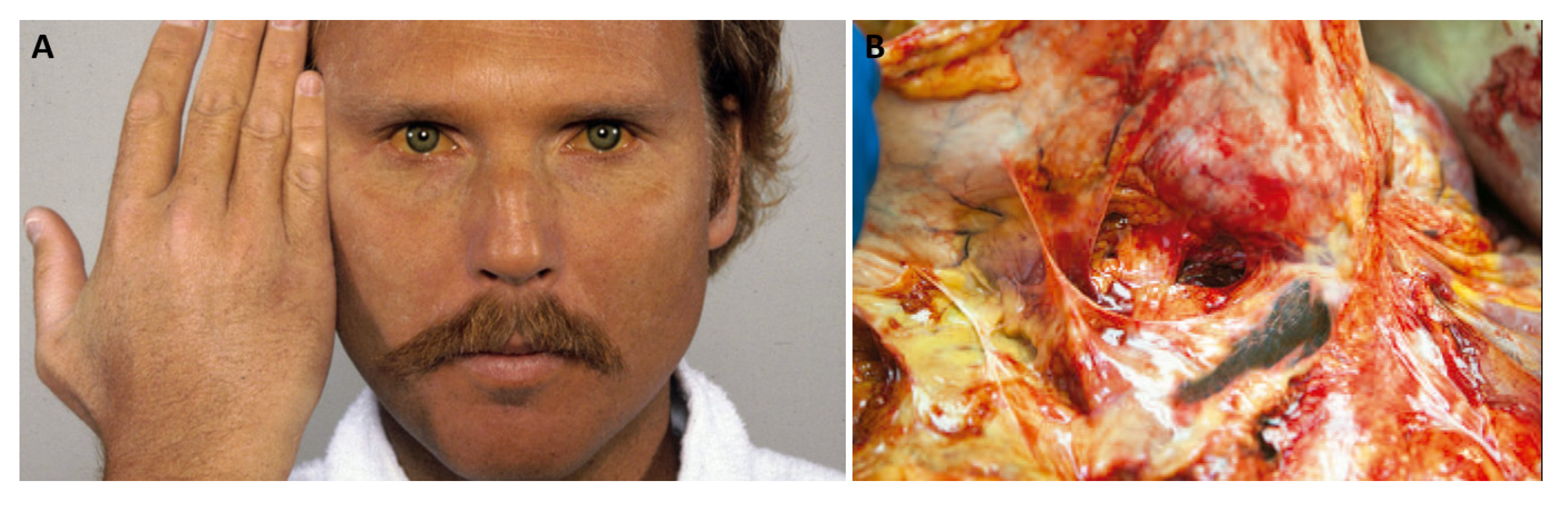
3. Thallium
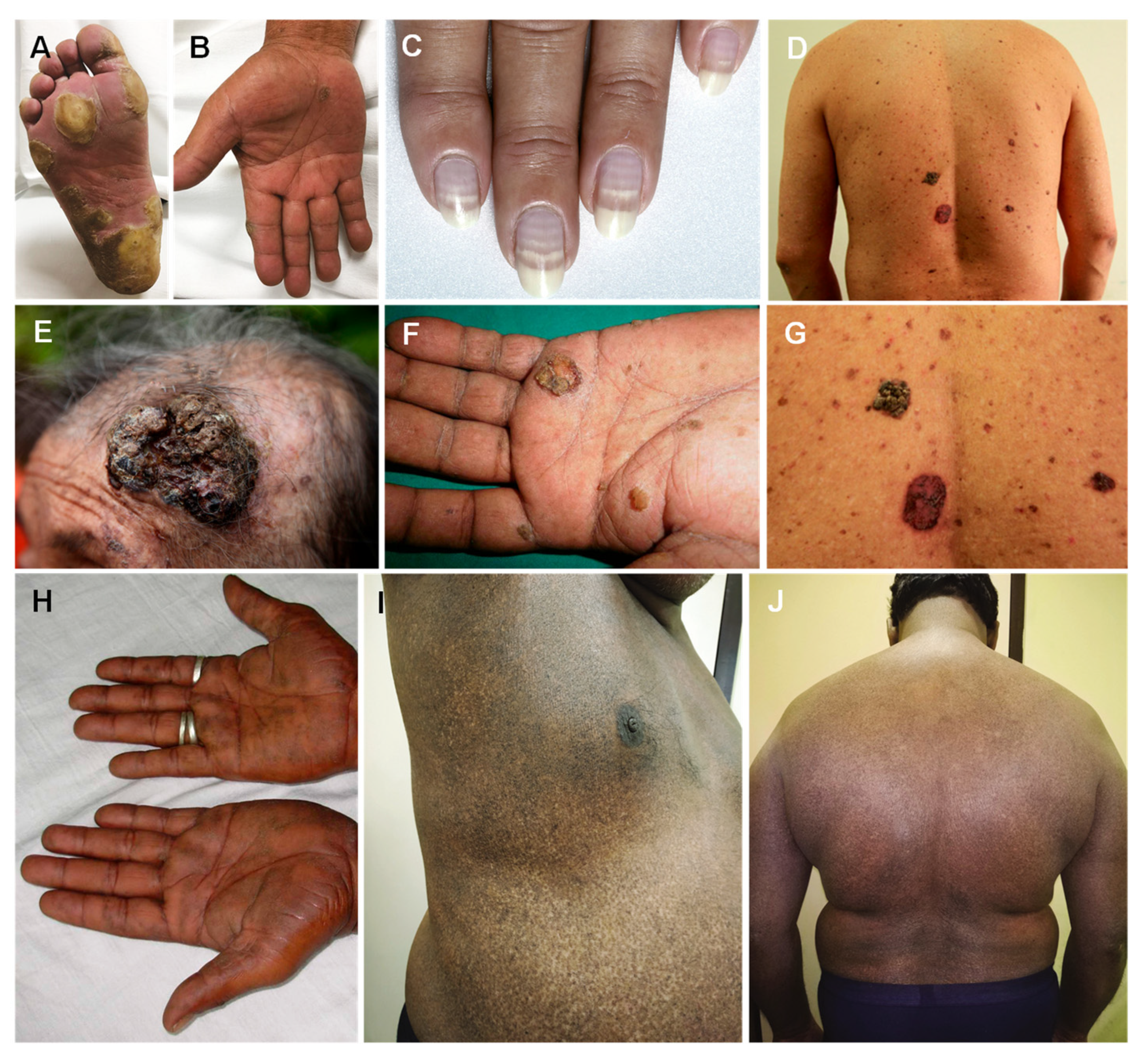
4. Arsenic
5. Lead
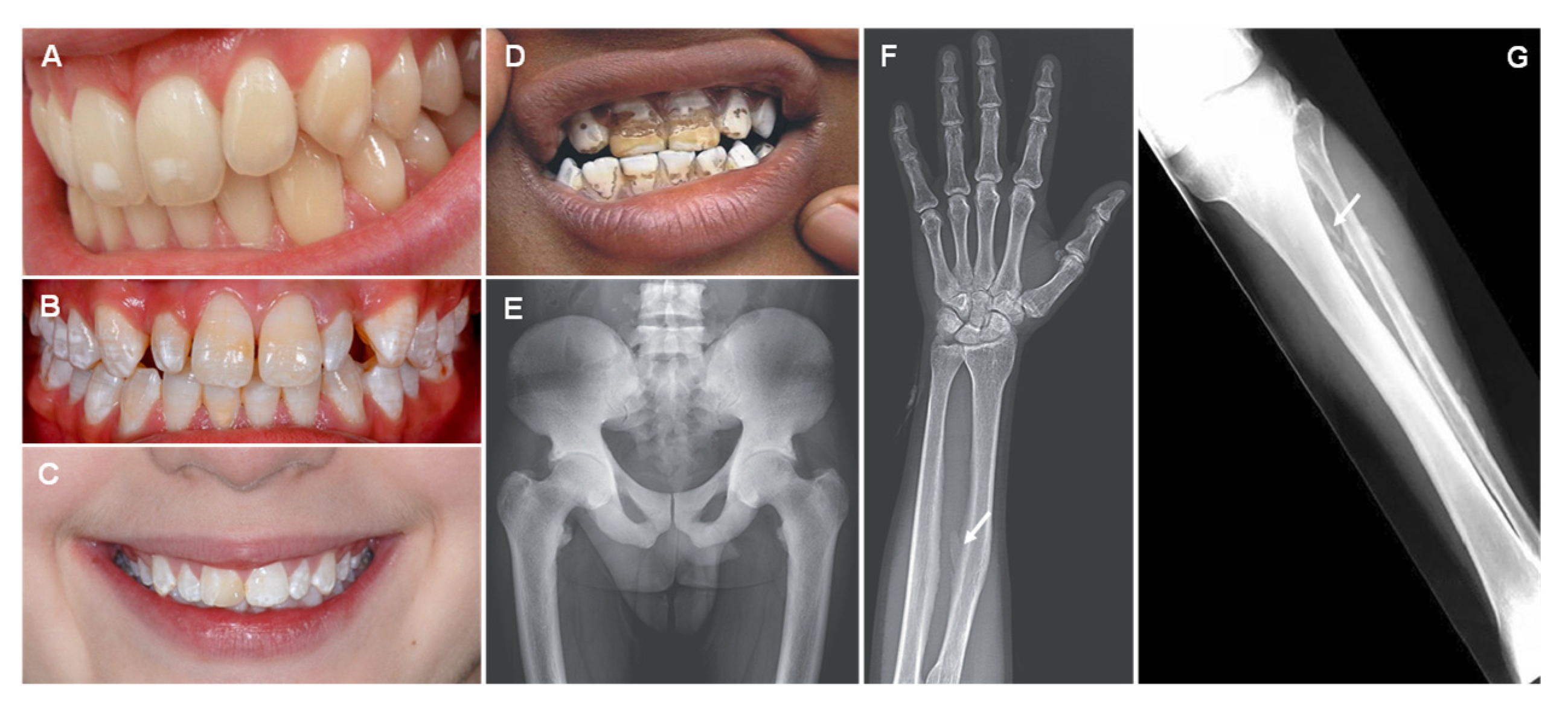
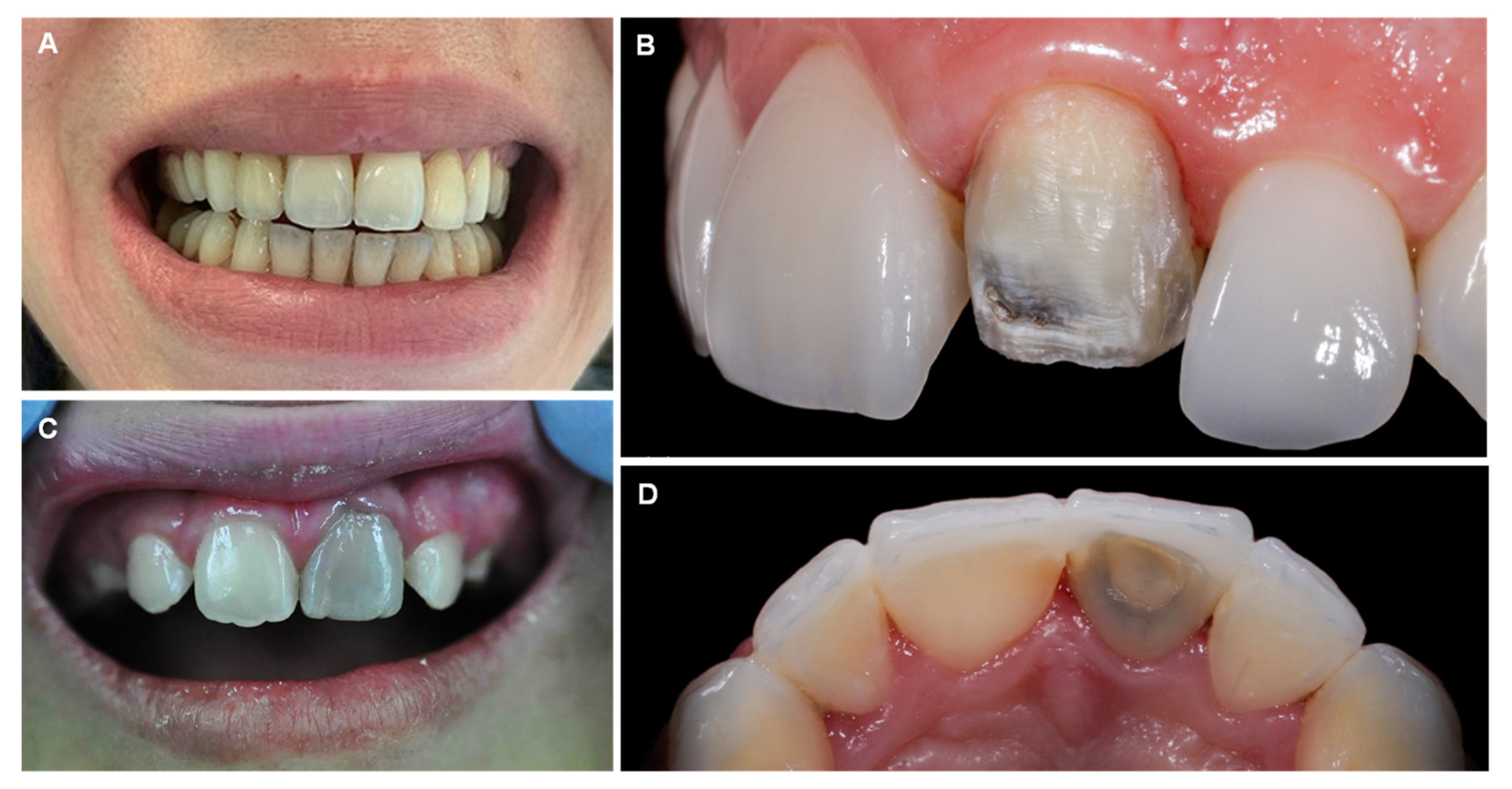
6. Fluorine
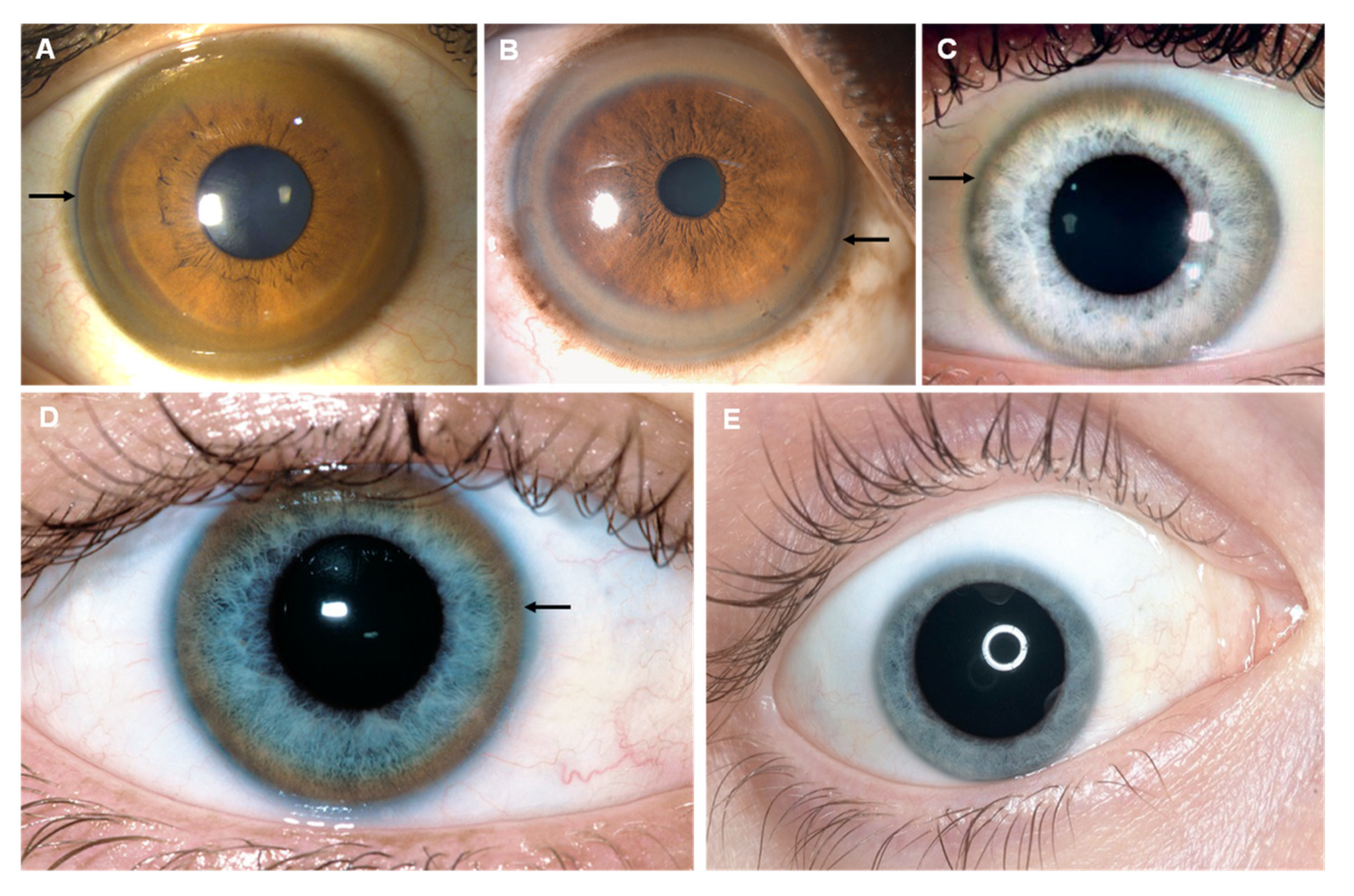
7. Copper
8. Selenium
9. Mercury
9.1. Elemental Mercury
9.2. Inorganic Mercury
9.3. Organic Mercury

10. Iron
11. Cadmium
12. Bismuth
13. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibrahim, D.; Froberg, B.; Wolf, A.; Rusyniak, D.E. Heavy metal poisoning: Clinical presentations and pathophysiology. Clin. Lab. Med. 2006, 26, 67–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, J.F., II. Difficult diagnoses in toxicology: Poisons not detected by the comprehensive drug screen. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 1991, 38, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusyniak, D.E.; Arroyo, A.; Acciani, J.; Froberg, B.; Kao, L.; Furbee, B. Heavy metal poisoning: Management of intoxication and antidotes. Exs 2010, 100, 365–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, A.; Pillay, V.; Adhikari, P.; Venkatesh, T.; Chakrapani, M.; Jayaprakash Rao, H.; Bastia, B.K.; Rajeev, A.; Saralaya, K.; Rai, M. Clinical manifestations of lead workers of Mangalore, India. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2006, 22, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozuah, P.O. Mercury poisoning. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. 2000, 30, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, D.; Seng, C.K. Textbook of Occupational Medicine Practice; World Scientific: Singapore, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin, R.E.; Smith, R.P.; Hodge, H.C.; Braddock, J.E. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products; Williams & Wilkins Baltimore: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1984; Volume 1085. [Google Scholar]
- Lohiya, G.S.; Lohiya, S. Lead poisoning in a radiator repairer. West. J. Med. 1995, 162, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Desenclos, J.C.; Wilder, M.H.; Coppenger, G.W.; Sherin, K.; Tiller, R.; VanHook, R.M. Thallium poisoning: An outbreak in Florida, 1988. South Med. J. 1992, 85, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, A.L.; Viraraghavan, T. Thallium: A review of public health and environmental concerns. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharquie, K.E.; Ibrahim, G.A.; Noaimi, A.A.; Hamudy, H.K. Outbreak of thallium poisoning among Iraqi patients. J. Saudi Soc. Dermatol. Dermatol. Surg. 2011, 15, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.B.; Gary, R. Clinical Environmental Health and Toxic Exposures; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vahidnia, A.; van der Voet, G.B.; de Wolff, F.A. Arsenic neurotoxicity–A review. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2007, 26, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. One image is worth more than a thousand words: Producing an atlas of medical signs for teaching clinical and forensic toxicology. Forensic Sci. Res. 2022, 7, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Carvalho, F.; Duarte, J.A.; Proença, J.B.; Santos, A.; Magalhães, T. Clinical and forensic signs related to cocaine abuse. Curr. Drug Abuse Rev. 2012, 5, 64–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Carvalho, F.; Moreira, R.; Duarte, J.A.; Proenca, J.B.; Santos, A.; Magalhaes, T. Clinical and forensic signs related to opioids abuse. Curr. Drug Abuse Rev. 2012, 5, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Metabolic Profiles of Propofol and Fospropofol: Clinical and Forensic Interpretative Aspects. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6852857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Magalhães, T.; Moreira, R.; Proença, J.B.; Pontes, H.; Santos, A.; Duarte, J.A.; Carvalho, F. Clinical and forensic signs related to ethanol abuse: A mechanistic approach. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2014, 24, 81–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, M.I.; Rocha, A.; Buchner, G.; Moreira, Z.; Rodrigues, R.M. Acute iron intoxication in pregnancy: Case report Intoxicação aguda por ferro na gravidez: A propósito de um caso clínico. Acta Obstet. Ginecol. Port. 2015, 9, 417–420. [Google Scholar]
