Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates in a Multi-Profile Hospital over 5 Years (2017–2021)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Microbiological Tests
2.2.1. Automatic Systems
2.2.2. The Disk Diffusion Method
2.2.3. Enzyme and Immunochromatographic Tests
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evolution of Resistance of Selected Bacteria to Antibiotics Used in Therapy
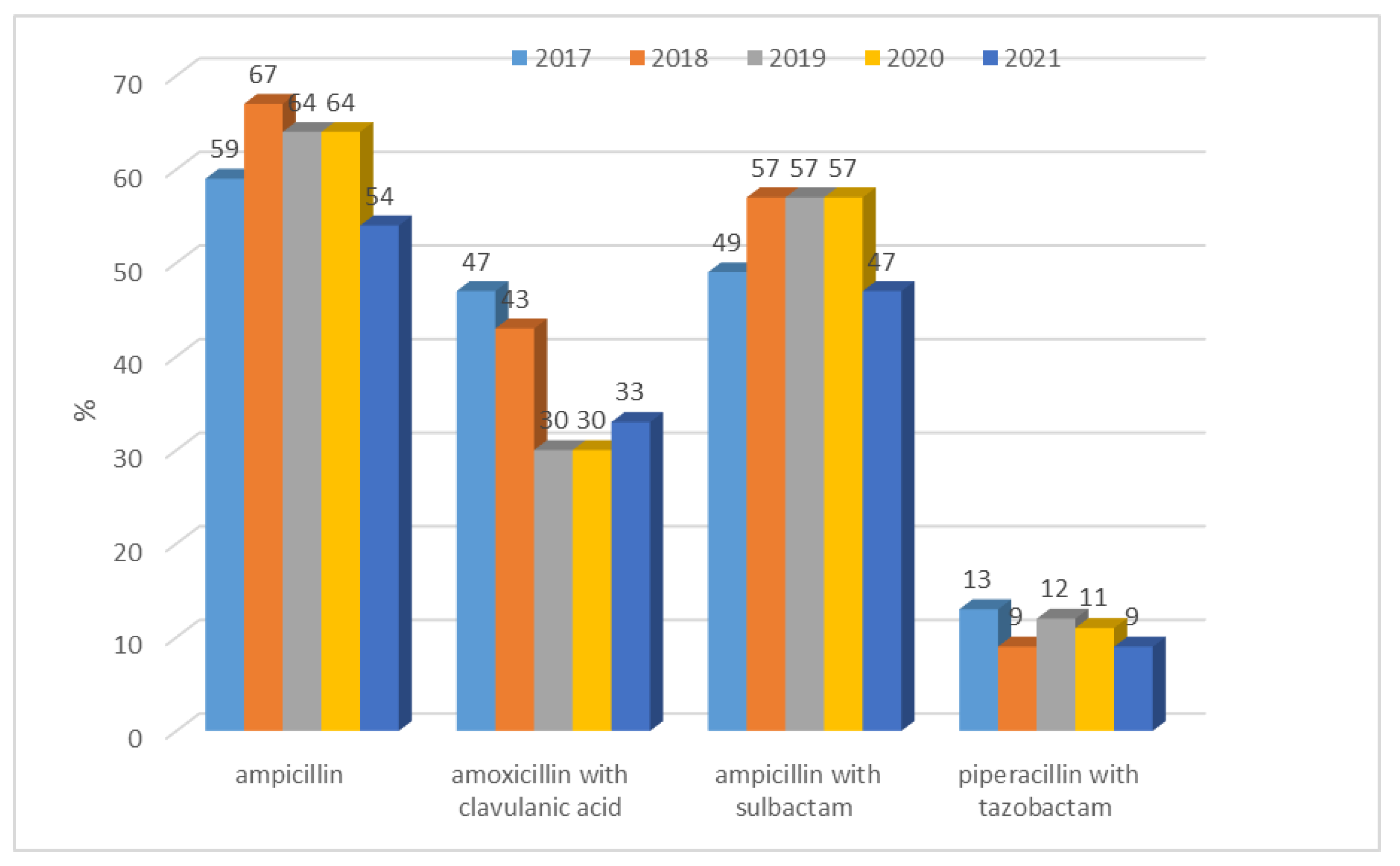
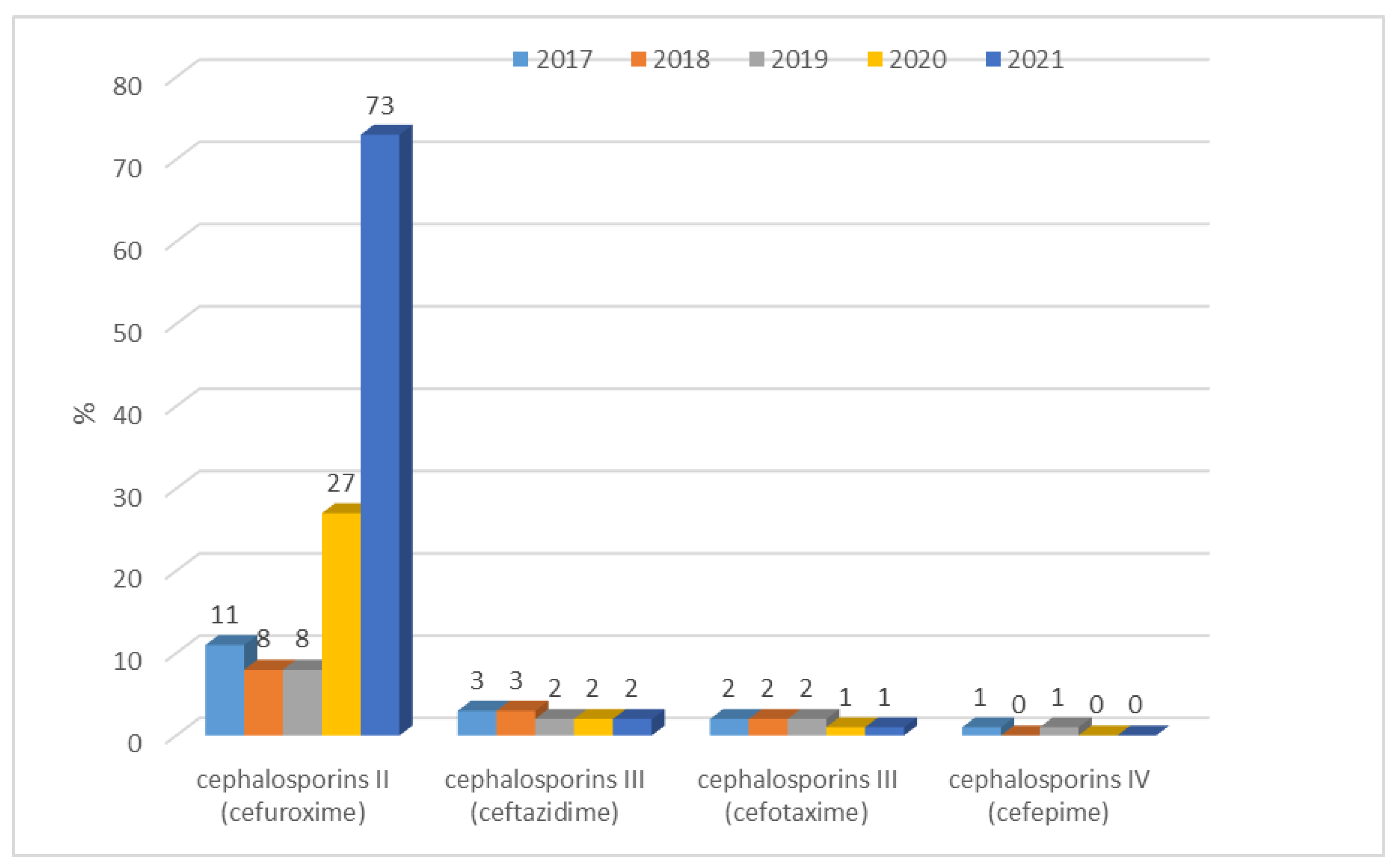
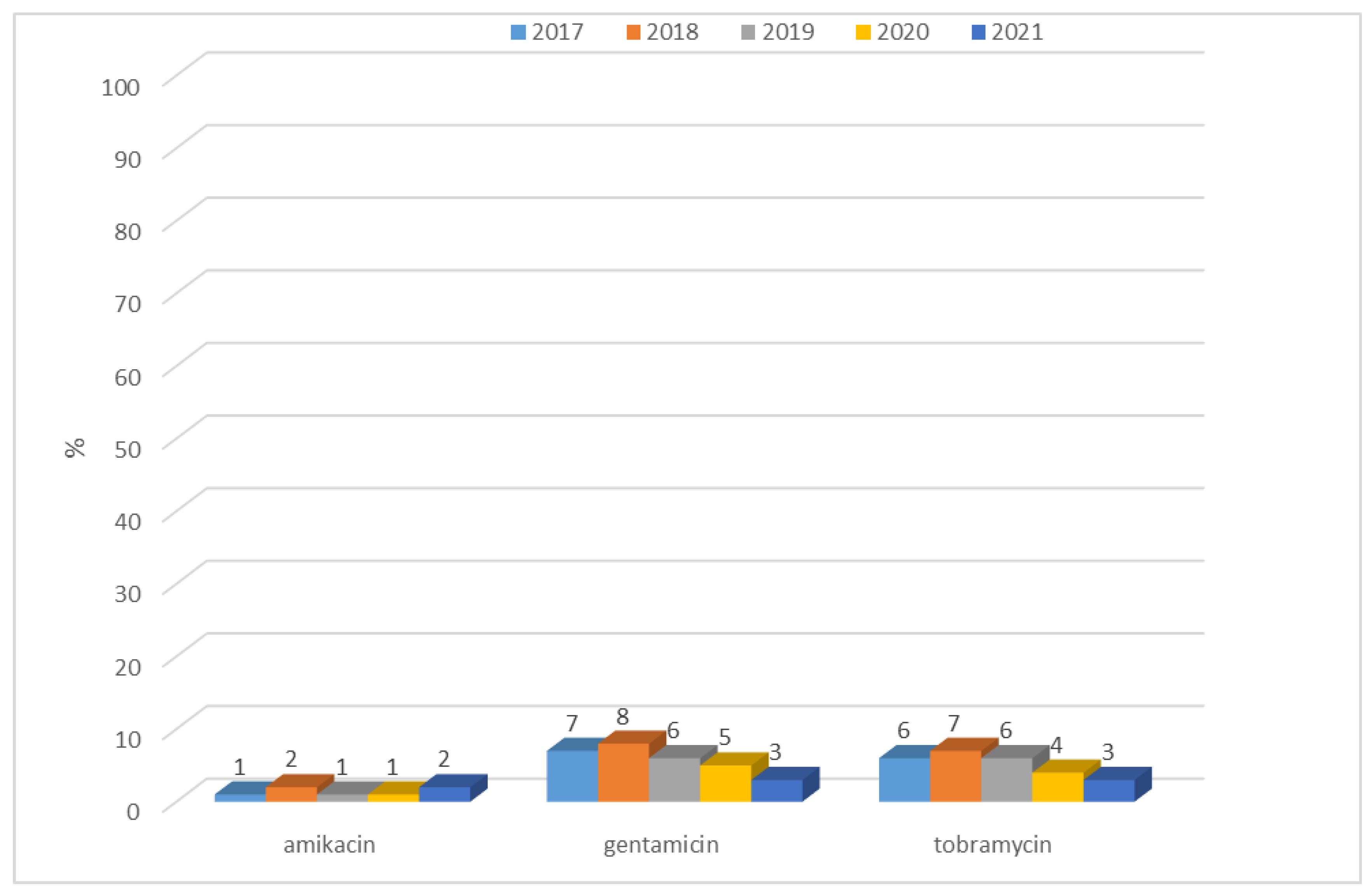
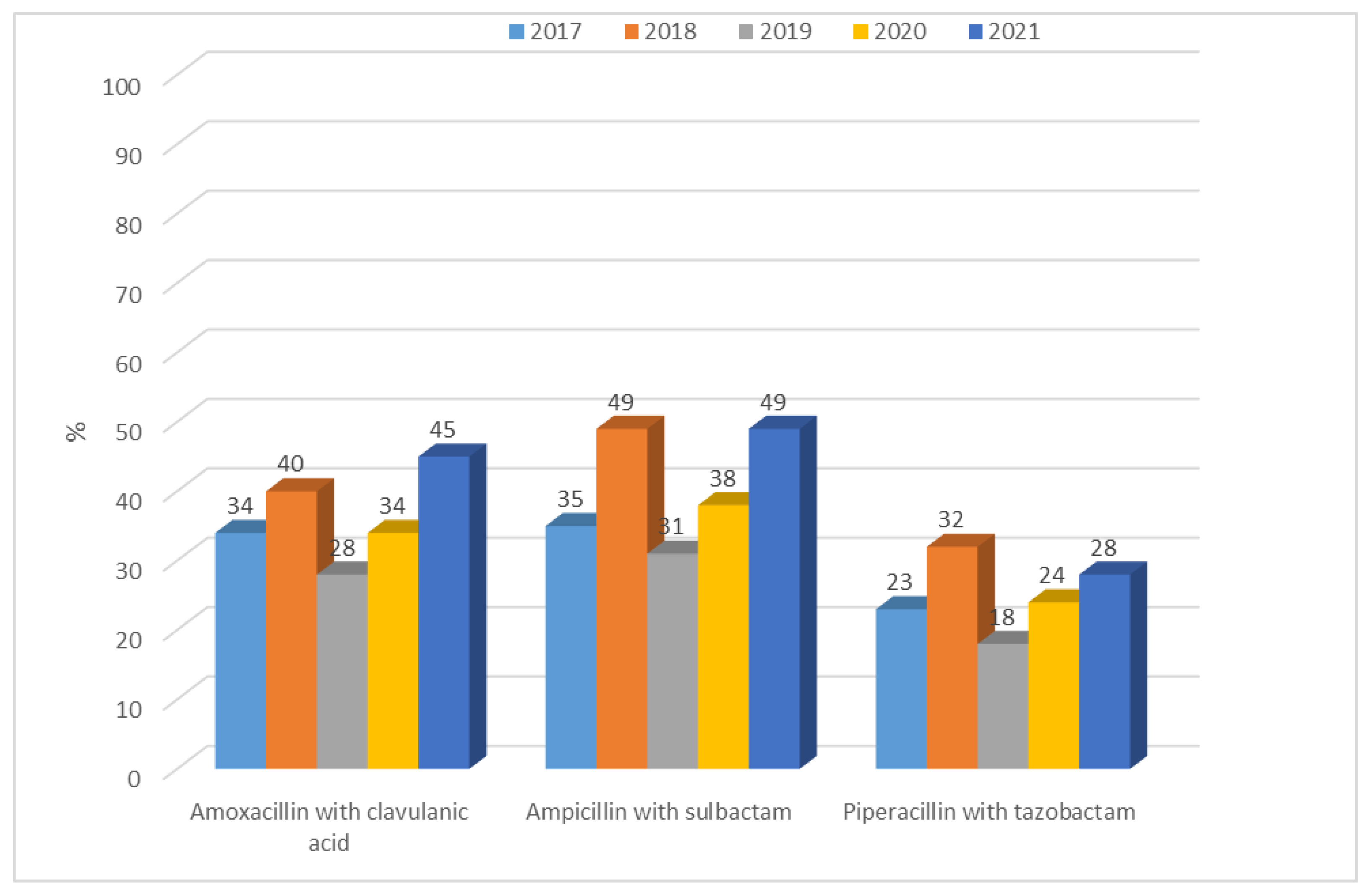
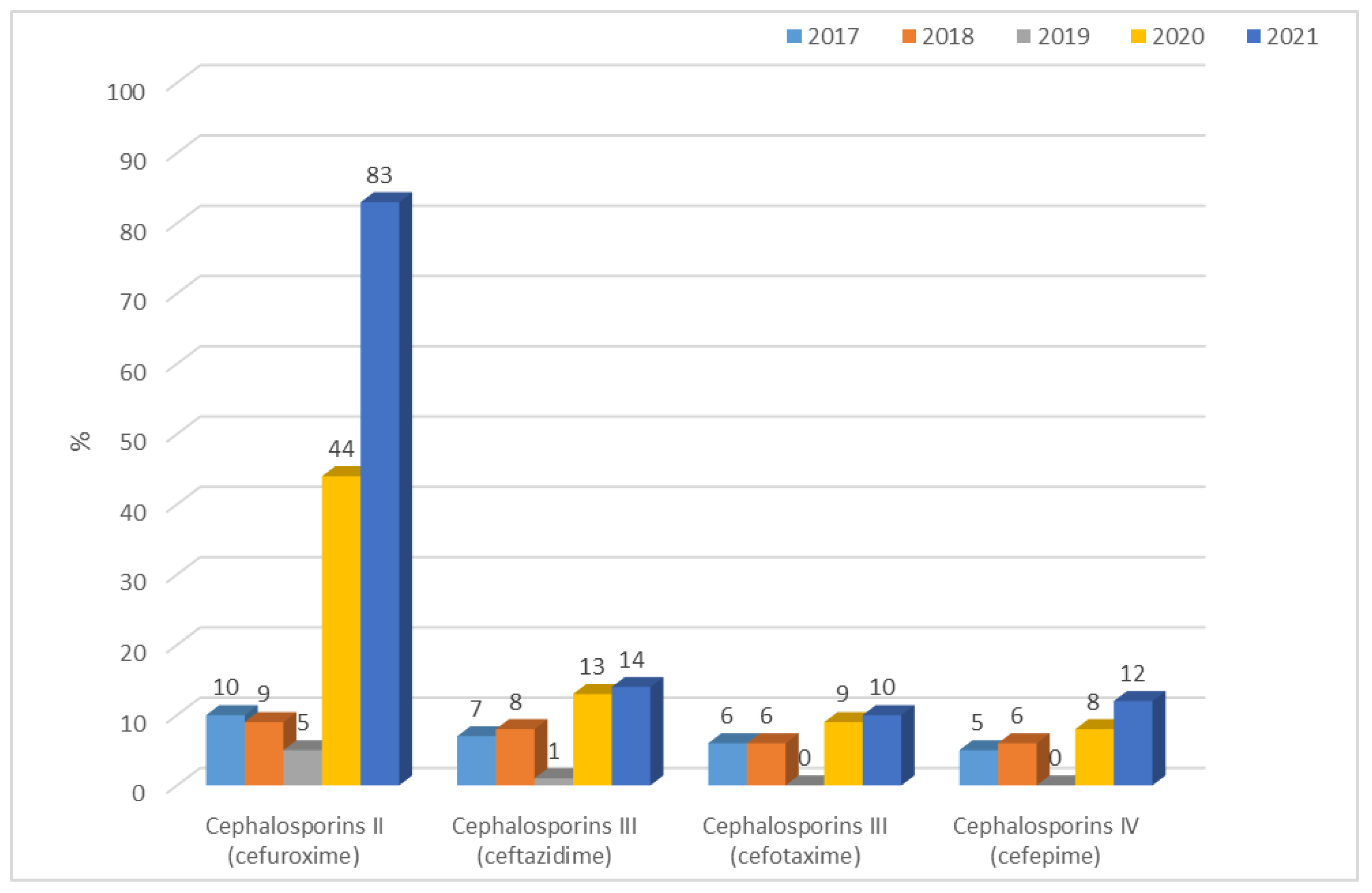
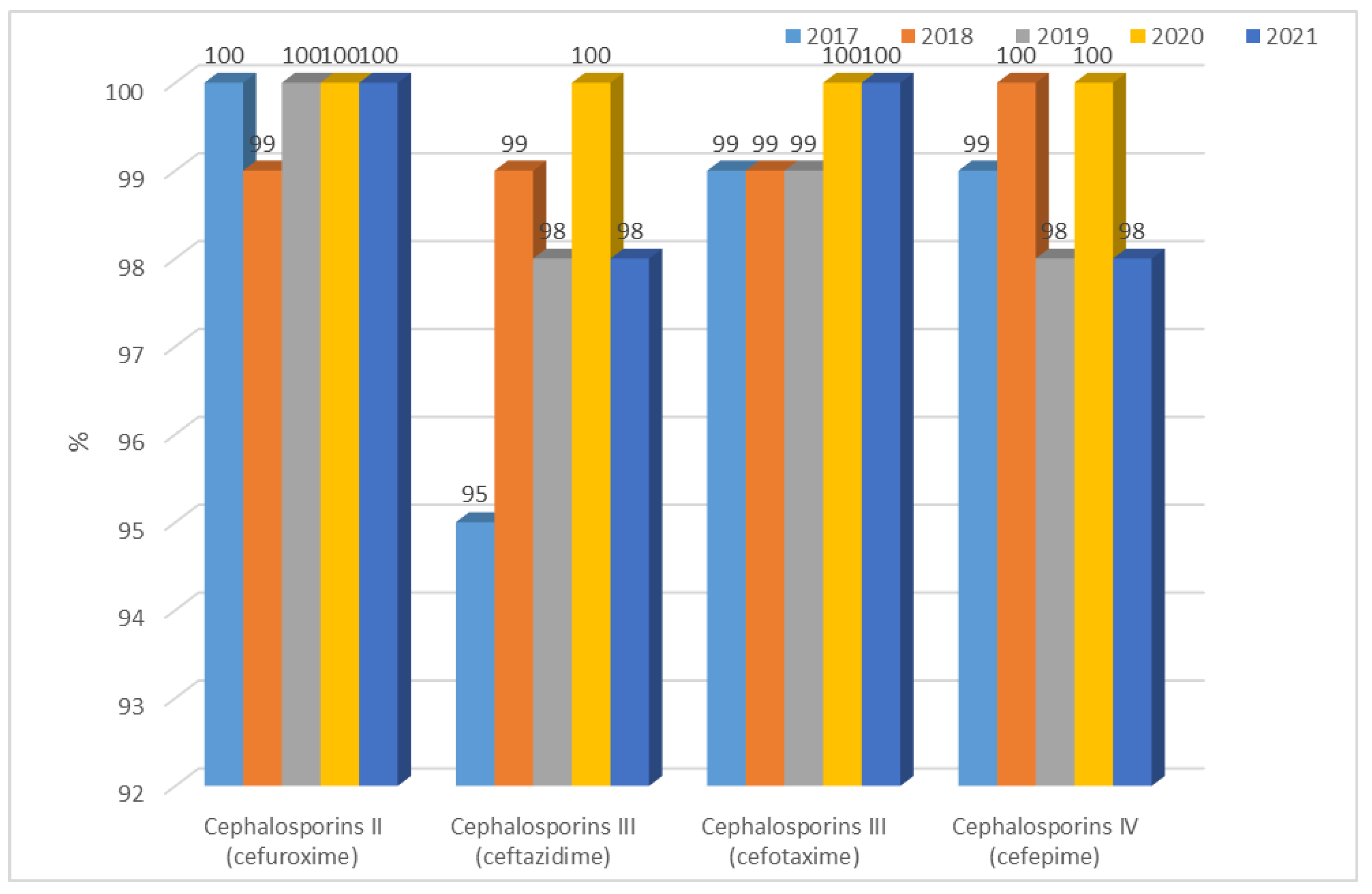
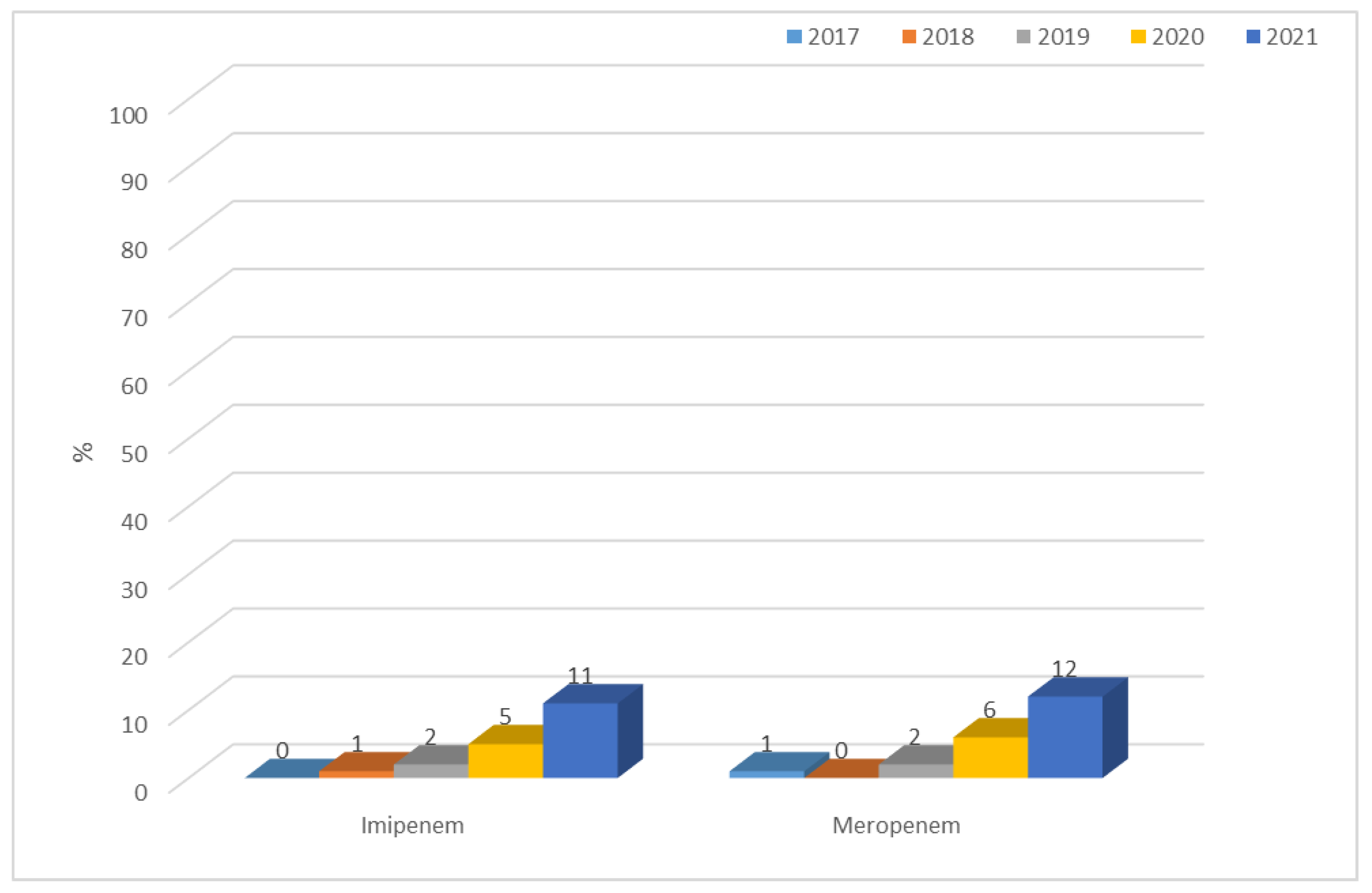
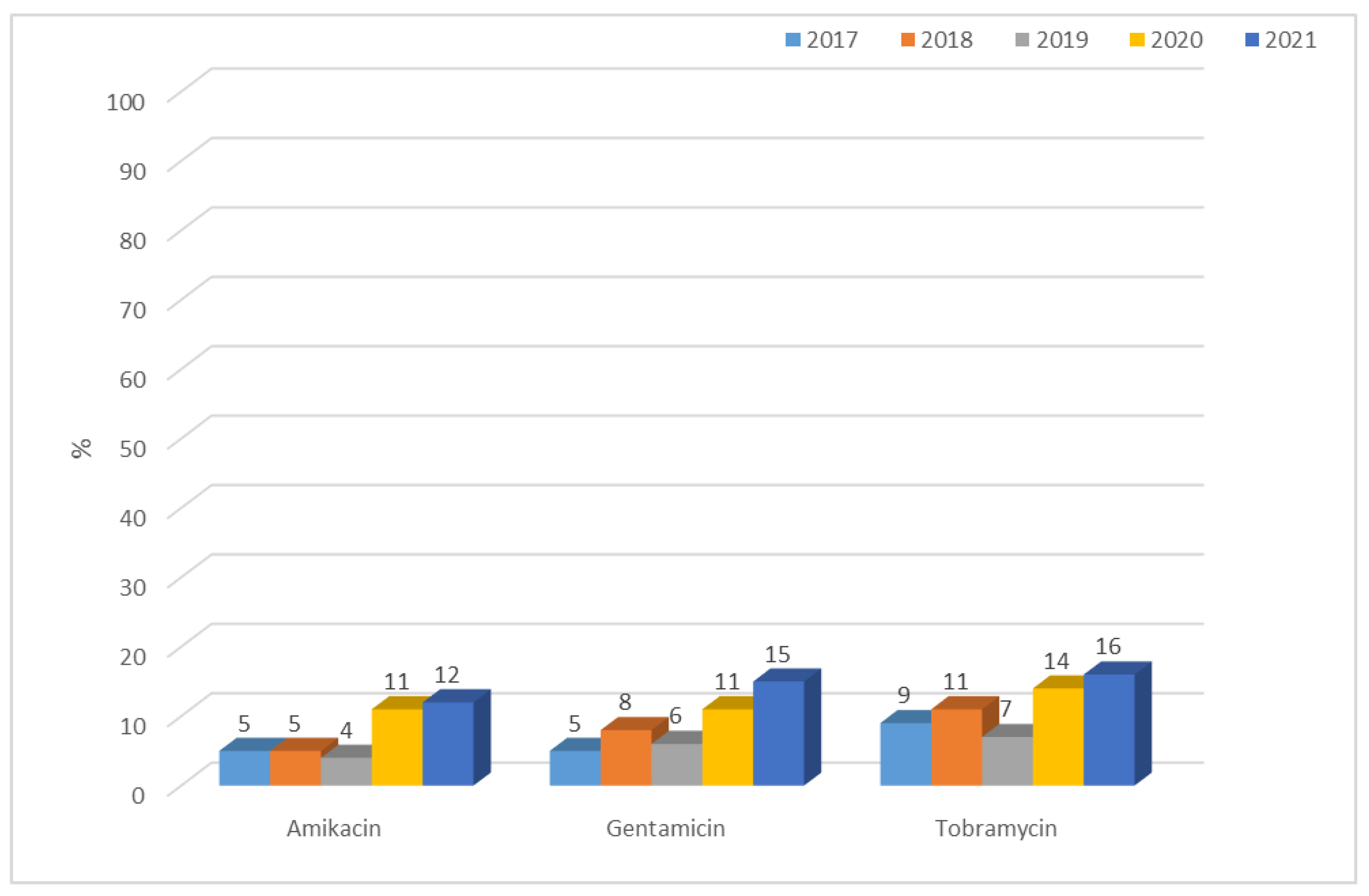
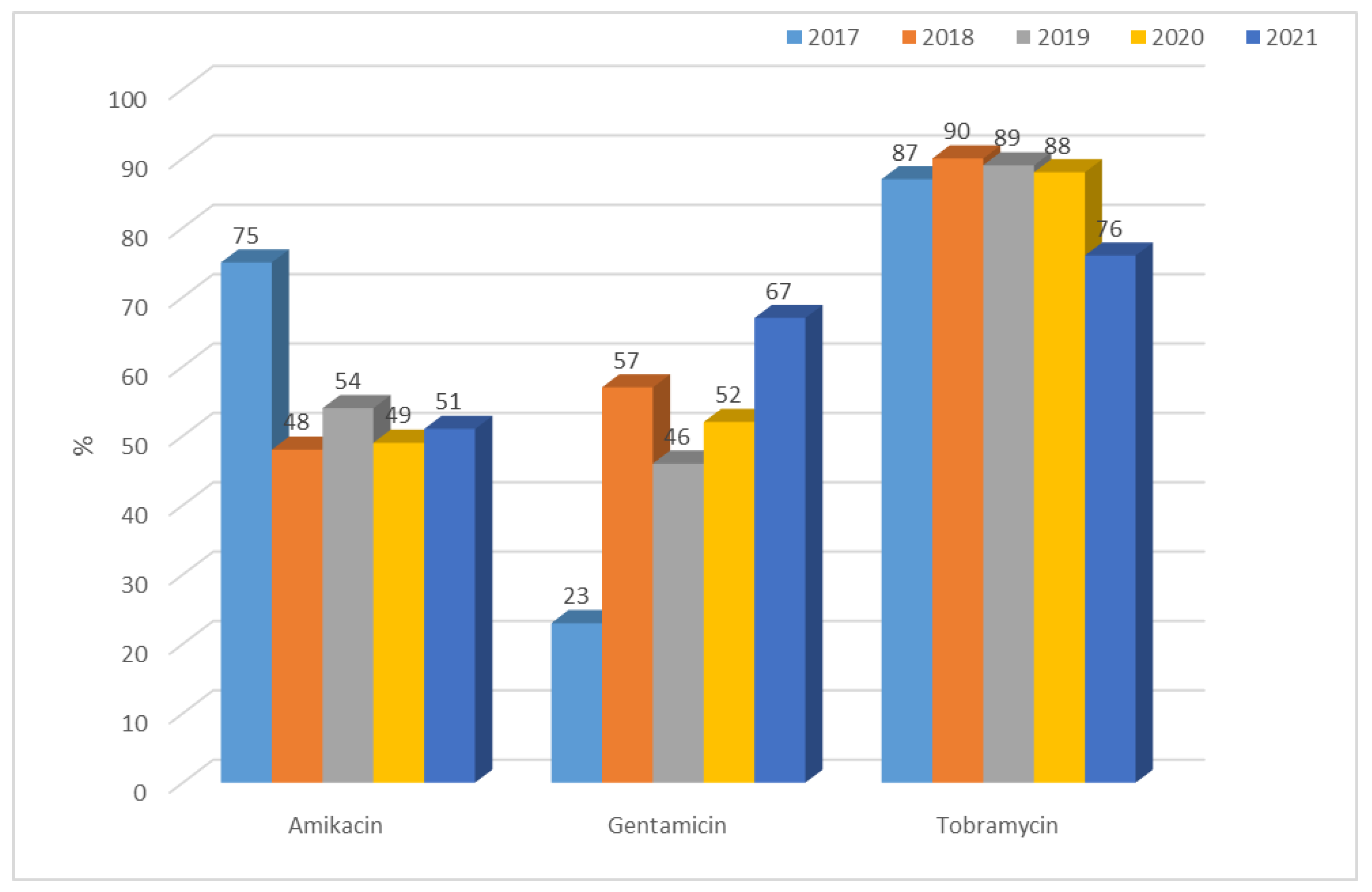
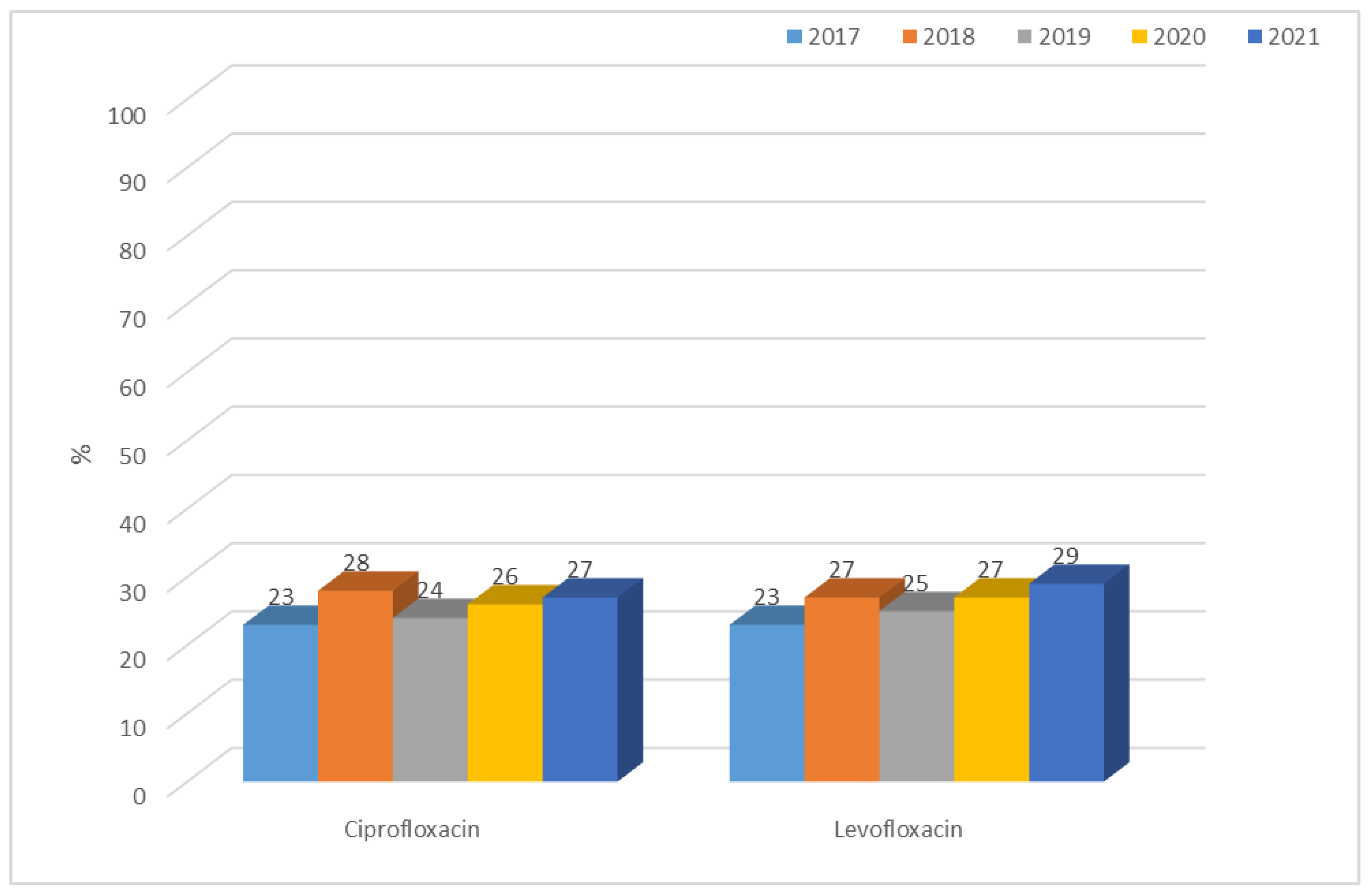
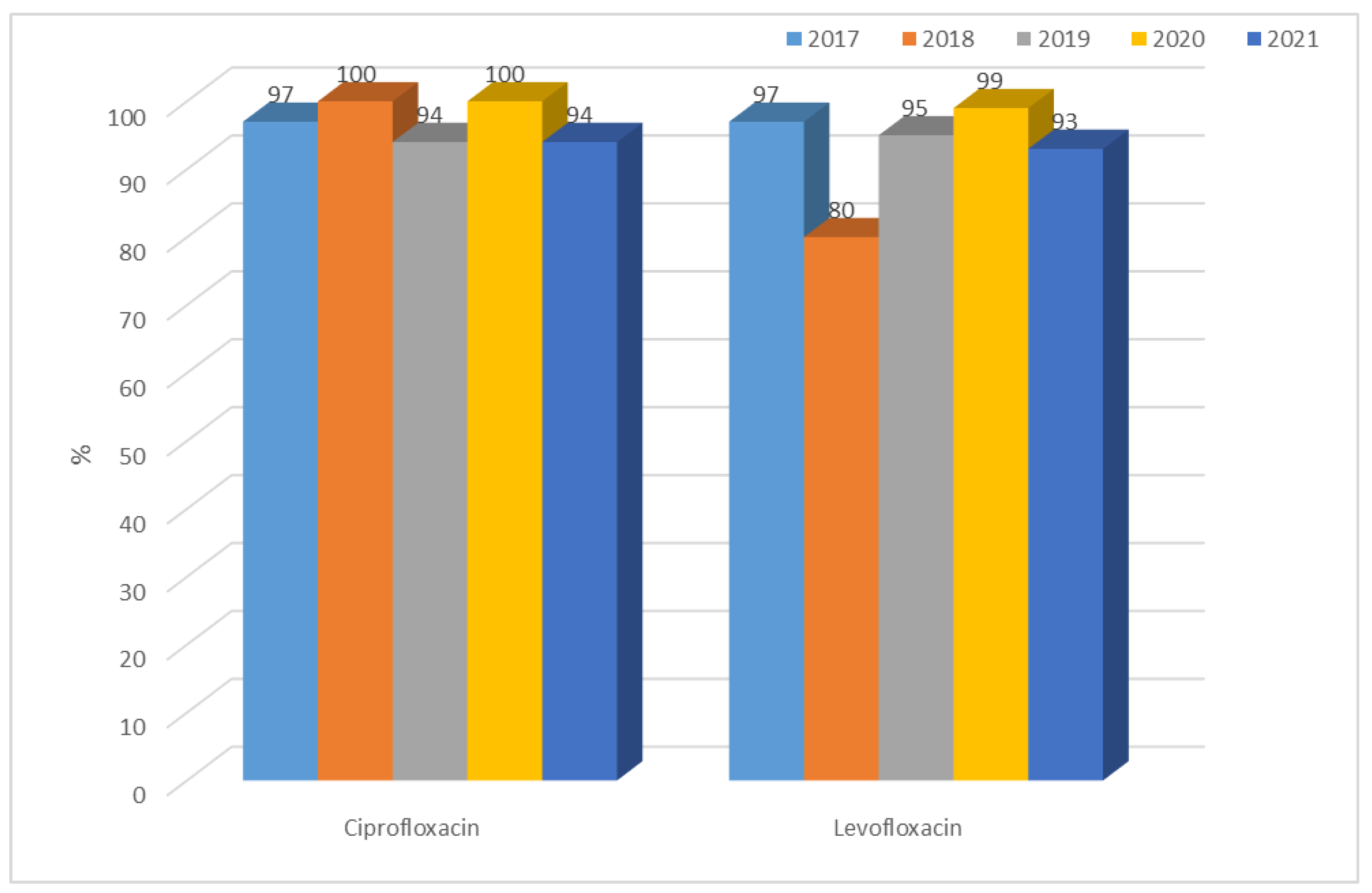
3.1.1. Antibiotic Resistance of E. coli Strains from 2017 to 2021
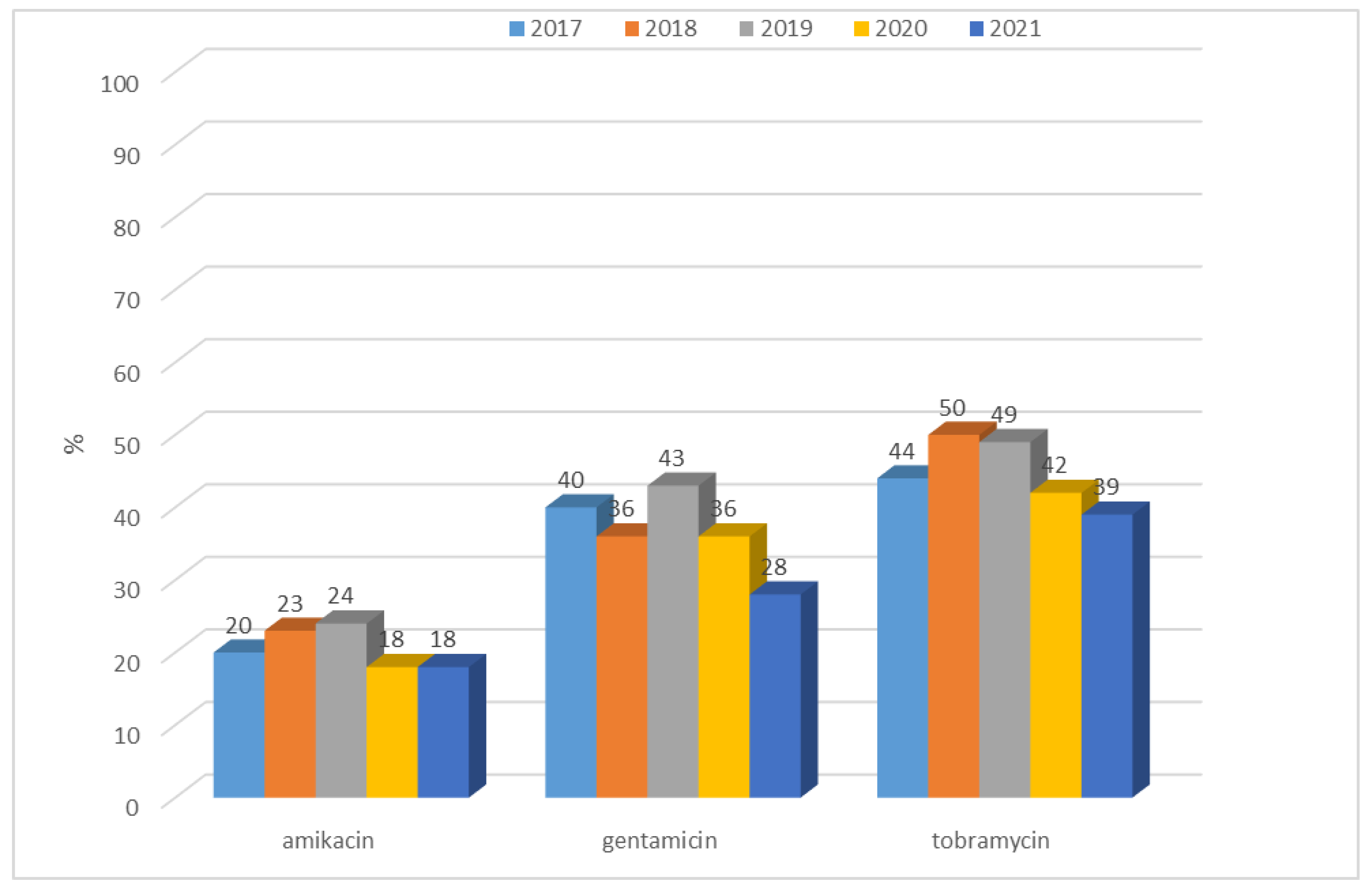
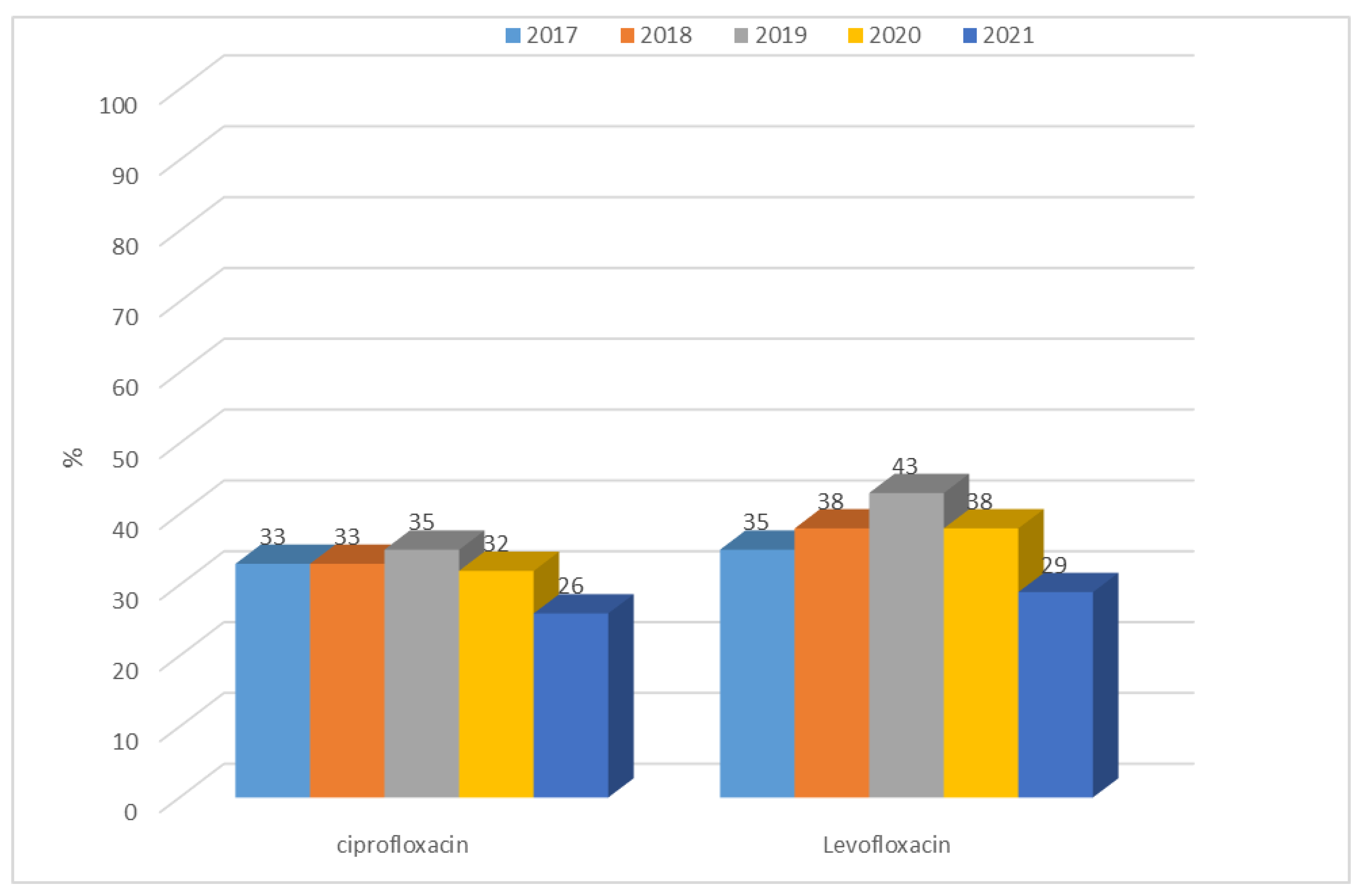
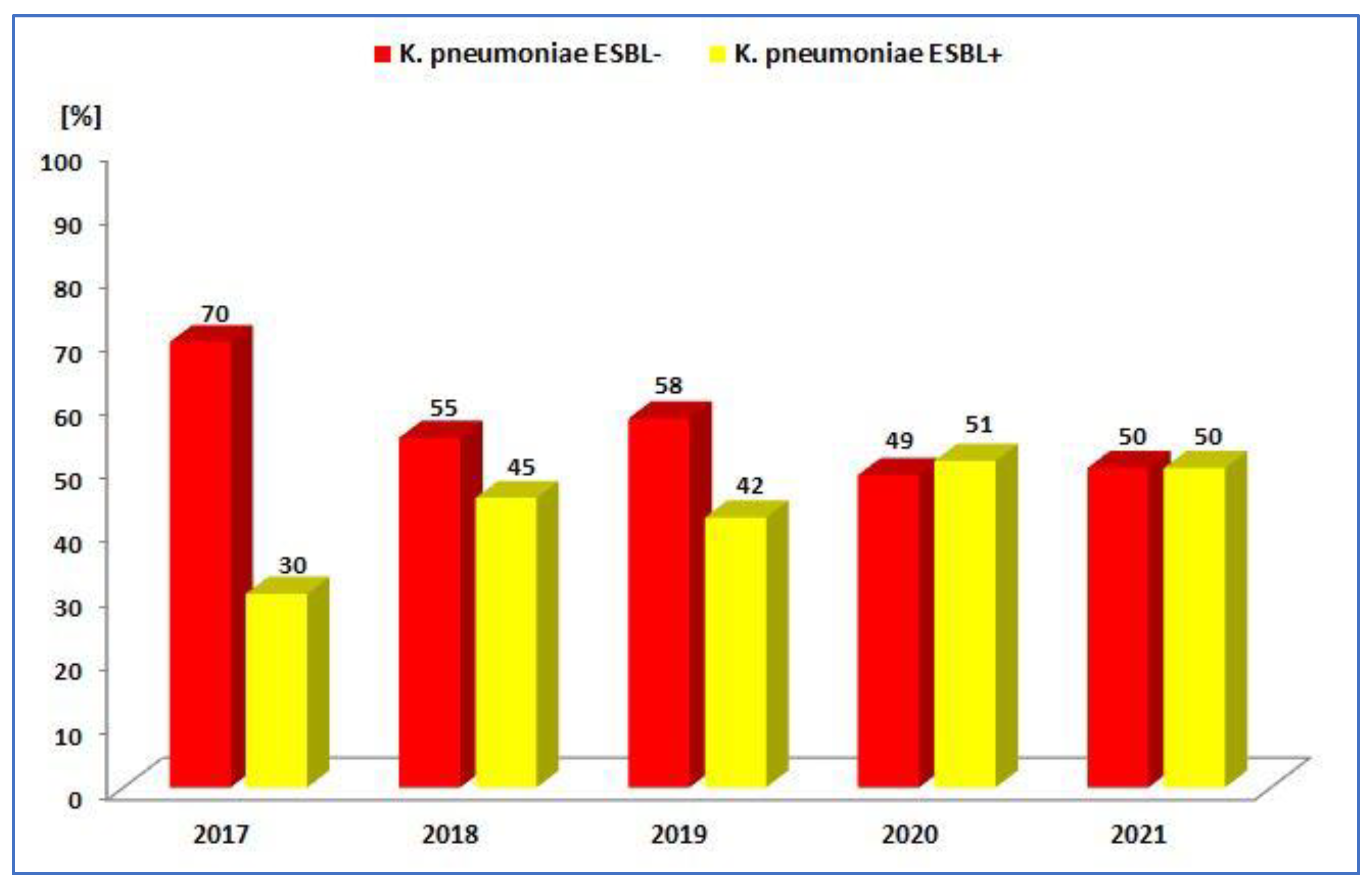
3.1.2. Antibiotic Resistance of K. pneumoniae Strains in 2017–2021
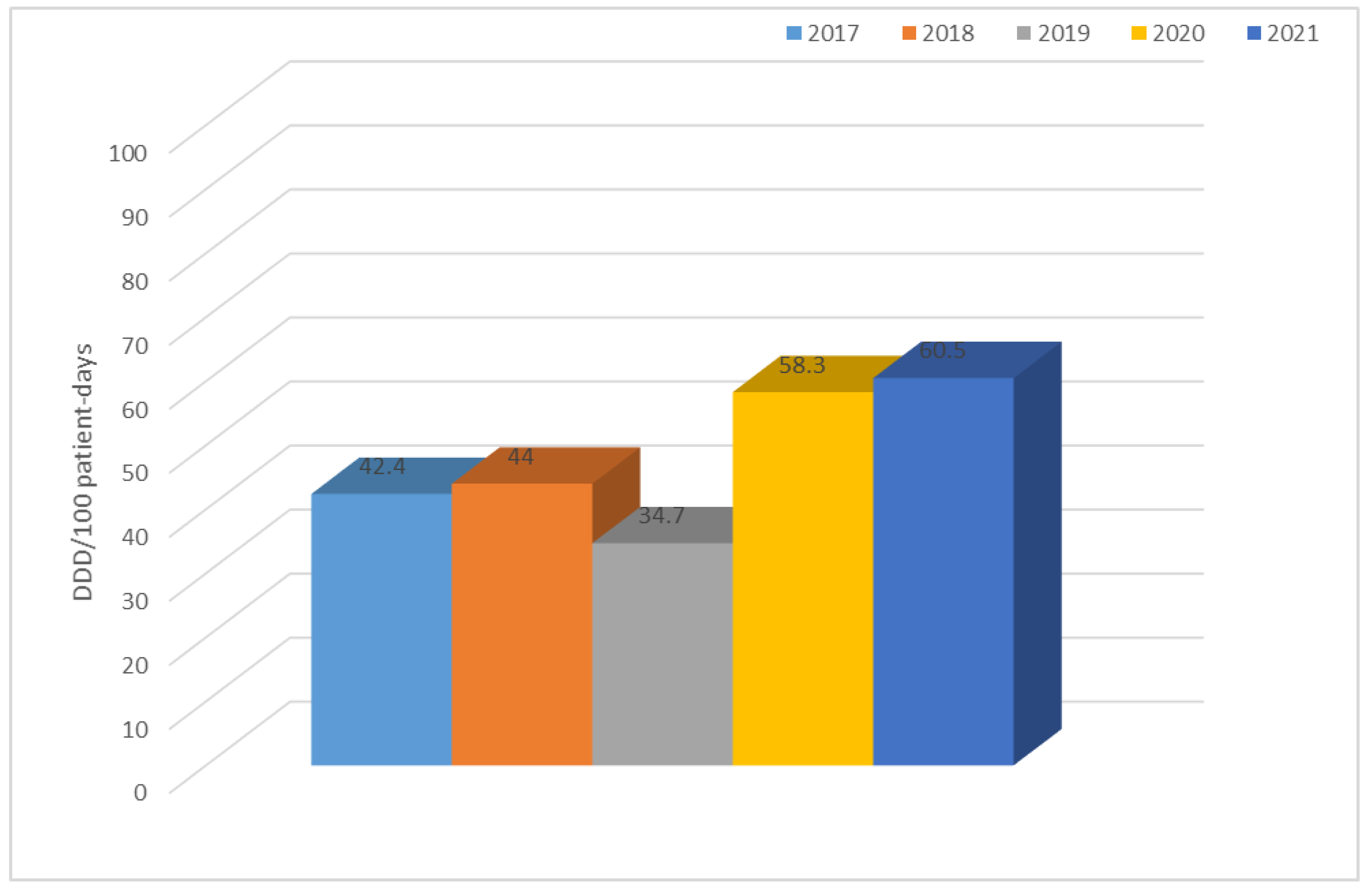
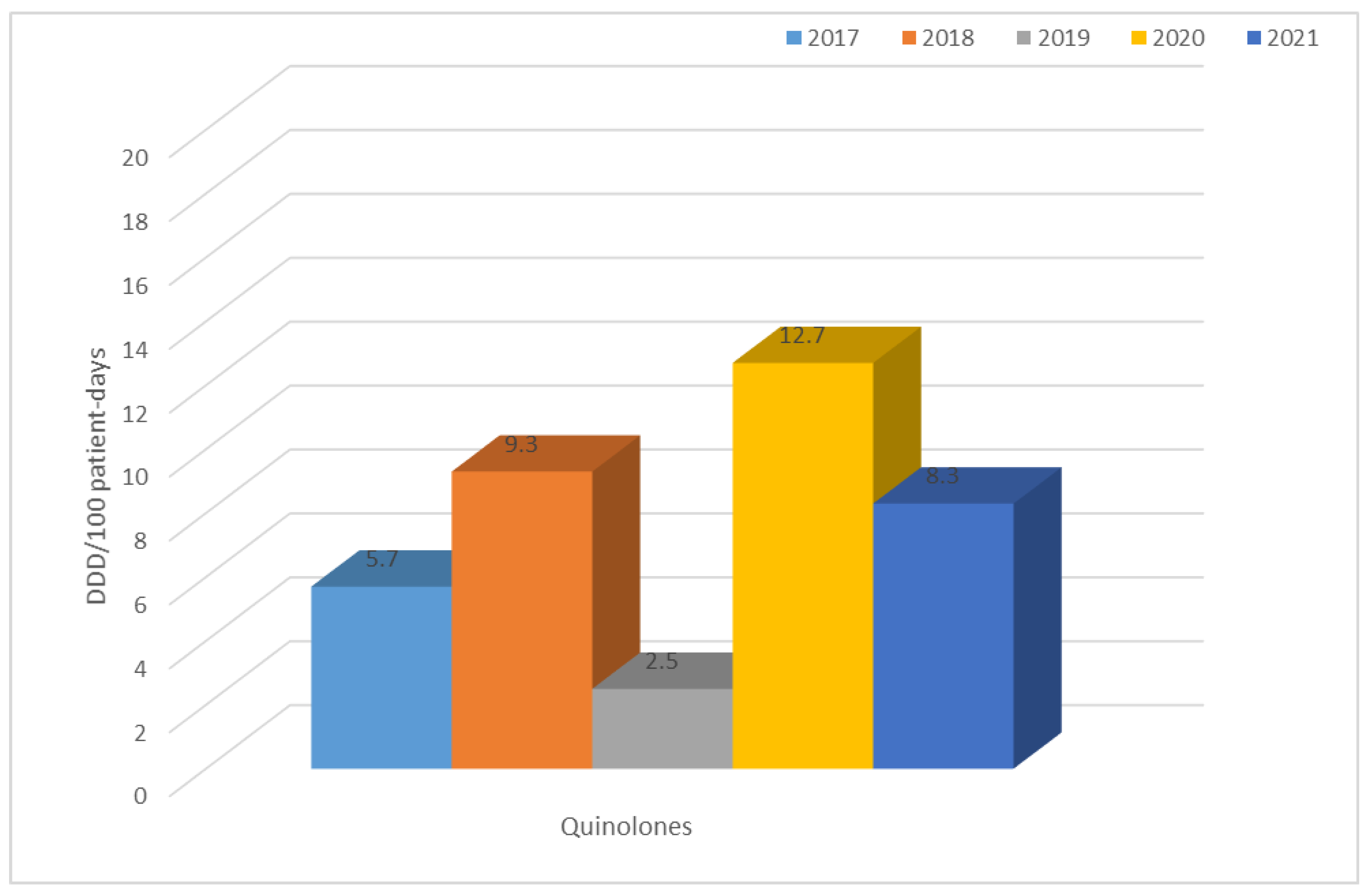
3.2. Consumption of Antibiotics in the Hospital in the Studied Five-Year Period (in DDD/100 Patient Days)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pilmis, B.; Le Monnier, A.; Zahar, J.R. Gut Microbiota, Antibiotic Therapy and Antimicrobial Resistance: A Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leekha, S.; Terrell, C.L.; Edson, R.S. General principles of antimicrobial therapy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, T.M.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Khusro, A.; Zidan, B.R.M.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Dhama, K.; Ripon, M.K.H.; Gajdács, M.; Sahibzada, M.U.K.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in microbes: History, mechanisms, therapeutic strategies and future prospects. