Metabolic Health, Obesity, and Intraocular Pressure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
- Abdominal obesity, defined as waist circumference ≥90 cm in men or ≥ 85 cm in women for Koreans [22]
- Dyslipidemia, defined as either previously diagnosed as dyslipidemia or triglyceride ≥150 mg/dL
- HDL cholesterol <40 mg/dL in men or <50 mg/dL in women
- Hypertension, defined as either previously diagnosed hypertension, systolic BP ≥ 130 mmHg, or diastolic BP ≥ 85 mmHg
- Diabetes mellitus, defined as either previously diagnosed diabetes or FPG ≥ 100 mg/dL
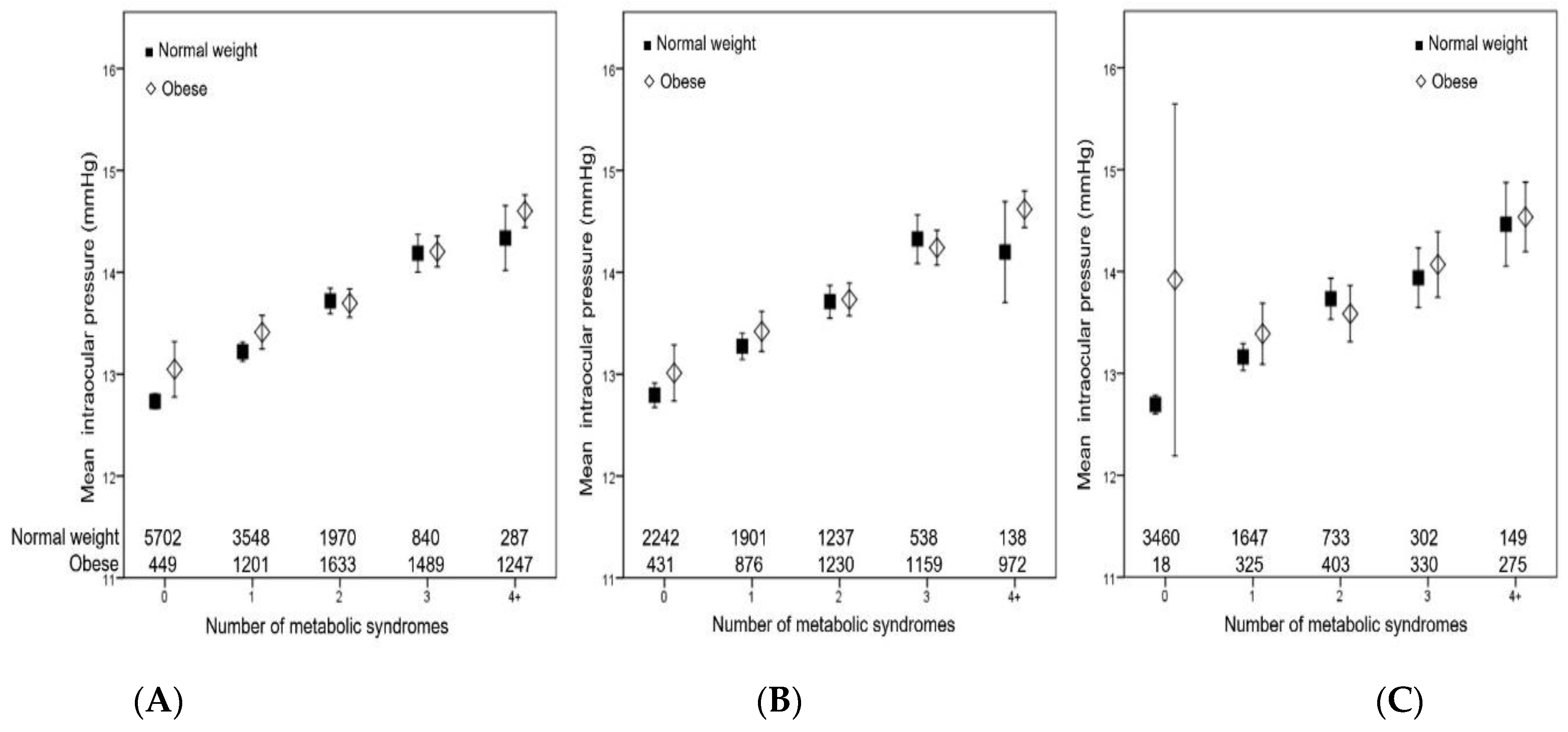
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tham, Y.C.; Li, X.; Wong, T.Y.; Quigley, H.A.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.Y. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, H.A. Glaucoma. Lancet 2011, 377, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Aung, T.; Medeiros, F.A. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: A review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Khaw, P.T. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Lancet 2004, 363, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinci, A.; Cetinkaya, E.; Aycan, Z.; Oner, O. Relationship between intraocular pressure and obesity in children. J. Glaucoma 2007, 16, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.D.; Kim, D.H.; Han, K.; Ha, S.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.W.; Park, J.Y.; Yoon, S.J.; Jung, D.W.; Park, S.W.; et al. Relationship between Intraocular Pressure and Parameters of Obesity in Korean Adults: The 2008–2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Curr. Eye Res. 2015, 40, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Ando, F.; Nomura, H.; Sato, Y.; Shimokata, H. Relationship between intraocular pressure and obesity in Japan. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 29, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.; Halenda, K.; Cromer, P.; Chen, L.; Butler, J.; Raed, A.; Bhagatwala, J.; Sponseller, T.; Bollinger, K.; Zhu, H.; et al. The Association of Intraocular Pressure with Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk in a Young Farmworker Population. J. Glaucoma 2021, 30, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Leske, M.C. Associations with intraocular pressure in the Barbados Eye Study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1997, 115, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, B.E.; Klein, R.; Linton, K.L. Intraocular pressure in an American community. The Beaver Dam Eye Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 2224–2228. [Google Scholar]
- Karadag, R.; Arslanyilmaz, Z.; Aydin, B.; Hepsen, I.F. Effects of body mass index on intraocular pressure and ocular pulse amplitude. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 5, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karelis, A.D.; Faraj, M.; Bastard, J.P.; St-Pierre, D.H.; Brochu, M.; Prud’homme, D.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R. The metabolically healthy but obese individual presents a favorable inflammation profile. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4145–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobini, C.; Pugliese, G.; Blasetti Fantauzzi, C.; Federici, M.; Menini, S. Metabolically healthy versus metabolically unhealthy obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, T.F.; Alves, R.D.; Moreira, A.P.; Peluzio Mdo, C. Main characteristics of metabolically obese normal weight and metabolically healthy obese phenotypes. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorak, R.V.; DeNino, W.F.; Ades, P.A.; Poehlman, E.T. Phenotypic characteristics associated with insulin resistance in metabolically obese but normal-weight young women. Diabetes 1999, 48, 2210–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Giffney, H.E.; Arthur, R.S.; Rohan, T.E.; Dannenberg, A.J. Cancer Risk in Normal Weight Individuals with Metabolic Obesity: A Narrative Review. Cancer Prev. Res. 2021, 14, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Somers, V.K.; Sierra-Johnson, J.; Korenfeld, Y.; Boarin, S.; Korinek, J.; Jensen, M.D.; Parati, G.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Normal weight obesity: A risk factor for cardiometabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular mortality. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Han, K.; Park, H.Y.L.; Lee, S.H.; Park, C.K. Metabolic Health, Obesity, and the Risk of Developing Open-Angle Glaucoma: Metabolically Healthy Obese Patients versus Metabolically Unhealthy but Normal Weight Patients. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020, 44, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Yang, H.K.; Song, H.J.; Chang, H.J.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Han, S.; Kim, Y.K. Metabolic health is more closely associated with decrease in lung function than obesity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Park, H.S.; Kim, D.J.; Han, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Cho, G.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, H.S.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, C.B.; et al. Appropriate waist circumference cutoff points for central obesity in Korean adults. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 75, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for the Western Pacific. In The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefining Obesity and Its Treatment; Health Communications Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.K.; Han, K.; Kwon, H.S.; Park, Y.M.; Cho, J.H.; Yoon, K.H.; Kang, M.I.; Cha, B.Y.; Lee, S.H. Obesity, metabolic health, and mortality in adults: A nationwide population-based study in Korea. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchie, A.; Dallegri, F.; Carbone, F.; Bonaventura, A.; Liberale, L.; Portincasa, P.; Fruhbeck, G.; Montecucco, F. Obesity phenotypes and their paradoxical association with cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 48, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Hong, H.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, D.S.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, K.M. Association of metabolically abnormal but normal weight (MANW) and metabolically healthy but obese (MHO) individuals with arterial stiffness and carotid atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2014, 234, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Chan, Z.; Magkos, F. Lean, but not healthy: The ‘metabolically obese, normal-weight’ phenotype. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Lin, J.W.; Wang, L.C.; Chen, H.M.; Hwang, J.J.; Chuang, L.M. Association of intraocular pressure with the metabolic syndrome and novel cardiometabolic risk factors. Eye 2010, 24, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Park, J.O.; Kang, H.T.; Lee, Y.J. Elevated intraocular pressure is associated with metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Menopause 2013, 20, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Kong, E.H.; Cho, B.M.; Tak, Y.J.; Hwang, H.R.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Metabolic syndrome as a risk factor for high intraocular pressure: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2010. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokomichi, H.; Kashiwagi, K.; Kitamura, K.; Yoda, Y.; Tsuji, M.; Mochizuki, M.; Sato, M.; Shinohara, R.; Mizorogi, S.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Evaluation of the associations between changes in intraocular pressure and metabolic syndrome parameters: A retrospective cohort study in Japan. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennis, A.; Wu, S.Y.; Nemesure, B.; Leske, M.C.; Barbados Eye Studies, G. Hypertension, diabetes, and longitudinal changes in intraocular pressure. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carel, R.S.; Korczyn, A.D.; Rock, M.; Goya, I. Association between ocular pressure and certain health parameters. Ophthalmology 1984, 91, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.W.; Lee, S.; Park, C.; Kim, D.J. Elevated intraocular pressure is associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2005, 21, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Roy, S. Effect of high glucose on fibronectin expression and cell proliferation in trabecular meshwork cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Mapstone, R.; Clark, C.V. Prevalence of diabetes in glaucoma. Br. Med. J. 1985, 291, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.H.; Han, K.; Park, S.H.; Park, K.M.; Yim, H.W.; Lee, W.C.; Park, Y.G.; Park, Y.M. Insulin resistance is associated with intraocular pressure elevation in a non-obese Korean population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e112929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainer, V.; Aldhoon-Hainerova, I. Obesity paradox does exist. Diabetes Care 2013, 36 (Suppl. S2), S276–S281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Del Gobbo, V.; Premrov, M.G.; Bigioni, M.; Galvano, F.; Di Renzo, L. Normal-weight obese syndrome: Early inflammation? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| MHNW n = 11,220 (61.1%) | MHO n = 3283 (17.8%) | MUNW n = 1127 (6.1%) | MUO n = 2736 (14.9%) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 46.47 ± 10.67 †‡ | 46.57 ± 10.08 §‖ | 56.65 ± 10.62 †§¶ | 50.64 ± 10.65 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Sex (male, %) | 5380 (48.0) | 2537 (77.3) | 676 (60.0) | 2131 (77.9) | <0.001 |
| Height (cm) | 165.95 ± 8.27 †‡ | 169.35 ± 8.34 *§ | 165.91 ± 8.79 §¶ | 169.21 ± 8.56 ‡¶ | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 60.95 ± 8.62 *†‡ | 77.11 ± 9.14 *§‖ | 64.16 ± 8.00 †§¶ | 80.77 ± 11.42 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.01 ± 1.71 *†‡ | 26.83 ± 1.89 *§‖ | 23.23 ± 1.33 †§¶ | 28.12 ± 2.62 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 79.09 ± 5.31 *†‡ | 91.37 ± 6.15 *§‖ | 84.78 ± 4.79 †§¶ | 96.26 ± 7.38 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 91.86 ± 4.17 *†‡ | 100.25 ± 4.66 *§‖ | 93.38 ± 4.47 †§¶ | 102.45 ± 5.86 