- Galván-Arzate, S.; Santamaría, A. Thallium toxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 1998, 99, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, V.B.; Mohr, C.O. Rodenticides in bubonic-plague control. Bull. World Health Organ. 1953, 9, 585–596. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, L.S.; Howland, M.A.; Lewin, N.A.; Smith, S.W.; Goldfrank, L.R.; Hoffman, R.S. PESTICIDES. In Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, 11th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.; House, I.; Dixon, A. Thallium Poisoning: Diagnosis May Be Elusive But Alopecia Is the Clue. BMJ Br. Med. J. 1993, 306, 1527–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusyniak, D.E.; Furbee, R.B.; Kirk, M.A. Thallium and arsenic poisoning in a small midwestern town. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2002, 39, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.R.; Marshall, W.J. Heavy metal poisoning and its laboratory investigation. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1999, 36 Pt 3, 267–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yumoto, T.; Tsukahara, K.; Naito, H.; Iida, A.; Nakao, A. A Successfully Treated Case of Criminal Thallium Poisoning. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, OD01–OD02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Li, C.; Long, Y.; Sheng, L. Hair Loss: Evidence to Thallium Poisoning. Case Rep. Emerg. Med. 2018, 2018, 1313096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelclová, D.; Urban, P.; Ridzon, P.; Senholdová, Z.; Lukás, E.; Diblík, P.; Lacina, L. Two-year follow-up of two patients after severe thallium intoxication. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.J.; Mosqueda-Tapia, G.; Altamirano-Lozano, M. Genotoxicity Assessment of Human Peripheral Lymphocytes Induced by Thallium(I) and Thallium(III). Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2017, 99, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, D.; Kalantri, A. Electrophysiologic investigation of thallium poisoning. Muscle Nerve 1990, 13, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-T.; Wen, B.; Yu, X.-N.; Ji, Z.-G.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.-L.; Cao, Y.-L.; Wang, M.; Jian, X.-D.; et al. Early diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes of five patients with acute thallium poisoning. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 5082–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-C. Occupational Neurotoxic Diseases in Taiwan. Saf. Health Work. 2012, 3, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, J.B. What have we learnt from Graham Frederick Young? Reflections on the mechanism of thallium neurotoxicity. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1991, 17, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulkey, J.P.; Oehme, F.W. A review of thallium toxicity. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1993, 35, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, J.; Levisohn, D.R. Acute alopecia: Clue to thallium toxicity. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1993, 10, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-I.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Kuo, H.-C.; Chuang, Y.-H.; Shih, T.-S. Short-term thallium intoxication: Dermatological findings correlated with thallium concentration. Arch. Dermatol. 2007, 143, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeschlin, S. Thallium poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 1980, 17, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin, P.; Bandino, D.M.E. Acute-Onset Alopecia. Cutis 2019, 103, E24–E26. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, U.; Kalita, J.; Yadav, R.; Ranjan, P. Thallium poisoning: Emphasis on early diagnosis and response to haemodialysis. Postgrad. Med. J. 2003, 79, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almassri, I.; Sekkarie, M. Cases of thallium intoxication in Syria: A diagnostic and a therapeutic challenge. Avicenna J. Med. 2018, 8, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, E.; Hader, S.L.; Files, D.; Corey, G.R. Arsenic poisoning seen at Duke Hospital, 1965–1998. N. C. Med. J. 1999, 60, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, E.; Braithwaite, R. A review of the clinical and toxicological aspects of ‘traditional’ (herbal) medicines adulterated with heavy metals. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2005, 4, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.T.; Chan, H.L.; Teo, S.K. The spectrum of cutaneous and internal malignancies in chronic arsenic toxicity. Singap. Med. J. 1998, 39, 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Hemond, H.F.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M. Children’s exposure to arsenic from CCA-treated wooden decks and playground structures. Risk Anal. 2004, 24, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, R.C.; Hui, X.; Barbadillo, S.; Maibach, H.I.; Lowney, Y.W.; Schoof, R.A.; Holm, S.E.; Ruby, M.V. In Vivo Percutaneous Absorption of Arsenic from Water and CCA-Treated Wood Residue. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 79, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of health and human services, U.S.A. Toxicological Profile for Arsenic; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007.