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniak, A.; Izdebski, R.; Fiett, J.; Gawryszewska, I.; Bojarska, K.; Herda, M.; Literacka, E.; Żabicka, D.; Tomczak, H.; Pewińska, N.; et al. NDM-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Poland, 2012–2014: Inter-regional outbreak of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 and sporadic cases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paluchowska, P.; Skałkowska, M.; Spelak, A.; Budak, A. Occurrence of alert pathogens in hospital environment. Part I. ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae strains. Med. Dosw. Mikrobiol. 2012, 64, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, H.I.; Aqib, A.I.; Seleem, M.N.; Shabbir, M.A.; Hao, H.; Iqbal, Z.; Kulyar, M.F.; Zaheer, T.; Li, K. Genetic basis of molecular mechanisms in β-lactam resistant gram-negative bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allocati, N.; Masulli, M.; Alexeyev, M.F.; Di Ilio, C. Escherichia coli in Europe: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 6235–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.C.; Jacoby, G.A. Mechanisms of drug resistance: Quinolone resistance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1354, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, R.J.; Tor, Y. Antibiotics and bacterial resistance in the 21st century. Perspect. Medicin. Chem. 2014, 6, 25–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradigaravand, D.; Martin, V.; Peacock, S.J.; Parkhill, J. Evolution and Epidemiology of Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in the United Kingdom and Ireland. mBio 2017, 8, e01976-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballén, V.; Gabasa, Y.; Ratia, C.; Ortega, R.; Tejero, M.; Soto, S. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Isolated From Different Clinical Sources. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbial. 2021, 11, 738223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanfar, H.S.; Bindayna, K.M.; Senok, A.C.; Botta, G.A. Extended spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBL) in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae: Trends in the hospital and community settings. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2009, 3, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, G.; Del Giacomo, P.; Posteraro, B.; Sanguinetti, M.; Tumbarello, M. Molecular Mechanisms, Epidemiology, and Clinical Importance of β-Lactam Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvonen, V.H.A.; Spencer, J.; van der Kamp, M.W. Antimicrobial Resistance Conferred by OXA-48 β-Lactamases: Towards a Detailed Mechanistic Understanding. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e00184-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, S.M.; Abd El-Aziz, A.M.; Hassan, R.; Abdelmegeed, E.S. β-lactam resistance associated with β-lactamase production and porin alteration in clinical isolates of E. coli and K. pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Peghin, M.; Vena, A.; Giacobbe, D.R. Treatment of Infections Due to MDR Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochońska, D.; Klamińska-Cebula, H.; Dobrut, A.; Bulanda, M.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M. Clonal Dissemination of KPC-2, VIM-1, OXA-48-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST147 in Katowice, Poland. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamarellou, H.; Karaiskos, I. Current and Potential Therapeutic Options for Infections Caused by Difficult-to-Treat and Pandrug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria in Critically Ill Patients. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altayb, H.N.; Elbadawi, H.S.; Alzahrani, F.A.; Baothman, O.; Kazmi, I.; Nadeem, M.S.; Hosawi, S.; Chaieb, K. Co-Occurrence of β-Lactam and Aminoglycoside Resistance Determinants among Clinical and Environmental Isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli: A Genomic Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, P.V.; Aishwarya, K.V.L.; Mariappan, S.; Sekar, U. Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella Pneumonia e. J. Lab. Physicians 2020, 12, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criteria for Diagnosis of an Outbreak in a Hospital/Health Care Facility Caused by Carbapenamase-Producing Strains of Enterobacteriaceae (CPE). Guidelines of the National Antibiotic Protection Program. Available online: http://antybiotyki.edu.pl/wpcontent/uploads/dokumenty/CPE_NDM-Ognisko-epidemiczne.