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Waist–hip ratio | 0.86 ± 0.04 *†‡ | 0.91 ± 0.04 *‖ | 0.91 ± 0.04 †¶ | 0.94 ± 0.04 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Skeletal muscle mass (kg) | 24.96 ± 5.51 *†‡ | 31.09 ± 5.63 *§‖ | 25.80 ± 5.26 †§¶ | 31.66 ± 6.11 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Body fat mass (kg) | 15.23 ± 3.31 *†‡ | 21.96 ± 5.01 *§‖ | 17.31 ± 3.37 †§¶ | 24.66 ± 5.81 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Body fat (%) | 25.35 ± 5.70 *†‡ | 28.67 ± 6.16 *§‖ | 27.35 ± 6.13 †§¶ | 30.67 ± 6.00 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 114.88 ± 12.79 *†‡ | 119.95 ± 11.44 *§‖ | 129.59 ± 13.45 †§ | 129.67 ± 12.77 ‡‖ | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 71.58 ± 9.05 *†‡ | 75.91 ± 8.56 *§‖ | 78.58 ± 9.45 †§¶ | 80.98 ± 9.06 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | 92.57 ± 13.29 *†‡ | 95.60 ± 13.75 *§‖ | 116.78 ± 32.63 †§¶ | 112.24 ± 27.63 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| HbA1C (%) | 5.49 ± 0.47 *†‡ | 5.56 ± 0.44 *§‖ | 6.19 ± 1.07 †§¶ | 6.04 ± 0.93 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Fasting insulin (µU/mL) | 6.63 ± 2.41 *†‡ | 8.44 ± 3.53 *‖ | 8.84 ± 3.63 †¶ | 10.96 ± 5.16 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| HOMA IR | 1.58 ± 0.66 *†‡ | 1.98 ± 0.88 *§‖ | 2.76 ± 1.65 †§ | 3.17 ± 1.85 ‡‖ | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 199.87 ± 34.26 *‡ | 204.15 ± 35.23 *§ | 200.49 ± 42.46 §¶ | 204.62 ± 40.97 ‡¶ | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 98.98 ± 62.37 *†‡ | 124.38 ± 71.62 *§‖ | 189.53 ± 119.75 †§¶ | 208.24 ± 136.52 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 58.67 ± 13.26 *†‡ | 51.95 ± 10.34 *§‖ | 47.54 ± 11.71 †§¶ | 45.34 ± 10.09 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 120.10 ± 30.72 *‡ | 128.91 ± 32.23 *§‖ | 118.20 ± 36.64 §¶ | 124.35 ± 35.39 ‡‖¶ | <0.001 |
| Diabetes (%) | 1941 (17.3) | 722 (22.0) | 930 (82.5) | 1991 (72.8) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension (%) | 1991 (17.7) | 790 (24.1) | 864 (76.7) | 1949 (71.2) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 1800 (16.0) | 766 (23.3) | 981 (87.0) | 2100 (76.8) | <0.001 |
| MHNW (n = 11,220) | MHO (n = 3283) | MUNW (n = 1127) | MUO (n = 2736) | p Value | Post Hoc Analyses | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean intraocular pressure | Model 1 | 13.06 ± 0.03 | 13.50 ± 0.05 | 14.22 ± 0.08 | 14.38 ± 0.06 | <0.001 | MHNW = MHO < MUNW < MUO |
| Model 2 | 13.08 ± 0.03 | 13.47 ± 0.05 | 14.20 ± 0.09 | 14.34 ± 0.06 | <0.001 | MHNW = MHO < MUNW < MUO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, Y.; Kim, G.N.; Oh, E.B.; Ohn, K.; Moon, J.I. Metabolic Health, Obesity, and Intraocular Pressure. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052066
Jung Y, Kim GN, Oh EB, Ohn K, Moon JI. Metabolic Health, Obesity, and Intraocular Pressure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052066
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Younhea, Gyoung Nyun Kim, Eun Byeol Oh, Kyoung Ohn, and Jung Il Moon. 2023. "Metabolic Health, Obesity, and Intraocular Pressure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052066
APA StyleJung, Y., Kim, G. N., Oh, E. B., Ohn, K., & Moon, J. I. (2023). Metabolic Health, Obesity, and Intraocular Pressure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052066