- Gorby, M.S. Arsenic poisoning. West J. Med. 1988, 149, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lai, V.W.; Sun, Y.; Ting, E.; Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J. Arsenic speciation in human urine: Are we all the same? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.C.; Lu, X.; Ma, M.; Cullen, W.R.; Aposhian, H.V.; Zheng, B. Speciation of key arsenic metabolic intermediates in human urine. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 5172–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benramdane, L.; Accominotti, M.; Fanton, L.; Malicier, D.; Vallon, J.J. Arsenic speciation in human organs following fatal arsenic trioxide poisoning–A case report. Clin Chem 1999, 45, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H. Heavy Metal Poisoning. In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 20th ed.; Jameson, J.L., Fauci, A.S., Kasper, D.L., Hauser, S.L., Longo, D.L., Loscalzo, J., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vantroyen, B.; Heilier, J.F.; Meulemans, A.; Michels, A.; Buchet, J.P.; Vanderschueren, S.; Haufroid, V.; Sabbe, M. Survival after a lethal dose of arsenic trioxide. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Yamasaki, H.; Ogawa, K.; Nishi, M.; Nanjo, K. An epidemic of arsenic neuropathy from a spiked curry. Neurology 2001, 56, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donofrio, P.D.; Wilbourn, A.J.; Albers, J.W.; Rogers, L.; Salanga, V.; Greenberg, H.S. Acute arsenic intoxication presenting as Guillain-Barré-like syndrome. Muscle Nerve 1987, 10, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.; Grainge, J.W. Arsenic and cancer. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1975, 113, 396–401. [Google Scholar]
- Caussy, D. A Field Guide: Detection, Management and Surveillance of Arsenicosis in South-East Asia Region; WHO Regional Office for South-East Asia: New Delhi, India, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Arsenicosis Case-Detection, Management and Surveillance. Report of a Regional Consultation; WHO Regional Office for South-East Asia: New Delhi, India, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chilvers, D.; Peterson, P. Global cycling of arsenic. Lead Mercury Cadmium Arsen. Environ. 1987, 31, 279–301. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, D.G.; Ragaini, R.C.; Ondov, J.M.; Fisher, G.L.; Silberman, D.; Prentice, B.A. Chemical studies of stack fly ash from a coal-fired power plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1979, 13, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapaj, S.; Peterson, H.; Liber, K.; Bhattacharya, P. Human health effects from chronic arsenic poisoning–a review. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2006, 41, 2399–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.N.; Focht, D.D. Production of arsine and methylarsines in soil and in culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1979, 38, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Matsuzono, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Hashimoto, Y. Chemical Form of Arsenic Compounds and Distribution of Their Concentrations in the Atmosphere; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990; Volume 4, pp. 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Mees, R. Een verschijnsel bij polyneuritis arsenicosa. Verloskd Gynaecol. Ned. Tijdschr. Verloskd. Gynaecol. 1919, 1, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Milton, A.H.; Hasan, Z.; Rahman, A.; Rahman, M. Non-cancer effects of chronic arsenicosis in Bangladesh: Preliminary results. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2003, 38, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, K.C. Diagnosis of arsenicosis. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2003, 38, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadono, T.; Inaoka, T.; Murayama, N.; Ushijima, K.; Nagano, M.; Nakamura, S.; Watanabe, C.; Tamaki, K.; Ohtsuka, R. Skin manifestations of arsenicosis in two villages in Bangladesh. Int. J. Dermatol. 2002, 41, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattner, H.; Dorne, M. Arsenical pigmentation and keratoses. Arch. Dermatol. Syphilol. 1943, 48, 458–460. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, P.; Roy, C.; Das, N.K.; Sengupta, S.R. Epidemiology and prevention of chronic arsenicosis: An Indian perspective. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2008, 74, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Chowdhury, J.; Ghoshal, L. An introspection into the cutaneous manifestations of chronic arsenicosis as reported in a tertiary care centre in Kolkata. J. Pak. Assoc. Dermatol. 2014, 24, 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, K.; Gin, A.; Scardamaglia, L. Palmoplantar keratosis caused by arsenic toxicity. Med. J. Aust. 2021, 214, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richir, M.C.; Langenhorst, B.L.A.M. Een vrouw met ‘jaarringen’ op haar nagels. Ned. Tijdschr. Voor Geneeskd. 2011, 155, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ye, F.; Wang, A.; Wang, D.; Yang, B.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, G.; Gao, X. Chronic arsenic poisoning probably caused by arsenic-based pesticides: Findings from an investigation study of a household. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Toshniwal, A.; Majumdar, K. Rain drop pigmentation in chronic arsenic poisoning. Pigment. Int. 2020, 7, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guideline for Elemental Impurities Q3D; ICH, 2014; pp. 1–75.
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Exp. Suppl. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assi, M.A.; Hezmee, M.N.; Haron, A.W.; Sabri, M.Y.; Rajion, M.A. The detrimental effects of lead on human and animal health. Vet. World 2016, 9, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernberg, S. Lead poisoning in a historical perspective. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2000, 38, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, H. James Hardy and the Devonshire colic. Med. Hist. 1969, 13, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, J.S. Man, Medicine, and Work in America: A Historical Series: III. Benjamin Franklin and His Awareness of Lead Poisoning. J. Occup. Med. 1967, 9, 543–554. [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger, D.C.; Bellinger, A.M. Childhood lead poisoning: The torturous path from science to policy. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.D. Pediatric lead poisoning. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1964, 8, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisolm, J.J., Jr.; Harrison, H.E. The exposure of children to lead. Pediatrics 1956, 18, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.M.; Zappella, M. Lead poisoning in childhood with particular reference to pica and mental sequelae. J. Ment. Defic. Res. 1964, 8, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, T. Diseases of occupations-a short history of their recognition and prevention. In Hunter’s Diseases of Occupations; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, R.; Strayer, D.S.; Rubin, E. Rubin’s Pathology: Clinicopathologic Foundations of Medicine; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, G.W. Neurologic concepts of lead poisoning in children. Pediatr. Ann. 1992, 21, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidsky, T.I.; Schneider, J.S. Lead neurotoxicity in children: Basic mechanisms and clinical correlates. Brain 2003, 126, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Latif Wani, A.A.; Usmani, J.A. Lead toxicity: A review. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldine, M.; Venkatesh, T. Evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of lead poisoning in a patient with occupational lead exposure: A case presentation. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2007, 2, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Smitherman, J.; Harber, P. A case of mistaken identity: Herbal medicine as a cause of lead toxicity. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1991, 20, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J. Burton’s line in lead poisoning. Eur. Neurol. 2007, 57, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowski, M.J.; Sisson, G. Systemic Lead Poisoning due to an Intra-Articular Bullet; Slack Incorporated Thorofare: West Deptford, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 28, pp. 411–412. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfrank, L.; Flomenbaum, N.; Nelson, L.; Hoffman, R.; Howland, M.A.; Lewin, N. (Eds.) Goldfrank’s Toxicological Emergencies, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill Companies: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, M.; Sundriyal, D. Burton’s Line. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 367–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Santhosh, A.; Shukla, S.; Gupta, P.; Mandavdhare, H.; Dutta, U.; Sharma, V. Gastrointestinal: An oral clue to an unusual cause of pain abdomen: Burton’s line. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.K.; Chow, T.Y.A.; Chan, C.K.; Chan, Y.C.; Ng, C.H.V.; Ng, S.H.; Tse, M.L. Hong Kong poison information centre: Annual report 2017. Hong Kong J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 25, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, S.; Flora, S.J. Arsenic and fluoride: Two major ground water pollutants. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 48, 666–678. [Google Scholar]
- Lennon, M.A. One in a million: The first community trial of water fluoridation. Bull. World Health Organ. 2006, 84, 759–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpunar, S.M.; Burt, B. Dental caries, fluorosis, and fluoride exposure in Michigan schoolchildren. J. Dent. Res. 1988, 67, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control. Ten Great Public Health Achievements in the 20th Century; CDC: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Fejerskov, O.; Manji, F.; Baelum, V. The nature and mechanisms of dental fluorosis in man. J. Dent. Res. 1990, 69, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Connell, S.; Kirkham, J.; Brookes, S.J.; Shore, R.C.; Smith, A.M. The effect of fluoride on the developing tooth. Caries Res. 2004, 38, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoba, T.; Fejerskov, O. Dental fluorosis: Chemistry and biology. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2002, 13, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Li, B.; Gao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yao, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, D. Fluoride decreased osteoclastic bone resorption through the inhibition of NFATc1 gene expression. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 29, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, H. Analysis of the Role of Insulin Signaling in Bone Turnover Induced by Fluoride. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 171, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teotia, S.P.S.; Teotia, M.; Singh, K.P. Highlights of Forty Years of Research on Endemic Skeletal Fluorosis in India. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Fluorosis Prevention and Defluoridation of Water, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2–6 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Water for Life: Making It Happen; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Taves, D.R. Dietary intake of fluoride ashed (total fluoride) v. unashed (inorganic fluoride) analysis of individual foods. Br. J. Nutr. 1983, 49, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.M.; Guha-Chowdhury, N. Total fluoride intake and implications for dietary fluoride supplementation. J. Public Health Dent. 1999, 59, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Gupta, N.; Chhabra, P. Image Diagnosis: Dental and Skeletal Fluorosis. Perm. J. 2016, 20, e105–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, M.S.; Whiting, P.F.; Wilson, P.M.; Sutton, A.J.; Chestnutt, I.; Cooper, J.; Misso, K.; Bradley, M.; Treasure, E.; Kleijnen, J. Systematic review of water fluoridation. BMJ 2000, 321, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, B.A. Fluoridation and social equity. J. Public Health Dent. 2002, 62, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DenBesten, P.; Li, W. Chronic fluoride toxicity: Dental fluorosis. Fluoride Oral Environ. 2011, 22, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar-Díaz, F.D.C.; Morales-Corona, F.; Cintra-Viveiro, A.C.; Fuente-Hernández, J. Prevalence of dental fluorosis in Mexico 2005–2015: A literature review. Salud Publica Mex. 2017, 59, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Levy, S.M.; Broffitt, B.; Warren, J.J.; Kanellis, M.J.; Wefel, J.S.; Dawson, D.V. Timing of fluoride intake in relation to development of fluorosis on maxillary central incisors. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2006, 34, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Levy, S.M.; Warren, J.J.; Broffitt, B.; Cavanaugh, J. Fluoride intake levels in relation to fluorosis development in permanent maxillary central incisors and first molars. Caries Res. 2006, 40, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröncke, A. Perikymata. Dtsch. Zahnarztl. Z. 1966, 1, 1397–1401. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Moller, I. Fluorides and dental fluorosis. Int. Dent. J. 1982, 32, 135–147. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, G.E. Fluoride, teeth and bone. Med. J. Aust. 1985, 143, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, P.J.; Aldred, M.J. X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta: Presentation of two kindreds and a review of the literature. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1992, 73, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejerskov, O. Dental Fluorosis: A Handbook for Health Workers; Mosby Inc.: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kurdi, M.S. Chronic fluorosis: The disease and its anaesthetic implications. Indian J. Anaesth. 2016, 60, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Hlaing, T.; Whitford, G.M.; Compston, J.E. Skeletal fluorosis due to excessive tea and toothpaste consumption. Osteoporos. Int. 2011, 22, 2557–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlappa, N.; Qureshi, I.A.; Srinivas, R. Fluorosis in India: An overview. Int. J. Res. Dev. Health 2013, 1, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik, S.; Saha, D. The genetic influence in fluorosis. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 56, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, M.; Riahi, H.; Maatallah, K.; Ferjani, H.; Bouaziz, M.C.; Ladeb, M.F. Skeletal fluorosis: Don’t miss the diagnosis! Skeletal. Radiol. 2020, 49, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairuddin, M.N.I.; Iskanderdzulkarnein, P.M.B.u.A.; Halil, M.H.M. Resin Infiltration Technique as Minimal Invasive Approach Towards Mild to Moderate Dental Fluorosis in an Adolescent: A Case Report. IIUM J. Orofac. Health Sci. 2021, 2, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.; Roy, M.M.; Chakraborti, D. Dental fluorosis. Clin. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanie, V.; Sherman, M.D. (Eds.) Skeletal Fluorosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, C.G.; Zappettini, E.O.; Vivallo, W.; Celada, C.M.; Quispe, J.; Singer, D.A.; Briskey, J.A.; Sutphin, D.M.; Gajardo, M.; Diaz, A. Quantitative mineral resource assessment of copper, molybdenum, gold, and silver in undiscovered porphyry copper deposits in the Andes Mountains of South America. USGS Open-File Rep 2008-1253 2008, 1–282. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, B.R.; Ayuso, R.A.; Wynn, J.C.; Seal, R.R. Preliminary model of porphyry copper deposits. US Geol. Surv. Open-File Rep. 2008, 1321, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, D.P.; Lindsey, D.A.; Singer, D.A.; Diggles, M.F. Sediment-Hosted Copper Deposits of the World: Deposit Models and Database; USGS: Liston, VA, USA, 2007.