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters; Version 10.0; The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Basel, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Routine and Extended Internal Quality Control for MIC Determination and Disk Diffusion as Recommended by EUCAST; Version 10.0; The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Basel, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Skov, R.; Skov, G. EUCAST Guidelines for Detection of Resistance Mechanisms and Specific Resistances of Clinical and/or Epidemiological Importance. 2017, 6, pp. 1–47. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Resistance_mechanisms/EUCAST_detection_of_resistance_mechanisms_170711.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Van Dijk, K.; Voets, G.M.; Scharringa, J.; Voskuil, S.; Fluit, A.C.; Rottier, W.C.; Leverstein-Van Hall, M.A.; Cohen Stuart, J.W. A disc diffusion assay for detection of class A, B and OXA-48 carbapenemases in Enterobacteriaceae using phenyl bo ronic acid, dipicolinic acid and temocillin. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniak, A.; Grabowska, A.; Izdebski, R.; Fiett, J.; Herda, M.; Bojarska, K.; Żabicka, D.; Kania-Pudło, M.; Młynarczyk, G.; Zak-Puławska, Z.; et al. Molecular characteristics of KPC-producing Enterobacteriaceae at the early stage of their dissemination in Poland, 2008–2009. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5493–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dortet, L.; Poirel, L.; Errera, C.; Nordmann, P. CarbAcineto NP test for rapid detection of carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2359–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolhouse, M.; Ward, M.; van Bunnik, B.; Farrar, J. Antimicrobial resistance in humans, livestock and the wider environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial resistance: A global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathog. Glob