- Doebrich, J.L. Copper: A Metal for the Ages; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Liston, VA, USA, 2009.
- Gamakaranage, C.S.; Rodrigo, C.; Weerasinghe, S.; Gnanathasan, A.; Puvanaraj, V.; Fernando, H. Complications and management of acute copper sulphate poisoning; a case discussion. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2011, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, M.M.; Lee, J.; Thiele, D.J. A delicate balance: Homeostatic control of copper uptake and distribution. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotilio, G.; Carr, M.; Rossi, L.; Ciriolo, M. Copper-dependent oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. IUBMB Life 2000, 50, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Cooper, J.; Butler, P.; Walker, A.; Mistry, P.; Dooley, J.; Schapira, A. Oxidative-phosphorylation defects in liver of patients with Wilson’s disease. Lancet 2000, 356, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentealba, I.C.; Aburto, E.M. Animal models of copper-associated liver disease. Comp. Hepatol. 2003, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Ghosh, S.; Pal, D. Acute copper sulphate poisoning. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 1961, 36, 330–336. [Google Scholar]
- Nastoulis, E.; Karakasi, M.; Couvaris, C.; Kapetanakis, S.; Fiska, A.; Pavlidis, P. Greenish-blue gastric content: Literature review and case report on acute copper sulphate poisoning. Forensic Sci. Rev. 2017, 29, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Gow, P.J.; Smallwood, R.; Angus, P.W.; Smith, A.; Wall, A.; Sewell, R.B. Diagnosis of Wilson’s disease: An experience over three decades. Gut 2000, 46, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, P.C.; Thomas, G.R.; Rommens, J.M.; Forbes, J.R.; Cox, D.W. The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P–type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat. Genet. 1993, 5, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrukhin, K.; Fischer, S.; Pirastu, M.; Tanzi, R.; Chernov, I.; Devoto, M.; Brzustowicz, L.; Cayanis, E.; Vitale, E.; Russo, J. Mapping, cloning and genetic characterization of the region containing the Wilson disease gene. Nat. Genet. 1993, 5, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzi, R.; Petrukhin, K.; Chernov, I.; Pellequer, J.; Wasco, W.; Ross, B.; Romano, D.; Parano, E.; Pavone, L.; Brzustowicz, L. The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat. Genet. 1993, 5, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merle, U.; Weiss, K.H.; Eisenbach, C.; Tuma, S.; Ferenci, P.; Stremmel, W. Truncating mutations in the Wilson disease gene ATP7B are associated with very low serum ceruloplasmin oxidase activity and an early onset of Wilson disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.R.; Forbes, J.R.; Roberts, E.A.; Walshe, J.M.; Cox, D.W. The Wilson disease gene: Spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nat. Genet. 1995, 9, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozma, I.; Atherley, C.; James, N. Influence of ethnic origin on the incidence of keratoconus and associated atopic disease in Asian and white patients. Eye 2005, 19, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, B. Zwei weitere Falle von grunlicher Verfarbung der Kornea. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilk. 1903, 41, 489–491. [Google Scholar]
- Kayser, B. Über einen Fall von angeborener grünlicher Verfärbung der Cornea. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 1902, 40, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, W.; Rohrschneider, W. Besteht das Pigmet des Kayser-Fleischerschen Hornhautringes aus sliber? Klin. Wochenschr. 1949, 13, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandmann, O.; Weiss, K.H.; Kaler, S.G. Wilson’s disease and other neurological copper disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusek, P.; Litwin, T.; Czlonkowska, A. Wilson disease and other neurodegenerations with metal accumulations. Neurol. Clin. 2015, 33, 175–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, D.; Fauci, A.; Hauser, S.; Longo, D.; Jameson, J.; Loscalzo, J. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 19th ed.; Mcgraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, J.E.; Williams, H.P.; Walshe, J.M. “Sunflower Cataract” in Wilson’s Disease. Br. Med. J. 1969, 3, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, E.A.; Schilsky, M.L. Diagnosis and treatment of Wilson disease: An update. Hepatology 2008, 47, 2089–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langwińska-Wośko, E.; Litwin, T.; Dzieżyc, K.; Członkowska, A. The sunflower cataract in Wilson’s disease: Pathognomonic sign or rare finding? Acta Neurol. Belg. 2016, 116, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association For The Study Of The Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Wilson’s disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walshe, J. The eye in Wilson disease. QJM Int. J. Med. 2011, 104, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebers, D.O.; Hollenhorst, R.; Goldstein, N. The ophthalmologic manifestations of Wilson’s disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1977, 52, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, V.; Tripathi, M. Sunflower cataract in Wilson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 69, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.-J.; Liao, R.-D.; Chen, X.-M. Ophthalmic manifestations of Wilson’s disease. [Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi] Chin. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 44, 128–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lössner, A.; Lössner, J.; Bachmann, H.; Zotter, J. The Kayser-Fleischer ring during long-term treatment in Wilson’s disease (hepatolenticular degeneration). Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1986, 224, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.-C.; Tsai, Y.-Y. Sunflower cataract. Postgrad. Med. J. 2016, 92, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, N.; Bhat, P.; Goel, R.; Pannu, A.K.; Malhotra, P.; Suri, V. Kayser-Fleischer ring. QJM 2020, 113, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, A.; Bhattacharjee, M.S. Kayser-Fleischer Rings in Wilson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigdon, E.; Feuerstacke, J.; Steinhorst, N.A.; Spitzer, M. Diagnosis of Kayser Fleischer Ring: Can Early Diagnosis Improve the Outcome of Wilson’s Disease? Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 2020, 237, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrag, A.; Schott, J.M. Images in clinical medicine. Kayser-Fleischer rings in Wilson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koay, C.L.; Zahari, M.; Lee, W.S. Kayser-Fleisher Ring and Sunflower Cataract in a Child with Wilson’s Disease. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2017, 58, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguti, M.M.; Tietge, U.J.; Barbosa, E.R.; Cancado, E.L. The eye in Wilson’s disease: Sunflower cataract associated with Kayser-Fleischer ring. J. Hepatol. 2002, 37, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Sahay, P.; Maharana, P.K.; Titiyal, J.S. Ocular manifestations of Wilson’s disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e229662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, J.; Gupta, A. Kayser-Fleischer ring and sunflower cataract in Wilson disease. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014, 132, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunde, R.A. Selenium. In Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease; Shils, M.E., Shike, M., Ross, C.A., Caballero, B., Cousins, R.J., Eds.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bopp, B.A.; Bonders, R.C.; Kesterson, J.W. Metabolic fate of selected selenium compounds in laboratory animals and man. Drug Metab. Rev. 1982, 13, 271–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.G.; Burk, R.F. Selenium retention in tissues and sperm of rats fed α torula yeast diet. J. Nutr. 1973, 103, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomassen, Y.A.J. Selenium in human tissues. In Occurrence and Distribution of Selenium; Ihnat, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, K.W. A new toxicant occurring naturally in certain samples of plant foodstuffs. 1. Results obtained in preliminary feeding trials. J. Nutr. 1934, 8, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moxon, A.L. Alkali Disease or Selenium Poisoning; South Dakota State University: Brookings, SD, USA, 1937. [Google Scholar]
- Reilly, C. The biology of selenium. Selenium Food Health 2006, 20–42. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Trace Elements in Human Nutrition and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Selenium; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- IOM. Selenium. In Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 284–324. [Google Scholar]
- Levander, O.A. Scientific rationale for the 1989 recommended dietary allowance for selenium. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1991, 91, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Selenium in Drinking-Water. In Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; (WHO/HSE/WSH/10.01/14); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Spallholz, J.E. On the nature of selenium toxicity and carcinostatic activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 17, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunsaker, D.M.; Spiller, H.A.; Williams, D. Acute selenium poisoning: Suicide by ingestion. J. Forensic Sci. 2005, 50, JFS2004247-2004245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, K.L. Evaluating selenium poisoning. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2006, 36, 409–420. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Ogra, Y. Metabolic pathway for selenium in the body: Speciation by HPLC-ICP MS with enriched Se. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, R.F.; Hill, K.E.; Motley, A.K. Selenoprotein metabolism and function: Evidence for more than one function for selenoprotein P. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1517S–1520S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockitch, G. Selenium: Clinical significance and analytical concepts. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1989, 27, 483–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civil, I.; McDonald, M. Acute selenium poisoning: Case report. N. Z. Med. J. 1978, 87, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alderman, L.C.; Bergin, J.J. Hydrogen selenide poisoning: An illustrative case with review of the literature. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1986, 41, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonen, J.; Alfthan, G.; Huttunen, J.; Pikkarainen, J.; Puska, P. Association between cardiovascular death and myocardial infarction and serum selenium in a matched-pair longitudinal study. Lancet 1982, 320, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manati, W.; Vaillant, F.; Bost, M.; Maffre, V.; Belhani, D.; Descotes, J.; Tabib, A.; Bui-Xuan, B.; Hamdan, L.; Timour, Q. Protective role of selenium supplementation against cardiac lesions induced by the combination of levomepromazine and risperidone in the rabbit. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, C. The chemopreventive role of selenium in carcinogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1986, 206, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.F.; Strukle, E.; Williams, S.R.; Manoguerra, A.S. Selenium poisoning from a nutritional supplement. JAMA 1996, 275, 1087–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, L.; Hewett, J.; Lim, J.K. Hydroxycut hepatotoxicity: A case series and review of liver toxicity from herbal weight loss supplements. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2008, 14, 6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, C.A.; Meier, K.H.; Olson, K.R. Seizures reported in association with use of dietary supplements. Clin. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Engel, A.; Fattinger, K.; Marbet, U.A.; Criblez, D.; Reichen, J.; Zimmermann, A.; Oneta, C.M. Herbal does not mean innocuous: Ten cases of severe hepatotoxicity associated with dietary supplements from Herbalife® products. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition, U.S., Food and Drug Administration. Overview of Dietary Supplements. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/Food/DietarySupplements/ConsumerInformation/ucm110417.htm (accessed on 11 February 2009).