Health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Flach, C.F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, M.; Azak, E.; Bilgin, H.; Menekse, S.; Asan, A.; Mert, H.T.E.; Yulugkural, Z.; Altunal, L.N.; Hatipoğlu, Ç.A.; Tuncer Ertem, G.; et al. Changes in antimicrobial resistance and outcomes of health care-associated infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.; Zoubiane, G.; Walsh, D.; Ward, R.; Goossens, H. Public founding for research on antibacterial resistance in the JPIAMR countries, the European Commission, and related European Union agencies: A systematic observational analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Singh, P.; Rajurkar, M. Multidrug Resistant and Extensively Drug Resistant Bacteria: A Study. J. Pathog. 2016, 2016, 4065603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuretzbacher, U. Global antibacterial resistance: The never-ending story. J. Glob. Antimicrobal Resist. 2013, 1, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net)—Annual Epidemiological Report 2017; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2018.
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net)—Annual Epidemiological Report 2018; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019.
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net)—Annual Epidemiological Report 2019; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2020.
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net)—Annual Epidemiological Report 2020; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022.
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net)—Annual Epidemiological Report 2021; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022.
- Sarowska, J.; Futoma-Koloch, B.; Jama-Kmiecik, A.; Frej-Madrzak, M.; Ksiazczyk, M.; Bugla-Ploskonska, G.; Choroszy-Krol, I. Virulence factors, prevalence and potential transmission of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from different sources: Recent reports. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Shen, P.; Lu, X.; Xiao, Y. Association between the rate of fluoroquinolones-resistant gram-negative bacteria and antibiotic consumption from China based on 145 tertiary hospitals data in 2014. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellberg, B.; Doi, Y. The Rise of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Escherichia coli in the Community: Scarier Than We Thought. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1853–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zhu, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, M. Current Status and Trends of Antibacterial Resistance in China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial resistance surveillance in Europe 2012. In Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net); ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Maczynska, B.; Paleczny, J.; Oleksy-Wawrzyniak, M.; Choroszy-Krol, I.; Bartoszewicz, M. In Vitro Susceptibility of Multi-Drug Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Causing Nosocomial Infections to Fosfomycin. A Comparison of Determination Methods. Pathogens 2021, 10, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiru-Oredope, D.; Hopkins, S.; Vasandani, S.; Umoh, E.; Oloyede, O.; Nilsson, A.; Kinsman, J.; Elsert, L.; Monnet, D.L.; the #ECDCAntibioticSurvey Project Advisory Group. Healthcare workers’ knowledge, attitudes and behaviours with respect to antibiotics, antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance across 30 EU/EEA countries in 2019. Euro. Surveill. 2021, 26, 1900633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global-Antimicrobial-Resistance-Surveillance-System-Glass; World Health Organization: Geneva, Sweden, 2021.
- Zhou, N.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lv, C.; Guo, C.; Liu, H.; Dong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Chang, Y.F.; et al. Global antimicrobial resistance: A system-wide comprehensive investigation using the Global One Health Index. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | 791 (71.2%) | 917 (69.4%) | 851 (73.7%) | 742 (73.3%) | 770 (69.5%) |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 320 (28.8%) | 404 (30.6%) | 303 (26.3%) | 270 (26.7%) | 338 (30.5%) |
| Total | 1111 | 1321 | 1154 | 1012 | 1108 |
| p-Value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Bacteria | Selected Antibiotics |