- Schellmann, B.; Raithel, H.; Schaller, K. Acute fatal selenium poisoning. Arch. Toxicol. 1986, 59, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.; Gerson, B.; Subramaniam, S. The role of copper, molybdenum, selenium, and zinc in nutrition and health. Clin. Lab. Med. 1998, 18, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PenteL, P.; Fletcher, D.; Jentzen, J. Fatal acute selenium toxicity. J. Forensic Sci. 1985, 30, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruta, D.; Haider, S. Attempted murder by selenium poisoning. BMJ Br. Med. J. 1989, 299, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, R. Selenium intoxication-New York. Morbid. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 1984, 33, 157–158. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Wang, S.Z.; Zhou, R.; Sun, S. Endemic selenium intoxication of humans in China. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 37, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtman, T.C. Selenium biochemistry. Science 1974, 183, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stárka, L.; Čermáková, I.; Dušková, M.; Hill, M.; Doležal, M.; Poláček, V. Hormonal profile of men with premature balding. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2004, 112, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint, F. Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition; Diamond Pocket Books (P) Ltd.: Delhi, India, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, P.; Sharma, S.; Agarwal, U. Selenium toxicity: A rare diagnosis. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2016, 82, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumaran, S.; Balamurugan, N.; Vohra, R.; Thirumalaikolundusubramanian, P. Paradise nut paradox: Alopecia due to selenosis from a nutritional therapy. Int. J. Trichology 2012, 4, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosary, B.M.; Sutter, M.E.; Schwartz, M.; Morgan, B.W. Case series of selenium toxicity from a nutritional supplement. Clin. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbertson, K.; Jarrett, R.; Bayliss, S.J.; Berk, D.R. Scalp discoloration from selenium sulfide shampoo: A case series and review of the literature. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2012, 29, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, L.R.; Shannon, M.W.; Committee on Environmental Health. Technical report: Mercury in the environment: Implications for pediatricians. Pediatrics 2001, 108, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin-Zaki, L.; Majeed, M.; Clarkson, T.; Greenwood, M. Methylmercury poisoning in Iraqi children: Clinical observations over two years. Br. Med. J. 1978, 1, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, K.B.; Tutkun, E.; Yilmaz, H.; Dilber, C.; Dalkiran, T.; Cakir, B.; Arslantas, D.; Cesaretli, Y.; Aykanat, S.A. Acute mercury poisoning among children in two provinces of Turkey. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2013, 172, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul Oz, S.; Tozlu, M.; Yalcin, S.S.; Sozen, T.; Sain Guven, G. Mercury vapor inhalation and poisoning of a family. Inhal. Toxicol. 2012, 24, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurissen, J.P. History of mercury and mercurialism. NY State J. Med. 1981, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Sunderman, F.W. Perils of mercury. Ann. Clin. Lab Sci. 1988, 18, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Goldwater, L.J. From Hippocrates to Ramazzini: Early history of industrial medicine. Ann. Med. Hist. 1936, 8, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Goldwater, L.J. Mercury: A history of quicksilver. In Hat Industry; Goldwater, L.J., Ed.; York Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- O’shea, J. ‘Two minutes with venus, two years with mercury’-mercury as an antisyphilitic chemotherapeutic agent. J. R. Soc. Med. 1990, 83, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advisory, F.C. An important message for pregnant women and women of childbearing age who may become pregnant about the risks of mercury in fish. FDA Newsl. 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shenker, B.J.; Guo, T.L.; Shapiro, I.M. Low-level methylmercury exposure causes human T-cells to undergo apoptosis: Evidence of mitochondrial dysfunction. Environ. Res. 1998, 77, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glezos, J.D.; Albrecht, J.E.; Gair, R.D. Pneumonitis after inhalation of mercury vapours. Can. Respir. J. 2006, 13, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risher, J. Toxicological Profile for Mercury; Department Of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Graeme, K.A.; Pollack, C.V., Jr. Heavy metal toxicity, part I: Arsenic and mercury. J. Emerg. Med. 1998, 16, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risher, J.F.; Amler, S.N. Mercury exposure: Evaluation and intervention: The inappropriate use of chelating agents in the diagnosis and treatment of putative mercury poisoning. Neurotoxicology 2005, 26, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Internet Version 2005; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, A.S.; Seger, D.; Vannucci, S.; Langley, M.; Abraham, J.L.; King, L.E., Jr. Mercury exposure and cutaneous disease. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000, 43, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L. Mercury neurotoxicity: Effects and mechanisms. Handb. Neurotoxicol. 1995, 31–59. [Google Scholar]
- Seiler, H.G.; Sigel, H.; Sigel, A. Handbook on Toxicity of Inorganic Compounds; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hursh, J.B.; Clarkson, T.W.; Cherian, M.G.; Vostal, J.J.; Mallie, R.V. Clearance of mercury (Hg-197, Hg-203) vapor inhaled by human subjects. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1976, 31, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, A. Massive elemental mercury ingestion. Clin. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusyniak, D.E.; Nañagas, K.A. Conservative management of elemental mercury retained in the appendix. Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Leon, L. Elemental mercury embolism to the lung. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowens, B.; Guerrero-Betancourt, D.; Gottlieb, C.A.; Boyes, R.J.; Eichenhorn, M.S. Respiratory failure and death following acute inhalation of mercury vapor: A clinical and histologic perspective. Chest 1991, 99, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguado, S.; De Quiros, J.F.B.; Marin, R.; Gago, E.; Gómez, E.; Fdez-Vega, F.; Alvarez Grande, J. Acute mercury vapour intoxication: Report of six cases. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1989, 4, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lilis, R.; Miller, A.; Lerman, Y. Acute mercury poisoning with severe chronic pulmonary manifestations. Chest 1985, 88, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, T.W.; Magos, L.; Myers, G.J. The toxicology of mercury—Current exposures and clinical manifestations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunnessen, W.W.; McMahon, K.J.; Baser, M. Acrodynia: Exposure to mercury from fluorescent light bulbs. Pediatrics 1987, 79, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkany, J.; Hubbard, D.M. Adverse mercurial reactions in the form of acrodynia and related conditions. AMA Am. J. Dis. Child. 1951, 81, 335–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, H.; Ferguson, S.; Kell, R.; Samuel, A. Mercury as a health hazard. Arch. Dis. Child. 1987, 62, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, J.J.; Bercovitch, L.; Muglia, J.J. Acrodynia and hypertension in a young girl secondary to elemental mercury toxicity acquired in the home. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2012, 29, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, H.; Shono, M.; Hada, S. Mercury exanthem. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1984, 11, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedano, H.O. Mercury poisoning and acrodynia. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1998, 85, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henningsson, C.; Hoffmann, S.; McGonigle, L.; Winter, J. Acute mercury poisoning (acrodynia) mimicking pheochromocytoma in an adolescent. J. Pediatr. 1993, 122, 252–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.D.; Rai, A.N.; Hardiek, M.L. Mercury intoxication and arterial hypertension: Report of two patients and review of the literature. Pediatrics 2000, 105, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wossmann, W.; Kohl, M.; Grüning, G.; Bucsky, P. Mercury intoxication presenting with hypertension and tachycardia. Arch. Dis. Child. 1999, 80, 556–557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beuter, A.; De Geoffroy, A. Can tremor be used to measure the effect of chronic mercury exposure in human subjects? Neurotoxicology 1996, 17, 213–227. [Google Scholar]
- Netterstrøm, B.; Guldager, B.; Heebøll, J. Acute mercury intoxication examined with coordination ability and tremor. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1996, 18, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckell, M.; Hunter, D.; Milton, R.; Perry, K.M.A. Chronic mercury poisoning. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1946, 3, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhoft, R.A. Mercury toxicity and treatment: A review of the literature. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012, 460508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Vorwald, A.; Patil, L.; Mooney, T. Effects of exposure to mercury in the manufacture of chlorine. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1970, 31, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moneim, R.A.A.; El Deeb, M.; Rabea, A.A. Gingival pigmentation (cause, treatment and histological preview). Future Dent. J. 2017, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-D.; Zheng, W. Human exposure and health effects of inorganic and elemental mercury. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2012, 45, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broussard, L.A.; Hammett-Stabler, C.A.; Winecker, R.E.; Ropero-Miller, J.D. The toxicology of mercury. Lab. Med. 2002, 33, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bont, B.; Lauwerys, R.; Govaerts, H.; Moulin, D. Yellow mercuric oxide ointment and mercury intoxication. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1986, 145, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargan, P.I.; Giles, L.J.; Wallace, C.I.; House, I.M.; Thomson, A.H.; Beale, R.J.; Jones, A.L. Case report: Severe mercuric sulphate poisoning treated with 2, 3-dimercaptopropane-1-sulphonate and haemodiafiltration. Critical. Care 2003, 7, R1–R6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M. Minamata disease: Methylmercury poisoning in Japan caused by environmental pollution. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1995, 25, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, G.J.; Davidson, P.W. Prenatal methylmercury exposure and children: Neurologic, developmental, and behavioral research. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aberg, B.; Ekman, L.; Falk, R.; Greitz, U.; Persson, G.; Snihs, J.O. Metabolism of methyl mercury (203Hg) compounds in man: Excretion and distribution. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1969, 19, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, M.; Carlson, J.; Norseth, T. Dose-dependence of methylmercury metabolism: A study of distribution: Biotransformation and excretion in the squirrel monkey. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1975, 30, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.P. Mercury, vaccines, and autism: One controversy, three histories. Am. J. Public Health 2008, 98, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, N.; Olver, R.; Issler, H.; Wrong, O. Domestic metallic mercury poisoning. Lancet 1984, 323, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, F.; Damluji, S.F.; Amin-Zaki, L.; Murtadha, M.; Khalidi, A.; Al-Rawi, N.; Tikriti, S.; Dhahir, H.; Clarkson, T.; Smith, J. Methylmercury poisoning in Iraq. Science 1973, 181, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eto, K. Minamata Disease. Neuropathology 2000, 20, S14–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eto, K.; Tokunaga, H.; Nagashima, K.; Takeuchi, T. An autopsy case of Minamata disease (methylmercury poisoning)—Pathological viewpoints of peripheral nerves. Toxicol. Pathol. 2002, 30, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, O.; Parsi, K.K.; Wu, D.; Konia, T.H.; Younts, A.; Sinha, N.; McNelis, A.; Sharon, V.R. Mercury toxicity presenting as acrodynia and a papulovesicular eruption in a 5-year-old girl. Dermatol. Online J. 2016, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, S.Y.; Lee, C.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Moon, Y.H.; Kim, M.S.; Bae, I.H.; Song, H.S. Cases of acute mercury poisoning by mercury vapor exposure during the demolition of a fluorescent lamp factory. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 29, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, C.; Angermann, J.; Sugarman, J. Erethism Mercurialis and Reactions to Elemental Mercury. Cutis 2021, 107, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhilash, K.P.; Arul, J.J.; Bala, D. Fatal overdose of iron tablets in adults. Indian J. Crit. Care Med 2013, 17, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, E.L.; Iwasaki, K.; Tsuji, Y. Comprehensive Invited Review. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, M.; Ben-Shachar, D.; Riederer, P.; Youdim, M.B. Altered brain metabolism of iron as a cause of neurodegenerative diseases? J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, A.K.; Singhi, S.C. Acute iron poisoning: Management guidelines. Indian Pediatr. 2003, 40, 534–540. [Google Scholar]
- Singhi, S.C.; Baranwal, A.K. Acute iron poisoning: Clinical picture, intensive care needs and outcome. Indian Pediatr. 2003, 40, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Pestaner, J.P.; Ishak, K.G.; Mullick, F.G.; Centeno, J.A. Ferrous sulfate toxicity: A review of autopsy findings. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1999, 69, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madiwale, T.; Liebelt, E. Iron: Not a benign therapeutic drug. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2006, 18, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sane, M.R.; Malukani, K.; Kulkarni, R.; Varun, A. Fatal Iron Toxicity in an Adult: Clinical Profile and Review. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 22, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.R.; Lin, J.L.; Liaw, S.J.; Bullard, M.J. Acute iron intoxication: A case report with ferric chloride ingestion. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 1993, 52, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Lacoste, H.; Goyert, G.L.; Goldman, L.S.; Wright, D.J.; Schwartz, D.B. Acute iron intoxication in pregnancy: Case report and review of the literature. Obstet. Gynecol. 1992, 80, 500–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Wax, J.R.; Philput, C.; Steinfeld, J.D.; Ingardia, C.J. Intentional iron overdose in pregnancy--management and outcome. J. Emerg. Med. 2000, 18, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Wax, J.R.; Steinfeld, J.D.; Ingardia, C.J. Acute intentional iron overdose in pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 92, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, H.W.; Becker, W. Iron Toxicity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2023; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.C.; Ahmed, N.; Hanna, M. Non-transferrin-bound iron in long-term transfusion in children with congenital anemias. J. Pediatr. 1986, 108, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoczynska, A.; Kwiecinska, D.; Kielbinski, M.; Łukaszewski, M. Acute iron poisoning in adult female. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2007, 26, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacouture, P.G.; Wason, S.; Temple, A.R.; Wallace, D.K.; Lovejoy, F.H., Jr. Emergency assessment of severity in iron overdose by clinical and laboratory methods. J. Pediatr. 1981, 99, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covey, T.J. Ferrous sulfate poisoning. J. Pediatr. 1954, 64, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, V.V. Modern Medical Toxicology, 4th ed.; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, M.J. Iron absorption. Clin. Toxicol. 1971, 4, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebelt EL, K.R. Acute Iron Poisoning. 2013. Available online: www.uptodate.com (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Simonse, E.; Valk-Swinkels, C.G.; van ‘t Veer, N.E.; Ermens, A.A.; Veldkamp, E.J. Iron autointoxication in a 16-year-old girl: A protective role for hepcidin? Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 50, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahesh, K.; Rani, R. A case of iron poisoning-case report. Int. J. Basic Appl. Med. Sci. 2014, 4, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, A.; Tenenbein, M. Hepatotoxicity in acute iron poisoning. Hum. Exp. Toxicol 2005, 24, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, R.K.; Robarts, F.H. Hour-glass stricture of the stomach and pyloric stenosis due to ferrous sulphate poisoning. Br. J. Surg. 1962, 49, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, J.N.; Gnirke, A.; Thomas, W.; Tsuchihashi, Z.; Ruddy, D.A.; Basava, A.; Dormishian, F.; Domingo, R., Jr.; Ellis, M.C.; Fullan, A.; et al. A novel MHC class I-like gene is mutated in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, L.W.; Seckington, R.C.; Deugnier, Y. Haemochromatosis. Lancet 2016, 388, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, B.R.; Powell, L.W.; Adams, P.C.; Kresina, T.F.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Molecular medicine and hemochromatosis: At the crossroads. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgaonkar, M.R. Hemochromatosis. More common than you think. Can. Fam. Physician 2003, 49, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brissot, P.; de Bels, F. Current approaches to the management of hemochromatosis. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2006, 2006, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavill, A.S. Diagnosis and management of hemochromatosis. Hepatology 2001, 33, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limdi, J.K.; Crampton, J.R. Hereditary haemochromatosis. QJM 2004, 97, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrangelo, A. Juvenile hemochromatosis. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 892–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, D.; Roddick, C.; Powell, L.W. Recent advances in hemochromatosis: A 2015 update: A summary of proceedings of the 2014 conference held under the auspices of Hemochromatosis Australia. Hepatol. Int. 2015, 9, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissot, P.; Troadec, M.B.; Bardou-Jacquet, E.; Le Lan, C.; Jouanolle, A.M.; Deugnier, Y.; Loréal, O. Current approach to hemochromatosis. Blood Rev. 2008, 22, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrangelo, A. Hereditary hemochromatosis--a new look at an old disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2383–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajioka, R.S.; Kushner, J.P. Clinical consequences of iron overload in hemochromatosis homozygotes. Blood 2003, 101, 3351–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.J.; Gurrin, L.C.; Constantine, C.C.; Osborne, N.J.; Delatycki, M.B.; Nicoll, A.J.; McLaren, C.E.; Bahlo, M.; Nisselle, A.E.; Vulpe, C.D.; et al. Iron-overload-related disease in HFE hereditary hemochromatosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, E.; Felitti, V.J.; Koziol, J.A.; Ho, N.J.; Gelbart, T. Penetrance of 845G--> A (C282Y) HFE hereditary haemochromatosis mutation in the USA. Lancet 2002, 359, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulaj, Z.J.; Ajioka, R.S.; Phillips, J.D.; LaSalle, B.A.; Jorde, L.B.; Griffen, L.M.; Edwards, C.Q.; Kushner, J.P. Disease-related conditions in relatives of patients with hemochromatosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurrin, L.C.; Osborne, N.J.; Constantine, C.C.; McLaren, C.E.; English, D.R.; Gertig, D.M.; Delatycki, M.B.; Southey, M.C.; Hopper, J.L.; Giles, G.G.; et al. The natural history of serum iron indices for HFE C282Y homozygosity associated with hereditary hemochromatosis. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, J.P.; Speechley, M.R.; Kertesz, A.E.; Chakrabarti, S.; Adams, P.C. Natural history of C282Y homozygotes for hemochromatosis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 16, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, D.L.; Crosby, W.H.; Edwards, C.Q.; Fairbanks, V.F.; Mitros, F.A. Practice guideline development task force of the College of American Pathologists. Hereditary hemochromatosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 1996, 245, 139–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittelkow, M.R.; Flores, S. Hemochromatosis. 2017. Available online: https://www.dermatologyadvisor.com/home/decision-support-in-medicine/dermatology/hemochromatosis-3/ (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Chmieliauskas, S.; Banionis, D.; Laima, S.; Andriuskeviciute, G.; Mazeikiene, S.; Stasiuniene, J.; Jasulaitis, A.; Jarmalaite, S. Autopsy relevance determining hemochromatosis: Case report. Medicine 2017, 96, e8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogawa, K. Kanazawa Medical University Uchinada, Ishikawa, Japan. In Proceedings of the Changing Metal Cycles and Human Health: Report of the Dahlem Workshop on Changing Metal Cycles and Human Health, Berlin, Germany, 20–25 March 1983; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; p. 275. [Google Scholar]