|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | Gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, ampicillin, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, ampicillin/sulbactam, piperacillin/tazobactam, cefuroxime, ceftazidime, cefotaxime, cefepime, imipenem, meropenem |
| Escherichia coli ESBL(+) | Gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, ampicillin/sulbactam, piperacillin/tazobactam, cefuroxime, ceftazidime, cefotaxime, cefepime, imipenem, meropenem |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, ampicillin/sulbactam, piperacillin/tazobactam, cefuroxime, ceftazidime, cefotaxime, cefepime, imipenem, meropenem |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae ESBL(+) | Gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, meropenem, imipenem, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, ampicillin/sulbactam, piperacillin/tazobactam, cefuroxime, ceftazidime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, cefepime, imipenem, meropenem, colistin |
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
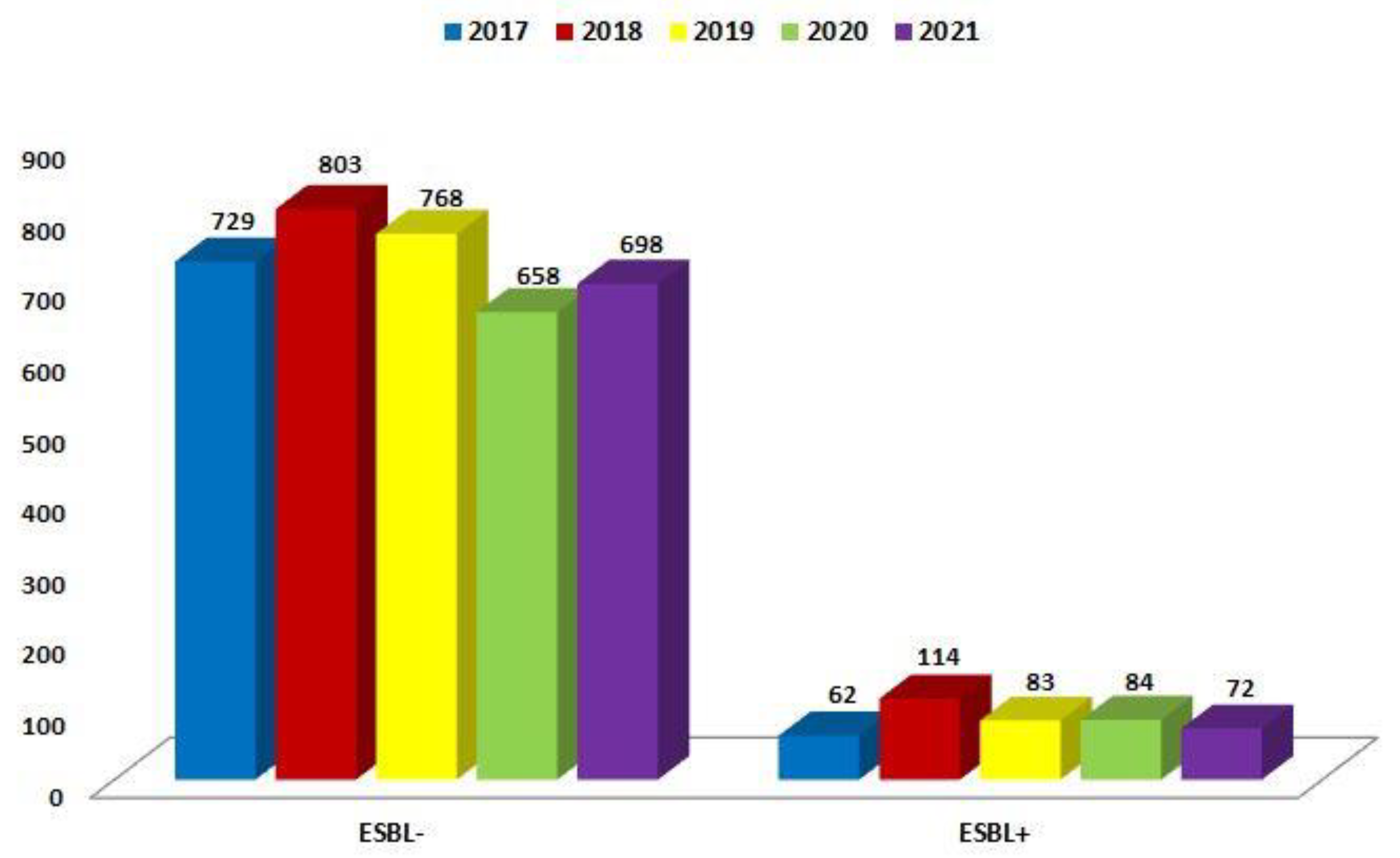
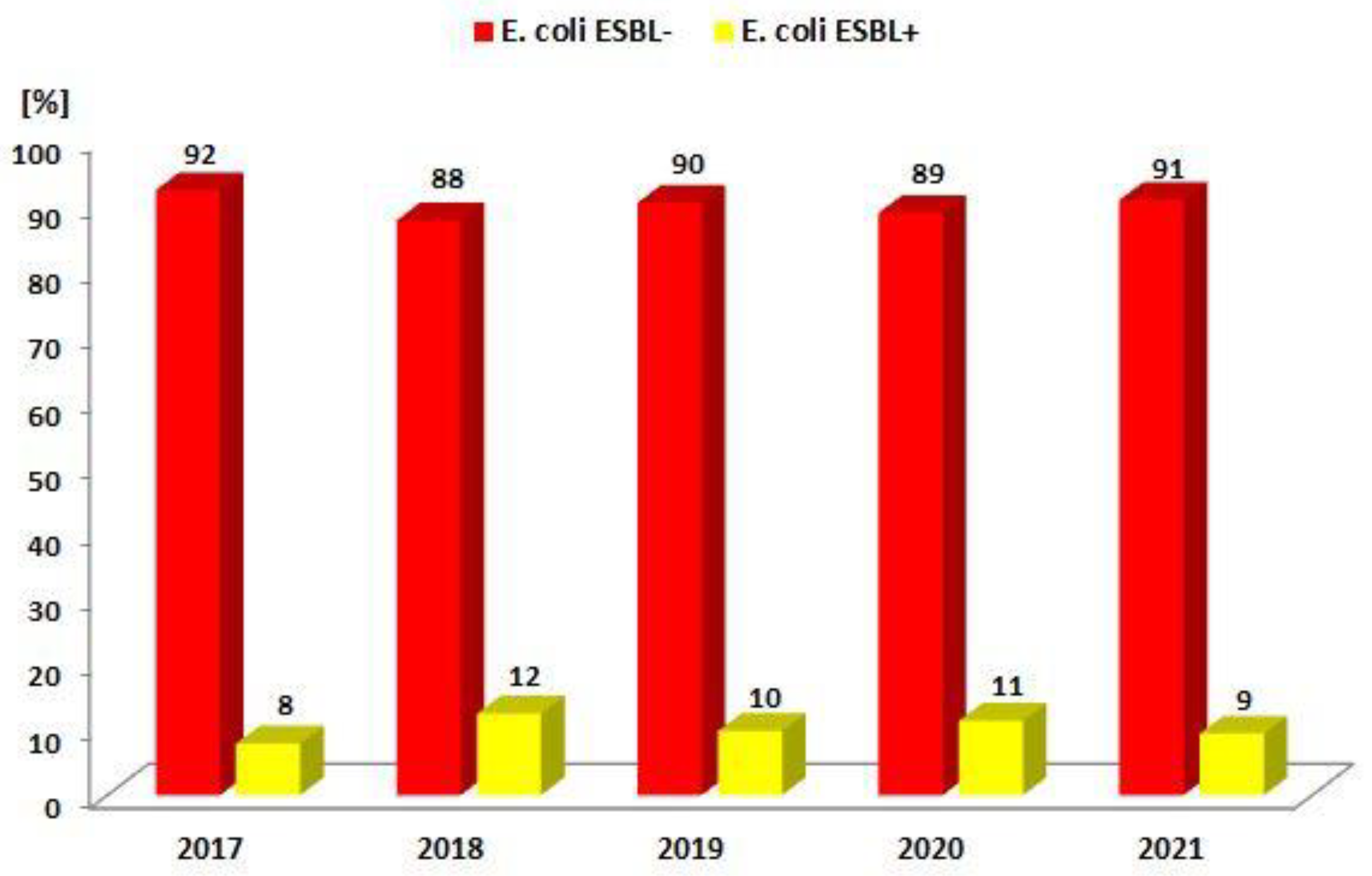
| ESBL(−) | 729 (92.1%) | 803 (87.6%) | 768 (90.2%) | 658 (88.7%) | 698 (90.6%) |
| ESBL(+) | 62 (7.9%) | 114 (12.4%) | 83 (9.8%) | 84 (11.3%) | 72 (9.4%) |
| Total | 791 | 917 | 851 | 742 | 770 |
| p-Value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
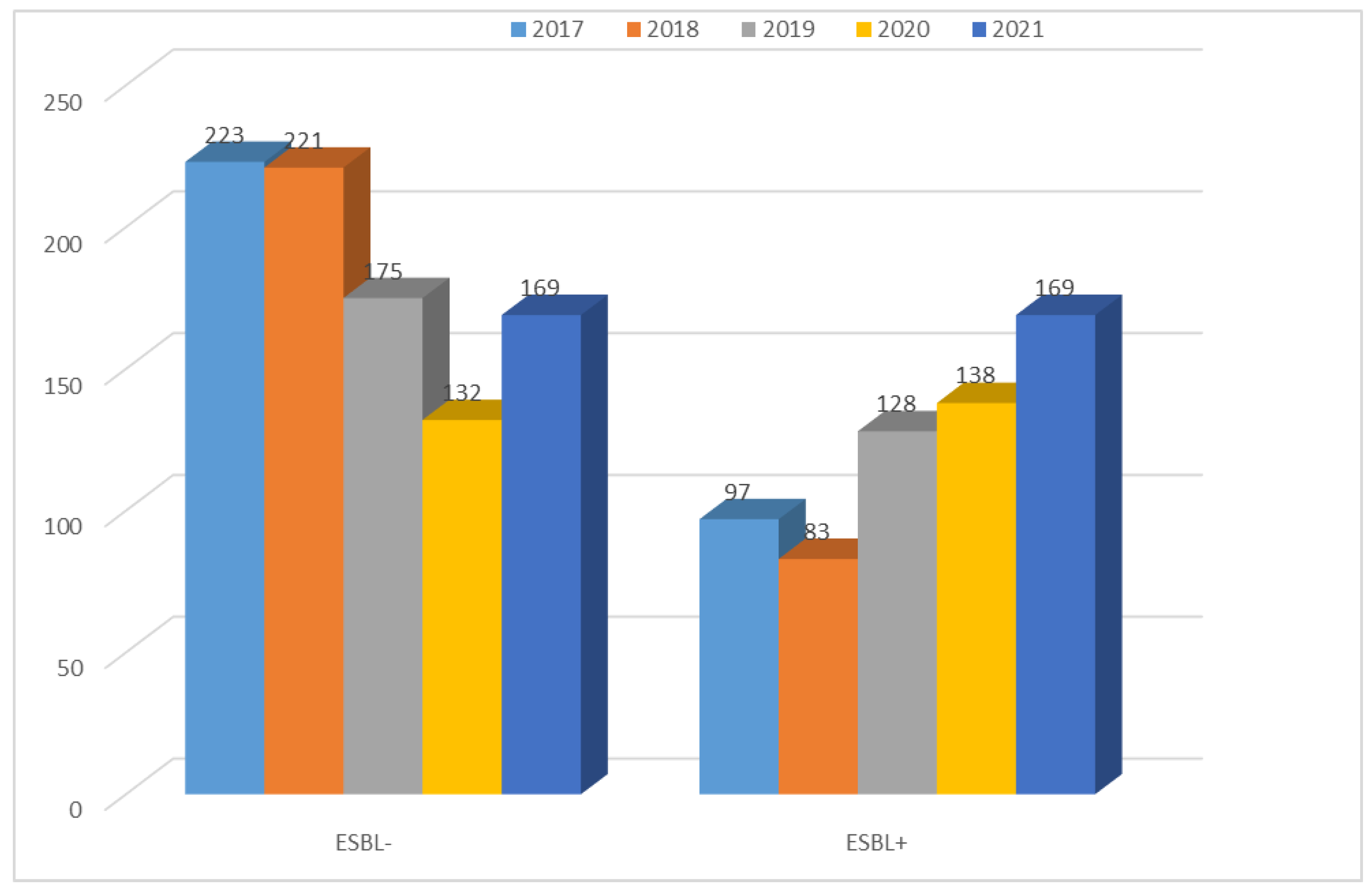
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESBL− | 223 (69.7%) | 221 (72.7%) | 175 (57.8%) | 132 (48.9%) | 169 (50.0%) |
| ESBL+ | 97 (30.3%) | 83 (23.3%) | 128 (42.2%) | 138 (51.1%) | 169 (50.0%) |
| Total | 320 | 304 | 303 | 270 | 338 |
| p-Value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 |
| Antibiotic Consumption [DDD/100 Person-Days]. | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | TET | PES | PES + in. | C II | C III | C IV | KARB | MAK | LINK | AM | CH | GP | POL | Total |
| 2017 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 7.3 | 9.3 | 2.6 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 3.4 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 5.7 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 42.4 |