- Probst, G. Cadmium: Absorption and excretion in mammals. In Cadmium Toxicity; Mennear, J.H., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 29–59. [Google Scholar]
- Świergosz, R.; Zakrzewska, M.; Sawicka-Kapusta, K.; Bacia, K.; Janowska, I. Accumulation of cadmium in and its effect on bank vole tissues after chronic exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1998, 41, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godt, J.; Scheidig, F.; Grosse-Siestrup, C.; Esche, V.; Brandenburg, P.; Reich, A.; Groneberg, D.A. The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2006, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johri, N.; Jacquillet, G.; Unwin, R. Heavy metal poisoning: The effects of cadmium on the kidney. Biometals 2010, 23, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L.; Berglund, M.; Elinder, C.G.; Nordberg, G.; Vanter, M. Health effects of cadmium exposure–a review of the literature and a risk estimate. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 1998, 24, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elinder, C.G.; Lind, B.; Kjellström, T.; Linnman, L.; Friberg, L. Cadmium in kidney cortex, liver, and pancreas from Swedish autopsies. Estimation of biological half time in kidney cortex, considering calorie intake and smoking habits. Arch. Environ. Health 1976, 31, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Cadmium. In Environmental Health Criteria; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992; Volume 134. [Google Scholar]
- Zalups, R.K.; Ahmad, S. Molecular handling of cadmium in transporting epithelia. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 186, 163–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Leonard, S.S.; Rao, K.M. Cadmium inhibits the electron transfer chain and induces reactive oxygen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svartengren, M.; Elinder, C.G.; Friberg, L.; Lind, B. Distribution and concentration of cadmium in human kidney. Environ. Res. 1986, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orłowski, C.; Piotrowski, J.K. Biological levels of cadmium and zinc in the small intestine of non-occupationally exposed human subjects. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2003, 22, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, O.; Jacquillet, G.; Tauc, M.; Cougnon, M.; Poujeol, P. Effect of heavy metals on, and handling by, the kidney. Nephron. Physiol. 2005, 99, p105–p110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A. Renal dysfunction induced by cadmium: Biomarkers of critical effects. Biometals 2004, 17, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, N.A.; Abouhamed, M.; Verroust, P.J.; Thévenod, F. Megalin-dependent internalization of cadmium-metallothionein and cytotoxicity in cultured renal proximal tubule cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Nordberg, M.; Frech, W.; Dumont, X.; Bernard, A.; Ye, T.T.; Kong, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Lundström, N.G.; et al. Cadmium biomonitoring and renal dysfunction among a population environmentally exposed to cadmium from smelting in China (ChinaCad). Biometals 2002, 15, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, P.R.; McLellan, J.S.; Haist, J.; Cherian, G.; Chamberlain, M.J.; Valberg, L.S. Increased dietary cadmium absorption in mice and human subjects with iron deficiency. Gastroenterology 1978, 74 Pt 1, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiguchi, H.; Oguma, E.; Sasaki, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Machida, M.; Kayama, F. Comprehensive study of the effects of age, iron deficiency, diabetes mellitus, and cadmium burden on dietary cadmium absorption in cadmium-exposed female Japanese farmers. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 196, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunshin, H.; Mackenzie, B.; Berger, U.V.; Gunshin, Y.; Romero, M.F.; Boron, W.F.; Nussberger, S.; Gollan, J.L.; Hediger, M.A. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature 1997, 388, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidal, K.; Jörgensen, N.; Elinder, C.G.; Sjögren, B.; Vahter, M. Fatal cadmium-induced pneumonitis. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1993, 19, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D.; Goldman, K. Acute cadmium poisoning in a foreman plater welder. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1990, 47, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.F. Historical perspectives on cadmium toxicology. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.F. Cadmium and health in the 21st century--historical remarks and trends for the future. Biometals 2004, 17, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, T.; Kobayashi, E.; Suwazono, Y.; Uetani, M.; Oishi, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Nogawa, K. Estimation of cumulative cadmium intake causing Itai-itai disease. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 159, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogawa, K.; Hagino, N.; Ishizaki, A.; Fukushima, M. [Itai-itai disease]. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi 1975, 30, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Nogawa, K.; Kobayashi, E.; Okubo, Y.; Suwazono, Y. Environmental cadmium exposure, adverse effects and preventive measures in Japan. Biometals 2004, 17, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantzis, G. Renal tubular dysfunction and abnormalities of calcium metabolism in cadmium workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 1979, 28, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfvén, T.; Elinder, C.G.; Carlsson, M.D.; Grubb, A.; Hellström, L.; Persson, B.; Pettersson, C.; Spång, G.; Schütz, A.; Järup, L. Low-level cadmium exposure and osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2000, 15, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, G.; Jin, T.; Bernard, A.; Fierens, S.; Buchet, J.P.; Ye, T.; Kong, Q.; Wang, H. Low bone density and renal dysfunction following environmental cadmium exposure in China. Ambio 2002, 31, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessen, J.A.; Roels, H.A.; Emelianov, D.; Kuznetsova, T.; Thijs, L.; Vangronsveld, J.; Fagard, R. Environmental exposure to cadmium, forearm bone density, and risk of fractures: Prospective population study. Public Health and Environmental Exposure to Cadmium (PheeCad) Study Group. Lancet 1999, 353, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parizek, J.; Zahor, Z. Effect of cadmium salts on testicular tissue. Nature 1956, 177, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, C.J.; Frithsen, I.L. Association of urinary cadmium and myocardial infarction. Environ. Res. 2008, 106, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieker, C.; Zidek, W.; Zumkley, H. Cadmium and hypertension. Nephron 1987, 47 (Suppl. S1), 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Il’yasova, D.; Ivanova, A. Urinary cadmium, impaired fasting glucose, and diabetes in the NHANES III. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagstaff, A.J.; Benfield, P.; Monk, J.P. Colloidal bismuth subcitrate. Drugs 1988, 36, 132–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbach, S.L. Bismuth therapy in gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R. Green bismuth. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.; Midolo, P. The actions of bismuth in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 11, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierer, D.W. Bismuth subsalicylate: History, chemistry, and safety. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1990, 12 (Suppl. S1), S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menge, H.; Gregor, M.; Brosius, B.; Hopert, R.; Lang, A. Pharmacology of bismuth. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1992, 4, S41–S47. [Google Scholar]
- Morison, R. The treatment of infected suppurating war wounds. Lancet 1916, 188, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H. Biological Chemistry of Arsenic, Antimony and Bismuth; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, B.; Warren, J.R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet 1984, 323, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, D.; Griffith, D.M. The prevalence of metal-based drugs as therapeutic or diagnostic agents: Beyond platinum. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 13239–13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J. Bipp: A case of toxicity? Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1990, 69, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, K.; Farboud, A.; Jardine, A. Bismuth iodoform paraffin paste: A review. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2012, 126, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Neo, S.; Gan, J.; Fu, E.; Lim, M.Y.; Li, H. Myoclonus From Intoxication by Bismuth Iodoform Paraffin Paste (BIPP) Nasopharyngeal Packing. Cureus 2021, 13, e18530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouk, V.; Nordberg, G.; Friberg, L. Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals; Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Cengiz, N.; Uslu, Y.; Gök, F.; Anarat, A. Acute renal failure after overdose of colloidal bismuth subcitrate. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2005, 20, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slikkerveer, A.; Noach, L.A.; Tytgat, G.N.; Van der Voet, G.B.; De Wolff, F.A. Comparison of enhanced elimination of bismuth in humans after treatment with meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid and D,L-2,3-dimercaptopropane-1-sulfonic acid. Analyst 1998, 123, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, R.H.; Whitehead, M.W.; Lacey, S.; Champion, M.; Thompson, R.P.; Powell, J.J. Solubility, absorption, and anti–Helicobacter pylori activity of bismuth subnitrate and colloidal bismuth subcitrate: In vitro data do not predict in vivo efficacy. Helicobacter 2000, 5, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slikkerveer, A.; de Wolff, F.A. Pharmacokinetics and toxicity of bismuth compounds. Med. Toxicol. Advers. Drug Exp. 1989, 4, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwokolo, C.U.; Gavey, C.J.; Smith, J.T.; Pounder, R.E. The absorption of bismuth from oral doses of tripotassium dicitrato bismuthate. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 1989, 3, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Quesne, P.M. Toxic substances and the nervous system: The role of clinical observation. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1981, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benet, L.Z. Safety and pharmacokinetics: Colloidal bismuth subcitrate. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 1991, 185, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, A.M.; Smith, A.C. Iatrogenic bismuth poisoning. Case report. Aust. Dent. J. 1994, 39, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karelitz, S.; Freedman, A.D. Hepatitis and nephrosis due to soluble bismuth. Pediatrics 1951, 8, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.M., Jr.; Fazekas-May, M.A.; Bowen, W.R. Nephrotoxic and ototoxic agents. Clin. Lab. Med. 1990, 10, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.P. Neuropsychiatric symptoms following bismuth intoxication. Postgrad. Med. J. 1988, 64, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, J.F. Mental illness or metal illness? Bismuth subgallate. Med. J. Aust. 1974, 1, 887–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teepker, M.; Hamer, H.M.; Knake, S.; Bandmann, O.; Oertel, W.H.; Rosenow, F. Myoclonic encephalopathy caused by chronic bismuth abuse. Epileptic Disord. 2002, 4, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Erden, A.; Karahan, S.; Bulut, K.; Basak, M.; Aslan, T.; Cetinkaya, A.; Karagoz, H.; Avci, D. A case of bismuth intoxication with irreversible renal damage. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2013, 6, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loghman-Adham, M. Aminoaciduria and glycosuria following severe childhood lead poisoning. Pediatr. Nephrol. 1998, 12, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaizu, K.; Uriu, K. Tubulointerstitial injuries in heavy metal intoxications. Nihon Rinsho. 1995, 53, 2052–2056. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saini, V.; Chalfin, R.; Leon, J.; Margolesky, J. Pearls & Oy-sters: Bismuth neurotoxicity from use of topical bismuth dressing for burns. Neurology 2019, 92, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.; Thomas, D.W.; Barron, V.J. Reversible encephalopathy possibly associated with bismuth subgallate ingestion. Br. Med. J. 1974, 1, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngman, L.; Harris, S. BIPP madness; an iatrogenic cause of acute confusion. Age Ageing 2004, 33, 406–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.R.; Cast, I.P.; Redfern, R.M.; O’Brien, C. Extradural application of bismuth iodoform paraffin paste causing relapsing bismuth encephalopathy: A case report with CT and MRI studies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovaska, H.; Wood, D.M.; House, I.; Dargan, P.I.; Jones, A.L.; Murray, S. Severe iatrogenic bismuth poisoning with bismuth iodoform paraffin paste treated with DMPS chelation. Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 855–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, F.D.; Dexter, S. Oral manifestations of bismuth. N. Engl. Med. 1925, 213, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grund, J. Erythema of the ninth day following bismuth therapy for syphilis. Arch. Dermatol. Syphilol. 1940, 41, 1076–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfield, W. Untersuchungen uber die toxischen und therapeutischen wirkungen des wismuths. Arch. Fur. Exp. Pathol. Und. Pharm. 1886, 20, 40–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohe, H.; Rosenfeld, H. Ein einfaches symptom zur Erkennung der wismut intoxication bei der syphilisbehandlung. Med. Klin. 1927, 23, 1295. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, E. Bismuth stomatitis and albuminuria. Am. J. Syph. Gonorrhoea Vener. Dis. 1942, 26, 84–95. [Google Scholar]
- Pohanish, R.P. Sitting’s Handbook of Toxic and Hazardous Chemicals and Carcinogens; Chemical Emergency Preparedness Program: Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Neville, B.W.; Damm, D.D.; Allen, C.M.; Chi, A.C. Physical and chemical injuries. In Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, 4th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 288–289. [Google Scholar]
- Borbinha, C.; Serrazina, F.; Salavisa, M.; Viana-Baptista, M. Bismuth encephalopathy- a rare complication of long-standing use of bismuth subsalicylate. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, P.C.; Chaves, G.S.; Decurcio, D.A.; Decurcio, R.A.; Rossi-Fedele, G.; de Magalhães, A.P.R. Late discolouration of root-treated teeth and subsequent restorative retreatment: Three case reports. Aust. Endod. J. 2022, 48, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, J.; Borg, J.; Damidot, D.; Salvadori, E.; Pilecki, P.; Zaslansky, P.; Darvell, B.W. Colour and chemical stability of bismuth oxide in dental materials with solutions used in routine clinical practice. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, S.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Seshadri, B.; Choppala, G.; Naidu, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.-G.; Li, F. Sources, distribution, bioavailability, toxicity, and risk assessment of heavy metal (loid) s in complementary medicines. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachanek, T.; Starosławska, E.; Wolańska, E.; Jarmolińska, K. Heavy metal poisoning in glass worker characterised by severe. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2000, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sienczuk, W. Toksykologia; PZWL: Warszawa, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkumar, V.; Gupta, V. Heavy Metal Toxicity; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hepler, B.; Sutheimer, C.; Sunshine, I. Role of the toxicology laboratory in suspected ingestions. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 1986, 33, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kumar, V. Heavy metal toxicity: An update of chelating therapeutic strategies. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 54, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudinger, K.C.; Roth, V.S. Occupational lead poisoning. Am. Fam. Physician 1998, 57, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Mercury (Hg) |
|---|
| Acrodynia: pruritus, erythematous rash, pink discoloration of nails, erythematous gingiva, pink hyperpigmentation on the skin, ulceration of oral mucosa. Erethism: memory loss, lethargy, depression, irritability, insomnia, confusion, hallucinations. Gingivitis Tremors and paresthesia |
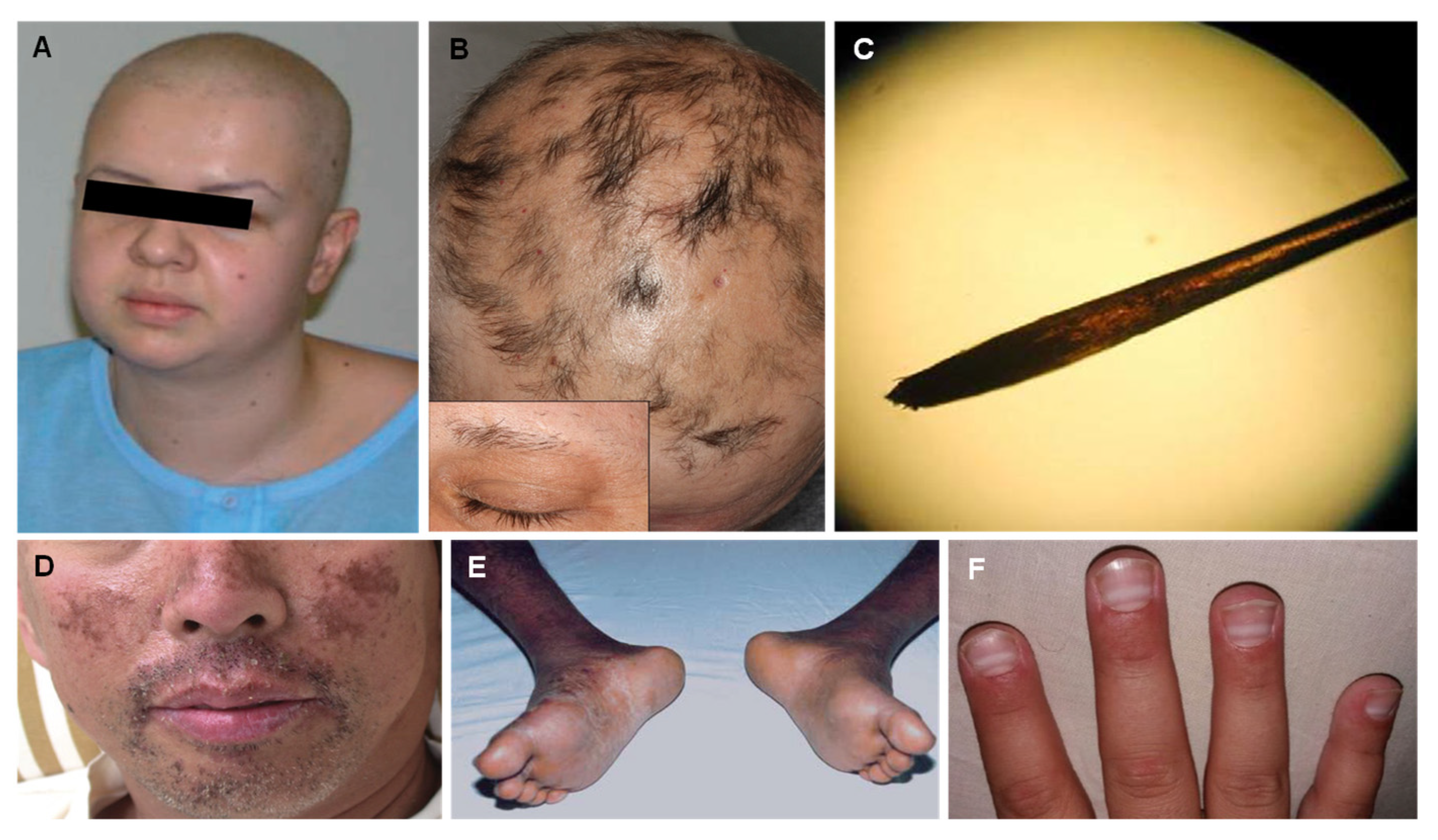
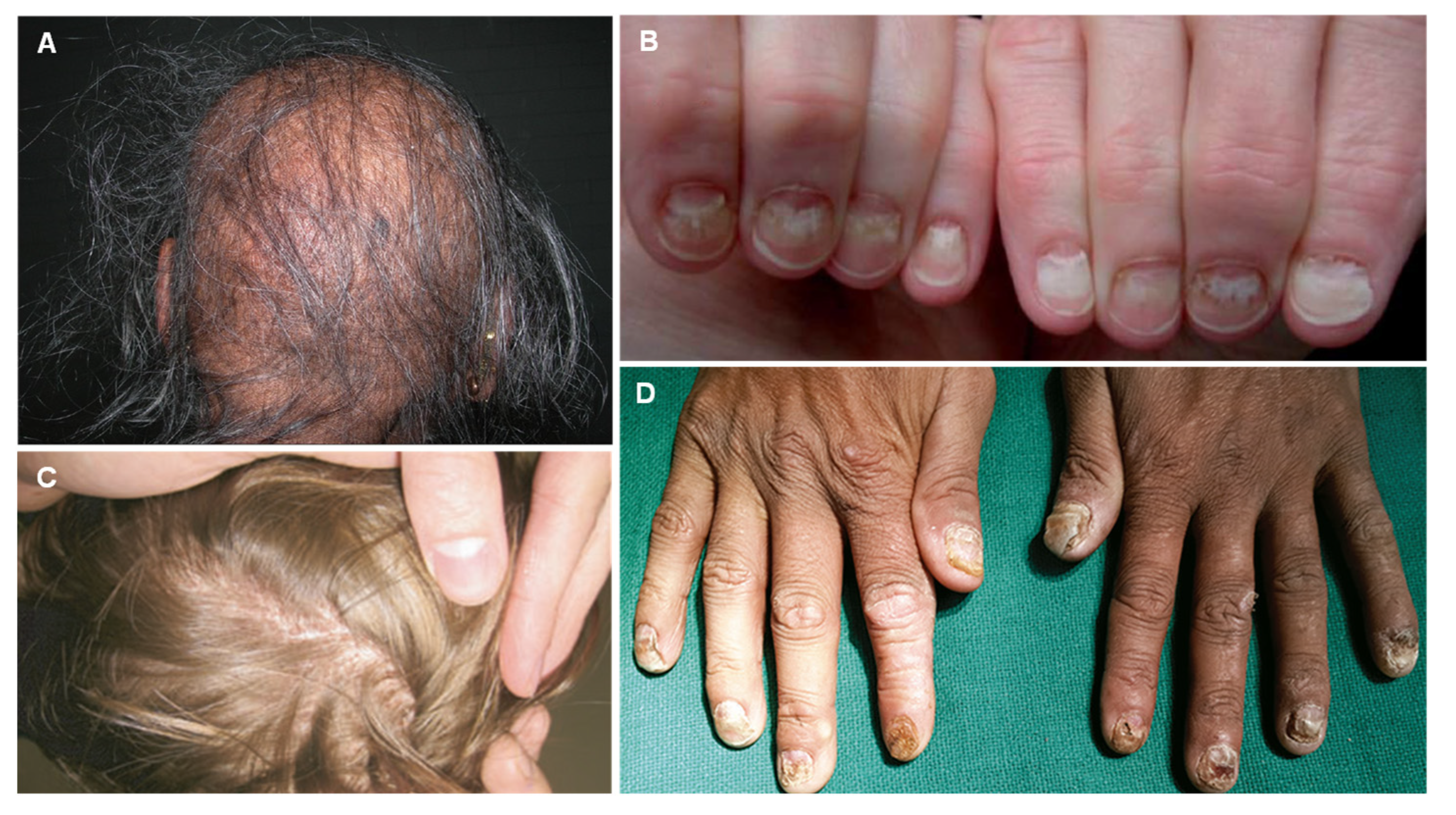
| Thallium (Tl) |
| Alopecia Palmar and solar keratosis Glossitis and stomatitis Mee’s lines in the nails Bayonet hair |
| Fluorine (F) |
| Dental fluorosis Skeletal fluorosis: diffuse bone condensation and interosseous membrane calcification, osteosclerosis and osteoporosis. |
| Arsenic (As) |
| Palmar and solar keratosis Hyperpigmentation Mee’s lines in the nails Raindrop pigmentation |
| Iron (Fe) |
| Hemochromatosis: skin hyperpigmentation—a bronze or slate-gray coloration. |
| Selenium (Se) |
| Alopecia Nail dystrophy/Paronychia Pink pigmentation of nails and eyelids Dermatitis and skin lesions Reddish pigmentation of the skin |
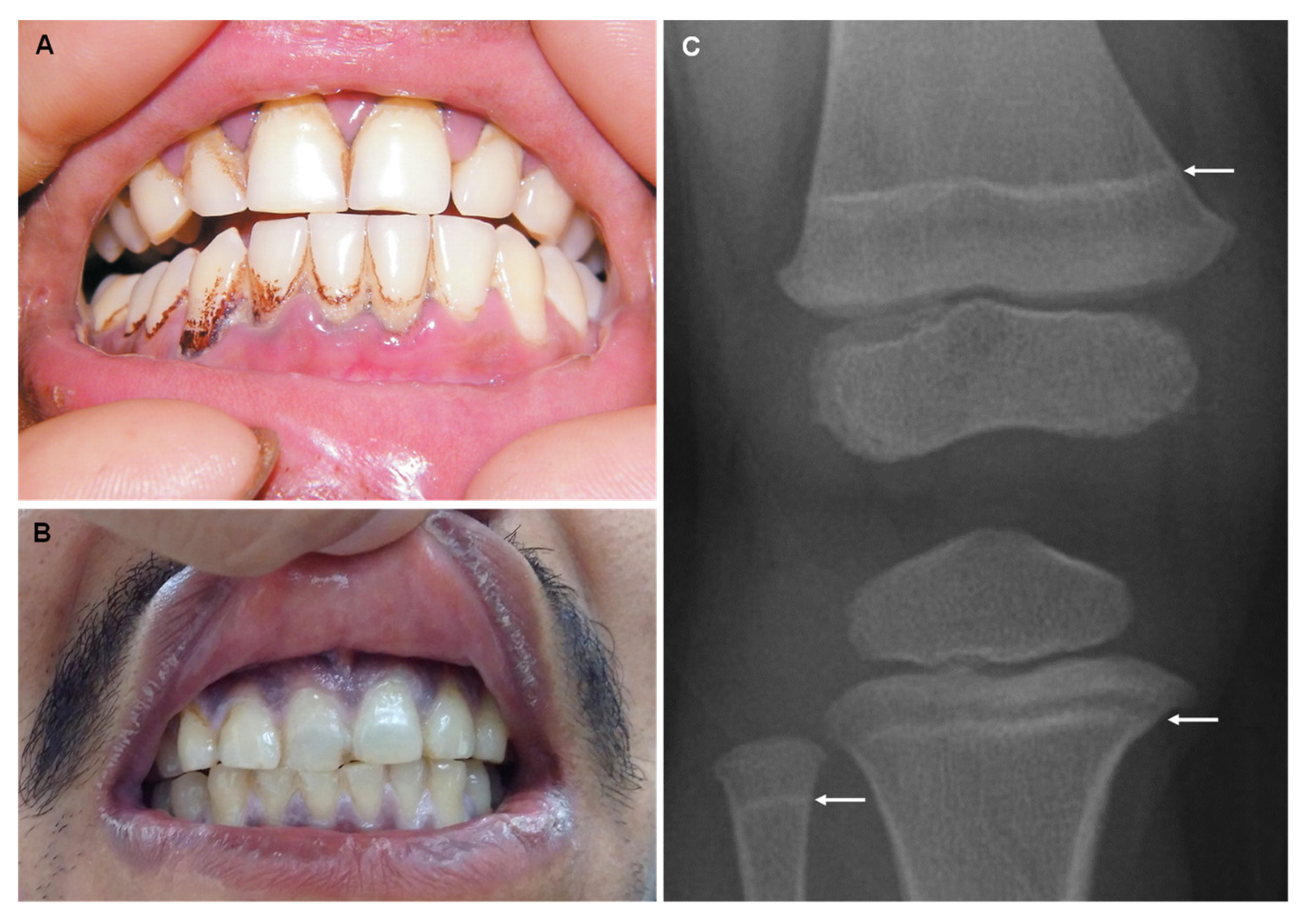
| Bismuth (Bi) |
| “Bismuth line”: bluish black gum discoloration Gingivostomatitis and ulceration Blackening of the tongue and teeth |
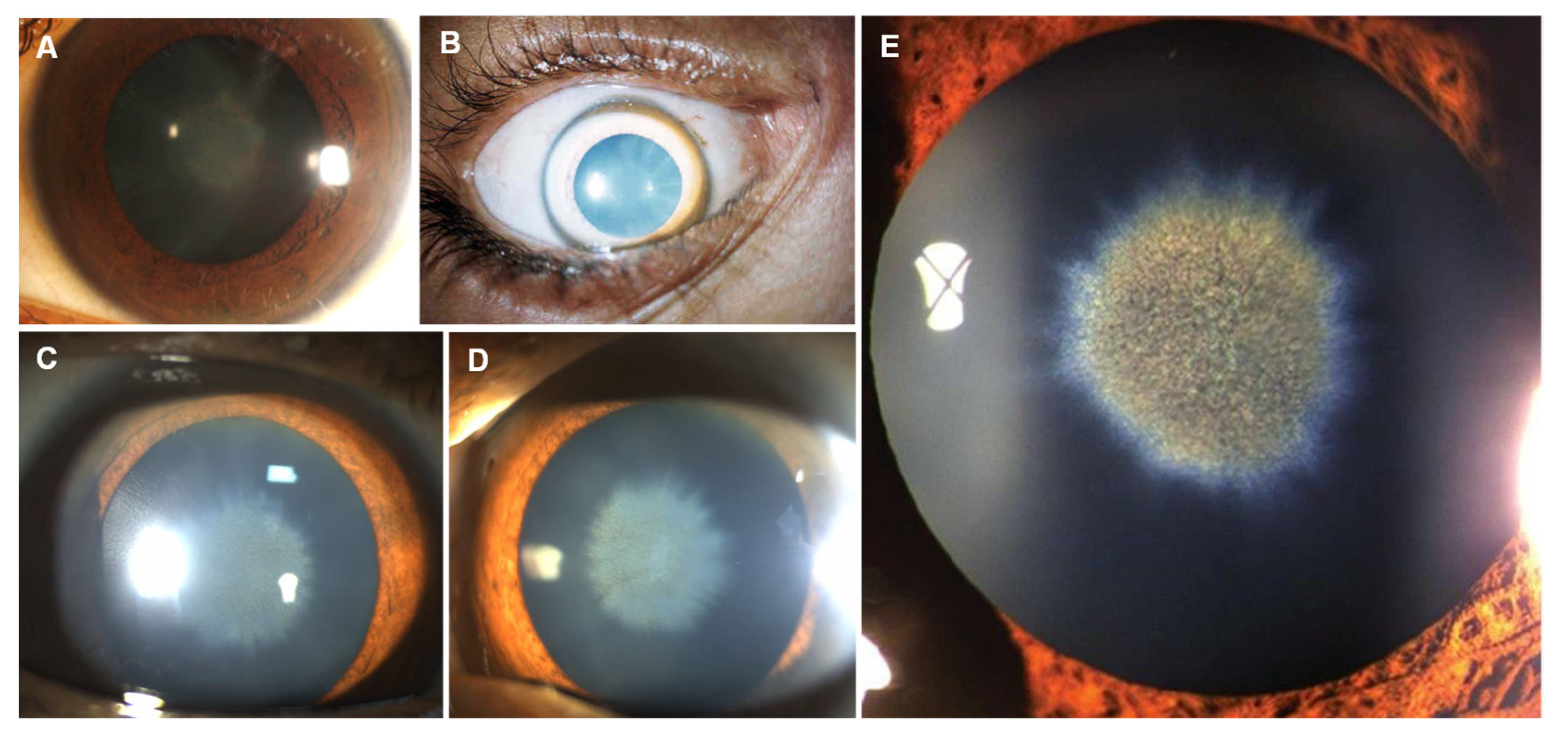
| Cooper (Cu) |
| Kayser–Fleischer ring Sunflower cataract |
| Lead (Pb) |
| Burton’s line in the gums Lead lines on X-ray of long bones |
| Cadmium (Cd) |
| Osteomalacia and osteoporosis Long exposure causes anosmia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Carvalho Machado, C.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Clinical and Forensic Signs Resulting from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Other Chemical Elements of the Periodic Table. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072591
de Carvalho Machado C, Dinis-Oliveira RJ. Clinical and Forensic Signs Resulting from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Other Chemical Elements of the Periodic Table. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(7):2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072591
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Carvalho Machado, Carolina, and Ricardo Jorge Dinis-Oliveira. 2023. "Clinical and Forensic Signs Resulting from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Other Chemical Elements of the Periodic Table" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 7: 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072591
APA Stylede Carvalho Machado, C., & Dinis-Oliveira, R. J. (2023). Clinical and Forensic Signs Resulting from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Other Chemical Elements of the Periodic Table. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(7), 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072591