| 2018 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 7.2 | 11.0 | 3.1 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 9.3 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 44.0 |
| 2019 | 2.4 | 1.3 | 8.4 | 1.4 | 2.7 | 0.2 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 34.7 |
| 2020 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 8.3 | 2.6 | 15.7 | 0.3 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 12.7 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 58.3 |
| 2021 | 0.7 | 3.9 | 22.3 | 1.8 | 7.4 | 0.2 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 8.3 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 60.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mączyńska, B.; Frej-Mądrzak, M.; Sarowska, J.; Woronowicz, K.; Choroszy-Król, I.; Jama-Kmiecik, A. Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates in a Multi-Profile Hospital over 5 Years (2017–2021). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062414
Mączyńska B, Frej-Mądrzak M, Sarowska J, Woronowicz K, Choroszy-Król I, Jama-Kmiecik A. Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates in a Multi-Profile Hospital over 5 Years (2017–2021). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(6):2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062414
Chicago/Turabian StyleMączyńska, Beata, Magdalena Frej-Mądrzak, Jolanta Sarowska, Krystyna Woronowicz, Irena Choroszy-Król, and Agnieszka Jama-Kmiecik. 2023. "Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates in a Multi-Profile Hospital over 5 Years (2017–2021)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 6: 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062414
APA StyleMączyńska, B., Frej-Mądrzak, M., Sarowska, J., Woronowicz, K., Choroszy-Król, I., & Jama-Kmiecik, A. (2023). Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates in a Multi-Profile Hospital over 5 Years (2017–2021). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(6), 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062414






